A Bibliometric Analysis of Electrospun Nanofibers for Dentistry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Technology for Electrospinning
2.1.1. Principle of Electrospinning
2.1.2. Parameters Affecting Electrospinning
2.2. Materials for Electrospinning in Dentistry
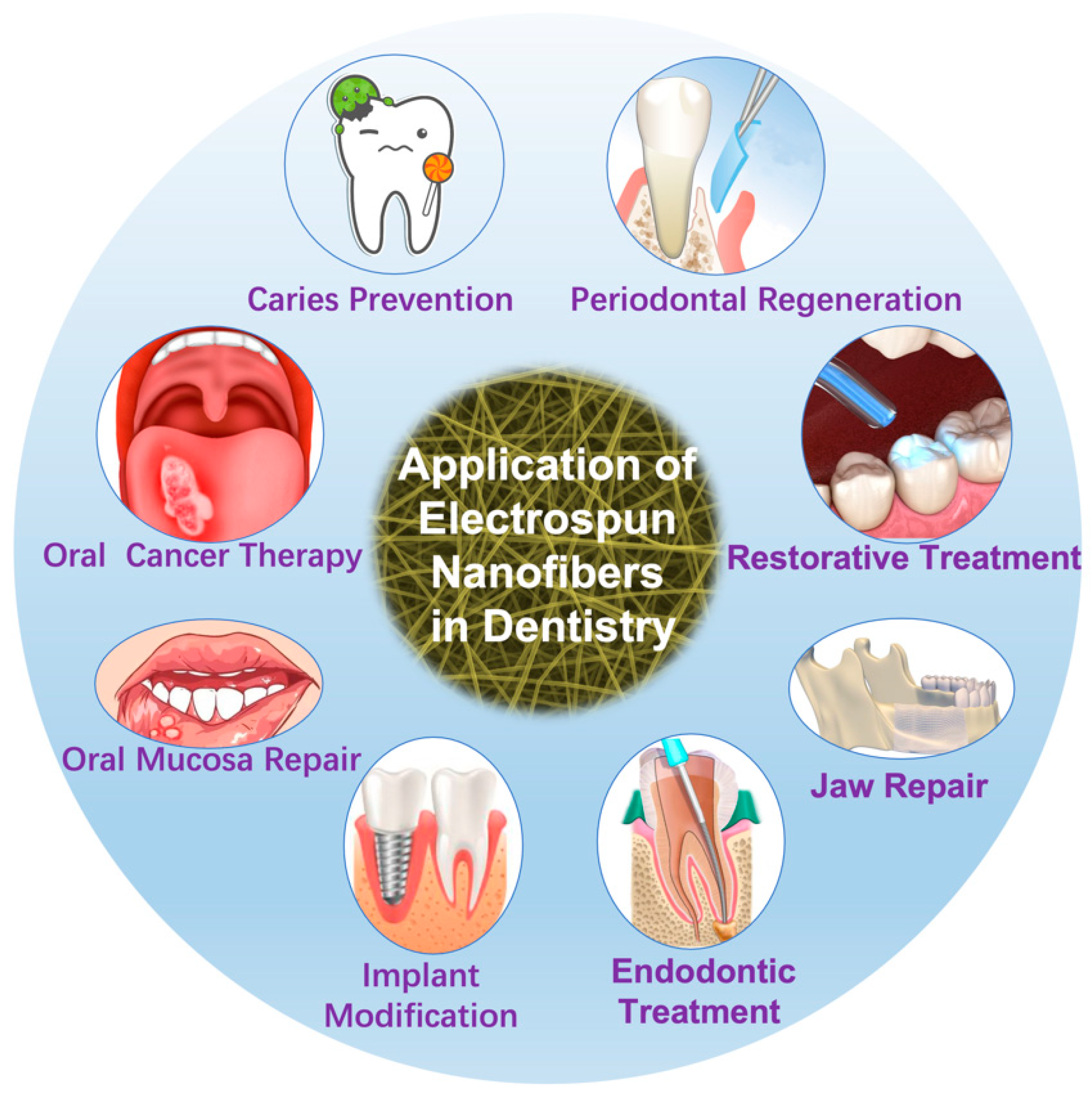
2.3. Applications of Electrospinning in Dentistry
2.3.1. Periodontal Regeneration
2.3.2. Restorative Treatment
2.3.3. Endodontic Treatment
2.3.4. Implant Modification
2.3.5. Jaw Repair
2.3.6. Oral Mucosa Repair
2.3.7. Oral Cancer Therapy
2.3.8. Caries Prevention
3. Data Sources and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Publication and Trend Analysis
4.2. Journal Analysis
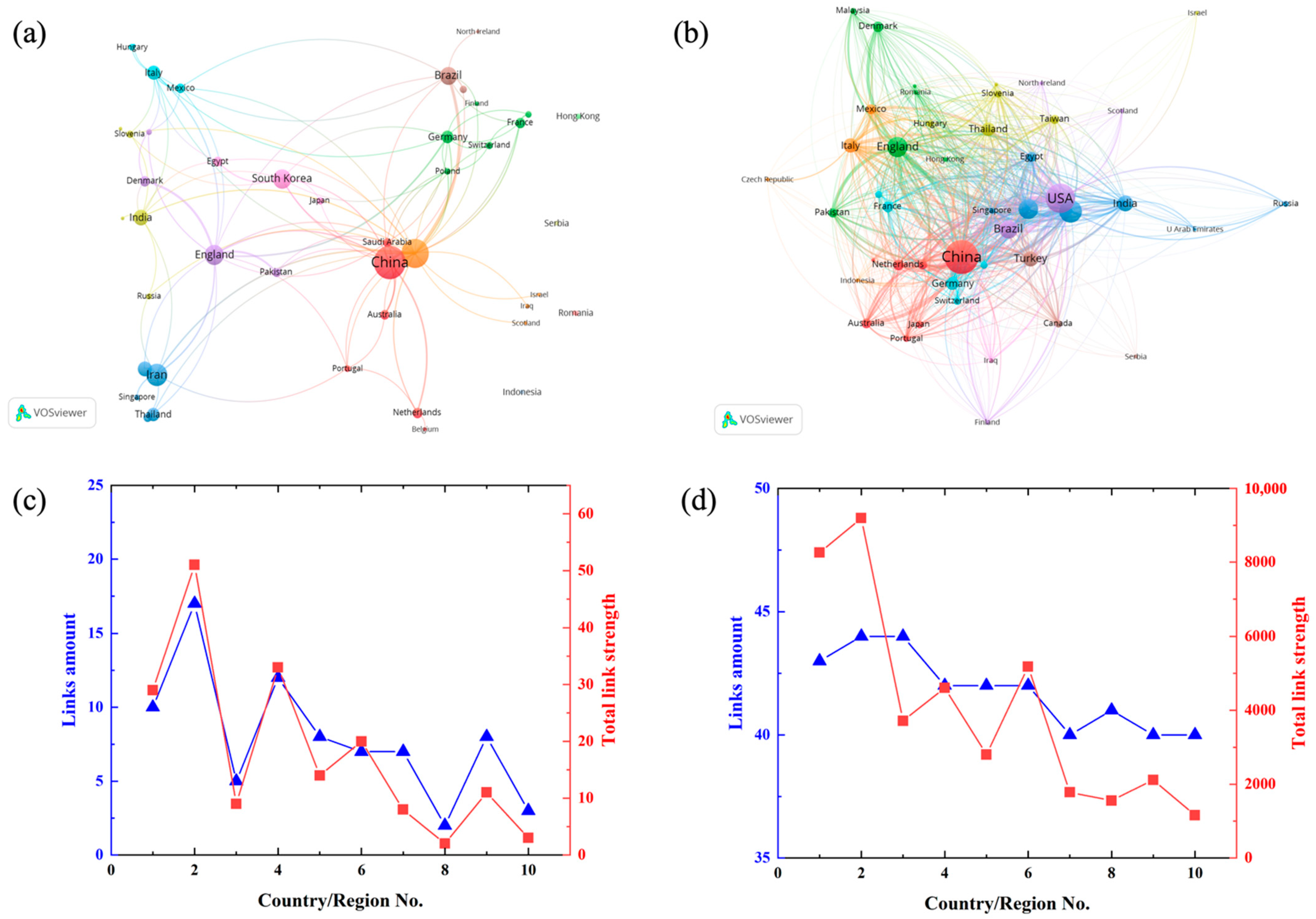
4.3. Contribution of Country/Region
4.4. Contribution of Institution
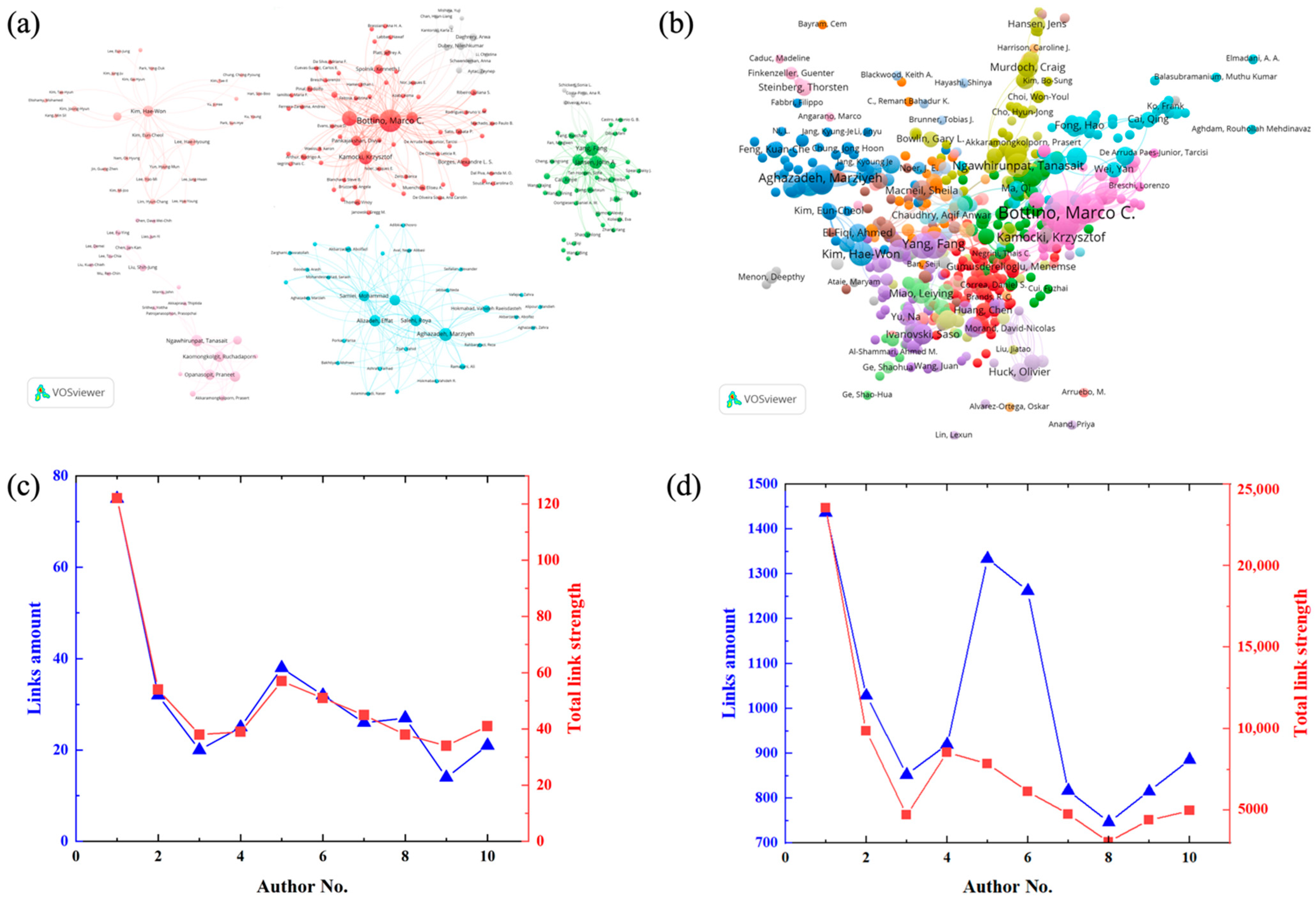
4.5. Contribution of Author
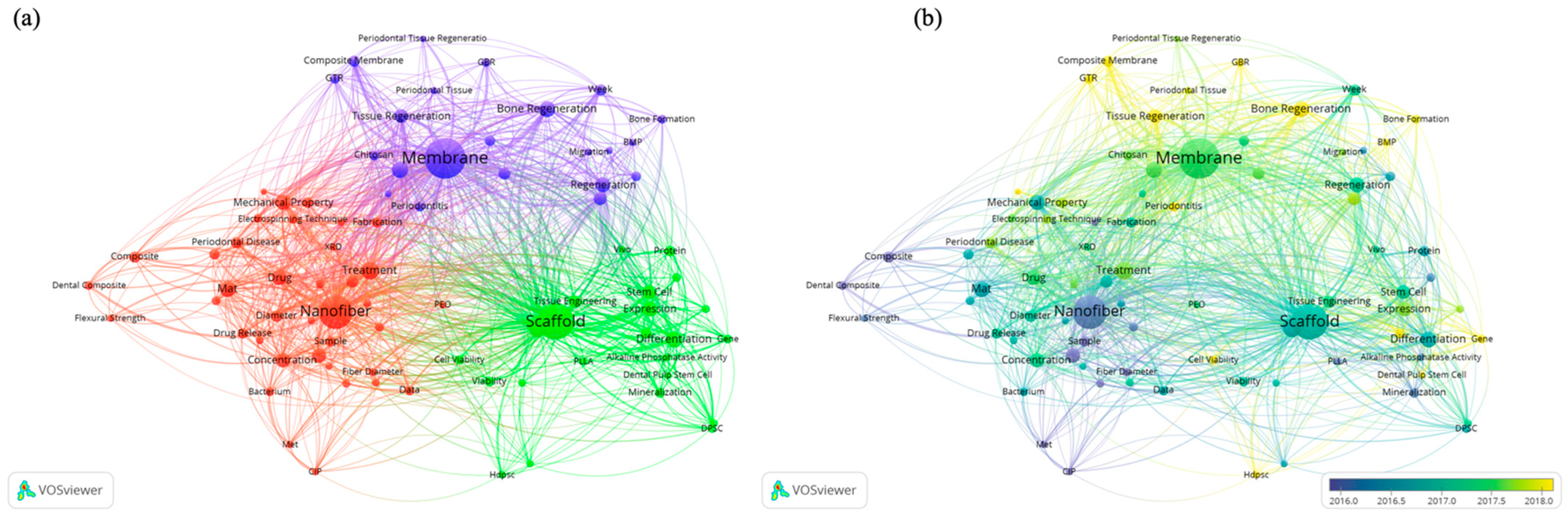
4.6. Keywords Analysis
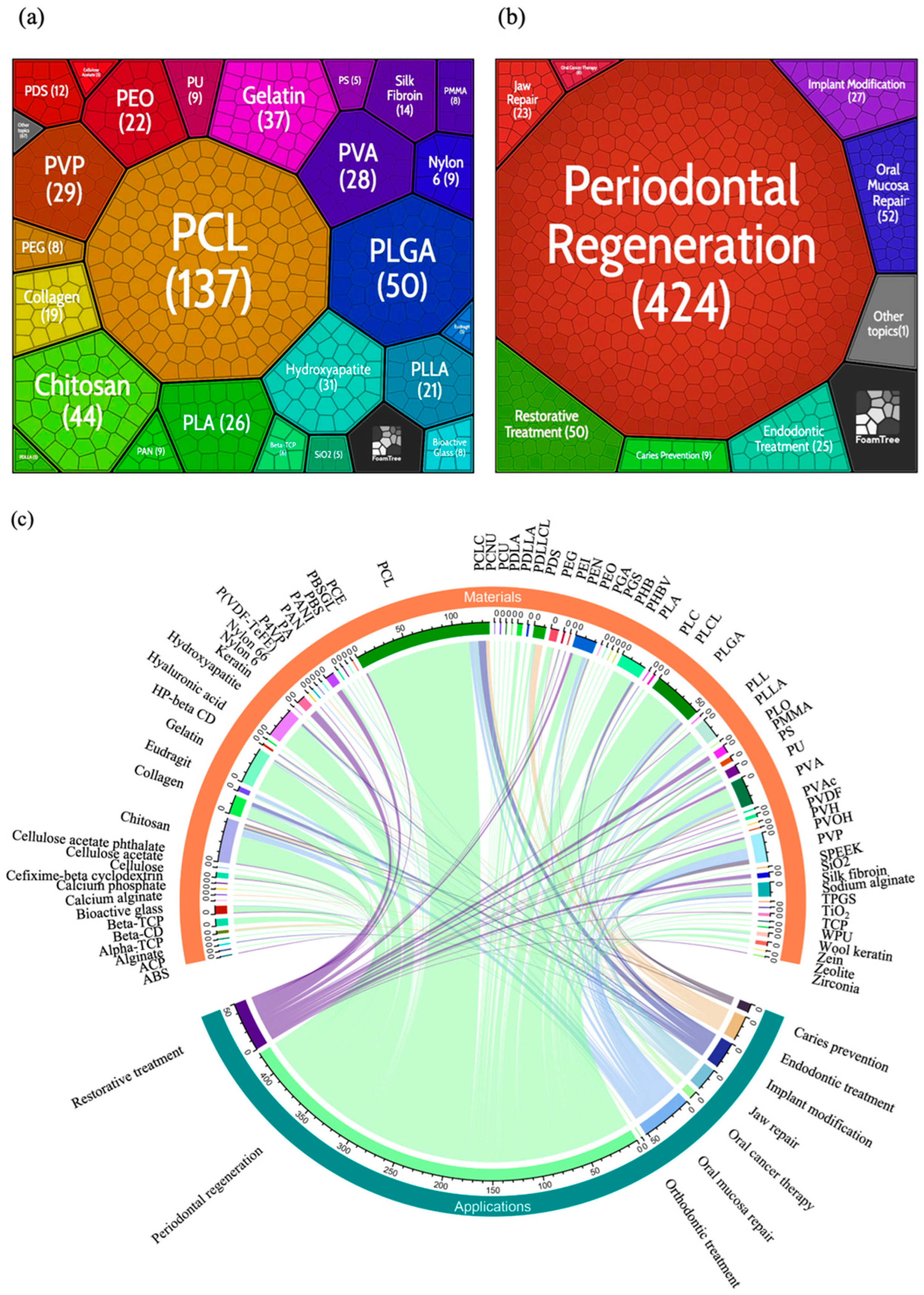
4.7. Materials and Applications Analysis
4.8. Limitations and Trends Outlooks
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Xin, B.; Meng, N.; Helian, X. Effects of surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene fiber on its air filtration performance. J. Ind. Text. 2020, 1528083720909462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnappan, A.; Baskar, C.; Baskar, S.; Ratheesh, G.; Ramakrishna, S. An overview of electrospun nanofibers and their application in energy storage, sensors and wearable/flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 12657–12673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Gas sensors based on electrospun nanofibers. Sensors 2009, 9, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Wu, C.; Li, X.; Yao, Y.; Lan, L.; Zhao, F.; Ye, Z.; Ying, Y.; Ping, J. All-electrospun flexible triboelectric nanogenerator based on metallic MXene nanosheets. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Yang, K. Electrochemical properties of carbon nanofiber web as an electrode for supercapacitor prepared by electrospinning. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 83, 1216–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yin, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Luo, J.; Tang, W.; Cao, R.; Yuan, Z.; Li, N. Self-powered electrospinning system driven by a triboelectric nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 10439–10445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhmatia, Y.D.; Ayukawa, Y.; Furuhashi, A.; Koyano, K. Current barrier membranes: Titanium mesh and other membranes for guided bone regeneration in dental applications. J. Prosthodont. Res. 2013, 57, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sill, T.J.; Von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente, A.; Rivero, P.J.; García, P.; Mora, J.; Carreño, F.; Palacio, J.F.; Rodríguez, R. Icephobic and Anticorrosion Coatings Deposited by Electrospinning on Aluminum Alloys for Aerospace Applications. Polymers 2021, 13, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, S.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, J.; Han, G.; Ben, H.; Jiang, W. Biodegradable and Reusable Cellulose-Based Nanofiber Membrane Preparation for Mask Filter by Electrospinning. Membranes 2021, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Kan, C.-W. Review on fabrication of structurally colored fibers by electrospinning. Fibers 2018, 6, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Freitas, R.A., Jr. Nanodentistry. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2000, 131, 1559–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannig, M.; Hannig, C. Nanomaterials in preventive dentistry. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahrari, F.; Eslami, N.; Rajabi, O.; Ghazvini, K.; Barati, S. The antimicrobial sensitivity of Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sangius to colloidal solutions of different nanoparticles applied as mouthwashes. Dent. Res. J. 2015, 12, 44. [Google Scholar]
- Melo, M.A.S.; Cheng, L.; Weir, M.D.; Hsia, R.C.; Rodrigues, L.K.; Xu, H.H. Novel dental adhesive containing antibacterial agents and calcium phosphate nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2013, 101, 620–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corrêa, J.M.; Mori, M.; Sanches, H.L.; Cruz, A.D.d.; Poiate, E.; Poiate, I.A.V.P. Silver nanoparticles in dental biomaterials. Int. J. Biomater. 2015, 2015, 485275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, J.; Guo, J.; Ding, R.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Xiao, D.; Zhou, C. An electrospun fibrous platform for visualizing the critical pH point inducing tooth demineralization. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 4292–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y. Carbon Nanomaterials Modified Biomimetic Dental Implants for Diabetic Patients. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2977. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, F.; Bao, C.; Weir, M.D.; Reynolds, M.A.; Ma, J.; Gu, N.; Xu, H.H. Gold nanoparticles in injectable calcium phosphate cement enhance osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-C.; Chang, C.-C.; Yang, F.; Simon, M.; Rafailovich, M. TiO2 nanoparticles synergize with substrate mechanics to improve dental pulp stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, K.; Kotaki, M.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, X.; Ramakrishna, S. Recent advances in polymer nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004, 4, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lxy, D.; Xia, Y.N. Electrospinning of Nanofibers: Reinventing the Wheel? Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1151–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, B.; Wang, X.; Yu, J. Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wendorff, J.H.; Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A. Electrospinning: Materials, Processing, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: Methods, materials, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, H. Electrospun nylon 6 nanofiber reinforced BIS-GMA/TEGDMA dental restorative composite resins. Polymer 2004, 45, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhang, H.; Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. A bibliometric analysis and review of supercritical fluids for the synthesis of nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, A.W.K.; Tzvetkov, N.T.; Durazzo, A.; Lucarini, M.; Souto, E.B.; Santini, A.; Gan, R.-Y.; Jozwik, A.; Grzybek, W.; Horbańczuk, J.O. Natural products in diabetes research: Quantitative literature analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2021, 35, 5813–5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yeung, A.W.; Pow, E.H.; Tsoi, J.K. Current status and research trends of lithium disilicate in dentistry: A bibliometric analysis. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, J.F. Apparatus for Electrically Dispersing Fluids. U.S. Patent US692631A, 4 February 1902. [Google Scholar]
- Formhals, A. Process and Apparatus for Preparing Artificial Threads. U.S. Patent 1975504A, 2 October 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, H.; Chun, I.; Reneker, D.H. Beaded nanofibers formed during electrospinning. Polymer 1999, 40, 4585–4592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneker, D.H.; Yarin, A.L.; Fong, H.; Koombhongse, S. Bending instability of electrically charged liquid jets of polymer solutions in electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 4531–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, Y.-Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, J.; Yu, M. Electrospinning: The setup and procedure. In Electrospinning: Nanofabrication and Applications; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 21–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, C.S.; Yoo, W.S.; Jo, N.G.; Kim, H.S. Electrospinning mechanism for producing nanoscale polymer fibers. J. Macromol. Sci. Part B Phys. 2010, 49, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, H.; Meng, Z. Melt electrospinning vs. solution electrospinning: A comparative study of drug-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) fibres. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 74, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutmacher, D.W.; Dalton, P.D. Melt electrospinning. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Xiao, C.; Xiao, H.; Yang, H.; Zhuang, X.; Chen, X. Electrospun polymer biomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 90, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Greiner, A.; Wendorff, J.H. Functional materials by electrospinning of polymers. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 963–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koski, A.; Yim, K.; Shivkumar, S. Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angammana, C.J.; Jayaram, S.H. Analysis of the effects of solution conductivity on electrospinning process and fiber morphology. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2011, 47, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xin, B.; Zheng, Y. Preparation and characterization of polysulfone amide nanoyarns by the dynamic rotating electrospinning method. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, R.; Yu, J.Y. Effect of applied voltage on diameter and morphology of ultrafine fibers in bubble electrospinning. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Xin, B.; Xu, Y. Coaxial Electrospinning: Jet Motion, Core–Shell Fiber Morphology, and Structure as a Function of Material Parameters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 6301–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Zheng, Y.; Xin, B. Surface morphologies of electrospun polystyrene fibers induced by an electric field. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 3850–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Guan, Z.; Zahn, M. A shield ring enhanced equilateral hexagon distributed multi-needle electrospinning spinneret. IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 2010, 17, 1592–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The effect of flow rate on morphology and deposition area of electrospun nylon 6 nanofiber. J. Eng. Fibers Fabr. 2012, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hejazi, F.; Mirzadeh, H.; Contessi, N.; Tanzi, M.C.; Fare, S. Novel class of collector in electrospinning device for the fabrication of 3D nanofibrous structure for large defect load-bearing tissue engineering application. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 1535–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrieze, S.; Van Camp, T.; Nelvig, A.; Hagström, B.; Westbroek, P.; De Clerck, K. The effect of temperature and humidity on electrospinning. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, R.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L.; Truong, Y.B.; Arnold, L. Effect of viscosity and electrical conductivity on the morphology and fiber diameter in melt electrospinning of polypropylene. Text. Res. J. 2013, 83, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Haoqing, H.; Schaper, A.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Poly-L-lactide nanofibers by electrospinning–Influence of solution viscosity and electrical conductivity on fiber diameter and fiber morphology. e-Polymers 2003, 3, 009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, S.; Zeng, Y. Effects of electric field on multineedle electrospinning: Experiment and simulation study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 5336–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Hou, L.; Wang, L.; Guan, Z. Effect of electric field distribution uniformity on electrospinning. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 104307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Lu, B.; Xie, Y.; Ma, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Duan, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, J. Temperature effect on electrospinning of nanobelts: The case of hafnium oxide. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 285609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, C.L.; Stephens, J.S.; Tassi, N.G.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Controlling surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene fibers: Effect of humidity and molecular weight in the electrospinning process. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.B.; Wu, D.; Holmes, B.N. An application of nanotechnology in advanced dental materials. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 2003, 134, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCabe, J.F.; Walls, A.W. Applied Dental Materials; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hokmabad, V.R.; Davaran, S.; Aghazadeh, M.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Salehi, R.; Ramazani, A. Fabrication and characterization of novel ethyl cellulose-grafted-poly(ɛ-caprolactone)/alginate nanofibrous/macroporous scaffolds incorporated with nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 1128–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, C.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, X.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun cellulose/nano-hydroxyapatite nanofibers for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 97, 568–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samprasit, W.; Kaomongkolgit, R.; Sukma, M.; Rojanarata, T.; Ngawhirunpat, T.; Opanasopit, P. Mucoadhesive electrospun chitosan-based nanofibre mats for dental caries prevention. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, K.; Hayashi, S.; Kameyama, N.; Yamamoto, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kimoto, S.; Kurata, S.; Shinji, H. Synthesis of Collagen-Like Sequential Polypeptides Containing O-Phospho-l-Hydroxyproline and Preparation of Electrospun Composite Fibers for Possible Dental Application. Macromol. Biosci. 2009, 9, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Meng, S.; Dai, X.; Han, B.; Deng, X. Enhanced critical size defect repair in rabbit mandible by electrospun gelatin/β-TCP composite nanofibrous membranes. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 396916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karatepe, U.Y.; Ozdemir, T. Improving mechanical and antibacterial properties of PMMA via polyblend electrospinning with silk fibroin and polyethyleneimine towards dental applications. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seonwoo, H.; Jang, K.-J.; Lee, D.; Park, S.; Lee, M.; Park, S.; Lim, K.-T.; Kim, J.; Chung, J.H. Neurogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells on graphene-polycaprolactone hybrid nanofibers. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qasim, S.B.; Najeeb, S.; Delaine-Smith, R.M.; Rawlinson, A.; Rehman, I.U. Potential of electrospun chitosan fibers as a surface layer in functionally graded GTR membrane for periodontal regeneration. Dent. Mater. 2017, 33, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohandesnezhad, S.; Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi, Y.; Alizadeh, E.; Goodarzi, A.; Davaran, S.; Khatamian, M.; Zarghami, N.; Samiei, M.; Aghazadeh, M.; Akbarzadeh, A. In vitro evaluation of Zeolite-nHA blended PCL/PLA nanofibers for dental tissue engineering. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 252, 123152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei-rad, P.; Jamshidi, D.; Adel, M.; Seyedjafari, E. Electrospun poly(L-lactide) nanofibers coated with mineral trioxide aggregate enhance odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2021, 32, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Zhu, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yao, F. Electrospun PDLLA/PLGA composite membranes for potential application in guided tissue regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 58, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chor, A.; Gonçalves, R.P.; Costa, A.M.; Farina, M.; Ponche, A.; Sirelli, L.; Schrodj, G.; Gree, S.; Andrade, L.R.d.; Anselme, K. In vitro degradation of electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA) for oral mucosa regeneration. Polymers 2020, 12, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Lee, S.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kang, W.-S.; Cho, H.-J. Angelica gigas Nakai extract-loaded fast-dissolving nanofiber based on poly(vinyl alcohol) and Soluplus for oral cancer therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 526, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Yang, Y.C.; Yang, J.C. Processing and properties of hydrophilic electrospun polylactic acid/beta-tricalcium phosphate membrane for dental applications. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2013, 53, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.-J.; Min, K.-S.; Kim, J.-J.; Kim, J.-J.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, E.-C. Odontogenic responses of human dental pulp cells to collagen/nanobioactive glass nanocomposites. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Hussain, A.; Sidra, L.; Sarfraz, Z.; Khalid, H.; Khan, M.; Manzoor, F.; Shahzadi, L.; Yar, M.; Rehman, I. Fabrication and in vivo evaluation of hydroxyapatite/carbon nanotube electrospun fibers for biomedical/dental application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 80, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Deng, X. Improved performance of Bis-GMA/TEGDMA dental composites by net-like structures formed from SiO2 nanofiber fillers. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 59, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, M.C.; Thomas, V.; Schmidt, G.; Vohra, Y.K.; Chu, T.-M.G.; Kowolik, M.J.; Janowski, G.M. Recent advances in the development of GTR/GBR membranes for periodontal regeneration—A materials perspective. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 703–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Lamster, I.; Greenspan, J.; Pitts, N.; Scully, C.; Warnakulasuriya, S. Global burden of oral diseases: Emerging concepts, management and interplay with systemic health. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Lin, K.; Yu, H. Advance of nano-composite electrospun fibers in periodontal regeneration. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez de Grado, G.; Keller, L.; Idoux-Gillet, Y.; Wagner, Q.; Musset, A.-M.; Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Bornert, F.; Offner, D. Bone substitutes: A review of their characteristics, clinical use, and perspectives for large bone defects management. J. Tissue Eng. 2018, 9, 2041731418776819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Y.; Kauffmann, F.; Maekawa, S.; Sarment, L.V.; Sugai, J.V.; Schmiedeler, C.A.; Doherty, E.J.; Holdsworth, G.; Kostenuik, P.J.; Giannobile, W.V. Sclerostin antibody stimulates periodontal regeneration in large alveolar bone defects. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, M.; Sun, B.; Qiao, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, D.; He, C.; Zhang, X. Bi-layered electrospun nanofibrous membrane with osteogenic and antibacterial properties for guided bone regeneration. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 176, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ren, S.; Li, L.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, W.; Xu, Y. Biodegradable engineered fiber scaffolds fabricated by electrospinning for periodontal tissue regeneration. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 36, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, T.P.; Srivastava, R.; Srivastava, A.K.; Gupta, V.; Verma, P.K. Evaluation of metronidazole nanofibers in patients with chronic periodontitis: A clinical study. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 2, 213. [Google Scholar]
- Srithep, Y.; Akkaprasa, T.; Pholharn, D.; Morris, J.; Liu, S.-J.; Patrojanasophon, P.; Ngawhirunpat, T. Metronidazole-loaded polylactide stereocomplex electrospun nanofiber mats for treatment of periodontal disease. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 64, 102582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.-U.; Um, H.-S.; Chang, B.-S.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yoo, K.-Y.; Choi, W.-Y.; Lee, J.-K. Controlled releasing properties of gelatin nanofabric device containing chlorhexidine. Oral Biol. Res. 2021, 45, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Miao, L.; Wang, Y.; Ren, S.; Yang, X.; Hu, Y.; Sun, W. Controlled release of recombinant human cementum protein 1 from electrospun multiphasic scaffold for cementum regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 3145. [Google Scholar]
- Vaquette, C.; Fan, W.; Xiao, Y.; Hamlet, S.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Ivanovski, S. A biphasic scaffold design combined with cell sheet technology for simultaneous regeneration of alveolar bone/periodontal ligament complex. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5560–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtos, G.; Rivero, G.; Rapuntean, S.; Abraham, G.A. Amoxicillin-loaded electrospun nanocomposite membranes for dental applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, J.-I.; Abe, G.L.; Li, A.; Thongthai, P.; Tsuboi, R.; Kohno, T.; Imazato, S. Barrier membranes for tissue regeneration in dentistry. Biomater. Investig. Dent. 2021, 8, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasajpour, A.; Ansari, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Rad, A.S.; Aghaloo, T.; Shin, S.R.; Mishra, Y.K.; Adelung, R.; Swieszkowski, W.; Annabi, N. A multifunctional polymeric periodontal membrane with osteogenic and antibacterial characteristics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1703437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, M.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Claudia, J.; Lin, T.-C.; Chang, P.-C. PDGF-metronidazole-encapsulated nanofibrous functional layers on collagen membrane promote alveolar ridge regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xie, H.; Gu, N. Nanoparticle-reinforced resin-based dental composites. J. Dent. 2008, 36, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.W. Polyacid-modified composite resins (“compomers”) and their use in clinical dentistry. Dent. Mater. 2007, 23, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, T.; Çökeliler, D.; Doğan, M.; Koçum, I.C.; Karatay, O.; Denkbaş, E.B. Electrospun nanofiber reinforcement of dental composites with electromagnetic alignment approach. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, A.L.; Münchow, E.A.; de Oliveira Souza, A.C.; Yoshida, T.; Vallittu, P.K.; Bottino, M.C. Effect of random/aligned nylon-6/MWCNT fibers on dental resin composite reinforcement. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 48, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sagi, S.; Zhang, L.; Liao, Y.; Cowles, D.M.; Sun, Y.; Fong, H. Electrospun nano-scaled glass fiber reinforcement of bis-GMA/TEGDMA dental composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 2063–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sagi, S.; Chandrasekar, R.; Zhang, L.; Hedin, N.E.; Fong, H. Preparation and characterization of electrospun SiO2 nanofibers. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2008, 8, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Cai, Q.; Li, P.; Deng, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, M.; Yang, X. Post-draw PAN–PMMA nanofiber reinforced and toughened Bis-GMA dental restorative composite. Dent. Mater. 2010, 26, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.E.; García-Godoy, F. The outlook for implants and endodontics: A review of the tissue engineering strategies to create replacement teeth for patients. Dent. Clin. 2006, 50, 299–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, P.E.; Garcia-Godoy, F.; Hargreaves, K.M. Regenerative endodontics: A review of current status and a call for action. J. Endod. 2007, 33, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, M.; Kamocki, K.; Yassen, G.; Platt, J.; Vail, M.; Ehrlich, Y.; Spolnik, K.; Gregory, R. Bioactive nanofibrous scaffolds for regenerative endodontics. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, M.C.; Yassen, G.H.; Platt, J.A.; Labban, N.; Windsor, L.J.; Spolnik, K.J.; Bressiani, A.H. A novel three-dimensional scaffold for regenerative endodontics: Materials and biological characterizations. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2015, 9, E116–E123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-J.; Bae, W.-J.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, E.-J.; Kim, H.-W.; Kim, E.-C. Mineralized polycaprolactone nanofibrous matrix for odontogenesis of human dental pulp cells. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 28, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eap, S.; Bécavin, T.; Keller, L.; Kökten, T.; Fioretti, F.; Weickert, J.L.; Deveaux, E.; Benkirane-Jessel, N.; Kuchler-Bopp, S. Nanofibers implant functionalized by neural growth factor as a strategy to innervate a bioengineered tooth. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcıa-Alonso, M.; Saldana, L.; Valles, G.; González-Carrasco, J.L.; Gonzalez-Cabrero, J.; Martınez, M.; Gil-Garay, E.; Munuera, L. In vitro corrosion behaviour and osteoblast response of thermally oxidised Ti6Al4V alloy. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, B.; Guo, Z.; Li, X.; Li, S.; Gao, P.; Xiao, X.; Wu, J.; Shen, C.; Jiao, Y.; Hou, W. Electroactive barium titanate coated titanium scaffold improves osteogenesis and osseointegration with low-intensity pulsed ultrasound for large segmental bone defects. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, T.-K.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, T.-S.; Choi, S.; Oh, J.B.; Ye, G.; Lee, S. Modification of titanium implant and titanium dioxide for bone tissue engineering. In Novel Biomaterials for Regenerative Medicine; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2018; pp. 355–368. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.G.; Myers, D.E.; Wallace, G.G.; Brandt, M.; Choong, P.F. Bioactive coatings for orthopaedic implants—Recent trends in development of implant coatings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11878–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maver, T.; Mastnak, T.; Mihelič, M.; Maver, U.; Finšgar, M. Clindamycin-based 3D-printed and electrospun coatings for treatment of implant-related infections. Materials 2021, 14, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Pan, W.; Xi, D.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Xue, M.; Xu, N.; Wen, J.; Wang, W.; He, H. Optimization, characterization and evaluation of ZnO/polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposites for orthopedic applications: Improved antibacterial ability and promoted osteoblast growth. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saniei, H.; Mousavi, S. Surface modification of PLA 3D-printed implants by electrospinning with enhanced bioactivity and cell affinity. Polymer 2020, 196, 122467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandran, R.; Ng, C.C.; Liao, S.; Pliszka, D.; Raghunath, M.; Ramakrishna, S.; Chan, C.K. Biomimetic surface modification of titanium surfaces for early cell capture by advanced electrospinning. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 7, 015001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, R.; Albuquerque, M.; Münchow, E.; Blanchard, S.; Gregory, R.; Bottino, M. Novel bioactive tetracycline-containing electrospun polymer fibers as a potential antibacterial dental implant coating. Odontology 2017, 105, 354–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, M.C.; Münchow, E.A.; Albuquerque, M.T.; Kamocki, K.; Shahi, R.; Gregory, R.L.; Chu, T.M.G.; Pankajakshan, D. Tetracycline-incorporated polymer nanofibers as a potential dental implant surface modifier. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 2085–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Palau, J.; Prieto-Gundin, A.; Cazalla, A.A.; Serrano, M.B.; Fructuoso, G.G.; Ferrandis, F.P.; Baró, A.R. Three-dimensional planning in craniomaxillofacial surgery. Ann. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 6, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, A.H. Autologous bone graft: Is it still the gold standard? Injury 2021, 52, S18–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qiu, Y.; Lv, H.; Si, Y.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, J.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Ding, B. 3D superelastic scaffolds constructed from flexible inorganic nanofibers with self-fitting capability and tailorable gradient for bone regeneration. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Su, J. Restoration of critical defects in the rabbit mandible using osteoblasts and vascular endothelial cells co-cultured with vascular stent-loaded nano-composite scaffolds. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 124, 104831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mao, J.J.; Chen, L. Epithelial–mesenchymal interactions as a working concept for oral mucosa regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2011, 17, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goh, Y.-F.; Shakir, I.; Hussain, R. Electrospun fibers for tissue engineering, drug delivery, and wound dressing. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 48, 3027–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khil, M.S.; Cha, D.I.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, I.S.; Bhattarai, N. Electrospun nanofibrous polyurethane membrane as wound dressing. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2003, 67, 675–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttayarat, P.; Jetawattana, S.; Suwanmala, P.; Eamsiri, J.; Tangthong, T.; Pongpat, S. Antimicrobial electrospun silk fibroin mats with silver nanoparticles for wound dressing application. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, S.P.; Simões, D.; Moreira, A.F.; Sequeira, R.S.; Correia, I.J. Production and characterization of electrospun silk fibroin based asymmetric membranes for wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.W.; Lee, O.J.; Lee, J.M.; Moon, B.M.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.R.; Lee, M.C.; Kim, S.H.; Chao, J.R.; Ki, C.S. Wound healing effect of electrospun silk fibroin nanomatrix in burn-model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassburg, S.; Caduc, M.; Stark, G.B.; Jedrusik, N.; Tomakidi, P.; Steinberg, T.; Simunovic, F.; Finkenzeller, G. In vivo evaluation of an electrospun gelatin nonwoven mat for regeneration of epithelial tissues. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chor, A.; Gonçalves, R.P.; Costa, A.M.; Farina, M.; Ponche, A.; Sirelli, L.; Schrodj, G.; Gree, S.; De Andrade, L.R.; Anselme, K. In vitro degradation of electrospun poly(lactide-co-glycolic acid)(PLGA) in three different solutions for oral mucosa regeneration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1853. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, F.; Ge, Z.; Liu, X.; Lu, Q. Buccal mucosa repair with electrospun silk fibroin matrix in a rat model. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2015, 38, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Xin, T.; Xiao, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Cheng, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, W.; Ge, Z. Vascularized silk electrospun fiber for promoting oral mucosa regeneration. NPG Asia Mater. 2020, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Han, S.H.; Hyun, C.; Yoo, H.S. Buccal adhesive nanofibers containing human growth hormone for oral mucositis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2016, 104, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaraev, A.; Koniaeva, A.; Krikova, S.; Shesterikov, E.; Bolbasov, E.; Nemoykina, A.; Bouznik, V.; Stankevich, K.; Zhukov, Y.; Mishin, I. Piezoelectric polymer membranes with thin antibacterial coating for the regeneration of oral mucosa. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 504, 144068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnakulasuriya, S. Global epidemiology of oral and oropharyngeal cancer. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Nanavati, R.; Modi, T.G.; Dobariya, C. Oral cancer: Etiology and risk factors: A review. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Z.; Sigdel, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Xuan, M.; Wang, X.; Gu, Z.; Wu, J.; Xie, H. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for enhanced diagnosis and therapy of oral cancer. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 8781–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calixto, G.; Bernegossi, J.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Chorilli, M. Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems for treatment of oral cancer: A review. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Zanjanizadeh Ezazi, N.; Liu, D.; Santos, H.A. Electrospun fibrous architectures for drug delivery, tissue engineering and cancer therapy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1802852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadinejad, R.; Madamsetty, V.S.; Kumar, A.; Varzandeh, M.; Dehshahri, A.; Zarrabi, A.; Sharififar, F.; Mohammadi, M.; Fahimipour, A.; Ramakrishna, S. Electrospun nanocarriers for delivering natural products for cancer therapy. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Lee, S.Y.; Cho, H.-J. Phloretin-loaded fast dissolving nanofibers for the locoregional therapy of oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 508, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangaraju, E.; Dhanapal, D. Biocompatible Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold for Oral Cancer Treatment. In Biological Synthesis of Nanoparticles and Their Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Maheswari, S.U.; Raja, J.; Kumar, A.; Seelan, R.G. Caries management by risk assessment: A review on current strategies for caries prevention and management. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2015, 7 (Suppl. 2), S320–S324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Li, J.; He, L.; Zhou, X. Natural products and caries prevention. Caries Res. 2015, 49 (Suppl. 1), 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Z.; Gu, L.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M.; Brors, B. Circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2811–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



| Material | Representative Applications | References |
|---|---|---|
| Natural polymer | ||
| Alginate (AL) | Periodontal regeneration | [59] |
| Cellulose (CE) | Periodontal regeneration | [60] |
| Chitosan (CS) | Caries prevention | [61] |
| Collagen (CO) | Restorative treatment | [62] |
| Gelatin (GEL) | Jaw repair | [63] |
| Silk fibroin (SF) | Implant modification | [64] |
| Synthetic polymer | ||
| Polyamide 6 (Nylon 6) | Restorative treatment | [26] |
| Polycaprolactone (PCL) | Endodontic treatment | [65] |
| Polyethylene oxide (PEO) | Periodontal regeneration | [66] |
| Polylactic acid (PLA) | Periodontal regeneration | [67] |
| Poly L-lactic acid (PLLA) | Endodontic treatment | [68] |
| Poly l-lactide-co-d, l-lactide (PDLLA) | Periodontal regeneration | [69] |
| Poly lactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA) | Oral mucosa regeneration | [70] |
| Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) | Oral cancer therapy | [71] |
| Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) | Caries prevention | [17] |
| Other Nanomaterials | ||
| β-tricalcium phosphate (β-TCP) | Periodontal regeneration | [72] |
| Bioactive glass (BG) | Endodontic treatment | [73] |
| Hydroxyapatite (HA) | Periodontal regeneration | [74] |
| Silicon oxide (SiO2) | Restorative treatment | [75] |
| No. | Journal | TP * | IF | JIF Quartile | JIF Rank | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications | 20 | 7.328 | Q1 | 7/41 | Materials science, Biomaterials |
| 2 | Acta Biomaterialia | 11 | 8.947 | Q1 | 5/41 | Materials science, Biomaterials |
| 3 | Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A | 11 | 4.396 | Q2 | 25/89 | Engineering, Biomedical |
| 4 | ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces | 10 | 9.229 | Q1 | 44/334 | Materials science, Multidisciplinary |
| 5 | Polymers | 9 | 4.329 | Q1 | 18/90 | Polymer science |
| 6 | Biomedical Materials | 8 | 3.715 | Q2 | 39/89 | Engineering, Biomedical |
| 7 | International Journal of Nanomedicine | 8 | 3.715 | Q1 | 28/276 | Pharmacology & Pharmacy |
| 8 | Dental Materials | 7 | 5.304 | Q1 | 8/92 | Dentistry, Oral Surgery & Medicine |
| 9 | Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Biomaterials | 7 | 3.368 | Q2 | 43/89 | Engineering, Biomedical |
| 10 | Nanomaterials | 7 | 5.076 | Q2 | 103/334 | Materials science, Multidisciplinary |
| 11 | Biomaterials | 6 | 12.479 | Q1 | 1/41 | Materials science, Biomaterials |
| 12 | Carbohydrate Polymers | 6 | 9.381 | Q1 | 1/63 | Chemistry, Organic |
| 13 | Journal of Biomaterials Applications | 6 | 2.646 | Q3 | 63/106 | Engineering, Biomedical |
| 14 | Materials | 6 | 3.623 | Q2 | 152/334 | Materials science, Multidisciplinary |
| 15 | Journal of Dental Research | 5 | 6.116 | Q1 | 5/92 | Dentistry, Oral Surgery & Medicine |
| No. | Country/Region | TP | Ratio % | h-Index | TC * | AC * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 91 | 17.60 | 28 | 2648 | 29.10 |
| 2 | USA | 70 | 13.54 | 24 | 1954 | 27.91 |
| 3 | Iran | 42 | 8.12 | 13 | 748 | 17.81 |
| 4 | England | 34 | 6.58 | 17 | 906 | 26.65 |
| 5 | South Korea | 32 | 6.19 | 18 | 1636 | 51.13 |
| 6 | Brazil | 28 | 5.42 | 13 | 432 | 15.43 |
| 7 | India | 20 | 3.87 | 9 | 337 | 16.85 |
| 8 | Turkey | 19 | 3.68 | 10 | 299 | 15.74 |
| 9 | Italy | 17 | 3.29 | 11 | 255 | 15.00 |
| 10 | Thailand | 15 | 2.90 | 7 | 267 | 17.80 |
| No. | Institutes | TP | h-Index | TC | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University of Sheffield (England) | 19 | 11 | 518 | 27.26 |
| 2 | Indiana University (USA) | 18 | 15 | 626 | 34.78 |
| 3 | Seoul National University (South Korea) | 11 | 9 | 793 | 72.09 |
| 4 | Sichuan University (China) | 11 | 7 | 442 | 40.18 |
| 5 | University of Michigan (USA) | 11 | 9 | 145 | 13.18 |
| 6 | Tabriz University of Medical Sciences (Iran) | 10 | 8 | 154 | 15.40 |
| 7 | Radboud University (Netherlands) | 8 | 8 | 573 | 71.63 |
| 8 | Naresuan University (Thailand) | 8 | 6 | 222 | 27.75 |
| 9 | Queensland University of Technology (Australia) | 7 | 7 | 420 | 60.00 |
| 10 | Silpakorn University (Thailand) | 7 | 5 | 179 | 25.57 |
| 11 | Fourth Military Medical University (China) | 7 | 7 | 157 | 22.43 |
| 12 | Soochow University (China) | 7 | 4 | 145 | 20.71 |
| 13 | Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Iran) | 7 | 6 | 129 | 18.43 |
| 14 | Nanjing University (China) | 7 | 5 | 105 | 15.00 |
| 15 | Donghua University (China) | 7 | 5 | 98 | 14.00 |
| 16 | Hacettepe University (Turkey) | 7 | 5 | 80 | 11.43 |
| No. | Authors | TP | h-Index | TC | AC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bottino, Marco C. | 24 | 15 | 741 | 30.88 |
| 2 | Gregory, Richard L. | 11 | 10 | 398 | 36.18 |
| 3 | Aghazadeh, Marziyeh | 9 | 8 | 133 | 14.78 |
| 4 | Kamocki, Krzysztof | 9 | 9 | 368 | 40.89 |
| 5 | Yang, Fang | 9 | 9 | 599 | 66.56 |
| 6 | Jansen, John A. | 8 | 8 | 584 | 73.00 |
| 7 | Alizadeh, Effat | 7 | 6 | 110 | 15.71 |
| 8 | Kim, Hae-Won | 7 | 6 | 206 | 29.43 |
| 9 | Ngawhirunpat, Tanasait | 7 | 5 | 179 | 25.57 |
| 10 | Salehi, Roya | 7 | 6 | 100 | 14.29 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, S.; Yeung, A.W.K.; Zhang, C.; Tsoi, J.K.-H. A Bibliometric Analysis of Electrospun Nanofibers for Dentistry. J. Funct. Biomater. 2022, 13, 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13030090
Jin S, Yeung AWK, Zhang C, Tsoi JK-H. A Bibliometric Analysis of Electrospun Nanofibers for Dentistry. Journal of Functional Biomaterials. 2022; 13(3):90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13030090
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Shixin, Andy Wai Kan Yeung, Chengfei Zhang, and James Kit-Hon Tsoi. 2022. "A Bibliometric Analysis of Electrospun Nanofibers for Dentistry" Journal of Functional Biomaterials 13, no. 3: 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13030090
APA StyleJin, S., Yeung, A. W. K., Zhang, C., & Tsoi, J. K.-H. (2022). A Bibliometric Analysis of Electrospun Nanofibers for Dentistry. Journal of Functional Biomaterials, 13(3), 90. https://doi.org/10.3390/jfb13030090








