Abstract
Problems of preeclampsia sign diagnosis are mostly based on symptom data with the characteristics of data collected periodically in uncertain, ambiguous, and obstetrician opinions. To reduce the effects of preeclampsia, many studies have investigated the disease, prevention, and complication. Conventional fuzzy inference techniques can solve several diagnosis problems in health such as fuzzy inference systems (FIS), and Mamdani complex fuzzy inference systems with rule reduction (M-CFIS-R), however, the computation time is quite high. Recently, the research direction of approximate inference based on fuzzy knowledge graph (FKG) has been proposed in the M-CFIS-FKG model with the combination of regimens in traditional medicine and subclinical data gathered from medical records. The paper has presented a proposed model of FKG-Pairs3 to support patients’ disease diagnosis, together with doctors’ preferences in decision-making. The proposed model has been implemented in real-world applications for disease diagnosis in traditional medicine based on input data sets with vague information, quantified by doctor’s preferences. To validate the proposed model, it has been tested in a real-world case study of preeclampsia signs in a hospital for disease diagnosis with the traditional medicine approach. Experimental results show that the proposed model has demonstrated the model’s effectiveness in the decision-making of preeclampsia signs.
1. Introduction
Recently, preeclampsia signs have several typical clinical symptoms such as high blood pressure, proteinuria, and edema. Severe cases may be accompanied by convulsions and narcotisms [1,2,3]. Preeclampsia is a sort of multi-organ dysfunction related to pregnancy, accounting for about 2–10% during the entire pregnancy [1,3,4]. Over the past two decades, the preeclampsia rate has increased by about 25%, especially in the early preeclampsia group. In Asia, a statistic from 2001 to 2014 shows that preeclampsia increased quickly, from 0.5% to 0.8% during the entire pregnancy [1]. In Viet Nam, the preeclampsia rate before 34 weeks is 0.43%, the preeclampsia rate from 34 to 37 weeks is 0.7%, and the preeclampsia rate after 37 weeks is 1.68% compared to the entire pregnancy. A series of studies from 2012 to 2016 in Hue showed the preeclampsia rate is about 2.8–5.5% [2]. In applied AI healthcare applications, many studies of preeclampsia pathology in recent years have focused on the field of disease occurrence prediction, disease progression prediction, and pregnancy outcomes diagnosis as well as preeclampsia prophylaxis.
Preeclampsia is a pathology with multi-variable evidence for both mother and fetus. This causes of death maternal and perinatal mortality worldwide. Maternal mortality associated with hypertension in general pregnancy and preeclampsia accounts for about 14%. Death rate maternal mortality is associated with an increase in hypertension during pregnancy in the range of 12.9–16.1% [1,4]. Besides, the effects of preeclampsia are given after birth, in relation to subsequent births, and are a risk factor for later cardiovascular diseases [5]. Despite efforts in the management of the prenatal phase, preeclampsia is still one of the disease burdens in maternal and child healthcare. To reduce the effects of preeclampsia, many investigations have been given to aim disease forecasting and prophylaxis, optimally export prophylaxis presents the disease, prevents severe progression, and prevents complications. Since 2011, WHO has issued recommendations for forecasting and prophylaxis of preeclampsia pathology [1]. Many organizations (Federation Obstetrics and Gynecology International (FIGO), American Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), Healthcare Institute British National and Clinical Health (NICE), Canadian Society of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (SOGC)) and other specialized associations have also provided guidance on forecasting and redundancy preeclampsia [6,7,8,9]. With the motivation to apply information technology in early disease diagnosis, the authors have endeavored to deploy an application based on regimes in traditional medicine to solve the problem of preeclampsia sign diagnosis in pregnant women.
To handle problems in disease diagnosis, a knowledge graph-based approach is considered to support doctors in disease diagnosis [10,11,12]. KG is considered a powerful technique to support decision support systems, predictive analysis systems, and recommendation systems. It can be combined with other techniques to find the output labels of new samples. However, knowledge graphs face difficulties in representing knowledge and making approximate inferences based on input data sets with unclear information (such as subclinical symptom data with amplitude factor in the medical sector).
To solve the limitations of the knowledge graph, several techniques based on fuzzy inference systems are applied to build real-world applications. It has received much attention from many researchers all over the world, such as fuzzy inference systems (FIS) [13,14,15,16,17,18], complex fuzzy inference systems (CFIS) [19,20,21], and Mamdani-type complex fuzzy inference systems (M-CFIS) [22], M-CFIS-R [23]. These techniques cannot generate the output labels when new samples are not in the fuzzy rule base. Furthermore, these techniques can also show that the computation time is still quite high. Nevertheless, the M-CFIS-FKG still has low accuracy with incomplete information input data sets. Recently, the research direction of approximate inference based on fuzzy knowledge graph (FKG) has been proposed in the M-CFIS-FKG model [24] with the combination of regimens in traditional medicine and subclinical data gathered from electric medical records. This helps FKG to overcome the previous works’ drawbacks.
From the above limitations of the M-CFIS-FKG, a new model (so-called FKG-Pairs) was proposed in [25]. It is considered an extension of FKG in the M-CFIS-FKG model [24]. It improved the single-pairs FKG (FKG-Pairs1) by using combinations of attribute pairs to compute the weights and inference of the output label (e.g., double-pairs FKG (FKG-Pairs2), triple-pairs FKG (FKG-Pairs3), quadruple-pairs FKG (FKG-Pairs4), and quintuple-pairs FKG (FKG-Pairs5)). These methods have been applied to improve the inference performance of decision-making systems in terms of accuracy. In related works [26,27,28], the investigations have proposed Decision Support System to apply ontology-based for diabetic patients [26], Fuzzy Knowledge applied to give decision-making in diagnosis Decision Support System [27]. Further investigations have focused on human hearing abilities classification [28], applied U-Net with Deep Learning of glaucoma [29], and multiple Machine Learning techniques for decision making of chronic kidney disease [30], Prediction and analysis using dynamic neural network, genetic algorithm [31], and medical system has been applied to use deep learning techniques for clinic diagnosis [32]. In clinical decision support systems, knowledge reasoning and linguistics can be used in decision-making [33], multi-attribute decision-making [34,35], and group decision-making [36] for significant contributions to medical diagnosis. As mentioned in the related works, with incomplete information input data sets, conventional methods or fuzzy inference techniques have not been considered fully effective solutions. Studying to deploy easy and convenient FKG-Pairs-based applications is to meet the requirements for real-world problems.
The paper has presented a proposed model of FKG-Pairs3 to support patients’ disease diagnosis, together with doctors’ preferences in decision-making. The proposed model has been tested in a real-world case study of preeclampsia signs in a hospital for disease diagnosis with the traditional medicine approach. The main contributions of this study are as follows:
- Proposing the FKG-Pairs3-based preeclampsia sign diagnosis model. This proposed model is used to quantify incomplete and vague information input data sets including qualitative and quantitative factors, quantified from doctor’s preferences.
- Applying FKG-Pairs3 for consideration of patient’s symptom pairs to approximate reasoning to find the output labels of new samples, matched with the class of classification in decision-making problems with incomplete information input data sets.
- Implementing the proposed model for the development of real-world applications using datasets collected from medical records in accordance with the preferences of doctors through a case study of preeclampsia sign diagnosis for support of traditional medicine inpatient medical records.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Part 2 presents the background knowledge of the research process. Part 3 describes the detailed proposed model in medical diagnosis including the problem statement and the process of building and applying the FKG-Pairs to solve the problem. Experimental results and performance evaluation of the application are shown in Part 4. The final part is to give conclusions and future investigations.
2. Research Background
2.1. Fuzzy Sets
Fuzzy sets were first introduced by Zadeh in 1965 [37], introduced as a new mathematical tool for solving problems with ambiguous, uncertain information. Unlike normal sets, which evaluate the membership of the set according to the binary logic “an element belongs or not to the set”, fuzzy logic [38,39] evaluates the membership of a part element through a membership function μ → [0, 1], which represents the membership of an element to a set.
2.2. Fuzzy Inference System
A fuzzy inference system (FIS) is a popular computational framework based on the concept of fuzzy set theory, often applied when building decision support systems in case the input information is not clear [16]. The general framework of the FIS as shown in Figure 1 can be summarized with three main parts: fuzzification, knowledge base, and defuzzification. The FIS has the basic structure as follows:
- Fuzzification: It is responsible for converting input values into language values.
- The knowledge base consists of two parts: The database (definition of fuzzy set membership functions used in fuzzy rules) and the set of rules (including IF-THEN structural fuzzy rules).
- Engine: Perform inference operations in the fuzzy rule base.
Defuzzification: It is responsible for converting the fuzzy result values of the fuzzy inference system into clear values.
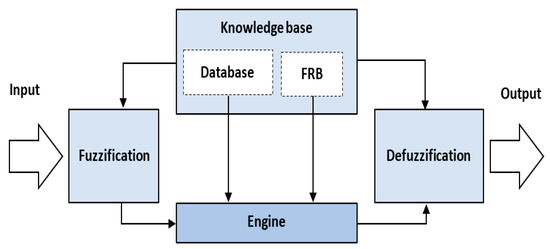

Figure 1.
The general framework of the FIS.
Fuzzy inference is the process of finding a conclusion for a set of input values, based on the synthesized fuzzy rule system. Fuzzy inference methods are regularly referred to as FIS, CFIS, and M-CFIS. These inference systems, also known as classical inference methods, have been widely used in automatic control systems and decision support systems. The FKG [24] is known as a new, efficient, and more accurate inference method than previous fuzzy inference methods. Fuzzy inference systems are classified into three main methods: Mamdani fuzzy inference systems, Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy inference systems, and Tsukamoto fuzzy inference systems.
2.3. Knowledge Graph
Knowledge graph (KG) was first introduced by Google in 2012 [40]. The main purpose of KG is to analyze to maximize the value of knowledge, detect and avoid errors, and to be able to infer new conclusions from existing data. The selection of new entity representations and their relationships through the KG model can gain a lot of useful information and can be more supportive for practical applications. It is for this reason that KG is researched, proposed, and applied by the community of researchers in many practical problems, especially in models with approximate reasoning. It is considered a powerful technique to support decision support systems, predictive analysis systems, and recommendation systems [41,42,43].
2.4. Fuzzy Knowledge Graph
The FKG was first proposed in 2020 [24] to solve the limitations of KG in representing knowledge and making approximate inferences based on input data sets with unclear or incomplete information by using linguistic labels for the attributes in the training set connected to the output labels. It represents inference through natural law where the impact of language labels is capable of generating corresponding output labels. By accumulating single events (or single pairs in the FKG), it can determine the final output of a new sample. The FKG has two main phases including representation and approximate reasoning.
In the representation phase, the weights of edges are calculated and are briefly summarized as follows. Firstly, for edges connecting among vertices or input attributes’ labels on FKG, the weight of these edges is calculated by using Equation (1):
where: are input attribute vertices, is therule,.
Secondly, for edges connecting the input attribute label and the output label on FKG, the weight of these edges is calculated by using Equation (2):
where: is input attribute vertex, is therule,, is output label vertex and .
The results of the two sets of weights are stored in an adjacency matrix, which can be used in the FISA algorithm in the next phase.
In the approximate reasoning phase, the FISA algorithm [24] is applied to approximate reasoning and find the output labels of the new records.
2.5. Approximate Reasoning and Decision Making
Approximate reasoning is defined as a tool for inferences from propositions of unspecified meaning through fuzzy logic [43]. Usually, the approximate inference method has a lower accuracy than the conventional inference techniques based on clear data, but the advantage of approximation reasoning unclear data with language variables. In [24], it is applied in the FISA algorithm to find the output labels of the new records.
Decision-making is considered the core of decision-support systems. It supports leaders and managers make accurate, timely, and effective decisions. It is applied in many sectors in the real world, such as healthcare, finance, stock, transportation, environment, agriculture, business, and other studies [31,42,43,44,45,46].
3. The Proposed Model for Preeclampsia Sign Diagnosis in Decision Making
This section describes the preeclampsia sign diagnosis proposed model in detail. The main contents are presented in this section including the problem statement, the proposed model, and a numerical example to elucidate the solving problem.
3.1. Problem Statement
Input: Suppose that we have an original database after extracting from pregnancy patients’ medical records. By supporting of doctors and obstetricians, the subclinical features are selected to construct the FKG-Pairs (such as Blood Pressure, HGB, PLT, Urea, Creatinine, Acid Uric, ALT, AST, Total Protein, Albumin, LDH, Proteinuria and so on). The training and testing data sets, with splitting 70% and 30% respectively, are obtained after applying the data preprocessing method and the rule-generated mechanism.
A fuzzy rule base of the training data set is described in detail in Table 1. It includes rules representing patients’ medical records, input features representing the symptoms of the preeclampsia, and output labels ) representing the doctor’s diagnosis results.
In addition, the testing data set includes samples after applying the rule-generated mechanism with the IF-THEN structure similar to the rules in Table 1. For instance:
IF is and is and is and is and … and is and is THEN Output label = 3.


Table 1.
The fuzzy rule bases.
Table 1.
The fuzzy rule bases.
| Output Labels | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | ||||||
| 1 | ||||||
| … | … | … | … | … | ||
| 1 | ||||||
| 3 | ||||||
| Patients’ symptoms | } | } | } | } |
Output: Find the output label of the new records with subclinical data inputted by doctors or patients based on the preeclampsia sign diagnosis module.
3.2. Proposed Model
In this subsection, we have presented the main contents related to the construction of triple-pairs FKG (FKG-Pairs3) for the problem of disease diagnosis based on symptom data, namely: Giving a model for the problem of preeclampsia sign diagnosis in gestational women; Describing steps to follow the proposed model; and give numerical examples to illustrate the proposed model.
3.2.1. The Preeclampsia Sign Diagnosis Proposed Model
The preeclampsia sign diagnosis proposed model consists of two phases (preparation phase; diagnosis phase) as shown in Figure 2. In the problem statement, assuming we have a fuzzy rule base of the preeclampsia sign diagnosis problem after applying several steps (including the pre-processing, the rule-generated mechanism, and the training). Then, the preeclampsia sign diagnosis module (based on FKG-Pairs3) is constructed by using the training data set and is validated by using the testing data set. Finally, obstetricians and gestational women can use this module to check the preeclampsia signs by inputting the subclinical data.
3.2.2. The Steps to Implement the Application
To implement the preeclampsia sign diagnosis application based on FKG-Pairs3, several steps are obligated strictly as follows:
Step 1. Gather data sets to establish the original database.
From the medical records of the patients, the features related to the preeclampsia signs are extracted. Then, the clinical and subclinical signs data are gathered with the doctor’s support. The data are stored in a database (considered the original database).
Step 2. Prepare the fuzzy rule base.
In this step, we conduct some tasks before constructing the FKG-Pairs3 as follows:
- Conducting the data preprocessing.
- Applying the rule-generated mechanism (herein FIS or M-CFIS).
- Applying the cluster sampling method and splitting the dataset into two parts including the training set and testing set with rates of 70% and 30% respectively.
Step 3. Construct the FKG-Pairs3 based on the training data set.
This step is considered the most important step to implement the preeclampsia sign diagnosis application in the proposed model as shown in Figure 2. There are three main tasks in this step as follows:


Figure 2.
The proposed model of preeclampsia sign diagnosis.
Firstly, for the edges connecting among vertices (input features’ labels) on FKG, the weight of these edges is calculated by using Equation (3):
in which is the number of rules in the training data set.
Secondly, for edges connecting the input feature label and the output label on FKG, the weight of these edges is calculated by using Equation (4):
in which is the number of rules in the training data set.
Finally, the FKG-Pairs algorithm in [37] (with or FKG-Pairs3) is applied to approximate reasoning and find the output labels of the new records. The algorithm is described briefly below.
Calculating the sum of the weights of the edges connecting from the super-nodes (i.e., each node is the combination among three features’ labels) is given to the output label by using Equation (5).
in which
Calculating the membership value () by using the operator, given by Equation (6).
in which
Finding the labels of the new records by using the operator, given by Equation (7).
Step 4. Validate the testing data set.
Before applying the preeclampsia sign diagnosis module for new records validated on the testing data set, which supports the application becoming more reliable. In case, the confidence of the diagnosis module cannot meet the doctors‘ requirements, we have to return to step 1 to get more data from new medical records to enrich the fuzzy rule base.
Step 5. Input the subclinical data of a gestational woman.
This step permits the patients (or users) to input the subclinical data to check the preeclampsia signs. Note that the data entered into the program has to meet the system’s requirements (i.e., in the valued range).
Step 6. Get the diagnosis results.
After processing and approximate reasoning based on the subclinical data entered by patients or users, the application calculates and finds the output label corresponding to the diagnosis result (users can recheck it from obstetricians if possible).
3.2.3. A numerical Example to Illustrate the Proposed Model
To deeply understand the proposed model, a numerical example is given in this subsection.
Input: Suppose that we have six rules {} representing six gestational women. Each gestational woman has five features {} representing the preeclampsia signs test results. The above cases of gestational women were examined and diagnosed based on the test results by the doctor. The output labels are 0, 1, and 2 corresponding to the doctor’s diagnosis conclusions “Normal”, “Preeclampsia” and “Severe Preeclampsia” respectively. After going through the data preprocessing step as well as applying the fuzzification of the input value by using the linguistic variables, a fuzzy rule base system is obtained as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
The fuzzy rule base assumes that the medical examination results of six gestational women have been concluded to be diagnosed by doctors.
In addition, we have also a new gestational woman after applying the rule-generated mechanism with the IF-THEN structure similar to the rules in Table 2. For instance: IF is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” THEN the output label = ?
Output: Find the output label of several new gestational women based on the fuzzy rule base in Table 2.
To solve the requirements given in the output, two steps are performed as follows:
Step 1: Constructing the FKG-Pairs3 based on the fuzzy rule base as shown in Table 2.
Firstly, we calculate the set of weights by applying Equation (3). With the rule , we have:
By the same calculation, we obtain the weights for six rules in Table 3 as follows.

Table 3.
Results of weight matrix calculation .
Secondly, after calculating the set of weights , we calculate the set of weights by applying the Equation (4). With the rule , it is expressed by:
By similar calculation, we find .
After applying Equation (4) for six rules, we obtain results of the entire weighted matrix , given in Table 4.

Table 4.
Results of weight matrix calculation .
Finally, the FKG-Pairs3 module is built by applying the FKG-Pairs algorithm in [37] (with or FKG-Pairs3) to approximate reasoning and find the output labels.
After calculating the weights and for six rules in the fuzzy rule base, we calculate the sum of the weights of the edges connecting from the super-nodes (i.e., each node is the combination among three feature labels) to the output label by using Equation (5). Let’s consider the rule :
- With label , we have:
- With label , we have:
- With label , we have:
By the same calculation with the rules , we obtain results of the set of weights , given in Table 5.

Table 5.
Results of calculating the set of weights .
From the values () in Table 5, we continue to compute the membership value () for each label by using the operator, given by Equation (6). For instance, in rule we have:
By using the operator, given by Equation (7), the label of rule is 2 because of . Similarly, we obtain the labels of rules being 1, 2, 0, 1, 2 respectively.
Step 2: Validating with the new records.
Case 1: The new record is in the fuzzy rule base system in Table 1, the output label is the same as the result of one of the six rules.
Case 2: The new record is not in the fuzzy rule base system in Table 1. For instance, IF is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” THEN the output label = ?. The output label of this new record is found by applying Equations (5)–(7). We have:
- With label ,
- With label ,
- With label ,
Therefore, , . The result of the new record: IF is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” and is “” THEN the output label = 2. The output label is 2 corresponding to the doctor’s diagnosis conclusion “Severe Preeclampsia”.
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experiments
To simulate the proposed model in real-world applications, the data set was gathered from pregnant women who came for regular check-ups to monitor the fetus at the National Hospital of Obstetrics and Gynecology in Vietnam. After receiving expert comments from the obstetrician, the preeclampsia data set includes 210 samples with 19 test parameters, such as Blood Pressure, Hemoglobin (HGB), Platelet Count (PLT), Urea, Creatinine, Acid Uric, Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT), Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST), Total Protein, Albumin, Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), Proteinuria and so on (in detail given in Table 6). In this data set, according to the diagnostic conclusion (in which 118 women with signs of normal pregnancy, 60 preeclampsia women, and 32 severe preeclampsia women).

Table 6.
List of features in the preeclampsia dataset.
The preeclampsia application is built using Python 3.10 language installed on a laptop (ASUS Intel(R) Core (TM) i5-8300H CPU @ 2.30 GHz).
4.2. Evaluation Method
To evaluate the proposed model-based system’s performance, the parameters are used including the accuracy and calculation time, specifically as follows:
Accuracy is evaluated by the ratio of the number of correctly classified samples over the total number of performed samples, estimated by Formula (8).
where:
- TP: True Positive
- TN: True Negative
- FP: False Positive
- FN: False Negative
Time is estimated by the total execution time of the classification system (unit: seconds).
4.3. Test Results in Simulations
After implementing the application based on the above data set, the authors established three different scenarios, namely:
- Scenario 1: the systematic random sampling method and the splitting method with training set (70%) and testing set (30%).
- Scenario 2: the systematic random sampling method and the splitting method with training set (10%) and testing set (90%).
- Scenario 3: the systematic random sampling method and the splitting method with training set (5%) and testing set (95%).
The comparison criteria include accuracy and computation time as given in Section 4.2. The experimental results are shown in Figure 3 and Figure 4.
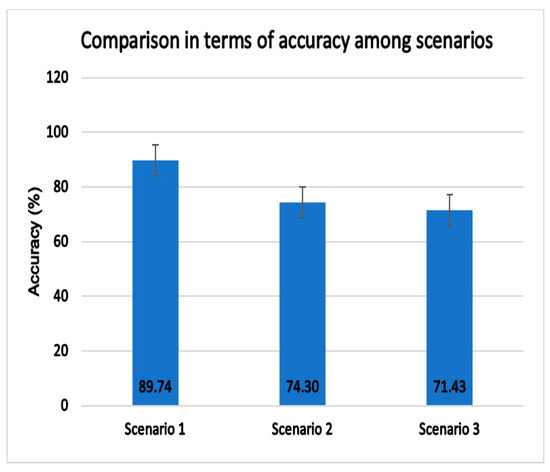
Figure 3.
Comparison in terms of accuracy among scenarios.

Figure 4.
Comparison in terms of computation time among scenarios.
As shown in the results of Figure 3, it is clear to see that the accuracy of scenario 1 is significantly higher than that of the other two scenarios. For example, the accuracy of scenario 1 is 15.44% higher than scenario 2 and 18.31% higher than scenario 3. It proves that the accuracy depends on the number of samples in the training data set.
However, the data in Figure 4 shows that the computation time of scenario 1 is also much higher than that of the other scenarios. Specifically, the computation time of scenario 1 is approximately 20 times higher than that of scenario 2, and nearly 50 times that of scenario 3. This demonstrated that the data set splitting method contributed significantly to improving the application’s performance in terms of time consumption.
After building and evaluating the model’s confidence, the authors proceed to build a simple application to diagnose the preeclampsia signs of the built model. Several illustrated images of the preeclampsia sign diagnosis application have been shown in Figure 5, Figure 6, Figure 7 and Figure 8.
Figure 5.
The main screen of the application.
Figure 6.
Screen for entering demographic information.
Figure 7.
Screen for entering subclinical test results.
Figure 8.
Diagnostic results screen and recommendations.
5. Conclusions
This paper has proposed the FKG-Pairs3-based preeclampsia signs in the diagnosis by combining regimens in traditional medicine and the information in medical records. The proposed model has been performed as a case study on the diagnosis of preeclampsia signs in gestational women based on the clinical and subclinical data collected from pregnant women attending routine antenatal care. The proposed model has been tested for an accuracy performance of 89.74% with the implementation designed scenario, in which the systematic random sampling method and the splitting method with training set (70%) and testing set (30%).
With complete information input data sets, the accuracy of the preeclampsia sign diagnosis system will continue to improve. However, the limitation of the proposed model is identified with two drawbacks in extreme cases as follows:
- Firstly, with large input data sets, the computation time is high based on the traditional data set splitting method (e.g., in scenario 1).
- Secondly, with too-small training data sets, the accuracy is low (e.g., in scenario 2 and scenario 3).
To expand this research work, the investigation will continue to study the approach of using the FKG-Pairs3 proposed model combined with Q-learning techniques in reinforcement learning to improve the accuracy of a system in extreme cases in which the training data set is much smaller than the testing data set (e.g., in cases scenarios 2 and 3 where the training sets only 10% and 5%, respectively).
6. Patents
This section is not mandatory but may be added if there are patents resulting from the work reported in this manuscript.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, C.K.L. and H.V.P.; software, P.H.K. and C.K.L.; validation, H.V.P., C.K.L. and H.Q.T.; formal analysis, C.K.L. and H.Q.T.; investigation, C.K.L. and P.H.K.; data curation, P.H.K.; writing—original draft preparation, C.K.L. and P.H.K.; writing—review and editing, H.V.P. and H.Q.T.; project administration, H.V.P.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research is funded by Vietnam National Foundation for Science and Technology Development (NAFOSTED) under grant number 102.05-2019.316.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset and source codes of this paper can be downloaded at: https://github.com/FKGHUST/Preeclampsia.git (accessed on 15 December 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This research does not involve any human or animal participation. All authors have checked and agreed with the submission.
References
- World Health Organization. WHO Recommendations for Prevention and Treatment of Pre-Eclampsia and Eclampsia; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Bui, T.C.; Vo, T.M.; Tran, Q.M.; Luu, L.T.; Nguyen, T.D. Predictive value of the sFlt-1 and PlGF in women at risk for preeclampsia in the south of Vietnam. Pregnancy Hypertens 2018, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masini, G.; Foo, L.F.; Tay, J.; Wilkinson, I.B.; Valensise, H.; Gyselaers, W.; Lees, C.C. Preeclampsia has two phenotypes which require different treatment strategies. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 226, S1006–S1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Hypertension in Pregnancy: Executive Summary. Obstet. Gynecol. 2013, 122, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, D.; Syngelaki, A.; Akolekar, R.; Poon, L.C.; Nicolaides, K.H. Competing risks model in screening for preeclampsia by maternal characteristics and medical history. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 213, 62.e1–62.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 202: Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 133, e1–e25. [Google Scholar]
- SOGC guideline, Diagnosis, Evaluation, and Management of the Hypertensive Disoder of Pregnancy: Executive Summary. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Can. 2014, 36, 416–438. [CrossRef]
- NICE. Hypertension in pregnancy: The management of hypertensive disorders during pregnancy. NICE Clin. Guidel 2019. No. 107. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, L.C.; Shennan, A.; Hyett, J.A.; Kapur, A.; Hadar, E.; Divakar, H.; McAuliffe, F.; da Silva Costa, F.; von Dadelszen, P.; McIntyre, H.D.; et al. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics initiative on pre-eclampsia: A pragmatic guide for first-trimester screening and prevention. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2019, 145, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Tian, Y.; Shun, X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Gao, H. Knowledge graph for TCM health preservation: Design, construction, and applications. Artif. Intell. Med. 2017, 77, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyrard, A.; Gaur, M.; Shekarpour, S.; Thirunarayan, K.; Sheth, A. Personalized health knowledge graph. In CEUR workshop proceedings; NIH Public Access: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2018; Volume 2317. [Google Scholar]
- Chai, X. Diagnosis Method of thyroid disease combining knowledge graph and deep learning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 149787–149795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troussas, C.; Chrysafiadi, K.; Virvou, M. An intelligent adaptive fuzzy-based inference system for computer-assisted language learning. Expert Syst. Appl. 2019, 127, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhshipour, A.; Zareiforoush, H.; Bagheri, I. Application of decision trees and fuzzy inference system for quality classification and modeling of black and green tea based on visual features. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 1402–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, L.; Raja, R.; Sharma, V.; Miri, R. Fuzzy Inference System for Efficient Lung Cancer Detection. In Computer Vision and Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Analysis, Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, L.C.; Otero, L.D.; Otero, C. Fuzzy Inference System Framework to Prioritize the Deployment of Resources in Low Visibility Traffic Conditions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174368–174379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johann, G.; dos Santos, C.S.; Montanher, P.F.; de Oliveira, R.A.P.; Carniel, A.C. Fuzzy inference systems for predicting the mass yield in extractions of chia cake extract. Softw. Impacts 2021, 10, 100145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, J.; Dutta, M.; Marques, G. Fuzzy Inference System Tree with Particle Swarm Optimization and Genetic Algorithm: A novel approach for PM10 forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 183, 115376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Dick, S. Towards inductive learning of complex fuzzy inference systems. In Proceedings of the NAFIPS 2007: 2007 Annual Meeting of the North American Fuzzy Information Processing Society, San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 June 2007; pp. 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, C.H.; Li, C. Multiple Function Approximation-A New Approach Using Complex Fuzzy Inference System. In Intelligent Information and Database Systems. ACIIDS 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 10751. [Google Scholar]
- Ngan, T.T.; Lan, L.T.H.; Tuan, T.M.; Son, L.H.; Tuan, L.M.; Minh, N.H. Colorectal Cancer Diagnosis with Complex Fuzzy Inference System. In Frontiers in Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing; Springer: Singapore, 2019; Volume 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvachandran, G.; Quek, S.G.; Lan, L.T.H.; Son, L.H.; Giang, N.L.; Ding, W.; Abdel-Basset, M.; de Albuquerque, V.H.C. A New Design of Mamdani Complex Fuzzy Inference System for Multiattribute Decision Making Problems. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2019, 29, 716–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, T.M.; Lan, L.T.H.; Chou, S.-Y.; Ngan, T.T.; Son, L.H.; Giang, N.L.; Ali, M. M-CFIS-R: Mamdani complex fuzzy inference system with rule reduction using complex fuzzy measures in granular computing. Mathematics 2020, 8, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, L.T.H.; Tuan, T.M.; Ngan, T.T.; Son, L.H.; Giang, N.L.; Ngoc, V.T.N.; Van Hai, P. A New Complex Fuzzy Inference System With Fuzzy Knowledge Graph and Extensions in Decision Making. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 164899–164921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.K.; Van Hai, P.; Tuan, T.M.; Lan, L.T.H.; Chuan, P.M.; Son, L.H. A Novel Fuzzy Knowledge Graph Pairs Approach in Decision Making. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 26505–26534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherimon, P.C.; Krishnan, R. OntoDiabetic: An Ontology-Based Clinical Decision Support System for Diabetic Patients. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2015, 41, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweidan, S.; El-Sappagh, S.; El-Bakry, H.; Sabbeh, S.; Badria, F.A.; Kwak, K.-S. A Fibrosis Diagnosis Clinical Decision Support System Using Fuzzy Knowledge. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2018, 44, 3781–3800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, I.A.; Ting, H.-N.; Moghavvemi, M. Formulation of a Novel Classification Indices for Classification of Human Hearing Abilities According to Cortical Auditory Event Potential signals. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2019, 44, 7133–7147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhan, M.; Sinthuja, M.; Raja, S.P.; Amutharaj, J.; Latha, G.C.P.; Rachel, S.S.; Anitha, T.; Rajendran, T.; Waji, Y.A. Segmentation and Classification of Glaucoma Using U-Net with Deep Learning Model. J. Healthc. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1601354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhou, M.-J.; Chen, M.-S.; Lee, T.-S.; Yang, C.-T.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Lu, C.-J. A Hybrid Risk Factor Evaluation Scheme for Metabolic Syndrome and Stage 3 Chronic Kidney Disease Based on Multiple Machine Learning Techniques. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, L.H.; Ciaramella, A.; Huyen, D.T.T.; Staiano, A.; Tuan, T.M.; Van Hai, P. Predictive reliability and validity of hospital cost analysis with dynamic neural network and genetic algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2020, 32, 15237–15248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, V.T.N.; Viet, D.H.; Tuan, T.M.; Van Hai, P.; Thang, N.P.; Tuyen, D.N.; Son, L.H. VNU-diagnosis: A novel medical system based on deep learning for diagnosis of periapical inflammation from X-Rays images. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 43, 1417–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pham, H.; Moore, P.; Cuong, B.C. Applied picture fuzzy sets with knowledge reasoning and linguistics in clinical decision support system. Neurosci. Inform. 2022, 2, 100109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, H.; Ahmad, A.; Ullah, K.; Mahmood, T.; Ali, Z. Algorithm for multi-attribute decision-making using T-spherical fuzzy Maclaurin symmetric mean operator. Iran. J. Fuzzy Syst. 2022, 19, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, H.; Deng, Y.; Ali, Z.; Mahmood, T. Decision-making strategy based on Archimedean Bonferroni mean operators under complex Pythagorean fuzzy information. Comput. Appl. Math. 2022, 41, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Pham, H.; Khoa, N.D.; Bui, T.T.; Giang, N.T.; Moore, P. Applied Picture Fuzzy Sets for Group Decision-Support in the Evaluation of Pedagogic Systems. Int. J. Math. Eng. Manag. Sci. 2022, 7, 243–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zadeh, L. Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control. 1965, 8, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Hu, Z.; Sun, Y. Fuzzy Logic Based Logical Query Answering on Knowledge Graphs. Proc. Conf. AAAI Artif. Intell. 2022, 36, 3939–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L.A. Approximate reasoning based on fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 6th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Tokyo, Japan, 20–23 August 1979; Volume 2, pp. 1004–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Singhal, A. “Introducing the Knowledge Graph: Things, Not Strings”, Official Google Blog. Available online: https://blog.google/products/search/introducing-knowledge-graph-things-not/ (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Paulheim, H. Knowledge graph refinement: A survey of approaches and evaluation methods. Semantic Web 2016, 8, 489–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Y.-P.; Zhou, W.-T.; Zhang, J.-H.; Zhang, T.-S. Knowledge graph and knowledge reasoning: A systematic review. J. Electron. Sci. Technol. 2022, 20, 100159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, S.; Kacem, S.B.H. Symbolic approximate reasoning with fuzzy and multi-valued knowledge. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2017, 112, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, E.; Kafaie, S. Knowledge Graphs and Explainable AI in Healthcare. Information 2022, 13, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, S.; Bhalla, S. Using Knowledge Graph Structures for Semantic Interoperability in Electronic Health Records Data Exchanges. Information 2022, 13, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.K.; Van Hai, P.; Tuan, T.M.; Lan, L.T.H.; Ngan, T.T.; Chuan, P.M.; Son, L.H. A novel Q-learning-based FKG-Pairs approach for extreme cases in decision making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 120, 105920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).