Abstract
Integration of different energy networks will increase additional flexibility to system operation. The key component in such a coupled infrastructure is the energy router, which plays an important role in energy transition and storage to smoothing the prediction error both in renewables and load. The router has the multi-carrier energy generation capability, and builds physical linkages among the power network, heat network, and other networks in the micro energy internet. The economic dispatch problem of the micro energy internet is formulated as a bi-objective optimization problem. Golden section search method is adopted to locate a compromising solution in the sense of Nash Bargaining. Case studies on a typical test system verify the effectiveness of the proposed bi-objective dispatch model and solution method.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, pressures from global energy crisis and environment pollution have inspired the dramatic integration of renewable resources. Despite of their volatility, integration of systems with multiple energy carriers not only creates a flexible way to utilize various resources and facilitate system operation, but also enhances system reliability in the presence of high-level uncertain renewable penetration [].
Micro energy internet [] is typically characterized by involving multiple energy sources (wind, PV station, natural gas suppliers, heat suppliers, etc.), multi-network (power network, gas network, heating network, cooling network), multi-user (power users, heat users, natural gas users, central air conditioning systems, etc.) and various energy forms (electricity, gas, heat, cool, etc.). In other words, micro energy internet is a class of complex stochastic systems coupled laterally by electricity, gas, heat, cold, and other energy distribution infrastructures, and composed longitudinally by various decision-making agents including energy suppliers, dispatch centers, and multiple users [].
The micro energy internet [], integrated energy systems [], community integrated energy systems [], and multi-source multi-product systems [] are such energy distribution infrastructures capable of supplying energy in multiple forms including electricity, heat, natural gas, etc. In such integrated systems, the energy router is a key component to realize the transmission, conversion, and storage among different energy forms via coupling different energy networks []. Moreover, the prediction error exists both in the renewable output prediction due to its intermittency and load forecast cased by the flexible load brings additional challenges for the optimization of the micro energy internet. Energy storage is one of the effective ways to eliminate these prediction errors. To this end, compressed air energy storage system (CAES) is used to construct micro energy internet [] and study combined heat and electricity network [,].
Different from independent power distribution networks (PDN) and heat distribution networks (HDN), combined heat and power analysis is required in the planning and operation of the micro energy internet. The studies that are suitable for combined analysis of heat and power are available in [,,,,]. Decomposed and integrated electrical-hydraulic-thermal calculation methods have been developed in [] to analyze the operation of heating and electricity network. Optimal power flow of integrated electrical and heating system in a micro-grid is studied in []. However, both of them focus on a single-period dispatch without considering the temporal behavior of the load and renewable generation profile. Multiple-periods combined heat and power dispatch methods have been proposed respectively to reduce operation cost by incorporating CAES [], classic thermal energy storage [], and pipeline [], respectively.
From the perspective of sustainable development, the coordination between the carbon-emission and economic aspect during the planning and operation of micro energy system is important [,]. On the one hand, there are several bi/multi-objective economic dispatch model for the power systems [], and bi/multi-objective economic dispatch for the heating systems []. In power network optimization, environmental-economic dispatch model are used to coordinate these two aspects [] while environmic dispatch models have been developed to incorporate these two aspects in district heating optimization []. However, the bi-objective economic dispatch (BOED) of micro energy internet coupling electric and thermal networks remains an open problem. We shall try to narrow this gap through our work by considering the network flow in power networks and heating networks.
On the other hand, in general, it is difficult to reach the two minimums simultaneously due to the contradiction between carbon emission and system cost. The solution for bi/multi-objective economic dispatch is a set of inferior solutions, which are known as Pareto Front. Therefore, lots of evolutionary algorithms have been developed to tackle this problem as in []. With the capability of providing many non-inferior solutions, evolutionary algorithms methods have been viewed as effective ways to obtain the Pareto front. However, on the actual micro energy internet, the operator needs one balanced solution, and it is difficult to select one from the Pareto front. Most of the current methods just use the weight factors to add the objectives together to convert to a single objective model as the method []. To be specific, add the operation cost and carbon emission with a carbon tax. Certainly, the weight factor is typically hard to select with a strong subjectivity. To tackle the above two issues in the selection of weight factor as well as the determination of one specific solution from the set of the non-inferior solution. In our work, the bi-objective economic dispatch model is converted to a single-objective one with the Nash bargaining method. Nash bargaining theory is used to derive a fair trade-off solution that comprises the two objectives []. Thus, a bi-objective economic dispatch model for the micro energy internet is proposed in this paper. The Nash bargaining method is employed to get a satisfactory solution in terms of game theory. The Nash bargaining problem is then solved by a golden section search algorithm, which is adopted to locate a compromising solution in the sense of Nash Bargaining.
The contribution of this paper includes the bi-objective economic dispatch model of the micro energy internet, and a univariate parametric method for searching the Nash bargaining solution. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. The mathematic model of the energy router, PDN, and HDN, as well as the BOED are respectively developed in Section 2. In Section 3, the Nash bargaining method is introduced to convert the bi-objective economic dispatch as a single objective one. The golden section search algorithm is employed to obtain the bargain point. Illustrative studies are given in Section 4 to validate the effectiveness of the proposed BOED and algorithms. Conclusions and further research directions are drawn in Section 5.
2. Formulation of BOED
2.1. Energy Router
In this part, we introduce a novel energy storage system based on compressed air energy techniques, which captures the features of green, and combined heat and power energy storage and co-generation. The simplified structure and energy flow in the router are illustrated in Figure 1. In Figure 1, the black solid line represents the electric power; the black dashed line is the compressed air; the blue solid line is high temperature water; the dashed blue line represents the energy charging and discharging flow through the TES while the yellow solid line is the low temperature water. Because of the capability of combined heat and electricity generation and storage, the energy router is a natural linkage between PDN and HDN in the micro energy internet.
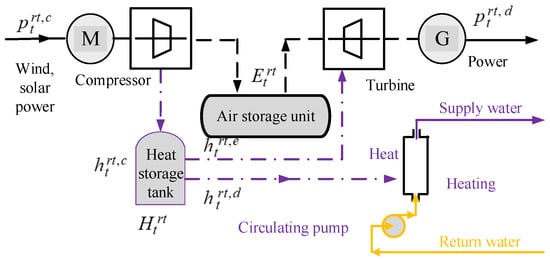
Figure 1.
Illustration of energy router.
With the coupling of electric dynamic, hydraulic dynamic, and thermal dynamic, accurate modeling of an energy router is difficult. For simplification, based on the model of router in [], the dispatch model of the router hub can be formulated as []:
Thereinto, Equation (1) represents the operating mode requirement, which indicates that the energy router cannot be in power charging and discharging modes simultaneously. Equation (2) and Equation (3) represent the power charging and discharging bounds of the router, respectively. Equation (4) indicates the state of the charge (SOC) of power energy while Equation (5) describes the power energy storage capacity. Equation (6) represents the operating mode requirement of TES, while Equations (7) and (8) represent the thermal charging and discharging capacity, respectively. Equation (9) indicates the SOC of thermal energy in energy routers and Equation (10) describes the thermal energy storage capacity. Equation (11) describes the requirement of thermal energy for power generation of router coupling the power energy storage and thermal energy storage.
2.2. Power Distribution Network
Different from the power transmission network, the power distribution network on the micro energy internet usually has a radial topology, and the bus voltage, rather than the bus angle, should be monitored. The power flow in such a radial PDN can be described by Branch Flow as in [,] and illustrated as:
Thereinto, Equations (12) and (13) model the active power and reactive power balance of PDN, respectively. The drops of the voltage along the distribution line is depicted in Equation (14). Equation (15) describes the connection between power, square of voltage, and square of current. The limits of square of current, square of voltage, active power, and reactive power are respectively shown in Equations (16)–(18). and are the squares of voltage at root node, usually at Bus 1.
Note that, in our current model, we do not take the time dynamics and delays into consideration. The inclusion of time dynamics or delays both in the power distribution network and heat network will definitely improve the accuracy of the dispatch model. Typically, the consideration of reactive power balance and nodal voltages may introduce more difficulties for the model, and we think the method in [] may work in our methodology. This is what we are doing in another work. The main focus of this paper lies in the introduction of the Nash Bargaining method to build the bi-objective dispatch model as well as the determination of the compromising solution on the Pareto front. The main advantages of Branch Flow model are listed as follows: (1) the reactive power balance and node voltage are considered in the power flow equations; and (2) the equations can be converted to linear ones or second order cone programming [] and the optimal solution can be easily obtained, which is similar to the direct current flow model of the transmission line that ignores reactive power.
2.3. District Heating Network
It is assumed that the heat requirements of HDN are mainly supplied by the energy router. Based on the model in [,,,], the dispatch model of a radial HDN can be formulated as:
Thereinto, Equation (19) describes the heat power supplied by the energy router while heat load demand depicted in Equations (20)–(22) are the limits of the supply water temperature and return, respectively. Equations (23) and (24) are the mass conservation law for each node in the supplying water system and returning water system, respectively. b is the index for pipe number in HDN. Equations (25) and (26) are the relationship between node temperature and temperature of pipe while Equation (27) shows the connection between node temperature and pipe temperature. Mass flow limits of each pipe due to physical character are depicted in Equations (28) and (29). Equations (30) and (31) show the relationship between inlet and outlet temperature of each pipe.
Usually, modeling HN involves a hydraulic-thermal model to determine the mass flow rates m within each pipe, and the load supply temperatures and the source return temperatures []. For HDN, it is assumed that the source supply temperatures and load return temperatures are specified; the mass flow rates or the heat power are specified at all nodes except the slack node []. For simplification, we assume that the mass flow rate is determined; then, the system (19)–(31) is linear.
2.4. Bi-Objective Economic Dispatch
For notation brevity, we define the set:
It is assumed that the energy router belongs to the PDN; thus, the operation of the micro energy internet has the following two objectives, i.e.,
The first term of Equation (33) is the cost of gas turbines, while the second term is the cost of buying electricity from utility, respectively. Equation (34) defines the carbon-emission of gas turbines.
The bi-objective economic dispatch of the micro energy internet can be formulated as a convex bi-objective optimization problem as:
3. Nash Bargaining Method for the Bi-Objective ED
3.1. Nash Bargaining Solution
Usually, the two objective functions in BOED Equation (35) are contradictory. Therefore, it is difficult to obtain the minimums of the two functions simultaneously. In this regard, Nash bargaining method is utilized to handle BOED.
The objectives Equations (33) and (34) are treated as two virtual players who negotiate with each other on how to dispatch generators and hub impartially, deriving a bargain game. We define Equation (36) within the compact feasible region X as:
By denoting as the Pareto front of Equation (35), the worst outcome of the system cost and emission over the can be given as:
Based on Nash’s theory, the bargaining solution of BOED Equation (35) is the optimal solution of Equation (38)
It is proved that the bargaining solution is located in the Pareto front.
In addition, both objectives in Equations (33) and (34) are convex quadratic functions, hence the Pareto optimum solution can be characterized by the following optimization problem whose objective is a weighted sum of and :
3.2. Golden Section Search for Nash Bargaining
Based on Equations (39) and (40), the bargaining value given by the objective Equation (38) over the Pareto front can be regarded as a univariate function in . In view of this fact, the golden section search is employed to find the balancing solution, and the detailed procedure is shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Golden Section Search for Nash Bargaining (Equation (38)). |
|
4. Case Studies
4.1. System Setting
Actually, different from the micro grid which has some benchmark datasets, the micro energy internet is lack of the benchmark datasets. Thus, it is hard to for us to use other benchmark datasets to verify our methods. Fortunately, some current papers give us some data of the micro energy internet, such as [,]. In this respect, we just borrow the system and data from [,] and reference therein to test our methods. Configuration of the test micro energy internet is given in Figure 2. The studying system is composed of a 33-bus PDN, an 8-node HDN, an energy router, one wind generator, as indicated with W, and three gas turbines(GT), indicated as GT in Figure 2. Time-of-use price of electric power and more detail on the system can be illustrated as in Figure 3 [,].
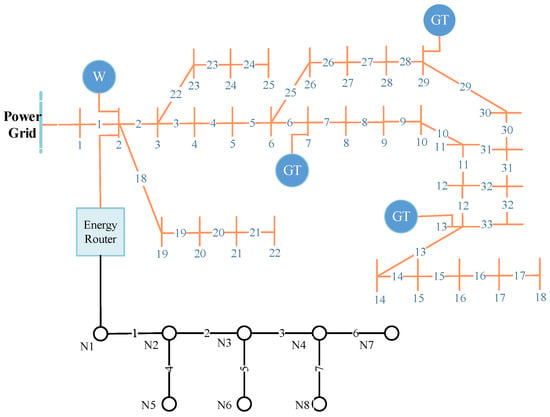
Figure 2.
Configuration of the studied micro energy internet.
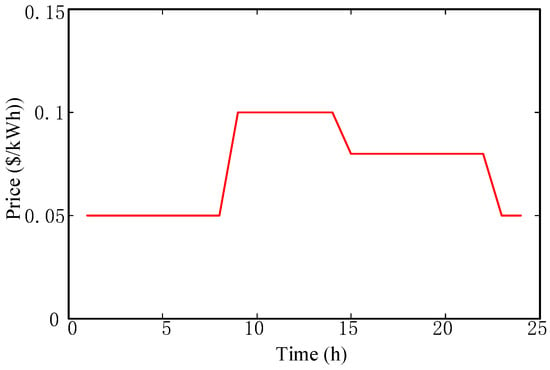
Figure 3.
Time-of-use power price.
The forecasted power load, heat demand, and predicted wind power output of the studied micro energy internet are shown in Figure 4. Note that, since we focus more on the economic dispatch of the micro energy internet, the load data presented in the simulation section is just borrowed from the literature. Actually, the correlation analysis among power load, heat demand, and predicted wind power are vital to develop a more realistic economic dispatch. However, we pay more attention to the dispatch model and solution methods in this paper. The detailed analysis of the power load, heat load, and renewable output will be discussed in our future work. Since the prediction of renewable output and load forecast might have certain errors, the energy storage system is usually deployed in the micro grid and micro energy internet. In this regard, we utilize the mentioned compressed air energy storage system as the representative of the energy storage facility in the system studied.
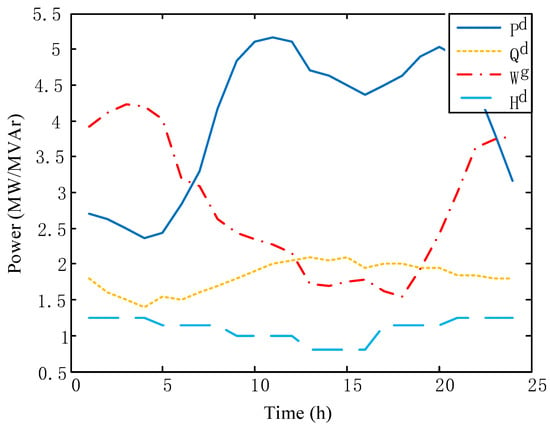
Figure 4.
The forecasted power load, heat demand, and predicted wind power output.
It is worth mentioning that we focus more on the method of Nash Bargaining to solve the bi-objective economic dispatch model. The different scenarios and cost coefficients has no impact for the usability of our method. In our future work, we shall build the robust bi-objective model; in that sense, we shall compare different scenarios and cost coefficients.
4.2. Pareto Front and Nash Bargaining Solution
The bargain solution for the BOED (Equation (35)) is uniquely determined regardless of the orders of magnitudes of the system cost and carbon emission, and normalization is not needed. The Pareto front and Nash bargaining point solved by the golden section search for the BOED (Equation (35)) is given in Figure 5. The system cost and carbon emission at Nash bargaining point are = 7.2794 and = 255.6157 kg. Moreover, we compared our methods by just adding the two different objective functions with the weighted factor used in []. The comparison results are also illustrated in Figure 5. Both electric power and thermal power demand, and electric power distribution among the gas turbine and power utility related to our methods are shown in Figure 6.
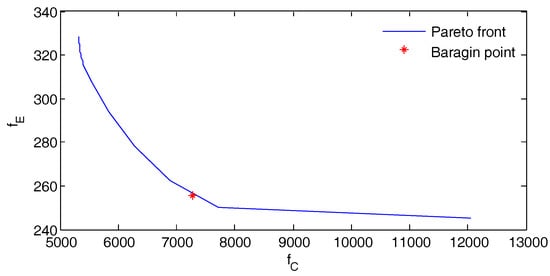
Figure 5.
Pareto front and balancing solution for BOED(Equation (35)).
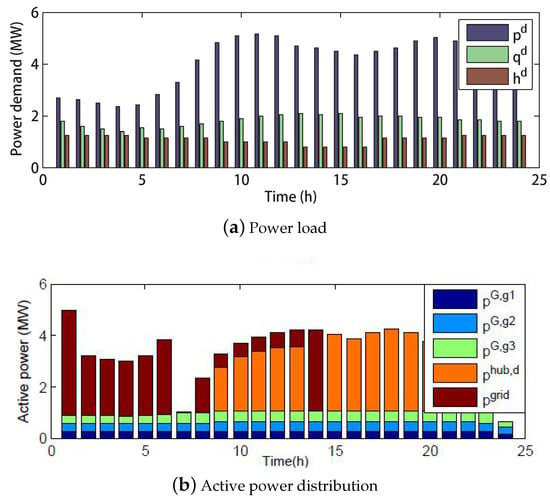
Figure 6.
Power load and active power distribution under the Nash balancing point.
4.3. Operation of Energy Router
Operation of the energy router in the micro energy internet studied under the Nash bargaining point is shown in Figure 7. The energy router operated in a charging mode with cheap electric power under off-peak power load time periods, including period from to , period from to . The stored electric power in router is used to supply an on-peak power load period to reduce system cost. Since the energy router is the only heat source for heat load in the micro energy internet studied, the operation status of the TES in the router is similar to the heat load curve. Please note that the electric power discharging of the router consumes some thermal energy of the TES; thus, on peak time, the router needs to supply more thermal energy for the micro energy internet studied.
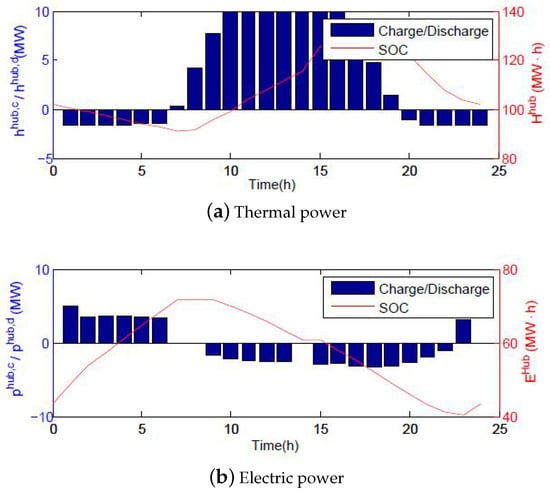
Figure 7.
State of the charge of thermal and electric power of the energy router.
4.4. Renewable Curtailment
Wind power curtailment under the Nash bargaining point is given in Figure 8. With the function of energy router and integrated utilization of electric and thermal power, most of the wind power is consumed. The curtailment of wind power is relatively small.
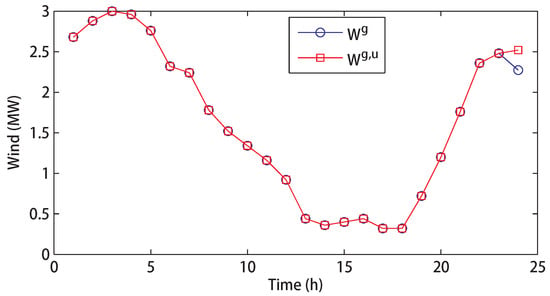
Figure 8.
Renewable energy consumption and curtailment.
5. Conclusions
This paper studies a micro energy internet to integrate power networks and heat networks in the distribution level. The bi-objective economic dispatch of the micro energy internet is developed to incorporate both the economic and environmental goal. The bi-objective economic dispatch model is converted to a single-objective one with the Nash bargaining method, and solved by a golden section search algorithm. The proposed method can offer a compromising solution for the micro energy internet operator to select one balancing solution on the Pareto Front. This compromising solution can be used to assist the operator in decision-making. In the future, we shall build the robust bi-objective model. In that sense, we shall compare different scenarios under the uncertainty of renewables. In addition, we shall include the time dynamics or delays both in the power distribution network and heat network to realize accurate modelling.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2017MS159, No. 2015MS130) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61377088, No. 51407074).
Author Contributions
T.L. and Y.L. conceived and designed the experiments; T.L. performed the experiments; T.L. and A.L. analyzed the data; T.L. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BOED | Bi-objective economic dispatch |
| HDN | Heat distribution network |
| PDN | Power distribution network |
| TES | Thermal energy storage |
| Sets | |
| Set of dispatch period | |
| Child buses of bus | |
| Pipes with node i as ’from’ node | |
| Pipes with node i as ’to’ node | |
| Superscripts | |
| Return/supply water system | |
| Charging/discharging | |
| Generation/demand | |
| Lower/upper bound | |
| Inlet/outlet of pipe | |
| Power utility | |
| Energy router | |
| Subscripts | |
| t | Dispatch time |
| ’from’ or ’to’ bus/node of line/pipe | |
| min/max | Minimum/maximum value |
| Parameters | |
| Cost coefficients of gas turbine | |
| Emission coefficients of gas turbine | |
| Charging/discharging efficiency | |
| c | Constant pressure specific heat |
| l | Length of pipe |
| Dissipation factor of thermal storage | |
| Temperature loss coefficient of pipe | |
| Mass flow rate of recycle water | |
| Price of electric power | |
| Decision Variables | |
| Binary variables denote the operation of electric and thermal storage in router | |
| Temperature at node, inlet/outlet of pipe | |
| h | Injected thermal power of load and source |
| Stored electric and thermal energy in router | |
| Injected active/reactive power | |
| Active/reactive power flow through the power line | |
| W | Injected wind power |
| Square of amplitude of current/voltage |
References
- Mancarella, P. MES (multi-energy systems): An overview of concepts and evaluation models. Energy 2014, 65, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Li, R.; Xue, X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Q.; Chen, X.; Ahrens, C.D.; Li, R.; Chen, L. Paving the Way to Smart Micro Energy Internet: Concepts, Design Principles, and Engineering Practices. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1612.09500v2. [Google Scholar]
- Geidl, M.; Andersson, G. Optimal power flow of multiple energy carriers. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2007, 22, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.; Ioakimidis, C.; Ferreao, P. On the planning and analysis of integrated community energy systems: A review and survey of available tools. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4836–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmes, K.; Zachariah-Wolf, J.L.; Geidl, M.; Andersson, G. Towards multi-source multi-product energy systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 1332–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, L.; Yuan, T.; Li, C. Optimal dispatch of zero-carbonemission micro energy internet integrated with non-supplementary fired compressed air energy storage system. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2016, 4, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Fang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, Z. Optimal operation of the integrated electrical and heating systems to accommodate the intermittent renewable sources. Appl. Energy 2016, 167, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Jenkins, N.; Bagdanavicius, A. Combined analysis of electricity and heat networks. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, B.; Chaudry, M.; Wu, J.; Jenkins, N. Integrated optimal power flow for electric power and heat in a microgrid. In Electricity Distribution-Part 1, Proceedings of the 20th International Conference and Exhibition on Electricity Distribution (CIRED 2009), Prague, Czech Republic, 8–11 June 2009; IET Conference Publications: Stevenage, UK, 2009; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Wu, W.; Shahidehpour, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B. Combined heat and power dispatch considering pipeline energy storage of district heating network. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2016, 7, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talaq, J.; El-Hawary, F.; El-Hawary, M. A summary of environmental/ economic dispatch algorithms. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 1994, 9, 1508–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molyneaux, A.; Leyland, G.; Favrat, D. Environomic multi-objective optimisation of a district heating network considering centralized and decentralized heat pumps. Energy 2010, 35, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, L.; Zhao, B.; Wei, W.; Liu, F.; Xue, X.; Mei, S.; Yuan, T. Economic Dispatch of Integrated Heat-power Energy Distribution System with Concentrating Solar Power Energy Hub. J. Energy Eng. 2017, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Liu, F.; Mei, S. Nash bargain and complementarity approach based environmental/economic dispatch. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2015, 30, 1548–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, M.E.; Wu, F.F. Network reconfiguration in distribution systems for loss reduction and load balancing. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 1989, 4, 1401–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Wang, J.; Begovic, M.M.; Chen, C. Coordinated energy management of networked microgrids in distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendato, I.; Bonfiglio, A.; Brignone, M.; Delfino, F.; Pampararo, F.; Procopio, R. A real-time Energy Management System for the integration of economical aspects and system operator requirements: Definition and validation. Renew. Energy J. 2017, 102, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baradar, M.; Hesamzadeh, M.R.; Ghandhari, M. Second-Order Cone Programming for Optimal Power Flow in VSC-Type AC-DC Grids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 4282–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Analysis, Modelling and Operational Optimazation of District Heating Systems; Centre for District Heating Technology, Technical University of Denmark: Lyngby, Denmark, 1995. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).