Integrating AI and IoT for Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Environments: A Practical Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
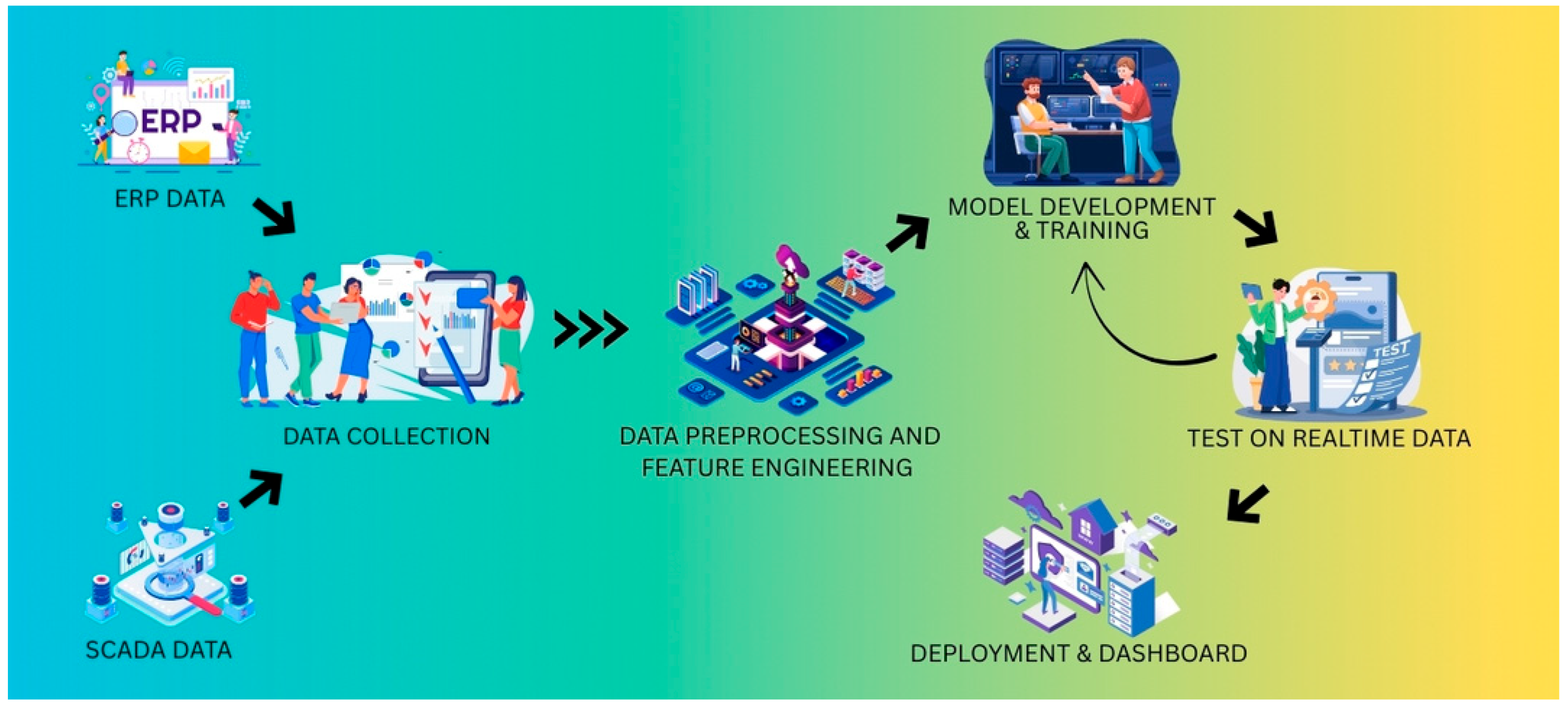
2. Data and Methodology
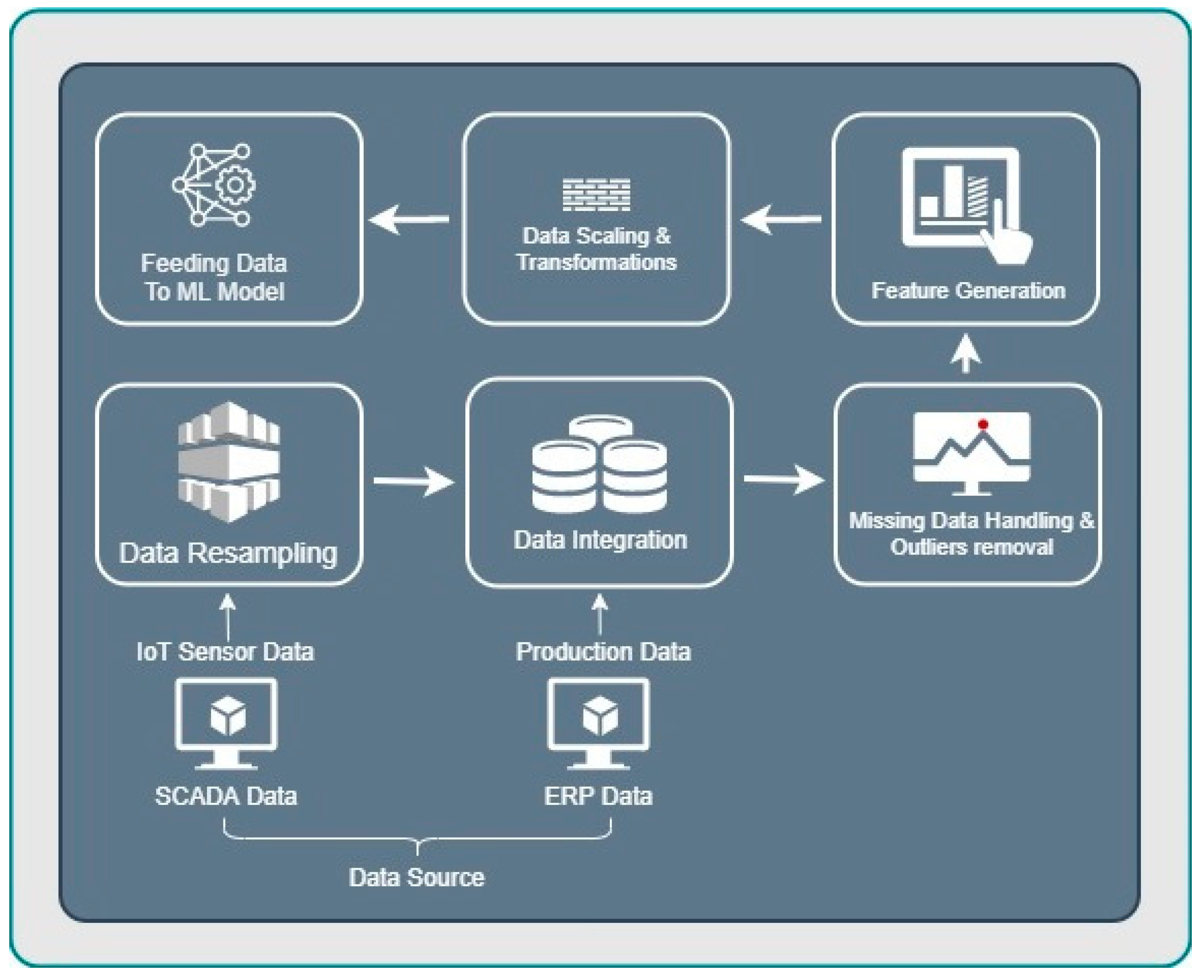
2.1. Data and Preprocessing
2.1.1. SCADA Data Retrieval and Handling Missing Data
2.1.2. Outlier Detection and Error Handling
2.1.3. Data Transformation and Feature Engineering
2.2. Methodology
Model Selection and End-to-End Pipeline
2.3. Performance Evaluation
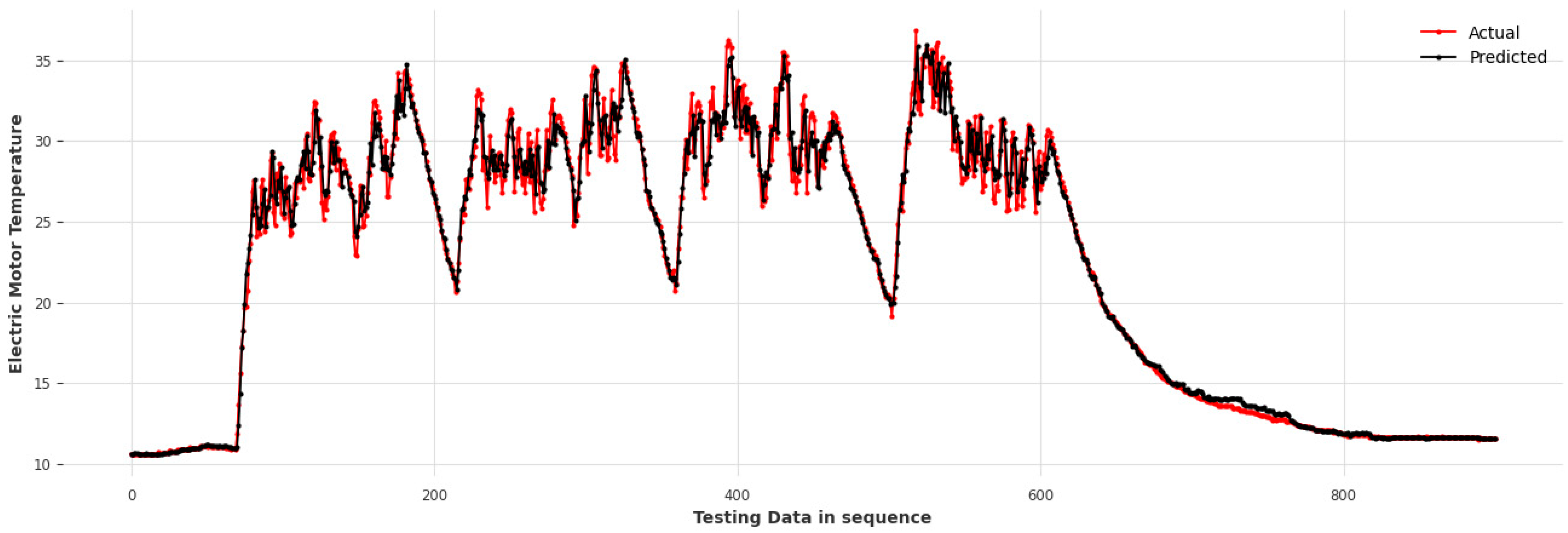
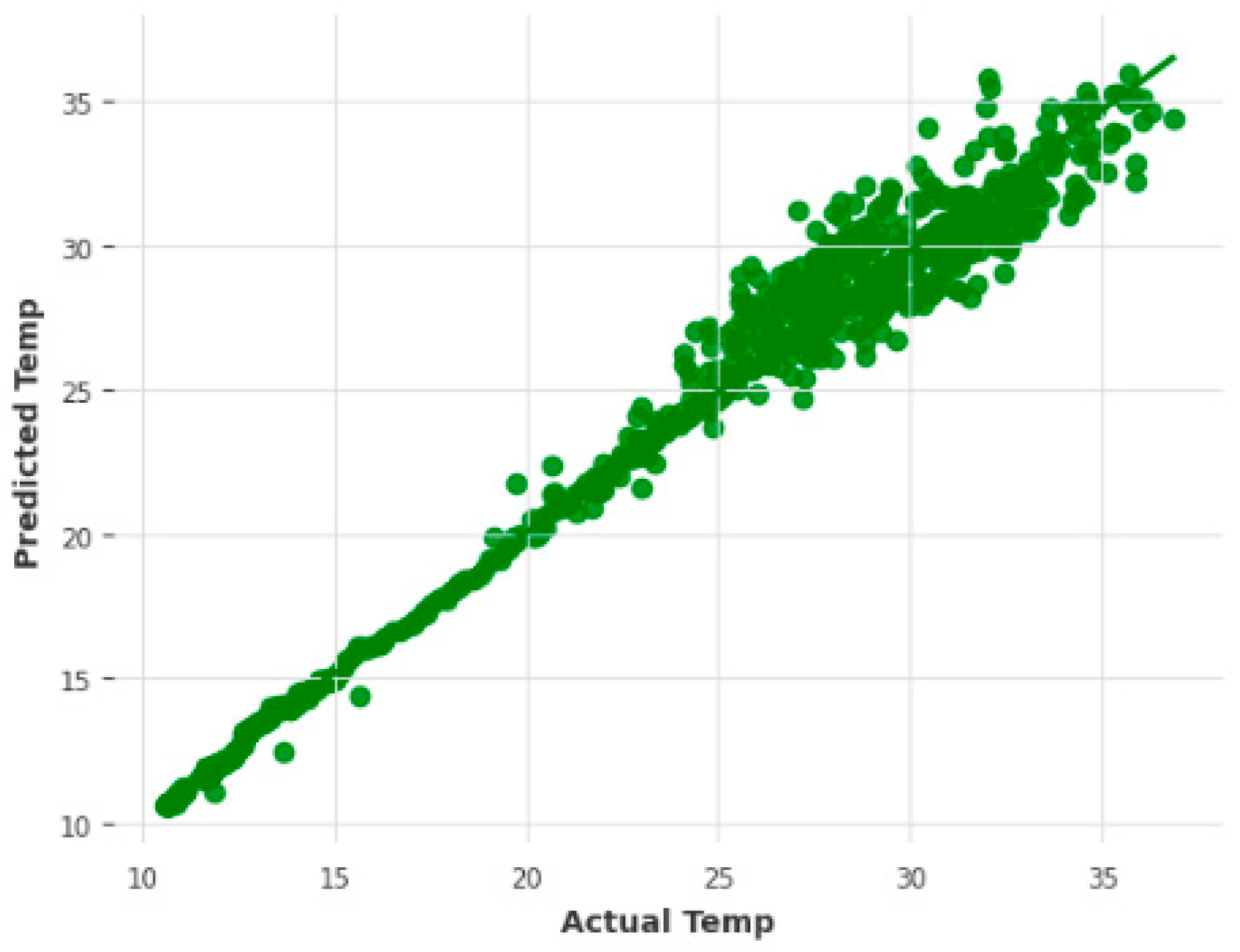
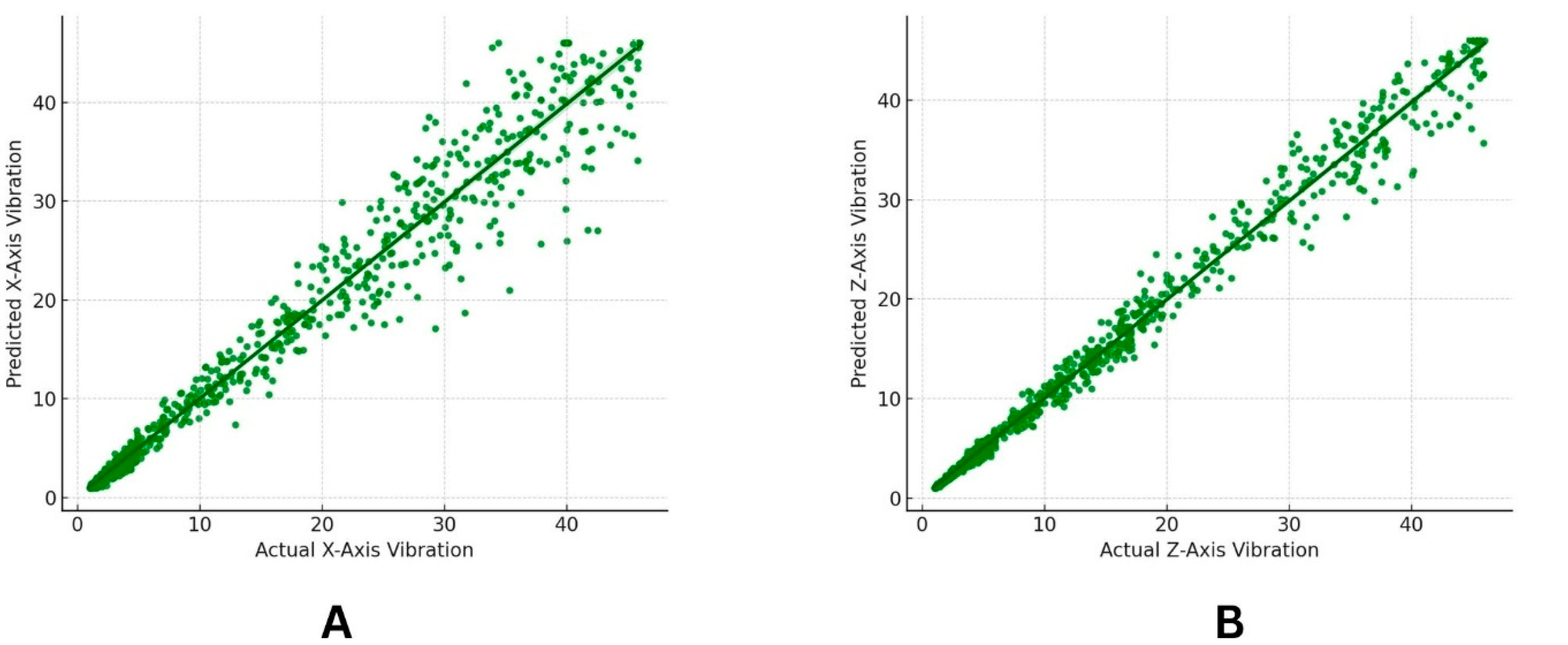
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shahin, M.; Chen, F.F.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Zand, N. Using machine learning and deep learning algorithms for downtime minimization in manufacturing systems: An early failure detection diagnostic service. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 128, 3857–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, R.; Tiwari, M.K.; Ivanov, D.; Dolgui, A. Machine learning in manufacturing and industry 4.0 applications. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 4773–4778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, Z.; Ahamed, F.; Mayer, W.; Patel, N.; Grossmann, G.; Stumptner, M.; Kuusk, A. Artificial intelligence for industry 4.0: Systematic review of applications, challenges, and opportunities. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 216, 119456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soori, M.; Arezoo, B.; Dastres, R. Internet of things for smart factories in industry 4.0, a review. Internet Things Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2023, 3, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.C.; Khang, A.; Mishra, S.K.; Patnaik, P.K.; Mohanty, G.K.; Dash, T. Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Technology Solutions in Smart Manufacturing. In Machine Vision and Industrial Robotics in Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 155–177. [Google Scholar]
- Visconti, P.; Rausa, G.; Del-Valle-Soto, C.; Velázquez, R.; Cafagna, D.; De Fazio, R. Machine learning and IoT-based solutions in industrial applications for Smart Manufacturing: A critical review. Future Internet 2024, 16, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzai, J.; Alam, F.; Dhafer, A.; Bojović; M; Altowaijri, S.M.; Niazi, I.K.; Mehmood, R. Machine learning-enabled Internet of Things (iot): Data, applications, and industry perspective. Electronics 2022, 11, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presciuttini, A.; Cantini, A.; Costa, F.; Portioli-Staudacher, A. Machine learning applications on IoT data in manufacturing operations and their interpretability implications: A systematic literature review. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 74, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Ghosh, T.; Aurna, N.F.; Kaiser, M.S.; Anannya, M.; Hosen, A.S. Machine learning and internet of things in industry 4. 0: A review. Meas. Sens. 2023, 28, 100822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, T.; Da Costa, C.A.; da Rosa Righi, R.; de Lima, M.J.; da Trindade, E.S.; Li, G.P. Predictive maintenance in the Industry 4. 0: A systematic literature review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 150, 106889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, S.; Alpay, K. Predictive maintenance system for production lines in manufacturing: A machine learning approach using IoT data in real-time. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 173, 114598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Alcazar, A.; Govea, J.; Villegas-Ch, W. Anomaly Detection in a Smart Industrial Machinery Plant Using IoT and Machine Learning. Sensors 2023, 23, 8286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassoun, A.; Aït-Kaddour, A.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Rathod, N.B.; Bader, F.; Barba, F.J.; Biancolilloi, A.; Cropotovaj, J.; Galanakis, C.M.; Regenstein, J.; et al. The fourth industrial revolution in the food industry—Part I: Industry 4. 0 technologies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 6547–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, I.; Rawat, J.; Mohd, N.; Husain, S. Opportunities of artificial intelligence and machine learning in the food industry. J. Food Qual. 2021, 2021, 4535567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatsu, V.; Shine, A.E.; Tharakan, J.M.; Peter, D.; Ranganathan, T.V.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Mugabi, R.; Muhsinah, A.B.; Waseem, M.; Nayik, G.A. Revolutionizing the food industry: The transformative power of artificial intelligence—A review. Food Chem. X 2024, 24, 101867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konur, S.; Lan, Y.; Thakker, D.; Morkyani, G.; Polovina, N.; Sharp, J. Towards design and implementation of Industry 4.0 for food manufacturing. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 23753–23765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.H.; Sablani, S.S.; Nayak, R.; Gu, Y. Machine learning-based modeling in food processing applications: State of the art. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 1409–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. XGBoost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable Name | Description | Temperature Prediction (Output 1) | x-Axis Vibration Prediction (Output 2) | z-Axis Vibration Prediction (Output 3) | Used as Future Covariate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| motor_temperature | The temperature of the motor, indicating potential overheating or malfunction. | Y | Y | Y | N |
| x_axis_vibrations | Vibration measurement along the x-axis, reflecting mechanical stability. | Y | Y | Y | N |
| z_axis_vibrations | Vibration measurement along the z-axis, used to detect motor imbalances. | Y | Y | Y | N |
| temp_rolling_mean | The simple rolling mean of motor_temperature computed over a fixed window that shifts incrementally. | Y | N | N | N |
| temp_ema | The Exponential Moving Average of motor temperature, giving more weight to recent data points. | Y | N | N | N |
| hour | The hour of the day, used to capture time-dependent behavior of the system. | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| weekday | The day of the week, indicating potential variations in motor behavior by day. | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| is_weekend | A binary indicator showing whether the data point falls on a weekend (True/False). | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| total_product _quantity | The quantity of products being processed, which affects motor load and performance. | Y | Y | Y | N |
| Parameter | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| booster | Indicates the algorithm used to build decision trees during training. | ‘gbtree’ |
| alpha | Controls L1 regularization on weights, helping to reduce model overfitting. | 1–2 |
| gamma | Threshold for minimum loss reduction before a split is made, promoting tree simplicity. | 0.3–0.4 |
| n_estimators | Total number of boosting iterations or trees generated during model training. | 800–1000 |
| colsample_bytree | Ratio of features randomly selected for each tree, enhancing model diversity. | 0.4–0.6 |
| min_child_weight | Minimum required sum of instance weight (hessian) in a node, regulating model complexity. | 4–6 |
| max_depth | Upper limit on tree depth, used to control overfitting and enhance generalization. | 4–6 |
| learning_rate | Controls how quickly the model adapts by scaling the weight updates. | 0.09–0.15 |
| Objective | Defines the learning task along with the associated loss function to optimize. | ‘poission’ |
| eval_metric | Performance indicator used to monitor model training progress and quality. | ‘rmse’ |
| num_leaves | Sets the maximum number of terminal nodes per tree to manage complexity vs. accuracy. | 21–25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rakholia, R.; Suárez-Cetrulo, A.L.; Singh, M.; Carbajo, R.S. Integrating AI and IoT for Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Environments: A Practical Approach. Information 2025, 16, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090737
Rakholia R, Suárez-Cetrulo AL, Singh M, Carbajo RS. Integrating AI and IoT for Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Environments: A Practical Approach. Information. 2025; 16(9):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090737
Chicago/Turabian StyleRakholia, Rajnish, Andrés L. Suárez-Cetrulo, Manokamna Singh, and Ricardo Simón Carbajo. 2025. "Integrating AI and IoT for Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Environments: A Practical Approach" Information 16, no. 9: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090737
APA StyleRakholia, R., Suárez-Cetrulo, A. L., Singh, M., & Carbajo, R. S. (2025). Integrating AI and IoT for Predictive Maintenance in Industry 4.0 Manufacturing Environments: A Practical Approach. Information, 16(9), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090737







