Advanced Cryptography Using Nanoantennas in Wireless Communication
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Background
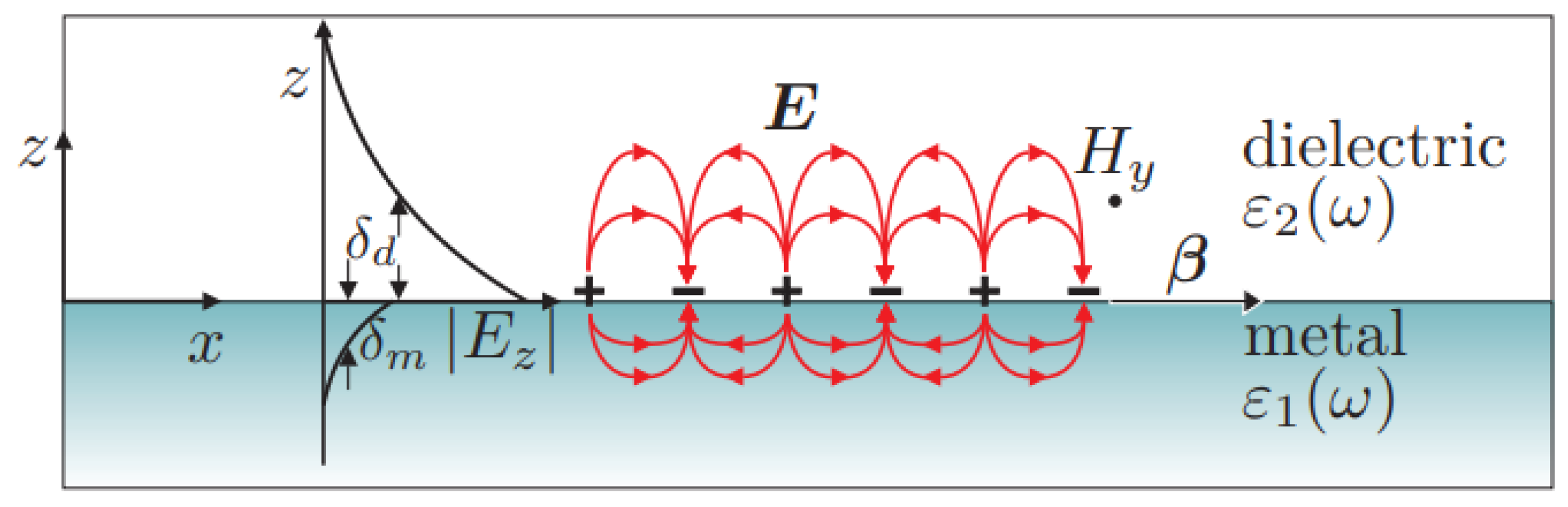
2.1. Nanoantennas in Wireless Communications
2.2. Security in Wireless Communication
2.3. Criptography in Eletromagnetic Signals
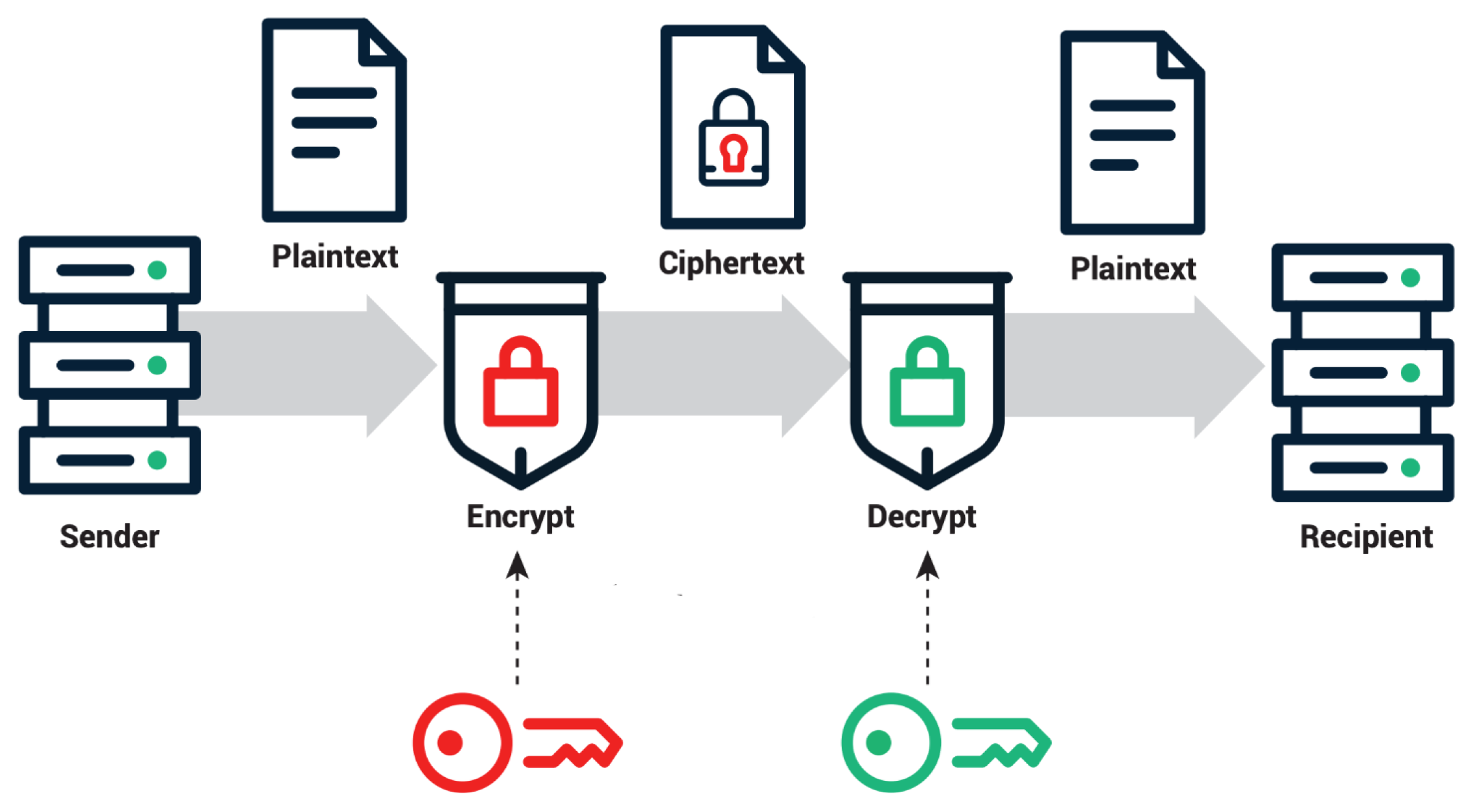
2.3.1. Public Key Encryption
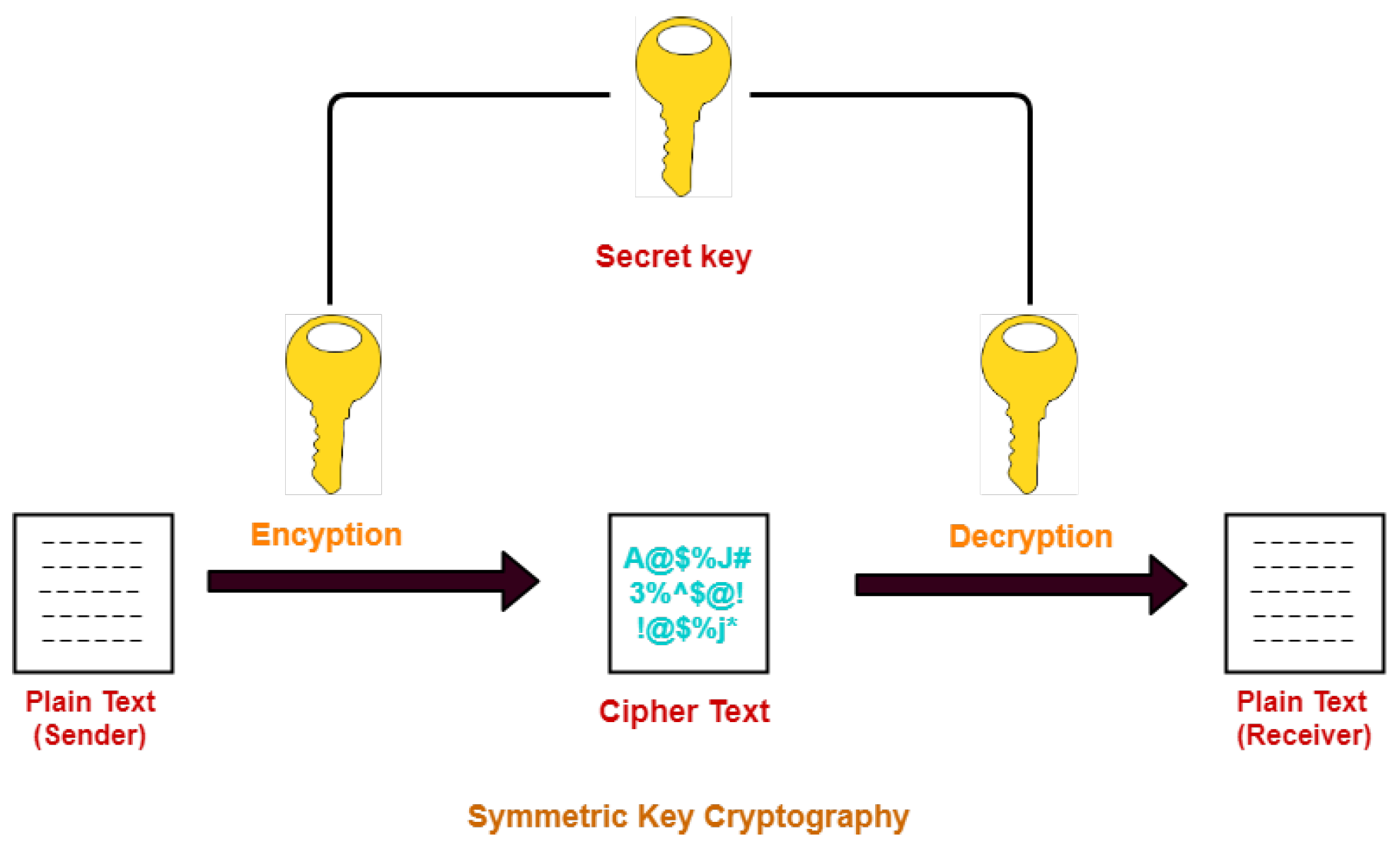
2.3.2. Secret Key Encryption
3. Related Work
3.1. Electromagnetic Analysis for Cryptography
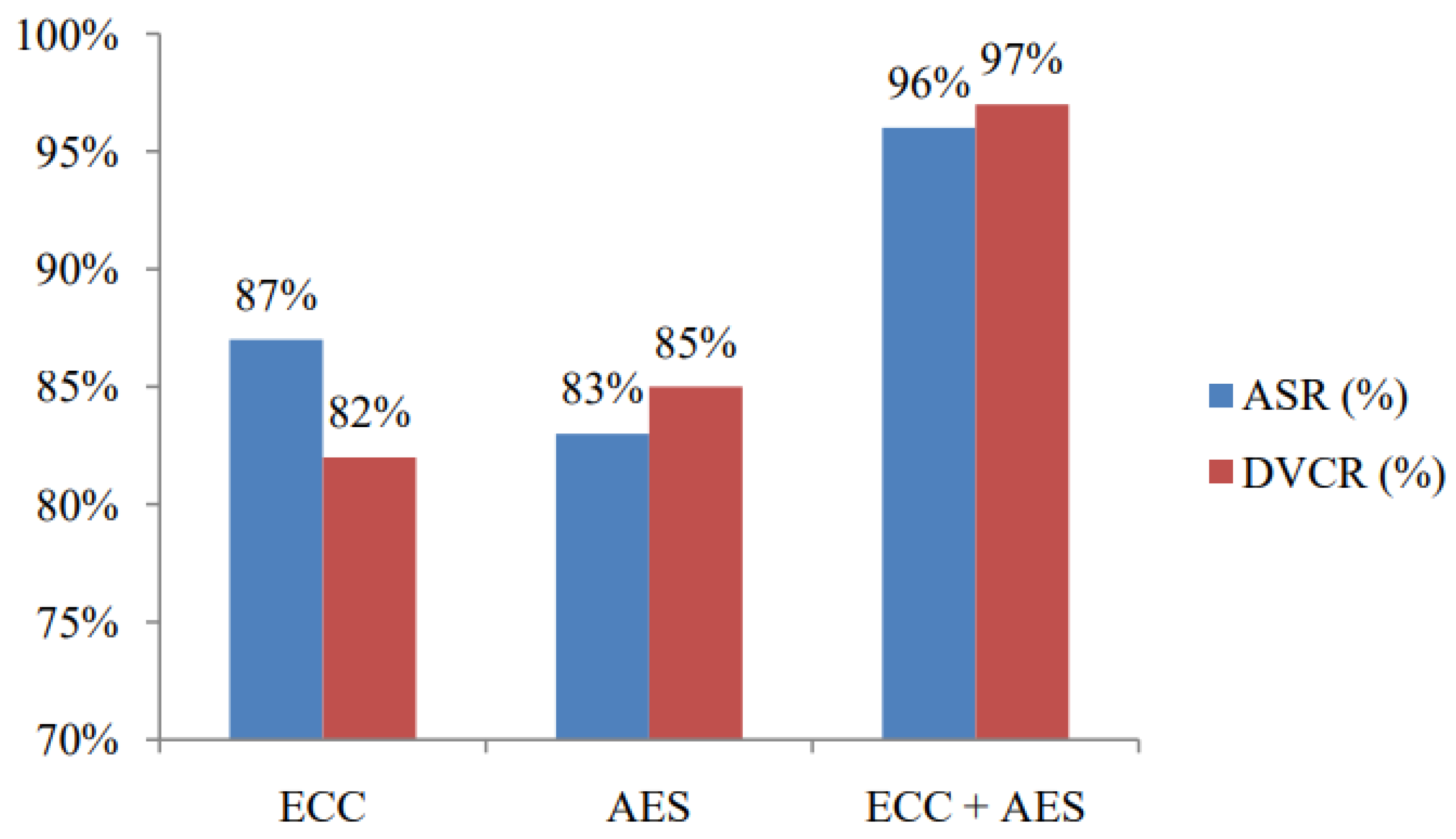
3.2. Elevating Security Using ECC and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) Algorithms
4. Proposed Model
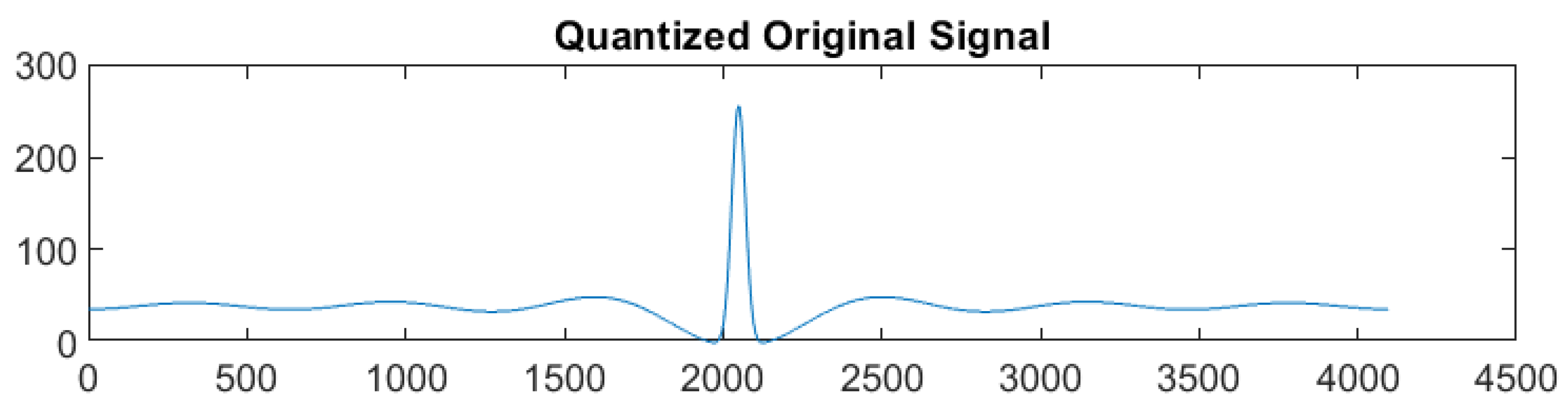
- Block 1—Nanoantenna Response Characterization:The process initiates with the design and full-wave modeling of a nanoantenna, developed from fundamental principles. The structure is used to amplify the signal transmitted.
- Block 2—Signal Quantization and Error Correction:The electromagnetic response at the output of the nanoantenna is captured, normalized, and quantized, resulting in a digital bitstream. Subsequently, the stream undergoes processing by an error correction module that is based on Reed–Solomon (255,223) coding. This coding provides resilience against transmission errors.
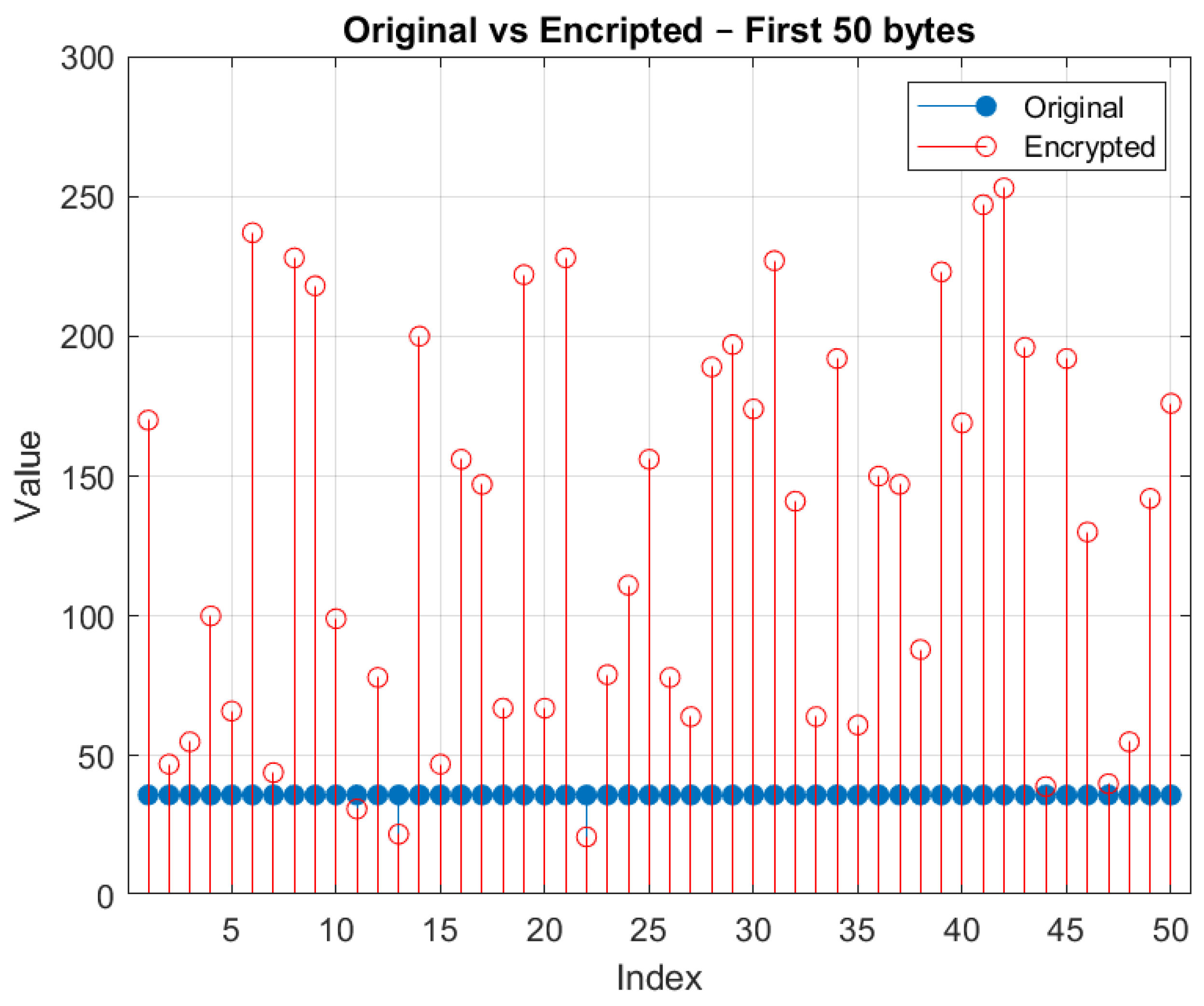
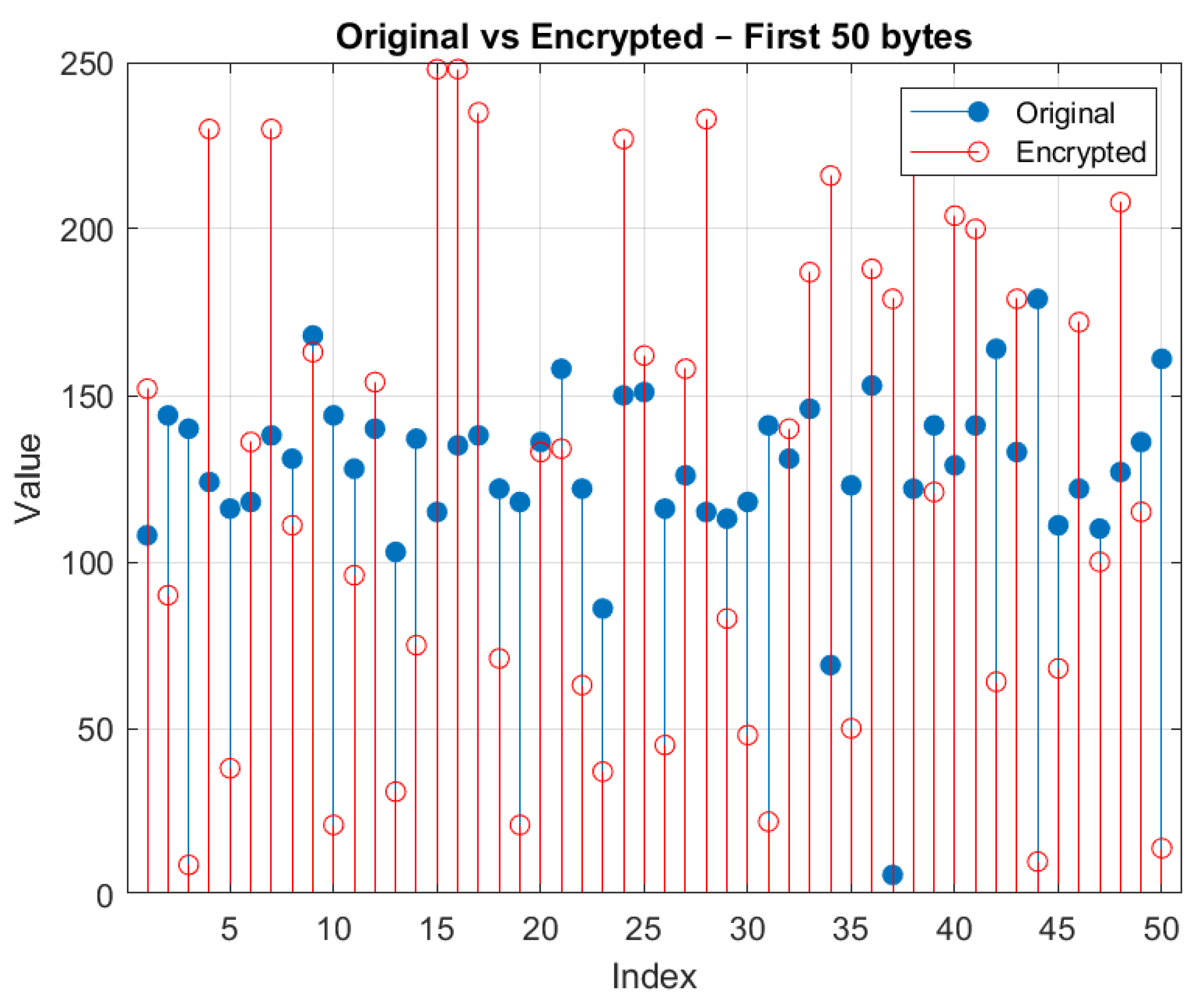
- Block 3—Key Generation and Bitwise Encryption:Symmetric key generation is performed using the ECDH (Elliptic Curve Diffie–Hellman) protocol, followed by a bit-by-bit encryption process using the XOR operation. The derived key is then applied cyclically to the data sequence, thereby ensuring the confidentiality of the transmitted signal.
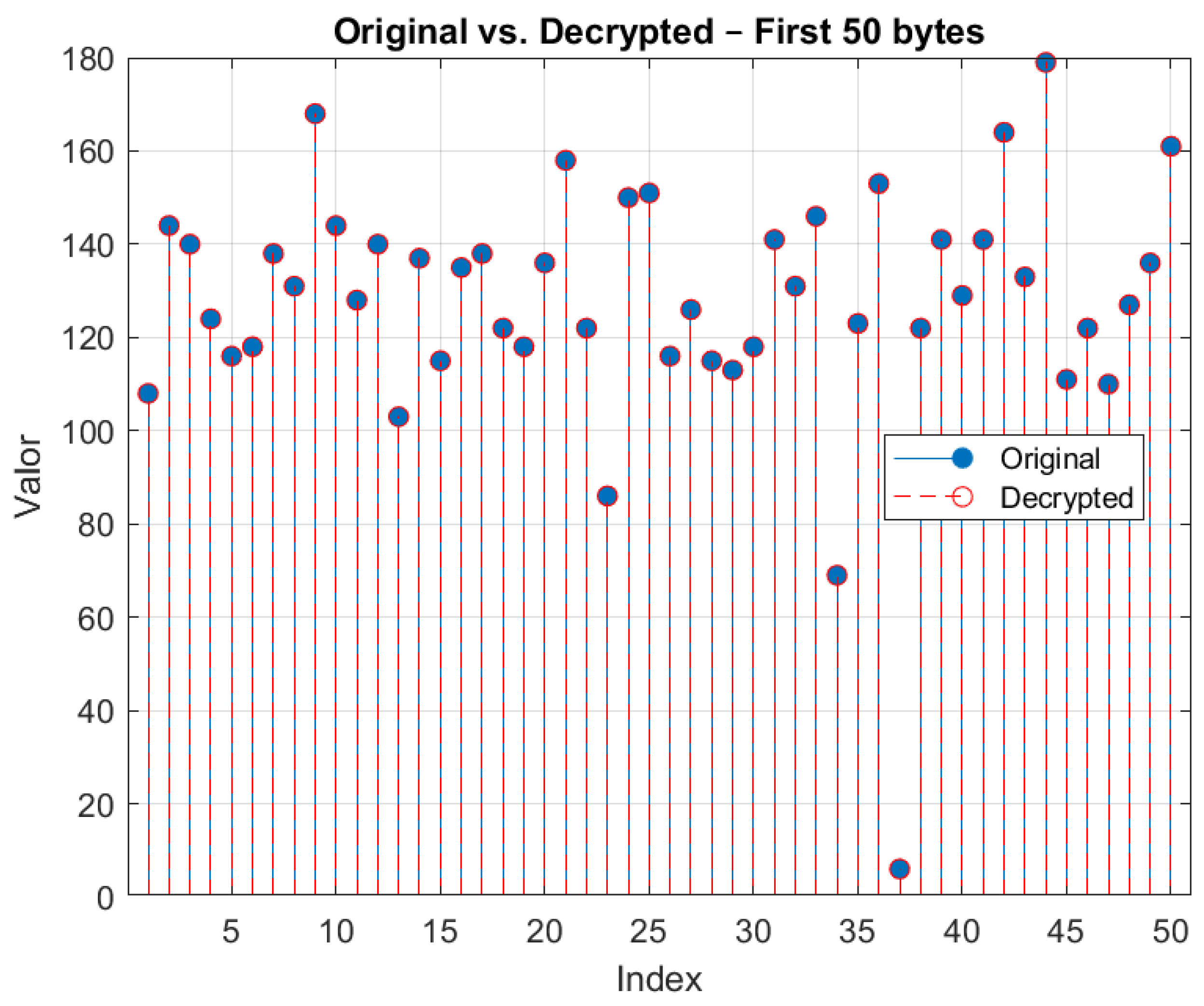
- Block 4—Decryption and Signal Recovery:The signal is decrypted by applying the XOR operation again with the same symmetric key, which allows the original data stream to be recovered. Subsequently to decryption, the signal undergoes reconstruction through the inversion of quantization and normalization, thereby restoring the original continuous signal.
4.1. Block 1—Nanoantenna Response Characterization
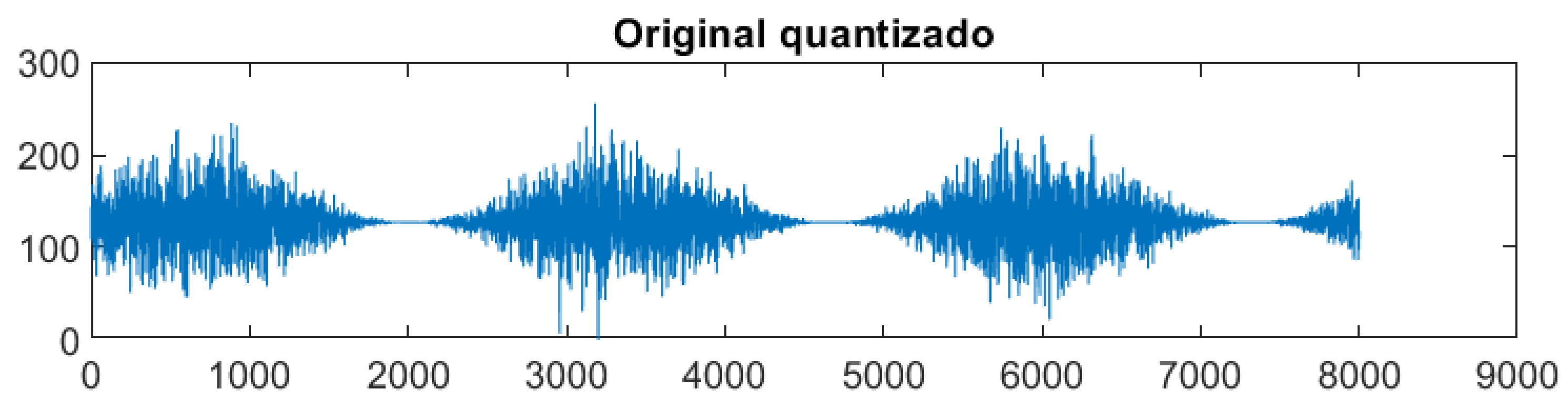
4.2. Block 2—Signal Quantization and Error Correction
4.3. Block 3—Key Generation and Bitwise Encryption
4.3.1. Key Generation with ECDH
4.3.2. Bitwise XOR Encryption
4.4. Block 4—Decryption and Signal Recovery
5. Results
5.1. Nanoantenna Response to Signals
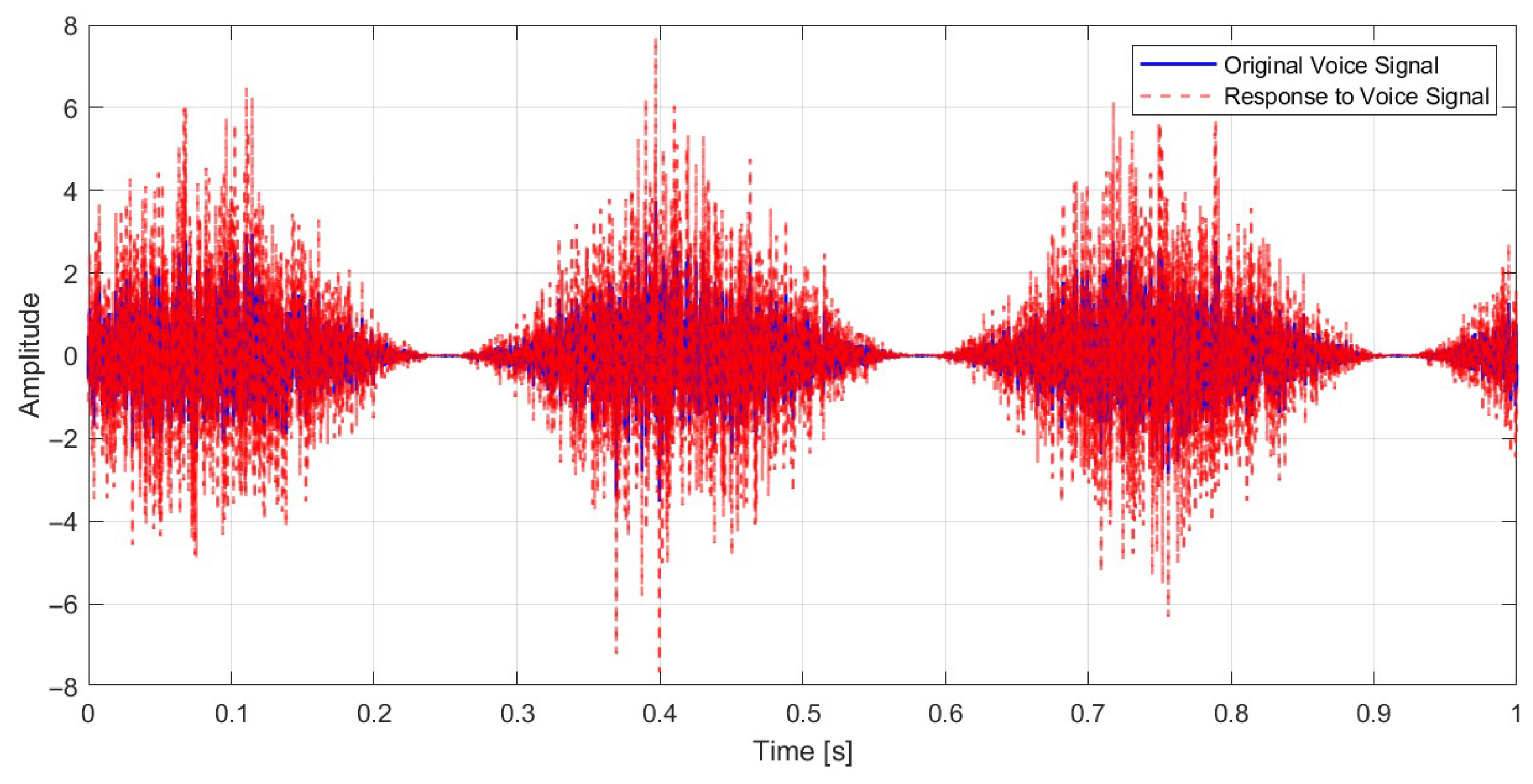
5.2. Proposed Cryptography Model Test
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AES | Advanced Encryption Standard |
| ECC | Elliptic Curve Cryptography |
| ECDH | Elliptic Curve Diffie–Hellman |
| EM | Electromagnetic |
| EOT | Extraordinary Optical Transmission |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| IFFT | Inverse Fast Fourier Transform |
| LSPR | Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| PLS | Physical Layer Security |
| PSNR | Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| RF | Radio-Frequency |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| SPP | Surface Plasmonic Polariton |
References
- Gomes, R.D.F.R.; Martins, M.J.; Baptista, A.; Torres, J.P.N. Study of a nano optical antenna for intersatellite communications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2017, 49, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, B.S.; Bhat, A.; Pištora, J. THz band nanoantennas for future mobile communication. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSC), Noida, India, 12–14 December 2013; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Alves, A.; Melo, M.C.; Siqueira, J.; Zanella, F.; Mejía-Salazar, J.R.; Arismar, C.S. Plasmonic nanoantennas for 6G intra/inter-chip optical-wireless communications. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd 6G wireless summit (6G SUMMIT), Levi, Finland, 17–20 March 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Balanis, C.A. Antenna theory: A review. Proc. IEEE 1992, 80, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavankova, I.; Kovar, S.; Valouch, J.; Adamek, M. Review of nanoantennas application. Prz. Elektrotechniczny 2023, 1, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksymov, I.S. Magneto-plasmonic nanoantennas: Basics and applications. Rev. Phys. 2016, 1, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhimi, M.J.; Akan, O.B. Nanoantennas and Nanoradars: The Future of Integrated Sensing and Communication at the Nanoscale. IEEE Trans. Mol. Biol. Multi-Scale Commun. 2024, 10, 493–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbesen, T.; Lezec, H.; Ghaemi, H.; Thio, T.; Wolff, P. Extraordinary Optical Transmission Through Sub-Wavelength Hole Arrays. Nature 1998, 391, 667–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J. Excitation and Detection of Highly Confined Plasmonic Gap Modes with Subwavelength Dimensions; Friedrich-Alexander-Universitaet Erlangen-Nuernberg: Erlangen, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maier, S.A. Plasmonics: Fundamentals and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Raether, H. Surface Plasmons on Smooth and Rough Surfaces and on Gratings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Piltan, S.; Sievenpiper, D. Field enhancement in plasmonic nanostructures. J. Opt. 2018, 20, 055401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geshev, P.; Klein, S.; Witting, T.; Dickmann, K.; Hietschold, M. Calculation of the electric-field enhancement at nanoparticles of arbitrary shape in close proximity to a metallic surface. Phys. Rev. B 2004, 70, 75402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, G.; Nirmala, P.; Ramesh, S.; Tamilselvi, M.; Ramkumar, G. A Novel Data Communication with Security Enhancement using Threat Management Scheme over Wireless Mobile Networks. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 28–29 January 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.k.; Robles, R.J.; Hong, C.H.; Kim, T.H. Wireless network security: Vulnerabilities, threats and countermeasures. Int. J. Multimed. Ubiquitous Eng. 2008, 3, 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sanenga, A.; Mapunda, G.A.; Jacob, T.M.L.; Marata, L.; Basutli, B.; Chuma, J.M. An overview of key technologies in physical layer security. Entropy 2020, 22, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liestyowati, D. Public key cryptography. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1477, 052062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gençoğlu, M.T. Importance of cryptography in information security. IOSR J. Comput. Eng 2019, 21, 65–68. [Google Scholar]
- Leighton, T.; Micali, S. Secret-key agreement without public-key cryptography. In Proceedings of the Annual International Cryptology Conference, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 22–26 August 1993; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 456–479. [Google Scholar]
- Gunathilake, N.A.; Al-Dubai, A.; Buchanan, W.J.; Lo, O. Electromagnetic analysis of an ultra-lightweight cipher: Present. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.15225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayana, D.S.; Pandian, R.; Babu, A.R.; Nirmalraj, S.; Jebaseelan, S.D.S.; V, M. Elevating Security in Wireless Sensor Networks using ECC and AES Cryptographic Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Innovative Computing, Intelligent Communication and Smart Electrical Systems (ICSES), Chennai, India, 14–15 December 2023; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
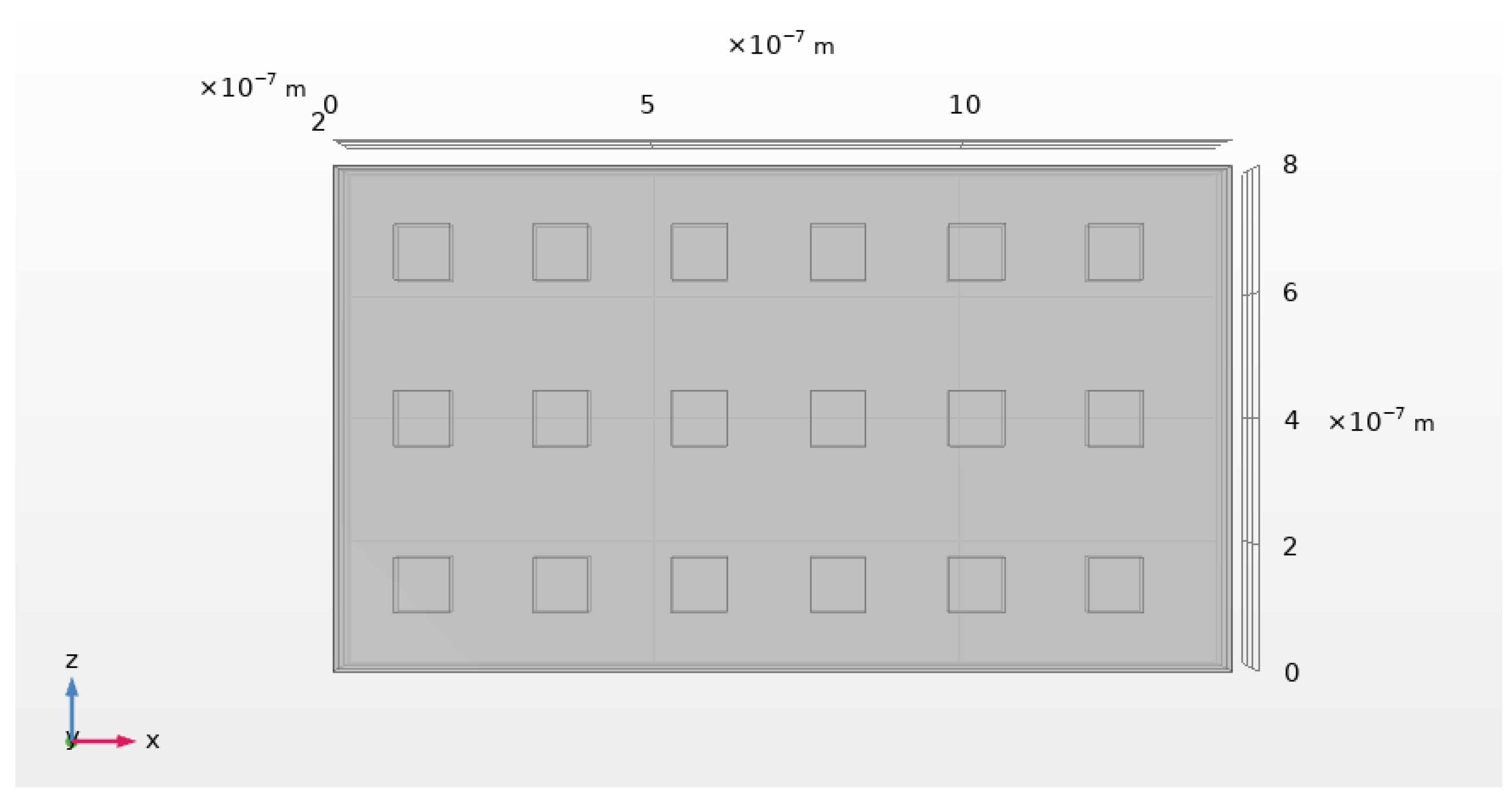
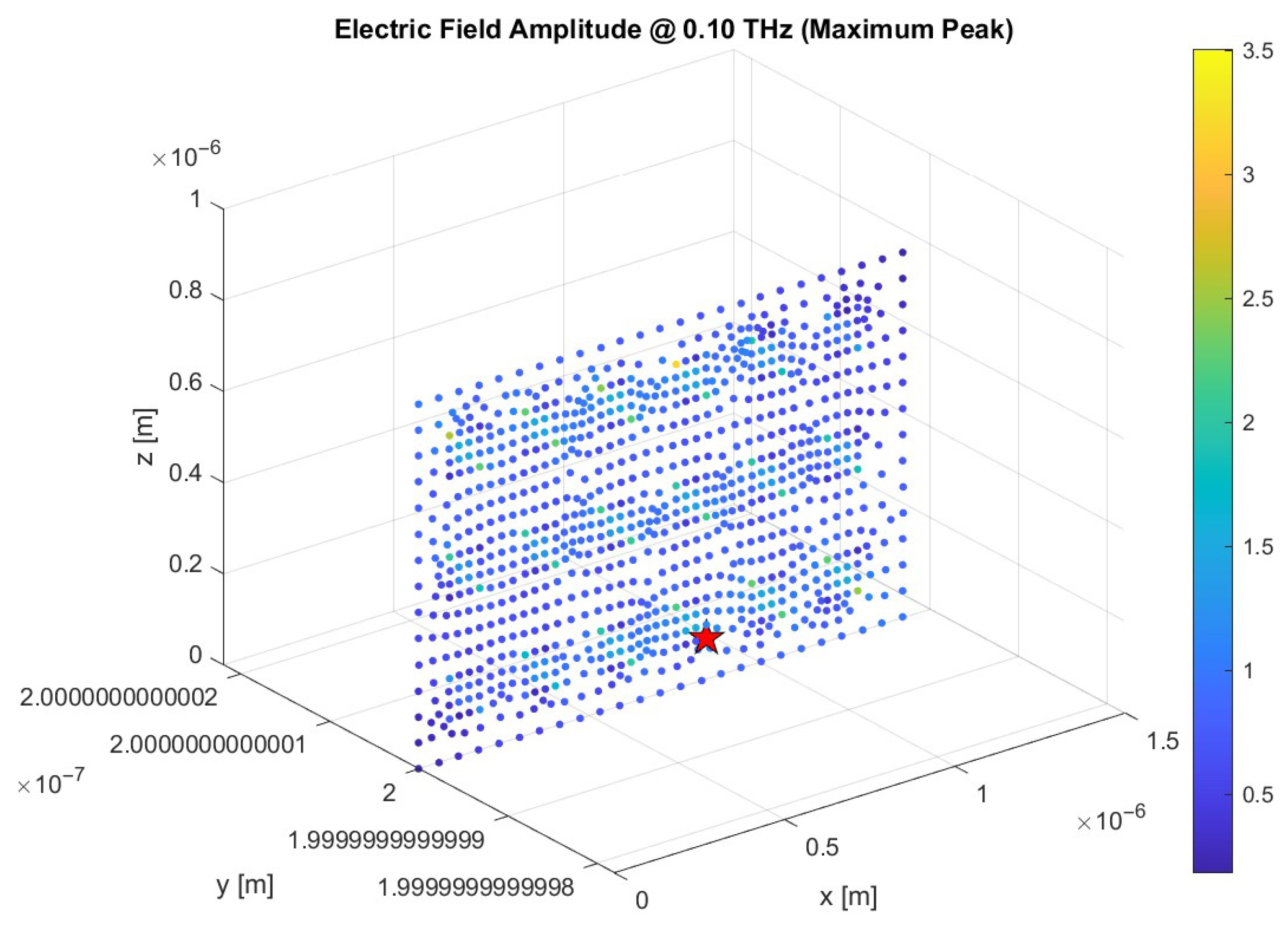
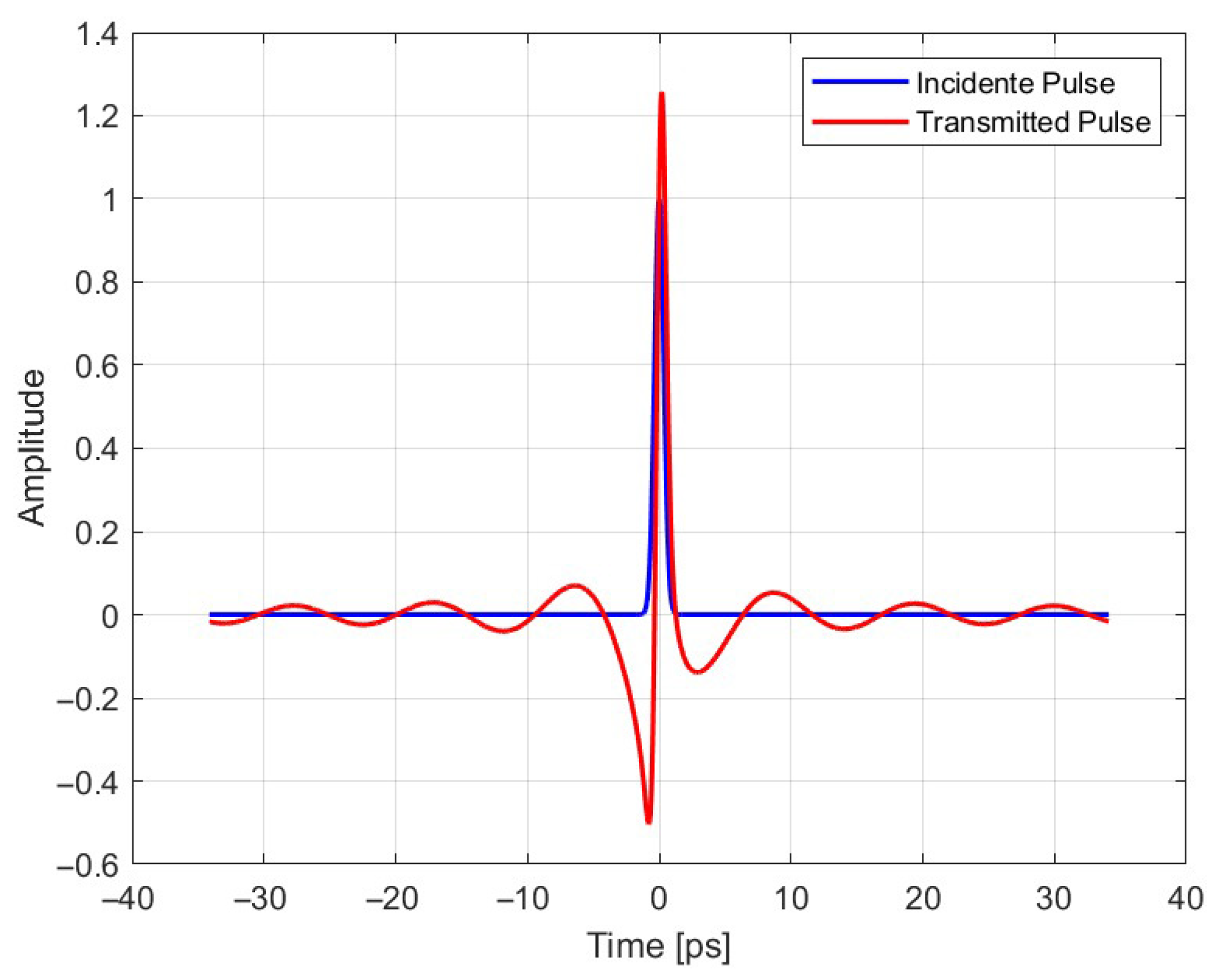



| Name | Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| E | m | Metal thickness | |
| m | Dielectric thickness | ||
| m | Design wavelength | ||
| L | m | Total length of structure | |
| m | Side length of apertures | ||
| m | Spacing between apertures | ||
| m | Aperture width | ||
| 3 | – | Number of apertures along x | |
| 6 | – | Number of apertures along z |
| Gaussian Signal | Voice Signal | |
|---|---|---|
| RMSE | 11.4235 | 15.1256 |
| MAE | 0.8574 | 2.5213 |
| PSNR | 26.97 dB | 24.54 dB |
| Pearson Correlation Coefficient | 0.8887 | 0.8062 |
| Entropy (Original Signal) | 2.4746 | 4.5371 |
| Entropy (Reconstructed Signal) | 2.5292 | 3.9869 |
| Avalanche effect (1-bit change) | 0.5052 | 0.4992 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, F.; Torres, J.P.N.; dos Santos, P.M.; Lameirinhas, R.A.M. Advanced Cryptography Using Nanoantennas in Wireless Communication. Information 2025, 16, 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090720
Alves F, Torres JPN, dos Santos PM, Lameirinhas RAM. Advanced Cryptography Using Nanoantennas in Wireless Communication. Information. 2025; 16(9):720. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090720
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Francisco, João Paulo N. Torres, P. Mendonça dos Santos, and Ricardo A. Marques Lameirinhas. 2025. "Advanced Cryptography Using Nanoantennas in Wireless Communication" Information 16, no. 9: 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090720
APA StyleAlves, F., Torres, J. P. N., dos Santos, P. M., & Lameirinhas, R. A. M. (2025). Advanced Cryptography Using Nanoantennas in Wireless Communication. Information, 16(9), 720. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16090720








