Multivariate Hydrological Modeling Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Water Level Forecasting †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Framework
2.1. Study Area
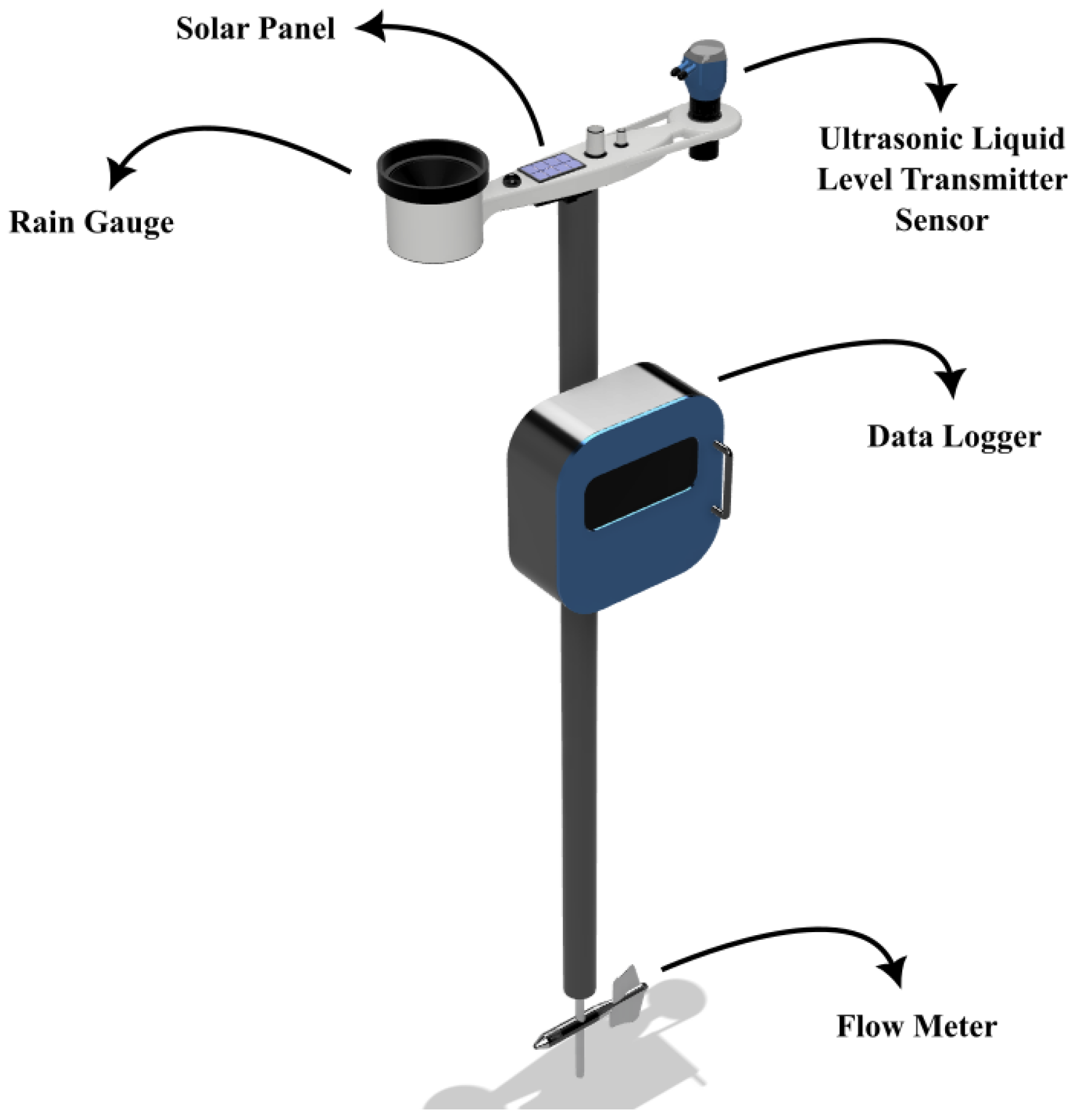
2.2. Experimental Setup
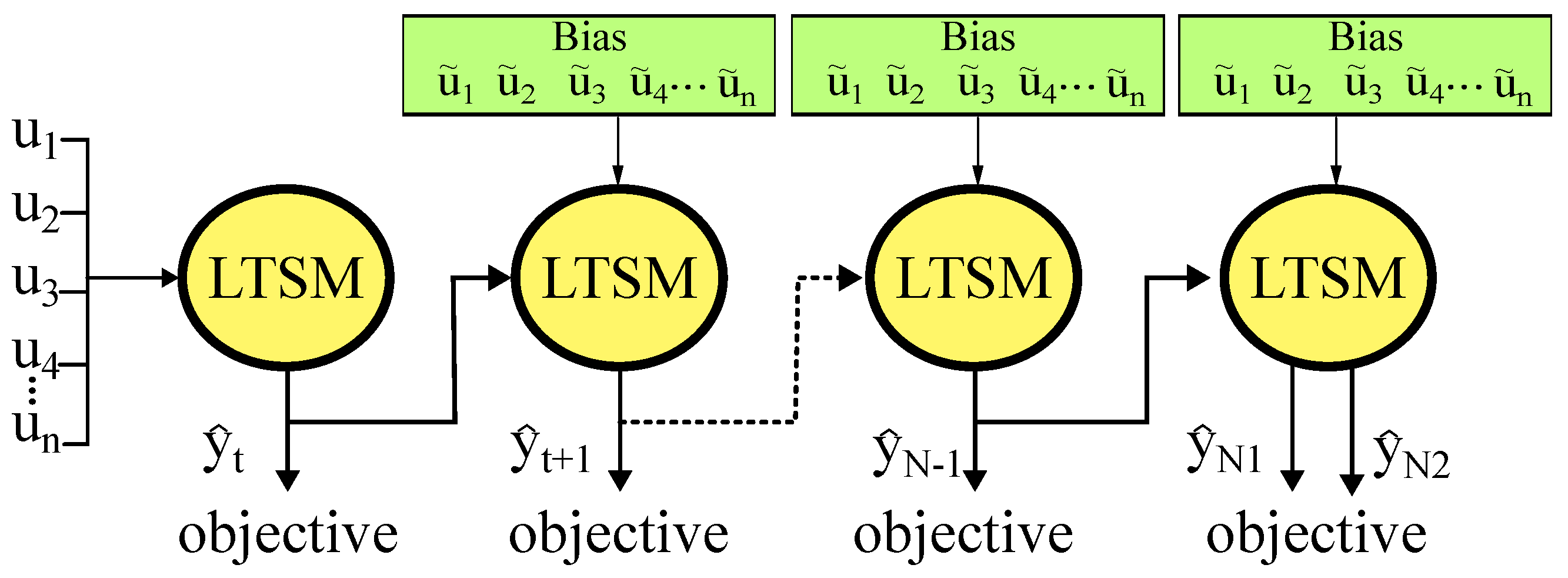
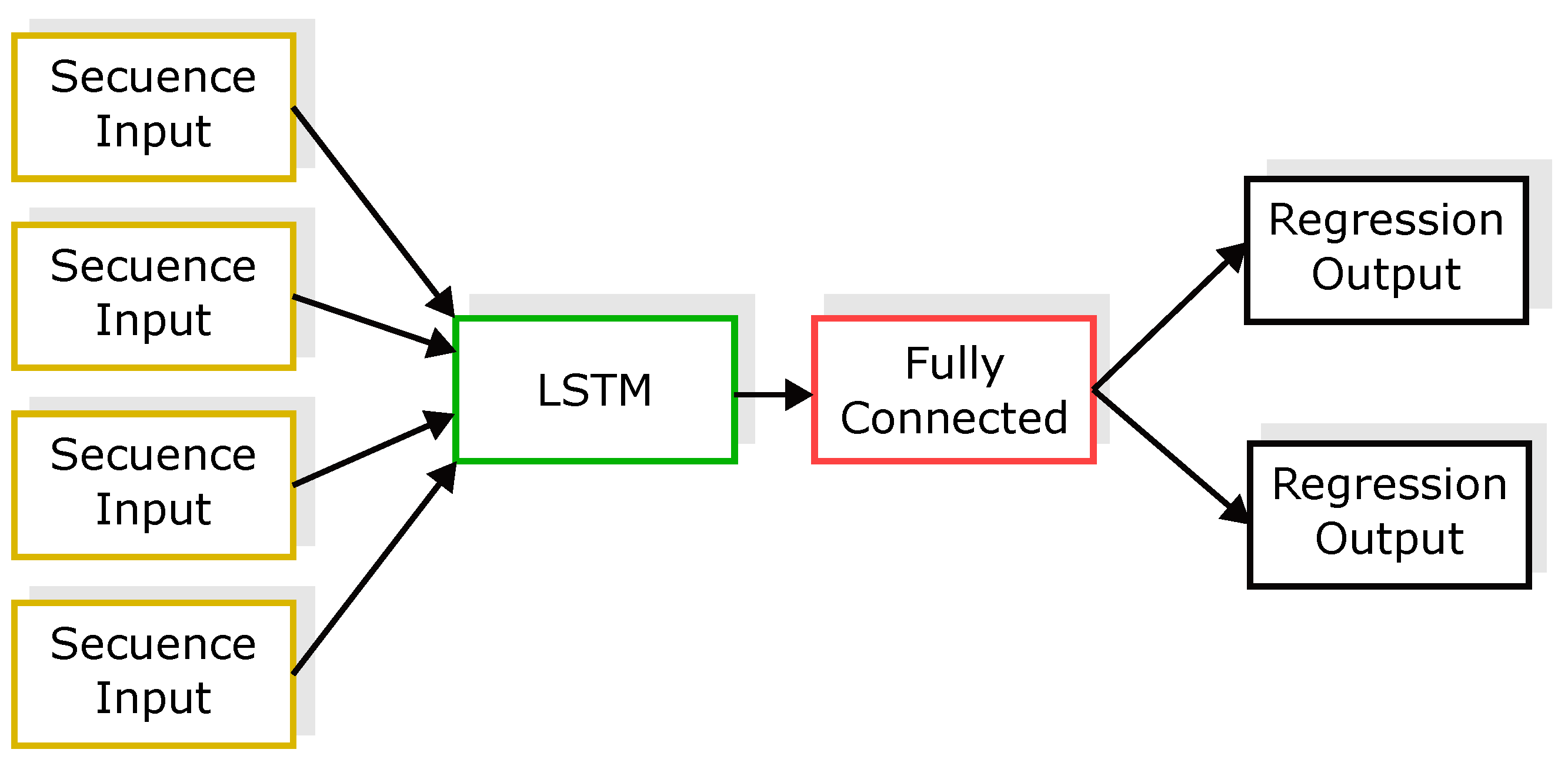
2.3. LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) Network
2.4. Hydrological Variables
2.5. NARX-Based Neural Network Structure
2.6. Regression Metrics for the Estimation of the Quadratic Error
3. Results
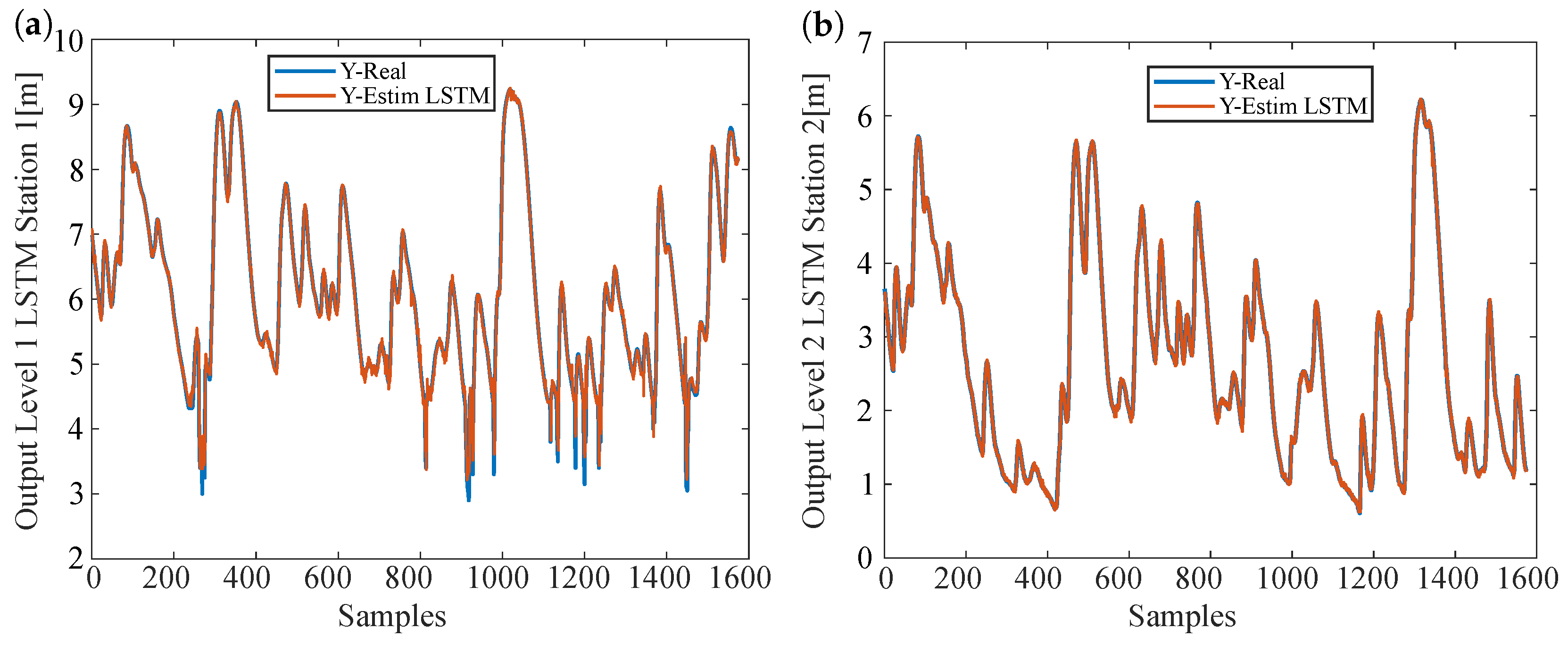
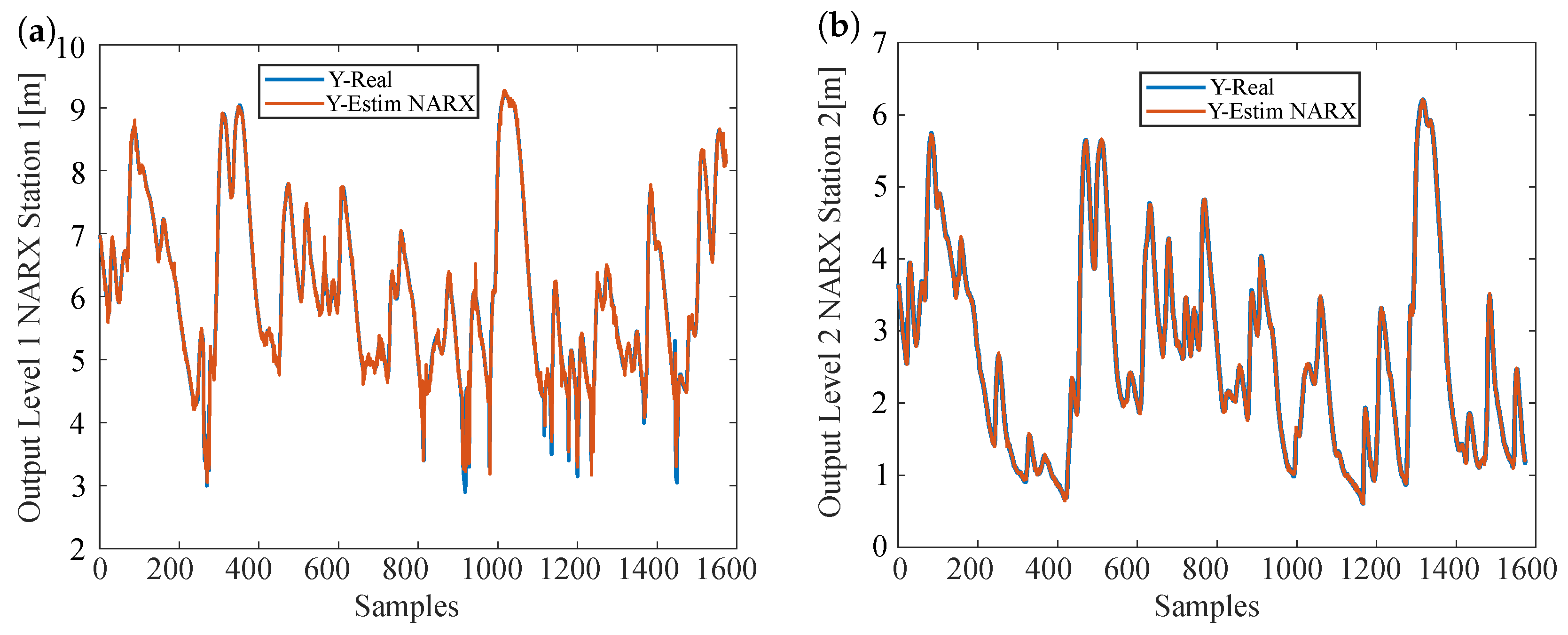
3.1. Estimation Results
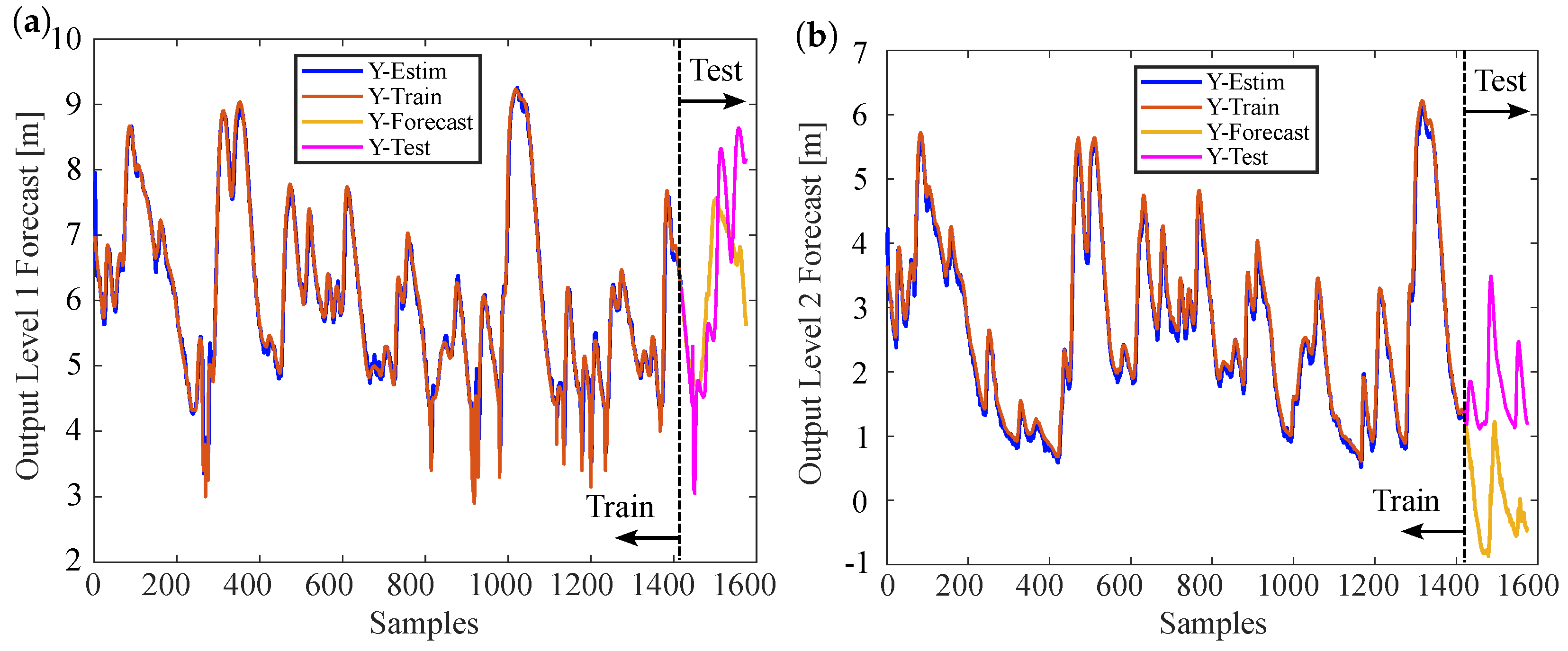
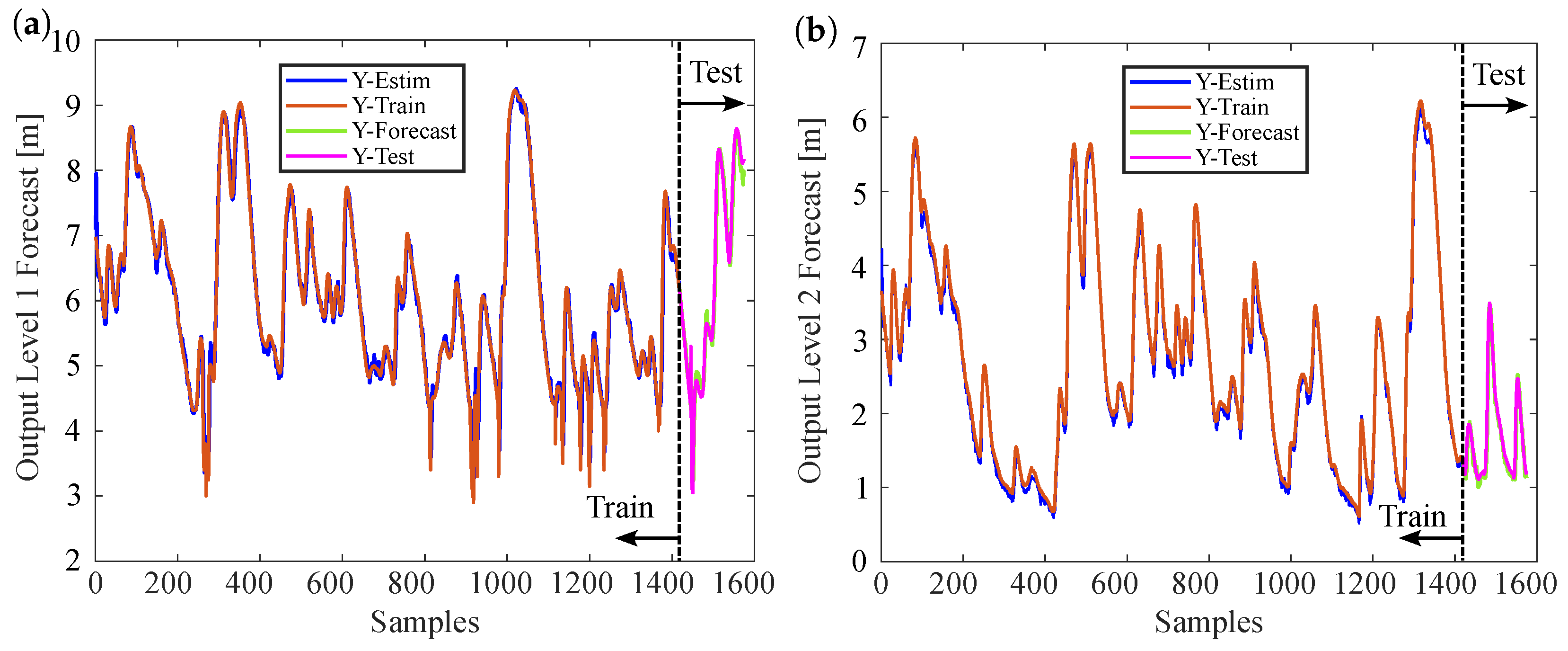
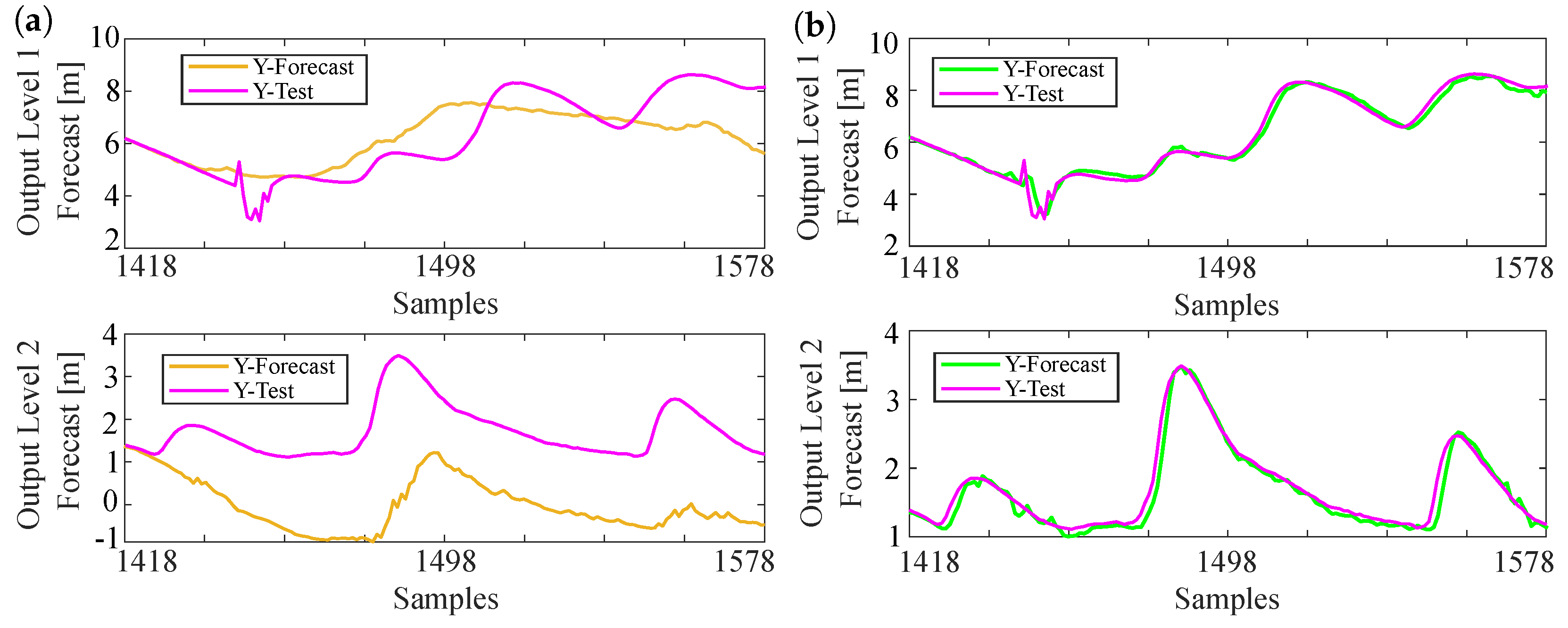
3.2. Forecasting Future Time Steps Based on Predictions and Forecasting Future Time Steps Based on Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bras, R.L.; Rodriguez-Iturbe, I. Random Functions and Hydrology; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi, M.; Samadi, M.; Soleimanian, E.; Chau, K.W. A comparative study of black-box and white-box data-driven methods to predict landfill leachate permeability. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muncharaz, J.O. Comparing Classic Time Series Models and the LSTM Recurrent Neural Network: An Application to S&P 500 Stocks [Comparativa de los Models Clásicos de Series Temporales con la Red Neuronal Recurrente LSTM: Una Aplicación a las Acciones del S&P 500]. Financ. Mark. Valuat. 2020, 6, 137–148. [Google Scholar]
- Fleuret, F. The Little Book of Deep Learning. A Lovely Concise Introduction. 2023. Available online: https://fleuret.org/public/lbdl.pdf (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Le, X.H.; Ho, H.V.; Lee, G.; Jung, S. Application of long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network for flood forecasting. Water 2019, 11, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Thé, J.V.G.; Yang, S.X.; Gharabaghi, B. The Discharge Forecasting of Multiple Monitoring Station for Humber River by Hybrid LSTM Models. Water 2022, 14, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, Y.M.; Lee, J.H.; Moon, H.T.; Moon, Y.I. Development and application of an urban flood forecasting and warning process to reduce urban flood damage: A case study of Dorim River basin, Seoul. Water 2022, 14, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Alonso, D. Pintando con acuarelas en el lugar más lluvioso del mundo. Revista Afluir. 2021. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=8141737 (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Akbari Asanjan, A.; Yang, T.; Hsu, K.; Sorooshian, S.; Lin, J.; Peng, Q. Short-term precipitation forecast based on the PERSIANN system and LSTM recurrent neural networks. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 12–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adaryani, F.R.; Mousavi, S.J.; Jafari, F. Short-term rainfall forecasting using machine learning-based approaches of PSO-SVR, LSTM and CNN. J. Hydrol. 2022, 614, 128463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.S.; Pyo, J.; Chun, J.A. Prediction of water level and water quality using a CNN-LSTM combined deep learning approach. Water 2020, 12, 3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzegar, R.; Aalami, M.T.; Adamowski, J. Coupling a hybrid CNN-LSTM deep learning model with a boundary corrected maximal overlap discrete wavelet transform for multiscale lake water level forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbari, A.; Bae, D.H. Application of Artificial Neural Networks for accuracy enhancements of real-time flood forecasting in the Imjin basin. Water 2018, 10, 1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabbussum, R.; Dar, A.Q. Comparative analysis of neural network training algorithms for the flood forecast modelling of an alluvial Himalayan river. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2020, 13, e12656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kow, P.Y.; Liou, J.Y.; Yang, M.T.; Lee, M.H.; Chang, L.C.; Chang, F.J. Advancing climate-resilient flood mitigation: Utilizing transformer-LSTM for water level forecasting at pumping stations. Sci. Total. Environ. 2024, 927, 172246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruma, J.F.; Adnan, M.S.G.; Dewan, A.; Rahman, R.M. Particle swarm optimization based LSTM networks for water level forecasting: A case study on Bangladesh river network. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, M.; Jayathilaka, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Rathnayake, U. Deep machine learning-based water level prediction model for Colombo flood detention area. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Zhang, M.; Nedjah, N.; Xu, D.; Ye, F. A hydrological data prediction model based on LSTM with attention mechanism. Water 2023, 15, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, M.; Zhou, S.; Xiong, B.; Jin, Z. Medium-long-term prediction of water level based on an improved spatio-temporal attention mechanism for long short-term memory networks. J. Hydrol. 2023, 618, 129163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, G.; Cohen, D.; Dube, V.; Gauch, M.; Gilon, O.; Harrigan, S.; Hassidim, A.; Klotz, D.; Kratzert, F.; Metzger, A.; et al. Global prediction of extreme floods in ungauged watersheds. Nature 2024, 627, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.E. Reinforcement Learning for Sequential Decision and Optimal Control; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal, C. Deep Reinforcement Learning. In Neural Networks and Deep Learning: A Textbook; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 389–433. [Google Scholar]
- Atashi, V.; Gorji, H.T.; Shahabi, S.M.; Kardan, R.; Lim, Y.H. Water level forecasting using deep learning time-series analysis: A case study of red river of the north. Water 2022, 14, 1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, P.; Orellana-Alvear, J.; Bendix, J.; Feyen, J.; Célleri, R. Flood Early Warning Systems Using Machine Learning Techniques: The Case of the Tomebamba Catchment at the Southern Andes of Ecuador. Hydrology 2021, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, K.G.M. “Con el agua al cuello”: Una historia de batallas perdidas contra el agua y desastres por inundaciones en Colombia, 1950–2011. Agua Territ. Water Landsc. 2023, 77–91. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz Agredo, H.A. Lo Natural Como un nodo de Educación y Tecnificación Agropecuaria. 2022. Available online: https://repositorioslatinoamericanos.uchile.cl/handle/2250/3564311 (accessed on 3 June 2024).
- Angulo, C.D.; Viviana, Y.; Oviedo-Barrero, F. Modelación numérica para la determinación de la cota máxima de inundación, en la Ensenada de Utría desde Playa de Diego hasta Ciudad El Valle-Chocó. Ing. Investig. Tecnol. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Johnson, A.; Williams, R. Advancements in Machine Learning Techniques for Hydrological Modeling. J. Hydroinform. 2020, 12, 45–58. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Schmidhuber, J. Framewise phoneme classification with bidirectional LSTM and other neural network architectures. Neural Netw. 2005, 18, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.; Kim, C.; Jung, K.; Jung, H. Water level prediction model applying a long short-term memory (lstm)–gated recurrent unit (gru) method for flood prediction. Water 2022, 14, 2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renteria-Mena, J.B.; Plaza, D.; Giraldo, E. Multivariable NARX Based Neural Networks Models for Short-Term Water Level Forecasting. Eng. Proc. 2023, 39, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A. Evaluación de Pronósticos de Modelos Lineales y no Lineales de la tasa de Cambio de Colombia. Ph.D. Thesis, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Bogotá, Colombia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jalil, M.A.; Misas, M. Evaluación de pronósticos del tipo de cambio utilizando redes neuronales y funciones de pérdida asimétricas. Rev. Colomb. Estadística 2007, 30, 143–161. [Google Scholar]





| Station 1 (E1) | Station 2 (E2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Longitude | 76° W | 76° W |
| Latitude | 5° N | 5° N |
| Altitude | 20.579 MASL | 20.83 MASL |
| City | Belén de Bajirá | Quibdó |
| Nonlinear Models | RMSE Output 1 | RMSE Output 2 | NSE Output 1 | NSE Output 2 | Tic-Toc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.0067 | 0.0028 | 0.9990 | 0.9991 | 0.0089 |
| NARX | 0.0052 | 0.0060 | 0.9990 | 0.9983 | 0.0051 |
| ARX | 0.0275 | 0.0071 | 0.9972 | 0.9980 | 0.0054 |
| Nonlinear Models | Learning Rate | # Input Nodes | # Hidden Nodes | # Output Nodes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 0.02 | 4 | 64 | 2 |
| NARX | 0.02 | 4 | 64 | 2 |
| ARX | 0.02 | 4 | - | 2 |
| Nonlinear Model | RMSE Output 1 | RMSE Output 2 | NSE Output 1 | NSE Output 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM Forecast—Future | 1.2325 | 3.4520 | 0.3849 | 0.1234 |
| LSTM Forecast—Measurements | 0.0620 | 0.0160 | 0.9692 | 0.9894 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renteria-Mena, J.B.; Plaza, D.; Giraldo, E. Multivariate Hydrological Modeling Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Water Level Forecasting. Information 2024, 15, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060358
Renteria-Mena JB, Plaza D, Giraldo E. Multivariate Hydrological Modeling Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Water Level Forecasting. Information. 2024; 15(6):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060358
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenteria-Mena, Jackson B., Douglas Plaza, and Eduardo Giraldo. 2024. "Multivariate Hydrological Modeling Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Water Level Forecasting" Information 15, no. 6: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060358
APA StyleRenteria-Mena, J. B., Plaza, D., & Giraldo, E. (2024). Multivariate Hydrological Modeling Based on Long Short-Term Memory Networks for Water Level Forecasting. Information, 15(6), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060358






