Abstract
Pedestrian tracking and detection have become critical aspects of advanced driver assistance systems (ADASs), due to their academic and commercial potential. Their objective is to locate various pedestrians in videos and assign them unique identities. The data association task is problematic, particularly when dealing with inter-pedestrian occlusion. This occurs when multiple pedestrians cross paths or move too close together, making it difficult for the system to identify and track individual pedestrians. Inaccurate tracking can lead to false alarms, missed detections, and incorrect decisions. To overcome this challenge, our paper focuses on improving data association in our pedestrian detection system’s Deep-SORT tracking algorithm, which is solved as a linear optimization problem using a newly generated cost matrix. We introduce a set of new data association cost matrices that rely on metrics such as intersections, distances, and bounding boxes. To evaluate trackers in real time, we use YOLOv5 to identify pedestrians in images. We also perform experimental evaluations on the Multiple Object Tracking 17 (MOT17) challenge dataset. The proposed cost matrices demonstrate promising results, showing an improvement in most MOT performance metrics compared to the default intersection over union (IOU) data association cost matrix.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the number of deaths caused by traffic accidents has significantly increased, in part due to the growth of the number of vehicles in use. Therefore, considerable efforts have been dedicated to detecting [1,2,3,4,5,6,7] and tracking [8,9,10,11,12] pedestrians at crosswalks, enabling drivers to exercise greater caution.
Multiple-object tracking (MOT) is a computer vision task that seeks to locate various objects in videos and assign them unique identities [13,14]. Over the years, many MOT methods have been proposed and widely used in various applications, including autonomous driving [15] and object collision avoidance [16]. However, MOT performance may be compromised by configuration issues in crowded environments, as well as partial or full object occlusions, which can limit its effectiveness in such scenarios. Despite being a crucial task that finds applications in a wide range of areas [13,14,17], MOT remains a challenging problem.
To develop our pedestrian detection and tracking system, a variety of algorithms are required. The YOLOv5 [18,19,20,21] network is used to identify pedestrians in the images, while the Kalman Filter algorithm [22] is used to predict the position of pedestrians in the current frame. The results obtained by these algorithms are fed into the data association module. The SORT [23] method utilizes the overlap of bounding boxes to match detections to predicted tracks. However, SORT has difficulty tracking objects through occlusions, which are common in frontal view camera scenes. To address this issue, Deep-SORT [24] replaces the association metric with a more informed metric such as appearance features extracted from bounding box images using a separate convolutional neural network (CNN).
Data association metrics [25,26,27,28,29,30,31] play a crucial role in object tracking and have a rich history in computer vision and related fields. The problem of data association dates back to the early days of computer vision, where it was initially used to solve problems related to matching points and lines in two images. Over time, it has become a fundamental problem in object tracking, where the goal is to associate object detections across multiple frames of a video or image sequence. A variety of data association metrics have been developed over the years, including simple geometric metrics such as Euclidean distance and overlap-based metrics such as intersection over union (IoU), as well as more complex metrics based on appearance and motion cues. Data association metrics are crucial for robust and accurate tracking, as they determine how object detections are linked across time and how tracks are maintained in the face of occlusions, clutter, and other challenges.
This work presents our evaluation study of Deep-SORT for multi-pedestrian tracking by detection, utilizing novel data association metrics. Our objective is to demonstrate the importance of utilizing such metrics for achieving optimal tracking and detection performance. Our updated version of Deep-SORT was assessed on the MOT17 [32] dataset.
2. Related Work
2.1. Object Tracking
Object tracking is the process of following a particular object or multiple objects in a sequence of frames from a video or image sequence. The goal of object tracking is to locate the object of interest and monitor its movement over time, while dealing with potential challenges such as object occlusion, illumination variations, and changes in scale, orientation, or appearance. There are various approaches to object tracking, including correlation filters, optical flow, and deep learning-based approaches. Each approach has its strengths and weaknesses and may be better suited for different types of objects or tracking scenarios.
Object tracking can be defined by two levels: single-object tracking (SOT) [33,34,35,36,37] and multiple-object tracking (MOT) [38,39]. The objective of single-object tracking is to estimate the trajectory of a target object over time, given its initial location in the first frame of a video sequence, while multiple-object tracking (MOT) involves tracking multiple objects simultaneously.
Online tracking and offline tracking are two distinct approaches to the problem of object tracking in computer vision. In online tracking, the goal is to track an object of interest in real time as new frames of a video sequence become available. This requires fast and efficient algorithms that can process the data as they are acquired, with limited computational resources and minimal delay. In contrast, offline tracking involves processing an entire video sequence after it has been recorded, with the goal of accurately tracking the object’s trajectory and other properties over the entire sequence. This approach is more computationally intensive and may involve techniques such as batch processing, global optimization, or data-driven models.
Recent developments in the MOT literature have focused on two distinct strategies: tracking by detection and joint tracking and detection.
2.2. Tracking by Detection
Tracking by detection (TBD) is a widely used approach in computer vision that relies on detecting objects in each frame of a video sequence and then linking the detections across frames to track the objects.
In 1979, D. Reid [40] proposed a method for tracking multiple objects that uses multiple hypothesis tracking (MHT) to handle occlusions and track objects in complex scenes. The MHT algorithm generates multiple hypotheses for each object in each frame, and then uses a Bayesian filter to select the most likely hypothesis.
In 2008, a novel approach to multiple-object tracking was presented by Li Zhang [41], which utilizes all available observations for optimizing global data association. The proposed framework takes into account factors such as false alarms, occlusions, and trajectory initialization and termination. By using min-cost network flow algorithms, the framework offers an optimal solution, which was found to be efficient in practical use. The results of the experiments demonstrated that global data association enhances trajectory consistency while reducing trajectory fragments. Furthermore, the framework is adaptable to track any object class with suitable detectors and is highly versatile.
In 2009, B. Babenko et al. [42] proposed a tracking method that uses online multiple instance learning (MIL) to track objects in a video sequence. The method learns to classify object patches as either positive or negative examples on the basis of their appearance, and then uses this classifier to track the object across frames.
In 2012, Z. Kalal et al. [43] proposed a framework called Tracking–Learning–Detection (TLD) that combines detection and tracking in a single algorithm. The TLD algorithm uses a detector to locate the object in each frame and then uses a classifier to learn the appearance of the object over time, enabling it to track the object even when it becomes occluded.
In 2014, B. Wang et al. [44] proposed a method for associating tracklets (short trajectories) of objects in a video sequence. The method uses online discriminative metric learning to learn a distance metric that can distinguish between the appearance of different objects, enabling it to match tracklets even when they have different appearances.
In 2017, N. Wojke et al. [24] proposed Deep-SORT, a deep learning-based method for tracking objects in a video sequence. Deep-SORT uses a combination of a deep neural network for feature extraction and a simple online tracking algorithm for object association, enabling it to achieve state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks.
In 2018, J. Zhu et al. [45] proposed a novel approach for online multi-object tracking that uses dual matching attention networks to match object detections across frames. The method achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of attention-based approaches for the tracking by detection problem.
2.3. Joint Tracking
On the other hand, joint tracking and detection methods aim to achieve detection and tracking simultaneously in a single stage.
In 2002, N. J. Gordon et al. [46] proposed a joint tracking method using particle filters to estimate the positions of multiple targets. The method takes into account the interactions between objects and demonstrates the effectiveness of particle filter-based approaches for the joint tracking problem.
In 2004, T. Vercauteren et al. [47] proposed a collaborative tracking method for multiple targets using sensor networks. The method combines data from multiple sensors to estimate the positions of the targets, taking into account the interactions between them.
In 2012, Zheng Wu et al. [48] presents a new approach for multiple-object tracking using a single objective function that combines object detection and data association. The framework uses Lagrange dual decomposition and a coupling formulation to avoid error propagation that traditional detection–tracking approaches suffer from. The joint image likelihood is modeled instead of applying independent likelihood assumptions, and the method can handle partial or complete occlusions without severe scalability issues. The experiments demonstrate that the approach can achieve results comparable to state-of-the-art approaches even without a heavily trained object detector.
In 2021, Y. Wang et al. [49] put forth a novel approach for joint multi-object tracking (MOT) that utilizes graph neural networks (GNNs). Their approach leverages the ability of GNNs to capture the relationships between objects of varying sizes across both spatial and temporal domains, which is critical for obtaining meaningful features for detection and data association. By conducting thorough experiments on the MOT15/16/17/20 datasets, the researchers proved the efficacy of their GNN-based joint MOT approach and established its superior performance for both detection and MOT tasks.
2.4. Tracking Applied in Pedestrian Detection Systems
Tracking methods applied to pedestrian detection often rely on detecting the pedestrian in each frame of a video sequence and then linking the detections across frames to track the pedestrian.
In 2006, D. M. Gavrila et al. [50] proposed a real-time multi-cue vision system for the detection and tracking of pedestrians from a moving vehicle. The detection component consists of a series of modules that use complementary visual criteria to progressively reduce the image search space. The consecutive modules including (sparse) stereo-based ROI generation, shape-based detection, texture-based classification, and (dense) stereo-based verification. An example of the integration is the activation of a weighted combination of texture-based classifiers by shape-based detection, with each classifier attuned to a specific body pose. Extensive experiments in difficult urban traffic conditions showed that the system reaches a correct recognition percentage of 62–100% at the cost of 0.3–5 false classifications per minute. The performance of the stereo version of the system was significantly better than the mono version, and this was further improved by limiting the sensor coverage area and increasing the processing time.
In 2011, M. D. Breitenstein et al. [51] addressed the issue of automatically detecting and tracking a variable number of individuals in complex environments with an uncalibrated, potentially moving camera. To achieve this, they introduced a new approach for multi-person tracking using particle filtering. In addition to utilizing final high-confidence detections, the algorithm incorporates the continuous confidence of pedestrian detectors and online-trained, instance-specific classifiers as a graded observation model. The algorithm can detect and track many individuals who are dynamically moving in complex scenes with occlusions, without relying on background modeling, requiring a camera or ground-plane calibration, and only using past information. As a result, it is well suited for online applications with minimal restrictions. Experiments demonstrated that their approach performs well in various highly dynamic scenarios, including typical surveillance videos, webcam footage, and sports sequences. Additionally, they compared the method with other approaches that rely on additional information and showed that it outperforms them.
In 2013, F. Basso et al. [52] proposed a method for multi-person tracking using RGB-D data. The method uses a combination of appearance and depth features to detect and track pedestrians. The methodology includes a proficient clustering method based on depth information from point clouds, a classification algorithm resembling HOG for reliable person tracking initialization, and a person identification classifier that incorporates online learning to enable accurate matching of individuals even in cases of complete occlusion. The algorithm demonstrated a high level of accuracy, correctly tracking 96% of individuals with minimal ID switches and a low incidence of false positives. The algorithm also maintained an average frame rate of 25 fps.
In 2018, M. Thoreau et al. [53] proposed a method for pedestrian tracking using deep neural networks. The method uses a combination of a deep neural network for feature extraction and a simple online tracking algorithm for object association, achieving state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks.
In 2021, X. Zhang et al. [54] demonstrated how the use of a deep similarity metric can enhance three crucial aspects of pedestrian tracking in a multiple-object tracking benchmark. Their approach involves training a convolutional neural network to acquire an embedding function in a Siamese configuration, using a vast dataset focused on person re-identification. The embedding network, which is trained offline, is subsequently integrated into the tracking framework to improve performance while retaining real-time processing capabilities. The proposed tracking mechanism involves storing appearance metrics during periods of strong detections, which enables the system to avoid identity switches, link tracklets during occlusion, and identify new detections in instances where the detector confidence is low. These techniques result in competitive results, particularly when compared to other online, real-time approaches.
Both joint tracking and tracking by detection methods can be used for online tracking in pedestrian detection. Joint tracking methods typically use a single model for both pedestrian detection and tracking, and they aim to simultaneously detect and track pedestrians in a video stream. These methods can be effective in situations where the number of pedestrians is relatively small and the pedestrian appearance varies little over time. On the other hand, tracking by detection methods use a separate pedestrian detector to identify pedestrians in each frame, and then use a tracking algorithm to link the detections into tracks over time. These methods are more robust to changes in pedestrian appearance and can handle a larger number of pedestrians, but they may require more computational resources.
In practice, the choice of tracking method depends on the specific application and the requirements for accuracy, speed, and robustness. Some researchers have proposed hybrid methods that combine joint tracking and tracking by detection to leverage the strengths of both approaches. Ultimately, the best approach depends on the specific needs of the application and the available resources for computation and data processing. Hence, for the purpose of this work, tracking by detection methods are more suitable.
3. Methodology
3.1. YOLOv5
The YOLO [19] algorithm, which stands for “You Only Look Once,” is an object detection algorithm that divides images into grids. Each grid cell is responsible for detecting objects within itself. Due to its speed and accuracy, YOLO is one of the most well-known object detection algorithms.
Glenn Jocher introduced YOLOv5 [18] shortly after the release of YOLOv4 [20], using the PyTorch framework. The small size and fast calculation speed of the model are at the heart of the YOLO target detection algorithm. YOLO’s structure is straightforward, and its neural network can directly output the position and category of the bounding box, enabling YOLO to perform real-time detection in videos. By detecting objects directly using the global image, YOLO can encode global information and reduce the likelihood of detecting the background as an object. The structure of YOLOv5 is illustrated in Figure 1.
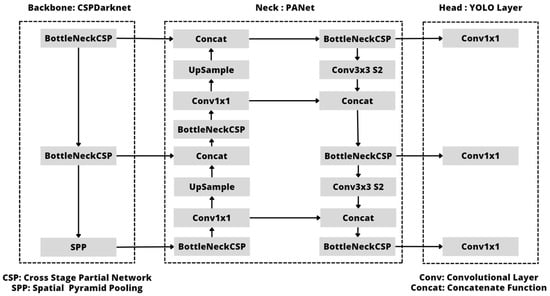
Figure 1.
YOLOv5 architecture.
3.2. SORT
The Simple Online and Real-Time Tracking (SORT) [23] algorithm is a widely used method for tracking objects in video streams. It is a multi-object tracker that uses a combination of a Kalman filter and a Hungarian algorithm [55] to estimate the position and velocity of objects in each frame and match them across multiple frames. The Kalman filter helps to smooth out the noisy measurements obtained from the video stream and make accurate predictions of object positions, while the Hungarian algorithm solves the data association problem by finding the optimal assignment of object tracks to detections. SORT can handle complex scenarios such as occlusion, appearance changes, and variable object speeds, making it highly effective in various computer vision applications such as surveillance, autonomous driving, and robotics. SORT is known for its high accuracy, efficiency, and ability to track multiple objects in real-time. Figure 2 depicts a detailed overview of the SORT algorithm.
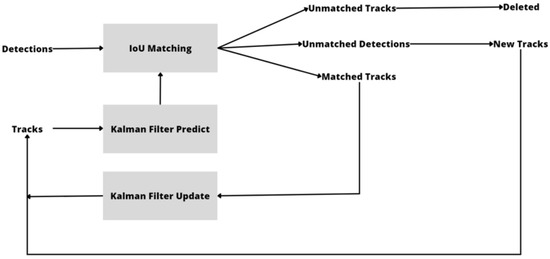
Figure 2.
Overview of the object tracking SORT algorithm.
The matching of the predicted bounding boxes from the Kalman filter (KF) with the measured bounding boxes from the object detector in the image is handled by the SORT data association module. This module plays a crucial role in the SORT algorithm by associating detections with existing object tracks and improving the tracking performance in real time.
This module accepts N-detected bounding boxes and M-predicted bounding boxes as input (acquired from their respective KF). By computing a cost matrix between each detected bounding box and all predicted bounding boxes, the module formulates a linear assignment problem (Di, i∈{1…N}, and Pj, j∈{1…M}, respectively), with the intersection over union (IOU) as a metric:
To formulate the issue as a minimization problem, to be solved using the Hungarian algorithm, the IOU between a detected bounding box and a predicted bounding box is given by
The Hungarian algorithm is used to associate the bounding boxes after computing the cost matrix. The obtained associations are represented in an N × M array, with N measurements corresponding to M tracks. Associations are also filtered by considering a minimum IOU threshold. All associations with IOU less than the threshold are discarded.
The module responsible for KF estimation employs a linear constant velocity model to represent the motion of each object. When an object is associated with a tracked object or “track”, the state of the track is updated using the object’s bounding box. If there is no association between an object and a track, the track’s state is only predicted.
The tracking management module is tasked with creating and deleting tracks. When detections do not overlap or do so with tracks that have an IOU (intersection over union) value below a certain threshold, new tracks are created. The bounding box of the detection is used to initialize the KF state. Since the object’s bounding box is the only available data, the velocity of the object in the KF is set to zero, and its covariance is set to high to signal the uncertainty of the state.
If a new track does not receive any updates due to the lack of associations, or if a track stops receiving associations, it is deleted to avoid retaining a large number of tracks that could be false positives or objects that are no longer in the scene.
3.3. Deep-SORT
Deep-SORT [24] is an advanced object tracking algorithm that uses deep learning to improve the accuracy and robustness of object tracking in real-time video streams. It is an extension of the SORT algorithm, which is a simple and efficient online tracking algorithm. However, SORT has limitations in tracking multiple objects that are close to each other or occluded. Deep-SORT addresses these limitations by using deep learning to associate detections of the same object across frames. The algorithm extracts features from the object detection output and calculates the similarity between detections. This enables Deep-SORT to accurately track multiple objects that are in close proximity to each other and are occluded, allowing the reidentification of tracks, after a long period of occlusion. The use of deep learning also makes Deep-SORT more robust to changes in appearance and lighting conditions, resulting in more accurate object tracking. The corresponding Deep-SORT modules are similar to the KF estimation and track management modules. An overview of the method is presented in Figure 3.
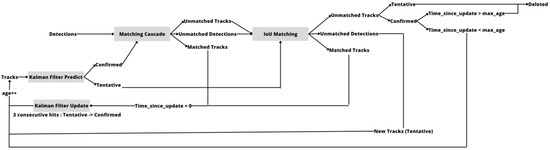
Figure 3.
Overview of the object tracking Deep-SORT algorithm.
Similar to SORT, the Hungarian algorithm employs a two-stage matching cascade to assign detected bounding boxes to tracks. In the first stage, the Deep-SORT technique is employed to match valid tracks on the basis of motion and appearance metrics.
Using the same data association strategy as SORT, the second stage links unpaired and tentative tracks (which were recently established) with unpaired detections.
The incorporation of motion information involves calculating the (squared) Mahalanobis distance between predicted states and detections. Along with this distance metric, a second metric that utilizes the smallest cosine distance is used to measure the distance between each track and the appearance features of each measurement.
3.4. Data Association
The data associations [56,57,58] on the SORT algorithm and the second stage of the Deep-SORT algorithm are fundamental components of object tracking in computer vision. They can be represented as a linear assignment problem, which is a critical step in solving the tracking problem. The linear assignment problem is typically formulated using a cost matrix, and there are multiple approaches for constructing these matrices with proposed bounding box metrics. As such, understanding these methods is crucial in developing accurate and efficient object tracking systems.
The Sorensen metric, also called the Sorensen–Dice coefficient, is a similarity measure used in various applications, particularly in image segmentation and object detection. It quantifies the similarity between two sets by computing the ratio of twice the intersection and the sum of the sizes of the sets. The Sorensen metric is closely related to the intersection over union (IOU), which is also widely used in object detection and segmentation tasks. However, the Sorensen metric is considered more sensitive to small or detailed objects, as it emphasizes the overlap between the sets more than the IoU metric. Our proposed Sorensen cost matrix is defined by
In order to express the problem as a minimization task that can be solved with the Hungarian algorithm, the Sorensen metric between a predicted bounding box and a detected bounding box is defined as
The cosine metric based on intersection, known as the Otsuka–Ochiai coefficient or Ochiai index, is calculated as the ratio of the size of the intersection of two sets to the square root of the product of their sizes. This makes it a useful tool for evaluating the accuracy of image segmentation algorithms, as well as for measuring the similarity of sets of data in other fields. Our proposed Cosinei cost matrix is defined by
The problem can be reformulated as a minimization problem, which can be solved using the Hungarian algorithm. In this formulation, the Cosinei metric between a detected bounding box and a predicted bounding box is given by
The overlap coefficient or Szymkiewicz–Simpson coefficient is a statistical measure used to evaluate the similarity between two sets of data. It is defined as the ratio of the size of the intersection of two sets to the size of the smaller set. Our proposed overlap cost matrix is defined by
The overlap metric between a detected bounding box and a predicted bounding box is given by
We propose a new metric called the overlap ratio based on the overlap metric, which is defined as the size of the intersection divided by the biggest size of the two sets. Our proposed Overlapr cost matrix is defined by
The Overlapr metric between a detected bounding box and a predicted bounding box is given by
Let us examine a bounding box, which is denoted by the image coordinates of its center (xc, yc) as well as its width and height (w, h). Additionally, we work with a detection set D, comprising N bounding boxes, and a prediction set P, consisting of M bounding boxes. To compare the bounding boxes in these sets, we propose the below cost matrix formulations.
Euclidean distance based cost matrix (Euclidean (D,P)):
through which the Euclidean distance metric between a detected bounding box and a predicted bounding box can be obtained by calculating the distance between their central points, which is normalized to half of the image dimension:
where W and H represent the width and height of the input image, while Di and Pi refer to a bounding box from the detection set and a bounding box from the prediction set, respectively.
Manhattan distance-based cost matrix (Manhattan (D,P)):
which represents the distance between the bounding box’s central points. It is the sum of the lengths of the line segment projections between the points onto the coordinate axes. The Manhattan distance between bounding box central points is normalized into the half sum of the image dimension, as follows:
Chebychev distance-based cost matrix (Chebychev (D,P)):
The Chebychev distance is a distance metric which is the maximum absolute distance in one dimension of two bounding box central points as follows:
Cosine distance-based cost matrix (Cosine (D,P)):
The cosine similarity is simply the cosine of the angle between two vectors made by bounding box central points. The cosine distance is defined as follows:
The bounding box ratio-based cost matrix (R(D,P)), proposed by Ricardo Pereira [59], is implemented as a ratio between the product of each width and height:
In addition, for boxes with similar shapes, this metric outcome with a value closer to 1 contrasts values close to 0 or much greater than 1. For that reason, the minimum between the bounding box ratio and its inverse is applied to get a value that falls within the [0,1] range.
We proposed two modified bounding box ratio-based cost matrices (R1(D,P)) and (R2(D,P)):
We also propose different cost matrices based on a combination of the above-listed cost matrices:
4. Results and Discussion
The goal of this work is to accurately track pedestrians in a video, which involves assigning person-specific IDs to corresponding tracks that are coherent throughout the entire tracking sequence. By achieving a perfect tracking result, we can ensure that the pedestrian movements are accurately monitored and analyzed.
The proposed work was evaluated using the challenging MOT17 [32] dataset, which is designed for multi-object tracking. The dataset consists of 14 video sequences—seven for training and seven for testing—covering both indoor and outdoor scenarios involving pedestrian tracking. The high degree of pedestrian occlusion and fast motion in the MOT17 dataset make tracking even more challenging. In this study, we focused on the 02-04-10 DPM training sequences to evaluate the performance of our multi-object tracking methods. Since the methods we used do not require a training process, we were able to use the training sequences exclusively for evaluation. All training video sequences in our dataset are uniformly rescaled to a resolution of 960 × 540 pixels. Correspondingly, ground truth annotations are adjusted to match this resolution.
In order to assess the effectiveness of our proposed cost matrices, we use a set of standard evaluation metrics [60,61]. These metrics include the ID F1 score (IDF1), ID precision (IDP), ID recall (IDR), Recall (Rcll), Precision (Prcn), false acceptance rate (FAR), ground truth (GT), mostly tracked (MT), partially tracked (PT), mostly lost (ML), false positives (FP), false negatives (FN), identification switch (IDs), fragmentation (FM), multi-object tracking accuracy (MOTA), multi-object tracking precision (MOTP), and MOTA logarithmic (MOTAL).
We are primarily interested in two metrics: IDF1 and MOTA. IDF1 is more concerned with association performance, whereas MOTA is more concerned with detection performance.
All modules were implemented on Ubuntu 20.04 LST using the Python 3.8.1 programming language. Deep learning networks were also implemented using the Torch framework (version 1.13.0). The YOLOv5 network was trained using an image size of 416 × 416. In addition, the YOLOv5 weights were initialized using the yolov5m.pt COCO pre-trained model. For the Deep-SORT, TLost = 30 and association gating threshold = 0.4; Cost_matrix associations with cost larger than 0.7 were disregarded. Our Deep-SORT tracking uses the default mars-small128.pb TensorFlow model trained on MARS dataset for extracting features from bounding boxes. Moreover, all experiments were performed using an Nvidia 1650 GPU 4 GB and an Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-9400F CPU 2.90 GHz (six cores) with 16 GB RAM. The experimental results are shown in the Table 1 and Table 2.

Table 1.
Evaluation of Deep-SORT using our proposed data association cost matrices on the MOT17 dataset.

Table 2.
Evaluation of Deep-SORT using a combination of our proposed data association cost matrices on the MOT17 dataset.
The implementation presented in this study provides several important insights into the performance of various tracking methods.
Firstly, the proposed ratio association cost matrix, R1, is shown to outperform both R and R2 in the majority of tracking metrics. However, while the cosine cost matrix based on angular distance can produce good results that exceed those of the ratio cost matrices, it still falls short of the performance achieved by the distance cost matrices (refer to Table 1 for results).
Secondly, the proposed distance association cost matrix, Chebyshev, is found to outperform other distance matrices such as Euclidean and Manhattan (refer to Table 1 for results). This suggests that the Chebyshev distance metric may be a more appropriate choice for tracking applications in certain scenarios.
Moreover, the proposed Sorensen and Overlapr matrices, which are based on the intersection of the tracked and detected bounding boxes, demonstrate superior performance compared to other cost matrices in Table 1 concerning association and detection, respectively. This highlights the potential benefits of using intersection-based methods for tracking tasks.
Furthermore, the proposed combination cost matrices, C7 and C4, are found to deliver the best performances among all cost matrices in Table 1 and Table 2, in terms of association and detection, respectively. This suggests that combining different cost matrices may be a promising approach for improving tracking/detection accuracy.
However, it is worth noting that the implementation presented in this study has some limitations. Specifically, the system based on combination cost matrices can achieve approximately 46 frames per second (FPS) without tracking, but this drops to 8 FPS with tracking due to the nonuse of the GPU on the tracking part and hardware limitations. Additionally, the study cannot explicitly balance the effect of performing accurate detection, association, and localization when comparing trackers using the established metrics (IDF1 and MOTA). This may limit the generalizability of the findings to certain tracking scenarios.
5. Conclusions
The advanced driver assistance system (ADAS) proposed in this paper is a significant contribution to the field of autonomous vehicles. By leveraging the power of the YOLOv5 and the Deep-SORT algorithms, our system can efficiently detect and track pedestrians, making it a valuable addition to the existing ADAS technologies.
One of the key features of our proposed system is the use of a new tracking data association metric. Our proposed cost matrices exhibit excellent performance in terms of association and detection, outperforming the default data association cost matrix. This improvement in tracking accuracy can enhance the safety of pedestrians and autonomous vehicles on the road.
However, there are still some limitations to our work that we aim to address in future research. One of these limitations is the ability to track pedestrians over longer periods, which requires reidentification of the same individual over time. To address this challenge, we plan to use our proposed system as a baseline and develop new methods for re-identification.
Another area on which we plan to focus our future research is the utilization of parallel computing technology, such as GPU acceleration, for the tracking component in order to enhance the system’s frames per second (FPS). This enhancement will enable our ADAS to operate more efficiently and quickly, thereby further improving its overall performance.
Lastly, we intend to evaluate the performance of our system using HOTA, a novel metric for evaluating multi-object tracking (MOT) performance. Unlike previous metrics such as MOTA and IDF1, HOTA was designed to overcome many of the limitations of earlier metrics, and it provides a more accurate assessment of tracking accuracy.
Overall, we believe that our proposed ADAS has the potential to make a significant impact on the field of autonomous vehicles, and we are excited to continue our research and development in this area.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, investigation: M.R. and A.B.; formal analysis, M.R., A.B. and Y.R.; writing, M.R., A.B., I.E.M., Y.R. and A.S; supervision: M.R., A.B., I.E.M., Y.R. and A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Technology of Information and Communication Center of University Hassan II Casablanca as a part of the “Big data and connected objects” research project. We would like to thank the University Hassan II of Casablanca for financing this project.
Data Availability Statement
Data available in a publicly accessible repository. Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. Data can be found here: https://motchallenge.net/data/MOT17/ (accessed on 24 March 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Razzok, M.; Badri, A.; Ruichek, Y.; Sahel, A. Street crossing pedestrian detection system a comparative study of descriptor and classification methods. In Colloque sur les Objets et systèmes Connectés; Higher School of Technology of Casablanca (ESTC): Casablanca, Morocco; University Institute of Technology of Aix-Marseille: Marseille, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Razzok, M.; Badri, A.; Mourabit, I.E.L.; Ruichek, Y.; Sahel, A. A new pedestrian recognition system based on edge detection and different census transform features under weather conditions. IAES Int. J. Artif. Intell. 2022, 11, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzok, M.; Badri, A.; Mourabit, I.E.L.; Ruichek, Y.; Sahel, A. Pedestrian Detection System Based on Deep Learning. IJAAS Int. J. Adv. Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Wu, T.; Sun, K.; Zhang, C. Towards high accuracy pedestrian detection on edge gpus. Sensors 2022, 22, 5980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Zhu, C.; Yin, X.-C. Occluded Pedestrian Detection via Distribution-Based Mutual-Supervised Feature Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 10514–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.; Thopalli, K.; Malarvezhi, P.; Thiagarajan, J.J. Improving Single-Stage Object Detectors for Nighttime Pedestrian Detection. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 2250034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velázquez, J.A.A.; Huertas, M.R.; Eleuterio, R.A.; Gutiérrez, E.E.G.; Del Razo López, F.; Lara, E.R. Pedestrian Localization in a Video Sequence Using Motion Detection and Active Shape Models. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, Y.; Tong, X.; Li, Z. Research on Pedestrian Detection and DeepSort Tracking in Front of Intelligent Vehicle Based on Deep Learning. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Wu, F.; Du, X.; Zhang, G. Cascade-SORT: A robust fruit counting approach using multiple features cascade matching. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 200, 107223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Su, Y.-K. MobileNet-JDE: A lightweight multi-object tracking model for embedded systems. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 9915–9937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cai, C. Research on Vision-based pedestrian detection and tracking algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Guilin, China, 7–10 August 2022; pp. 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, M.; Bayat, M.H.; Tarvirdizadeh, B. A motion model based on recurrent neural networks for visual object tracking. Image Vis. Comput. 2022, 126, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.; Basmaji, T.; Yaghi, M.; Alheeh, H.; Alkhedher, M.; Ghazal, M. Multiple Object Tracking in Robotic Applications: Trends and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasó, G.; Cetintas, O.; Leal-Taixé, L. Multi-Object Tracking and Segmentation Via Neural Message Passing. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2022, 130, 3035–3053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, W. Online Multiple Object Tracking Using a Novel Discriminative Module for Autonomous Driving. Electronics 2021, 10, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Ju, Z. Multiple pedestrian tracking under first-person perspective using deep neural network and social force optimization. Optik 2021, 240, 166981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fu, C.; Ding, F.; Ye, J.; Lin, F. All-day object tracking for unmanned aerial vehicle. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; Tian, Y.; Tang, H.; Guo, X. Real-Time Vehicle Detection Based on Improved YOLO v5. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.M.; Bose, R.; Bhaduri, J. A fast accurate fine-grain object detection model based on YOLOv4 deep neural network. Neural Comput. Applic. 2022, 34, 3895–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.M.; Bhaduri, J.; Kumar, T.; Raj, K. WilDect-YOLO: An efficient and robust computer vision-based accurate object localization model for automated endangered wildlife detection. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, G.F. Kalman filter. In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Bewley, A.; Ge, Z.; Ott, L.; Ramos, F.; Upcroft, B. Simple online and realtime tracking. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP 2016), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 25–28 September 2016; pp. 3464–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojke, N.; Bewley, A.; Paulus, D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17–20 September 2017; pp. 3645–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinova, P.; Udvarev, A.; Semerdjiev, T. A Study of a Target Tracking Algorithm Using Global Nearest Neighbor Approach. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference Conference on Computer Systems and Technologies: E-Learning, Rousse, Bulgaria, 19–20 June 2003; pp. 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirubarajan, T.; Bar-Shalom, Y. Probabilistic data association techniques for target tracking in clutter. Proc. IEEE 2004, 92, 536–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Tomasi, C. Efficient Visual Object Tracking with Online Nearest Neighbor Classifier. Comput. Vis. ACCV 2010, 2011, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huynh, D.Q. Multiple Pedestrian Tracking from Monocular Videos in an Interacting Multiple Model Framework. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 1361–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezatofighi, S.H.; Milan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Shi, Q.; Dick, A.; Reid, I. Joint Probabilistic Data Association Revisited. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Li, F.; Ciptadi, A.; Rehg, J.M. Multiple Hypothesis Tracking Revisited. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4696–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, G.d.S. Kalman Filter-Based Object Tracking Techniques for Indoor Robotic Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidade de Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Milan, A.; Leal-Taixé, L.; Reid, I.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. MOT16: A benchmark for multi-object tracking. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.00831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Payandeh, S. Understanding Tracking Methodology of Kernelized Correlation Filter. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 9th Annual Information Technology, Electronics and Mobile Communication Conference (IEMCON), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 1–3 November 2018; pp. 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalakshmi, V.; Alex, M.G. Visual object tracking using discriminative correlation filter. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Communication and Electronics Systems (ICCES), Coimbatore, India, 21–22 October 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yao, H.; Sun, X.; Lu, X. Sparse coding based visual tracking: Review and experimental comparison. Pattern Recognit. 2013, 46, 1772–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller-Meier, E.B.; Ade, F. Tracking multiple objects using the Condensation algorithm. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2001, 34, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, D.; Thrun, S.; Savarese, S. Learning to Track at 100 FPS with Deep Regression Networks. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 749–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocur, V.; Ftacnik, M. Multi-Class Multi-Movement Vehicle Counting Based on CenterTrack. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, W.; Liu, W. FairMOT: On the Fairness of Detection and Re-identification in Multiple Object Tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 3069–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, D. An algorithm for tracking multiple targets. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1979, 24, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Nevatia, R. Global data association for multi-object tracking using network flows. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Anchorage, AK, USA, 23–28 June 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babenko, B.; Yang, M.-H.; Belongie, S. Visual tracking with online Multiple Instance Learning. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalal, Z.; Mikolajczyk, K.; Matas, J. Tracking-Learning-Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 34, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Chan, K.L.; Wang, L. Tracklet Association with Online Target-Specific Metric Learning. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, N.; Kim, M.; Zhang, W.; Yang, M.-H. Online Multi-Object Tracking with Dual Matching Attention Networks. In Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, N.J.; Maskell, S.; Kirubarajan, T. Efficient particle filters for joint tracking and classification. In Proceedings of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets 2002, Orlando, FL, USA, 7 August 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercauteren, T.; Guo, D.; Wang, X. Joint multiple target tracking and classification in collaborative sensor networks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Information Theory, 2004, ISIT, Chicago, IL, USA, 27 June–2 July 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Thangali, A.; Sclaroff, S.; Betke, M. Coupling detection and data association for multiple object tracking. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kitani, K.; Weng, X. Joint Object Detection and Multi-Object Tracking with Graph Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrila, D.M.; Munder, S. Multi-cue Pedestrian Detection and Tracking from a Moving Vehicle. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2006, 73, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitenstein, M.D.; Reichlin, F.; Leibe, B.; Koller-Meier, E.; Van Gool, L. Online Multiperson Tracking-by-Detection from a Single, Uncalibrated Camera. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2011, 33, 1820–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, F.; Munaro, M.; Michieletto, S.; Pagello, E.; Menegatti, E. Fast and Robust Multi-people Tracking from RGB-D Data for a Mobile Robot. Intell. Auton. Syst. 2013, 12, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreau, M.; Kottege, N. Deep Similarity Metric Learning for Real-Time Pedestrian Tracking. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1806.07592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Gu, C. Online multi-object tracking with pedestrian re-identification and occlusion processing. Vis Comput. 2021, 37, 1089–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Pal, S. A note on Hungarian method for solving assignment problem. J. Inf. Optim. Sci. 2015, 36, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korepanova, A.A.; Oliseenko, V.D.; Abramov, M.V. Applicability of similarity coefficients in social circle matching. In Proceedings of the 2020 XXIII International Conference on Soft Computing and Measurements (SCM), Saint Petersburg, Russia, 27–29 May 2020; pp. 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijaymeena, M.; Kavitha, K. A survey on similarity measures in text mining. Mach. Learn. Appl. Int. J. 2016, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gragera, A.; Suppakitpaisarn, V. Semimetric Properties of Sørensen-Dice and Tversky Indexes. WALCOM Algorithms Comput. 2016, 9627, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Carvalho, G.; Garrote, L.; Nunes, U.J. Sort and Deep-SORT Based Multi-Object Tracking for Mobile Robotics: Evaluation with New Data Association Metrics. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristani, E.; Solera, F.; Zou, R.; Cucchiara, R.; Tomasi, C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. 2016, 9914, 17–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardin, K.; Stiefelhagen, R. Evaluating multiple object tracking performance: The clear mot metrics. EURASIP J. Image Video Process. 2008, 2008, 246309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).