Feature Encodings and Poolings for Action and Event Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
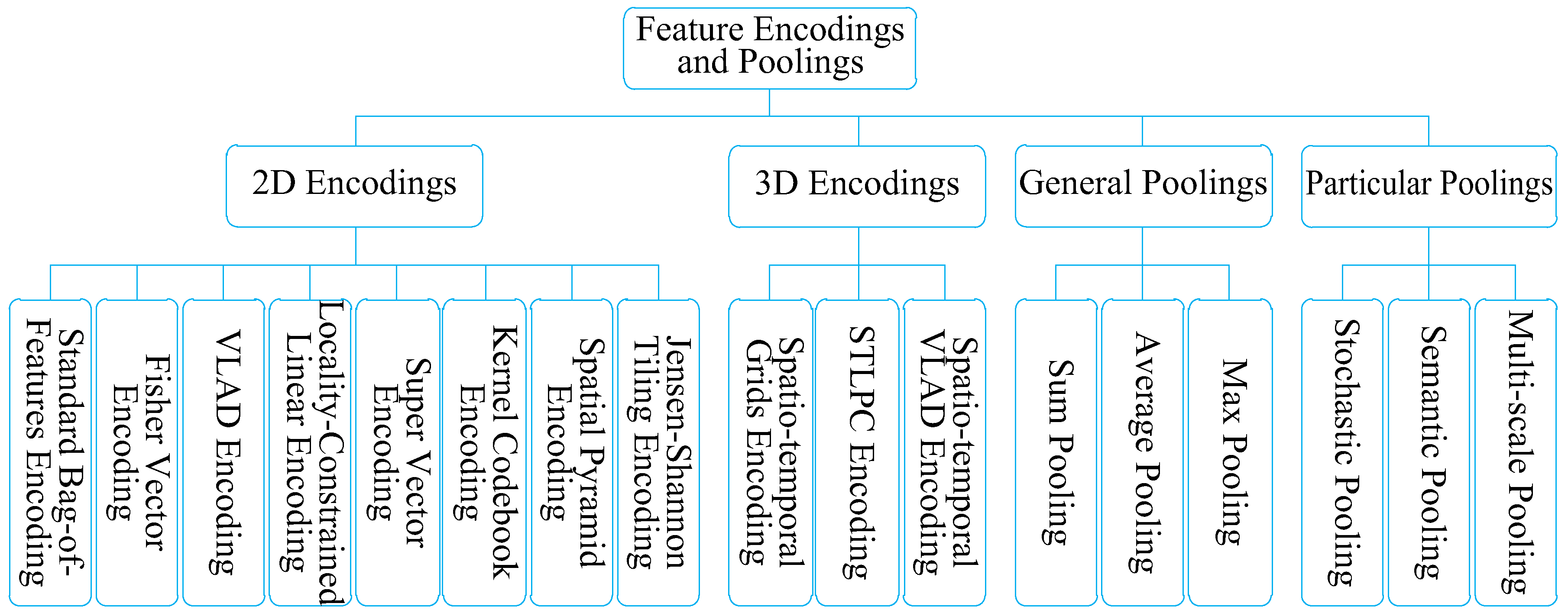
2. Feature Encoding and Pooling Taxonomy
3. 2D Encodings
3.1. Standard Bag-of-Features Encoding
3.2. Fisher Vector Encoding
- (1)
- (2)
- Both and are computed, where and .
- (3)
- The final fisher vector of the image is the concatenation of and for .
3.3. VLAD Encoding
3.4. Locality-Constrained Linear Encoding
3.5. Super Vector Encoding
3.6. Kernel Codebook Encoding
3.7. Spatial Pyramid Encoding
- (1)
- A 400-dimension visual vocabulary is formed by performing k-means clustering on random subset of interest patches, such as sized SIFT patches, from the training dataset.
- (2)
- A 4-level spatial pyramid is applied to the scene image or frame , such that there are cells along each dimension of level , resulting in a total of 85 cells in the pyramid, where .
- (3)
- For each cell, a 400-dimension bag-of-features histogram is computed. The histograms from all 85 cells are then concatenated and normalized to generate a 34,000-dimension feature vector as the spatial pyramid encoding of .
- (4)
3.8. Jensen-Shannon Tiling Encoding
- (1)
- It generates systematically all possible tilings, i.e., all vectors , from a base mask by the proposed Algorithm 1, such that the resulting masks can be denoted by , where and is the tiling operator.
- (2)
- It selects the best tiling as the encoding layout, such that , based on the assumption that an optimal tiling tends to separate positive and negative samples with maximum distance, i.e., JS divergence, where the cost is got by , indicates tile number, is a regularized parameter, is the JS divergence, (or ) is the normalized (or ), (or ) is average histogram of all positive (or negative) samples for the tile, and (or ) denotes the total number of positive (or negative) samples.
4. 3D Encodings
4.1. Spatiotemporal Grids Encoding
- (1)
- A -dimension, e.g., , visual vocabulary is constructed by clustering interest patches sampled from the training videos, such as HOG patches or HOF patches around detected interest points, with k-means algorithm.
- (2)
- For a given test video clip , 3D interest points are obtained firstly by the spatiotemporal detector, such as Harris 3D detector. Then, spatiotemporal features, such as HOG or HOF, are extracted from patches around those interest points.
- (3)
- The whole test video clip is divided by a sized grid into cuboids, e.g., spatial sizes , , and temporal size . For each cuboid, a -dimension bag-of-features histogram is formed.
- (4)
- All histograms are further concatenated and normalized to form a dimensional feature vector to represent the video clip .
4.2. STLPC Encoding
- (1)
- Frame difference volume buliding. For the original video sequence volume , the difference approach is applied as a preprocessing step to generate its frame difference volume .
- (2)
- Spatiotemporal gaussian pyramid buliding. Firstly, generate a four-level frame difference volume pyramid by subsampling the volume with resolution. Then, generate a four-level spatiotemporal gaussian pyramid by convolving a 3-D Gaussian function with each level of the pyramid .
- (3)
- Spatiotemporal laplacian pyramid buliding. In the beginning, generate a four-level revised pyramid by expanding each level of the into the same size as of the bottom level. After that, generate a three-level spatiotemporal laplacian pyramid by differencing all two consecutive levels on the revised with , where is the level number.
4.3. Spatiotemporal VLAD Encoding
- (1)
- Spatiotemporal deep video features extraction using two stream ConvNet or Improved Dense Trajectories (iDT). For two stream ConvNet, frames are resized to size of . Then, VGG19 ConvNet is pretrained on ImageNet and then adopted to extract feature vectors with dimentions by each vector for each frame in spatial stream, and VGG16 ConvNet is pretrained on UCF101 and then adopted to extract feature vectors with dimentions feature for each ten frames in temporal stream. For iDT, the resulted dimensionality is 96 for HOG, MBHx and MBHy, and 108 for HOF. Finally, all extracted features are reduced by PCA.
- (2)
- VLAD encoding. Suppose is a set of local low level dimensional spatial temporal deep video features extracted with approaches in the first step, and is the appearance encoding dictionary with words. Then, VLAD encoding is defined as a dimensional feature vector , where , and .
- (3)
- Spatiotemporal encoding. Suppose is a function to generate a three dimensional normalized position vector, and is the spatiotemporal encoding dictionary with three dimensional words. Then, the ST encoding is defined as a dimensional feature vector by , where , , and is its membership vector.
- (4)
- ST-VLAD encoding. The final representation, i.e., ST-VLAD, of a video concatenates VLAD encoding and ST encoding in a dimensional vector.
5. Pooling Strategies
5.1. General Poolings
5.1.1. Sum Pooling
5.1.2. Average Pooling
5.1.3. Max Pooling
5.2. Particular Poolings
5.2.1. Stochastic Pooling
5.2.2. Semantic Pooling
5.2.3. Multi-Scale Pooling
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coşar, S.; Donatiello, G.; Bogorny, V.; Garate, C.; Alvares, L.O.; Brémond, F. Toward abnormal trajectory and event detection in video surveillance. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2017, 27, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Martín, Á.; Martínez, J.M. People detection in surveillance: Classification and evaluation. IET Comput. Vis. 2015, 9, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Nevatia, R. Hierarchical abnormal event detection by real time and semi-real time multi-tasking video surveillance system. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Fei, F.; Fang, Y.; Lee, C.; Xiong, N.; Shu, L.; Chen, S. Abnormal event detection in crowded scenes based on deep learning. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 14617–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Ma, Z.; Lin, M.; Yang, Y.; Hauptmann, A. Feature interaction augmented sparse learning for fast Kinect motion detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3911–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morariu, V.I.; Davis, L.S. Multi-agent event recognition in structured scenarios. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Colorado Springs, CO, USA, 20–25 June 2011; pp. 3289–3296. [Google Scholar]
- Rautaray, S.S.; Agrawal, A. Interaction with virtual game through hand gesture recognition. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Multimedia, Signal Processing and Communication Technologies, Aligarh, India, 17–19 December 2011; pp. 244–247. [Google Scholar]
- Fothergill, S.; Mentis, H.; Kohli, P.; Nowozin, S. Instructing people for training gestural interactive systems. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 5–10 May 2012; pp. 1737–1746. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.; Wang, A.; Cavuoto, L.; Xu, W. Toward unobtrusive patient handling activity recognition for injury reduction among at-risk caregivers. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2017, 21, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathy, A.K.; Carvalho, R.; Pawaskar, K.; Yadav, S.; Yadav, V. Mobile based healthcare management using artificial intelligence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Technologies for Sustainable Development, Mumbai, India, 4–6 February 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Uddin, M.Z.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, T.S. Daily human activity recognition using depth silhouettes and ℜ transformation for smart home. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Smart Homes and Health Telematics: Toward Useful Services for Elderly and People with Disabilities, Montreal, QC, Canada, 20–22 June 2011; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury-Jones, C.; Taylor, J.; Kroll, T.; Duncan, F. Domestic abuse awareness and recognition among primary healthcare professionals and abused women: A qualitative investigation. J. Clin. Nurs. 2014, 23, 3057–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Xu, X.; Chen, L.; Duan, L.; Xu, D. Action and event recognition in videos by learning from heterogeneous web sources. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2017, 28, 1290–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Wang, P.; Song, J.; Shen, H.T. Web video event recognition by semantic analysis from ubiquitous documents. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5689–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, A.; Zeb, M.A. Security enhancement for e-learning portal. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. Secur. 2008, 8, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ladan, M.I. E-Commerce security issues. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud, Barcelona, Spain, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Shahzad, A. Multiple facial feature detection using vertex-modeling structure. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Interactive Computer Aided Learning, Villach, Austria, 26–28 September 2007; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A. Security architecture for third generation (3G) using GMHS cellular network. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Emerging Technologies, Islamabad, Pakistan, 12–13 November 2007; pp. 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Over, P.; Fiscus, J.; Sanders, G.; Joy, D.; Michel, M.; Awad, G.; Smeaton, A.; Kraaij, W.; Quénot, G. TRECVID 2012—An Overview of the Goals, Tasks, Data, Evaluation Mechanisms, and Metrics. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv12.papers/tv12overview.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Jiang, Y.G.; Bhattacharya, S.; Chang, S.F.; Shah, M. High-level event recognition in unconstrained videos. Int. J. Multimedia Inf. Retr. 2013, 2, 73–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara, O.D.; Labrador, M.A. A survey on human activity recognition using wearable sensors. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2013, 15, 1192–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, T.S. Development of a life logging system via depth imaging-based human activity recognition for smart homes. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Sustainable Healthy Buildings, Seoul, Korea, 19 September 2012; pp. 91–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.Y.; Iyengar, S.; Kuryloski, P.; Jafari, R. Distributed segmentation and classification of human actions using a wearable motion sensor network. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Tang, J.; Liu, F.; Yan, S. Body surface context: A new robust feature for action recognition from depth videos. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2014, 24, 952–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Sarif, N.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, T.S. Human activity recognition via recognized body parts of human depth silhouettes for residents monitoring services at smart home. Indoor Built Environ. 2013, 22, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althloothi, S.; Mahoor, M.H.; Zhang, X.; Voyles, R.M. Human activity recognition using multi-features and multiple kernel learning. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Shape and motion features approach for activity tracking and recognition from kinect video camera. In Proceedings of the IEEE 29th International Conference on Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops, Gwangju, Korea, 25–27 March 2015; pp. 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. A depth video sensor-based life-logging human activity recognition system for elderly care in smart indoor environments. Sensor 2014, 14, 11735–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, S.; Azurdia-Meza, C.A.; Lee, K. Family of Nyquist-I pulses to enhance orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system performance. IETE Tech. Rev. 2016, 33, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jin, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; He, Q.; Huang, Q. Using multi-stream hierarchical deep neural network to extract deep audio feature for acoustic event detection. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Raj, B. Audio event and scene recognition: A unified approach using strongly and weakly labeled data. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 3475–3482. [Google Scholar]
- Farooq, A.; Jalal, A.; Kamal, S. Dense RGB-D map-based human tracking and activity recognition using skin joints features and self-organizing map. KSII Trans. Internet Inf. Syst. 2015, 9, 1856–1869. [Google Scholar]
- Siswanto, A.R.S.; Nugroho, A.S.; Galinium, M. Implementation of face recognition algorithm for biometrics based time attendance system. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on ICT for Smart Society, Bandung, Indonesia, 23–24 September 2014; pp. 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Manwatkar, P.M.; Yadav, S.H. Text recognition from images. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Innovations in Information, Embedded and Communication Systems, Coimbatore, India, 19–20 March 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Hauptmann, A.G. Bi-level semantic representation analysis for multimedia event detection. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 1180–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, A.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Depth Silhouettes Context: A new robust feature for human tracking and activity recognition based on embedded HMMs. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence, Goyang City, Korea, 28–30 October 2015; pp. 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, S.; Jalal, A.; Kim, D. Depth images-based human detection, tracking and activity recognition using spatiotemporal features and modified HMM. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2016, 11, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalal, A.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.J.; Kamal, S.; Kim, D. Robust human activity recognition from depth video using spatiotemporal multi-fused features. Pattern Recognit. 2017, 61, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma, S.; Agrawal, A. A survey on activity recognition and behavior understanding in video surveillance. Vis. Comput. 2013, 29, 983–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Lai, A. A survey on still image based human action recognition. Pattern Recognit. 2014, 47, 3343–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, J.K.; Xia, L. Human activity recognition from 3D data: A review. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2014, 48, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaeefard, M.; Bergevin, R. Semantic human activity recognition: A literature review. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 2329–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoglu, L.; Tong, H.; Koutra, D. Graph based anomaly detection and description: A survey. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2015, 29, 626–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, X.; Shao, L. Action recognition via spatio-temporal local features: A comprehensive study. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 50, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Tian, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J. A survey on aggregating methods for action recognition with dense trajectories. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2016, 75, 5701–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Shao, L.; Xie, J.; Fang, Y. From handcrafted to learned representations for human action recognition: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2016, 55, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Sharma, N.; Blumenstein, M. Recent advances in video-based human action recognition using deep learning: A review. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Anchorage, AK, USA, 14–19 May 2017; pp. 2865–2872. [Google Scholar]
- Herath, S.; Harandi, M.; Porikli, F. Going deeper into action recognition: A survey. Image Vis. Comput. 2017, 60, 4–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csurka, G.; Dance, C.; Fan, L.; Willamowski, J.; Bray, C. Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. In Proceedings of the ECCV International Workshop on Statistical Learning in Computer Vision, Prague, Czech Republic, 11–14 May 2004; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sivic, J.; Zisserman, A. Video Google: A text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Nice, France, 13–16 October 2003; pp. 1470–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Perronnin, F.; Liu, Y.; Sánchez, J.; Poirier, H. Large-scale image retrieval with compressed fisher vectors. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3384–3391. [Google Scholar]
- Perronnin, F.; Dance, C. Fisher kernels on visual vocabularies for image categorization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–22 June 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Perronnin, F.; Sánchez, J.; Mensink, T. Improving the fisher kernel for large-scale image classification. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez, J.; Perronnin, F.; Mensink, T.; Verbeek, J. Image classification with the Fisher vector: Theory and practice. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 105, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jégou, H.; Douze, M.; Schmid, C.; Pérez, P. Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3304–3311. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Yu, K.; Lv, F.; Huang, T.; Gong, Y. Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 3360–3367. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Yu, K.; Zhang, T.; Huang, T.S. Image classification using super-vector coding of local image descriptors. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Crete, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 141–154. [Google Scholar]
- Van Gemert, J.C.; Geusebroek, J.M.; Veenman, C.J.; Smeulders, A.W.M. Kernel codebooks for scene categorization. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; pp. 696–709. [Google Scholar]
- Lazebnik, S.; Schmid, C.; Ponce, J. Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categorie. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; pp. 2169–2178. [Google Scholar]
- Grauman, K.; Darrell, T. The pyramid match kernel: Discriminative classification with sets of image features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Beijing, China, 17–20 October 2005; pp. 1458–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Tong, W.; Meng, D.; Hauptmann, A.G. Towards efficient learning of optimal spatial bag-of-words representations. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval 2014, Glasgow, UK, 1–4 April 2014; pp. 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I.; Marszalek, M.; Schmid, C.; Rozenfeld, B. Learning realistic human actions from movies. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Laptev, I.; Pérez, P. Retrieving actions in movies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 14–21 October 2007; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Zhen, X.; Tao, D.; Li, X. Spatio-temporal Laplacian pyramid coding for action recognition. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duta, I.C.; Ionescu, B.; Aizawa, K.; Sebe, N. Spatio-temporal VLAD encoding for human action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Reykjavik, Iceland, 4–6 January 2017; pp. 365–378. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Qiao, Y. Bag of visual words and fusion methods for action recognition: Comprehensive study and good practice. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2016, 150, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, Y. A probabilistic analysis of sparse coded feature pooling and its application for image retrieval. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Beijbom, O.; Zhang, N.; Darrell, T. Compact bilinear pooling. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 317–326. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohedano, E.; McGuinness, K.; O’Connor, N.E.; Salvador, A.; Marqués, F.; Giró-i-Nieto, X. Bags of local convolutional features for scalable instance search. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval, New York, NY, USA, 6–9 June 2016; pp. 327–331. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, N.; Cox, D.; DiCarlo, J. Why is real-world visual object recognition hard. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boureau, Y.L.; Ponce, J.; LeCun, Y. A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Boureau, Y.L.; Bach, F.; LeCun, Y.; Ponce, J. Learning mid-level features for recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010; pp. 2559–2566. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Sainath, T.N.; Kingsbury, B.; Mohamed, A.; Dahl, G.E.; Saon, G.; Soltau, H.; Beran, T.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Ramabhadran, B. Improvements to deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 8–13 December 2013; pp. 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, D.; Wang, H.; Chen, P.; Wei, Z. Mixed pooling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Rough Sets and Knowledge Technology, Shanghai, China, 24–26 October 2014; pp. 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Serre, T.; Wolf, L.; Poggio, T. Object recognition with features inspired by visual cortex. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, CA, USA, 20–25 June 2005; pp. 994–1000. [Google Scholar]
- Sainath, T.N.; Mohamed, A.; Kingsbury, B.; Ramabhadran, B. Deep convolutional neural networks for LVCSR. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 26–31 May 2013; pp. 8614–8618. [Google Scholar]
- Scherer, D.; Müller, A.; Behnke, S. Evaluation of pooling operations in convolutional architectures for object recognition. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks, Thessaloniki, Greece, 15–18 September 2010; pp. 92–101. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Y.; Xia, W.; Lin, M.; Huang, J.; Ni, B.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, S. HCP: A flexible CNN framework for multi-label image classification. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 38, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeiler, M.D.; Fergus, R. Stochastic pooling for regularization of deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representation, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 2–4 May 2013; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.J.; Yu, Y.L.; Yang, Y.; Xing, E.P. Semantic pooling for complex event analysis in untrimmed videos. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 1617–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Yu, K.; Gong, Y.; Huang, T. Linear spatial pyramid matching using sparse coding for image classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1794–1801. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, R.; Lazebnik, S. Multi-scale orderless pooling of deep convolutional activation features. In Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision, Zurich, Switzerland, 6–12 September 2014; pp. 392–407. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Ren, S.Q.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kerkyra, Greece, 20–27 September 1999; pp. 1150–1157. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kläser, A.; Marszałek, M.; Schmid, C. A spatio-temporal descriptor based on 3d-gradients. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2008, Leeds, UK, 1–4 September 2008; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Schmid, C. Action recognition with improved trajectories. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 3551–3558. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, Z.; Jiang, L.; Yu, S.I.; Gao, C.; Rawat, S.; Cai, Y.; Xu, S.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Informedia @ TRECVID 2013. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv13.papers/informedia.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Luisier, F.; Tickoo, M.; Andrews, W.; Ye, G.; Liu, D.; Chang, S.F.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Morariu, V.; Davis, L.; Gupta, A.; et al. BBN VISER TRECVID 2013 Multimedia Event Detection and Multimedia Event Recounting Systems. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv13.papers/bbnviser.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Jaakkola, T.; Haussler, D. Exploiting generative models in discriminative classifiers. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 30 November–5 December 1998; pp. 487–493. [Google Scholar]
- Chellappa, R.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Ramanathan, N.; Yam, C.Y.; Nixon, M.S.; Elgammal, A.; Boyd, J.E.; Little, J.J.; Lynnerup, N.; Larsen, P.K.; et al. Chapter 533: Gaussian mixture models. In Encyclopedia of Biometrics; Li, S.Z., Jain, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 659–663. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Sapiro, G.; Mallat, S. Solving inverse problems with piecewise linear estimators: From Gaussian mixture models to structured sparsity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2012, 21, 2481–2499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jian, B.; Vemuri, B.C. Robust point set registration using gaussian mixture models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1633–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerroum, M.A.; Hammouch, A.; Aboutajdine, D. Textural feature selection by joint mutual information based on Gaussian mixture model for multispectral image classification. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2010, 31, 1168–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Storck, D.J. Pattern Classification, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, H.H.; Chuang, J.H.; Liu, T.L. Regularized background adaptation: A novel learning rate control scheme for Gaussian mixture modeling. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perronnin, F.; Dance, C.; Csurka, G.; Bressan, M. Adapted vocabularies for generic visual categorization. In Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision, Graz, Austria, 7–13 May 2006; pp. 464–475. [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan, G.J.; Basford, K.E. Mixture Models: Inference and Applications to Clustering (Statistics: Textbooks & Monographs); CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Jegou, H.; Douze, M.; Schmid, C. Product quantization for nearest neighbor search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R. Vector quantization. IEEE ASSP Mag. 1984, 1, 4–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Yu, S.I.; Lan, Z.; Ma, Z.; Hauptmann, A.G. E-LAMP: Integration of innovative ideas for multimedia event detection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 2014, 25, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Chen, Q.; Brown, L.; Datta, A.; Fan, Q.; Feris, R.; Yan, S.; Hauptmann, A.; Pankanti, S. CMU-IBM-NUS @ TRECVID 2012: Surveillance Event Detection (SED). Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv12.slides/tv12.cmu.sed.slides.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Cao, L.; Chang, S.F.; Codella, N.; Cotton, C.; Ellis, D.; Gong, L.; Hill, M.; Hua, G.; Kender, J.; Merler, M.; et al. IBM Research and Columbia University TRECVID-2011 Multimedia Event Detection (MED) System. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv11.papers/ibm.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Yang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zavesky, E.; Gibbon, D.; Shahraray, B.; Tian, Y. AT&T Research at TRECVID 2013: Surveillance Event Detection. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv13.papers/att.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Merler, M.; Huang, B.; Xie, L.; Hua, G.; Natsev, A. Semantic model vectors for complex video event recognition. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 2012, 14, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Y.; Rong, X.J.; Yang, X.D.; Tian, Y.L. CCNY at TRECVID 2014: Surveillance Event Detection. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv14.papers/ccny.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
- Shi, F.; Petriu, E.; Laganiere, R. Sampling strategies for real-time action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Portland, OR, USA, 23–28 June 2013; pp. 2595–2602. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.W.; Chen, J.; Huang, P.Y.; Li, X.C.; Jiang, L.; Lan, Z.Z.; Pan, P.B.; Fan, H.H.; Jin, Q.; Sun, J.; et al. Informedia @ TRECVID 2016. Available online: http://www-nlpir.nist.gov/projects/tvpubs/tv16.papers/inf.pdf (accessed on 26 October 2017).
| Approaches | References |
|---|---|
| Standard bag-of-features encoding | Csurka et al., 2004 [49]; Sivic et al., 2003 [50] |
| Fisher vector encoding | Perronnin et al., 2010 [51]; Perronnin et al., 2007 [52]; Perronnin et al., 2010 [53]; Sánchez et al., 2013 [54] |
| VLAD encoding | Jégou et al., 2010 [55] |
| Locality-constrained linear encoding | Wang et al., 2010 [56] |
| Super vector encoding | Zhou et al., 2010 [57] |
| Kernel codebook encoding | van Gemert et al., 2008 [58] |
| Spatial pyramid encoding | Lazebnik et al., 2006 [59]; Grauman et al., 2005 [60] |
| Jensen-Shannon tiling encoding | Jiang et al., 2014 [61] |
| Approaches | References |
|---|---|
| Spatiotemporal grids encoding | Laptev et al., 2008 [62]; Laptev et al., 2007 [63] |
| STLPC encoding | Shao et al., 2014 [64] |
| Spatiotemporal VLAD encoding | Duta et al., 2017 [65] |
| Approaches | References |
|---|---|
| Sum pooling | Peng et al., 2016 [66]; Zhang et al., 2015 [67]; Gao et al., 2016 [68]; LeCun et al., 1998 [69]; Mohedano et al., 2016 [70] |
| Average pooling | Pinto et al., 2008 [71]; Boureau et al., 2010 [72]; Boureau et al., 2010 [73]; He et al., 2016 [74]; Sainath et al., 2013 [75]; Yu et al., 2014 [76] |
| Max pooling | Serre et al., 2005 [77]; Sainath et al., 2013 [78]; Scherer et al., 2010 [79]; Wei et al., 2016 [80] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Lu, B.; Li, C. Feature Encodings and Poolings for Action and Event Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey. Information 2017, 8, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8040134
Liu C, Zhang Q, Lu B, Li C. Feature Encodings and Poolings for Action and Event Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey. Information. 2017; 8(4):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8040134
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Changyu, Qian Zhang, Bin Lu, and Cong Li. 2017. "Feature Encodings and Poolings for Action and Event Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey" Information 8, no. 4: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8040134
APA StyleLiu, C., Zhang, Q., Lu, B., & Li, C. (2017). Feature Encodings and Poolings for Action and Event Recognition: A Comprehensive Survey. Information, 8(4), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/info8040134





