A Knowledge–Data Dual-Driven Groundwater Condition Prediction Method for Tunnel Construction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A data classification method based on differences in the construction face, integrating detection data from similar groundwater discharge conditions.
- Designing a dual-driven prediction framework for groundwater conditions, which statistically analyzes detection data from various construction faces to derive suitable data-driven and knowledge-driven models, thereby significantly enhancing the accuracy of groundwater condition forecasting in the target area.
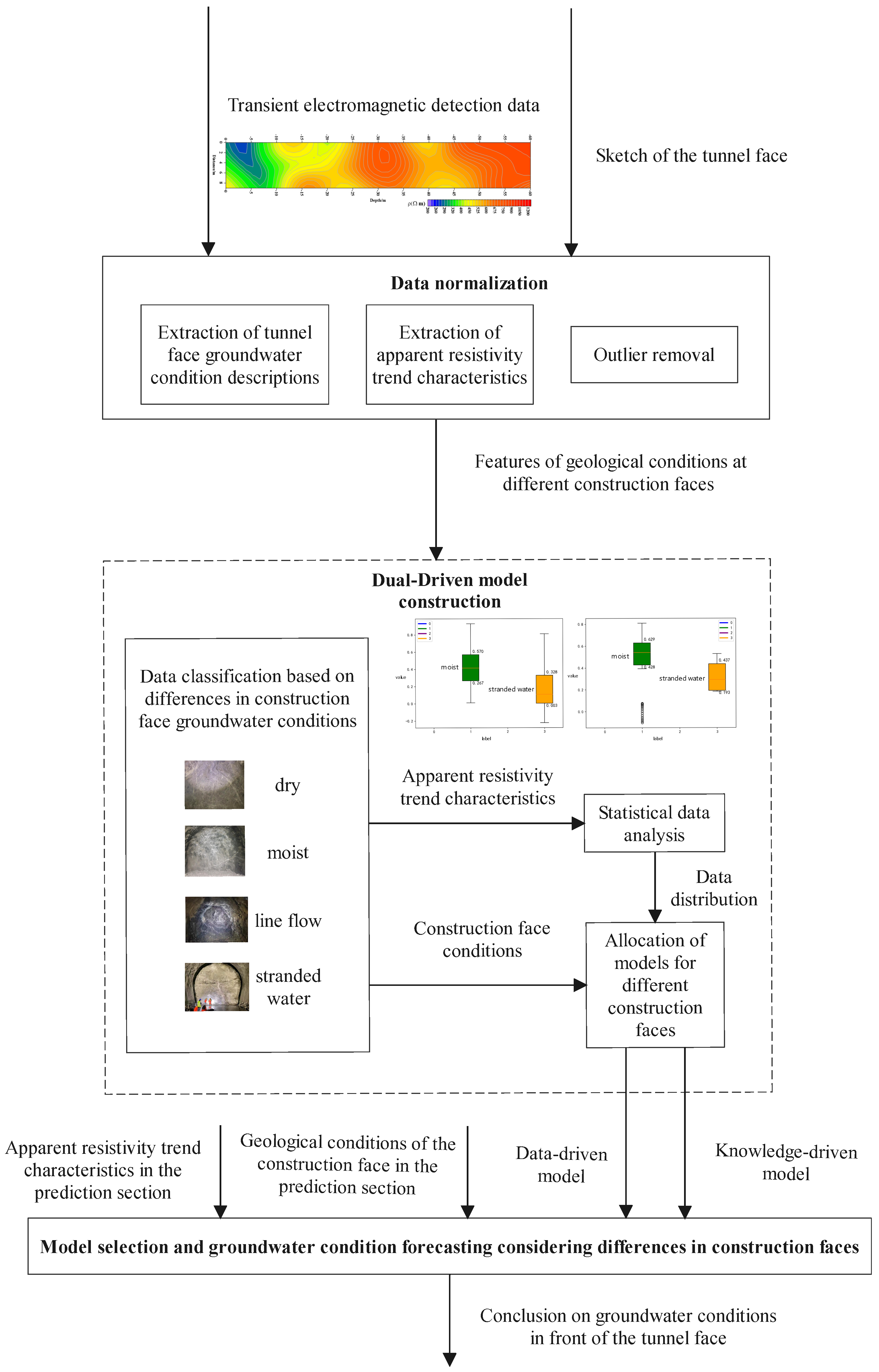
2. Analysis of the Groundwater Forecasting Process
3. An Intelligent Tunnel Groundwater Condition Forecasting Method
3.1. Groundwater Condition Description
3.2. Extraction of Trend Characteristics of Apparent Resistivity
3.3. Elimination of Apparent Resistivity Outliers
3.4. Transient Electromagnetic Knowledge-Driven Model
3.5. Transient Electromagnetic Data-Driven Model
4. Experiment and Results Analysis
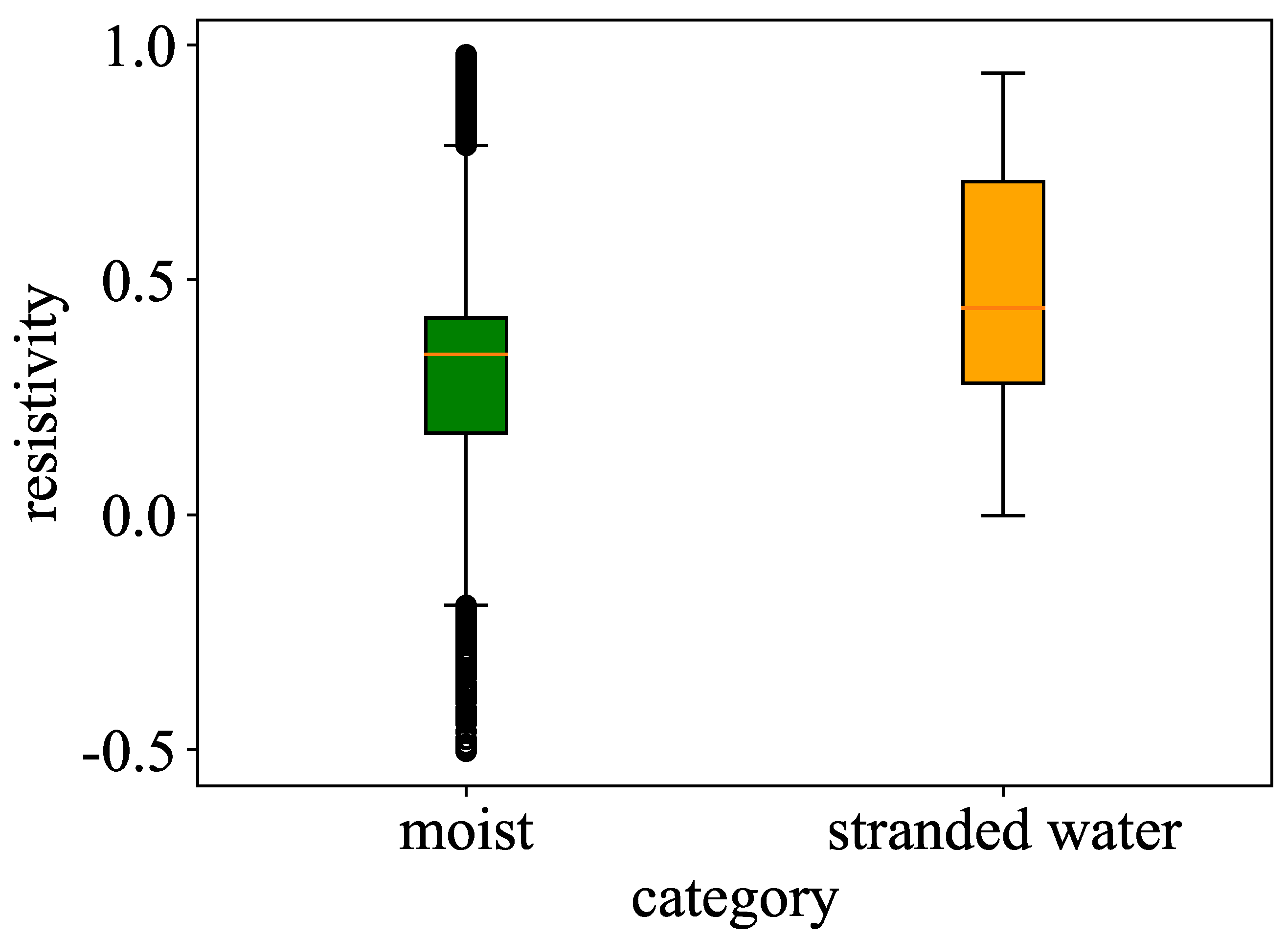
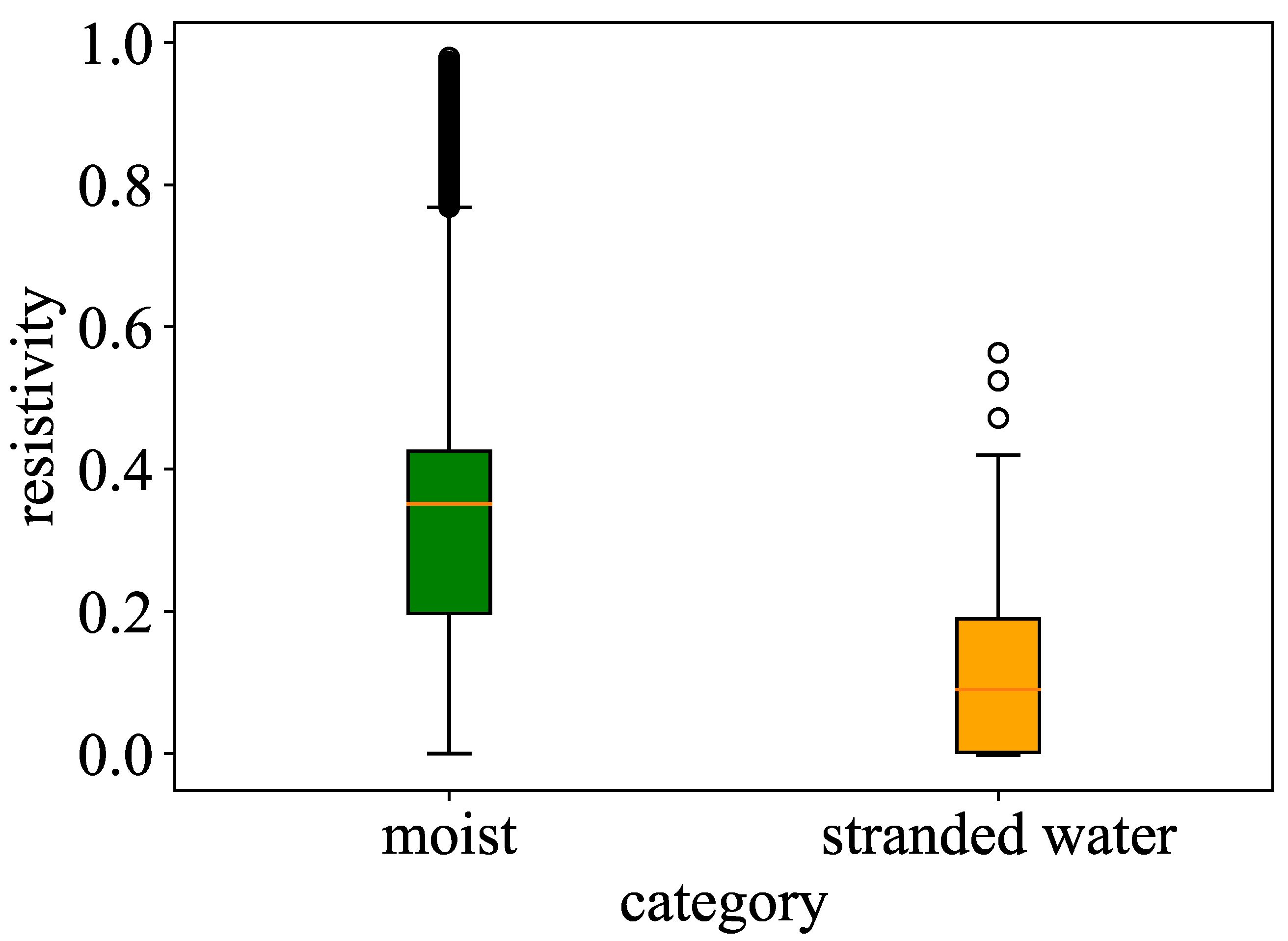
4.1. Apparent Resistivity Outlier Elimination Experiment
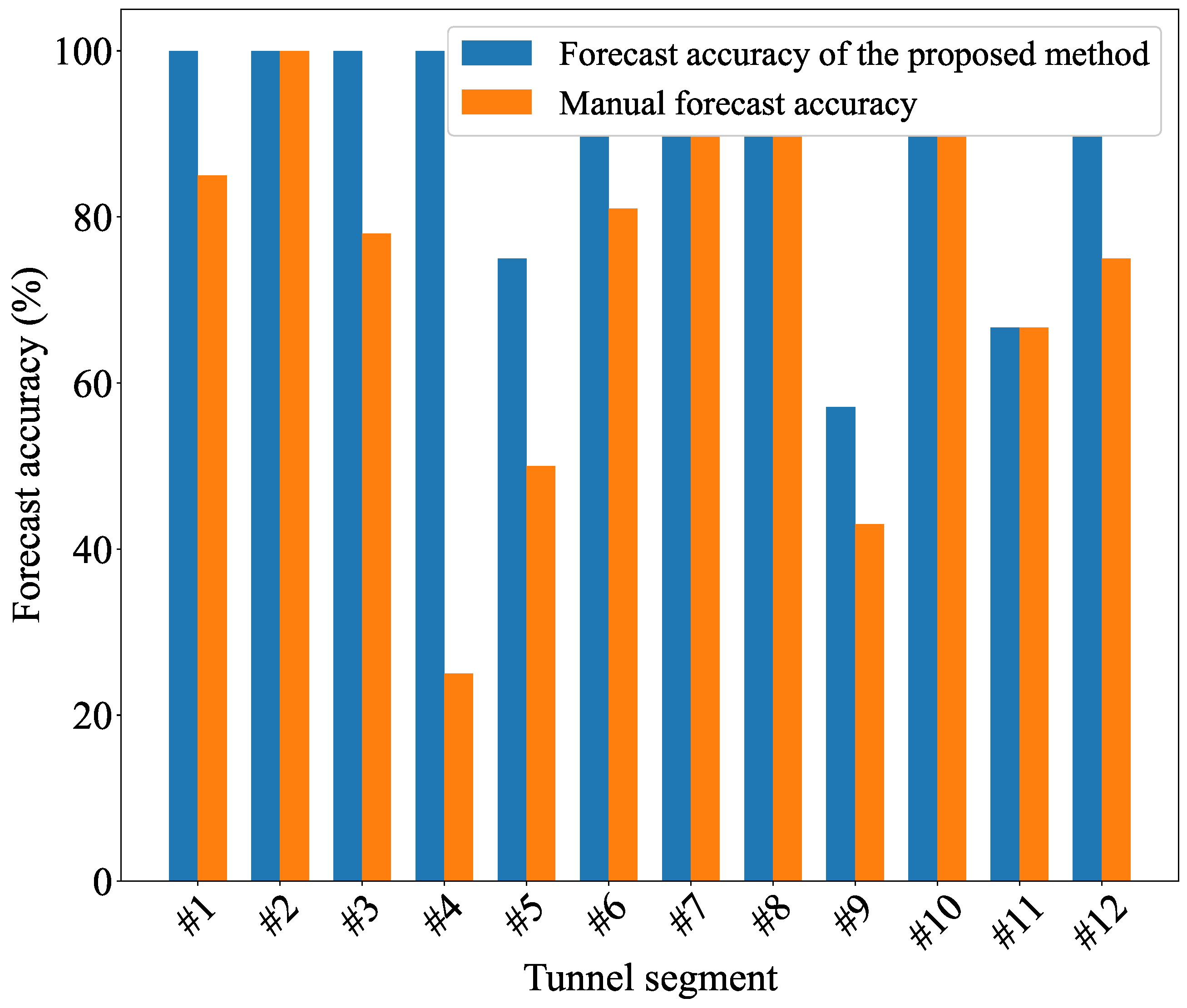
4.2. Groundwater Condition Forecast Result Comparison Experiment
4.3. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H.; Sun, J.C.; Liu, X.C.; Tu, P. Investigation and analysis on the setting of cross passage and auxiliary passage in extra-long highway tunnel. Procedia Eng. 2018, 211, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, Z.; Huang, X.; Lin, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Sun, H.; Pan, D. Classification, geological identification, hazard mode and typical case studies of hazard-causing structures for water and mud inrush in tunnels. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 2018, 37, 1041–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, Q. Study of mechanism of water inrush induced by hydraulic fracturing in karst tunnels. Rock Soil Mech. 2010, 31, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Jin, H.; Tu, W.; Zhou, Z. Study on the minimum safe thickness of water inrush prevention in karst tunnel under the coupling effect of blasting power and water pressure. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2024, 153, 105994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Song, Y.; Man, L.; Sun, Z. A new method for detecting karst and groundwater by 3D seismic wave: Case study of the karst tunnel in Zhangjihuai Railway, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2023, 82, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, G.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zou, J.; Tan, F.; Zhang, W. Collapse risk assessment of deep-buried tunnel during construction and its application. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 115, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Huang, M. Statistical analysis of major tunnel construction accidents in China from 2010 to 2020. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 124, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; He, P.; Li, L.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J. Gaussian process model of water inflow prediction in tunnel construction and its engineering applications. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 69, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Fu, H.; Chen, W.; Zhang, J.; Huang, H. Damage detection and quantitative analysis of shield tunnel structure. Autom. Constr. 2018, 94, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yin, K.; Cao, Y.; Ahmed, B. Application of time series analysis and PSO-SVM model in predicting the Bazimen landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Eng. Geol. 2016, 204, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, J.; Hung, S.L.; Chi, S.; Chern, J. Neural network forecast model in deep excavation. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2002, 16, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Liu, B. Intelligent information-based construction in tunnel engineering based on the GA and CCGPR coupled algorithm. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2019, 88, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Shi, S.; Yuan, Y. Multi-sources information fusion analysis of water inrush disaster in tunnels based on improved theory of evidence. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2021, 113, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, K.; Wang, K. Large scale three-dimensional seepage analysis model test and numerical simulation research on undersea tunnel. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2016, 59, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Ranjith, P.G.; Li, S. Criteria for assessment of internal stability of granular soil. Proc. Inst. Civ.-Eng.-Geotech. Eng. 2017, 170, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Rong, X.; Wang, M.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Z. Model test to investigate waterproof-resistant slab minimum safety thickness for water inrush geohazards. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2017, 62, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Rezania, M.; Yu, H.; Bai, H. Variations of hydraulic properties of granular sandstones during water inrush: Effect of small particle migration. Eng. Geol. 2017, 217, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Lou, F.; Yuan, R.; Shang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, K.; Bao, W. Rock mass characterization for shallow granite by integrating rock core indices and seismic velocity. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2017, 93, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, P.; Marmet, E.; Rejiba, F.; Cui, Y.J.; Tabbagh, A.; Charlery, Y. Correlations between geotechnical and electrical data: A case study at Garchy in France. J. Appl. Geophys. 2006, 60, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Jin, W.; Akhter, G. Site suitability for engineering-infrastructure (EI) development and groundwater exploitation using integrated geophysical approach in Guangdong, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, J.E.; Kuras, O.; Meldrum, P.I.; Ogilvy, R.D.; Hollands, J. Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic, hydrogeologic, and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site. Geophysics 2006, 71, B231–B239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marescot, L.; Monnet, R.; Chapellier, D. Resistivity and induced polarization surveys for slope instability studies in the Swiss Alps. Eng. Geol. 2008, 98, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y. Geophysical evaluation of geological model uncertainty for infrastructure design and groundwater assessments. Eng. Geol. 2022, 299, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhu, S. Comprehensive study on identification of water inrush sources from deep mining roadway. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 19608–19623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S. Advanced geological prediction technology of tunnel based on image recognition. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Segment(s) | Rock Type |
|---|---|
| 1–3 | Gneiss |
| 4 | Quartzite |
| 5–12 | Diorite |
| Method | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed | 0.9353 | 0.8763 | 0.9047 | 0.8886 |
| SVM | 0.9118 | 0.7820 | 0.7640 | 0.7660 |
| MLP | 0.9000 | 0.7036 | 0.7606 | 0.7226 |
| XGBoost | 0.9059 | 0.7334 | 0.7623 | 0.7424 |
| KNN | 0.8941 | 0.6975 | 0.7588 | 0.7202 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.; Fu, W.; Hu, X. A Knowledge–Data Dual-Driven Groundwater Condition Prediction Method for Tunnel Construction. Information 2025, 16, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080659
Huang Y, Fu W, Hu X. A Knowledge–Data Dual-Driven Groundwater Condition Prediction Method for Tunnel Construction. Information. 2025; 16(8):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080659
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yong, Wei Fu, and Xiewen Hu. 2025. "A Knowledge–Data Dual-Driven Groundwater Condition Prediction Method for Tunnel Construction" Information 16, no. 8: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080659
APA StyleHuang, Y., Fu, W., & Hu, X. (2025). A Knowledge–Data Dual-Driven Groundwater Condition Prediction Method for Tunnel Construction. Information, 16(8), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080659





