DIP-UP: Deep Image Prior for Unwrapping Phase
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Theory
2.2. Training Data Simulation
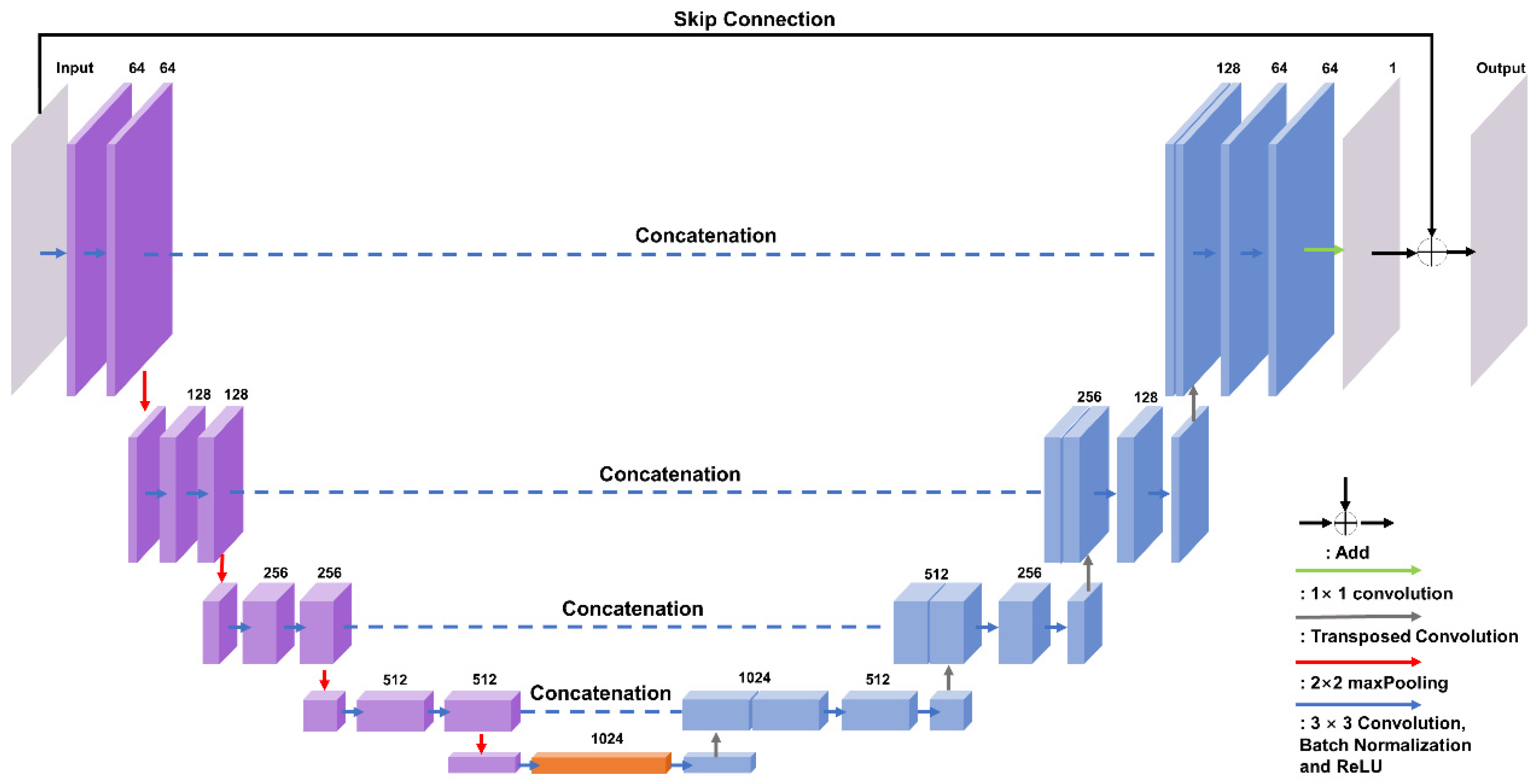
2.3. Network Framework
- (a)
- Voxel-wised cross-entropy loss function. Cross-entropy loss is used to classify the predicted wrapping counts:where N refers to the size of the image and Y and indicate the ground truth and predicted wrapping counts at the voxel coordination . The SoftMax classifier is connected as the output layer.
- (b)
- L1-norm loss function: The L1-norm between the predicted and the original unwrapped phase is given by the following:where and represent for the label and the reconstructed unwrapped phase (calculated from Equation (2)).
- (c)
- Gradient residue loss function. This is a redesigned version of the PhaseNet 2.0 loss function [30], which was extended to 3D data. In contrast to 2D inference data, 3D brain volumes require more specific and accurate tuning of wrapping boundary detection. As a result, we modified the PhaseNet 2.0 equation by calculating the sum of the squared image gradients across three dimensions. The modification is given bywhere () refers to the ‘wrapping-boundary masked’ gradient operation of the image via three dimensions. We modified the previous gradient operation and masked the gradient map using a threshold of 1.0π, which erased the border of wrapping while maintaining the brain tissue.
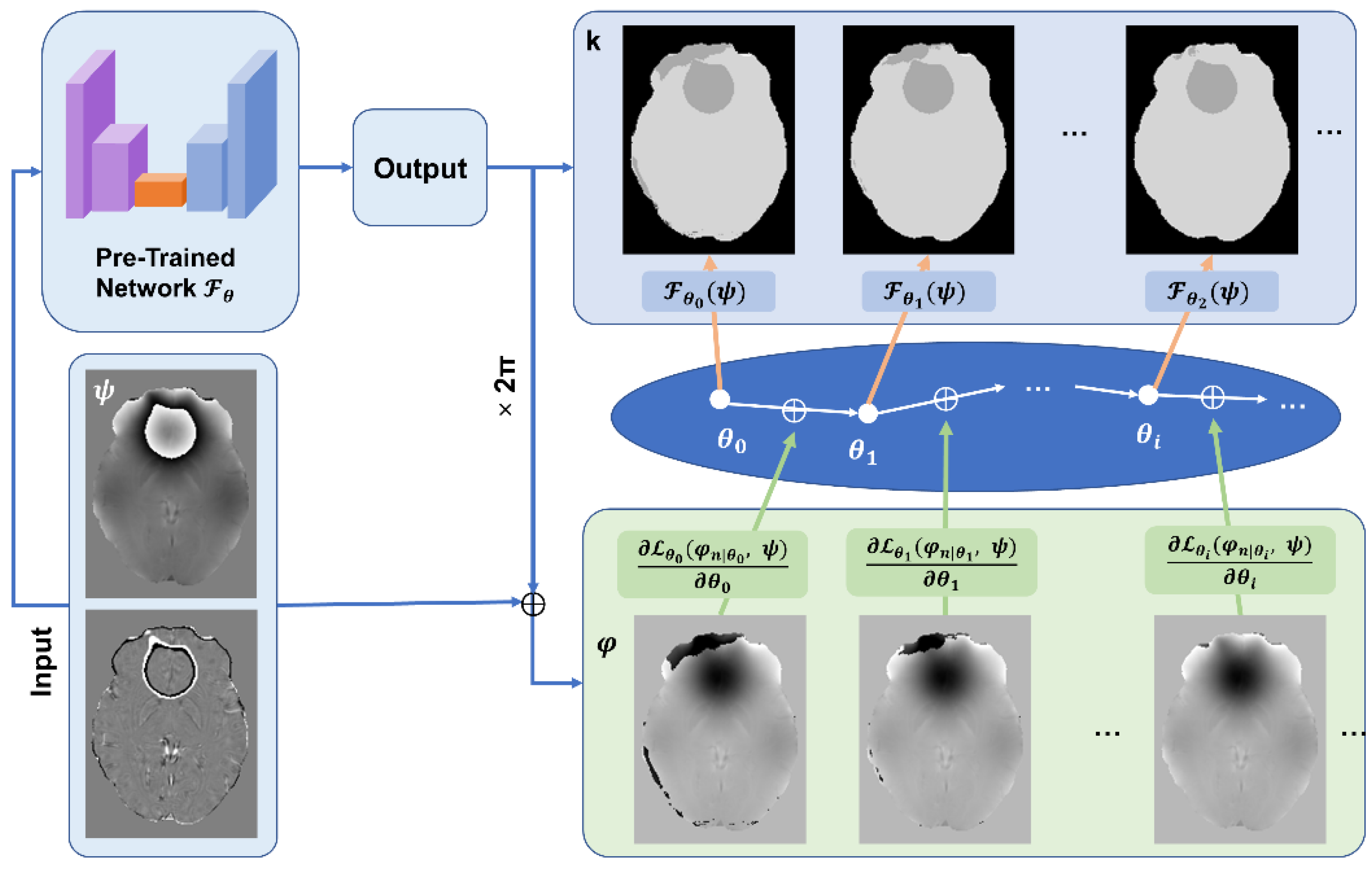
2.4. Deep Image Prior
- (1)
- The Laplacian loss: This loss function was established based on the physical model [17], such that the Laplacian of the unwrapped phase φ can be calculated from the raw wrapped phase ψ:where the Laplacian of unwrapped phase could be calculated through Equation (6), given that
- (2)
- Total Variation (TV) loss: To provide another regularization term to the reconstructed unwrapped phase map. TV loss is effective to minimize misclassified wrapping boundaries and encourage smooth phase reconstructions. Mathematically, TV loss is defined as the sum of absolute differences between adjacent pixel values in three dimensions across the image. In our quest to improve the Total Variation (TV) loss, we have incorporated a novel approach that leverages a brain tissue mask using BET. The tissue mask was then eroded in one voxel. Given an unwrapped phase φ, the TV loss is calculated aswhere () refers to the gradient operation of the image via x/y/z dimensions. The total loss of DIP is a sum of the two loss functions.
2.5. Simulated and In Vivo Experiments
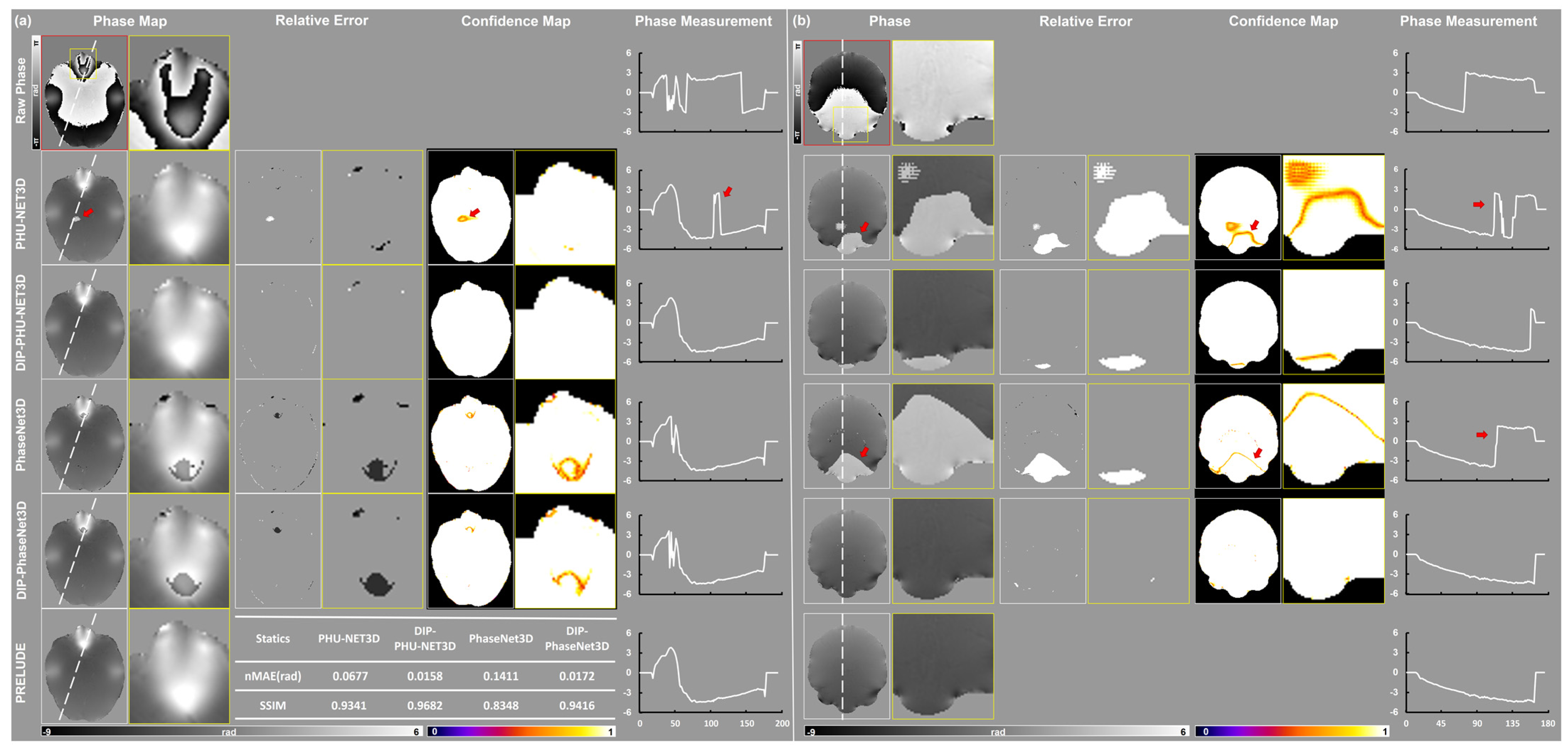
3. Results
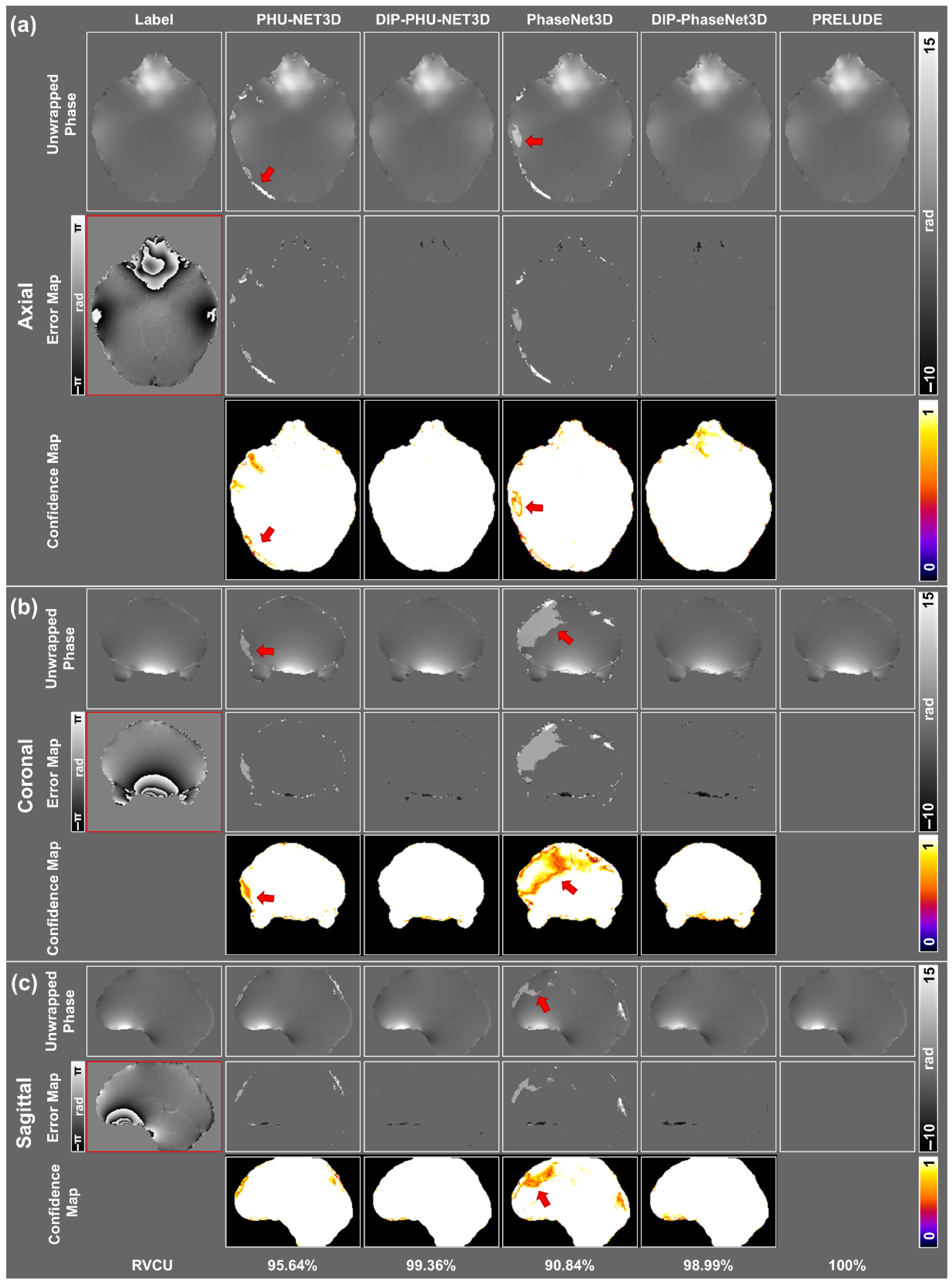
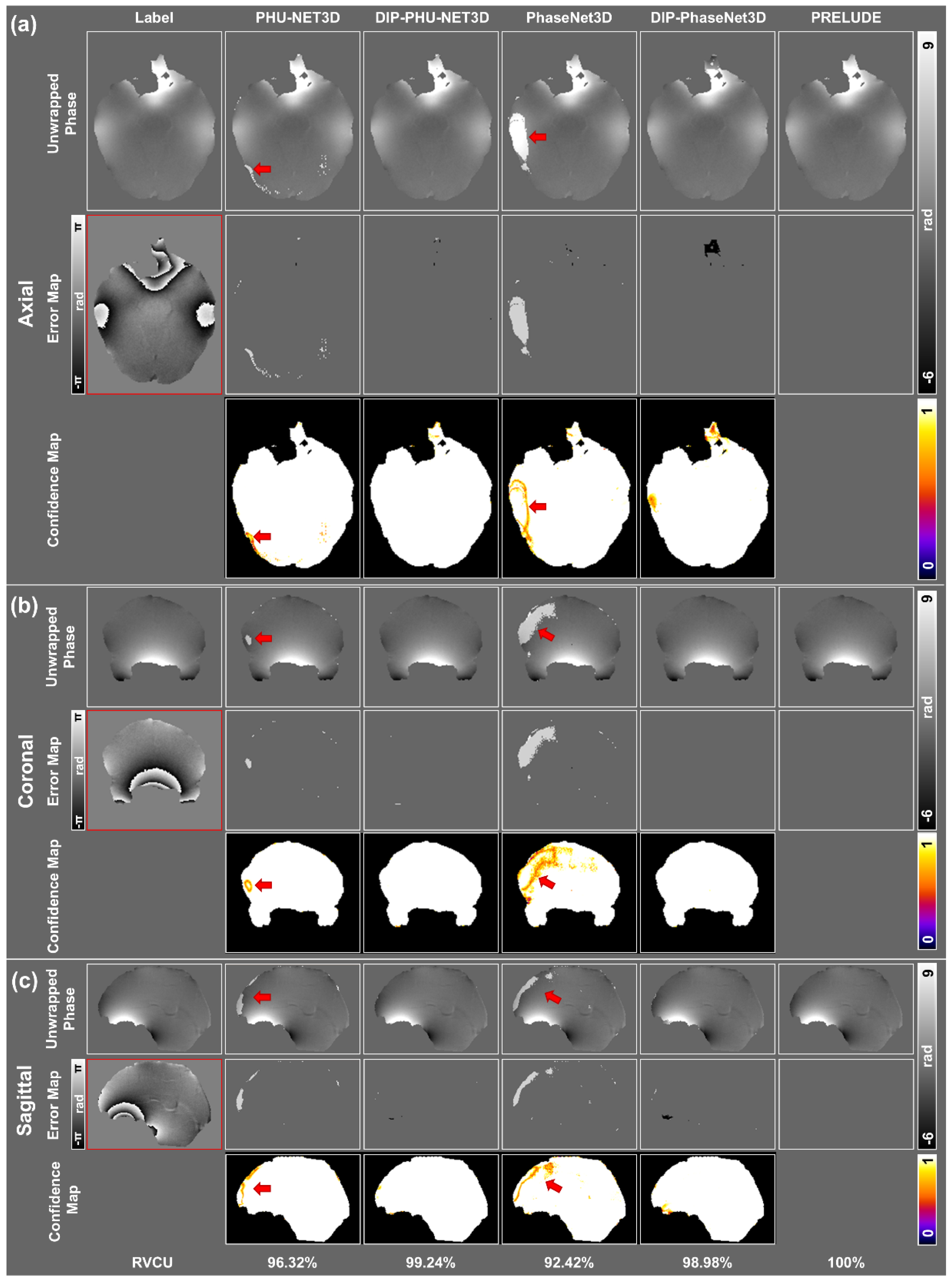
3.1. Simulation Results
3.2. In Vivo Experiments
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Image |
| GRE | Gradient Reverse Echo |
| DIP | Deep Image Prior |
| UP | Unwrap Phase |
| TE | Echo Time |
| QSM | Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping |
| BP | Best-Path |
| CE | Cross-Entropy |
| TV | Total Variation |
| BET | Brain Extraction Tool |
| RVCU | Ratio of Voxels that Correctly Unwrapped |
References
- Chen, Z.; Zhai, X.; Chen, Z. Proof of linear MRI phase imaging from an internal fieldmap. NMR Biomed. 2022, 35, e4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, F.; Cheng, J.Y.; Lustig, M. General phase regularized reconstruction using phase cycling. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 80, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.D.; Bredies, K.; Khabipova, D.; Dymerska, B.; Marques, J.P.; Schweser, F. An illustrated comparison of processing methods for MR phase imaging and QSM: Combining array coil signals and phase unwrapping. NMR Biomed. 2017, 30, e3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, K.A. One-dimensional Hilbert transform processing for N-dimensional phase unwrapping. WSEAS Trans. Circuits Syst. 2006, 5, 783–789. [Google Scholar]
- Barbieri, M.; Chaudhari, A.S.; Moran, C.J.; Gold, G.E.; Hargreaves, B.A.; Kogan, F. A method for measuring B0 field inhomogeneity using quantitative double-echo in steady-state. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 89, 577–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechler, E.; Stabinska, J.; Wittsack, H.J. Analysis of different phase unwrapping methods to optimize quantitative susceptibility mapping in the abdomen. Magn. Reson. Med. 2019, 82, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanspach, J.; Bollmann, S.; Grigo, J.; Karius, A.; Uder, M.; Laun, F.B. Deep learning—Based quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM) in the presence of fat using synthetically generated multi-echo phase training data. Magn. Reson. Med. 2022, 88, 1548–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, S.; Xiang, Q.-S.; An, L. Understanding phase maps in MRI: A new cutline phase unwrapping method. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2002, 21, 966–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S.; Sun, H. BFRnet: A deep learning-based MR background field removal method for QSM of the brain containing significant pathological susceptibility sources. Z. Med. Phys. 2022, 33, 578–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wilman, A.H. Background field removal using spherical mean value filtering and Tikhonov regularization. Magn. Reson. Med. 2014, 71, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Fazlollahi, A.; Nestor, P.J.; Vegh, V.; Nasrallah, F.; Winter, C. Instant tissue field and magnetic susceptibility mapping from MRI raw phase using Laplacian enhanced deep neural networks. NeuroImage 2022, 259, 119410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortier, V.; Levesque, I.R. Phase processing for quantitative susceptibility mapping of regions with large susceptibility and lack of signal. Magn. Reson. Med. 2018, 79, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xu, M.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, L.; Liu, L.; Han, S.; Chen, W. New 3D phase-unwrapping method based on voxel clustering and local polynomial modeling: Application to quantitative susceptibility mapping. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2023, 13, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, K.; Zaitsev, M.; Bao, S. Reliable two-dimensional phase unwrapping method using region growing and local linear estimation. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 62, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, F.; Fuentes, D.; Weinberg, J.S.; Hazle, J.D.; Stafford, R.J. Robust phase unwrapping for MR temperature imaging using a magnitude-sorted list, multi-clustering algorithm. Magn. Reson. Med. 2015, 73, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loecher, M.; Schrauben, E.; Johnson, K.M.; Wieben, O. Phase unwrapping in 4D MR flow with a 4D single-step laplacian algorithm. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, M.A.; Zhu, Y. Fast phase unwrapping algorithm for interferometric applications. Opt. Lett. 2003, 28, 1194–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkinson, M. Fast, automated, N-dimensional phase-unwrapping algorithm. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2003, 49, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsa, A.; Shmueli, K. SEGUE: A speedy region-growing algorithm for unwrapping estimated phase. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2018, 38, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahman, H.S.; Gdeisat, M.A.; Burton, D.R.; Lalor, M.J.; Lilley, F.; Moore, C.J. Fast and robust three-dimensional best path phase unwrapping algorithm. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6623–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Rahman, H.; Arevalillo-Herráez, M.; Gdeisat, M.; Burton, D.; Lalor, M.; Lilley, F.; Moore, C.; Sheltraw, D. Robust three-dimensional best-path phase-unwrapping algorithm that avoids singularity loops. Appl. Opt. 2009, 48, 4582–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Véron, A.S.; Lemaitre, C.; Gautier, C.; Lacroix, V.; Sagot, M.-F. Close 3D proximity of evolutionary breakpoints argues for the notion of spatial synteny. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Kemao, Q.; Di, J.; Zhao, J. Deep learning spatial phase unwrapping: A comparative review. Adv. Photonics Nexus 2022, 1, 014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Mei, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, G. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping by a high-resolution deep learning network. Measurement 2022, 200, 111566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, S.; Zhao, Z.; Dixit, K.; Zhou, X.; Hou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C. Rapid and robust two-dimensional phase unwrapping via deep learning. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 23173–23185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Kemao, Q.; Di, J.; Zhao, J. One-step robust deep learning phase unwrapping. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 15100–15115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhu, X.; Moffat, B.A.; Glarin, R.; Wilman, A.H.; Pike, G.B.; Crozier, S.; Liu, F. xQSM: Quantitative susceptibility mapping with octave convolutional and noise-regularized neural networks. NMR Biomed. 2021, 34, e4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F.; Crozier, S.; Sun, H. Deep grey matter quantitative susceptibility mapping from small spatial coverages using deep learning. Z. Für Med. Phys. 2022, 32, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoorthi, G.; Gorthi, S.; Gorthi, R.K.S.S. PhaseNet: A deep convolutional neural network for two-dimensional phase unwrapping. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2018, 26, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spoorthi, G.; Gorthi, R.K.S.S.; Gorthi, S. PhaseNet 2.0: Phase unwrapping of noisy data based on deep learning approach. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 4862–4872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yu, H.; Pascazio, V.; Xing, M. PU-GAN: A one-step 2-D InSAR phase unwrapping based on conditional generative adversarial network. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5221510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Cheng, C.; Peng, H.; Liang, D.; Liu, X.; Zheng, H.; Zou, C. The PHU-NET: A robust phase unwrapping method for MRI based on deep learning. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 86, 3321–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Quan, Y.; Ji, H. Unsupervised deep unrolling networks for phase unwrapping. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.; Chen, Q.; Feng, S.; Tao, T.; Huang, L.; Trusiak, M.; Asund, A.; Zuo, C. Temporal phase unwrapping using deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroujeni, S.P.H.; Razi, A. Ic-gan: An improved conditional generative adversarial network for rgb-to-ir image translation with applications to forest fire monitoring. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 121962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Deep image prior. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fazlollahi, A.; Nestor, P.; Liu, F.; Sun, H. Quantitative susceptibility mapping through model-based deep image prior (MoDIP). NeuroImage 2024, 291, 120583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pham, T.-A.; Brandenberg, N.; Lütolf, M.P.; Ma, J.; Unser, M. Robust phase unwrapping via deep image prior for quantitative phase imaging. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 7025–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.M. Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2002, 17, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Spincemaille, P.; De Rochefort, L.; Kressler, B.; Wang, Y. Calculation of susceptibility through multiple orientation sampling (COSMOS): A method for conditioning the inverse problem from measured magnetic field map to susceptibility source image in MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. Off. J. Int. Soc. Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Khalidov, I.; de Rochefort, L.; Spincemaille, P.; Liu, J.; Tsiouris, A.J.; Wang, Y. A novel background field removal method for MRI using projection onto dipole fields. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.K.; Sudarshan, V.P.; Gubbi, J.; Pal, A. Structural-Mr Informed QSM Reconstruction Using Deep Image Prior. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Kolkata, India, 28–31 March 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, X.; Gao, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Jiang, W.; Liu, F.; Sun, H. DIP-UP: Deep Image Prior for Unwrapping Phase. Information 2025, 16, 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070592
Zhu X, Gao Y, Xiong Z, Jiang W, Liu F, Sun H. DIP-UP: Deep Image Prior for Unwrapping Phase. Information. 2025; 16(7):592. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070592
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Xuanyu, Yang Gao, Zhuang Xiong, Wei Jiang, Feng Liu, and Hongfu Sun. 2025. "DIP-UP: Deep Image Prior for Unwrapping Phase" Information 16, no. 7: 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070592
APA StyleZhu, X., Gao, Y., Xiong, Z., Jiang, W., Liu, F., & Sun, H. (2025). DIP-UP: Deep Image Prior for Unwrapping Phase. Information, 16(7), 592. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070592







