NeRF-RE: An Improved Neural Radiance Field Model Based on Object Removal and Efficient Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
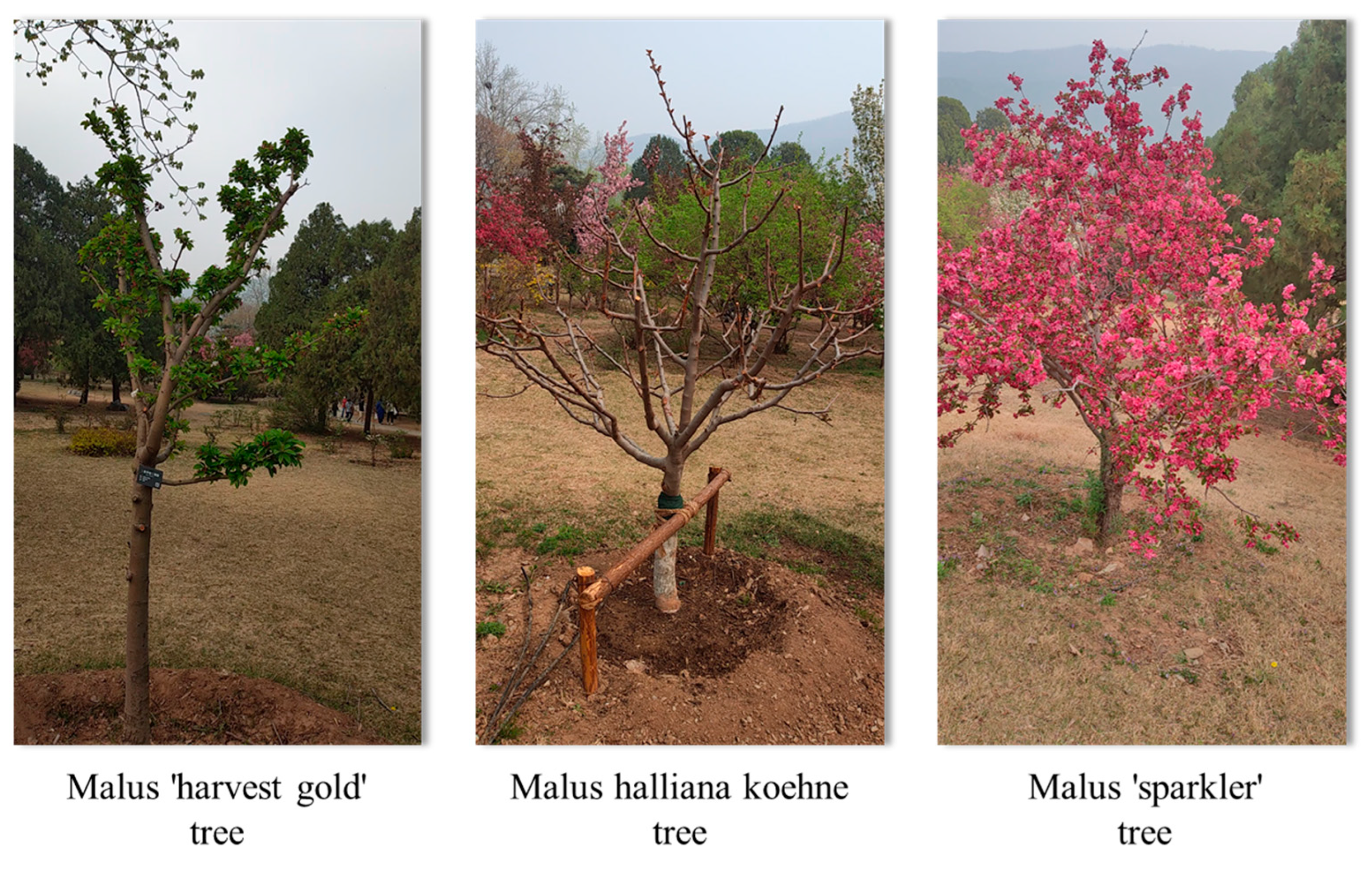
- Comparing NeRF-RE’s robustness with traditional methods in urban begonia reconstruction.
- (2)
- Analyzing ornamental begonia variations in unbounded scene reconstruction.
- (3)
- Quantifying RGB image quantity effects on reconstruction quality.
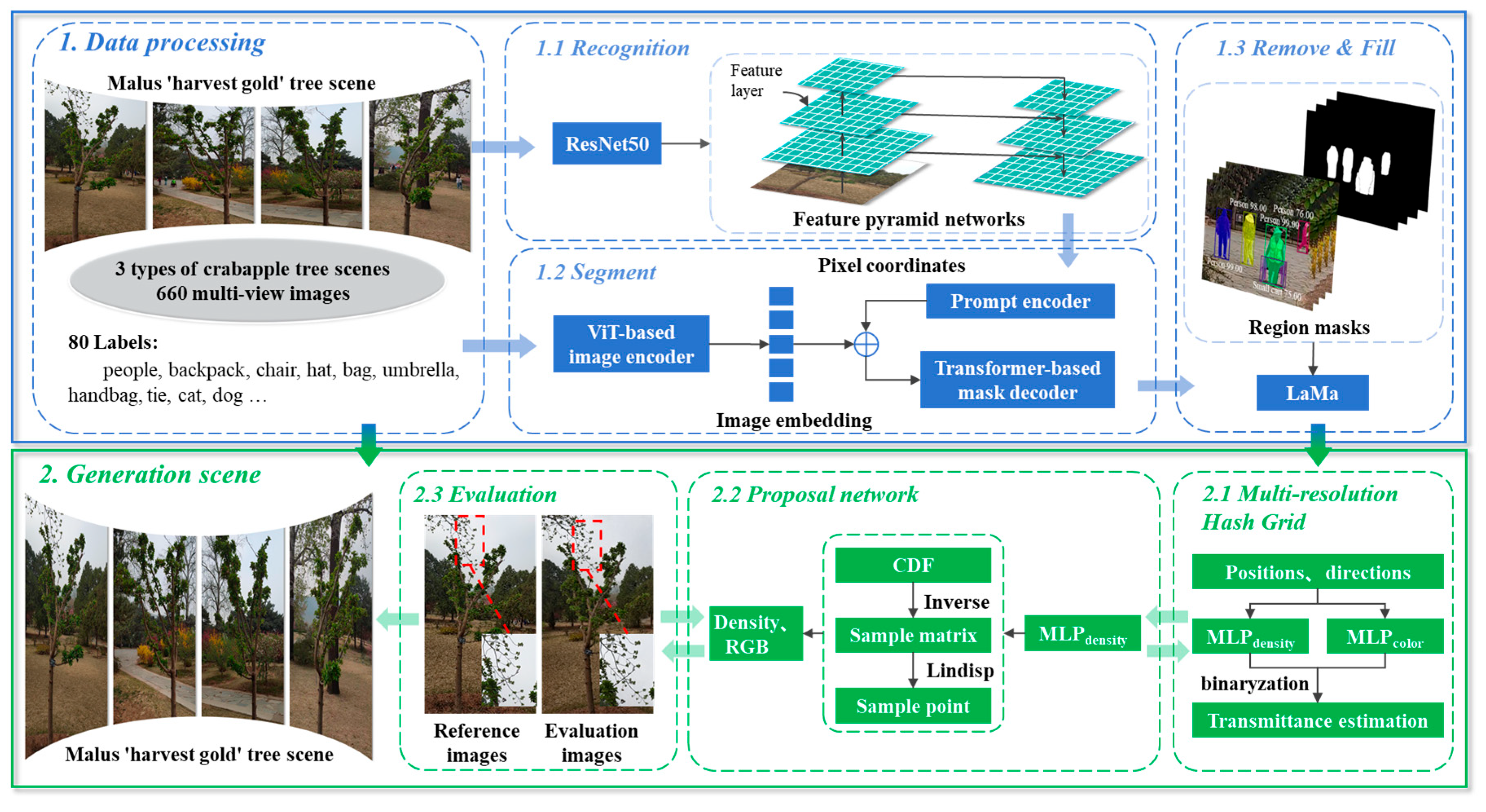
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Neural Radiance Fields Model
2.2. The NeRF-RE Model

- (1)
- Instant-NGP’s occupancy grid rapidly identifies empty areas via multi-resolution hashing of ray origin/direction data, skipping non-essential regions through binary density assessment;
- (2)
- Mip-NeRF 360’s proposal network refines transmittance estimates via importance sampling. Using probability density functions (PDFs), it samples critical regions via inverse transform sampling, optimizing color/density predictions along rays.
2.3. Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Performance Evaluation of Scene Reconstruction and Rendering
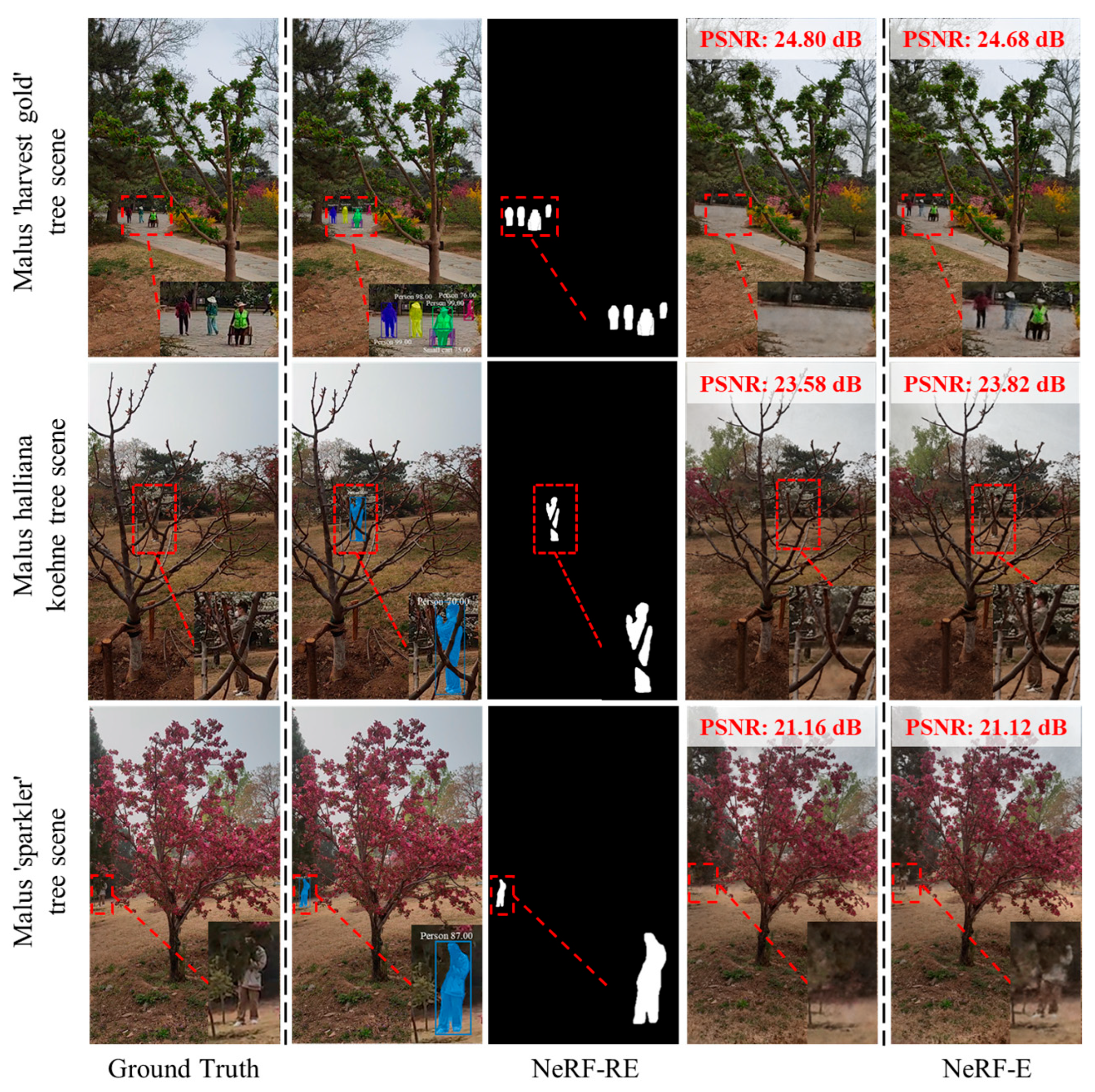
3.2. Recognition and Segmentation Results of Different Conditions
3.3. Rendering Results for Different Scenes
4. Discussion
4.1. The Number of Images Exerts a Minor Impact on the Performance of the NeRF-RE Model When Rendering Boundless Scenes
4.2. Significant Impact of Tree Geometric Complexity on Boundless Scenes Reconstruction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, S.H.M.; Qiu, L.; Esposito, G.; Mai, K.P. Vertical greenery buffers against stress: Evidence from psychophysiological responses in virtual reality. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2021, 213, 104127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, O.; Korhonen, A.; Pöyry, E.; Hauru, K.; Holopainen, J.; Parvinen, P. Restoration in a virtual reality forest environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2020, 107, 106295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanja-Dijkstra, K.; Pahl, S.; White, M.P.; Auvray, M.; Stone, R.J.; Andrade, J.; Mills, I.; Moles, D.R. The soothing sea: A virtual coastal walk can reduce experienced and recollected pain. Environ. Behav. 2018, 50, 599–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yin, L.; Tang, Y.; Miao, W.; Liu, S.; Yang, B. The algorithm of stereo vision and shape from shading based on endoscope imaging. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2022, 76, 103658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kan, J. CGAN-Based Forest Scene 3D Reconstruction from a Single Image. Forests 2024, 15, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, J.; Benes, B.; Deussen, O.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H. TreePartNet: Neural decomposition of point clouds for 3D tree reconstruction. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2021, 40, 232:1–232:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Chai, G.; Han, X.; Lei, L.; Wang, G.; Jia, X.; Zhang, X. SA-Pmnet: Utilizing Close-Range Photogrammetry Combined with Image Enhancement and Self-Attention Mechanisms for 3D Reconstruction of Forests. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, X.; Xu, S. Individual Tree Reconstruction Based on Circular Truncated Cones From Portable LiDAR Scanner Data. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2022, 20, 3229065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wu, C.; Qu, D.; Xu, F.; Sun, H.; Song, J. Accurate and efficient stereo matching by log-angle and pyramid-tree. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Ying, W.; Pan, Y.; Kang, H.; Chen, C. High-fidelity 3D reconstruction of plants using Neural Radiance Fields. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Ni, X.; Dong, F.; Tang, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y. Neural radiance fields for multi-scale constraint-free 3D reconstruction and rendering in orchard scenes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, S.; Miura, K.; Ito, K.; Aoki, T. Neural radiance field-inspired depth map refinement for accurate multi-view stereo. J. Imaging 2024, 10, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, V.; Billi, D.; Caroti, G.; Piemonte, A.; De Luca, L.; Véron, P. Comparative assessment of neural radiance fields and photogrammetry in digital heritage: Impact of varying image conditions on 3D reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Tancik, M.; Barron, J.T.; Ramamoorthi, R.; Ng, R. Nerf: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Commun. ACM 2021, 65, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, J. Point-Based Neural Scene Rendering for Street Views. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 2740–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hedman, P. Mip-nerf 360: Unbounded anti-aliased neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5470–5479. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, T.; Evans, A.; Schied, C.; Keller, A. Instant neural graphics primitives with a multiresolution hash encoding. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2022, 41, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weder, S.; Garcia-Hernando, G.; Monszpart, A.; Pollefeys, M.; Brostow, G.J.; Firman, M.; Vicente, S. Removing objects from neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16528–16538. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov, A.; Mintun, E.; Ravi, N.; Mao, H.; Rolland, C.; Gustafson, L.; Xiao, T.; Whitehead, S.; Berg, A.C.; Lo, W.-Y.; et al. Segment anything. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 4015–4026. [Google Scholar]
- Suvorov, R.; Logacheva, E.; Mashikhin, A.; Remizova, A.; Ashukha, A.; Silvestrov, A.; Kong, N.; Goka, H.; Park, K.P.; Lempitsky, V. Resolution-robust large mask inpainting with fourier convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 2149–2159. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Reiser, C.; Szeliski, R.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.; Mildenhall, B.; Geiger, A.; Barron, J.T.; Hedman, P. Merf: Memory-efficient radiance fields for real-time view synthesis in unbounded scenes. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2023, 42, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remondino, F.; Karami, A.; Yan, Z.; Mazzacca, G.; Rigon, S.; Qin, R. A critical analysis of nerf-based 3d reconstruction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Deng, B.; Debevec, P.; Freeman, W.T.; Barron, J.T. Nerfactor: Neural factorization of shape and reflectance under an unknown illumination. ACM Trans. Graph. TOG 2021, 40, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, H.; Muttukuru, S.; Upadhyay, R.; Chari, P.; Kadambi, A. Sparsegs: Real-time 360° sparse view synthesis using gaussian splatting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.00206. [Google Scholar]
- Kerr, J.; Kim, C.M.; Goldberg, K.; Kanazawa, A.; Tancik, M. Lerf: Language embedded radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 19729–19739. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Verbin, D.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Hedman, P. Zip-nerf: Anti-aliased grid-based neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 19697–19705. [Google Scholar]
- Barron, J.T.; Mildenhall, B.; Tancik, M.; Hedman, P.; Martin-Brualla, R.; Srinivasan, P.P. Mip-nerf: A multiscale representation for anti-aliasing neural radiance fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 5855–5864. [Google Scholar]
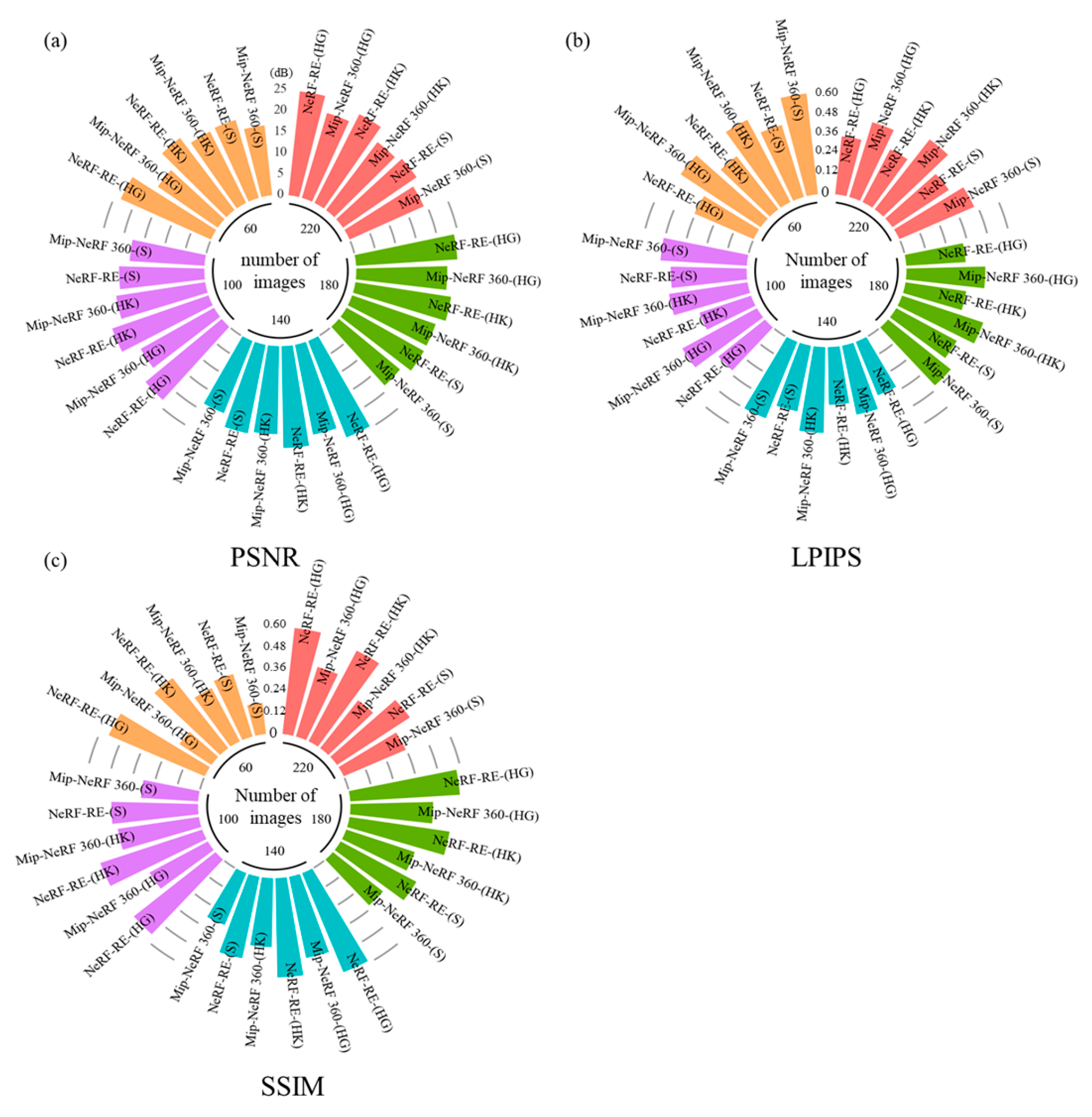

| Scene | Model | Evaluation Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSNR (dB)↑ | LPIPS↓ | SSIM↑ | Time (h) | ||
| Malus ‘harvest gold’ tree scene | NeRF-E | 24.68 | 0.34 | 0.74 | 0.51 |
| NeRF-RE | 24.80 | 0.34 | 0.74 | 0.51 | |
| Mip-NeRF 360 | 21.03 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 10.91 | |
| Malus halliana koehne tree scene | NeRF-E | 23.82 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.56 |
| NeRF-RE | 23.58 | 0.35 | 0.70 | 0.56 | |
| Mip-NeRF 360 | 20.23 | 0.51 | 0.41 | 10.92 | |
| Malus ‘sparkler’ tree scene | NeRF-E | 21.12 | 0.39 | 0.58 | 0.59 |
| NeRF-RE | 21.16 | 0.39 | 0.58 | 0.59 | |
| Mip-NeRF 360 | 19.27 | 0.46 | 0.45 | 10.93 | |
| Model | Recognition and Segment | Remove and Fill | MLP | Proposal Network | Multi-Resolution Hash Grid |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NeRF-Ag [11] | √ | √ | |||
| DS-NERF [12] | √ | ||||
| NeRF [13,14] | √ | ||||
| Mip-NeRF 360 [16] | √ | √ | |||
| NeRF-E | √ | √ | √ | √ | |
| NeRF-RE | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ |
| Scenes | Types | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Malus ‘harvest gold’ tree scene | Multiple targets + occlusion | People: 76~99% Small cart: 75% |
| Malus halliana koehne tree scene | Single target + occlusion | People: 70% |
| Malus ‘sparkler’ tree scene | Single target + local dense occlusion | People: 87% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Huai, Y.; Meng, Q.; Dong, S. NeRF-RE: An Improved Neural Radiance Field Model Based on Object Removal and Efficient Reconstruction. Information 2025, 16, 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080654
Li Z, Huai Y, Meng Q, Dong S. NeRF-RE: An Improved Neural Radiance Field Model Based on Object Removal and Efficient Reconstruction. Information. 2025; 16(8):654. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080654
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ziyang, Yongjian Huai, Qingkuo Meng, and Shiquan Dong. 2025. "NeRF-RE: An Improved Neural Radiance Field Model Based on Object Removal and Efficient Reconstruction" Information 16, no. 8: 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080654
APA StyleLi, Z., Huai, Y., Meng, Q., & Dong, S. (2025). NeRF-RE: An Improved Neural Radiance Field Model Based on Object Removal and Efficient Reconstruction. Information, 16(8), 654. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16080654






