Hybrid Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Containing Genipin-Crosslinked Gelatin–Hyaluronic Acid for Future Use in Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
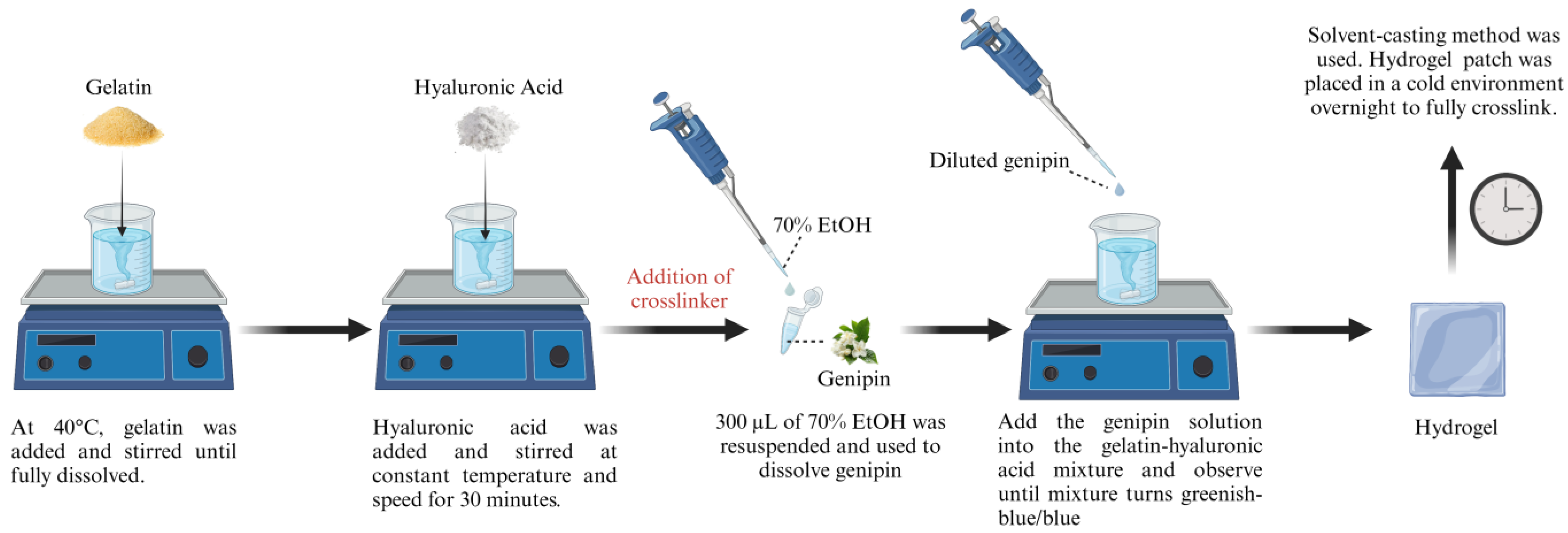
2.1. Preparation of Gelatin and Hyaluronic Acid-Based Hydrogels
2.2. Gross Appearance of the Hydrogel Patches, Weight, Thickness, and Folding Endurance
2.3. Adhesion Evaluation
2.4. Chemical Characterization of the Hydrogel Patches
2.4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.4.2. Simultaneous Thermal Analysis
2.4.3. Energy-Dispersive X-Ray (EDX)
2.5. Porosity Measurement
2.5.1. Liquid Displacement Method
2.5.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
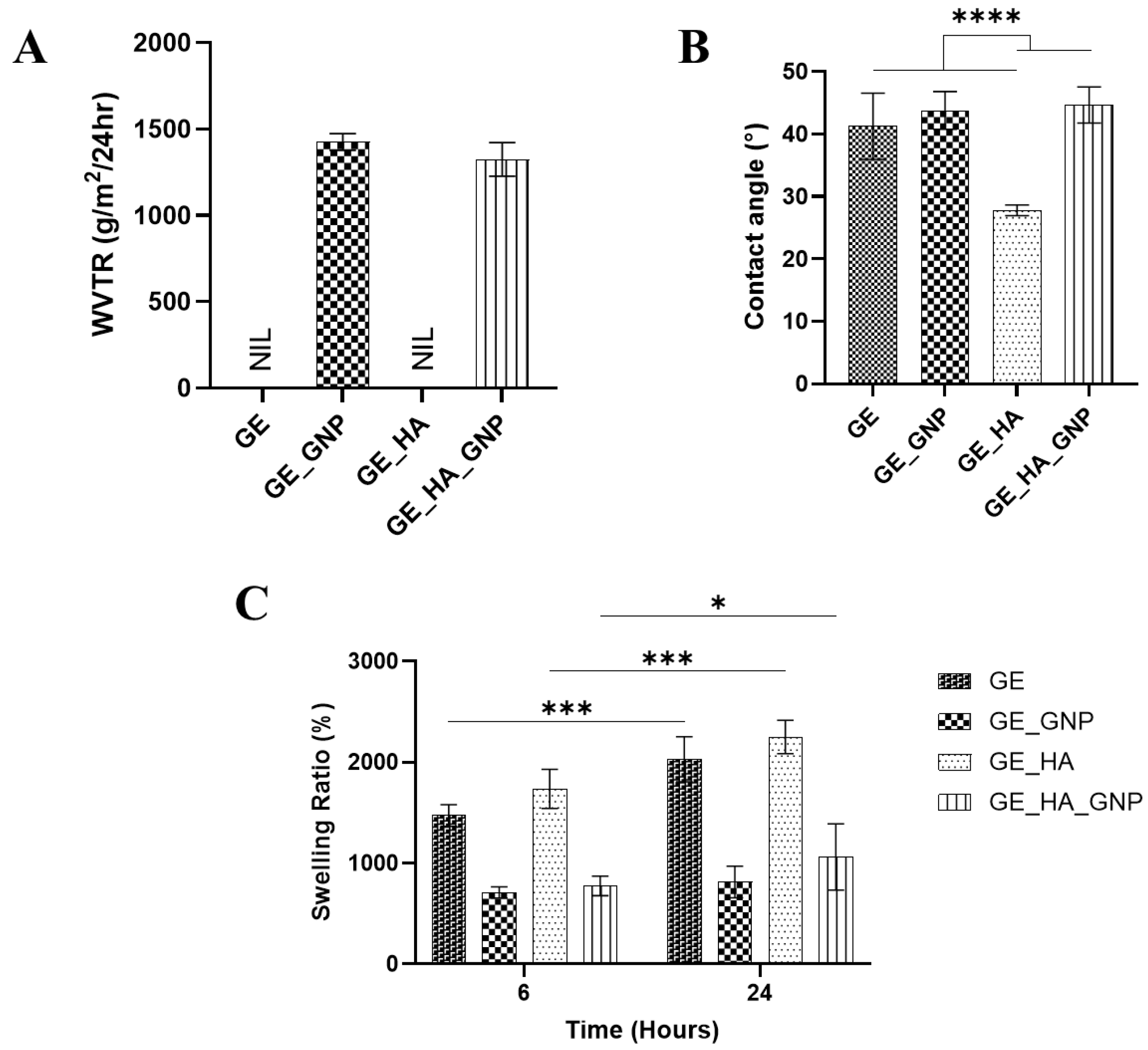
2.6. Swelling Ratio
2.7. Contact Angle
2.8. Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR)
2.9. Mechanical Property Analysis
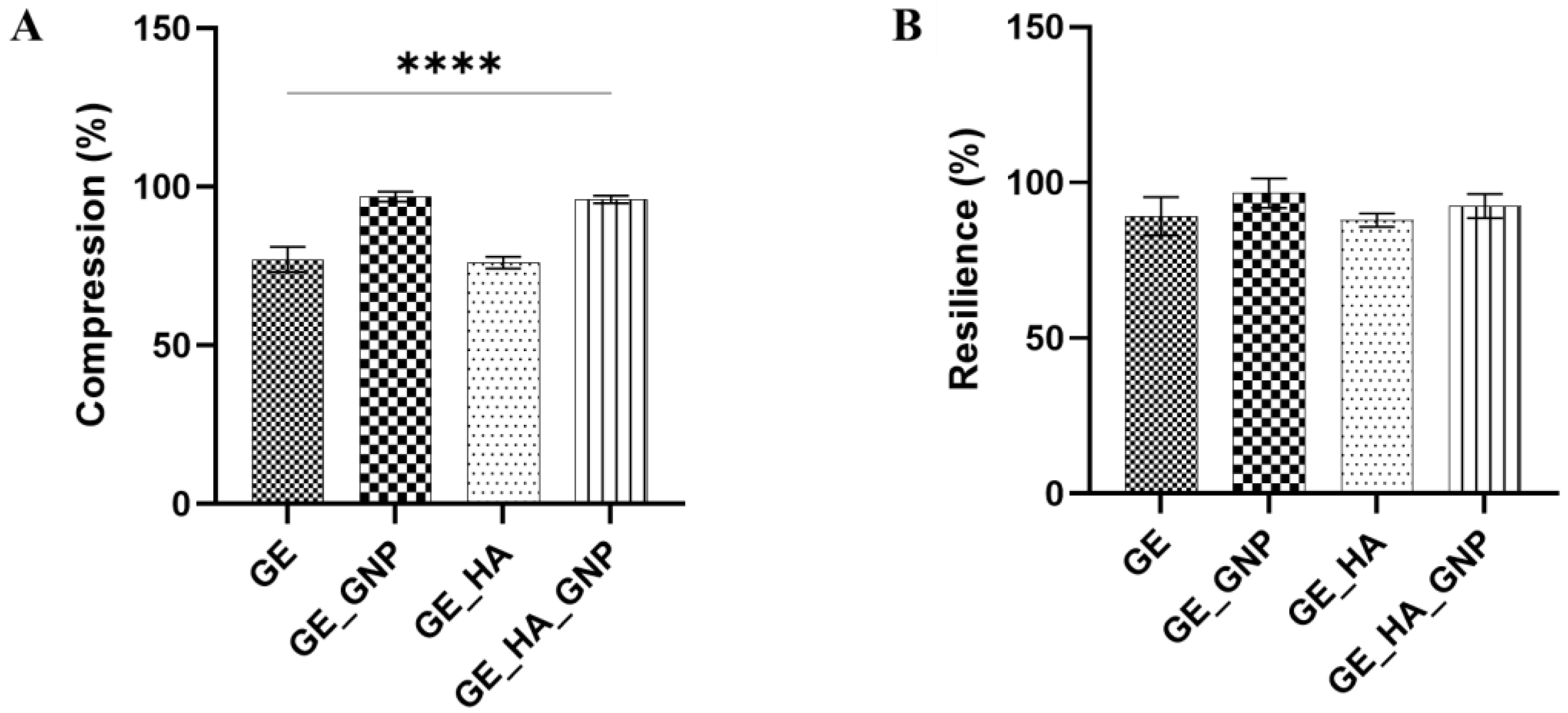
2.9.1. Compression and Resilience
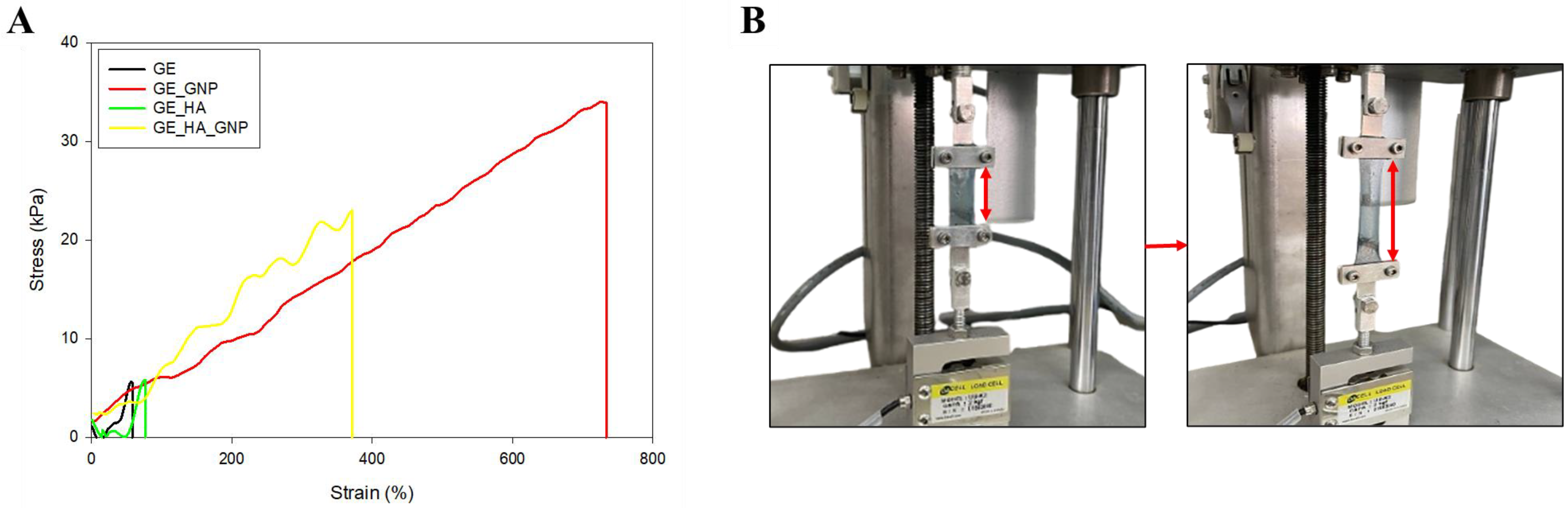
2.9.2. Tensile Strength Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
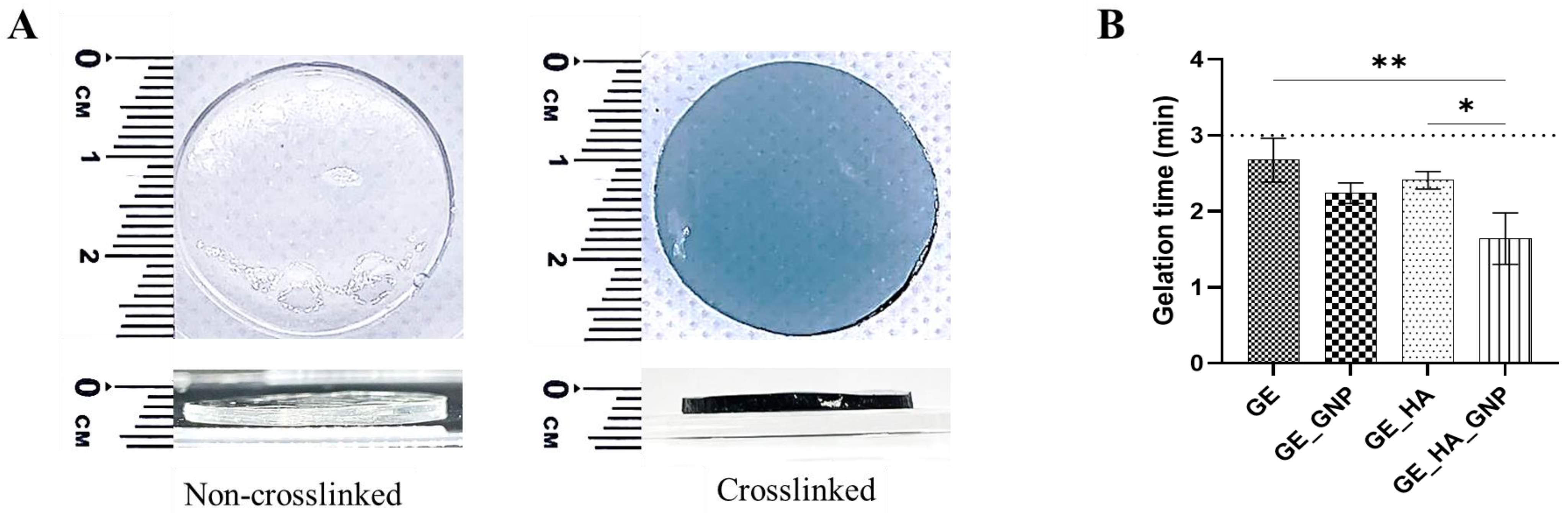
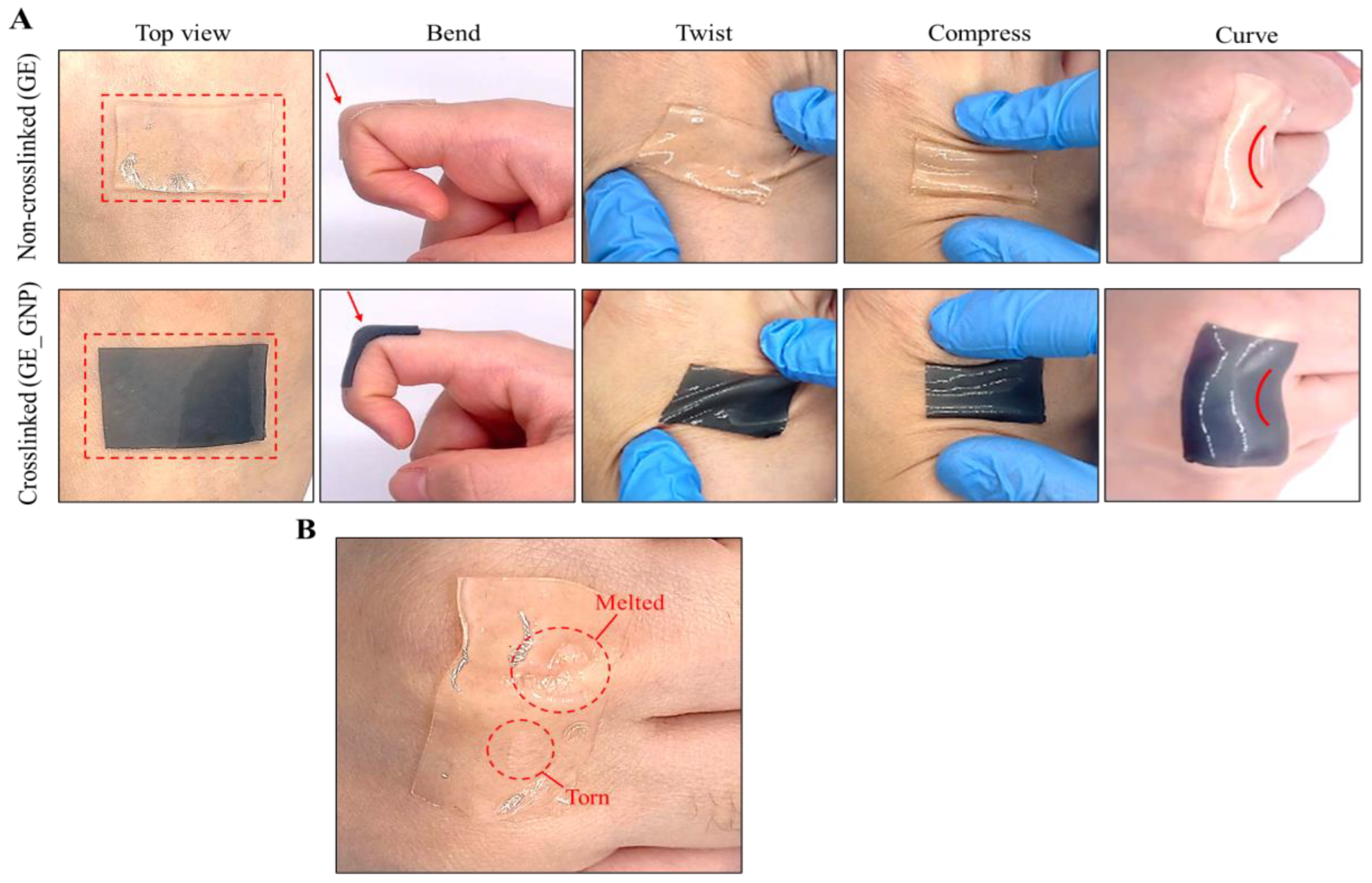
3.1. Characterization of the Adhesive Hydrogel Patches
3.2. Physical Characterization of the Adhesive Hydrogel Patches
3.3. Chemical Evaluation of the Hydrogel Patch
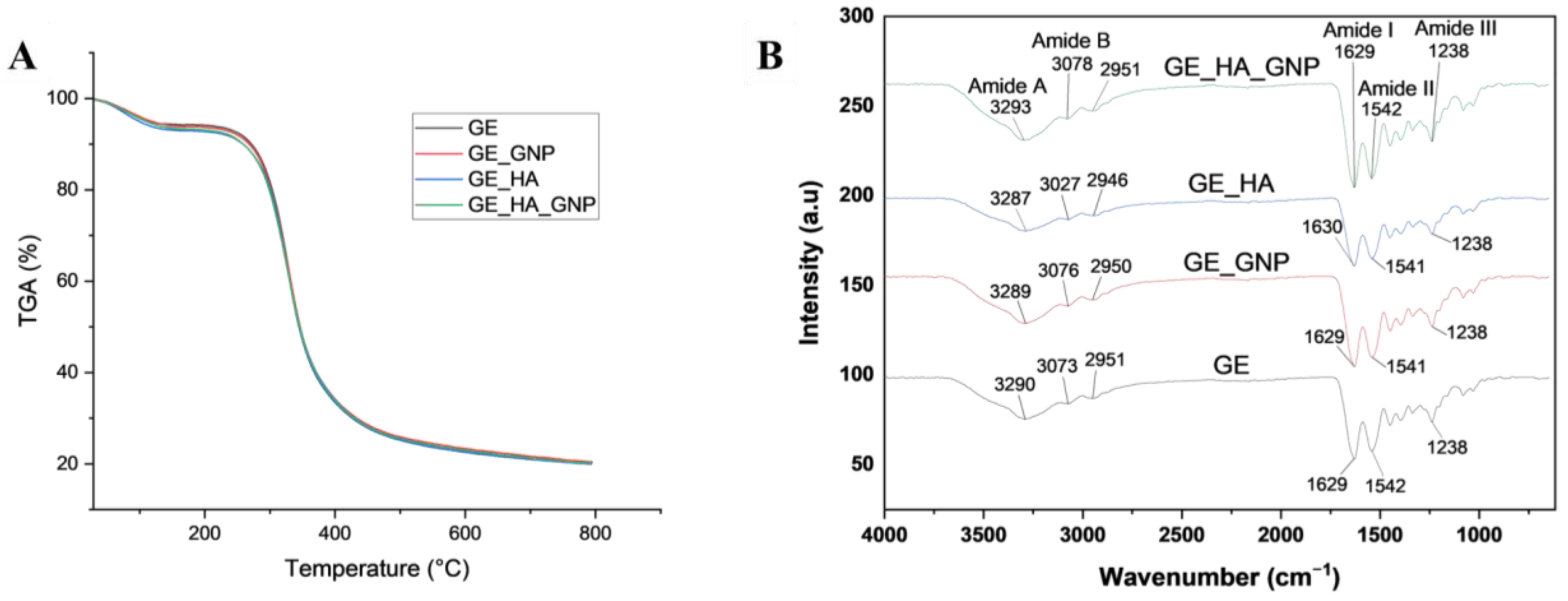
3.3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) and Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3.2. Dispersive X-Ray (EDX)
3.4. Micro-Morphological Evaluation of the Hydrogel Patches
3.5. Physicochemical Characterization of the Hydrogel Patches
3.6. Mechanical Characterization of the Hydrogel Patches
3.6.1. Physical Properties of Hydrogel Patches
3.6.2. Tensile Properties Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| WVTR | Water vapor transmission rate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TGA | Thermogravimetric analysis |
| GE | Gelatin |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| GNP | Genipin |
References
- Kiecka, A.; Szczepanik, M.; Kiecka, A.; Szczepanik, M. The potential action of SSRIs in the treatment of skin diseases including atopic dermatitis and slow-healing wounds. Pharmacol. Rep. 2022, 74, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawawi, N.A.; Ahmad, H.; Madatheri, R.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B.; Zawawi, N.A.; Ahmad, H.; Madatheri, R.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; et al. Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents in the Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lasse, S.; Lee, P.; Nakasaki, M.; Chen, S.-W.; Yamasaki, K.; Gallo, R.L.; Jamora, C.; Li, C.; Lasse, S.; et al. Development of atopic dermatitis-like skin disease from the chronic loss of epidermal caspase-8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 22249–22254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuutila, K.; Eriksson, E. Moist Wound Healing with Commonly Available Dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Dosan, R. Lessons From Epithelialization: The Reason Behind Moist Wound Environment. Open Dermatol. J. 2019, 13, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, C.K. Human Wound and Its Burden: Updated 2020 Compendium of Estimates. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolimi, P.; Narala, S.; Nyavanandi, D.; Youssef, A.A.A.; Dudhipala, N. Innovative Treatment Strategies to Accelerate Wound Healing: Trajectory and Recent Advancements. Cells 2022, 11, 2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nifontova, G.; Safaryan, S.; Khristidis, Y.; Smirnova, O.; Vosough, M.; Shpichka, A.; Timashev, P. Advancing wound healing by hydrogel-based dressings loaded with cell-conditioned medium: A systematic review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-C.; Lin, D.-J.; Wu, Y.-R.; Chang, C.-W.; Chen, C.-H.; Ko, C.-L.; Chen, W.-C. Characterization of genipin-crosslinked gelatin/hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel membranes and loaded with hinokitiol: In vitro evaluation of antibacterial activity and biocompatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 105, 110074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, M.R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Gunbayar, M.; Jung, M.; Noh, I.; Khatun, M.R.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Gunbayar, M.; Jung, M.; Noh, I. Study on Bioresponsive Gelatin-Hyaluronic Acid-Genipin Hydrogel for High Cell-Density 3D Bioprinting. Gels 2023, 9, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Jang, E.J.; Choi, K.H.; Na, Y.C. Comparative evaluation of hyaluronic acid-based dressing versus hydrocolloid dressing in rat dermal wound healing. Arch. Craniofacial Surg. 2024, 25, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, R.; Hira, N.U.A.; Wang, M.; Iqbal, S.; Yi, J.; Hemar, Y. Genipin, a natural blue colorant precursor: Source, extraction, properties, and applications—PubMed. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, A.; Rufino, I.; Martins, A.M.; Raposo, S.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J. Prevention of skin lesions caused by the use of protective face masks by an innovative gelatin-based hydrogel patch: Design and in vitro studies. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 638, 122941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, J.; Barkat, K.; Ashraf, M.U.; Badshah, S.F.; Ahmad, Z.; Anjum, I.; Shabbir, M.; Mehmood, Y.; Khalid, I.; Malik, N.S.; et al. Preparation and characterization of polymeric cross-linked hydrogel patch for topical delivery of gentamicin. e-Polymers 2023, 23, 20230045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salleh, A.; Mustafa, N.; Teow, Y.H.; Fatimah, M.N.; Khairudin, F.A.; Ahmad, I.; Fauzi, M.B.; Salleh, A.; Mustafa, N.; Teow, Y.H.; et al. Dual-Layered Approach of Ovine Collagen-Gelatin/Cellulose Hybrid Biomatrix Containing Graphene Oxide-Silver Nanoparticles for Cutaneous Wound Healing: Fabrication, Physicochemical, Cytotoxicity and Antibacterial Characterisation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawani, M.; Maarof, M.; Tabata, Y.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B.; Zawani, M.; Maarof, M.; Tabata, Y.; Motta, A.; Fauzi, M.B. Quercetin-Embedded Gelastin Injectable Hydrogel as Provisional Biotemplate for Future Cutaneous Application: Optimization and In Vitro Evaluation. Gels 2022, 8, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masri, S.; Maarof, M.; Mohd, N.F.; Hiraoka, Y.; Tabata, Y.; Fauzi, M.B. Injectable Crosslinked Genipin Hybrid Gelatin-PVA Hydrogels for Future Use as Bioinks in Expediting Cutaneous Healing Capacity: Physicochemical Characterisation and Cytotoxicity Evaluation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nizam, A.A.K.; Md Fadilah, N.I.; Ahmad, H.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Injectable Gelatin-Palmitoyl-GDPH Hydrogels as Bioinks for Future Cutaneous Regeneration: Physicochemical Characterization and Cytotoxicity Assessment. Polymers 2024, 17, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, S.; González, L.; Tapia, M.; Urbano, B.F.; Aguayo, C.; Fernández, K.; Carrasco, S.; González, L.; Tapia, M.; Urbano, B.F.; et al. Enhancing Alginate Hydrogels as Possible Wound-Healing Patches: The Synergistic Impact of Reduced Graphene Oxide and Tannins on Mechanical and Adhesive Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, S.; Ohi, H.; Taya, M. Gelatin/Hyaluronic Acid Content in Hydrogels Obtained through Blue Light-Induced Gelation Affects Hydrogel Properties and Adipose Stem Cell Behaviors. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdagi, S.I.; Ngwabebhoh, F.A.; Yildiz, U. Genipin crosslinked gelatin-diosgenin-nanocellulose hydrogels for potential wound dressing and healing applications—PubMed. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z.; Suo, Z. Adhesion between highly stretchable materials. Soft Matter 2016, 12, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Chaudhury, M.K. Direct Measurement of the Surface Tension of a Soft Elastic Hydrogel: Exploration of Elastocapillary Instability in Adhesion. Langmuir 2013, 29, 6926–6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavda, H.; Patel, C. Effect of crosslinker concentration on characteristics of superporous hydrogel. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2011, 1, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queen, D.; Gaylor, J.D.S.; Evans, J.H.; Courtney, J.M.; Reid, W.H. The preclinical evaluation of the water vapour transmission rate through burn wound dressings. Biomaterials 1987, 8, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.; Park, J.; Sutthiwanjampa, C.; Kim, H.; Bae, T.; Kim, W.; Choi, J.; Kim, M.; Kang, S.; Park, H. Surface Coating with Hyaluronic Acid-Gelatin-Crosslinked Hydrogel on Gelatin-Conjugated Poly(dimethylsiloxane) for Implantable Medical Device-Induced Fibrosis—PubMed. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngadaonye, J.I.; Geever, L.M.; Killion, J.; Higginbotham, C.L.; Ngadaonye, J.I.; Geever, L.M.; Killion, J.; Higginbotham, C.L. Development of novel chitosan-poly(N,N-diethylacrylamide) IPN films for potential wound dressing and biomedical applications. J. Polym. Res. 2013, 20, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Im, P.; Shin, S.; Kim, J.; Ji, D.; Im, P.; Shin, S.; Kim, J. Specimen Geometry Effect on Experimental Tensile Mechanical Properties of Tough Hydrogels. Materials 2023, 16, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Formulation | GE (g) | HA (g) | GNP (g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE | 0.9 | - | - |
| GE_GNP | 0.9 | - | 0.01 |
| GE_HA | 0.9 | 0.02 | - |
| GE_HA_GNP | 0.9 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| No. | Formulation | Thickness (mm) | Weight Variation (g) | Folding Endurance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GE | 1.24 ± 0.05 | 0.52 ± 0.02 | 64 ± 4.66 |
| 2 | GE_GNP | 1.04 ± 0.11 | 0.53 ± 0.01 | 233 ± 5.80 |
| 3 | GE_HA | 1.18 ± 0.19 | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 53 ± 4.02 |
| 4 | GE_HA_GNP | 1.02 ± 0.13 | 0.46 ± 0.02 | 300 ± 10.31 |
| Sample | C (%) | O (%) | N (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GE | 45.3 ± 1.25 | 30.8 ± 0.9 | 22.4 ± 1.75 |
| GE_GNP | 48.1 ± 1.36 | 30.33 ± 1.06 | 19.2 ± 1.93 |
| GE_HA | 46.95 ± 0.95 | 30.55 ± 0.8 | 21.0 ± 1.35 |
| GE_HA_GNP | 46.3 ± 1.05 | 31.3 ± 0.85 | 20.55 ± 1.45 |
| Hydrogel | Tensile Strength (kPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|
| GE | 5.88 ± 1.46 | 58.11 ± 0.51 |
| GE_GNP | 33.87 ± 9.58 | 733.5 ± 2.29 |
| GE_HA | 5.81 ± 2.23 | 76.87 ± 0.55 |
| GE_HA_GNP | 23.01 ± 6.83 | 371.62 ± 1.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zawawi, N.A.; Maarof, M.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Hao, D.L.Q.; Tabata, Y.; Fauzi, M.B. Hybrid Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Containing Genipin-Crosslinked Gelatin–Hyaluronic Acid for Future Use in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2025, 16, 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16060195
Zawawi NA, Maarof M, Fadilah NIM, Hao DLQ, Tabata Y, Fauzi MB. Hybrid Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Containing Genipin-Crosslinked Gelatin–Hyaluronic Acid for Future Use in Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2025; 16(6):195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16060195
Chicago/Turabian StyleZawawi, Nurul Ain, Manira Maarof, Nur Izzah Md Fadilah, Daniel Looi Qi Hao, Yasuhiko Tabata, and Mh Busra Fauzi. 2025. "Hybrid Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Containing Genipin-Crosslinked Gelatin–Hyaluronic Acid for Future Use in Atopic Dermatitis" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 16, no. 6: 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16060195
APA StyleZawawi, N. A., Maarof, M., Fadilah, N. I. M., Hao, D. L. Q., Tabata, Y., & Fauzi, M. B. (2025). Hybrid Adhesive Hydrogel Patch Containing Genipin-Crosslinked Gelatin–Hyaluronic Acid for Future Use in Atopic Dermatitis. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 16(6), 195. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb16060195








