Modality Information Aggregation Graph Attention Network with Adversarial Training for Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph Completion
Abstract
1. Introduction
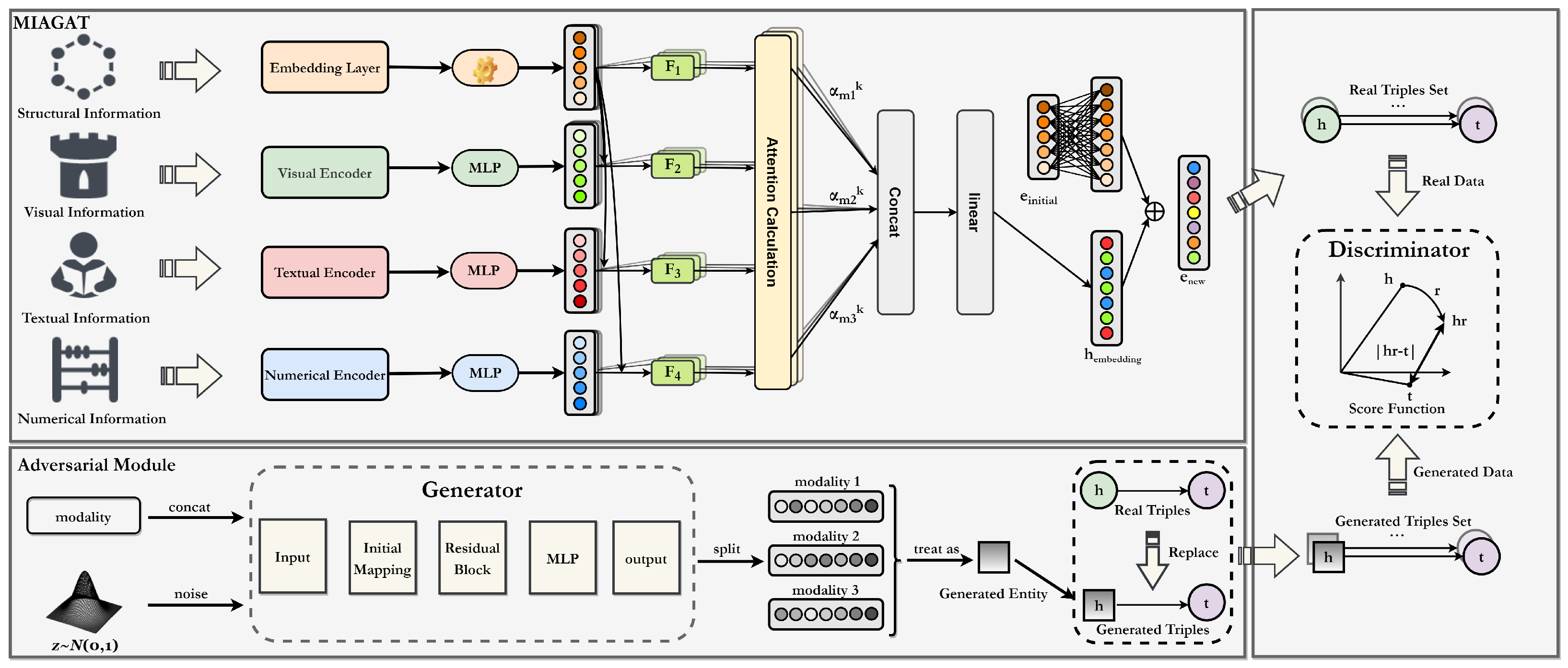
- We propose a novel modality information aggregation graph attention network (MIAGAT) designed to dynamically integrate four modalities (structural, textual, visual, and numerical features). By assessing the importance of each modality relative to the target entity, MIAGAT employs an adaptive attention mechanism to optimize weight allocation, producing integrated entity embeddings with deeply enriched multi- modal features.
- We propose an adversarial training (AT) module that generates synthetic adversarial entities as training examples, substantially enhancing the model robustness and generalization capability in complex multi-modal scenarios and concurrently strengthening its ability to comprehend and represent multi-modal knowledge with greater precision and effectiveness.
- We evaluated the performance of MIAGAT-AT through comprehensive experiments and analyses on link prediction tasks across three public benchmarks. The experimental results demonstrate that MIAGAT-AT significantly outperforms 18 existing baseline models, demonstrating its effectiveness.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph Completion
2.2. Adversarial Training in Knowledge Graph Completion
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Definition
3.2. Modal Feature Extraction
3.3. Modality Information Aggregation Module
3.4. Adversarial Training Module
3.4.1. Generator Design
3.4.2. Discriminator Choice
3.4.3. Optimization Objective
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Baselines
4.3. Implemention Details
5. Experimental Results
5.1. Comparison with Existing Methods
5.2. Generalization Experiment
5.3. Case Study
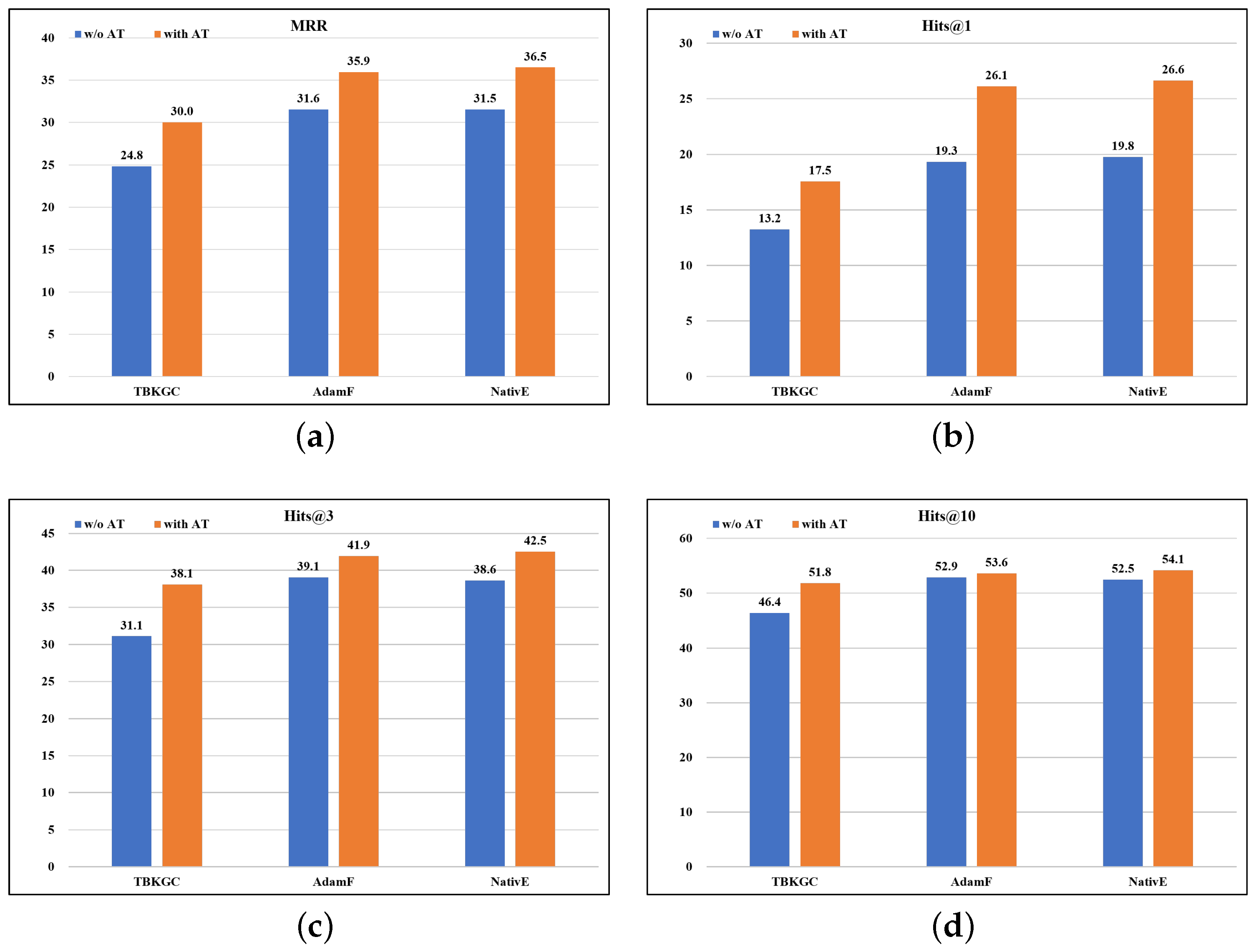
5.4. Ablation Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Z.; Cruz, M.J.; Guevara, M.; Wang, T.; Deshpande, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Retrieval-augmented generation with knowledge graphs for customer service question answering. In Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 2905–2909. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cheng, D.; Li, C.; Morimoto, Y. Ripple knowledge graph convolutional networks for recommendation systems. Mach. Intell. Res. 2024, 21, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Peng, H.; Li, L. Sublinear smart semantic search based on knowledge graph over encrypted database. Comput. Secur. 2025, 151, 104319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.; Meng, L.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Tu, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, S.; Liu, X.; Sun, F.; He, K. A survey of knowledge graph reasoning on graph types: Static, dynamic, and multi-modal. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 9456–9478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, L.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, Y.; Pan, J.Z.; Song, W.; et al. Meaformer: Multi-modal entity alignment transformer for meta modality hybrid. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023; pp. 3317–3327. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J. Hyper-node relational graph attention network for multi-modal knowledge graph completion. ACM Trans. Multim. Comput. Commun. Appl. 2023, 19, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wei, X.; Nogueira dos Santos, C.N.; Wang, Z.; Nallapati, R.; Arnold, A.; Xiang, B.; Yu, P.S.; Cruz, I.F. Mixed-curvature multi-relational graph neural network for knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021, Ljubljana, Slovenia, 19–23 April 2021; pp. 1761–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xing, C. IMF: Interactive multimodal fusion model for link prediction. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 30 April–4 May 2023; pp. 2572–2580. [Google Scholar]
- Mousselly-Sergieh, H.; Botschen, T.; Gurevych, I.; Roth, S. A multimodal translation-based approach for knowledge graph representation learning. In Proceedings of the Seventh Joint Conference on Lexical and Computational Semantics, New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–6 June 2018; pp. 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, X.; Qi, G. Is visual context really helpful for knowledge graph? A representation learning perspective. In Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Virtual, 20–24 October 2021; pp. 2735–2743. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, R.; Liu, Z.; Luan, H.; Sun, M. Image-embodied knowledge representation learning. In Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2017), Melbourne, Australia, 19–25 August 2017; pp. 3140–3146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Zeng, D. Multimodal data enhanced representation learning for knowledge graphs. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2019), Budapest, Hungary, 14–19 July 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Yang, Z.; He, Y.; Cao, X.; Huang, Q. Otkge: Multi-modal knowledge graph embeddings via optimal transport. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 39090–39102. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W. Knowledge graph completion with pre-trained multimodal transformer and twins negative sampling. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2209.07084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, T.; Wu, S.; Zhou, J.; Chen, E. Relation-enhanced negative sampling for multimodal knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (ACM MM 2022), Lisbon, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 3857–3866. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, W. Modality-aware negative sampling for multi-modal knowledge graph embedding. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN 2023), Gold Coast, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Han, Q.; Sun, H.; Liu, C. Multi-modal knowledge graph representation based on counterfactual data enhanced learning link prediction. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Behavioural and Social Computing (BESC 2024), Okayama, Japan, 30 October–1 November 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W. Unleashing the power of imbalanced modality information for multi-modal knowledge graph completion. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Turin, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 17120–17130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Guo, L.; Xu, Y.; Hu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Chen, H. Native: Multi-modal knowledge graph completion in the wild. In Proceedings of the 47th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval (SIGIR 2024), Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 91–101. [Google Scholar]
- Velickovic, P.; Cucurull, G.; Casanova, A.; Romero, A.; Liò, P.; Bengio, Y. Graph attention networks. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2018), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Deng, Z.-H.; Nie, J.-Y.; Tang, J. RotatE: Knowledge graph embedding by relational rotation in complex space. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2019), New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Garcia-Duran, A.; Niepert, M.; Onoro-Rubio, D.; Rosenblum, D.S. MMKG: Multi-modal knowledge graphs. In Proceedings of the 16th Extended Semantic Web Conference (ESWC 2019), Portorož, Slovenia, 2–6 June 2019; pp. 459–474. [Google Scholar]
- Auer, S.; Bizer, C.; Kobilarov, G.; Lehmann, J.; Cyganiak, R.; Ives, Z. Dbpedia: A nucleus for a web of open data. In Proceedings of the 6th International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC 2007), Busan, Republic of Korea, 11–15 November 2007; pp. 722–735. [Google Scholar]
- Vrandečić, D.; Krötzsch, M. Wikidata: A free collaborative knowledgebase. Commun. ACM 2014, 57, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchanek, F.M.; Kasneci, G.; Weikum, G. Yago: A core of semantic knowledge. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on World Wide Web (WWW 2007), Banff, AB, Canada, 8–12 May 2007; pp. 697–706. [Google Scholar]
- Bordes, A.; Usunier, N.; Garcia-Duran, A.; Weston, J.; Yakhnenko, O. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2013, 26, 2787–2795. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.; He, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, K.; Zhao, J. Knowledge graph embedding via dynamic mapping matrix. In Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (ACL-IJCNLP 2015), Beijing, China, 26–31 July 2015; pp. 687–696. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Yih, S.W.-T.; He, X.; Gao, J.; Deng, L. Embedding entities and relations for learning and inference in knowledge bases. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2015), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Trouillon, T.; Welbl, J.; Riedel, S.; Gaussier, É.; Bouchard, G. Complex embeddings for simple link prediction. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2016), New York, NY, USA, 19–24 June 2016; pp. 2071–2080. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.; He, S.; Liu, S. MMKRL: A robust embedding approach for multi-modal knowledge graph representation learning. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 7480–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chung, C.; Lee, H.; Jo, S.; Whang, J. VISTA: Visual-textual knowledge graph representation learning. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 7314–7328. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L.; Wang, W.Y. KBGAN: Adversarial learning for knowledge graph embeddings. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT 2018), New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–6 June 2018; pp. 1470–1480. [Google Scholar]
| Datasets | Entities | Relations | Train | Valid | Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MKG-W | 15,000 | 169 | 34,196 | 4276 | 4274 |
| MKG-Y | 15,000 | 28 | 21,310 | 2665 | 2663 |
| DB15K | 12,842 | 279 | 79,222 | 9902 | 9904 |
| Baselines | DB15K | MKG-W | MKG-Y | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRR | H@1 | H@3 | H@10 | MRR | H@1 | H@3 | H@10 | MRR | H@1 | H@3 | H@10 | |
| TransE [26] | 24.9 | 12.8 | 31.5 | 47.1 | 29.2 | 21.1 | 33.2 | 44.2 | 30.7 | 23.5 | 35.2 | 43.4 |
| TransD [27] | 21.5 | 8.3 | 29.9 | 44.2 | 25.6 | 15.9 | 33.0 | 40.2 | 26.4 | 17.0 | 33.6 | 40.3 |
| DistMult [28] | 23.0 | 14.8 | 26.3 | 39.6 | 21.0 | 15.9 | 22.3 | 30.9 | 25.0 | 19.3 | 27.8 | 36.0 |
| ComplEx [29] | 27.5 | 18.4 | 31.6 | 45.4 | 24.9 | 19.1 | 26.7 | 36.7 | 28.7 | 22.3 | 32.1 | 40.9 |
| RotatE [21] | 29.3 | 17.9 | 36.1 | 49.7 | 33.7 | 26.8 | 36.7 | 46.7 | 35.0 | 29.1 | 38.4 | 45.3 |
| IKRL [11] | 26.8 | 14.1 | 34.9 | 49.1 | 32.4 | 26.1 | 34.8 | 44.1 | 33.2 | 30.4 | 34.3 | 38.3 |
| TBKGC [9] | 28.4 | 15.6 | 37.0 | 49.9 | 31.5 | 25.3 | 34.0 | 43.2 | 34.0 | 30.5 | 35.3 | 40.1 |
| TransAE [12] | 28.1 | 21.3 | 31.2 | 41.2 | 30.0 | 21.2 | 34.9 | 44.7 | 28.1 | 25.3 | 29.1 | 33.0 |
| MMKRL [30] | 26.8 | 13.9 | 35.1 | 49.4 | 30.1 | 22.2 | 34.1 | 44.7 | 36.8 | 31.7 | 39.8 | 45.3 |
| RSME [10] | 29.8 | 24.2 | 32.1 | 40.3 | 29.2 | 23.4 | 32.0 | 40.4 | 34.4 | 31.8 | 36.1 | 39.1 |
| VBKGC [14] | 30.6 | 19.8 | 37.2 | 49.4 | 30.6 | 24.9 | 33.0 | 40.9 | 37.0 | 33.8 | 38.8 | 42.3 |
| OTKGE [13] | 23.9 | 18.5 | 25.9 | 34.2 | 34.4 | 28.9 | 36.3 | 44.9 | 35.5 | 32.0 | 37.2 | 41.4 |
| IMF [8] | 32.3 | 24.2 | 36.0 | 48.2 | 34.5 | 28.8 | 36.6 | 45.4 | 35.8 | 33.0 | 37.1 | 40.6 |
| VISTA [31] | 30.4 | 22.5 | 33.6 | 45.9 | 32.9 | 26.1 | 35.4 | 45.6 | 30.5 | 24.9 | 32.4 | 41.5 |
| AdaMF [18] | 35.1 | 25.3 | 41.1 | 52.9 | 35.9 | 29.0 | 39.0 | 48.4 | 38.6 | 34.3 | 40.6 | 45.8 |
| KBGAN [32] | 25.7 | 9.9 | 37.0 | 51.9 | 29.5 | 22.2 | 34.9 | 40.6 | 29.7 | 22.8 | 34.9 | 40.2 |
| MANS [16] | 28.8 | 16.9 | 36.6 | 49.3 | 30.9 | 24.9 | 33.6 | 41.8 | 29.0 | 25.3 | 31.4 | 34.5 |
| MMRNS [15] | 29.7 | 17.9 | 36.7 | 51.0 | 34.1 | 27.4 | 37.5 | 46.8 | 35.9 | 30.5 | 39.1 | 45.5 |
| MIAGAT-AT* | 35.7 | 26.0 | 41.4 | 53.2 | 36.7 | 30.0 | 39.8 | 48.9 | 38.8 | 34.7 | 40.7 | 45.9 |
| MIAGAT-AT | 37.0 | 28.5 | 41.9 | 53.0 | 36.7 | 30.0 | 39.8 | 48.9 | 38.8 | 34.7 | 40.7 | 45.9 |
| Missing Triple: (Matt Damon, actedIn, ?) | ||
| Rank | MIAGAT-AT | Score |
| 1 | The Good Shepherd | 2.21 |
| 2 | Rounders | 2.03 |
| 3 | Behind the Candelabra | 1.90 |
| Rank | Mean | Score |
| 1 | The Good Shepherd | 1.99 |
| 2 | Rounders | 1.74 |
| 3 | J.K.Simmons | 1.73 |
| Missing Triple: (German Iran, isLocatedIn, ?) | ||
| Rank | MIAGAT-AT | Score |
| 1 | Kharqan Rural District | 3.14 |
| 2 | Bastam District | 3.06 |
| 3 | Kalat-e Hay-ye Gharbi | 1.44 |
| Rank | Mean | Score |
| 1 | Kharqan Rural District | 2.94 |
| 2 | Bastam District | 2.84 |
| 3 | Kalat-e Hay-ye Gharbi | 1.08 |
| Module | Settings | MRR | Hits@1 | Hits@3 | Hits@10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIAGAT | w/o Visual | 31.3 | 18.7 | 39.2 | 53.1 |
| w/o Textual | 31.4 | 19.3 | 39.1 | 52.9 | |
| w/o Numerical | 31.1 | 18.3 | 39.2 | 53.0 | |
| w/o MS | 31.5 | 19.0 | 39.3 | 53.1 | |
| w/o AT | 32.5 | 20.1 | 40.3 | 53.1 | |
| AT | Residual-CNN | 36.2 | 27.1 | 41.4 | 53.1 |
| DenseResidual-CNN | 36.0 | 26.9 | 41.3 | 53.0 | |
| DenseResidual-MLP | 36.9 | 28.4 | 41.9 | 52.8 | |
| Residual-MLP | 37.0 | 28.5 | 41.9 | 53.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yilahun, H.; Aili, E.; Imam, S.; Hamdulla, A. Modality Information Aggregation Graph Attention Network with Adversarial Training for Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph Completion. Information 2025, 16, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100907
Yilahun H, Aili E, Imam S, Hamdulla A. Modality Information Aggregation Graph Attention Network with Adversarial Training for Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph Completion. Information. 2025; 16(10):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100907
Chicago/Turabian StyleYilahun, Hankiz, Elyar Aili, Seyyare Imam, and Askar Hamdulla. 2025. "Modality Information Aggregation Graph Attention Network with Adversarial Training for Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph Completion" Information 16, no. 10: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100907
APA StyleYilahun, H., Aili, E., Imam, S., & Hamdulla, A. (2025). Modality Information Aggregation Graph Attention Network with Adversarial Training for Multi-Modal Knowledge Graph Completion. Information, 16(10), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100907






