Fusion-Optimized Multimodal Entity Alignment with Textual Descriptions
Abstract
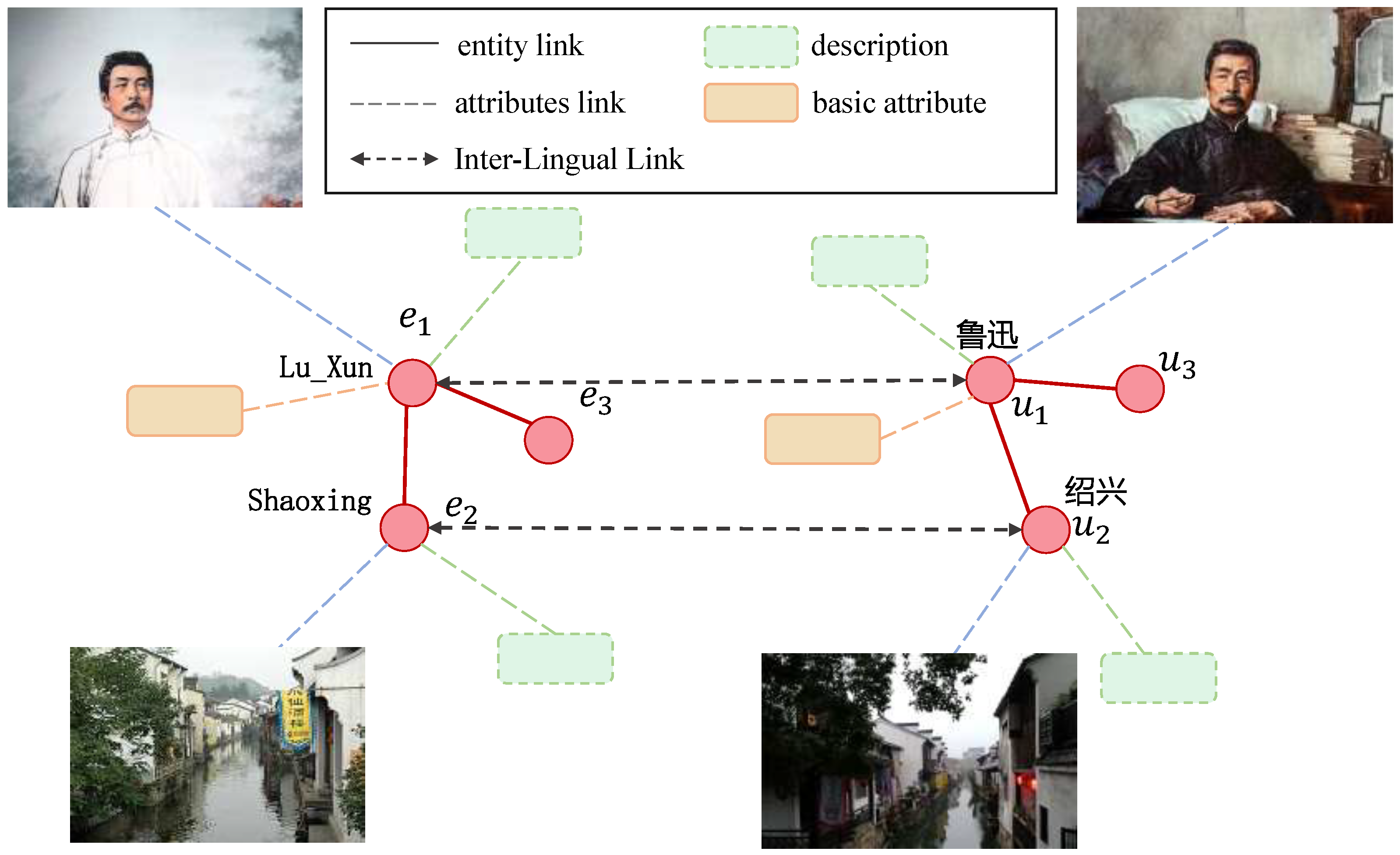
1. Introduction
- The FMEA-TD method focuses on leveraging the rich semantic information embedded in the textual descriptions of entities, including their attributes, relationships, and contexts. This textual information often provides valuable contextual support for other modalities, such as visual and speech data, helping the model to more accurately understand and represent the entity’s overall semantic characteristics.
- For information fusion in the multimodal knowledge graph, we employ a confidence predictor to calculate the confidence level of each modality. The collaborative confidence level across modalities not only reflects the quality of information from each individual modality but also considers the influence of all modalities, dynamically adjusting their weights to enhance the model’s robustness and generalization capabilities.
- FMEA-TD established a joint optimization of loss function (JOF), which improved the Inter-modal Alignment Loss (IAL). It not only considers the correlation between different modalities but also makes full use of the correlation between the rich semantic features contained in the entity textual description information and other modalities. By optimizing the loss function, FMEA-TD can effectively learn the deep association between the entity textual description information and other modal information, which helps the model to more accurately understand and represent the overall semantic features of the entity.
2. Problem Definition
3. Related Work
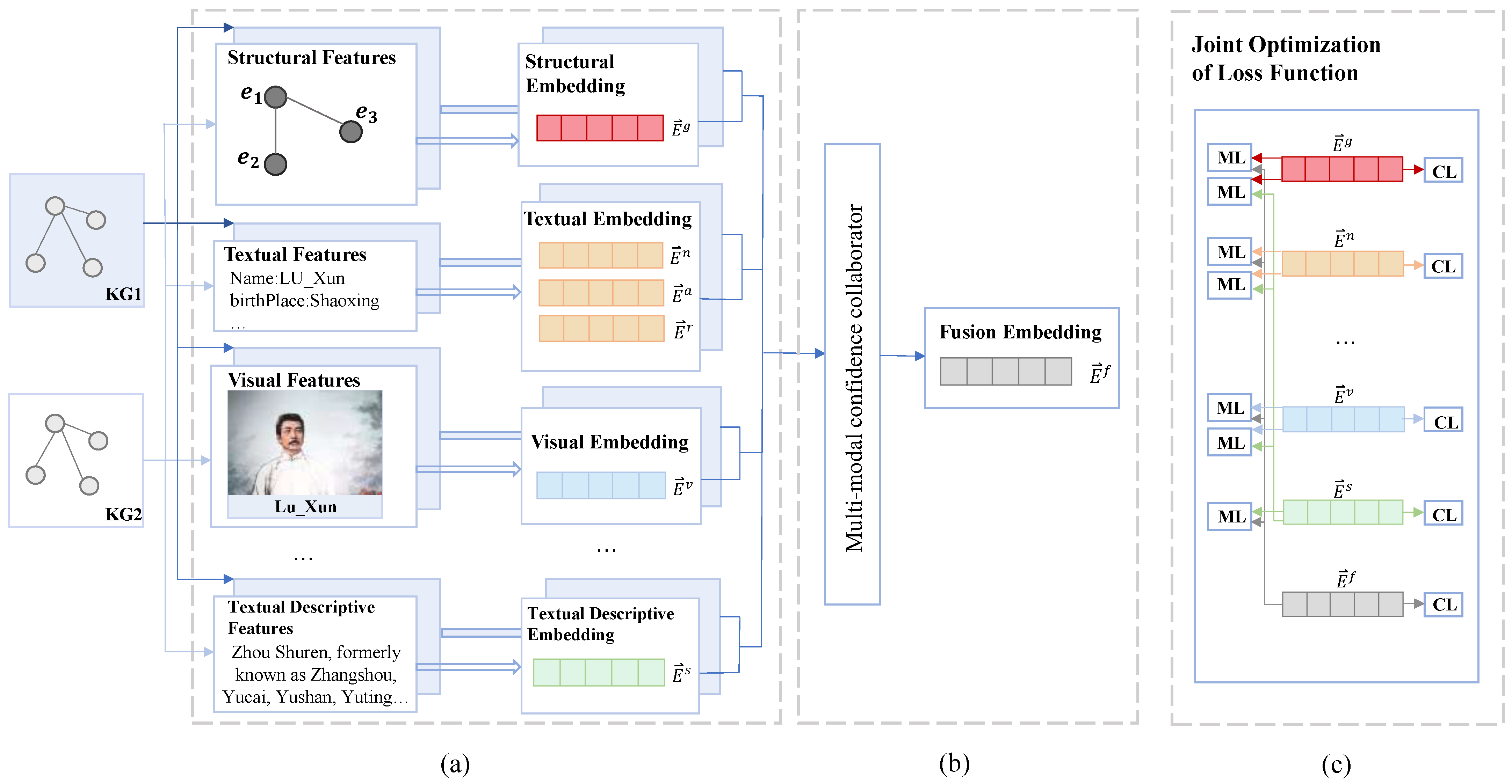
4. Methodology
4.1. Knowledge Embedding
4.1.1. Graph Structure Embedding
4.1.2. Text Embedding
4.1.3. Visual Embedding
4.1.4. Textual Description Embedding
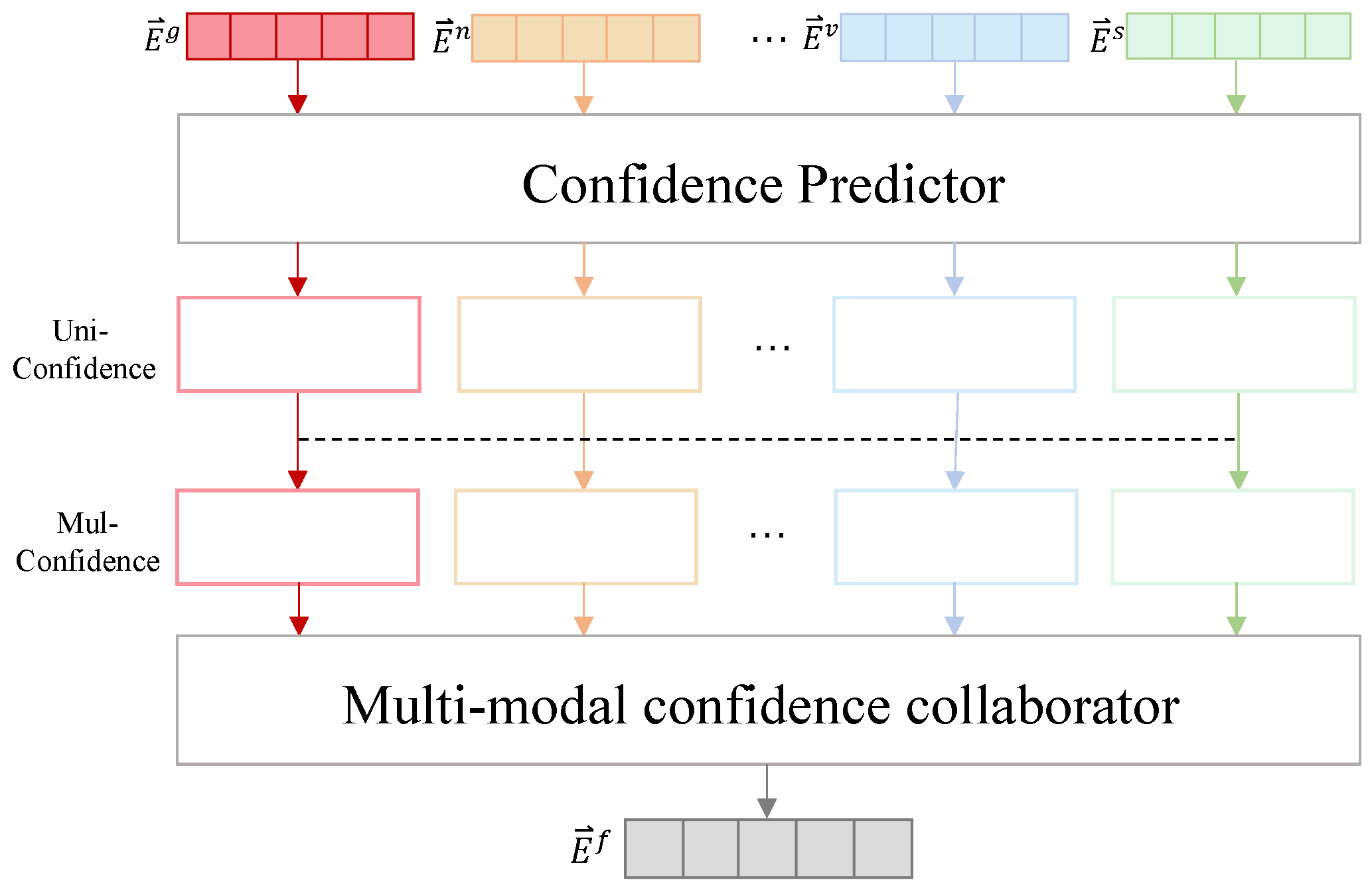
4.2. Feature Dynamic Fusion
4.2.1. Uni-Confidence
4.2.2. Mul-Confidence
4.3. Joint Optimization of Loss Functions
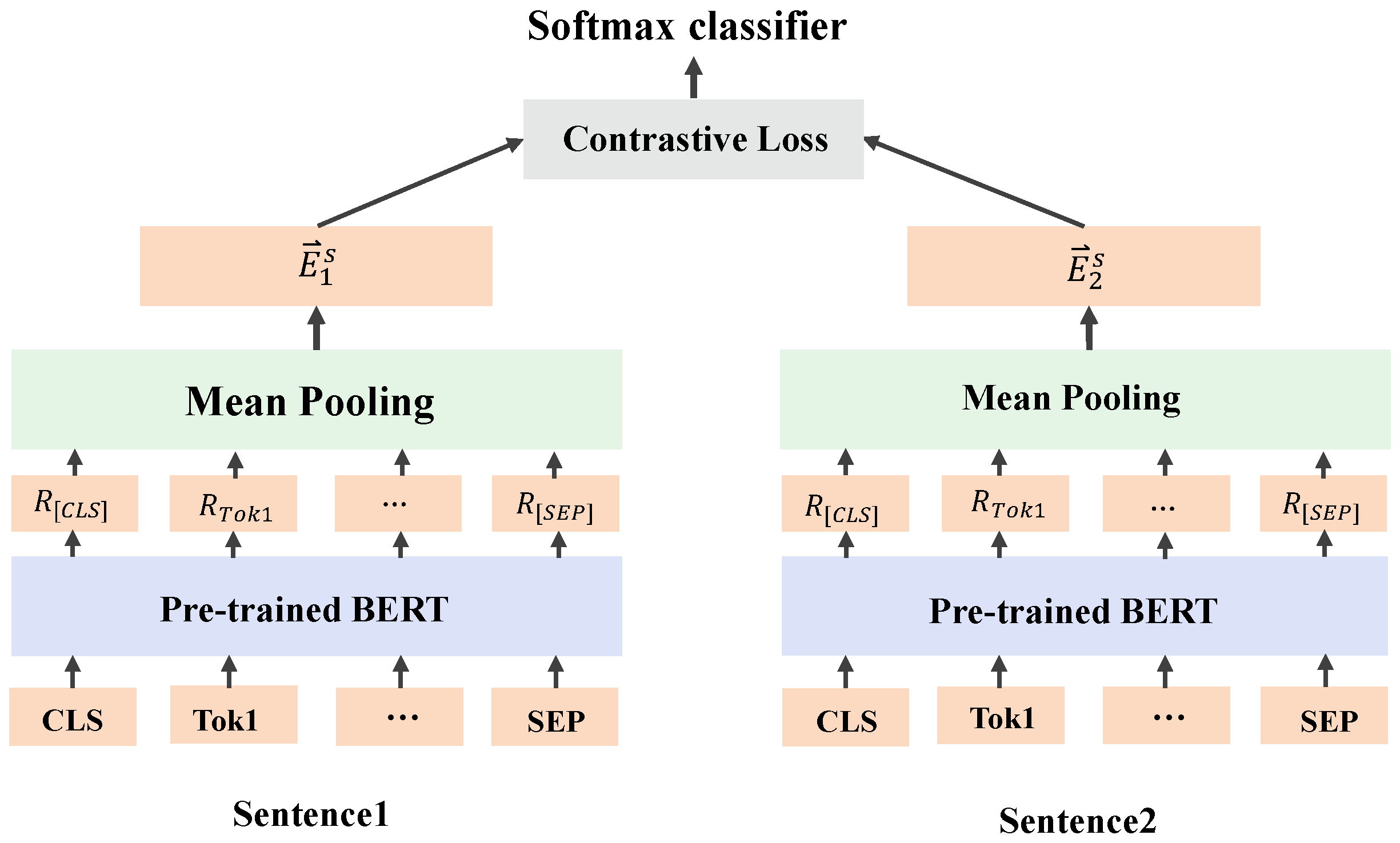
4.3.1. Multimodal Entity Contrastive Loss
4.3.2. Cross-Modal Similarity Loss
5. Experiments
5.1. Datasets
5.2. Evaluation Metrics
5.3. Competing Methods
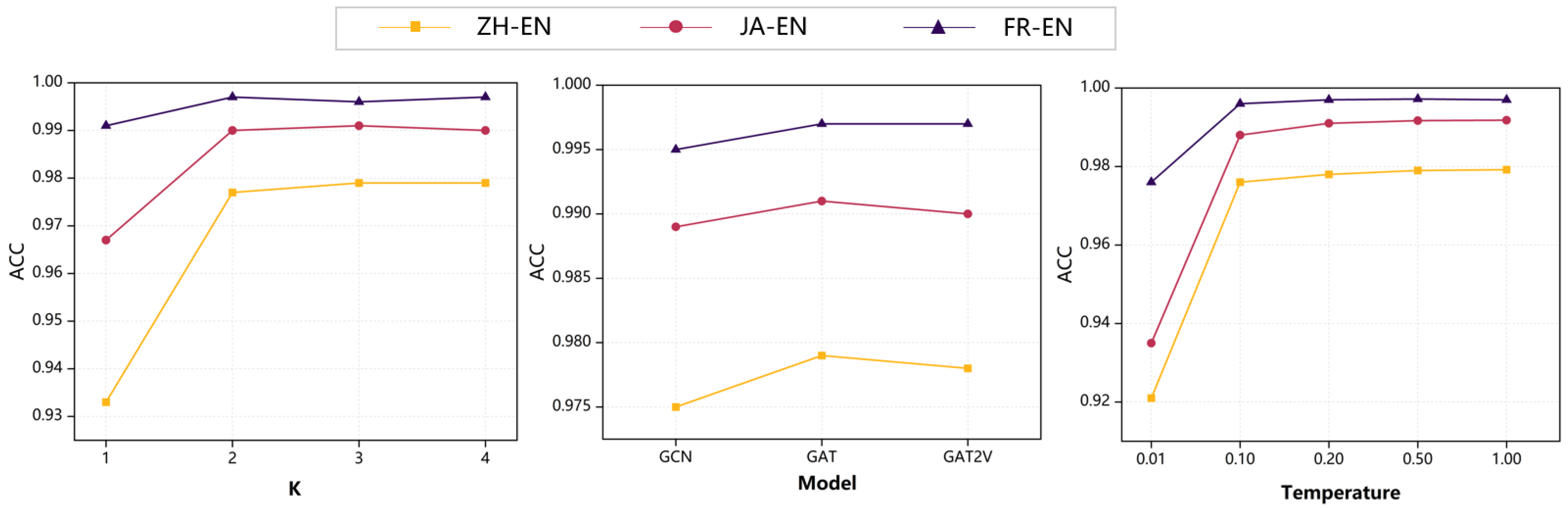
5.4. Effects of Parameters
5.5. Ablation Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FMEA-TD | Fusion-Optimized Multimodal Entity Alignment |
| SBERT | Sentence-BERT |
| JOF | Joint optimization of loss functions |
References
- Lehmann, J.; Isele, R.; Jakob, M.; Jentzsch, A.; Kontokostas, D.; Mendes, P.N.; Hellmann, S.; Morsey, M.; VanKleef, P.; Auer, S.; et al. Dbpedia—A large-scale, multilingual knowledge base extracted from wikipedia. Semant. Web 2015, 6, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, F.M.; Kasneci, G.; Weikum, G. Yago: A large ontology from wikipedia and wordnet. J. Web Semant. 2008, 6, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussallem, D.; Ngonga Ngomo, A.C.; Buitelaar, P.; Arcan, M. Utilizing knowledge graphs for neural machine translation augmentation. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Knowledge Capture, Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 19–21 November 2019; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, S.; Patidar, M.; Chowdhury, S.; Agarwal, P.; Bhattacharya, I.; Shroff, G. Complex question answering on knowledge graphs using machine translation and multi-task learning. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 19–23 April 2021; Main Volume. pp. 3428–3439. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, W.; Zhu, H.; Tan, K.; Wang, J.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yuan, P.; Lan, Y. Finqa: A training-free dynamic knowledge graph question answering system in finance with llm-based revision. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Vilnius, Lithuania, 8–12 September 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zareian, A.; Lin, Y.; Pan, X.; Whitehead, S.; Chen, B.; Wu, B.; Ji, H.; Chang, S.F.; Voss, C.; et al. Gaia: A fine-grained multimedia knowledge extraction system. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Online, 5–10 July 2020; pp. 77–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Lin, Y.; Lai, T.; Pan, X.; Li, S.; Lin, X.; Zhou, B.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. Resin: A dockerized schema-guided cross-document cross-lingual cross-media information extraction and event tracking system. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Demonstrations, Online, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X.; Sun, P.; Wang, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yuan, N.J. Multi-modal knowledge graph construction and application: A survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2022, 36, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, R.; Sun, J.; Xiao, J.; Yang, Y. Prior bilinear-based models for knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Vilnius, Lithuania, 8–12 September 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 317–334. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Zuo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, M.; Xu, T.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, J.; Yu, J. Graph attention network with relational dynamic factual fusion for knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Vilnius, Lithuania, 8–12 September 2024; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 89–106. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Chen, M.; Roth, D.; Collier, N. Visual pivoting for (unsupervised) entity alignment. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 19–21 May 2021; Volume 35, pp. 4257–4266. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, M.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Zheng, Y. Multi-modal contrastive representation learning for entity alignment. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.00891. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zheng, H.T. Vision, deduction and alignment: An empirical study on multi-modal knowledge graph alignment. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2023 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Rhodes Island, Greece, 4–10 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Lan, M. From alignment to assignment: Frustratingly simple unsupervised entity alignment. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2109.02363. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zheng, Y. Unsupervised knowledge graph alignment by probabilistic reasoning and semantic embedding. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.05596. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.; Qian, Y.; Chen, L.; Gu, Y.; Xie, X. Unsupervised deep cross-language entity alignment. In Proceedings of the Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases, Turin, Italy, 18–22 September 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, W.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X. Iterative representation learning for entity alignment leveraging textual information. In Proceedings of the Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases: International Workshops of ECML PKDD 2019, Würzburg, Germany, 16–20 September 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. Part I. pp. 489–494. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, E. Mmea: Entity alignment for multi-modal knowledge graph. In Proceedings of the Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management: 13th International Conference, KSEM 2020, Hangzhou, China, 28–30 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. Part I. Volume 13, pp. 134–147. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Yang, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, C. Bert-int: A bert-based interaction model for knowledge graph alignment. Interactions 2020, 100, e1. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.; Xia, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, C.; Hu, Q. Predictive dynamic fusion. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2406.04802. [Google Scholar]
- Veličković, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Lio, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.10903. [Google Scholar]
- Kipf, T.N.; Welling, M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.02907. [Google Scholar]
- Pennington, J.; Socher, R.; Manning, C.D. Glove: Global vectors for word representation. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1532–1543. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Reimers, N. Sentence-bert: Sentence embeddings using siamese bert-networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1908.10084. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Hadsell, R.; Chopra, S.; LeCun, Y. Dimensionality reduction by learning an invariant mapping. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’06), New York, NY, USA, 17–22 June 2006; Volume 2, pp. 1735–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.; Tian, Y.; Yang, M.; Zaniolo, C. Multilingual knowledge graph embeddings for cross-lingual knowledge alignment. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1611.03954. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Qu, Y. Bootstrapping entity alignment with knowledge graph embedding. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; Volume 18. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Hou, L.; Shi, J.; Li, J.; Chua, T.S. Semi-Supervised Entity Alignment via Joint Knowledge Embedding Model and Cross-Graph Mode; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.W.; Zou, Y.; Shi, P.; Lu, W.; Lin, J.; Sun, X. Aligning cross-lingual entities with multi-aspect information. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1910.06575. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, D. Jointly learning entity and relation representations for entity alignment. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.09317. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Huang, R.; Zhang, J. Multi-modal entity alignment method based on feature enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brody, S.; Alon, U.; Yahav, E. How attentive are graph attention networks? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.14491. [Google Scholar]
| Model | zh-en | ja-en | fr-en | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H@1 | H@10 | MRR | H@1 | H@10 | MRR | H@1 | H@10 | MRR | |
| MTransE | 0.308 | 0.614 | 0.364 | 0.279 | 0.575 | 0.349 | 0.244 | 0.996 | 0.335 |
| BootEA | 0.629 | 0.848 | 0.703 | 0.622 | 0.854 | 0.701 | 0.653 | 0.874 | 0.731 |
| KEGC | 0.478 | 0.835 | 0.598 | 0.490 | 0.844 | 0.610 | 0.486 | 0.851 | 0.610 |
| HMAN | 0.871 | 0.987 | - | 0.935 | 0.994 | - | 0.973 | 0.998 | - |
| EVA | 0.761 | 0.907 | 0.814 | 0.762 | 0.913 | 0.817 | 0.793 | 0.942 | 0.847 |
| HGCN | 0.720 | 0.857 | 0.768 | 0.766 | 0.897 | 0.813 | 0.892 | 0.961 | 0.917 |
| BERT-INT | 0.968 | 0.990 | 0.977 | 0.964 | 0.991 | 0.975 | 0.992 | 0.998 | 0.995 |
| MCLEA | 0.972 | 0.996 | 0.981 | 0.986 | 0.999 | 0.991 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.998 |
| MEAFE | 0.973 | 0.997 | 0.982 | 0.987 | 0.999 | 0.992 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.998 |
| FMEA-TD (ours) | 0.979 | 0.998 | 0.986 | 0.991 | 1.000 | 0.995 | 0.997 | 1.000 | 0.998 |
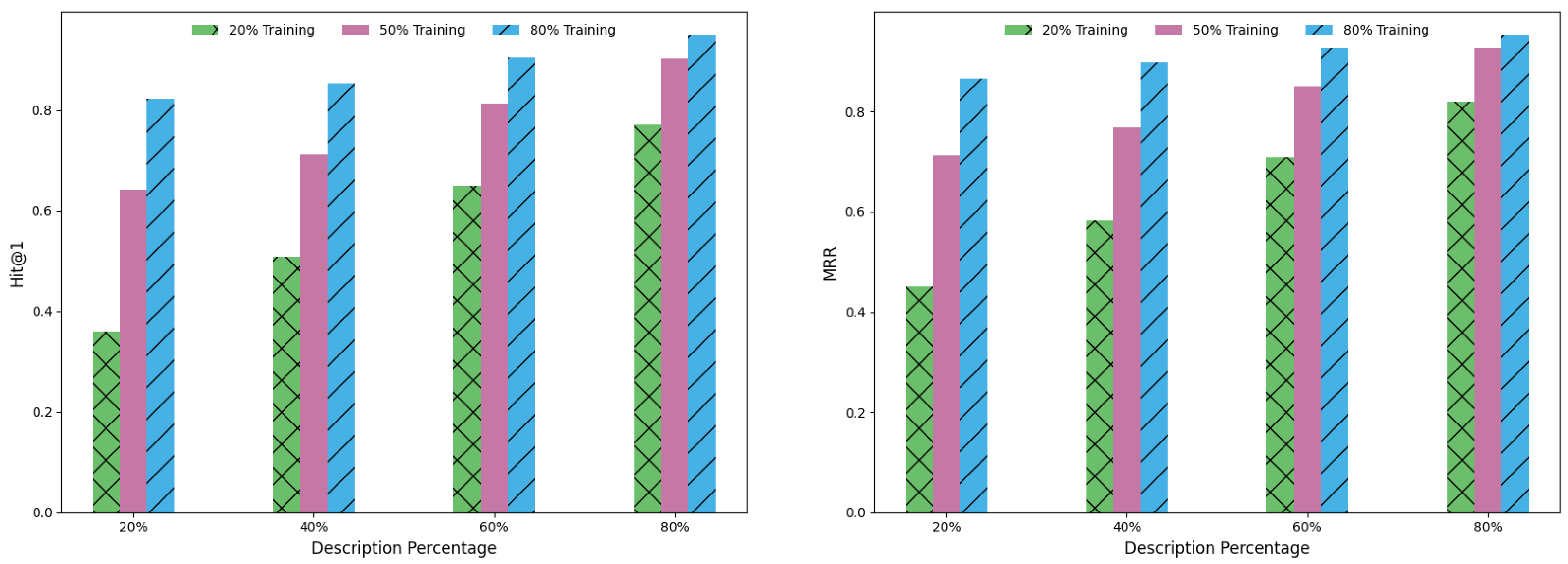
| Model | 20% | 50% | 80% | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H@1 | H@10 | MRR | H@1 | H@10 | MRR | H@1 | H@10 | MRR | ||
| 20% | 0.326 | 0.573 | 0.402 | 0.594 | 0.704 | 0.665 | 0.763 | 0.893 | 0.801 | |
| MCLEA | 40% | 0.458 | 0.649 | 0.502 | 0.647 | 0.766 | 0.701 | 0.818 | 0.912 | 0.842 |
| 60% | 0.595 | 0.735 | 0.634 | 0.738 | 0.84 | 0.783 | 0.863 | 0.937 | 0.902 | |
| 80% | 0.728 | 0.874 | 0.787 | 0.864 | 0.913 | 0.887 | 0.918 | 0.956 | 0.93 | |
| 20% | 0.297 | 0.552 | 0.388 | 0.436 | 0.654 | 0.585 | 0.625 | 0.864 | 0.766 | |
| MMEA | 40% | 0.412 | 0.636 | 0.498 | 0.59 | 0.754 | 0.634 | 0.766 | 0.886 | 0.803 |
| 60% | 0.547 | 0.628 | 0.586 | 0.678 | 0.831 | 0.747 | 0.843 | 0.898 | 0.855 | |
| 80% | 0.687 | 0.814 | 0.756 | 0.802 | 0.869 | 0.825 | 0.882 | 0.923 | 0.902 | |
| 20% | 0.359 | 0.627 | 0.451 | 0.641 | 0.801 | 0.713 | 0.823 | 0.933 | 0.865 | |
| FMEA-TD | 40% | 0.507 | 0.727 | 0.582 | 0.722 | 0.87 | 0.769 | 0.875 | 0.954 | 0.899 |
| 60% | 0.648 | 0.822 | 0.708 | 0.812 | 0.918 | 0.851 | 0.905 | 0.966 | 0.927 | |
| 80% | 0.773 | 0.903 | 0.82 | 0.906 | 0.966 | 0.927 | 0.948 | 0.984 | 0.963 | |
| zh-en | en-zh | ja-en | en-ja | fr-en | en-fr | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H@1 | MRR | H@1 | MRR | H@1 | MRR | H@1 | MRR | H@1 | MRR | H@1 | MRR | |
| w/o Gph | 0.920 | 0.943 | 0.916 | 0.941 | 0.960 | 0.974 | 0.958 | 0.971 | 0.991 | 0.999 | 0.992 | 0.995 |
| w/o Img | 0.970 | 0.983 | 0.969 | 0.993 | 0.981 | 0.991 | 0.983 | 0.991 | 0.994 | 0.999 | 0.994 | 0.998 |
| w/o Text | 0.864 | 0.891 | 0.861 | 0.888 | 0.903 | 0.914 | 0.907 | 0.918 | 0.962 | 0.978 | 0.958 | 0.973 |
| w/o Desc | 0.971 | 0.980 | 0.970 | 0.979 | 0.981 | 0.990 | 0.980 | 0.988 | 0.994 | 0.993 | 0.991 | 0.995 |
| w/o ML | 0.976 | 0.987 | 0.972 | 0.983 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
| w/o Fus | 0.973 | 0.982 | 0.971 | 0.981 | 0.983 | 0.991 | 0.984 | 0.991 | 0.994 | 0.996 | 0.993 | 0.997 |
| ours | 0.979 | 0.986 | 0.976 | 0.985 | 0.991 | 0.995 | 0.989 | 0.994 | 0.997 | 0.999 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Chaomurilige; Weng, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z. Fusion-Optimized Multimodal Entity Alignment with Textual Descriptions. Information 2025, 16, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070534
Wang C, Chaomurilige, Weng Y, Liu X, Liu Z. Fusion-Optimized Multimodal Entity Alignment with Textual Descriptions. Information. 2025; 16(7):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070534
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chenchen, Chaomurilige, Yu Weng, Xuan Liu, and Zheng Liu. 2025. "Fusion-Optimized Multimodal Entity Alignment with Textual Descriptions" Information 16, no. 7: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070534
APA StyleWang, C., Chaomurilige, Weng, Y., Liu, X., & Liu, Z. (2025). Fusion-Optimized Multimodal Entity Alignment with Textual Descriptions. Information, 16(7), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16070534






