Integrating Natural Language Processing with 4D BIM: A Review and Thematic Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
Research Aim
2. Research Methodology
2.1. Data Collection Process
2.2. Coding and Category Development Methodology
3. Data Collection Results
3.1. Building Information Modeling
3.1.1. BIM Functions and Benefits
3.1.2. BIM Domains and Applications
3.1.3. Automation in BIM
3.1.4. IFC Querying and Parsing
3.2. Scheduling of Construction Projects
3.2.1. Work Breakdown Structure
3.2.2. BIM and Scheduling
3.3. 4D BIM
3.3.1. Introduction to 4D BIM
3.3.2. Common Tools of 4D BIM
3.3.3. 4D BIM and Progress Measurement
3.3.4. 4D BIM and Lean Scheduling
3.3.5. Alignment of Activities and Objects
3.4. NLP Within the Review Context
3.4.1. AI Applications in the AEC Industry
3.4.2. Introduction to NLP
3.4.3. NLP Technologies and Software Tools
3.4.4. NLP Applications in AEC and BIM
4. Results, Coding, and Category Development
4.1. Statistics of Reviewed Articles
4.2. Results of the Coding Process
4.3. NLP-Related Categories
4.4. 4D BIM-Related Categories
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AGC. The Contractors’ Guide to BIM; AGC Publication: Arlington, VA, USA; Associated General Contractors of America: Arlington, VA, USA, 2006; Available online: https://books.google.com.sa/books?id=LDk7HQAACAAJ (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Aredah, A.S.; Baraka, M.A.; ElKhafif, M. Project Scheduling Techniques Within a Building Information Modeling (BIM) Environment: A Survey Study. IEEE Eng. Manag. Rev. 2019, 47, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Cho, Y.K. Construction-specific spatial information reasoning in Building Information Models. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chi, H.; Wu, P.; Shen, G.Q. Smart work packaging-enabled constraint-free path re-planning for tower crane in prefabricated products assembly process. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 43, 101008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, R.; Girolami, M.; Brilakis, I. Building Information Modelling, Artificial Intelligence and Construction Tech. Dev. Built Environ. 2020, 4, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Jeong, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hong, T. Deep Learning–Based Automation of Scan-to-BIM with Modeling Objects from Occluded Point Clouds. J. Manag. Eng. 2022, 38, 04022025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, P.; Shen, G.Q.; Wang, X.; Teng, Y. Mapping the knowledge domains of Building Information Modeling (BIM): A bibliometric approach. Autom. Constr. 2017, 84, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.R.; Martek, I.; Zavadskas, E.K.; Aibinu, A.A.; Arashpour, M.; Chileshe, N. Critical evaluation of off-site construction research: A Scientometric analysis. Autom. Constr. 2018, 87, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darko, A.; Chan, A.P.C.; Adabre, M.A.; Edwards, D.J.; Hosseini, M.R.; Ameyaw, E.E. Artificial intelligence in the AEC industry: Scientometric analysis and visualization of research activities. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Zhang, L. Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Autom. Constr. 2021, 122, 103517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinney, K.; Fischer, M. Generating, evaluating and visualizing construction schedules with CAD tools. Autom. Constr. 1998, 7, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, L.; Gillis, A.S.; Lutkevich, B.; Burns, E. A Guide to Artificial Intelligence in the Enterprise. TechTarget. 2024. Available online: https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/Ultimate-guide-to-artificial-intelligence-in-the-enterprise (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Creswell, J.W.; Poth, C.N. Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design; SAGE Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glaser, B.G.; Strauss, A.L. The Discovery of Grounded Theory: Strategies for Qualitative Research, 1st ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, R.; Koskela, L.; Dave, B.A.; Owen, R. Interaction of Lean and Building Information Modeling in Construction. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2010, 136, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovska-Georgievska, L.; Sandeva, I.; Krleski, A.; Spasevska, H.; Ginovska, M.; Panchevski, I.; Ivanov, R.; Perez Arnal, I.; Cerovsek, T.; Funtik, T. BIM in the Center of Digital Transformation of the Construction Sector—The Status of BIM Adoption in North Macedonia. Buildings 2022, 12, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzadi, M.; Sheikhkhoshkar, M.; Banihashemi, S. BIM applications toward key performance indicators of construction projects in Iran. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2020, 20, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-W.; Ballard, G. Management Thinking in the Earned Value Method System and the Last Planner System. J. Manag. Eng. 2010, 26, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-K.; Kim, K.-R.; Yu, J.-H. BIM and ontology-based approach for building cost estimation. Autom. Constr. 2014, 41, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarnezhad, A.; Ong, K.C.G.; Chandra, L.R. Economic and environmental assessment of deconstruction strategies using building information modeling. Autom. Constr. 2014, 37, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, R.; Sardroud, J.M.; Soto, B.G.D. BIM-based Applications of Metaheuristic Algorithms to Support the Decision-making Process: Uses in the Planning of Construction Site Layout. Procedia Eng. 2017, 196, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Ma, L.Y.H. A BIM-based system for demolition and renovation waste estimation and planning. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1539–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saieg, P.; Sotelino, E.D.; Nascimento, D.; Caiado, R.G.G. Interactions of Building Information Modeling, Lean and Sustainability on the Architectural, Engineering and Construction industry: A systematic review. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 174, 788–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, P. BIM to BEM as Teaching Methodology to Support Sustainable Construction Decisions. Period. Polytech. Archit. 2016, 47, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Hsu, Y.T.; Hu, H.T. BIM Model Management for BIM-Based Facility Management in Buildings. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1901201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Teizer, J.; Lee, J.-K.; Eastman, C.M.; Venugopal, M. Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Safety: Automatic Safety Checking of Construction Models and Schedules. Autom. Constr. 2013, 29, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Guo, F.; Guo, S. Toward an Efficient Construction Process: What Drives BIM Professionals to Collaborate in BIM-Enabled Projects. J. Manag. Eng. 2022, 38, 04022033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, C.; Cai, Y.; Lu, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, T. BIM-Based Visualization Research in the Construction Industry: A Network Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwisy, A.; Hamdan, S.B.; Barkokebas, B.; Bouferguene, A.; Al-Hussein, M. A BIM-based automation of design and drafting for manufacturing of wood panels for modular residential buildings. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2019, 19, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Shang, J.; Chen, P.; Zlatanova, S.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Z. Indoor mapping and modeling by parsing floor plan images. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2021, 35, 1205–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banfi, F.; Fai, S.; Brumana, R. BIM automation: Advanced modeling generative process for complex structures. In ISPRS Annals of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences; Copernicus GmbH: Göttingen, Germany, 2017; pp. 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, O.W.; Zhang, J. Logic representation and reasoning for automated BIM analysis to support automation in offsite construction. Autom. Constr. 2021, 129, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalov, K.; Ye, X.; König, M.; Hagedorn, P.; Blum, F.; Severin, B.; Hettmer, M.; Hückinghaus, P.; Wölkerling, J.; Groß, D. Automated Payment and Contract Management in the Construction Industry by Integrating Building Information Modeling and Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, H.; Xu, J. Towards fully BIM-enabled building automation and robotics: A perspective of lifecycle information flow. Comput. Ind. 2022, 135, 103570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, C.; Shabestari, A.Z.; Misic, T.; Gilani, S.; Litoiu, M.; McArthur, J.J. Building automation system—BIM integration using a linked data structure. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froese, T.; Grobler, F.; Ritzenthaler, J.; Yu, K.; Akinci, B.; Akbas, R.; Koo, B.; Barron, A.; Kunz, J.C. Industry Foundation Classes for Project Management—A Trial Implementation. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 1999, 4, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Eastman, C.; Teicholz, P.; Sacks, R.; Liston, K. BIM Handbook: A Guide to Building Information Modeling for Owners, Managers, Designers, Engineers, and Contractors, 1st ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazairac, W.; Beetz, J. BIMQL—An open query language for building information models. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2013, 27, 444–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solihin, W.; Eastman, C.; Lee, Y.-C.; Yang, D.-H. A simplified relational database schema for transformation of BIM data into a query-efficient and spatially enabled database. Autom. Constr. 2017, 84, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Lai, H.; Xu, J.; Zhao, Y. Generic Language for Partial Model Extraction from an IFC Model Based on Selection Set. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, Y. Research on Parsing and Storage of BIM Information Based on IFC Standard. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 643, 012172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OSArch. IfcOpenShell. 16 February 2024. Available online: https://wiki.osarch.org/index.php?title=IfcOpenShell (accessed on 1 March 2024).
- PMI. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide); Project Management Institute, Inc.: Newtown Square, PA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kenley, R.; Harfield, T. Reviewing the IJPM for WBS: The Search for Planning and Control. Procedia—Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 119, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami-Irdemoosa, E.; Dindarloo, S.R.; Sharifzadeh, M. Work breakdown structure (WBS) development for underground construction. Autom. Constr. 2015, 58, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSI. UniFormat®: A Uniform Classification of Construction Systems and Assemblies; Construction Specifications Institute (CSI): Alexandria, VA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- CSI. MasterFormat® Numbers & Titles; Construction Specifications Institute (CSI): Alexandria, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- CSI. OmniClass; Construction Specifications Institute (CSI): Alexandria, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- De Vries, B.; Harink, J.M.J. Generation of a construction planning from a 3D CAD model. Autom. Constr. 2007, 16, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, A.; Su, X.; Nasir, I.M. BIM Adoption and Its Impact on Planning and Scheduling Influencing Mega Plan Projects- (CPEC-) Quantitative Approach. Complexity 2021, 2021, 8818296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulakova, E.; König, M.; Tauscher, E.; Beucke, K. Knowledge-based schedule generation and evaluation. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2010, 24, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Anderson, K.; Lee, S.; Hildreth, J. Generating construction schedules through automatic data extraction using open BIM (building information modeling) technology. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-M.; (Bud) Griffis, F.H.; Chen, P.-H.; Chang, L.-M. A framework for an automated and integrated project scheduling and management system. Autom. Constr. 2013, 35, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusen, P.; Boonyung, W.; Nusen, S.; Panuwatwanich, K.; Champrasert, P.; Kaewmoracharoen, M. Construction Planning and Scheduling of a Renovation Project Using BIM-Based Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, V.; Reinschmidt, K.F.; Kang, J.H. Construction scheduling using Genetic Algorithm based on Building Information Model. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 7565–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, V.; Beucke, K.E.; Shapir, K.; König, M. Model-based Scheduling for Construction Planning. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computing in Civil and Building Engineering, Moscow, Russia, 27–29 June 2012; Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:17071843 (accessed on 10 April 2024).
- Liu, H.; Al-Hussein, M.; Lu, M. BIM-based integrated approach for detailed construction scheduling under resource constraints. Autom. Constr. 2015, 53, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Park, J.; Cho, C. Framework for Automated Generation of Constructible Steel Erection Sequences Using Structural Information of Static Indeterminacy Variation in BIM. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 24, 3169–3178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaac, S.; Shimanovich, M. Automated scheduling and control of mechanical and electrical works with BIM. Autom. Constr. 2021, 124, 103600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Cai, H. WBS-based dynamic multi-dimensional BIM database for total construction as-built documentation. Autom. Constr. 2017, 77, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallgren, M.V.; Roupé, M.; Johansson, M.; Bosch-Sijtsema, P. BIM tool development enhancing collaborative scheduling for pre-construction. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2020, 25, 374–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbiti, M.; Beddiar, K.; Beladjine, D.; Perrault, R.; Mazari, B. Toward BIM and LPS Data Integration for Lean Site Project Management: A State-of-the-Art Review and Recommendations. Buildings 2021, 11, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowther, J.; Ajayi, S.O. Impacts of 4D BIM on construction project performance. Int. J. Constr. Manag. 2021, 21, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallgren, M.V.; Roupé, M.; Johansson, M. 4D modelling using virtual collaborative planning and scheduling. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2021, 26, 763–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Zeng, N.; Ye, K.; König, M. An Empirical Study on the Acceptance of 4D BIM in EPC Projects in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jupp, J. 4D BIM for Environmental Planning and Management. Procedia Eng. 2017, 180, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-Y.; Yang, J.-B. Preliminary Evaluation of BIM-based Approaches for Schedule Delay Analysis. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 245, 062048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Zhang, L. Exact Overlap Rate Analysis and the Combination with 4D BIM of Time-Cost Tradeoff Problem in Project Scheduling. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2019, 2019, 9120795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloot, R.N.F.; Heutink, A.; Voordijk, J.T. Assessing usefulness of 4D BIM tools in risk mitigation strategies. Autom. Constr. 2019, 106, 102881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, B.C.; Leite, F.; Faust, K.M. 4D-BIM to enhance construction waste reuse and recycle planning: Case studies on concrete and drywall waste streams. Waste Manag. 2020, 116, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.H.; Ellul, C.; Swiderska, M. Decision Making in the 4th Dimension—Exploring Use Cases and Technical Options for the Integration of 4D BIM and GIS during Construction. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, S.V.-T.; Khan, N.; Lee, D.; Park, C. A Hazard Identification Approach of Integrating 4D BIM and Accident Case Analysis of Spatial–Temporal Exposure. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-Y.; Chang, N.-W. Dynamic construction material layout planning optimization model by integrating 4D BIM. Eng. Comput. 2019, 35, 703–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolarić, S.; Vukomanović, M.; Ramljak, A. Analyzing the Level of Detail of Construction Schedule for Enabling Site Logistics Planning (SLP) in the Building Information Modeling (BIM) Environment. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Donato, D.; Abita, M. Low-cost 4d bim modelling: A comparison between freecad and commercial software. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechyporchuk, Y.; Bašková, R. The conformity of the tools of selected software programs for 4D building modeling. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 867, 012034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Kim, C.; Cho, Y.K. Automated Schedule Updates Using As-Built Data and a 4D Building Information Model. J. Manag. Eng. 2017, 33, 04017012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.K.; Cline, D.; Golparvar-Fard, M. Formalized knowledge of construction sequencing for visual monitoring of work-in-progress via incomplete point clouds and low-LoD 4D BIMs. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2015, 29, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maalek, R.; Lichti, D.D.; Ruwanpura, J.Y. Automatic Recognition of Common Structural Elements from Point Clouds for Automated Progress Monitoring and Dimensional Quality Control in Reinforced Concrete Construction. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttas, S.; Braun, A.; Borrmann, A.; Stilla, U. Acquisition and Consecutive Registration of Photogrammetric Point Clouds for Construction Progress Monitoring Using a 4D BIM. PFG—J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinform. Sci. 2017, 85, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassier, M.; Vincke, S.; Mattheuwsen, L.; De Lima Hernandez, R.; Derdaele, J.; Vergauwen, M. Percentage of completion of in-situ cast concrete walls using point cloud data and bim. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 42, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Hou, X.; Zeng, Y. Review of Image-Based 3D Reconstruction of Building for Automated Construction Progress Monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.-E. 3D Point Cloud and BIM-Based Reconstruction for Evaluation of Project by As-Planned and As-Built. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamledari, H.; Sajedi, S.; McCabe, B.; Fischer, M. Automation of Inspection Mission Planning Using 4D BIMs and in Support of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle–Based Data Collection. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147, 04020179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kropp, C.; Koch, C.; König, M. Interior construction state recognition with 4D BIM registered image sequences. Autom. Constr. 2018, 86, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, E.W.T.; Moon, K.K.L.; Riggins, F.J.; Yi, C.Y. RFID research: An academic literature review (1995–2005) and future research directions. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 112, 510–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, G.Q.; Wu, P.; Fan, H.; Wu, H.; Teng, Y. RBL-PHP: Simulation of Lean Construction and Information Technologies for Prefabrication Housing Production. J. Manag. Eng. 2018, 34, 04017053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazars, T.; Francis, A. Chronographical spatiotemporal dynamic 4D planning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 112, 103076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, A.; Morin-Pepin, S. The Concept of Float Calculation Based on the Site Occupation using the Chronographical Logic. Procedia Eng. 2017, 196, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, H.G. The Last Planner System of Production Control; University of Birmingham: Birmingham, UK, 2000; Available online: https://etheses.bham.ac.uk/id/eprint/4789/1/Ballard00PhD.pdf (accessed on 15 April 2024).
- Ballard, G.; Tommelein, I. Lean management methods for complex projects. Eng. Proj. Organ. J. 2012, 2, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heigermoser, D.; De Soto, B.G.; Abbott, E.L.S.; Chua, D.K.H. BIM-based Last Planner System tool for improving construction project management. Autom. Constr. 2019, 104, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimanski, C.P.; Marcher, C.; Pasetti Monizza, G.; Matt, D.T. The Last Planner® System and Building Information Modeling in Construction Execution: From an Integrative Review to a Conceptual Model for Integration. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.C.P.; Tan, Y.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. A semi-automated approach to generate 4D/5D BIM models for evaluating different offshore oil and gas platform decommissioning options. Vis. Eng. 2017, 5, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassir, D.; Lodge, H.; Chang, H.; Majak, J.; Chen, G. Application of artificial intelligence and machine learning for BIM: Review. Int. J. Simul. Multidiscip. Des. Optim. 2023, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaeva, D.R.; Nikolenko, T.A. Methodological basis for using artificial intelligence technologies in a construction company. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 751, 012106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridgeirsson, T.V.; Ingason, H.T.; Jonasson, H.I.; Jonsdottir, H. An Authoritative Study on the Near Future Effect of Artificial Intelligence on Project Management Knowledge Areas. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wauters, M.; Vanhoucke, M. A comparative study of Artificial Intelligence methods for project duration forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 46, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajdasz, M. Flexible management of repetitive construction processes by an intelligent support system. Expert Syst. Appl. 2014, 41, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rada, R.; Mili, H.; Bicknell, E.; Blettner, M. Development and application of a metric on semantic nets. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1989, 19, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A.; Charles, W.G. Contextual correlates of semantic similarity. Lang. Cogn. Process. 1991, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.A.; Beckwith, R.; Fellbaum, C.; Gross, D.; Miller, K.J. Introduction to WordNet: An On-line Lexical Database *. Int. J. Lexicogr. 1990, 3, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Huang, R.; Gu, J. A Review of Semantic Similarity Measures in WordNet. Int. J. Hybrid Inf. Technol. 2013, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Wajid, U.; Namoun, A.; Marín, C.A.; Mehandjiev, N. Designing and evaluating a system of document recognition to support interoperability among collaborative enterprises. Comput. Ind. 2013, 64, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittoo, A.; Nguyen, L.M.; Van Den Bosch, A. Text analytics in industry: Challenges, desiderata and trends. Comput. Ind. 2016, 78, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.; Vorley, T. Big data text analytics: An enabler of knowledge management. J. Knowl. Manag. 2017, 21, 18–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Z. Extracting topic-sensitive content from textual documents—A hybrid topic model approach. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2018, 70, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Maitah, M. Text analytics for big data using rough–fuzzy soft computing techniques. Expert Syst. 2019, 36, e12463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Duan, N.; Liu, S.; Shum, H.-Y. Progress in Neural NLP: Modeling, Learning, and Reasoning. Engineering 2020, 6, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X. Applications of natural language processing in construction. Autom. Constr. 2022, 136, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-Training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, W. Steven Bird, Ewan Klein and Edward Loper: Natural Language Processing with Python, Analyzing Text with the Natural Language Toolkit. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2010, 44, 421–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.; Wang, M.; Yang, Z. Natural language processing for smart construction: Current status and future directions. Autom. Constr. 2022, 134, 104059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yu, F. A Natural-Language-Based Approach to Intelligent Data Retrieval and Representation for Cloud BIM. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2016, 31, 18–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Chen, X.; Chun, L. Matching Real-World Facilities to Building Information Modeling Data Using Natural Language Processing. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 119465–119475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; El-Gohary, N.M. Extending Building Information Models Semiautomatically Using Semantic Natural Language Processing Techniques. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2016, 30, C4016004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Ng, S.T.; Lee, S.H.; Xu, F.J.; Yang, Y. A domain knowledge incorporated text mining approach for capturing user needs on BIM applications. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2019, 27, 458–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Bhushan, B. Demystifying the Role of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in Smart City Applications: Background, Motivation, Recent Advances, and Future Research Directions. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023, 130, 857–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Ham, Y.; Yi, J.-S.; Son, J. Effective Risk Positioning through Automated Identification of Missing Contract Conditions from the Contractor’s Perspective Based on FIDIC Contract Cases. J. Manag. Eng. 2020, 36, 05020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yi, J.-S.; Son, J. Development of Automatic-Extraction Model of Poisonous Clauses in International Construction Contracts Using Rule-Based NLP. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2019, 33, 04019003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yi, J.-S. Predicting Project’s Uncertainty Risk in the Bidding Process by Integrating Unstructured Text Data and Structured Numerical Data Using Text Mining. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Xue, F.; Li, H. Project-Based As-Needed Information Retrieval from Unstructured AEC Documents. J. Manag. Eng. 2015, 31, A4014012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.-Y.; Kusoemo, D.; Gosno, R.A. Text mining-based construction site accident classification using hybrid supervised machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tixier, A.J.-P.; Hallowell, M.R.; Rajagopalan, B.; Bowman, D. Construction Safety Clash Detection: Identifying Safety Incompatibilities among Fundamental Attributes using Data Mining. Autom. Constr. 2017, 74, 39–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, M.; Seghezzi, E.; Pellegrini, L.; Tagliabue, L.C.; Di Giuda, G.M. Exploring Natural Language Processing in Construction and Integration with Building Information Modeling: A Scientometric Analysis. Buildings 2021, 11, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Zhou, X.; Xie, Q. Multi-scale Information Retrieval for BIM using Hierarchical Structure Modelling and Natural Language Processing. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2021, 26, 409–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Tang, L.; Webster, C.; Xu, S.; Li, X.; Ying, H. An ontology-aided, natural language-based approach for multi-constraint BIM model querying. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 76, 107066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, A.; Ramaji, I.; Sadeghi, N.; Anderson, A. Leveraging Natural Language Processing for Automated Information Inquiry from Building Information Models. J. Inf. Technol. Constr. 2023, 28, 266–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Meng, X.; Zhu, X. Improving knowledge capture and retrieval in the BIM environment: Combining case-based reasoning and natural language processing. Autom. Constr. 2022, 139, 104317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
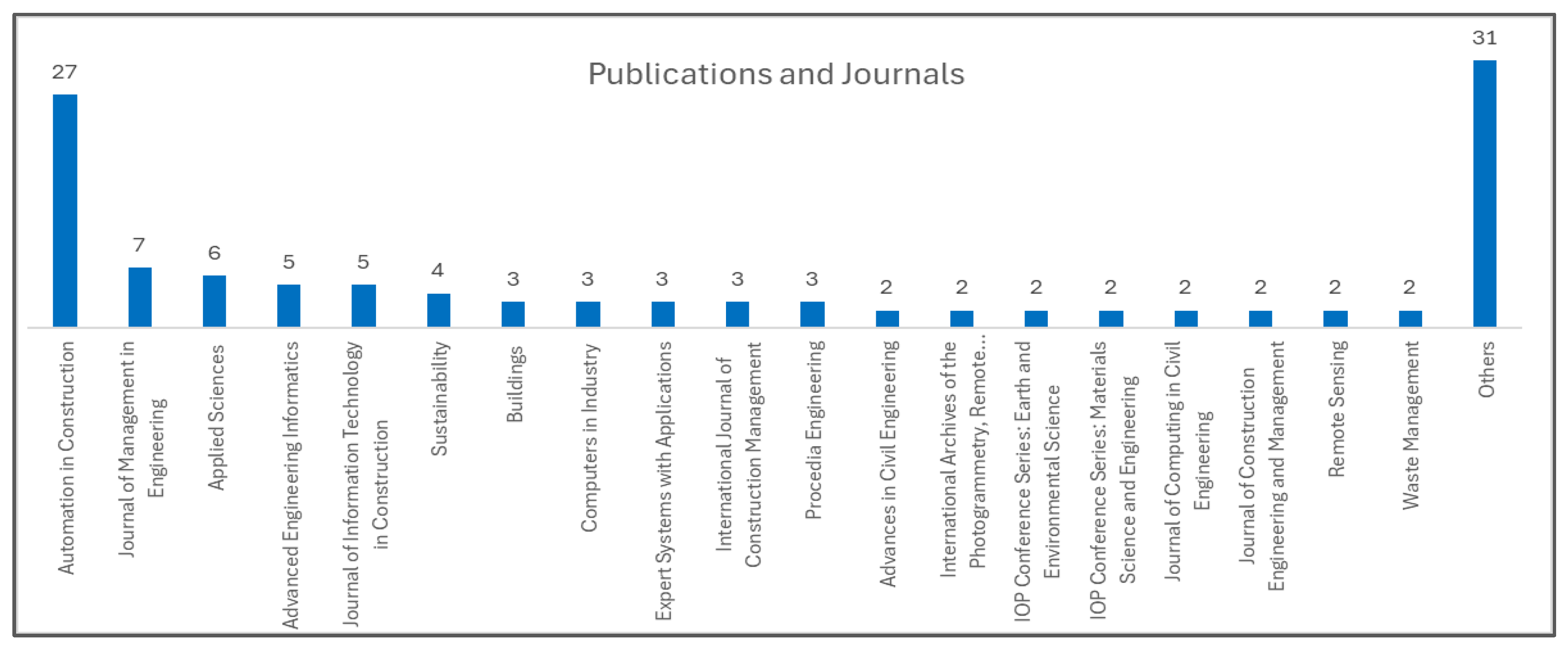
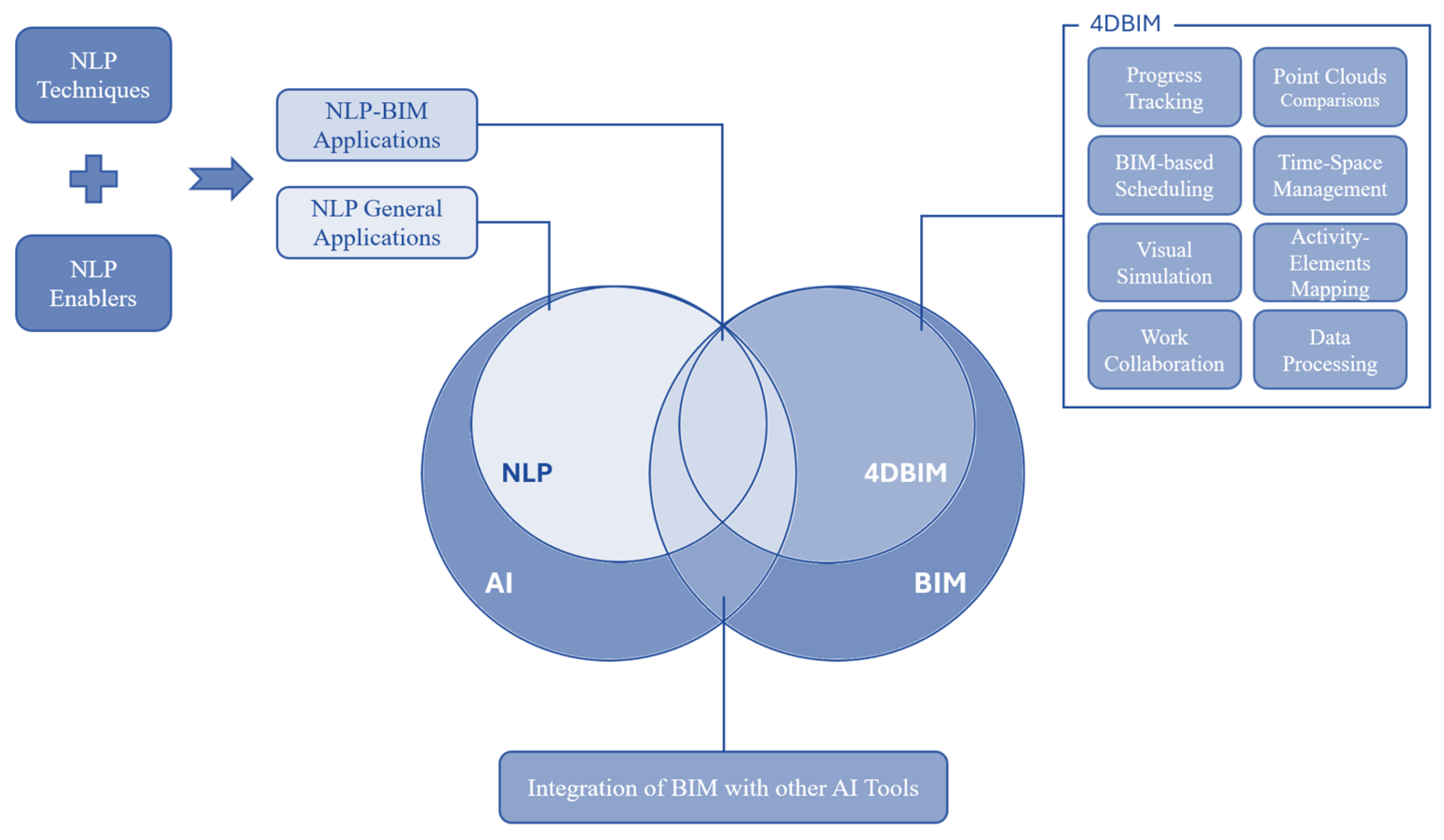

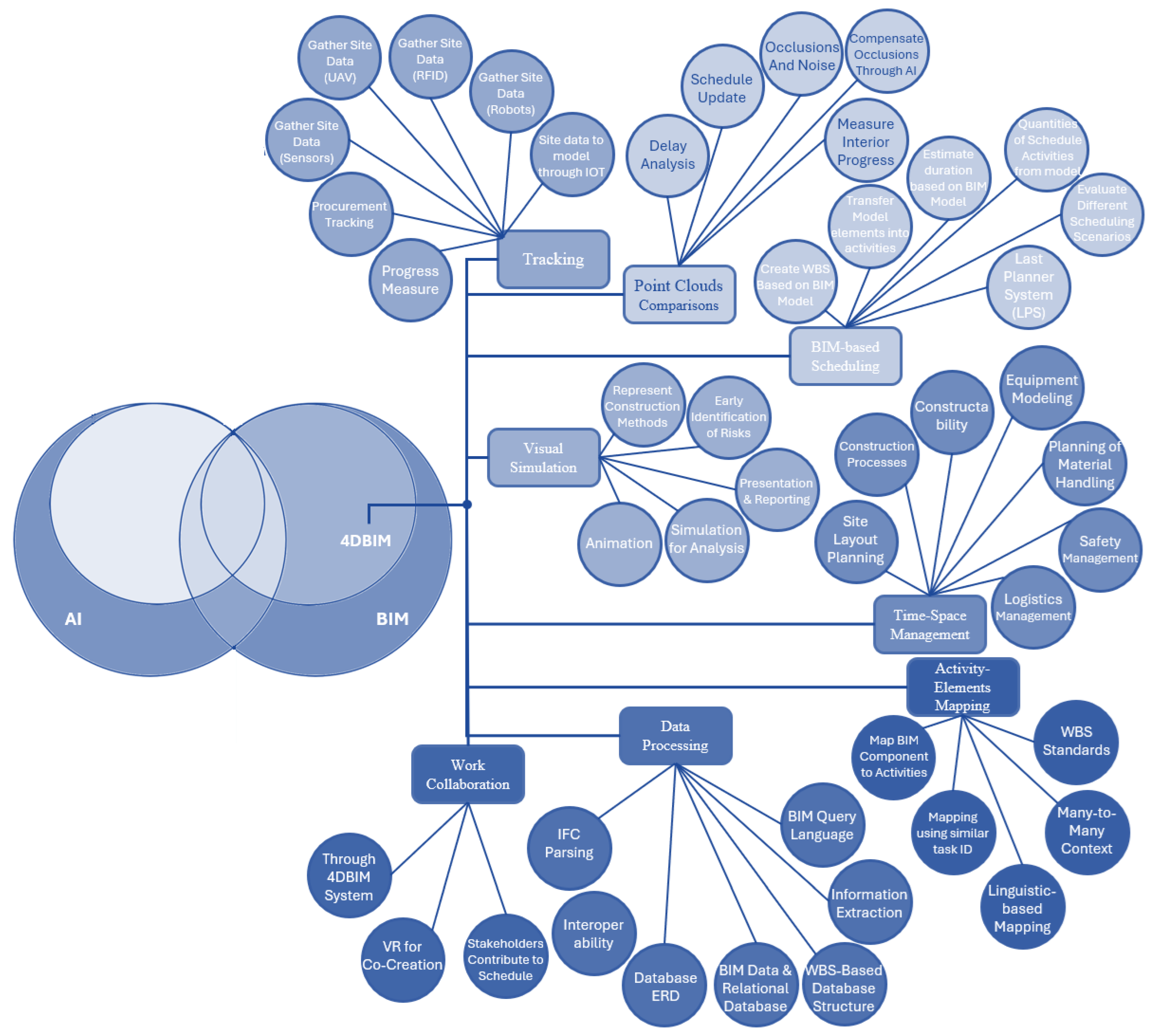
| Section | Code | Category | Section | Code | Category |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIM | Visualizing for presentation | Visual Simulation | 4D BIM | Point cloud challenges: Occlusions and noise | Point Cloud |
| BIM | Progress Measurement | Tracking | 4D BIM | Gathering progress data through unmanned Aerial Vehicles | Tracking |
| BIM | Safety Management based on as-planned simulation | Time-space management | 4D BIM | Interior progress measurement through image analysis | Point Cloud |
| BIM | Construction Processes | Time-space management | 4D BIM | AI techniques to compensate occluded elements | Point Cloud |
| BIM | IFC Parsing | Data Processing | 4D BIM | Gathering progress data through RFID | Tracking |
| BIM | constructibility | Time-space management | 4D BIM | Last planner system (LPS) using the model | BIM-based Scheduling |
| BIM | collaboration through the 4D BIM system | Collaboration | 4D BIM | Code-based mapping using Similarity of Task ID | Mapping |
| BIM | Site layout planning | Time-space management | 4D BIM | Linguistic-based mapping of components to activities | Mapping |
| BIM | Interoperability | Data Processing | 4D BIM | Many-to-many context for both model and schedule | Mapping |
| BIM | Simulation for Analysis | Visual Simulation | AI/NLP | Expert systems | Integration with other AI Tools |
| BIM | Information extraction | Data Processing | AI/NLP | Genetic algorithms | Integration with other AI Tools |
| BIM | Gathering and communicating site data through Robots | Tracking | AI/NLP | Nural network | Integration with other AI Tools |
| BIM | Gathering progress data through sensors | Tracking | AI/NLP | Fuzzy logic & Fuzzy sets | Integration with other AI Tools |
| BIM | Communicating site data to the model through IOT | Tracking | AI/NLP | Machine Learning | Integration with other AI Tools |
| BIM | BIM Query Languages | Data Processing | AI/NLP | Semantic Net | NLP Enablers |
| BIM | Representing BIM Data using relational Database | Data Processing | AI/NLP | Word Net | NLP Enablers |
| Scheduling | WBS Creation Based on the model | BIM-based Scheduling | AI/NLP | Tokenization | NLP Techniques |
| Scheduling | Duration estimate based on the model | BIM-based Scheduling | AI/NLP | Lemmatization | NLP Techniques |
| Scheduling | Transfer model components into activities | BIM-based Scheduling | AI/NLP | Stemming | NLP Techniques |
| Scheduling | Quantities of schedule activities based on the model | BIM-based Scheduling | AI/NLP | Document Recognition | NLP Functions |
| Scheduling | WBS Standards | Mapping | AI/NLP | Extraction of Topic-related Content | NLP Functions |
| Scheduling | WBS-based data base structure | Data Processing | AI/NLP | Machine Translation | NLP Functions |
| Scheduling | Data Entity Relationship Diagram | Data Processing | AI/NLP | Machine Reading | NLP Functions |
| Scheduling | Contribution of stakeholder to the schedule | Collaboration | AI/NLP | Chatbot | NLP Functions |
| Scheduling | Map BIM components to schedule activities | Mapping | AI/NLP | generative Pre-training (GPT) | Integration with other AI Tools |
| 4D BIM | Animation | Visual Simulation | AI/NLP | Syntactic Parsing (SP) | NLP Functions |
| 4D BIM | Procurement tracking | Tracking | AI/NLP | Part-of-speech | NLP Techniques |
| 4D BIM | Early identification of potential risks | Visual Simulation | AI/NLP | Topic modeling | NLP Techniques |
| 4D BIM | Schedule co-creation using VR | Collaboration | AI/NLP | Understanding Users’ Request | NLP-BIM Application |
| 4D BIM | Representing and understanding construction methodology | Visual Simulation | AI/NLP | Mapping User Request to BIM Components | NLP-BIM Application |
| 4D BIM | Evaluating different scheduling scenarios | BIM-based Scheduling | AI/NLP | BIM Querying—Attribute Constraints | NLP-BIM Application |
| 4D BIM | Planning of material handling | Time-space management | AI/NLP | Tagging | NLP Techniques |
| 4D BIM | Equipment modeling | Time-space management | AI/NLP | International framework for dictionaries | NLP Enablers |
| 4D BIM | Compare point cloud to as-planned for delay analysis | Point Cloud | AI/NLP | BIM Querying—Relational Constraints | NLP-BIM Application |
| 4D BIM | Logistics management | Time-space management | AI/NLP | Automated BIM Compliance Checking | NLP-BIM Application |
| 4D BIM | Progress measurement using point cloud to update the schedule | Point Cloud | AI/NLP | Continuous Capturing of Project Information | NLP-BIM Application |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
ElSaadany, M.; Motawa, I.; El Sheikh, A. Integrating Natural Language Processing with 4D BIM: A Review and Thematic Synthesis. Information 2025, 16, 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060457
ElSaadany M, Motawa I, El Sheikh A. Integrating Natural Language Processing with 4D BIM: A Review and Thematic Synthesis. Information. 2025; 16(6):457. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060457
Chicago/Turabian StyleElSaadany, Mohamed, Ibrahim Motawa, and Asser El Sheikh. 2025. "Integrating Natural Language Processing with 4D BIM: A Review and Thematic Synthesis" Information 16, no. 6: 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060457
APA StyleElSaadany, M., Motawa, I., & El Sheikh, A. (2025). Integrating Natural Language Processing with 4D BIM: A Review and Thematic Synthesis. Information, 16(6), 457. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16060457







