Abstract
The transformation of educational processes, derived from the technological disruption that has taken place in the educational field, has allowed for the development of certain methodologies and techniques that place emphasis on the students as an active element in their own learning. Among these methodologies is learning based on video games. Serious games are video games with an explicit educational objective, that facilitate the generation of motivating contexts, promoting relevant experiences, and with the possibility of creating challenges of a systemic nature. With a systematic literature review (SLR) methodology, this study analysed the pedagogical models and/or approaches that are implemented in the teaching–learning processes brought about by the use of serious games, with the aim of evidencing the potentialities derived from the conception of the video game as an educational resource. The results show a clear conceptual network in relation to the analysed subject, with little interaction between selected studies. A variety of pedagogical models were identified, pertaining to the use of serious games as an educational resource in the classroom context. As an overall conclusion, there is no one reference model able to generate a single pedagogy for serious games.
1. Introduction
The technological disruption that has taken place in today’s societies has led to the need for an educational response that is coherent with a hyperconnected social reality in a permanent state of change. The establishment of a digital paradigm has promoted the development of a liquid modernity [1], characterised by the culture of immediacy. This is a reality in which the relationships established through technology expand sociability in such a way that, for some authors, they represent the third evolutionary force of humanity [2].
In this context, it becomes necessary to rethink educational processes in order to meet the challenge of training individuals capable of performing effectively as active and participatory citizens in a global Knowmadic society [3]. To this end, it is essential to develop proficiency that enables students to become flexible and versatile individuals, digitally literate, and capable of managing the uncertainty of the unknown, in order to adapt to the needs of the future.
In this sense, it is important to implement teaching–learning models that meet new social demands. It is also convenient to create distance between those traditional practices that are characterised, in an exclusive manner, by the teaching of master classes, direct instruction, or logocentric models. Current trends include approaches oriented towards “learning by doing”, as well as meaningful and experience-based learning [4].
Similarly, it is necessary to develop digital competence in students [5], adapting the actions of institutions towards a more purposeful practice, effectively integrating the use of digital technologies. Therefore, it is crucial to find a convergence that allows for a transformation of the traditional roles associated with the figures of the teacher and the student, transmitting the ability to learn by creating, reconfiguring, unlearning, and relearning, and connecting learning in the classroom with what happens outside the classroom [6]. Thus, the renewal of educational models requires a change in the roles of all the agents involved in the teaching–learning process, in which students become the centre of the action as managers of their own study, with autonomy and self-regulation [7]. Therefore, it becomes essential to reconfigure the different implicated elements in formative action: teachers, students, materials, evaluation, content, activities, technologies, and methodologies, especially those that favour an active role by the student, meaningful learning, collaboration, and autonomy, in which digital technologies add value [8]. This is why it is critical to establish a teaching model consistent with a Knomadic reality, which allows for digital transformation that is implemented in the field of education. As a consequence, there is the implication that inside the classroom, teachers apply methodologies that make instruction more attractive, thereby avoiding or minimising student disconnection [9].
In the Knomadic proto-paradigm 3.0, emphasis is placed on the diversity of educational media, focusing on how to learn and not so much on what to learn. For this, it is necessary to promote meaningful schooling through the practical application of knowledge, allowing liquid individuals to be agents of awareness [10] in a dual online–offline reality. Learning to live in both multi-dimensional levels of reality implies, among other aspects, establishing a permanent commitment to personal development on the intellectual plane, seeking new sources and forms of understanding, and new contexts and training environments through creativity, innovation, idea generation, problem solving, emotionality, etc. In short, we summarise all of the aforementioned by saying: through knowledge.
With regards to the digital reality in which students develop, the literature evidences the existence of diverse technological profiles, as there is no homogeneous cyber generation, with significant differences emerging as determined by access to technological devices, the hours of exposure to them, and the types of uses [11]. Likewise, despite the use that young people make of technologies, since they possess computer skills that they use in social and leisure activities, they seem incapable of transferring these aptitudes to their learning and knowledge construction processes [12]. Based on the emphasis attributed to the relationship that the new generations establish with the digital world, the following order of categories can be laid out: the widespread use of ICTs; the impact of digital immersion, particularly in learning; and the distinctive personal and behavioural characteristics of this generation [13]. In this sense, technology acquires an undeniable importance in the reformulation of the educational models applied. Its use enables direct (synchronous or asynchronous) and dynamic communication between the educational agents involved in the teaching–learning process, allowing for, in addition, the emergence of educational modalities consistent with the current reality: electronic learning, or e-learning; hybrid learning, or b-learning; mobile learning, or m-learning; ubiquitous learning, or u-learning; experiential learning, or x-learning, etc. Therefore, an innovative use of digital technologies is previously required to convert students into protagonists of their own learning process, allowing them to decide, offer opinions, interact, and contribute knowledge to the network [14].
By way of contribution, this article addresses the pedagogical models and/or approaches that are implemented in the teaching–learning processes brought about by the use of serious games, with the aim of demonstrating the potentialities derived from the conception of the video game as an educational resource.
2. Implications of Serious Games in Education
The transformation of educational processes arising from the technological disruption that has taken place in the educational field has allowed for the development of certain methodologies and techniques that place emphasis on students as an active element in their own learning. These are considered emerging pedagogical approaches that refer to ideas (some still in the process of systematisation) dealing with the use of digital technologies in education and that attempt to wield such potential (communicative, informational, collaborative, interactive, creative, and innovative) to generate new learning environments [15]. Active and deep learning are essential to achieve not only a transfer of knowledge, but also an optimal education experience [16]. However, for a schooling practice to be able to promote deep training, it is necessary that there is, beforehand, a strong commitment on the part of the students involved in the teaching–learning process [17].
An educational game, properly planned, becomes an activity that promotes a state of immersion and involvement, and of transformation during its development, by presenting the qualities deemed best to encourage students to engage with their learning [18]. Some games even contribute to boosting cognitive processes in students and help to achieve learning objectives, taking advantage of the intrinsic motivation of the challenges proposed [19]. Games can become catalysts for learning to the extent that they foster exciting contexts that combine creativity, emotion, and interaction [20], and provide subjects with immersive tasks and challenges that involve the activation of their skills [21].
From this perspective, serious games promote an inspiring atmosphere that bolsters relevant experiences with the presentation of challenges of a systemic nature [22]. There are multiple authors who present evidence of the impact on the motivation and commitment of students when working with challenges that promote the acquisition of skills through experimentation and that invite them to devote time and effort to that which is considered a rewarding activity [23,24,25]. In this sense, an allusion is made to the possibility of developing educational processes brought about through serious games in the classroom context for the development of competencies, in combination with strategies typical of active methodologies such as problem-based learning, flipped classroom or gamified systems, among others [26,27]. Thus, the fun component of serious games is not currently undervalued, conceiving digital play to be capable of fostering such skills. In fact, games are considered to provide opportunities for students to link and transfer learning content to real contexts and their daily lives by also allowing for error, seen as an opportunity to test proficiency [28,29].
Furthermore, there is evidence of an impact on the improvement of students’ academic performance [30,31]. Mouaheb et al. [32] identify three educational dimensions involving the significance of serious games in the classroom: (1) autonomous acquisition of cognitive skills through the challenges set in the game; (2) active learning of conflict resolution skills, providing a solid building of capabilities (knowledge and attitudes); and (3) direct transfer of acquired ability and knowledge to the real world. With regards to the use of serious games, their application in the higher education setting seems to predominate [33].
3. Pedagogic Models and Serious Games
The introduction of serious games in the classroom has so far responded to two reference pedagogical models or approaches: game-based learning and experiential learning.
The game-based learning approach is linked to the work of Prensky [34] as a pedagogical strategy to foster student engagement in conjunction with serious learning and entertainment in a new environment, where positive emotion is harnessed as a motivational element in learning. Considering the implications for games in the acquisition of culture, as well as in the development of cognitive, social, and emotional aspects in individuals, their implementation in the educational environment is deemed convenient due to the teaching–learning processes that take place. In this sense, game-based learning is established as a methodological proposal, understood as a strategies based on the use, creation, and/or adaptation of games in a classroom context as a vehicle of education, serving as a relevant didactic resource for the acquisition of a variety of content and the development of determined skills [35,36].
In this regard, Martín Hierro and Pastor Seller [37] indicate that “it is an innovative methodology that offers a different and eminently practical educational experience that fosters a classroom climate in which students are more motivated to participate and learn” (p. 95). Among the implications of implementing game-based learning in the educational environment, Real Ramos and Yunda Lozano [38] highlight the value of games as a tool that allows for situations that influence student motivation, and furthermore, increase social interactions and participation in the classroom, such as those inherent to the teaching–learning process.
Numerous investigations have evidenced the strong potential of using game-based learning in educational environments, showing a positive correlation between play and learning [39,40,41]. Such learning involves introducing students to complex, inquiry-based problem spaces, whose activities generate continuous learning, either by overcoming problems or by reflection in the face of failure or error [18]. This requires constant feedback that allows students to be aware of their evolution according to the goals set, know what is needed to achieve objectives, and understand the nature of the processes that guide their activity as players. The effectiveness of game-based learning is achieved through the integration of five key elements: motivation, fun learning, autonomy, authenticity, and experiential learning [42,43]. Some research highlights the benefits of game-based education in increasing student engagement in the learning process and for the acquisition of transverse competencies [44,45].
At the same time, experiential learning theory (ELT) presents an integrative, holistic approach to schooling, combining experience, cognition, and behaviour [46]. Kolb [47] defined learning as a process by which knowledge is created through the transformation of practice. His proposal is based on six assumptions: learning (1) is conceived as a process, not an outcome; (2) is based on experience; (3) requires individuals to resolve dialectically opposing modes of adaptation; (4) is a holistic process; (5) involves interaction between a person and the environment; and (6) is a process of knowledge creation. Kolb’s experiential learning model is based on four stages: concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and experimentation. It assumes that individuals engage themselves without prejudice in new experiences (concrete experience); reflect on and observe this participation from a variety of perspectives (reflective observation); create concepts from which new implications and theories can be drawn for action (abstract conceptualization); and apply the steps derived from the implications and theories to experimentation (active experimentation). This model indicates that knowledge is constructed by the relationship between the four stages, each of which responds to contextual demands. Students must go through each stage: experiencing, reflecting, thinking, and acting [48]. According to this model, for effective and deep learning to occur, the student must go through the entire cycle. The four-stage training model describes two opposite dimensions of the grasping experience: concrete experience (CE) and abstract conceptualization (AC), and two opposite dimensions of the transforming experience: reflective observation (RO) and active experimentation (AE). The pupil must continually choose which set of learning skills to use in a specific situation. In the comprehension experience, the learner can perceive new information by experiencing the concrete, tangible, and felt qualities of the world, relying on his or her senses and immersing him- or herself in concrete reality. Alternatively, the learner may experience the opposite abstract conceptualization. Therefore, the process follows a cycle that begins with direct experience (concrete learning), which is followed by reflection (reflective observation). Reflection is assimilated in the form of theory (abstract conceptualization), and finally, this new (or reformulated) hypothesis is tested in new situations (active experimentation).
Thus, from a teaching perspective, it is essential to provide situational opportunities that allow students to experience, from an educational point of view, the knowledge they intend to build. To this end, a suitable environment must be supplied that enables the involvement of pupils in their own learning process, through active experimentation, as a fundamental source of training, understood as direct interaction with the content being acquired.
4. Materials and Methods
The developed study was approached using a systematic literature review (SLR) to analyse the research on pedagogical models for the use and implementation of serious games in education. To carry out this SLR process, the standards established by the PRISMA 2020 protocol were applied. Thus, eligibility criteria, information sources, a search strategy, selection process, data collection process, and data list were identified [49].
4.1. Objectives
The main objective of this study was to analyse the existing research on pedagogical models and approaches for the introduction of serious games in education.
The research questions were organised around three dimensions (Table 1): (a) the conceptual dimension, through the analysis of the relationships between the keywords identified in the literature on the analysed subject (RQ1) and the interactions generated between the authors of the studies (R22); (b) the documentary dimension, aimed at identifying the type of document, distribution in the database, and years of publication (RQ3-RQ4); and (c) the pedagogical dimension, in relation to RQ5, through the identification of the pedagogical models or approaches to using serious games in educational practice present in the literature.

Table 1.
Dimensions, research questions, and initial codification.
4.2. Eligibility Criteria
This review included scientific articles published from January 2010 to January 2022, a total of 12 years, which included, in title, abstract, or keywords, the concepts “pedagogic model”, “instructional model”, and “serious games”. All types of scientific papers were admitted, including theoretical and empirical studies, both with quantitative and qualitative methodologies and mixed studies. As an exclusion criterion, it was determined not to evaluate studies whose objective was the design of serious games (E1). Therefore, the pedagogical use of serious games in educational practice was considered an inclusion criterion.
4.3. Information Sources, Strategy, and Search Process
The flow diagram, a PRISMA figure (Figure 1), was created using the tool designed by Haddaway and McGuinness [50]. It can be seen that, for the selection of articles, the Web of Science, Scopus, and ERIC databases were used, taking the established concepts as a search reference, with a time delimitation between 2010 and 2022. In addition, a web search using the Mendeley search engine was added as a complementary search. The initial global exploration resulted in 172 articles, none of which were withdrawn before reading. The documents were analysed on the basis of the title and abstract according to the inclusion–exclusion criteria. After this analysis, 101 articles were excluded. The remaining 71 were located without difficulty and were analysed in full text in a second screening process. Thus, only 31 articles were omitted according to exclusion criterion E1, because they were articles that did not aim to include serious games in educational practice. This resulted in the final sample of documents for this systematic review (n = 40). The Zotero bibliographic manager was used for data collection. The synthesis of the information was carried out using a coding sheet in Calc. Three tools were used for the analysis of the results: VOSViewer, for the investigation of the conceptual network; Litmap, for the study of the network of interactions between authors; and RAWGraphs, for the representation of the documentary characteristics.
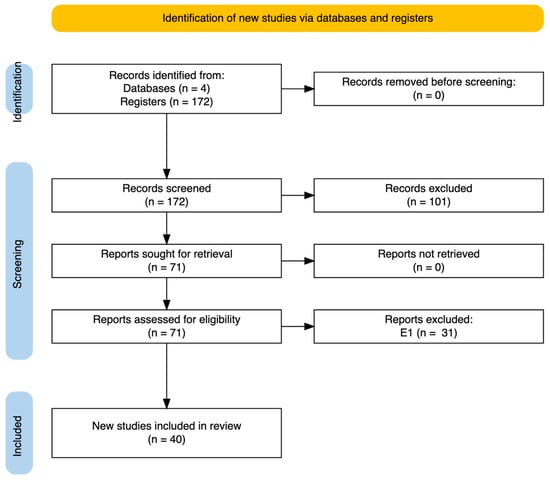
Figure 1.
Flow diagram.
5. Research Findings
The results of the systematic review are presented below, categorising the results according to the three established dimensions and responding to the different research questions. Firstly, we present the conceptual dimension on the integration of serious games in teaching practices; then a second block that refers to the documentary dimension of the studies; and, finally, a third block that shows the results obtained for the pedagogical dimension, seeking to respond to how the integration of serious games in educational practices is carried out.
5.1. What Is the Conceptual Framework around the Terms “Pedagogic Model”, “Instruction Model”, and Serious Games Drawn from the Literature?
The analysis of the conceptual framework started with the clusters generated by the co-occurrence of the keywords of the articles reviewed. This analysis was developed with VOSviewer (version 1.6.18). To visualise this conceptual framework, the programme works with different units of analysis (in this case, keywords) and units of measurement (in this case, co-occurrence). The technique applied is the normalisation of the strength of association, together with the visualisation of similarities mapping, and finally, the clustering technique. This cluster is a set of nodes, closely related according to the type of link being analysed; each node is assigned to exactly one cluster. Figure 2 shows three clusters in the image, with a network of relationships that places the blue cluster in the centre of the diagram as a link to the rest of the nodes. Each circle represents a key concept, and its size reflects the number of documents containing that keyword. The closeness or remoteness of one circle to another reflects the strength of the relationship between one concept and another. The colours indicate clusters that are relatively related to each other.
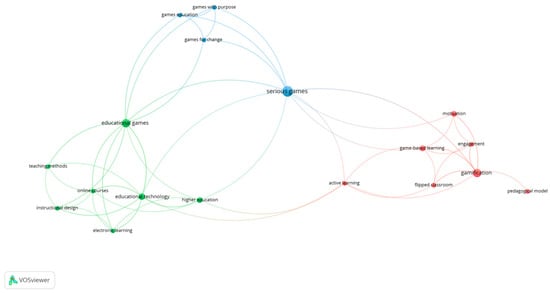
Figure 2.
Conceptual framework.
The blue cluster includes the term serious games, which is related to the green and red clusters through the concepts “educational games” and “gamification”. The key concept of this cluster is closely connected to “games for changes”, “games in education”, and “games with purpose”. A key concept identified in the green cluster is “educational games”, which is associated with “educational technology” and “learning methods”. The latter concept is closely related to “instructional design” and “online courses”. The concept “educational technology”, in turn, is linked to “higher education” and “electronic learning”, in addition to the other concepts indicated in the cluster. Finally, the red cluster has as the key term “gamification” related to the concept “engagement”, which in turn is connected with “motivation”. The key term is also joined to “pedagogic model”, as well as to “game-based learning” and “flipped classroom”, both of which are closely related to “active learning”.
5.2. What and How Are the Interactions and Relationships between the Authors of Each Study?
Figure 3, made with the Litmaps tool, shows the relationship between the articles that made up the review sample (among those with DOIs), shown in orange, and their interrelationship over time, not only with each other, but also with other relevant publications, shown in the grey area. Thus, de Carvalho is positioned as a reference author, having a constant presence in works related to serious games [27,51]. Similarly, Bellotti et al. [52] is also considered a reference author, but this time due to the number of citations in their article. The size of the orange circle is larger the more citations the article has. Likewise, Tsai et al. [53] stands out as the most cited work by the latest 2022 writings, which leads to consider that their article is relevant to the scientific community.
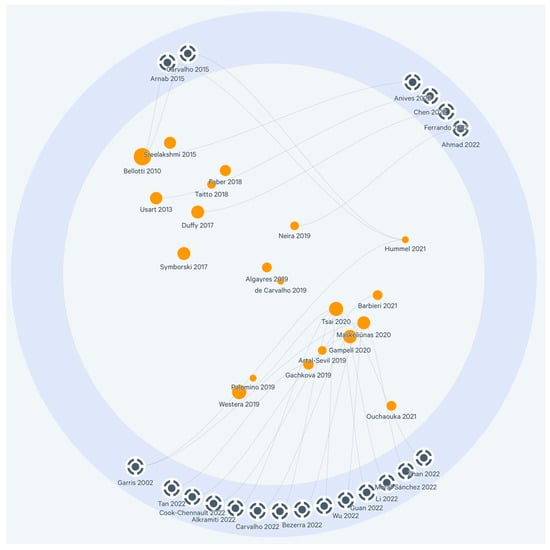
Figure 3.
Relationship between the articles.
However, in Figure 3, it can be observed that the connections between the different authors that made up the sample are relatively tiny, almost non-existent, except for the case of Artal-Sevil [54] and Artal-Sevil et al. [55], which could be discarded as self-citations, leaving only Tsai et al. [54] and Westera [56] standing out as interconnected authors. As such, it could be said that these graphs show a dispersed research community with a lack of cohesion.
5.3. What Is the Predominant Type of Document and Language among the Studies?
With regards to the documentary dimension, an identification of the different types of documents analysed was established. As can be seen in Figure 4, the predominant type of document was the scientific article (57.5%), followed by conference papers (40%). The percentage of books was reduced to 1%. The predominant language was English, with 92.5%, leaving Spanish (5%) and Portuguese (2.5%) as residual languages.
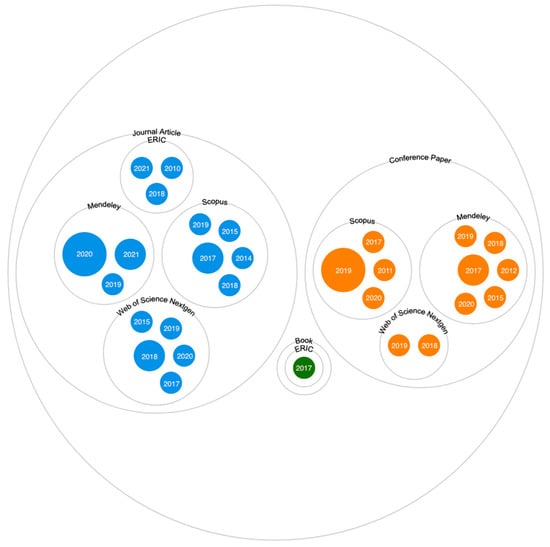
Figure 4.
Predominant type of document.
5.4. What Is the Distribution of Documents according to Database and Year of Publication?
Of the four databases analysed, Mendeley, with 37.5%, and Scopus, with 32.5% of the publications, stood out with the greatest volume of documents contributed. These were followed by Web of Science, with 20%. ERIC also made a significant contribution of documents to this review, with 10%.
The year of publication that stood out the most was 2019 (22.5% of the publications). It was striking how, from 2014 to 2019, the publications on the selected subject had a significant increase. A small decrease was noted in 2021 (10%).
5.5. What Are the Pedagogical Approaches or Models Adopted in the Literature regarding the Use of Serious Games in the Classroom?
Thirteen models and/or approaches for the implementation of serious games in classroom contexts were identified in the selected studies.
5.5.1. The TPACK Model
This research analysed the incorporation of serious games under the TPACK (technology, pedagogy, and content knowledge) model in different areas of knowledge (Figure 5). It is a model with ample empirical evidence based on multiple investigations that still generates interest today, which leads to updates and improvements that highlight the most significant evidence of the model [57,58]. Mishra and Koehler [59] proposed a model consisting of three basic knowledge components and their relationships: curricular content (CK, content knowledge), pedagogy (PK, pedagogical knowledge) and technology (TK, technological knowledge). This model involves four types of knowledge: declarative (knowing what: this includes definitions, terms, facts, and descriptions), procedural (knowing how, i.e., sequences of steps to complete a task or sub-task), schematic (knowing why: this is drawn from the previous two knowledge types and creates principles and mental models), and strategic (knowing when and where to use given knowledge and strategies, such as planning and problem solving, along with monitoring progress toward a goal) [60].

Figure 5.
TPACK model with serious games.
In the research by Barbieri et al. [57] and Zanichelli et al. [58], this model was applied to the use of serious games in the classroom, one in the area of mathematics and another for the development of digital competence aimed at evaluating the quality of content and avoiding misinformation.
5.5.2. Game-Based Learning
With a foundation in experiential learning, this approach refers to learning through active exploration [56,61,62,63,64]. Applied to serious games in the identified studies, this model is aimed at providing an educational environment based on teacher-driven game experience (exploration, discovery, problem solving, etc.). In one of the studies [64], this model was incorporated with Gagne’s learning model to incorporate nine events: capturing attention, informing the learner of the objective, stimulating recall by activating prior knowledge, presenting information, providing guidance, increasing performance, giving feedback, assessing performance, and improving retention and transfer.
5.5.3. Combined Model by Fernandez et al.
The model proposed by Fernández et al. [45] for experimentation with serious games in the classroom corresponds to the model by Garris, Ahlers, and Driskell [65] that combines game-based learning with an experiential learning cycle [48]. It hinges on the premise that people learn if there is active engagement with an activity and that experience, accompanied by support (scaffolding), provides an effective educational environment. Thus, motivation is considered a key element in the development of commitment to the activity and the effort and persistence put into it. In this sense, the model leverages elements of the video game activity in a learning cycle characterised by the commitment of the student to achieve the desired outcomes.
5.5.4. Model of Desire to Learn (D2L)
The D2L model [66] is based on the information processing theory, in which it is understood that the human brain processes data similarly to the way a computer does. Thus, if presented with extraneous material, the human brain will use working memory and associated processing to shift focus. The authors indicate that the information processing theory helps model and predict how humans receive, interpret, and store data. Thus, they used a quest game, in which each player chooses an avatar that will travel through a fictitious university campus, stopping at campus buildings online (the defined waypoints) to complete a series of activities. The goal of the game was to explore how games affect information retrieval and the understanding of learning in an online context.
5.5.5. Comprehensive Game-Bsed Pedagogical Model
This model is based on a game called Social Seducement, which seeks to facilitate the social reintegration of individuals who have been unemployed for a long period of time, by means of participation in the development of entrepreneurial activities within the field of social economy [67]. The game develops a series of skills to build a successful enterprise. The integral pedagogical model is based on the fundamentals of Kolb’s experiential learning with the help of an ADDIE instructional design, generating its own model of skill acquisition through serious play based on evaluation and decision making, and always guided by a teacher.
5.5.6. The Model PcaRD (Play, Curricular Activity, Reflection, and Discussion)
PCaRD is a pedagogical model aimed at incorporating digital play in the classroom to support student learning [68]. It is born out of a larger framework called Game Network Analysis (GaNA) (Figure 6), which aims to assist teachers and researchers in their introduction of game-based learning into the classroom, guiding them from game analysis to the integration of play into the curriculum. The PCaRD model leverages teachers’ technological pedagogical content knowledge (the TPACK model by Mishra and Koehler [59]) about games to create learning and assessment activities (Figure 7). This model attempts to engage students in an informal training process through play, followed by teacher-designed activities that connect to the subject matter of the game. The tasks should include reflection, writing, expression, and discussion activities, seeking the development of knowledge that connects the game process with the curricular activities. The process that is established should include the game, the curricular activity, reflection, and discussion.
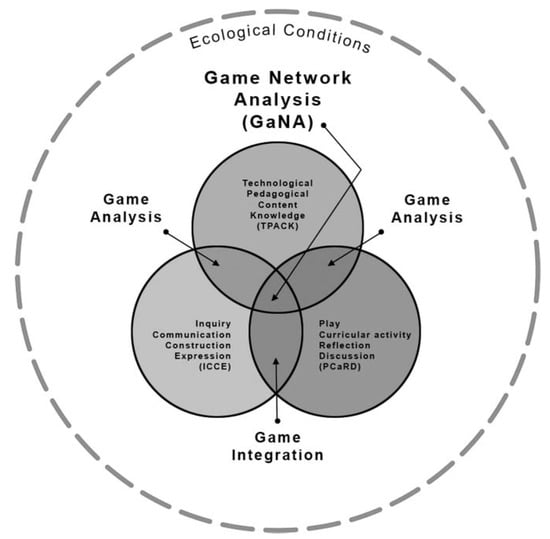
Figure 6.
GaNA pedagogical model.
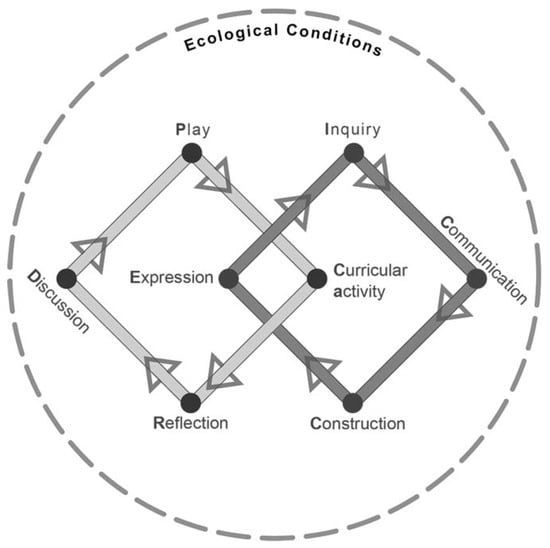
Figure 7.
PCaRD pedagogical model.
This is a model from which the authors have developed several investigations [68] recommending that teachers play digital games and identify methodologies and content (TPACK) that can be practised and acquired in such a game process.
5.5.7. The Collaborative Simulation Model
This pedagogical model [69] of collaborative simulation aims to make students think creatively and reflectively and discuss the reasons that lead them to make decisions to solve specific problems and situations (Figure 8). They start with a simulation called 4Decades, which deals with sustainable business leadership management.
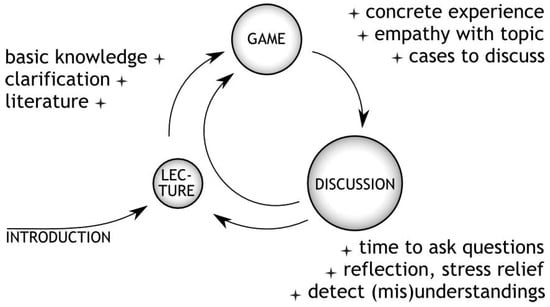
Figure 8.
Collaborative simulation pedagogical model by de Kreitmayer et al. [69].
The process begins with a basic knowledge of the subject and the fundamental concepts to start the game experience that will involve studying cases, asking questions, and probing, discussing, and searching, in a collaborative way, for solutions in a new process that leads back to the knowledge acquired and to a new game process.
5.5.8. Paulo Freire’s Pedagogical Model
This model for introducing serious games in the classroom is based on Paulo Freire’s pedagogy, working on objectives related to adolescent health education [70]. This game application model is designed to be used in collective actions and mediated by an educator who follows the principles of Freirean pedagogy, with experience in building horizontal relationships through dialogue, based on ethics and mutual respect, strengthening the bond between educators and learners and building educational experiences that contribute to the autonomy of students in the field of health. This model for the application of games has support guides for educators.
5.5.9. ACCORD Methodology
This model is aimed at improving teachers’ competencies in terms of intercultural conflict management, in the context of inclusive education, through a platform that incorporates a serious game aimed at improving three key competencies: intercultural literacy, conflict management, and inclusive education [67,68]. This game allows for the experience of direct participation through role-playing within the learning environments/scenario, where you act through a digital character. The game trains negotiation and intercultural communication skills through scenarios during the interaction with other characters. This model is based on two pedagogical approaches: scenario-based learning (part of Lave and Wenger’s situated learning) and game-based learning.
5.5.10. GAME Pedagogical Model
The GAME model seeks the acquisition of PISA science competencies in students through the use of serious games [53]. Starting from a game-based learning approach, there are four strategies, which are gamification, assessment, modelling, and inquiry-based learning. It is considered that a game-based educational model needs to be accompanied by other procedures that aid in the achievement of these scientific competencies. Gamification scenarios bring the mechanics, dynamics, and components of games to a non-game environment. Assessment is conceived to be the reflective process that students use in their own learning process. Modelling constitutes a concrete representation of a thing or system and the search for an explanation of the phenomenon. Finally, inquiry-based education constitutes an active learning process that consists of asking questions and promoting thinking skills in relation to scientific phenomena, rather than just presenting knowledge for study. The authors indicate that these four strategies of the GAME model can be incorporated into game-based learning.
5.5.11. Singapore Method or Singapore Pedagogical Model
This pedagogical model was proposed as an ideal in the use of serious games for teaching basic arithmetic operations to six-year-old children (addition and subtraction) [71]. The games are structured in a presentation of several challenges with levels of complexity, where the creation of visual scenarios and the iconic representation of knowledge is performed through the Singapore method. This method is a model for learning mathematics at an early childhood education level and is named after Singapore due to their good results in the PISA and TIMMS tests [72]. It focuses on mathematical problem solving in several contexts derived from the ideas of Bruner, Dienes, and Skemp: understanding; the CPA approach (the concrete–pictorial–abstract process); spiral progression curriculum; modes of representation with complete material; maturation and development; students as active learners; exercise and practice; and memory improvement. The components of the model are comprehension (initiation, abstraction, and schematisation), consolidation, transfer, and evaluation.
5.5.12. WeDraw Pedagogical Model
This model proposes the use of multisensory learning in the integration of serious games in the primary classroom for the exploration of mathematical concepts [73,74]. Its foundations come from neuroscientific understanding and the role of communication between sensory modalities during development. Specific sensory systems have specific functions for learning specific concepts. Researchers have developed a multisensory technology and three serious games aimed at learning arithmetic and geometric concepts, under a pedagogical framework that follows the principles of multisensory learning.
5.5.13. Flipped Classroom
The model used in two of the selected studies is the integration of serious games through flipped teaching [54,55], known as the inverted classroom methodology. This consists of students preparing certain learning content outside the classroom, and while in the classroom, they work on related activities, accompanied by the teacher. The approach of the three selected studies responds to a hybrid learning model, where serious games are integrated with face-to-face and virtual classes. In the model proposed by Ouchaouka et al. [75], serious games are seen as a complementary activity to be carried out during non-face-to-face time, which is then discussed during synchronous face-to-face moments.
6. Conclusions towards a (Multi-Methodological) Pedagogy of Serious Games
This systematic literature review establishes an index of pedagogical models oriented to the implementation of serious games in the educational environment. In this way, coinciding with other previous studies, the relevance of the instructional design of flexible, motivating, experiential, and meaningful educational processes through game-based learning is evidenced [53,76,77].
The main conclusion of this research determines that there is no single reference model to generate one serious game pedagogy. Although there are certainly models that predominate or are based on widely researched approaches, such as experiential learning, game-based learning, or the TPACK model, there are multiple ways to implement serious games in classroom contexts. In this sense, it was also observed that the conceptual network that characterises the pedagogical models for the use of serious games in the classroom is mainly related to the concept of educational games and gamification. These two terms are related, in turn, to a diversity of broad concepts that range from educational technology, pedagogical methods (supported by technologies), to commitment-motivation (of students), among other key elements that make the conceptual network of this topic more complex. This could explain the little interaction between research and reference authors of the articles identified when we analysed the relationships between these studies. All these issues may be accompanied by the fact that, at present, designers of serious games use a variety of pedagogical models, which could cause their introduction into the classroom to centre around the context (characteristics of the centre and students, infrastructure, educational level, etc.) in which they are implemented. It would be interesting to extend the study from this point of view to allow for the obtaining of data that would constitute a deeper exploration.
On the other hand, we identified that most of the research is disseminated in English and through scientific articles, with Scopus and Mendeley databases as priority and 2014–2019 as the five-year range in which scientific production on the analysed subject matter increased. It seems that, after the pandemic, there was a decrease in publications, which may point to the fact that, in this period in which teaching was virtual, the use of this type of video game as an educational resource also decreased.
It can also be seen that the current pedagogy of serious games is oriented towards more constructivist and cognitivist approaches, breaking, to a certain extent, with the behaviourist models that characterised, in a hegemonic way, these types of games in the past. With these models, the students are the centre of the game experience. The information is clear and easily accessible. The tendency is to build knowledge in order to make decisions and transfer what has been learned to a real context, and error is used as a learning tool, among other key markers.
Serious games have demonstrated their usefulness in classroom contexts to achieve competencies at all educational levels, but research is still scarce. Studies are needed that address this (multi-methodological) pedagogy of serious games so that their integration in classroom contexts is as simple and effective as possible. Explorations that address the advances in artificial intelligence applied to this type of video game for methodological adaptation (personalization, inclusion, and accessibility, among others) among students and geared toward their educational needs would also provide interesting data.
We also provided an Appendix A here, which includes the references that have been used to carry out the SLR research and which we make available to other authors in an orderly fashion.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.R.F.-S. and A.G.-F.; methodology, M.R.F.-S. and J.A.-B.; software, M.R.F.-S. and J.A.-B.; validation, M.R.F.-S., A.G.-F. and J.A.-B.; formal analysis, M.R.F.-S., A.G.-F. and J.A.-B.; investigation, M.R.F.-S., A.G.-F. and J.A.-B.; resources, M.R.F.-S., A.G.-F. and J.A.-B.; data curation, M.R.F.-S., A.G.-F. and J.A.-B.; writing—review and editing, M.R.F.-S., A.G.-F. and J.A.-B.; supervision, M.R.F.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
National R&D&I Plan. Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (Spain) Ref. RTI2018-097144-B-I00.
Data Availability Statement
A full list of references used in the SLR is provided at the end of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. Sample of Documents for the Systematic Review
- Abeyrathna, D.; Vadla, S.; Bommanapally, V.; Subramaniam, M.; Chundi, P.; Parakh, A. Analyzing and predicting player performance in a quantum cryptography serious game. In Proceedings of the Games and Learning Alliance: 7th International Conference, GALA 2018, Palermo, Italy, 5–7 December, 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 267–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11548-7_25.
- Agustin, R.D.; Purwarianti, A.; Surendro, K.; Suwardi, I.S. Instructional design in serious game for learning based on inquiry and situated learning theory. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2015, 21, 3667–3671. https://doi.org/10.1166/asl.2015.6568.
- Algayres, M.; Triantafyllou, E. Combining Game-Based Learning and the Flipped Classroom: A Scoping Review. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Games Based Learning, Odense, Denmark, 3–4th October 2019; Academic Conferences International Limited: Reading, United Kingdom; pp. 823–831.
- Artal-Sevil, J.S. Flipped Teaching and game-based learning in higher education: The good, the bad and the ugly. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation (iceri2019), Sevilla, Spain, 11–13th November 2019; Chova, L.G., Martinez, A.L., Torres, I.C., Eds.; International Association Technology Education & Development: Valencia, Spain, 2019; pp. 9271–9280.
- Artal-Sevil, J.S.; Gargallo-Castel, A.F.; Valero-Gracia, M.S. Flipped teaching and interactive tools. A multidisciplinary innovation experience in higher education. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Higher Education Advances, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 June 2020.
- Barbieri, G.G.; Barbieri, R.; Capone, R. Serious games in high school mathematics lessons: An embedded case study in europe. EURASIA J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2021, 17, https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/10857
- Bellotti, F.; Berta, R.; De Gloria, A.; Primavera, L. Supporting authors in the development of task-based learning in serious virtual worlds. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2010, 41, 86–107. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01039.x.
- Choquehuayta Palomino, S.; Herrera Quispe, J.; Alfaro, L.; Choquehuayta Llamoca, B. Intelligent pedagogical model with kinesthetic-static immersion based on the neuro-linguistic programming approach (NLP). Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2019, 10, 564–573.
- Donald, I.; Meyer, K.A.; Brengman, J.; Gillespie, S.H.; Bowness, R. Project sanitarium: Playing tuberculosis to its end game. J. Comput. High. Educ. 2017, 29, 599–617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-017-9145-1.
- Duffy, S.; Price, S.; Volpe, G.; Marshall, P.; Bianchi-Berthouze, N.; Cappagli, G.; Cuturi, L.; Balzarotti, N.; Trainor, D.; Gori1, M. WeDRAW: Using Multisensory Serious Games to Explore Concepts in Primary Mathematics. Available online: https://ictmt13.sciencesconf.org/148376/document (accessed on 5 April 2022).
- Faber, T.; Dankbaar, M.; van Merriënboer, J. Applying an instructional design method to serious games—experiences and lessons learned. In Proceedings of the 2018 9th International Conference on Information, Intelligence, Systems and Applications (IISA), Zakynthos, Greece, 23–25th July 2018; pp. 1–3.
- Fernández-Sánchez, M.R.; Sierra-Daza, M.C.; Valverde-Berrocoso, J. Serious Games para la adquisición de competencias profesionales para el desarrollo social y comunitario. Rev. Prism. Soc. 2020, 30, 141–160.
- Foster, A.; Shah, M. PCARD: Integrating Games into Classrooms. In Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Games Based Learning, Athens, Greece, 20–21 October 2011; pp. 183–194.
- Frossard, F.; Barajas, M. Enhancing Teachers’ Intercultural Conflict Management Competences through Digital Game-Based. Learning: A Pedagogical Framework. In EDEN Conference Proceedings; 2018. https://www.eden-online.org/proc-2485/index.php/PROC/article/view/1597
- Gachkova, M.; Somova, E. Plug-in for Creation of Gamified Courses in the e-Learning Environment Moodle. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, Kazimierz Dolny, Poland, 21–23 November 2019; Volume 618. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/618/1/012079
- Gampell, A.; Gaillard, J.C.; Parsons, M.; Le Dé, L. ‘Serious’ disaster video games: An innovative approach to teaching and learning about disasters and disaster risk reduction. J. Geogr. 2020, 119, 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1080/00221341.2020.1795225.
- Hotte, R.; Ferreira, S.M.; Abdessettar, S.; Gouin-Vallerand, C. Digital learning game scenario: A pedagogical pattern applied to serious game design. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2017), Porto, Portugal, 21–23 April 2017; Volume 2, pp. 87–94. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006260300870094
- Hummel, H.G.K.; Slootmaker, A.; Storm, J. Mini-games for entrepreneurship in construction: Instructional design and effects of the TYCON game. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2021, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1995759.
- Kreitmayer, S.; Rogers, Y.; Laney, R.; Peake, S. From participatory to contributory simulations: Changing the game in the classroom. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 5–10 May 2012; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 49–58. https://doi.org/10.1145/2207676.2207685
- Maskeliūnas, R.; Kulikajevas, A.; Blažauskas, T.; Damaševičius, R.; Swacha, J. An interactive serious mobile game for supporting the learning of programming in JavaScript in the context of eco-friendly city management. Computers 2020, 9, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers9040102.
- Monteiro, R.J.S.; Oliveira, M.P.C.A.; Belian, R.B.; de Lima, L.S.; Santiago, M.E.; Gontijo, D.T. DECIDIX: Meeting of the Paulo Freire pedagogy with the serious games in the field of health education with adolescents. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2018, 23, 2951–2962. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-81232018239.12782018.
- NeirPa, R.; Barba-Guaman, L.; González-Eras, A. MateBrun: Serious game as a strategy to teach basic arithmetic operations for six-years-old children.; CLIHC '19: Proceedings of the IX Latin American Conference on Human Computer InteractionSeptember 2019, 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1145/3358961.3358974
- Ouchaouka, L.; Laouina, Z.; Moussetad, M.; Talbi, M.; Amrani, N.E.; ElKouali, M. The Effectiveness of a Learner-centered pedagogical approach with flipped pedagogy and digital learning environment in higher education feedback on a cell biology course. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (IJET) 2021, 16, 4–15. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v16i12.19125.
- Paciarotti, C.; Bertozzi, G.; Sillaots, M. A New approach to gamification in engineering education: The learner-designer approach to serious games. Eur. J. Eng. Educ. 2021, 46, 1092–1116. https://doi.org/10.1080/03043797.2021.1997922.
- Padilla Beltran, J.E.; Caviativa Castro, Y.P.; Mantilla Pastrana, M.I. Strengthening cognitive processes in early childhood through a pedagogic tool with video games. Int. J. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2018, 12, 13–20.
- Padilla-Zea, N.; Aceto, S.; Burgos, D. Social seducement: Towards the foundations of a pedagogical model. Ing. Solidar. 2017, 13, 45–52. https://doi.org/10.16925/in.v13i21.1728.
- Price, S.; Duffy, S.; Gori, M. Developing a pedagogical framework for designing a multisensory serious gaming environment. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGCHI International Workshop on Multimodal Interaction for Education; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 13 November 2017; pp. 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1145/3139513.3139517
- Simic, G.; Jevremovic, A.; Kostic, Z.; Dordevic, D. Assessment based on serious gaming interactive questions (SGIQ). J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2015, 31, 623–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12105.
- Simonson, M.; Seepersaud, D. (Ed.). Annual Proceedings of Selected Papers on the Practice of Educational Communications and Technology Presented at the 40th Annual Convention of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology, Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2017. Association for Educational Communications and Technology: Bloomington, Indiana, USA, 2017; Volume 2.
- Sreelakshmi, R.; McLain, M.; Rajeshwaran, A.; Rao, B.; Jayakrishnan, R.; Bijlani, K. Gamification to enhance learning using gagne’s learning model. In Proceedings of the 2015 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Dallas-Fortworth, TX, USA, 13–15 July 2015; pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCCNT.2015.7395197
- Symborski, C.; Barton, M.; Quinn, M.M.; Korris, J.H.; Kassam, K.S.; Morewedge, C.K. The design and development of serious games using iterative evaluation. Games Cult. 2017, 12, 252–268. https://doi.org/10.1177/1555412016673262.
- Taitto, P.; Nevmerzhitskaya, J.; Virag, C. Using holistic approach to developing cybersecurity simulation environments. eLearning & Software for Education. 2018, Volume 4, p. 77-84.
- Tsai, C.-Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, S.-C. The effect of pedagogical GAME model on students’ PISA scientific competencies. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2020, 36, 359–369. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12406.
- Usart, M., Romero, M. (2014). Entrepreneurship Competence Assessment Through a Game Based Learning MOOC. In: De Gloria, A. (eds) Games and Learning Alliance. GALA 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8605. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-12157-4_20
- Vallone, F.; Dell’Aquila, E.; Zurlo, M.C.; Marocco, D. “ACCORD” e-Platform: Development and evaluation of an innovative multicultural training for school professionals.; 2020; Volume 2730. https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2730/paper6.pdf
- Vaz de Carvalho, C.; Durão, R.; Llamas-Nistal, M.; Caeiro Rodriguez, M.; Heidmann, O.; Tsalapatas, H. Development of professional competences in higher education through active learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Coimbra, Portugal, 19–22 June 2019; pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.23919/CISTI.2019.8760984.
- Westera, W. Why and how serious games can become far more effective: Accommodating productive learning experiences, learner motivation and the monitoring of learning gains. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2019, 22, 59–69.
- Zanichelli, F.; Thabet, B.; Maria, A.; Conti, G. Serious games for information literacy: Assessing learning in the NAVIGATE Project. 2021, 13. https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2816/paper7.pdf
- Zapatera Linares, A. El método Singapur para el aprendizaje de las matemáticas. Enfoque y concreción de un estilo de aprendizaje. Revista INFAD de Psicología. Int. J. Dev. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 1, 263–274. https://doi.org/10.17060/ijodaep.2020.n2.v1.1980.
- Zeglen, E.; Rosendale, J.A. Increasing online information retention: Analysing the effects of visual hints and feedback in educational games. J. Open Flex. Distance Learn. 2018, 22, 22–33.
References
- Bauman, Z.; Payás, D. Sobre La Educación En Un Mundo Líquido; Ediciones Paidós: Barcelona, Spain, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nowak, M.A.; Highfield, R. SuperCooperators: Altruism, Evolution, and Why We Need Each Other To Succeed; FreePress: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Moravec, J.W. Knowmads in Society 3.0; Education Futures: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott, D. Grown Up Digital: How the Net Generation Is Changing Your World; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-07-150863-6. [Google Scholar]
- Council of the European Union, E.C. 2015 Joint Report of the Council and the Commission on the Implementation of the Strategic Framework for European Cooperation in Education and Training (ET 2020)—New Priorities for European Cooperation in Education and Training. Off. J. Eur. Union 2015, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Cobo, C. La Innovación Pendiente. Reflexiones (y Provocaciones) Sobre Educación, Tecnología y Conocimiento; Colección Fundación Ceibal/ Debate: Montevideo, Uruguay, 2016; ISBN 978-9974-741-10-2. Available online: https://digital.fundacionceibal.edu.uy/jspui/handle/123456789/159 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Prendes, M.P.; Roman, M. Entornos Personales de Aprendizaje: Una Visión Actual de Cómo Aprender Con Tecnologías [Personal Learning Environments. A current vision of how to learn with technologies]. In Octaedro; Alfaguara: Madrid, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Silva Quiroz, J.; Maturana Castillo, D. Una propuesta de modelo para introducir metodologías activas en educación superior. Innov. Educ. México DF 2017, 17, 117–131. [Google Scholar]
- Castañeda, L.; Selwyn, N. Reiniciando la Universidad: Buscando un Modelo de Universidad en los Tiempos Digitales; UOC Editorial: Barcelona, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, M. The rise of the knowledge broker. Sci. Commun. 2010, 32, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, G.E.; Judd, T.S.; Churchward, A.; Gray, K.; Krause, K.-L. First year students’ experiences with technology: Are they really digital natives? Australas. J. Educ. Technol. 2008, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escofet Roig, A.; García Gonzalez, I.; Gros Salva, B. Las nuevas culturas de aprendizaje y su incidencia en la educación superior. RMIE Rev. Mex. Investig. Educ. 2011, 16, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar]
- Bullen, M.; Morgan, T.; Qayyum, A. Digital learners in higher education: Generation is not the issue. Can. J. Learn. Technol. 2011, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedró, F. The New Millennium Learners: Challenging Our Views on ICT and Learning; OECD: Paris, France, 2006; Available online: https://publications.iadb.org/en/new-millennium-learners-challenging-our-views-ict-and-learning (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Adell Segura, J.; Castañeda Quintero, L.J. Tecnologías emergentes, pedagogías emergentes In Tendencias Emergentes En Educación con TIC; Hernández Ortega, J., Pennesi, M., Sobrino López, D., Vázquez Gutiérrez, A., Eds.; D-Asociación Espiral, Educación y Tecnología: Barcelona, Spain, 2012; pp. 13–33. ISBN 978-84-616-0431-9. [Google Scholar]
- Karagiorgas, D.; Niemann, S. Gamification and game-based learning. J. Educ. Technol. Syst. 2017, 45, 499–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Berrocoso, J.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.R. Serious Games Para El Aprendizaje En Red. In Videojuegos en Redes Sociales: Perspectivas del “Edutainment” y la Pedagogía Lúdica en el Aula; Laertes: Barcelona, Spain, 2013; pp. 177–191. [Google Scholar]
- Valverde-Berrocoso, J.; Fernández-Sánchez, M.R. El laboratorio Nodo Play. Aprendizaje basado en juegos. EMTIC. 2019. Available online: https://emtic.educarex.es/listado-de-categorias-2/251-emtic/juegos-y-gamificacion/3260-laboratorio-noplay (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Hamari, J.; Shernoff, D.J.; Rowe, E.; Coller, B.; Asbell-Clarke, J.; Edwards, T. Challenging games help students learn: An empirical study on engagement, flow and immersion in game-based learning. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 54, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossad, F.; Barajas, M.; Trifonova, A. El diseño de juegos educativos por el profesor: Mejora su creatividad? In Aprendizaje y Educación en la Sociedad Digital; Rodríguez Illera, J.L., Ed.; Universidad de Barcelona: Barcelona, Spain, 2013; pp. 7–26. [Google Scholar]
- Torres Toukoumidis, Á.L.; Romero Rodríguez, L.M. Gamificación, simulación, juegos serios y aprendizaje basado en juegos. In Juegos y Sociedad: Desde la Interacción a la Inmersión Para el Cambio Social; Torres Toukoumidis, Á.L., Romero Rodríguez, L.M., Salgado Guerrero, J.P., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 113–120. ISBN 978-1-4562-7169-5. [Google Scholar]
- Hallinger, P.; Wang, R.; Chatpinyakoop, C.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Nguyen, U.-P. A bibliometric review of research on simulations and serious games used in educating for sustainability, 1997–2019. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso Martínez, D.; Navazo Ostúa, P. Juegos y simulaciones en la educación actual. Rev. Prisma Soc. 2019, 25, 537–548. [Google Scholar]
- Erhel, S.; Jamet, E. Improving instructions in educational computer games: Exploring the relations between goal specificity, flow experience and learning outcomes. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 91, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, R.L.; Annetta, L.; Firestone, J.; Etopio, E. A meta-analysis with examination of moderators of student cognition, affect, and learning outcomes while using serious educational games, serious games, and simulations. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 80, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokides, E.; Atsikpasi, P.; Kaimara, P.; Deliyannis, I. Let players evaluate serious games. Design and validation of the serious games evaluation scale. ICGA J. 2019, 41, 116–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz de Carvalho, C.; Durão, R.; Llamas-Nistal, M.; Caeiro Rodriguez, M.; Heidmann, O.; Tsalapatas, H. Development of Professional Competences in Higher Education through Active Learning. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Coimbra, Portugal, 19–22 June 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Almeida, F.; Simoes, J. The role of serious games, gamification and industry 4.0 tools in the education 4.0 paradigm. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2019, 10, 120–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorneles, S.O.; da Costa, C.A.; Rigo, S.J. A model for ubiquitous serious games development focused on problem based learning. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Cognition and Exploratory Learning in the Digital Age (CELDA), Greater Dublin, Ireland, 24–26 October 2015; International Association for Development of the Information Society (IADIS). Sampson, D.G., Spector, J.M., Ifenthaler, D., Isaias, P., Eds.; Distributed by ERIC Clearinghouse. 2015; p. 7, ISBN 978-989-8533-43-2. [Google Scholar]
- Nazry, M.N.; Romano, D.M. Mood and learning in navigation-based serious games. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2017, 73, 596–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-R.; Shih, J.-L. Game factors and game-based learning design model. Int. J. Comput. Games Technol. 2015, 2015, 549684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouaheb, H.; Fahli, A.; Moussetad, M.; Eljamali, S. The serious game: What educational benefits? Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 46, 5502–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo Sanguino, N.; Guzmán Mijangos, M.; Matus López, P.; Rivera García, C.; Marín Zavala, J.G. Serious Games y educación superior. RIESED Rev. Int. Estud. Sobre Sist. Educ. 2018, 2, 250–268. [Google Scholar]
- Prensky, M. Digital natives, digital immigrants part 1. On the Horizont. 2001, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral Pérez, M.E. Aprendizaje basado en juegos digitales. Comun. Pedagog. Nuevas Tecnol. Recur. Didácticos 2020, 321–322, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Martín Del Pozo, M.; García-Valcárcel Muñoz-Repiso, A.; Basilotta Gómez-Pablos, V.; Martín Del Pozo, M. Participación educativa en el desarrollo de serious games sobre bullying y uso seguro de Internet: Caminando se hace el camino. RIITE Rev. Interuniv. de Investig. en Tecnol. Educ. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Hierro, L.; Pastor Seller, E. El aprendizaje basado en el juego como herramienta socioeducativa en contextos comunitarios vulnerables. Prism. Soc. Rev. Investig. Soc. 2020, 88–114. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, Y.A.R.; Yunda, J.G. Aprendizaje basado en el juego aplicado a la enseñanza de la historia de la arquitectura prehispánica. Estoa 2021, 10, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backlund, P.; Hendrix, M. Educational games—Are they worth the effort? A literature survey of the effectiveness of serious games. In Proceedings of the 2013 5th International Conference on Games and Virtual Worlds for Serious Applications (VS-GAMES), Dorset, UK, 11–13 September 2013; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Connolly, T.M.; Stansfield, M.; Hainey, T. An alternate reality game for language learning: ARGuing for multilingual motivation. Comput. Educ. 2011, 57, 1389–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Sung, H.-Y.; Hung, C.-M.; Yang, L.-H.; Huang, I. A knowledge engineering approach to developing educational computer games for improving students’ differentiating knowledge. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2012, 44, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, C.; Featherstone, G.; Aston, H.; Houghton, E. Game-Based Learning: Latest Evidence and Future Directions; NFER: Slough, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Manzano, A.; Almela-Baeza, J. Gamification and transmedia for scientific promotion and for encouraging scientific careers in adolescents. Comunicar 2018, 26, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral Pérez, M.E.; Guzman Duque, A.P.; Fernández García, L.C. Game-based learning: Increasing the Logical-mathematical, naturalistic, and linguistic learning levels of primary school students. J. New Approaches Educ. Res. 2018, 7, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Sánchez, M.R.; Sierra-Daza, M.C.; Valverde-Berrocoso, J. Serious games para la adquisición de competencias profesionales para el desarrollo social y comunitario. Rev. Prisma Soc. 2020, 30, 141–160. [Google Scholar]
- Akella, D. Learning together: Kolb’s experiential theory and its application. J. Manag. Organ. 2010, 16, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, D.A. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, D.A.; Boyatzis, R.E.; Mainemelis, C. Experiential learning theory: Previous research and new directions. In Perspectives on Thinking, Learning, and Cognitive Styles; Routledge: London, UK, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; McGuinness, L.A.; Pritchard, C.C. PRISMA2020: R Package and ShinyApp for Producing PRISMA 2020 Compliant Flow Diagrams 2021. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, M.B.; Bellotti, F.; Berta, R.; De Gloria, A.; Sedano, C.I.; Hauge, J.B.; Hu, J.; Rauterberg, M. An activity theory-based model for serious games analysis and conceptual design. Comput. Educ. 2015, 87, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellotti, F.; Berta, R.; De Gloria, A.; Primavera, L. Supporting authors in the development of task-based learning in serious virtual worlds. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 2009, 41, 86–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, S. The effect of pedagogical GAME model on students’ PISA scientific competencies. J. Comput. Assist. Learn. 2019, 36, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal-Sevil, J.S. Flipped teaching and game-based learning in higher education: The good, the bad and the ugly. In Proceedings of the 12th Annual International Conference of Education, Research and Innovation, Seville, Spain, 11–13 November 2019; pp. 9271–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artal-Sevil, J.S.; Gargallo-Castel, A.F.; Valero-Gracia, M.S. Flipped teaching and interactive tools. A multidisciplinary innovation experience in higher education. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Higher Education Advances, Valencia, Spain, 2–5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Westera, W. Why and how serious games can become far more effective: Accommodating productive learning experiences, learner motivation and the monitoring of learning gains. J. Educ. Technol. Soc. 2019, 22, 59–69. [Google Scholar]
- Capone, R.; Barbieri, G.G.; Barbieri, R. Serious games in high school mathematics lessons: An embedded case study in europe. Eurasia J. Math. Sci. Technol. Educ. 2021, 17, em1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanichelli, F.; Thabet, B.; Maria, A.; Conti, G. Serious Games for Information Literacy: Assessing Learning in the Navigate Project, University of Padova (Virtual). 18 February 2021, p. 13. Available online: https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2816/paper7.pdf (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Mishra, P.; Koehler, M.J. Technological pedagogical content knowledge: A framework for teacher knowledge. Teach. Coll. Rec. Voice Scholarsh. Educ. 2006, 108, 1017–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrocoso, J.V.; Arroyo, M.D.C.G.; Sánchez, R.F. Enseñar y aprender con tecnologías: Un modelo teórico para las buenas prácticas educativas con TIC. Educ. Knowl. Soc. (EKS) 2010, 11, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gampell, A.; Gaillard, J.C.; Parsons, M.; Le Dé, L. ‘Serious’ disaster video games: An Innovative approach to teaching and learning about disasters and disaster risk reduction. J. Geogr. 2020, 119, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskeliūnas, R.; Kulikajevas, A.; Blažauskas, T.; Damaševičius, R.; Swacha, J. An interactive serious mobile game for supporting the learning of programming in JavaScript in the context of eco-friendly city management. Computers 2020, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usart, M.; Romero, M. Entrepreneurship Competence Assessment Through a Game Based Learning MOOC. In Proceedings of the Games and Learning Alliance: Second International Conference, GALA 2013, Paris, France, 23–25 October 2013; Revised Selected Papers 2. Springer: Cham, The Netherlands, 2014; Voume 8605, pp. 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreelakshmi, R.; McLain, M.L.; Rajeshwaran, A.; Rao, B.; Jayakrishnan, R.; Bijlani, K. Gamification to Enhance learning using gagne’s learning model. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Dallas-Fortworth, TX, USA, 13–15 July 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Garris, R.; Ahlers, R.; Driskell, J.E. Games, motivation, and learning: A research and practice model. Simul. Gaming 2002, 33, 441–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeglen, E.; Rosendale, J.A. Increasing online information retention: Analysing the effects of visual hints and feedback in educational games. J. Open Flex. Distance Learn. 2018, 22, 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zea, N.P.; Aceto, S.; Burgos, D. Social seducement: Towards the foundations for a pedagogical model. Ing. Solidar. 2017, 13, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, A.; Shah, M. The play curricular activity reflection discussion model for game-based learning. J. Res. Technol. Educ. 2015, 47, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitmayer, S.; Rogers, Y.; Laney, R.; Peake, S. From participatory to contributory simulations: Changing the game in the classroom. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Austin, TX, USA, 5–10 May 2012; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro, R.J.S.; Oliveira, M.P.C.D.A.; Belian, R.B.; De Lima, L.S.; Santiago, M.E.; Gontijo, D.T. DECIDIX: Encontro da pedagogia Paulo Freire com os serious games no campo da educação em saúde com adolescentes. Ciência Saúde Coletiva 2018, 23, 2951–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, R.; Barba-Guaman, L.; González-Eras, A. MateBrun: Serious Game as a Strategy to Teach Basic Arithmetic Operations for Six-Years-Old Children. In Proceedings of the IX Latin American Conference on Human Computer Interaction, Panama City, Panama, 30 September–4 October 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, A.Z. El método Singapur para el aprendizaje de las matemáticas. Enfoque y concreción de un estilo de aprendizaje. Int. J. Dev. Educ. Psychol. 2020, 1, 263–274. Available online: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=7873723 (accessed on 10 June 2022).
- Duffy, S.; Price, S.; Volpe, G.; Marshall, P.; Bianchi-Berthouze, N.; Cappagli, G.; Cuturi, L.; Balzarotti, N.; Trainor, D.; Gori1, M. WeDRAW: Using multisensory serious games to explore concepts in primary mathematics. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Technology In Mathematics Teaching, Lyon, France, 3–6 July 2017; Aldon, G., Trgalová, J., Eds.; Ens de Lyon: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Price, S.; Duffy, S.; Gori, M. Developing a pedagogical framework for designing a multisensory serious gaming environment. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM SIGCHI International Workshop on Multimodal Interaction for Education, New York, NY, USA, 13 November 2017; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Ouchaouka, L.; Laouina, Z.; Moussetad, M.; Talbi, M.; El Amrani, N.; ElKouali, M. The effectiveness of a learner-centered pedagogical approach with flipped pedagogy and digital learning environment in higher education feedback on a cell biology course. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. (iJET) 2021, 16, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustin, R.D.; Purwarianti, A.; Surendro, K.; Suwardi, I.S.; Dwi, A.R.; Ayu, P.; Kridanto, S.; Supriana, S.I. Instructional design in serious game for learning based on inquiry and situated learning theory. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2015, 21, 3667–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotte, R.; Ferreira, S.M.; Abdessettar, S.; Gouin-Vallerand, C. Digital learning game scenario—A pedagogical pattern applied to serious game design. In Proceedings of the CSEDU 2017—9th International Conference on Computer Supported Education, Porto, Portugal, 21–23 April 2017; Science and Technology Publication; Volume 2, pp. 87–94. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).