Mapping the Evolution of Digital Marketing Research Using Natural Language Processing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
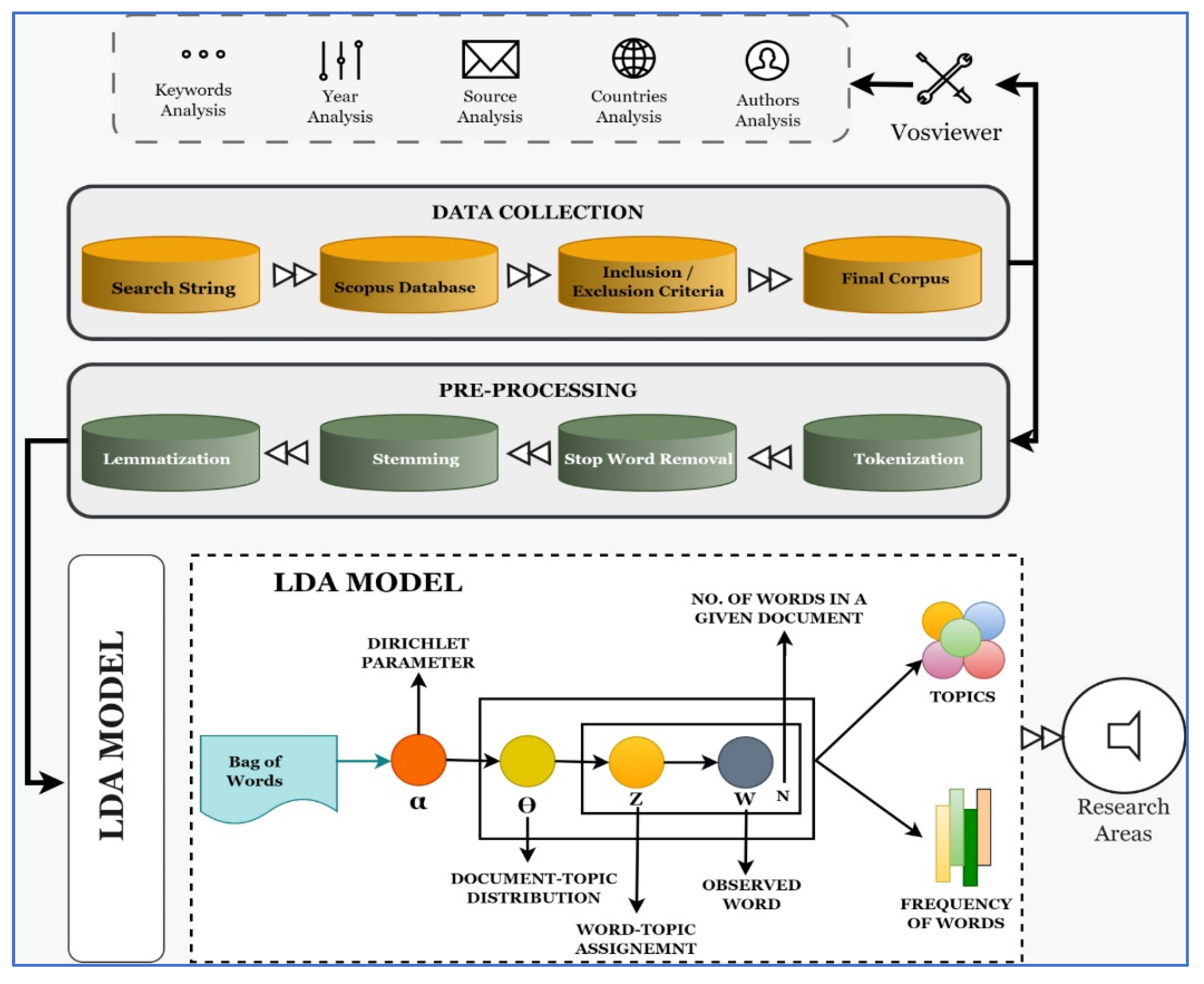
3. Methodology
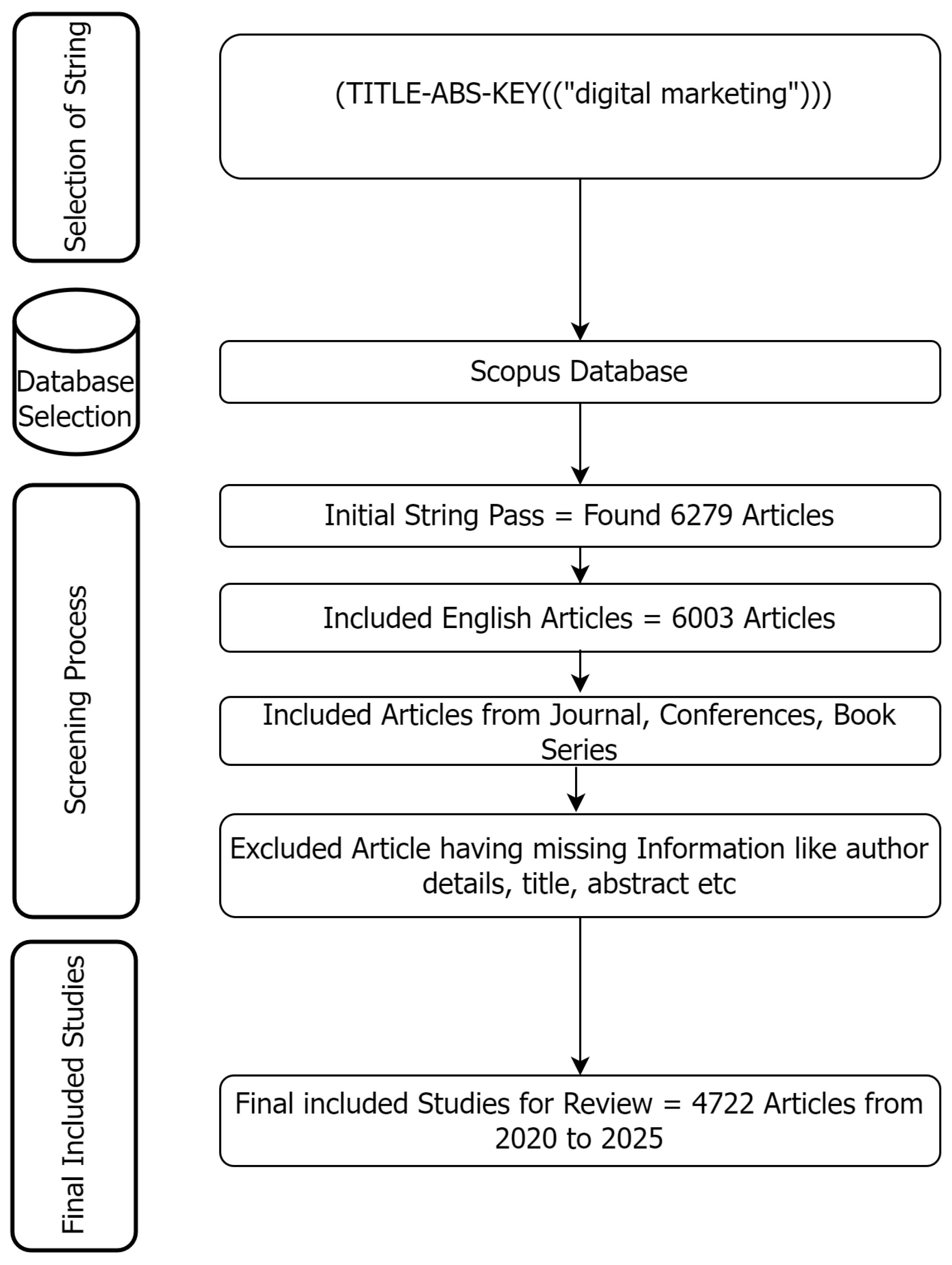
3.1. Data Collection
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
- •
- Lowercasing all text for consistency.
- •
- Tokenization to split text into words and tokens.
- •
- Stop-word removal to eliminate common non-informative terms.
- •
- Lemmatization to reduce words to their root forms.
- •
- Noise filtering to remove punctuation, numbers, and special characters.
3.3. Topic Modeling
3.4. Visualization and Interpretation
- •
- Intertopic Distance Map, showing how topics overlap or diverge within the semantic space.
- •
- Term Saliency Distribution, which identified the most informative and distinctive terms across the dataset.
3.5. Quantitative and Qualitative Validation
- •
- Quantitative Validation: Topic prevalence was assessed by calculating the number and percentage of documents assigned to each dominant topic. This allowed identification of both dominant and niche research themes.
- •
- Qualitative Validation: Representative documents with the highest contribution percentages were reviewed to verify the semantic coherence of topics. Abstracts and associated keywords were cross-checked against model-derived terms to ensure interpretive accuracy.
4. Temporal Evolution of Digital Marketing Research Through Bibliometric Analysis
4.1. Year-Wise Publication Analysis
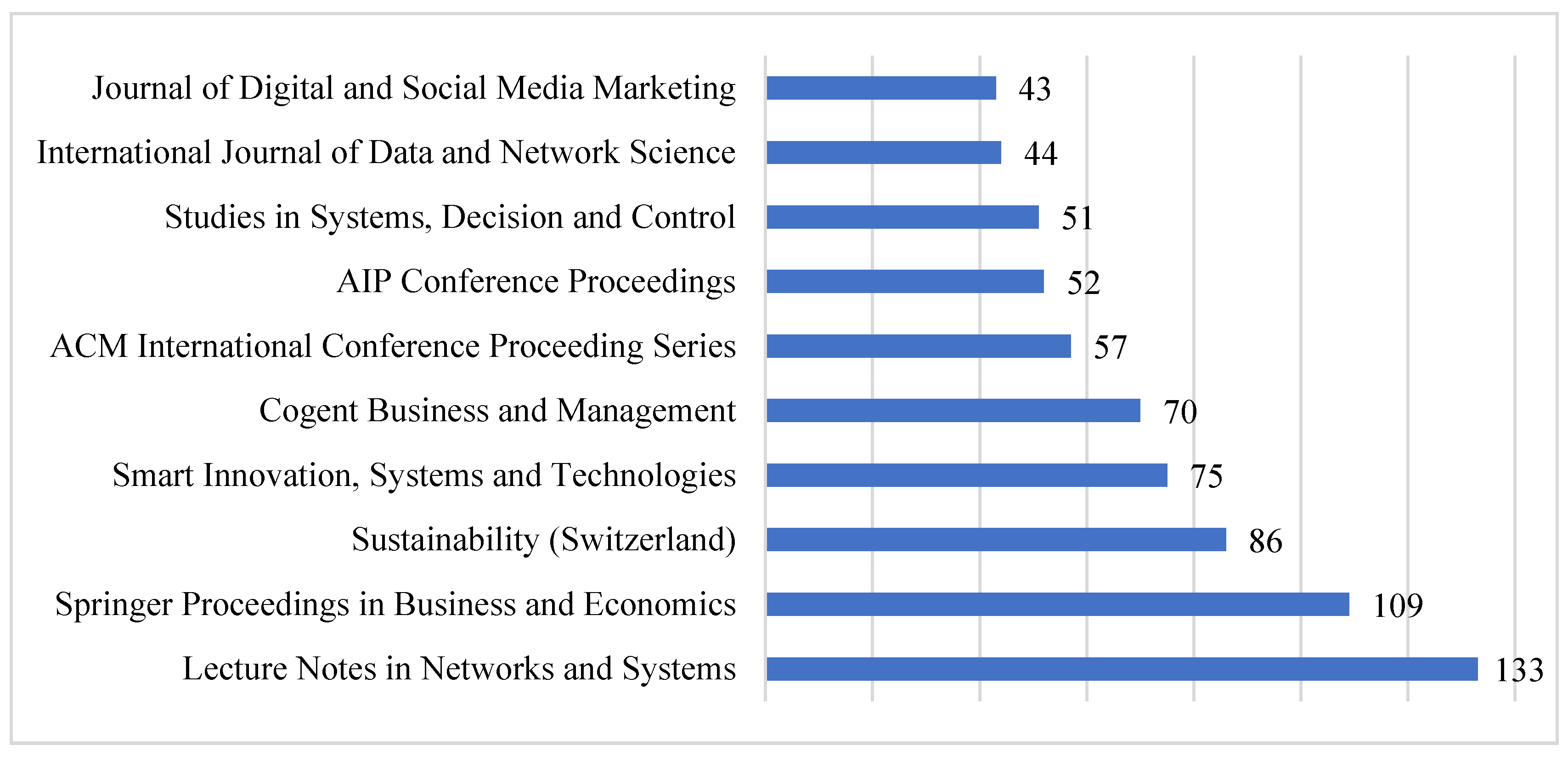
4.2. Top 10 Publication Avenues
4.3. Author’s Wise Analysis
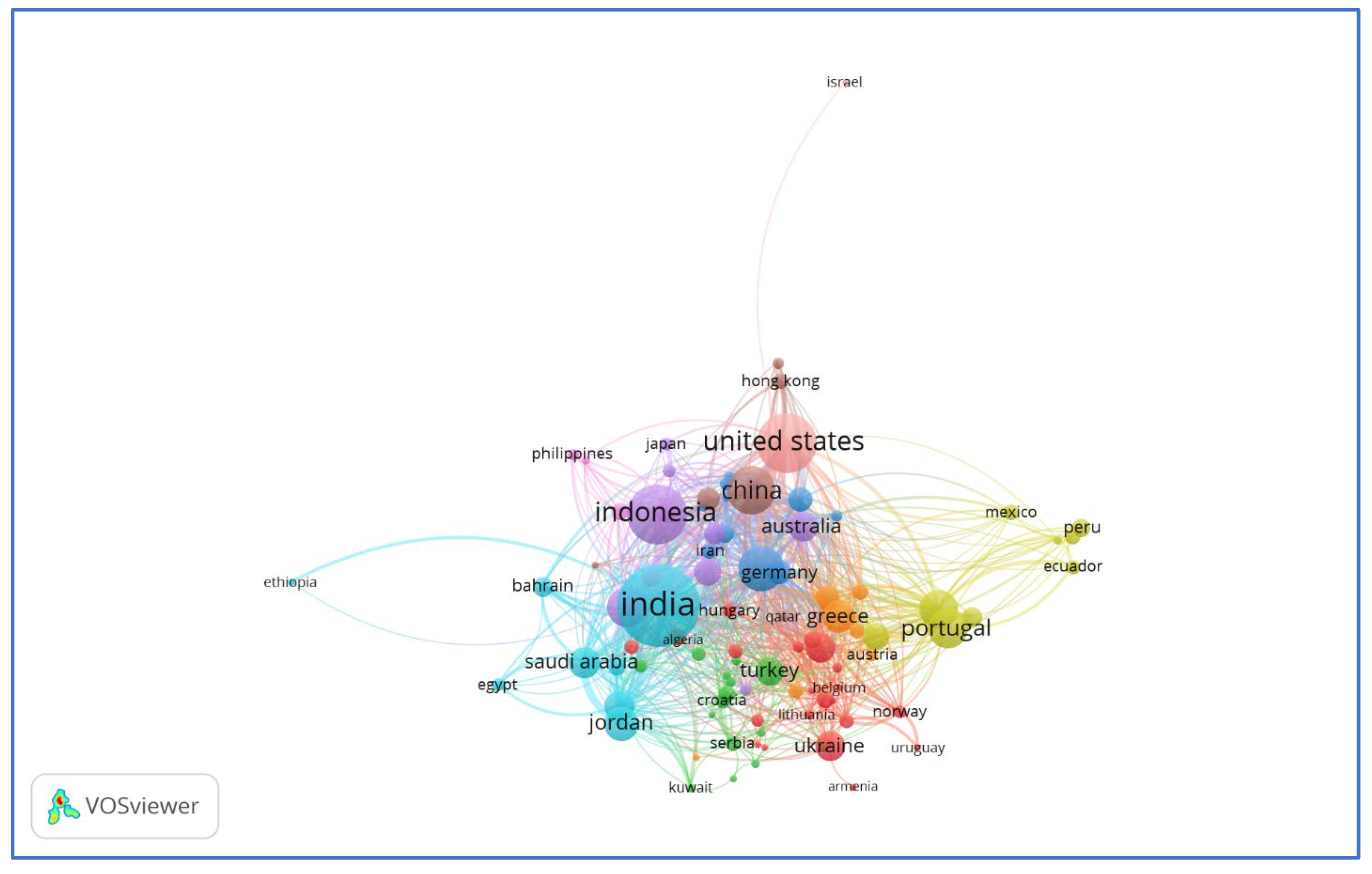
4.4. Country-Wise Analysis
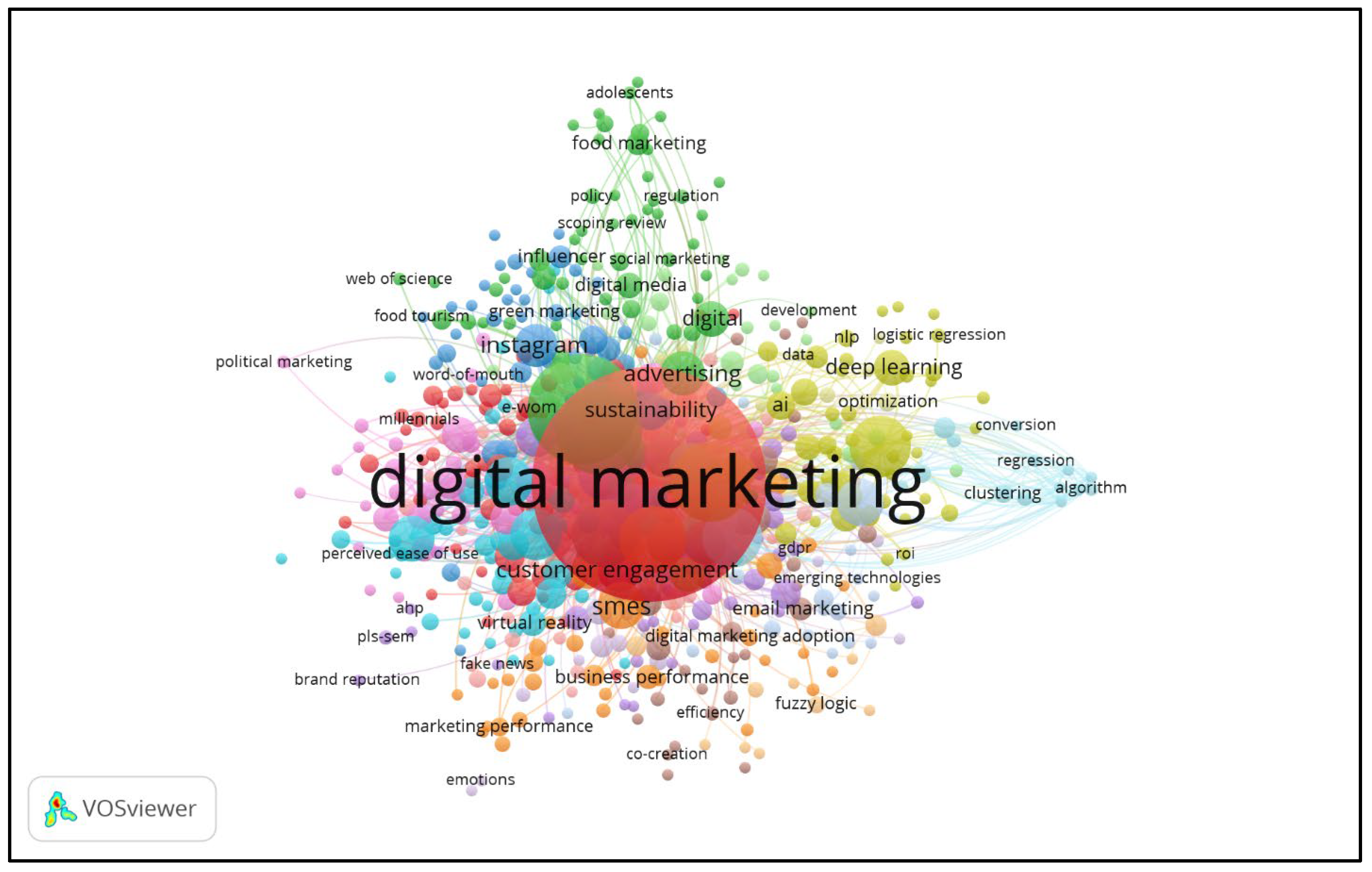
4.5. Keyword Analysis
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. Topic Distribution
5.2. Topic Characterization
5.2.1. Digital Marketing and Blockchain
5.2.2. Digital Marketing in Health and Food Industry
5.2.3. Digital Marketing in Higher Education and Skill Enhancement
5.2.4. Machine Learning and Analytics in Digital Marketing
5.2.5. Adoption of Digital Marketing for SMEs and Sustainable Business
5.2.6. Digital Marketing Trends and Ethics
5.2.7. Sales and Digital Transformation
5.2.8. Digital Marketing in Tourism and Hospitality
5.2.9. Digital Media and Audience Perception
5.2.10. Digital Marketing and Consumer Satisfaction Using Service Quality
5.3. Representative Documents
- •
- Within Topic 1, an example abstract highlighted the growing demand for optimized digital marketing strategies, integrating blockchain technologies to enhance consumer trust and transparency. Another document emphasized content marketing trends with a focus on search engine optimization (SEO). Both illustrate how Topic 1 is anchored in the convergence of marketing and emerging technologies.
- •
- For Topic 2, representative abstracts discussed the impact of digital media exposure on children’s dietary habits and broader implications for public health interventions. This validates the interpretation of Topic 2 as centered on nutrition and health behavior.
- •
- Topic 3 was exemplified by documents addressing the skills gap between industry requirements and university curricula, as well as studies on experiential learning approaches. These findings underscore the educational and pedagogical orientation of this cluster.
- •
- In Topic 10, abstracts consistently dealt with service quality measurement and customer satisfaction. For example, one study applied questionnaire-based models to evaluate consumer perceptions, highlighting the robustness of this topic in capturing quality assessment research.
5.4. Interpretation and Discussions
6. Implications of the Research
6.1. Academic Implications
6.2. Managerial and Industry Implications
6.3. Policy Implications
7. Conclusions and Future Scope
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akanfe, O.; Bhatt, P.; Lawong, D.A. Technology Advancements Shaping the Financial Inclusion Landscape: Present Interventions, Emergence of Artificial Intelligence and Future Directions. Inf. Syst. Front. 2025, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, C.T.P. A literature review. J. Media Res. 2020, 13, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, P.; Prabakaran, V.; Rudresh, S. Effectiveness of Digital Marketing Strategies in the Food Delivery Business Based on Hybrid BiGRU-CRF Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (IDCIoT), Bengaluru, India, 4–6 January 2024; pp. 773–778. [Google Scholar]
- Tarabasz, A. The impact of digital on marketing strategy. In Digital Marketing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak, R.K.A.; Jeyakumar, S. Marketing Management; Educreation Publishing: Delhi, India, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Magno, F.; Cassia, F. Establishing thought leadership through social media in B2B settings: Effects on customer relationship performance. J. Bus. Ind. Mark. 2019, 35, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagowati, D.; Dutta, D.M. A Study on Literature Review for Identifying the Factors Impacting Digital Marketing. Int. J. Sales. Mark. Manag. Res. Dev. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, J.; Raihan, A.; Tanchangya, T.; Ridwan, M. Optimizing the digital marketing landscape: A comprehensive exploration of artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, applications, advantages, and challenges. Front. Financ. 2024, 2, 6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.-C. Viral advertising in social media: Participation in Facebook groups and responses among college-aged users. J. Interact. Advert. 2011, 12, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangeshwer, D.K. E-commerce or Internet Marketing: A business Review from Indian context. Int. J. Serv. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ištvanić, M.; Milić, D.C.; Krpić, Z. Digital marketing in the business environment. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. Syst. 2017, 8, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, S. Digital marketing and its impact on buying behaviour of youth. Int. J. Res. Manag. Bus. Stud. 2017, 4, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Nadaraja, R.; Yazdanifard, R. Social media marketing: Advantages and disadvantages. Cent. South. N. Hempsh. Univ. 2013, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Trivedi, J.Y. A study on Marketing Strategies of small and Medium Sized Enterprises. Res. J. Manag. Sci. 2013, 2319, 1171. [Google Scholar]
- Yasmin, A.; Tasneem, S.; Fatema, K. Effectiveness of digital marketing in the challenging age: An empirical study. Int. J. Manag. Sci. Bus. Adm. 2015, 1, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, R. Digital marketing in Indian context. Int. J. Comput. Eng. Manag. 2016, 19, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Todor, R.D. Blending traditional and digital marketing. Bull. Transilv. Univ. Brasov. Econ. Sci. Ser. V. 2016, 9, 51. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, A. Usefulness of Digital Marketing to the Government of India. IJCSN Int. J. Comput. Sci. Netw. 2016, 5, 721–724. [Google Scholar]
- Kannan, P.K. Digital marketing: A framework, review and research agenda. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2017, 34, 22–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.; Frost, R.; Sinha, N. E-Marketing; Pearson Upper: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kaka, N. Digital India: Technology to Transform a Connected Nation; McKinsey & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Yamin, A. Bin Impact of digital marketing as a tool of marketing communication: A behavioral perspective on consumers of Bangladesh. Am. J. Trade Policy 2017, 4, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López García, J.J.; Lizcano, D.; Ramos, C.M.; Matos, N. Digital marketing actions that achieve a better attraction and loyalty of users: An analytical study. Futur. Internet 2019, 11, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.-L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Sakhuja, S.; Nijjer, S. Recent trends of green human resource management: Text mining and network analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 84916–84935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, S.; Omarkhail, E.A. Research constituent, intellectual structure and current trends in environmental sustainability-an analytical retrospective. Discov. Sustain. 2024, 5, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Sharma, C.; Sharma, S.; Asenso, E. Broadening the Research Pathways in Smart Agriculture: Predictive Analysis Using Semiautomatic Information Modeling. J. Sens. 2022, 2022, 5442865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Chanana, N. The intersection of artificial intelligence and human resources: Transforming journey using natural language processing. Iran. J. Comput. Sci. 2025, 8, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakas, D.P.; Giannakopoulos, N.T. Big data contribution in desktop and mobile devices comparison, regarding airlines’ digital brand name effect. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2021, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra, D.R.B.; Jalil, C.M.; Jalil, E.M.; Coelho, L.E.; Netto, E.C.; Freitas, J.; Monteiro, L.; Santos, T.; Souza, C.; Hoagland, B.; et al. Comparing web-based venues to recruit gay, bisexual, and other cisgender men who have sex with men to a large HIV prevention service in Brazil: Evaluation study. JMIR Form. Res. 2022, 6, e33309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killian, G.; McClure, T.; Smith, S. Course projects as value co-creation tools: Developing university collaboration opportunities. Mark. Educ. Rev. 2024, 34, 44–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkasi, N.; Rezakhah, S. A modified CRITIC with a reference point based on fuzzy logic and hamming distance. Knowledge-Based Syst. 2022, 255, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munizu, M.; Alam, S.; Pono, M.; Riyadi, S. Do digital marketing, integrated supply chain, and innovation capability affect competitiveness, and creative industry performance? Int. J. Data Netw. Sci. 2024, 8, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, V.; Ramachandran, K.K.; Chenxi, W.; Mangairkarasi, V.; Konecna, Z. AI in data-driven marketing: Decoding consumer choices and behaviours. In Data Engineering for Data-Driven Marketing; Emerald Publishing Limited: Leeds, UK, 2025; pp. 33–45. [Google Scholar]
- Drugova, E.S.; Zhelnovakova, M.F.; Pomuleva, Y.A.; Vayrakh, Y.V. Digital marketing technologies in the promotion of modern construction organizations. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings, Irkutsk, Russian, 29–30 April 2022; Volume 2434, p. 60002. [Google Scholar]
- Rumangkit, S.; Rahmatika, R.A. Virtual Influencers Revolutionizing Marketing: A Bibliometric Deep Dive into Emerging Trends and Future Prospects. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Informatics, Multimedia, Cyber and Information System (ICIMCIS), Jakarta, Indonesia, 20–21 November 2024; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mrad, M.; Ramadan, Z.; Tóth, Z.; Nasr, L.; Karimi, S. Virtual influencers versus real connections: Exploring the phenomenon of virtual influencers. J. Advert. 2025, 54, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alawi, A.I.; Saleh, Z.A.; Al Saffar, E.M.; Wahab, F. Factors Affecting Consumers’ Online Purchase Intention through Social Media Platforms in Saudi Arabia and Bahrain. Arab. Gulf J. Sci. Res. 2020, 38, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Panigrahi, A.; Das, A.; Krishnan, A.; Samanta, D.; Bhattacharya, A.; Dutta, S. Search engine optimization for digital marketing to raise the rank, traffic, and usability of the website. In Human-Centric Smart Computing: Proceedings of ICHCSC 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Boyland, E.; Thivel, D.; Mazur, A.; Ring-Dimitriou, S.; Frelut, M.-L.; Weghuber, D. Digital food marketing to young people: A substantial public health challenge. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2020, 76, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyland, E.; Spanakis, P.; O’Reilly, C.; Christiansen, P. Associations between everyday exposure to food marketing and hunger and food craving in adults: An ecological momentary assessment study. Appetite 2024, 196, 107241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabregu-Vokshi, M.; Ogruk-Maz, G.; Yildirim, S.; Dedaj, B.; Zeqiri, A. 21st century digital skills of higher education students during Covid-19—Is it possible to enhance digital skills of higher education students through E-Learning? Educ. Inf. Technol. 2024, 29, 103–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha, M.S.; Aseesh, Y.; Pise, A. Fundamentals of Data-Driven Marketing. In Predictive Analytics and Generative AI for Data-Driven Marketing Strategies; Chapman and Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, D.; Sharma, M.; Brahmbhatt, A.; Patra, P.K.; Shaikh, A.; Sattanathan, S. AI and Machine Learning in Digital Marketing: Revolutionizing Customer Engagement and Decision Making. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Materials (ICACCM), Dehradun, India, 22–23 November 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, D. Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) for industry applications: Enhancing transparency, trust, and informed decision-making in business operation. Trust. Inf. Decis. Bus. Oper. 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.-W.; Botella-Carrubi, D.; Blanco-González-Tejero, C. The empirical study of digital marketing strategy and performance in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2024, 200, 123142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Shah, J.; Joshi, S.; Youssef, A.B.; Misra, A. Digital Innovation and Sustainability Driven Consumer Behavior: A Review and Research Agenda. Preprints 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, L.; Free, C. Marketing dataveillance and digital privacy: Using theories of justice to understand consumers’ online privacy concerns. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 107–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthraa, A.; Dixitb, S.; Garga, S.; Singha, A.; Anchalc, M. Ethical Leadership in the Digital Age: Guiding Principles for Web 3.0. Web 3.0 Unleashed Transform. Ind. Build. Ethical Fram. 2025, 25, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Terho, H.; Singh, R.; Rangarajan, D. Enhancing B2B sales through digital transformation: Insights into effective sales enablement. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2025, 125, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groene, N.; Zakharov, S. Introduction of AI-based sales forecasting: How to drive digital transformation in food and beverage outlets. Discov. Artif. Intell. 2024, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.P. Leveraging Digital Transformation in Marketing of Home-Stay Businesses to Promote Tourism in the Hospitality Industry. In Technology and Luxury Hospitality; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2024; pp. 93–115. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Barua, C.S. Leveraging digital innovations in tourism marketing: A study of destination promotion strategies. Int. J. Bus. Manag. Res. 2024, 12, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisprimandoyo, D.A.; Sufa, S.A.; Wardani, D.T.; Widiyanto, S. Exploring the relationship between social media engagement, customer reviews, and brand perceptions: A comprehensive study in retail industry. Int. J. Business Law Educ. 2024, 5, 1584–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qashmal, M.; Adam, M.; Nizam, A. Evaluating the Influence of Digital Marketing, Service Quality, and Product Excellence on Loyalty Through the Mediating Role of Customer Satisfaction. Indatu J. Manag. Account. 2024, 2, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theocharis, D.; Tsekouropoulos, G. Sustainable consumption and branding for Gen Z: How brand dimensions influence consumer behavior and adoption of newly launched technological products. Sustainability 2025, 17, 4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
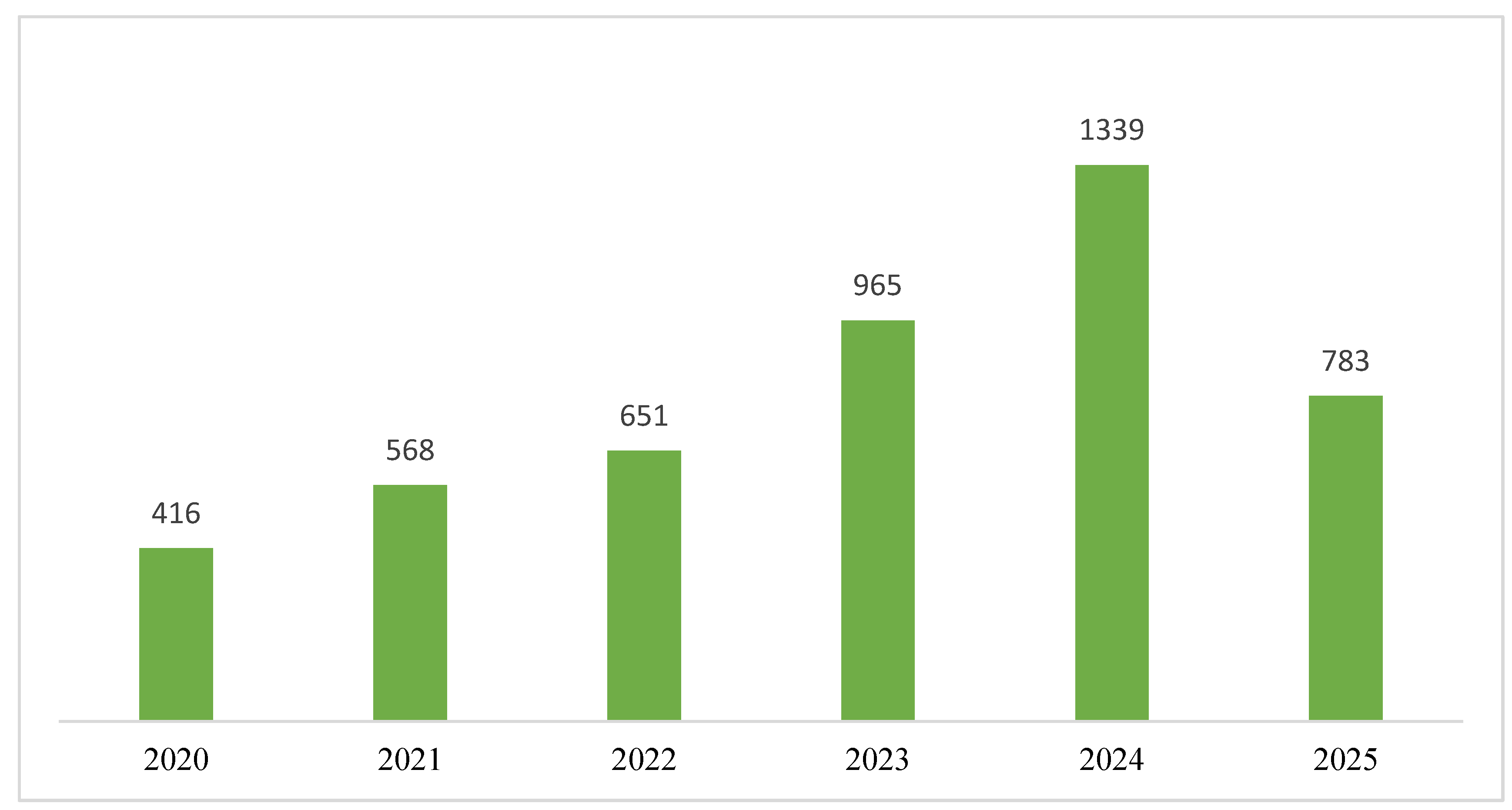


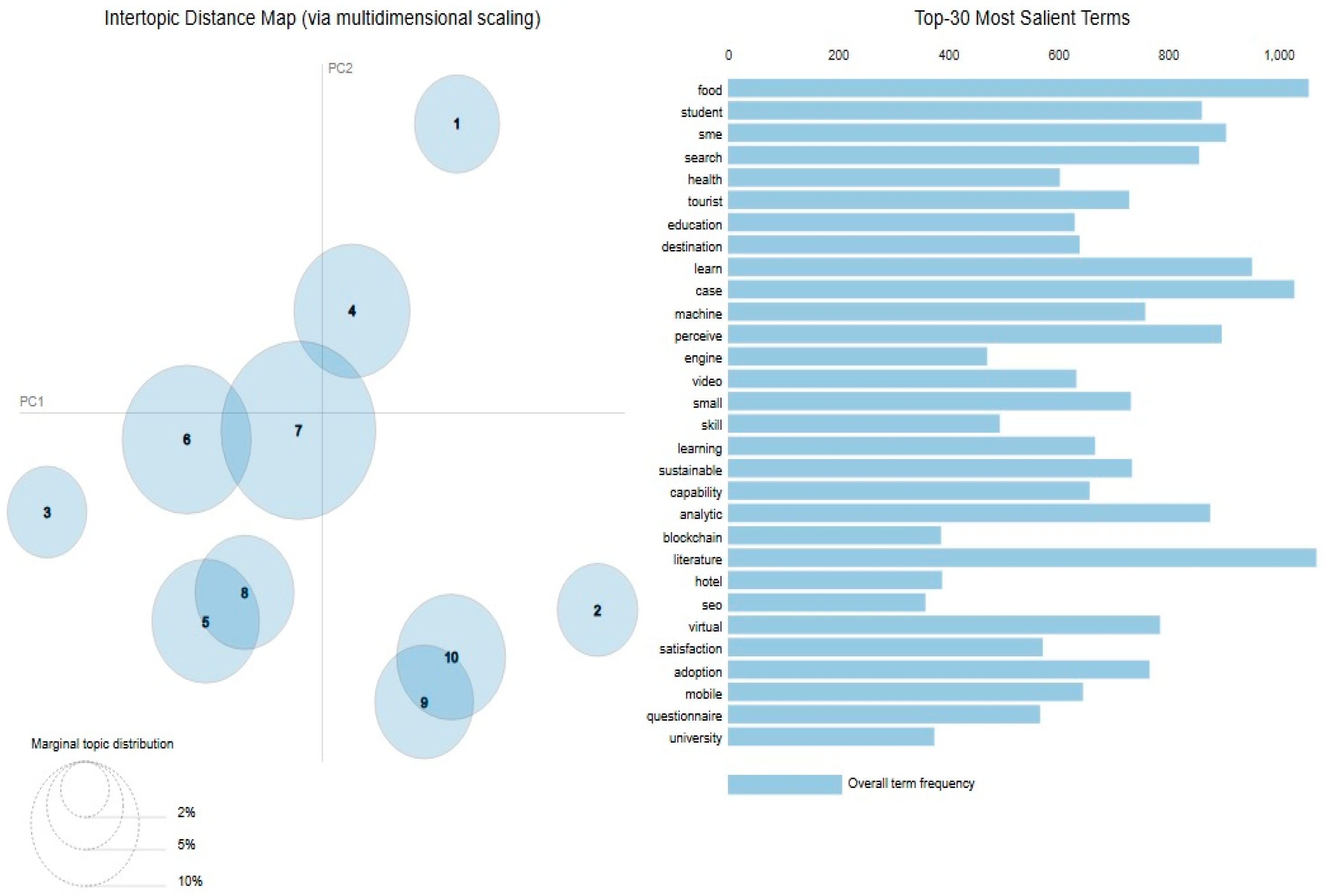
| Dominant Topic | Document Count | Total Document Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Marketing and Blockchain | 227 | 4.81 |
| Digital Marketing in the Health and Food Industry | 186 | 3.94 |
| Digital Marketing in Higher Education and Skill Enhancement | 196 | 4.15 |
| Machine Learning and Analytics in Digital Marketing | 542 | 11.48 |
| Adoption of Digital Marketing for SMEs and Sustainable Business | 483 | 10.23 |
| Digital Marketing Trends and Ethics | 740 | 15.67 |
| Sales and Digital Transformation | 1102 | 23.34 |
| Digital Marketing in Tourism and Hospitality | 399 | 8.45 |
| Digital Media and Audience Perception | 355 | 7.52 |
| Digital Marketing and Consumer Satisfaction using Service Quality | 492 | 10.42 |
| Topic | Top Article Contribution % | Topic Terms | Topic | Top Article |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 95.83 | search, engine, blockchain, seo, web, mobile, optimization, analytic, internet, security, iot, privacy, traffic, big, smart, page, cost, device, data, firm | Digital Marketing and Blockchain | [29] |
| 2 | 99.88 | food, health, post, child, exposure, beverage, healthcare, participant, advertisement, adolescent, policy, people, young, patient, unhealthy, medical, alcohol, target, country, relate | Digital Marketing in Health and Food Industry | [30] |
| 3 | 88.52 | student, education, case, skill, university, learn, institution, educational, sport, project, level, program, work, job, learning, startup, competency, knowledge, academic, educator | Digital Marketing in Higher Education and Skill Enhancement | [31] |
| 4 | 99.84 | machine, learn, learning, propose, technique, time, campaign, sentiment, algorithm, feature, deep, language, prediction, rate, accuracy, dataset, text, generate, target, analytic | Machine Learning and Analytics in Digital Marketing | [32] |
| 5 | 99.73 | sme, small, capability, sustainable, adoption, sustainability, msme, firm, financial, economic, resource, chain, green, entrepreneur, community, economy, supply, transformation, environmental, sector | Adoption of Digital Marketing for SMEs and Sustainable business | [33] |
| 6 | 99.73 | drive, chapter, marketer, practice, global, landscape, highlight, analytic, future, emerge, potential, book, ethical, dynamic, evolve, framework, opportunity, key, comprehensive, leverage | Digital Marketing Trends and Ethics | [34] |
| 7 | 99.8 | sale, activity, channel, pandemic, internet, covid, license, springer, promotion, article, transformation, main, environment, create, exclusive, time, sector, traditional, world, work | Sales and Digital Transformation | [35] |
| 8 | 99.33 | tourist, destination, literature, hotel, travel, article, luxury, future, fashion, trend, cultural, virtual, reality, bibliometric, area, field, systematic, hospitality, methodology, purpose | Digital Marketing in Tourism and Hospitality | [36] |
| 9 | 99.71 | video, virtual, theory, visual, live, emotional, interaction, generate, audience, message, perceive, attitude, perception, response, investigate, type, follower, positive, image, framework | Digital Media and Audience Perception | [37] |
| 10 | 99.72 | perceive, satisfaction, quality, questionnaire, survey, variable, structural, equation, loyalty, sample, positive, respondent, affect, behaviour, collect, trust, attitude, awareness, test, significantly | Digital Marketing and Consumer Satisfaction using Service Quality | [38] |
| Dominant Topic | Document Count | Papers in 2020–2021 | Papers in 2022–2023 | Papers in 2024–2025 | 2020–2021 (%) | 2022–2023 (%) | 2024–2025 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Marketing and Blockchain | 227 | 61 | 86 | 80 | 1.29 | 1.82 | 1.69 |
| Digital Marketing in Health and Food Industry | 186 | 50 | 69 | 67 | 1.06 | 1.46 | 1.42 |
| Digital Marketing in Higher Education and Skill Enhancement | 196 | 54 | 74 | 68 | 1.14 | 1.57 | 1.44 |
| Machine Learning and Analytics in Digital Marketing | 542 | 146 | 206 | 190 | 3.09 | 4.36 | 4.02 |
| Adoption of Digital Marketing for SMEs and Sustainable Business | 483 | 129 | 183 | 171 | 2.73 | 3.88 | 3.62 |
| Digital Marketing Trends and Ethics | 740 | 199 | 282 | 259 | 4.21 | 5.97 | 5.48 |
| Sales and Digital Transformation | 1102 | 295 | 417 | 390 | 6.25 | 8.83 | 8.26 |
| Digital Marketing in Tourism and Hospitality | 399 | 107 | 149 | 143 | 2.27 | 3.16 | 3.03 |
| Digital Media and Audience Perception | 355 | 95 | 129 | 131 | 2.01 | 2.73 | 2.77 |
| Digital Marketing and Consumer Satisfaction using Service Quality | 492 | 133 | 184 | 175 | 2.82 | 3.90 | 3.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sharma, C.; Rath, P.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Chen, H.-Y. Mapping the Evolution of Digital Marketing Research Using Natural Language Processing. Information 2025, 16, 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110942
Sharma C, Rath P, Kumar R, Sharma S, Chen H-Y. Mapping the Evolution of Digital Marketing Research Using Natural Language Processing. Information. 2025; 16(11):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110942
Chicago/Turabian StyleSharma, Chetan, Pranabananda Rath, Rajender Kumar, Shamneesh Sharma, and Hsin-Yuan Chen. 2025. "Mapping the Evolution of Digital Marketing Research Using Natural Language Processing" Information 16, no. 11: 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110942
APA StyleSharma, C., Rath, P., Kumar, R., Sharma, S., & Chen, H.-Y. (2025). Mapping the Evolution of Digital Marketing Research Using Natural Language Processing. Information, 16(11), 942. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16110942








