The Impact of the Organization on the Autonomy of Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. Research on Agent Autonomy
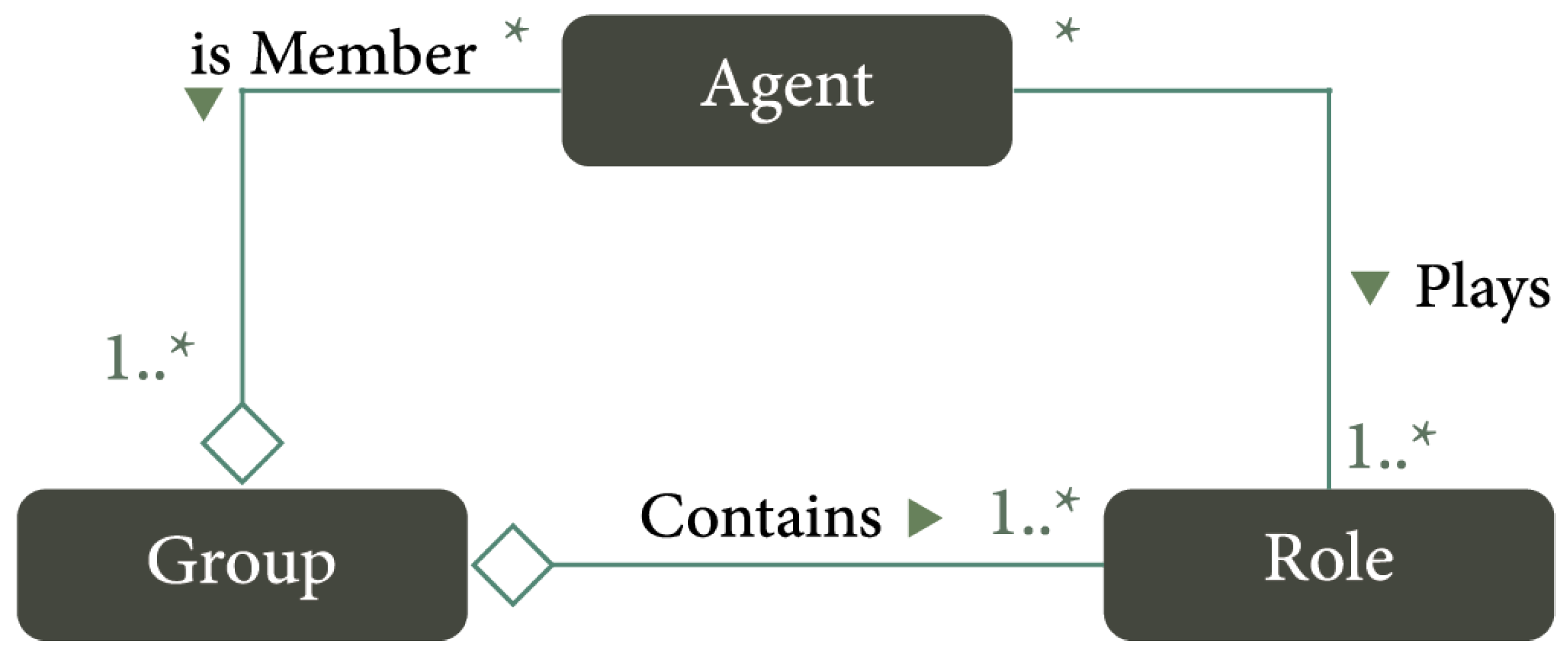
2.2. Research on Multi-Agent Organizations
2.3. The Relationship Between Autonomy and Organization
3. Proposed Metrics
3.1. Behavioral Wealth (BW)
3.2. Service Wealth (SW)
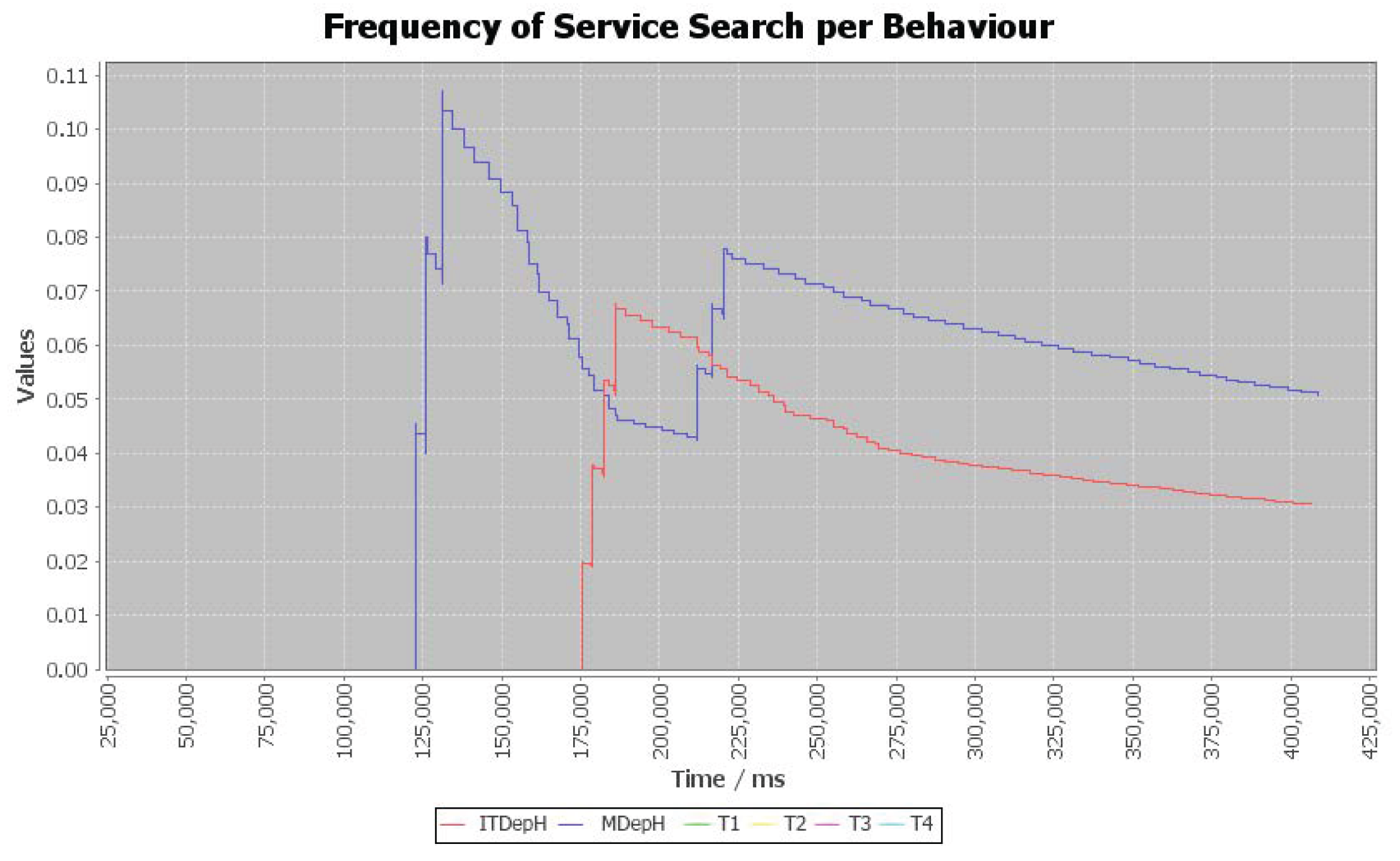
3.3. Frequency of Service Searches per Time (FoSST)
3.4. Frequency of Service Searches per Behavior (FoSSB)
3.5. Number of Service Searches (NoSS)
3.6. Number of Service Demands per Behavior (NoSDB)
3.7. Number of Provided Services per Demand (NoPSD)
- The two metrics, Behavioral Wealth (BW) and Service Wealth (SW), will not be affected by the development paradigm of the system (with or without organization). In fact, the number of behaviors in each agent will be the same in both cases, with only minor differences due to additional behaviors for managing the organization (in the case of developing a multi-agent system with organization). Similarly, the services provided by the system will not be affected by whether it is implemented with or without organization.
- The metrics related to searching services—Frequency of Service Searches per Behavior (FoSSB), Frequency of Service Searches per Time (FoSST), and Number of Service Searches (NoSS)—will be reduced in systems with organization, because the organization allows agents to know the services provided by others without searching.
- The metrics related to the effectiveness of service requests—Number of Service Demands per Behavior (NoSDB) and Number of Provided Services per Demand (NoPSD)—will be improved when implementing a system with organization, because the authority relationships between agents will limit the refusal of service.
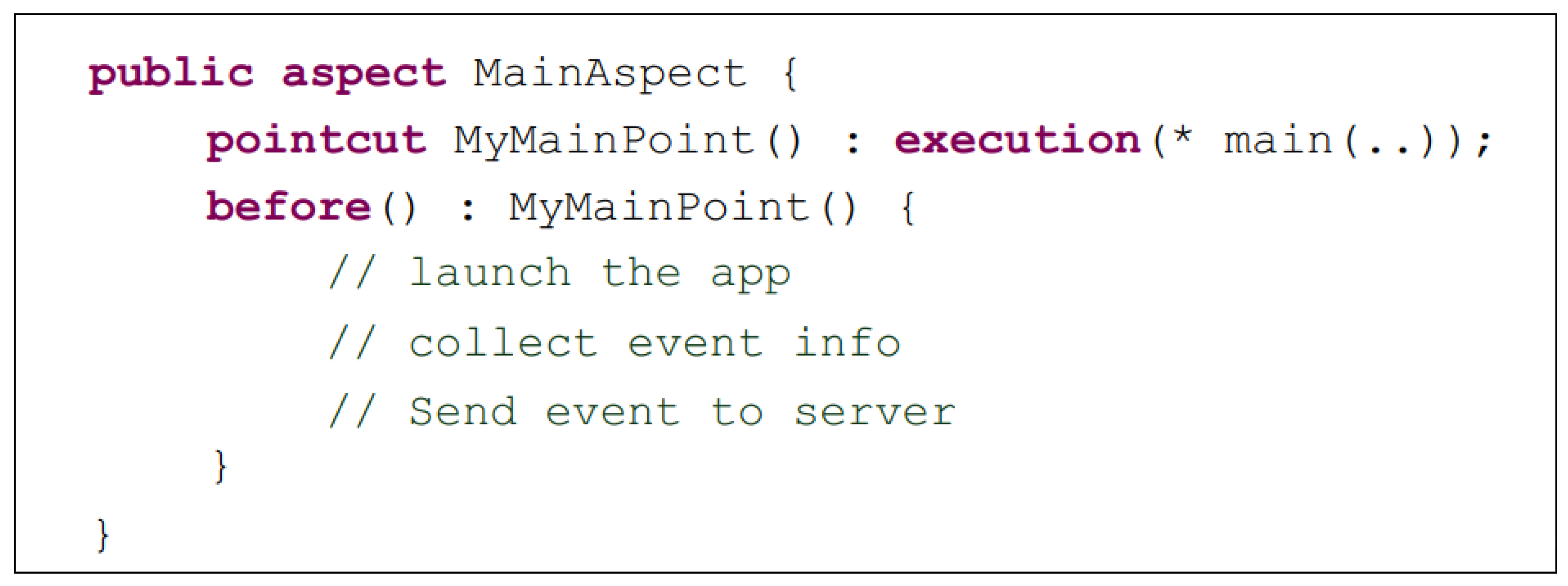
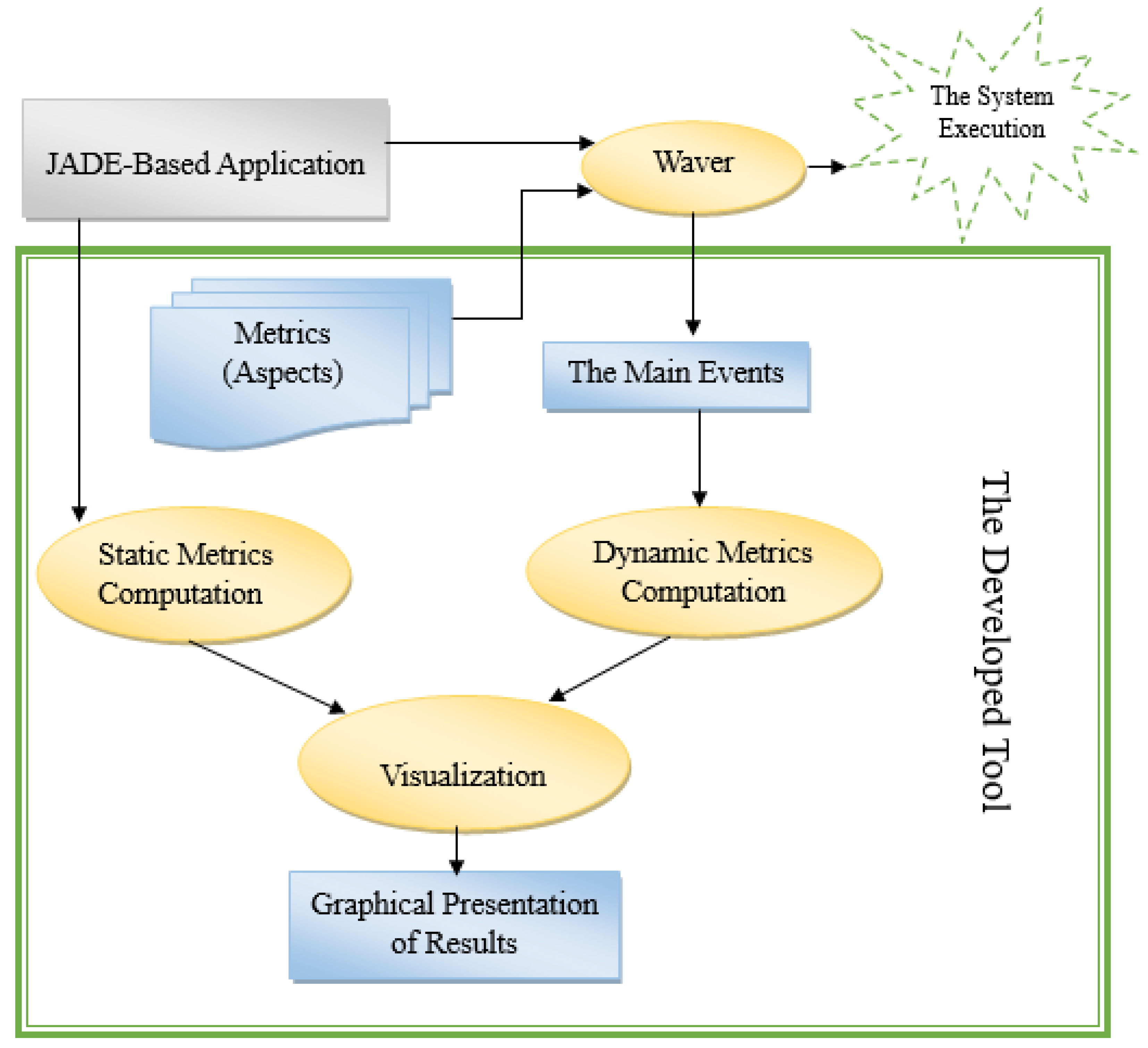
4. Measurement Tool
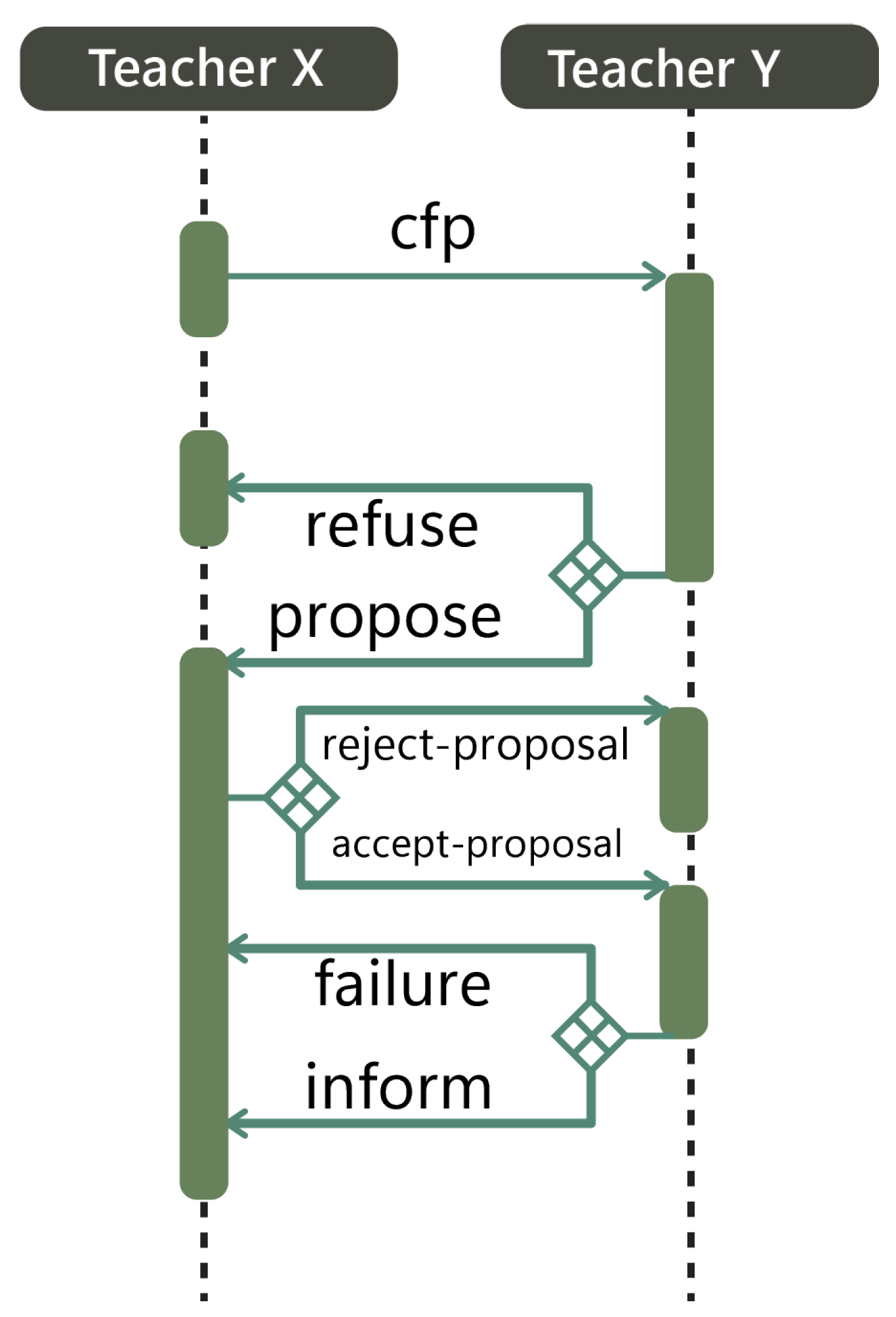
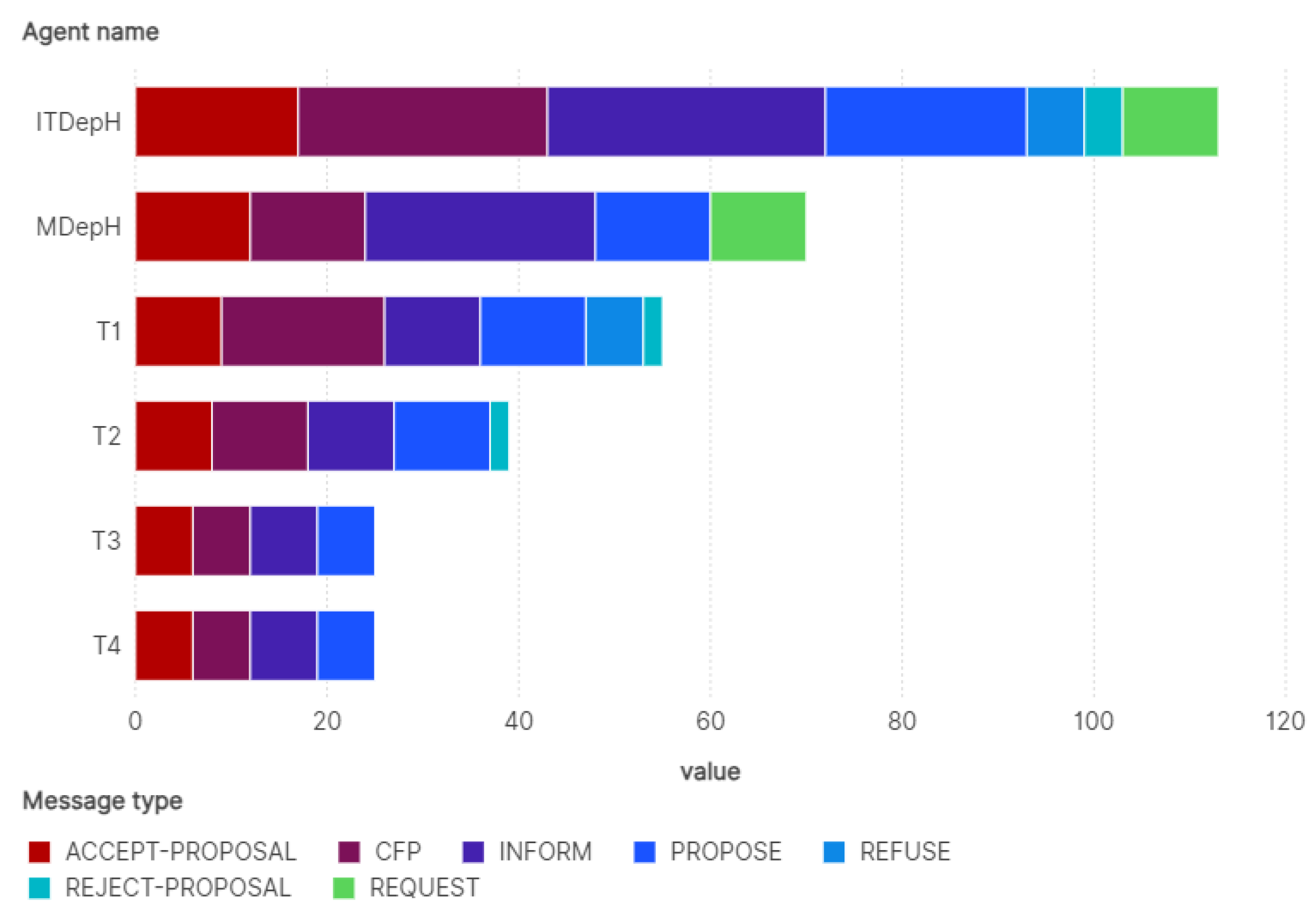
5. Case Study
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGR | Agent–Grou–Role |
| MAS | Multi-Agent Systems |
| BW | Behavioral Wealth |
| SW | Service Wealth |
| FoSST | Frequency of Service Searches per Time |
| FoSSB | Frequency of Service Searches per Behavior |
| NoSS | Number of Service Search |
| NoSDB | Number of Service Demands per Behavior |
| NoPSD | Number of Provided Services per Demand |
| JADE | Java Agent DEvelopment Framework |
| JADEX | Java Agent DEvelopment Framework Extension |
| GQM | Goal Question Metric |
References
- Wooldridge, M. An Introduction to Multiagent Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dorri, A.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jurdak, R. Multi-agent systems: A survey. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 28573–28593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.; Mascardi, V.; Rozier, K.Y.; Schlingloff, B.H.; Winikoff, M.; Yorke-Smith, N. Towards a framework for certification of reliable autonomous systems. Auton. Agents-Multi-Agent Syst. 2021, 35, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, J.; Egerstedt, M. Coordinated control of multi-robot systems: A survey. SICE J. Control. Meas. Syst. Integr. 2017, 10, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, S.A.; Ahmad, M.S.; Mustapha, A. Adjustable autonomy: A systematic literature review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2019, 51, 149–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ge, S.S.; He, W.; Ma, G.; Xie, L. Multilayer formation control of multi-agent systems. Automatica 2019, 109, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ren, W. On the Control of Multi-Agent Systems: A Survey; Foundations and Trends® in Systems and Control: Hanover, MA, USA, 2019; Volume 6, pp. 339–499. [Google Scholar]
- Tranier, J. Vers une Vision Intégrale des Systèmes Multi-Agents: Contribution à l’intégration des Concepts d’Agent, d’Environnement, d’Organisation et d’Institution. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Montpellier II-Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc, Montpellier, France, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Braynov, S.; Hexmoor, H. Quantifying relative autonomy in multiagent interaction. In Agent Autonomy; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 55–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ferber, J.; Gutknecht, O.; Michel, F. From agents to organizations: An organizational view of multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Agent-Oriented Software Engineering, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 15 July 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 214–230. [Google Scholar]
- Ferber, J.; Michel, F.; Báez, J. AGRE: Integrating environments with organizations. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environments for Multi-Agent Systems, New York, NY, USA, 19 July 2004; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 48–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, S.; Ferber, J. Agent Groupe Rôle et Service: Un modèle organisationnel pour les systèmes multi-agents ouverts. In Proceedings of the Actes du Colloque JFSMA, Carcassonne, France, 17–19 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Souidi, M.E.H.; Songhao, P.; Guo, L.; Lin, C. Multi-agent cooperation pursuit based on an extension of AALAADIN organisational model. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2016, 28, 1075–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebout, M.S.; Marir, T.; Gupta, V. NorAGR: A NORmative Agent Groupe Role Model for Organizational Centered Open Multi-Agent Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 Third International Conference on Theoretical and Applicative Aspects of Computer Science (ICTAACS), Skikda, Algeria, 5–6 December 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, H.A.; Shaheen, S. Towards a hybrid MAS organizational model: Combining the ACMAS and OCMAS viewpoints. Int. J. Organ. Collect. Intell. (IJOCI) 2017, 7, 18–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudjidj, A.; Merah, E.; Souidi, M.E.H. Towards a formal multi-agent organizational modeling framework based on category theory. Informatica 2021, 45, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laouadi, M.A.; Mokhati, F.; Seridi-Bouchelaghem, H. A formal framework for organization-centered multi-agent system specification: A rewriting logic based approach. Multiagent Grid Syst. 2017, 13, 395–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudeikat, J.; Kohler-Bußmeier, M. Towards integrating multi-agent organizations in OPC UA for developing adaptive cyber-physical systems. In Proceedings of the INFORMATIK 2022, Hambrug, Germany, 26–30 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, M.; d’Inverno, M. A Formal Framework for Agency and Autonomy. In Proceedings of the ICMAS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–14 June 1995; Volume 95, pp. 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, K.S.; Martin, C.E. Agent autonomy: Specification, measurement, and dynamic adjustment. In Proceedings of the Theautonomy Control Software Workshop at Autonomous Agents, Seattle, WA, USA, 1–5 May 1999; Citeseer: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 1999, pp. 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Alonso, F.; Fuertes, J.L.; Martínez, L.; Soza, H. Towards a set of measures for evaluating software agent autonomy. In Proceedings of the 2009 Eighth Mexican International Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Guanajuato, Mexico, 9–13 November 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Suzanne Barber, K.; Goel, A.; Martin, C.E. Dynamic adaptive autonomy in multi-agent systems. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2000, 12, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scerri, P.; Pynadath, D.; Tambe, M. Adjustable autonomy in real-world multi-agent environments. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Autonomous Agents, Montreal, QB, Canada, 28 May–1 June 2001; pp. 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich, M.A.; Adams, J.A.; Scheutz, M. Autonomy reconsidered: Towards developing multi-agent systems. In Intelligent Systems and Applications, Proceedings of the 2021 Intelligent Systems Conference (IntelliSys), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 3–4 September 2022; Springer: Berline/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 573–592. [Google Scholar]
- Dodig-Crnkovic, G.; Burgin, M. A systematic approach to autonomous agents. Philosophies 2024, 9, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jiang, Y.E.; Li, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, R.; Wang, S.; et al. Agents: An open-source framework for autonomous language agents. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2309.07870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putta, P.; Mills, E.; Garg, N.; Motwani, S.; Finn, C.; Garg, D.; Rafailov, R. Agent q: Advanced reasoning and learning for autonomous ai agents. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.07199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Tihanyi, N.; Debbah, M. From llm reasoning to autonomous ai agents: A comprehensive review. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.19678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.A.; Shaheen, S.I.; Amin, M.H. Organization of multi-agent systems: An overview. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.09032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignum, V.; Noriega, P.; Sensoy, M.; Sichman, J.S. Coordination, Organizations, Institutions, and Norms in Agent Systems XI; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boes, J.; Migeon, F. Self-organizing multi-agent systems for the control of complex systems. J. Syst. Softw. 2017, 134, 12–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhaksmana, K.M.; Murakami, Y.; Ishida, T. Role-based modeling for designing agent behavior in self-organizing multi-agent systems. Int. J. Softw. Eng. Knowl. Eng. 2018, 28, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dong, H.; Lesser, V.; Zhang, C. Roma: Multi-agent reinforcement learning with emergent roles. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.08039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, O. Autonomy in an organizational context. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Computational Autonomy, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 14 July 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 195–208. [Google Scholar]
- Schillo, M.; Fischer, K. A taxonomy of autonomy in multiagent organisation. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Computational Autonomy, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 14 July 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, M.A.; Ahmad, M.S.; Mohd Yusoff, M.Z.; Mustapha, A. A review of norms and normative multiagent systems. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 684587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carabelea, C.; Boissier, O.; Florea, A. Autonomy in multi-agent systems: A classification attempt. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Computational Autonomy, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 14 July 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 103–113. [Google Scholar]
- Beavers, G.; Hexmoor, H. Types and limits of agent autonomy. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Computational Autonomy, Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 14 July 2003; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Marir, T.; Mokhati, F.; Bouchelaghem-Seridi, H.; Benaissa, B. Dynamic Metrics for Multi-agent Systems Using Aspect-Oriented Programming: Application to DIMA Platform. In Proceedings of the German Conference on Multiagent System Technologies, Klagenfurt, Austria, 27–30 September 2016; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 58–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kiczales, G.; Lamping, J.; Mendhekar, A.; Maeda, C.; Lopes, C.; Loingtier, J.M.; Irwin, J. Aspect-oriented programming. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Object-Oriented Programming, Jyväskylä, Finland, 9–13 June 1997; Springer: Berline/Heidelberg, Germany, 1997; pp. 220–242. [Google Scholar]
- Kiczales, G.; Hilsdale, E.; Hugunin, J.; Kersten, M.; Palm, J.; Griswold, W.G. An Overview of AspectJ. In ECOOP 2001—Object-Oriented Programming, Proceedings of the 15th European Conference, Budapest, Hungary, 18–22 June 2001; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Knudsen, J.L., Ed.; Springer: Berline/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001; Volume 2072, pp. 327–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JADE. Java Agent DEvelopment Framework (JADE). 2024. Available online: https://jade.tilab.com/ (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Pokahr, A.; Braubach, L.; Lamersdorf, W. Jadex: A BDI reasoning engine. In Multi-Agent Programming: Languages, Platforms and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 149–174. [Google Scholar]
- Van Solingen, R.; Basili, V.; Caldiera, G.; Rombach, H.D. Goal question metric (gqm) approach. In Encyclopedia of Software Engineering; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]

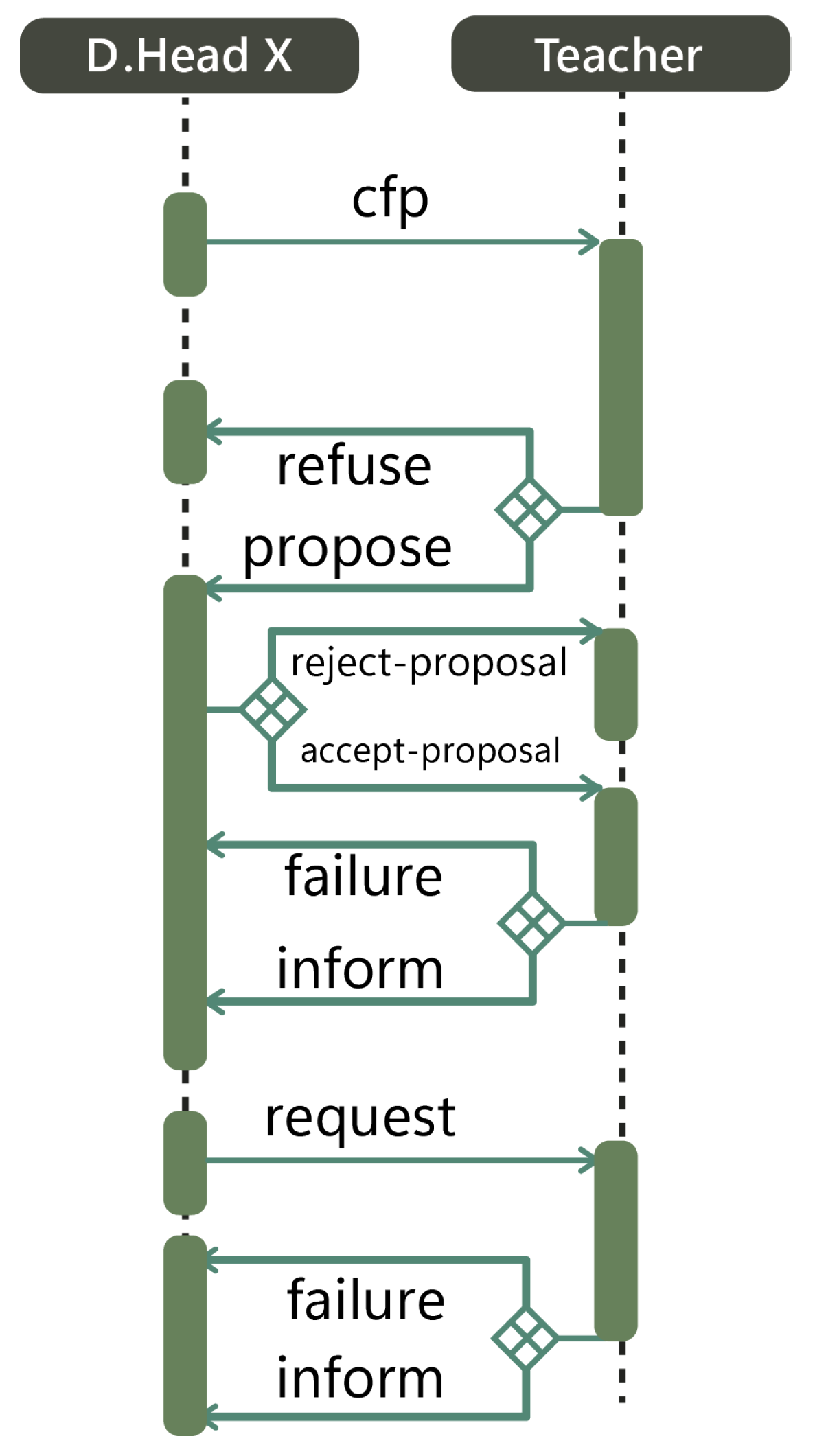
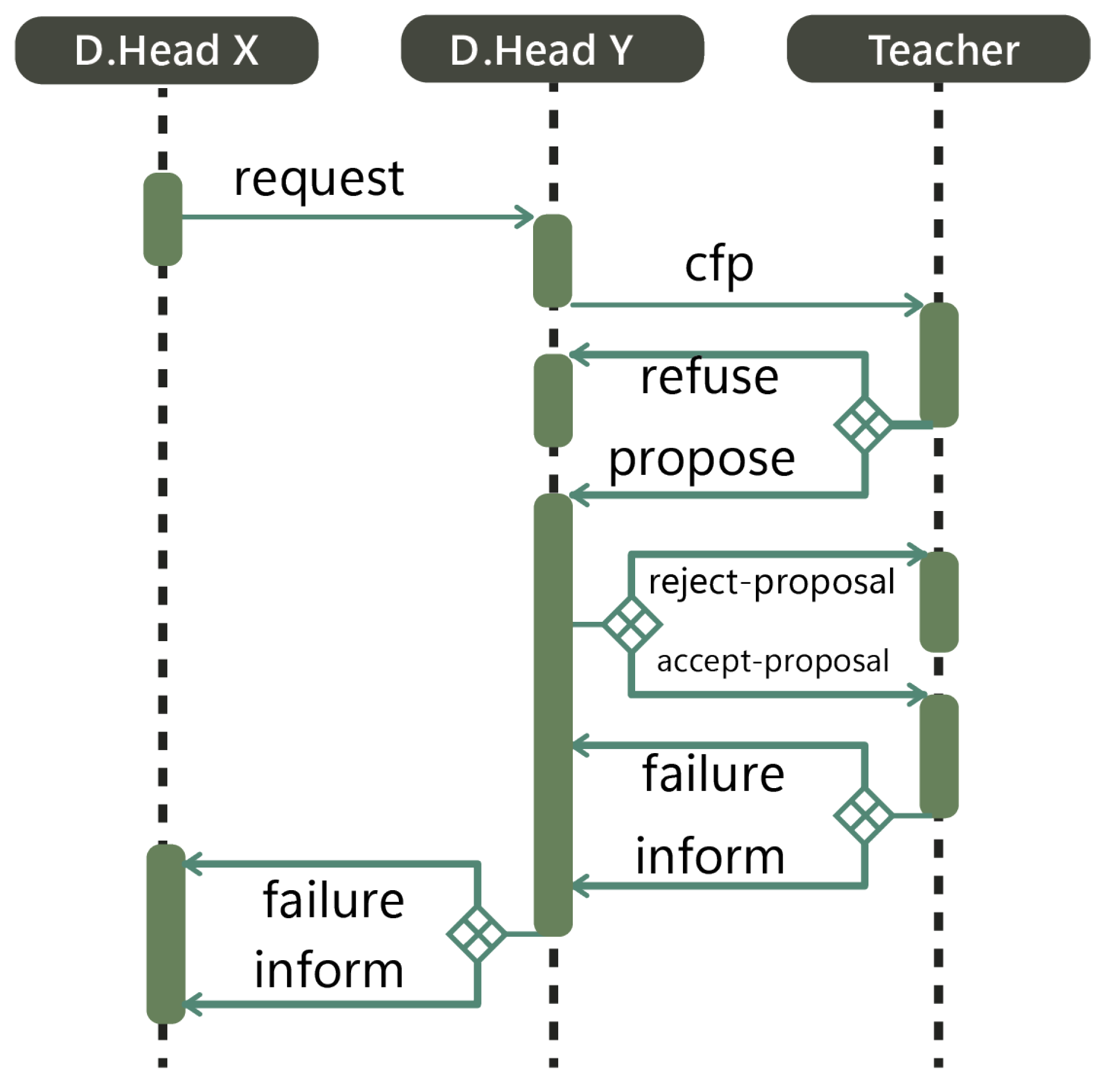
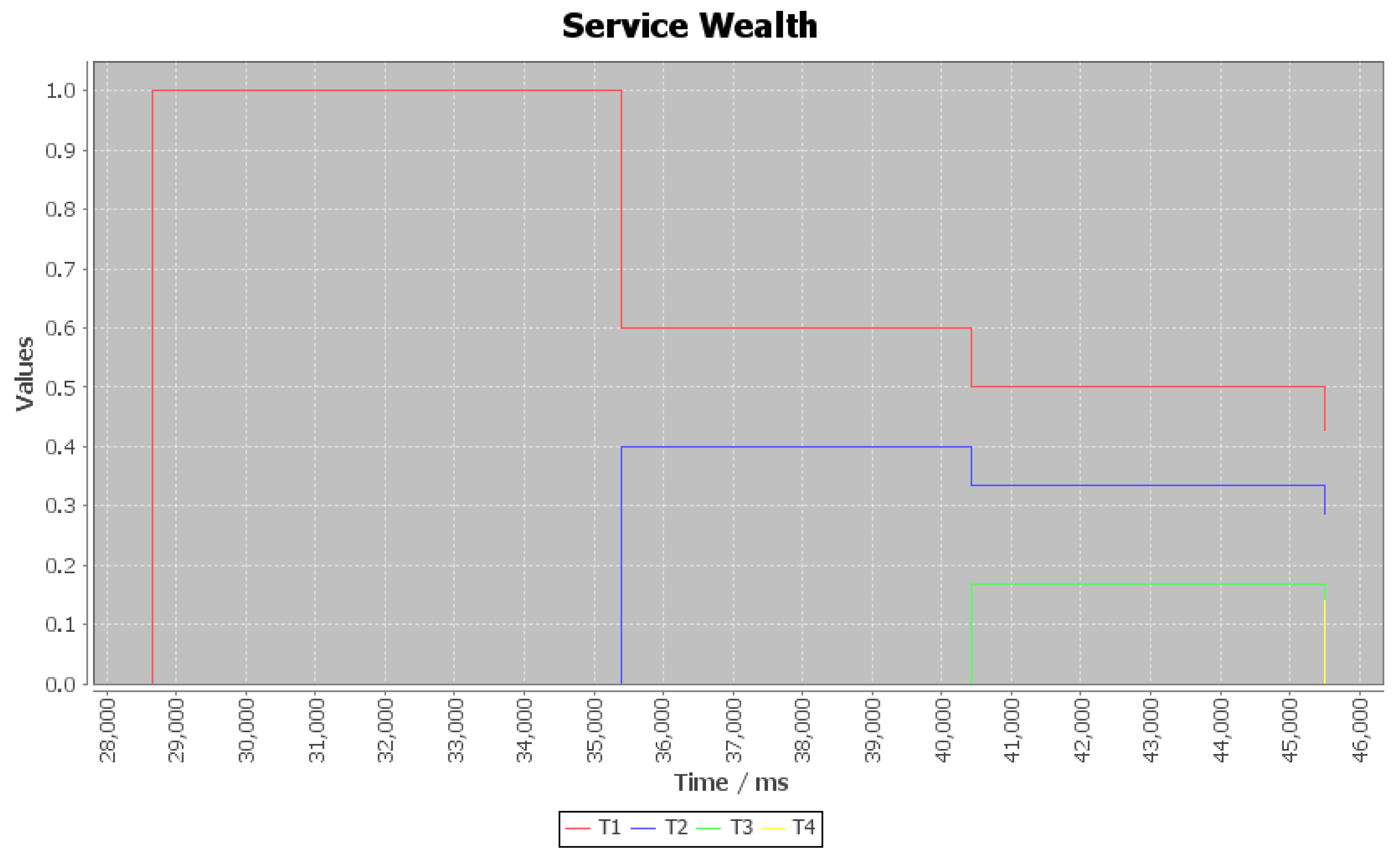
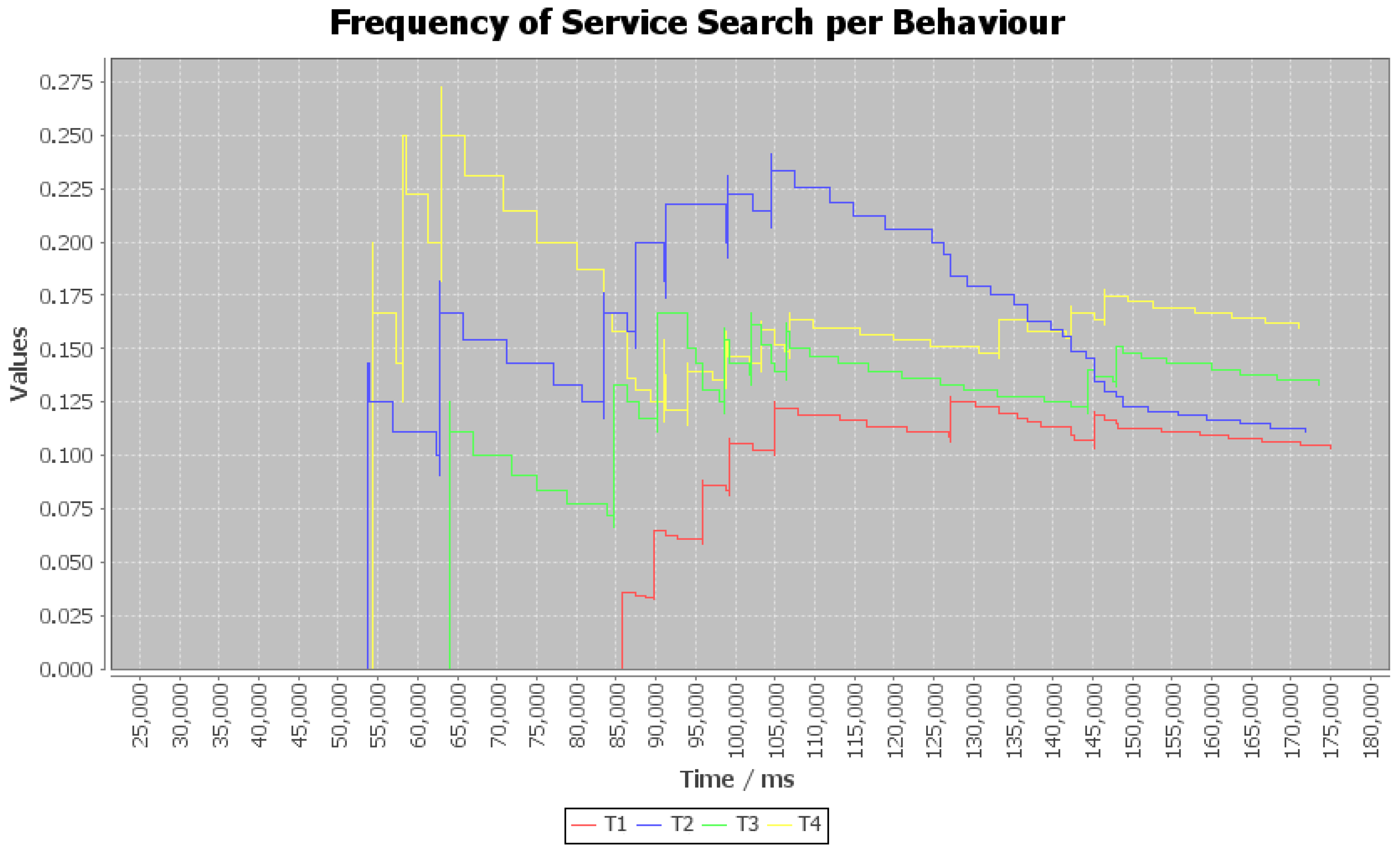


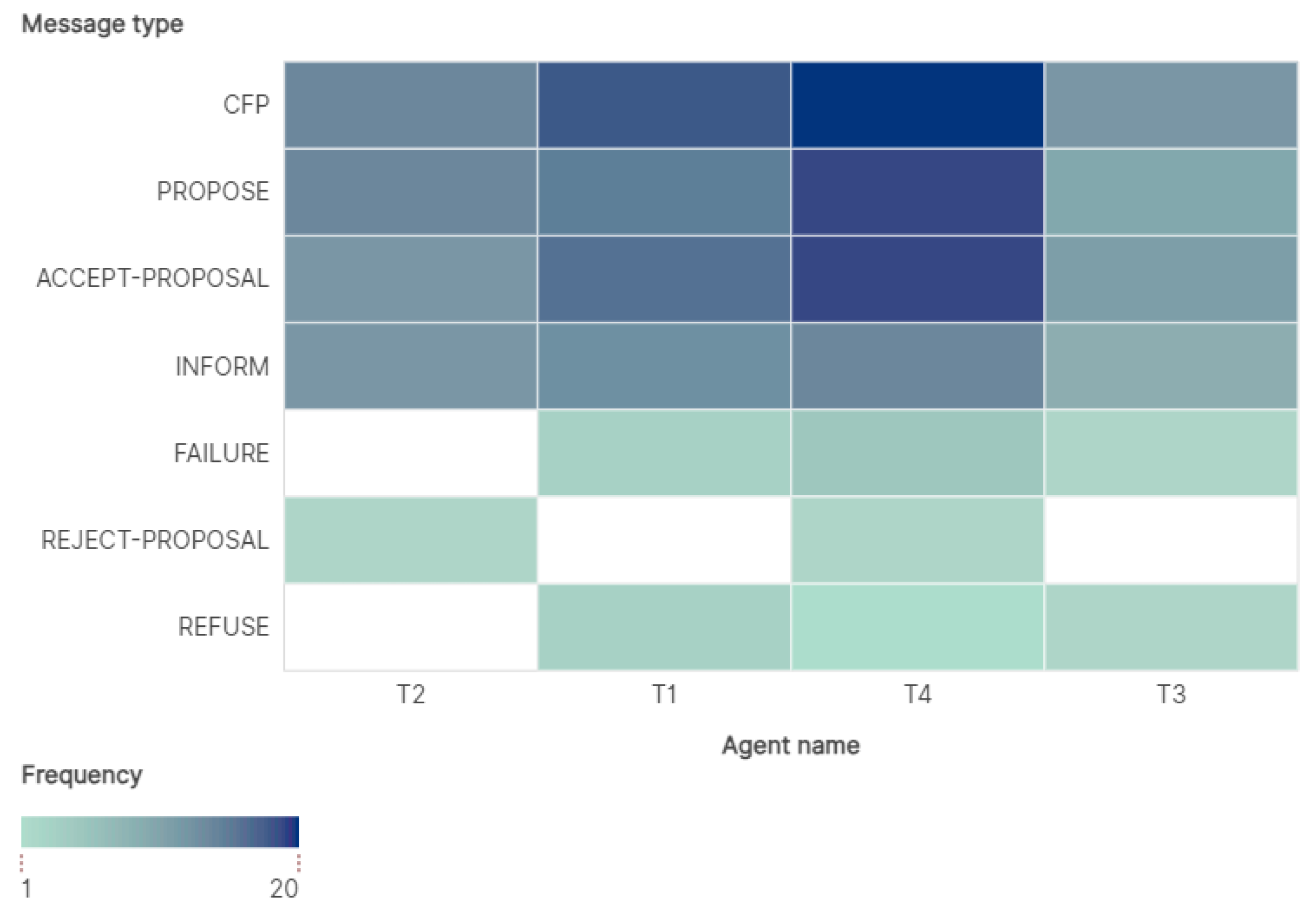
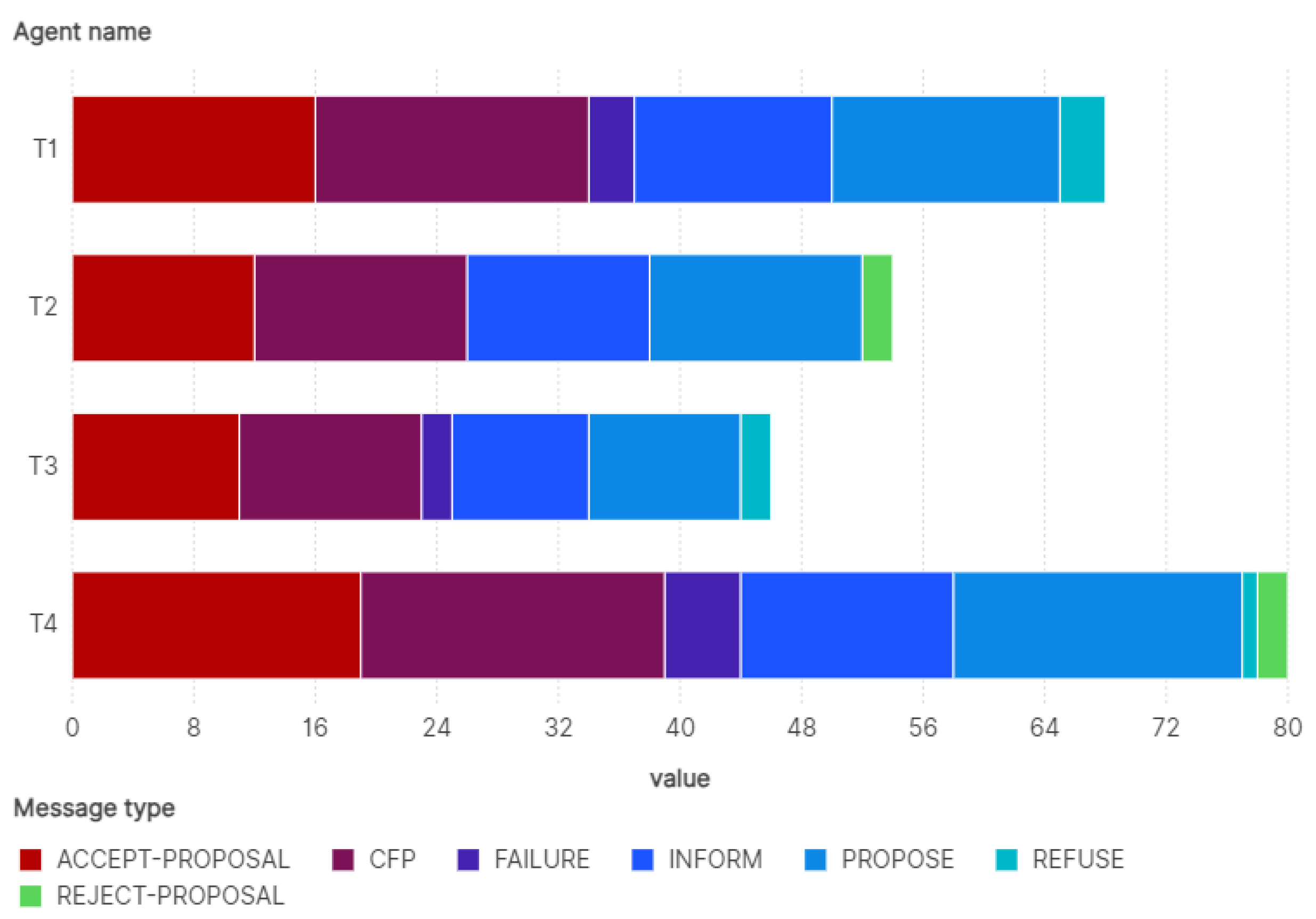
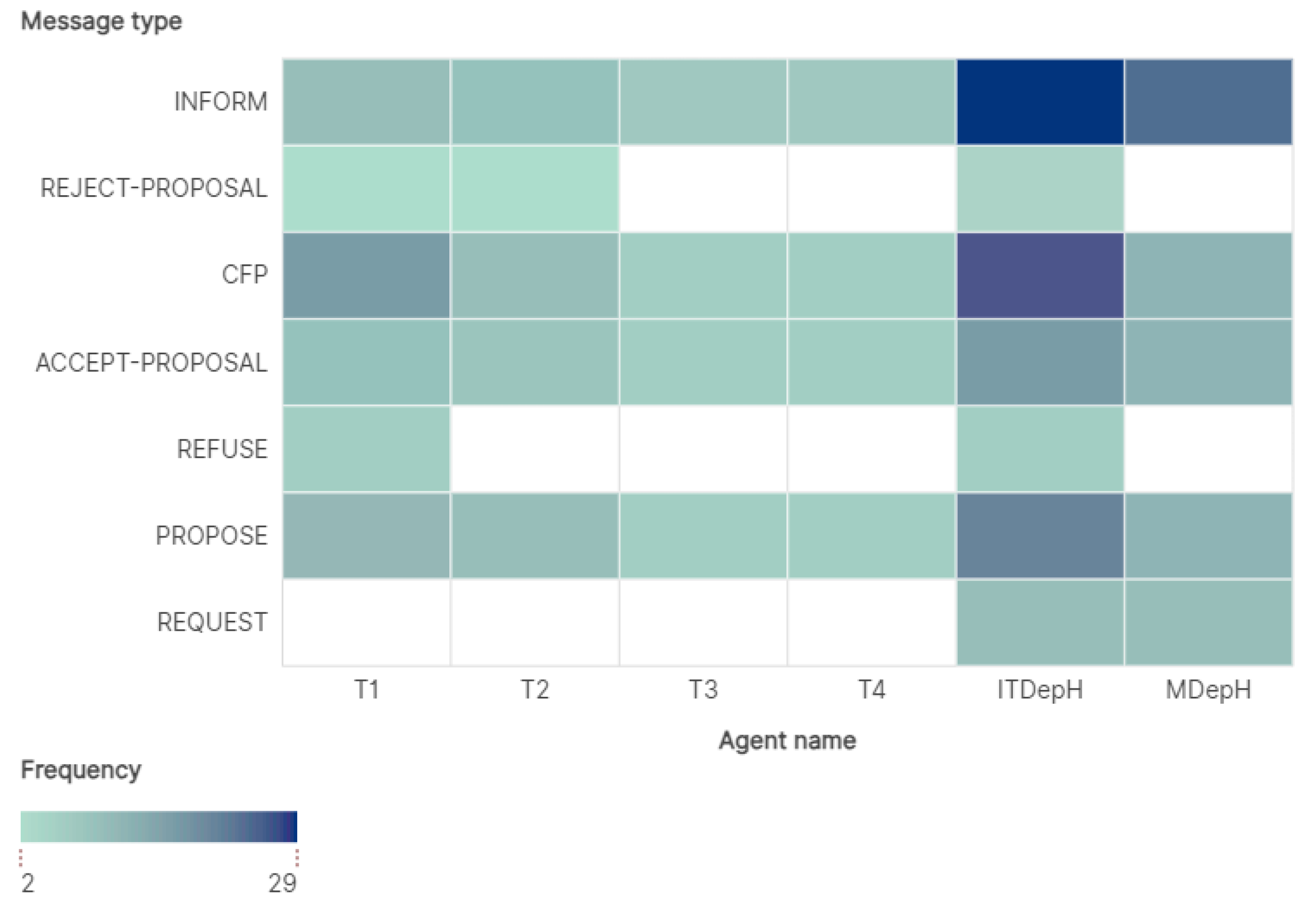
| Courses (Services) | Number of Sessions | Courses for T1 | Courses for T2 | Courses for T3 | Courses for T4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADT | 7 | X | |||
| Operating System | 6 | X | X | ||
| Network | 4 | X | X | ||
| Algebra | 6 | X | |||
| Analysis | 6 | X |
| Courses (Services) | Required Services in Mathematics Department | Required Services in IT Department |
|---|---|---|
| ADT | 3 | 4 |
| Operating System | 2 | 4 |
| Network | 1 | 3 |
| Algebra | 4 | 2 |
| Analysis | 4 | 2 |
| Without Organization | |
|---|---|
| Time/ms | Events |
| 0 | The beginning of execution |
| 28,615 | Creation of the agent T1 |
| 28,630 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T1 |
| 35,354 | Creation of agent T2 |
| 35,385 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T2 |
| 40,402 | Creation of agent T3 |
| 40,418 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T3 |
| 45,475 | Creation of agent T4 |
| 45,491 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T4 |
| With Organization | |
|---|---|
| Time/ms | Events |
| 0 | The beginning of execution |
| 42,669 | Creation of agent ITDepH |
| 42,700 | Behaviors scheduling of agent ITDepH |
| 51,863 | Creation of agent MDepH |
| 51,878 | Behaviors scheduling of agent MDepH |
| 68,578 | Creation of agent T1 |
| 68,593 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T1 |
| 76,743 | Creation of agent T2 |
| 76,754 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T2 |
| 86,520 | Creation of agent T3 |
| 86,552 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T3 |
| 94,303 | Creation of agent T4 |
| 94,319 | Behaviors scheduling of agent T4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tamrabet, Z.; Nessah, D.; Marir, T.; Gupta, V.; Mokhati, F. The Impact of the Organization on the Autonomy of Agents. Information 2025, 16, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100838
Tamrabet Z, Nessah D, Marir T, Gupta V, Mokhati F. The Impact of the Organization on the Autonomy of Agents. Information. 2025; 16(10):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100838
Chicago/Turabian StyleTamrabet, Zouheyr, Djamel Nessah, Toufik Marir, Varun Gupta, and Farid Mokhati. 2025. "The Impact of the Organization on the Autonomy of Agents" Information 16, no. 10: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100838
APA StyleTamrabet, Z., Nessah, D., Marir, T., Gupta, V., & Mokhati, F. (2025). The Impact of the Organization on the Autonomy of Agents. Information, 16(10), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/info16100838







