NUMSnet: Nested-U Multi-Class Segmentation Network for 3D Medical Image Stacks
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel multi-scan semantic segmentation model that propagates feature-level information from a few nested layers across ordered scans to enable feature learning from as few as 10% of annotated images per 3D medical image stack.
- The transfer learning performance analysis of the proposed model compared to existing Unet variants on multiple CT image stacks from Lung-CT (thoracic region) scans to Heart-CT regions. The NUMSnet model achieves up to 20% improvement in segmentation recall and 2–16% improvement in scores for multi-class semantic segmentation across image stacks.
- The identification of a minimal number of optimally located training images per volumetric stack for multi-class semantic segmentation.
- The identification of the optimal number of layers that can be transmitted across scans to prevent model over- or underfitting for the segmentation of up to seven ROIs with variables shapes and sizes.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
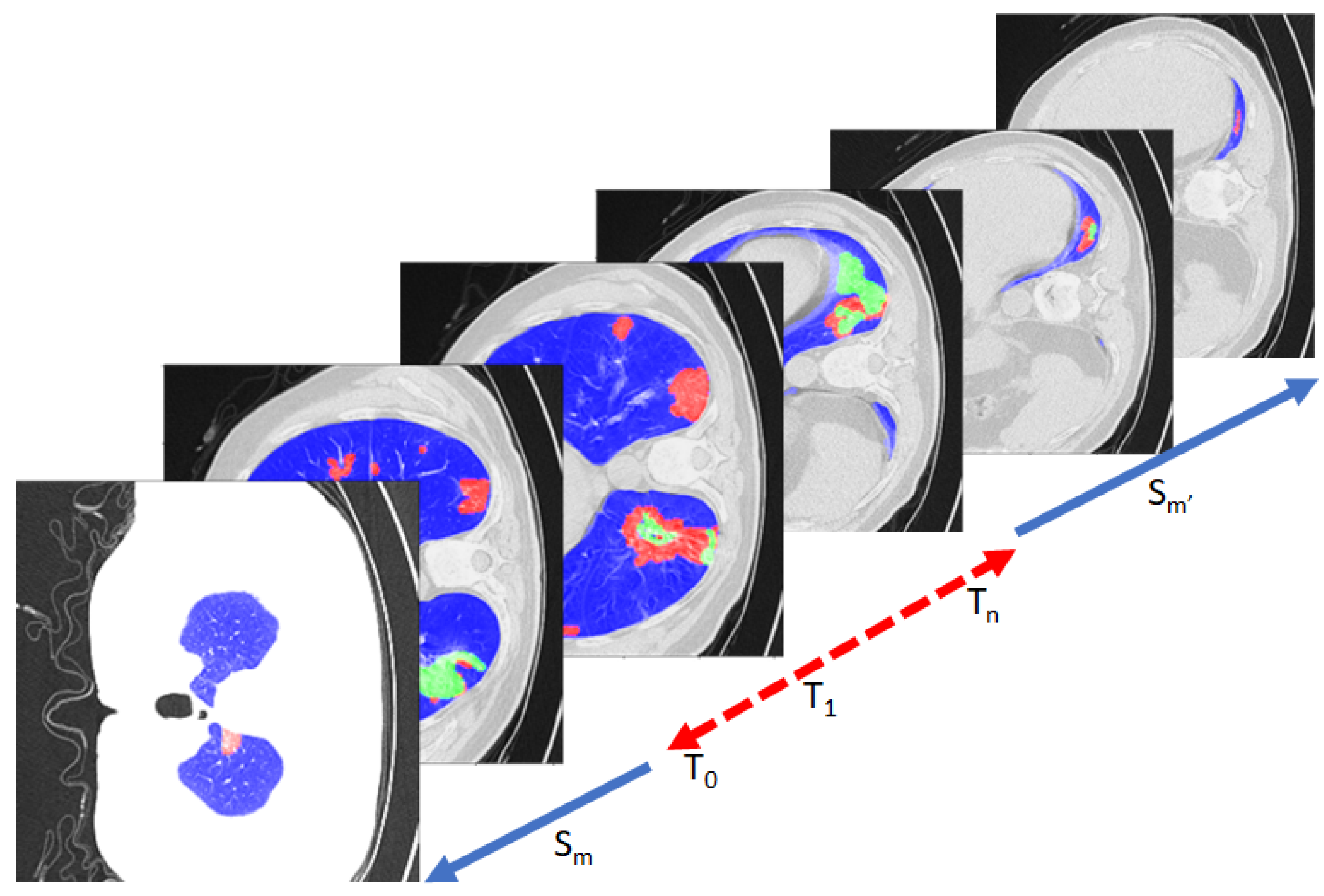
3.1. Data: Lung-CT and Heart-CT Stacks
3.2. Image Data Pre-Processing
3.3. Unet Model Variant Model Implementation
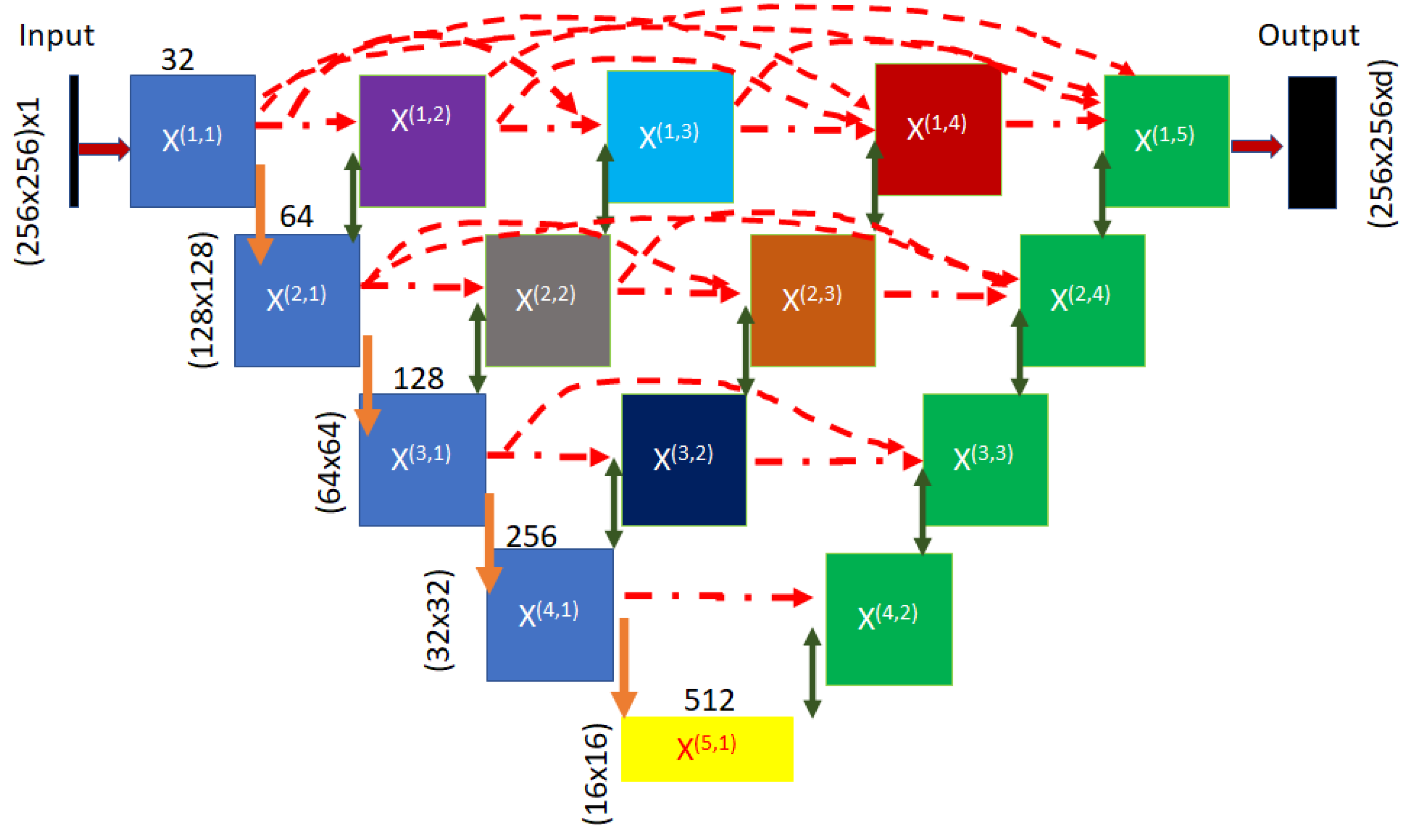
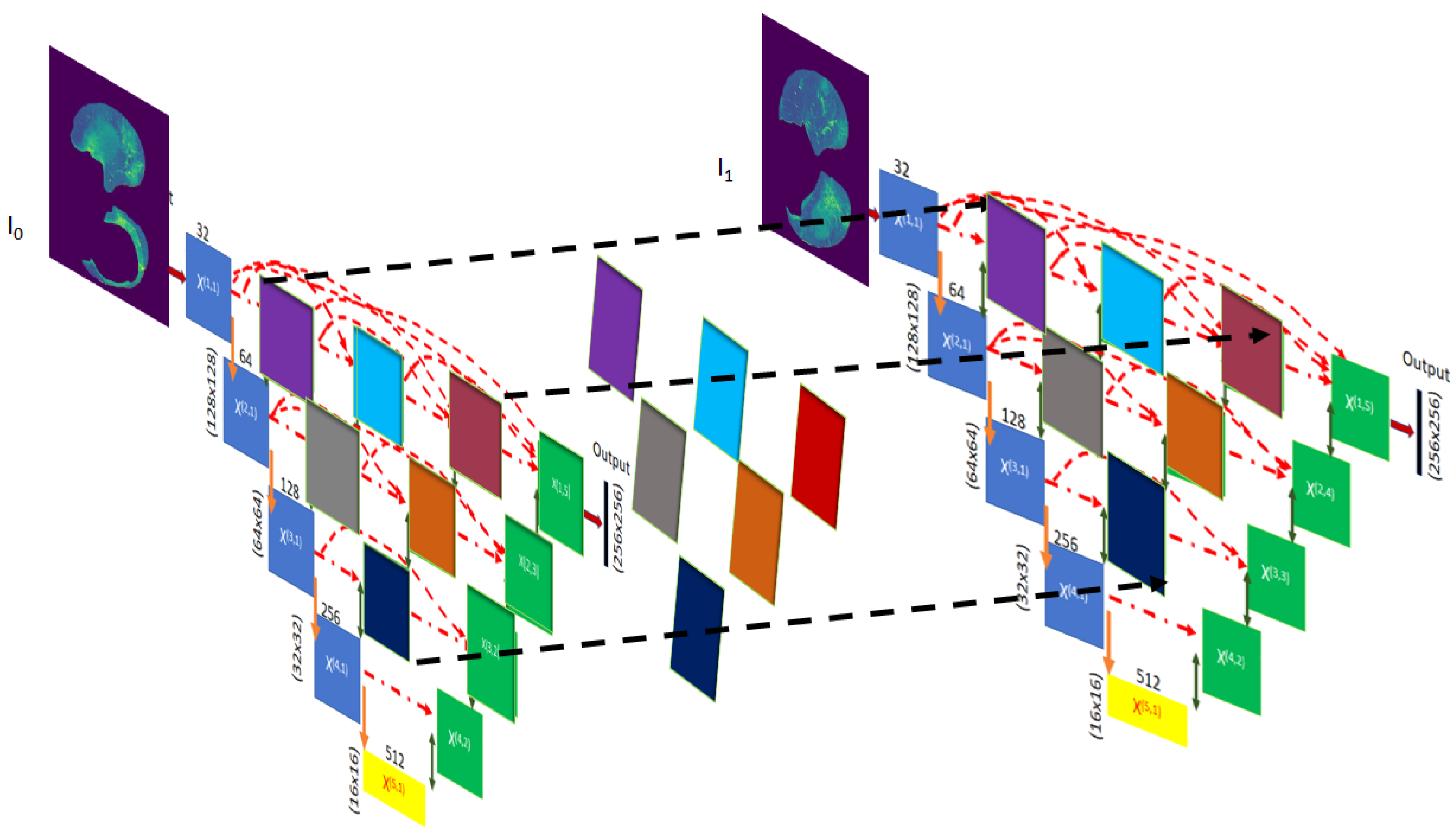
3.4. The NUMSnet Model
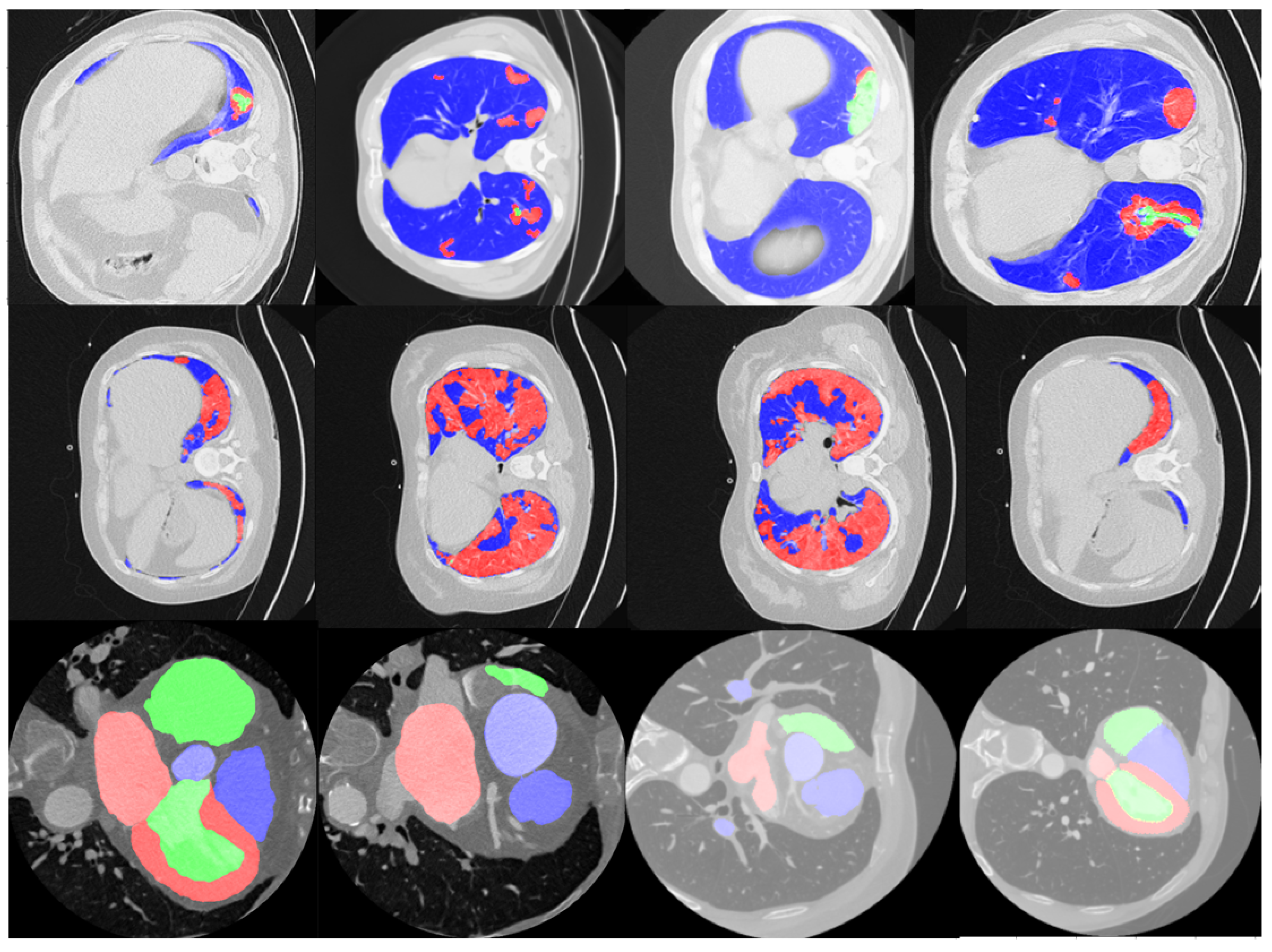
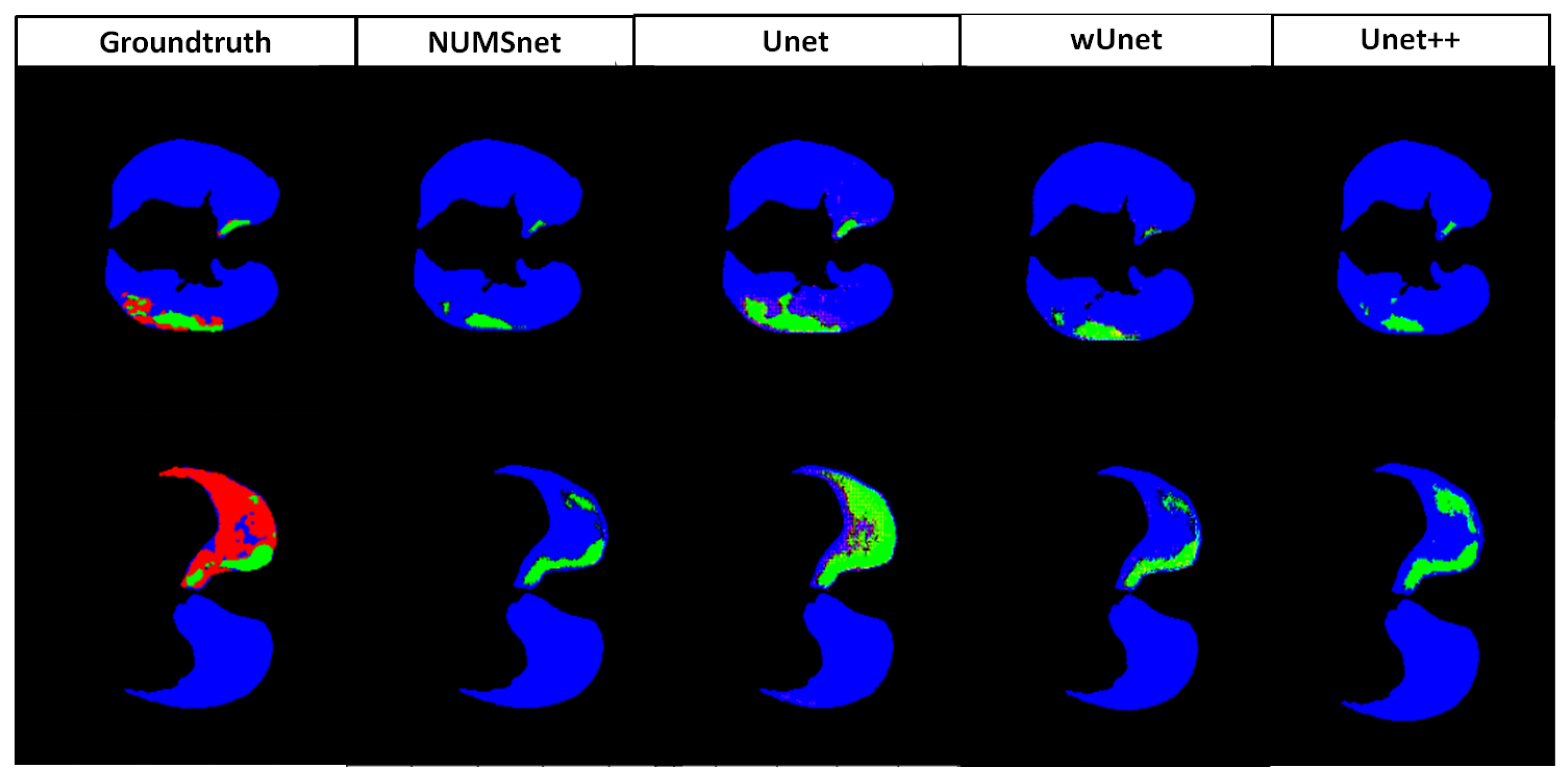
4. Experiments and Results
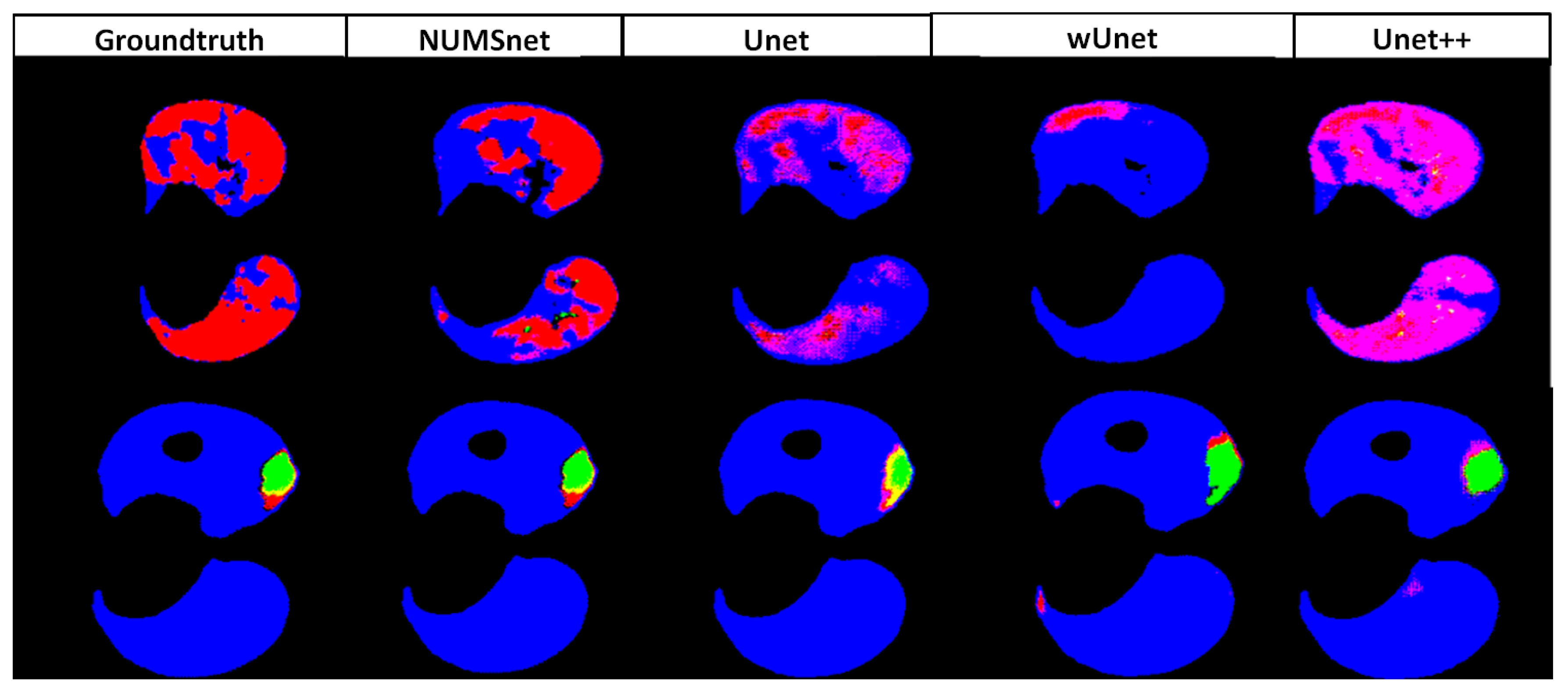
4.1. Multi-Class Segmentation Performance of Unet Variants
4.2. Sensitivity to Training Data
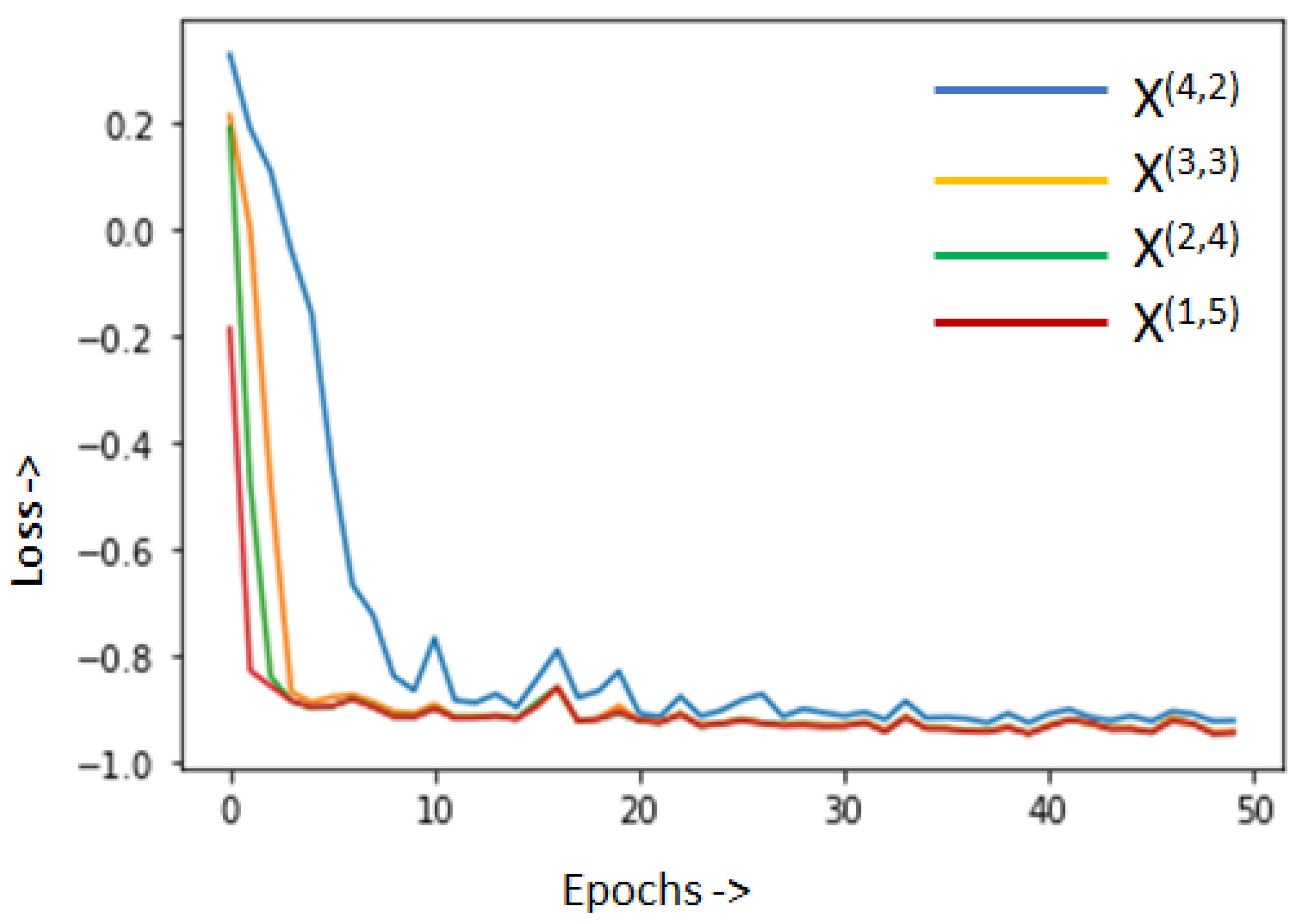
4.3. Performance Analysis for NUMSnet Variants
4.4. Transfer Learning for Heart-CT Images
4.5. Ablation Study and Comparative Assessment
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Model Graphs
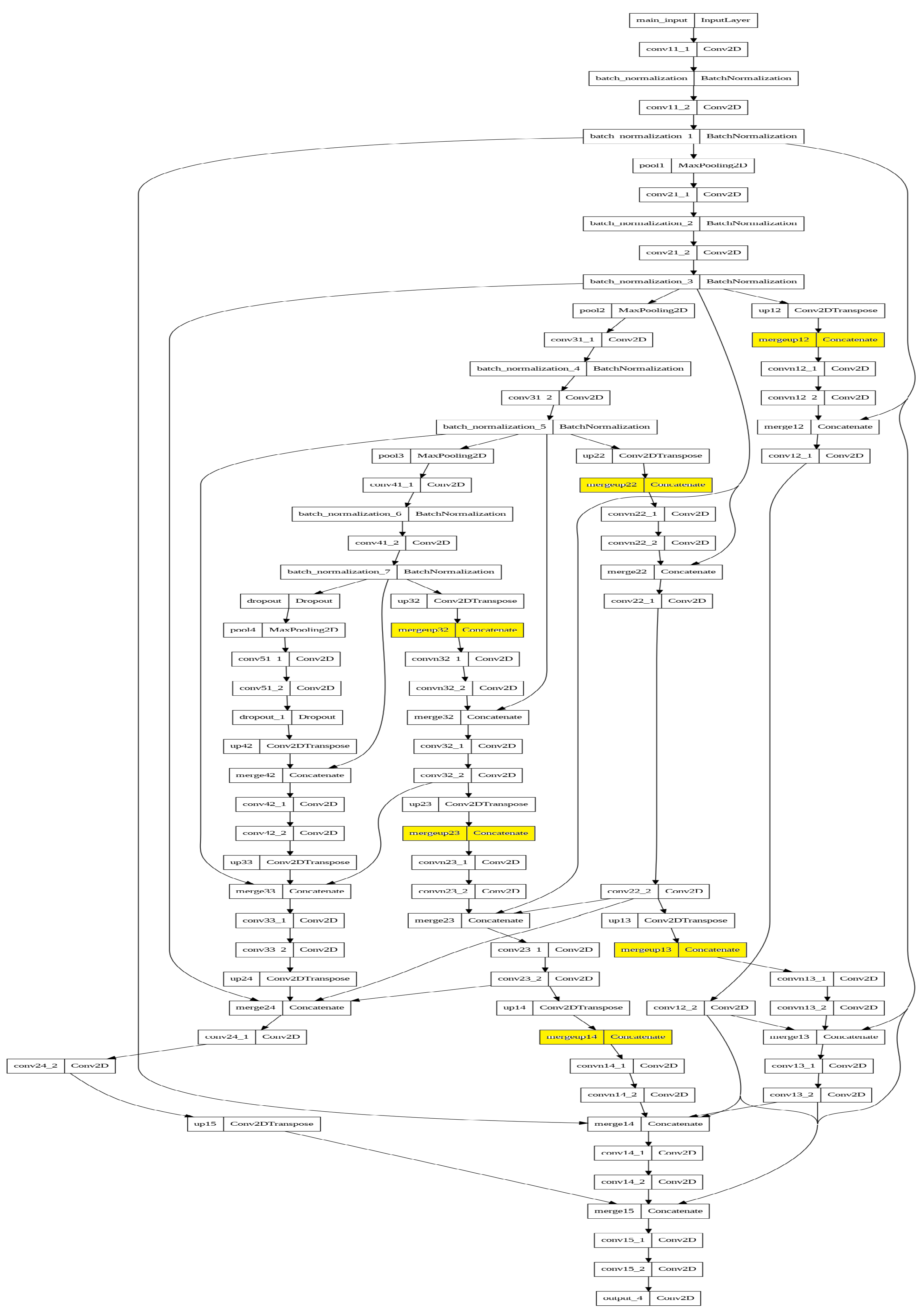
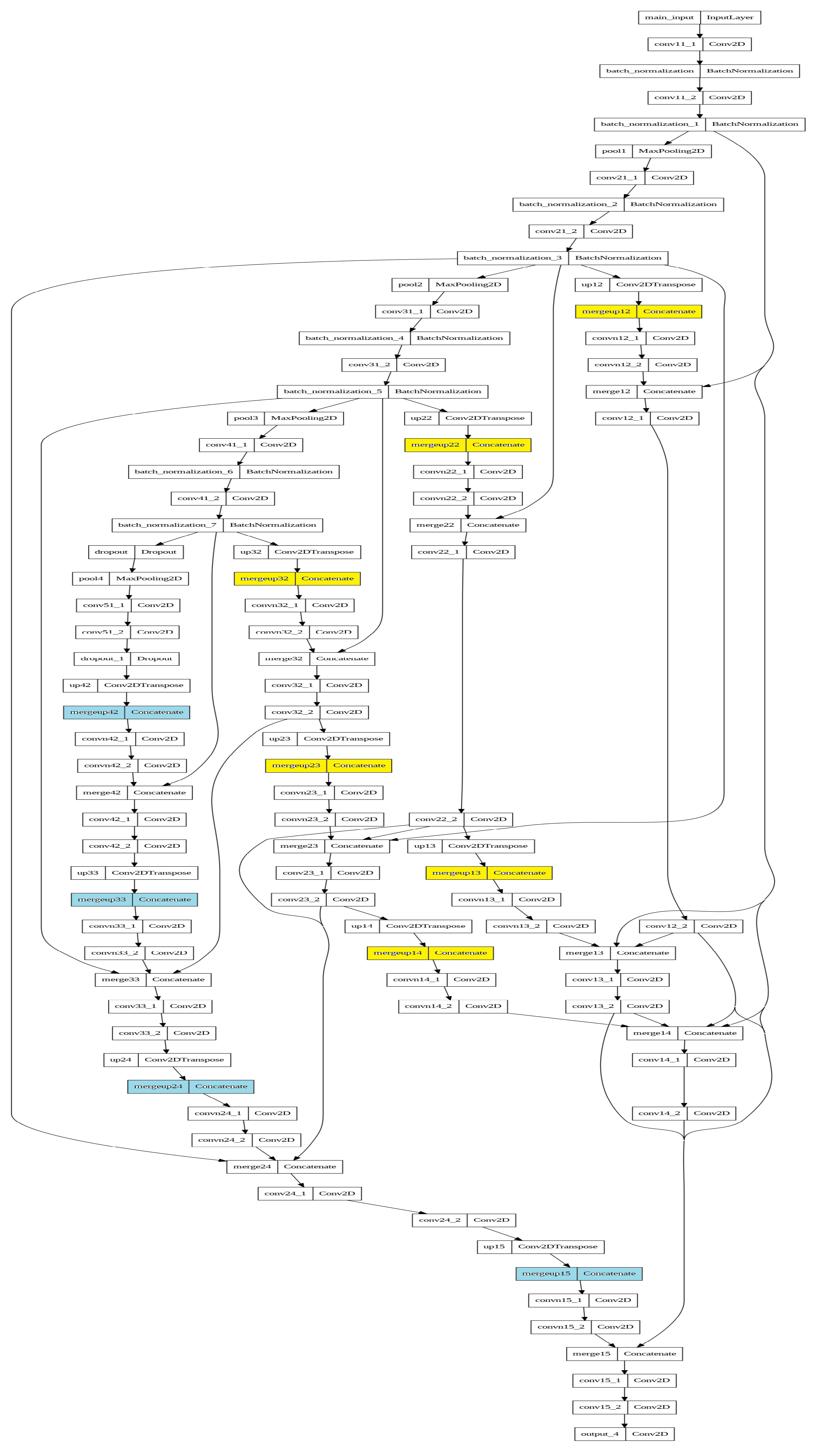
References
- Zhao, Z.Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.T.; Wu, X. Object detection with deep learning: A review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Zeng, H.; Li, A.; Ngai, E.W. Deep learning in computer vision: A critical review of emerging techniques and application scenarios. Mach. Learn. Appl. 2021, 6, 100134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Nezla, N.; Haridas, T.M.; Supriya, M. Semantic segmentation of underwater images using unet architecture based deep convolutional encoder decoder model. In Proceedings of the 2021 7th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 19–20 March 2021; Volume 1, pp. 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Darapaneni, N.; Raj, P.; Paduri, A.R.; Anand, E.; Rajarathinam, K.; Eapen, P.T.; Krishnamurthy, S. Autonomous car driving using deep learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 2nd International Conference on Secure Cyber Computing and Communications (ICSCCC), Jalandhar, India, 21–23 May 2021; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sampathila, N.; Chadaga, K.; Goswami, N.; Chadaga, R.P.; Pandya, M.; Prabhu, S.; Bairy, M.G.; Katta, S.S.; Bhat, D.; Upadya, S.P. Customized Deep Learning Classifier for Detection of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Using Blood Smear Images. Healthcare 2022, 10, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadaga, K.; Prabhu, S.; Sampathila, N.; Nireshwalya, S.; Katta, S.S.; Tan, R.S.; Acharya, U.R. Application of Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Monkeypox: A Systematic Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ait Nasser, A.; Akhloufi, M.A. A Review of Recent Advances in Deep Learning Models for Chest Disease Detection Using Radiography. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivagami, S.; Chitra, P.; Kailash, G.S.R.; Muralidharan, S. Unet architecture based dental panoramic image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Wireless Communications Signal Processing and Networking (WiSPNET), Chennai, India, 4–6 August 2020; pp. 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Luong, H.H.; Phan, P.T.; Nguyen, H.H.D.; Ly, D.; Phan, D.M.; Do, T.T. HS-UNET-ID: An approach for human skin classification integrating between UNET and improved dense convolutional network. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2022, 32, 1832–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safarov, S.; Whangbo, T.K. A-DenseUNet: Adaptive densely connected UNet for polyp segmentation in colonoscopy images with atrous convolution. Sensors 2021, 21, 1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, F.; Guedria, S.; Palma, N.D.; Vuillerme, N. Variability and reproducibility in deep learning for medical image segmentation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saood, A.; Hatem, I. COVID-19 lung CT image segmentation using deep learning methods: U-Net versus SegNet. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Rahman Siddiquee, M.M.; Tajbakhsh, N.; Liang, J. Unet++: A nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; MacGillivray, T.; Macnaught, G.; Yang, G.; Newby, D. A two-stage 3D Unet framework for multi-class segmentation on full resolution image. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.04341. [Google Scholar]
- Asnawi, M.H.; Pravitasari, A.A.; Darmawan, G.; Hendrawati, T.; Yulita, I.N.; Suprijadi, J.; Nugraha, F.A.L. Lung and Infection CT-Scan-Based Segmentation with 3D UNet Architecture and Its Modification. Healthcare 2023, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, A.; Pilevar, A.H.; Rafeh, R. Mass detection in lung CT images using region growing segmentation and decision making based on fuzzy inference system and artificial neural network. Int. J. Image Graph. Signal Process. 2013, 5, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Pang, M. Automatic lung segmentation based on image decomposition and wavelet transform. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2020, 61, 102032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbarzadeh, R.; Jafarzadeh Ghoushchi, S.; Bendechache, M.; Amirabadi, A.; Ab Rahman, M.N.; Baseri Saadi, S.; Aghamohammadi, A.; Kooshki Forooshani, M. Lung infection segmentation for COVID-19 pneumonia based on a cascade convolutional network from CT images. Biomed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE international Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Voulodimos, A.; Protopapadakis, E.; Katsamenis, I.; Doulamis, A.; Doulamis, N. Deep learning models for COVID-19 infected area segmentation in CT images. In Proceedings of the 14th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference, Corfu, Greece, 29 June–2 July 2021; pp. 404–411. [Google Scholar]
- Payer, C.; Štern, D.; Bischof, H.; Urschler, M. Multi-label whole heart segmentation using CNNs and anatomical label configurations. In Proceedings of the Statistical Atlases and Computational Models of the Heart, ACDC and MMWHS Challenges: 8th International Workshop, STACOM 2017, Held in Conjunction with MICCAI 2017, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 10–14 September 2017; Revised Selected Papers. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 190–198. [Google Scholar]
- Amyar, A.; Modzelewski, R.; Li, H.; Ruan, S. Multi-task deep learning based CT imaging analysis for COVID-19 pneumonia: Classification and segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunraj, H.; Wang, L.; Wong, A. Covidnet-ct: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 cases from chest ct images. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 608525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Zhou, T.; Ji, G.P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Inf-net: Automatic COVID-19 lung infection segmentation from ct images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Xie, J.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, W. MA-UNet++: A multi-attention guided U-Net++ for COVID-19 CT segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 13th Asian Control Conference (ASCC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 4–7 May 2022; pp. 682–687. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C. CT image segmentation of COVID-19 based on UNet++ and ResNeXt. In Proceedings of the 2021 11th International Conference on Information Technology in Medicine and Education (ITME), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27–28 May 2023; pp. 420–424. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Z.; Liu, B.; Geng, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y. Segmentation of lung nodules using improved 3D-UNet neural network. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, K. Multi-depth fusion network for whole-heart CT image segmentation. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 23421–23429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; He, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Xie, P. COVID-CT-dataset: A CT scan dataset about COVID-19. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.13865. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry for Primary Industries. COVID-19 CT Segmentation Dataset. 2020. Available online: http://medicalsegmentation.com/covid19/ (accessed on 9 January 2022).
- Girish, G.; Thakur, B.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Kothari, A.R.; Rajan, J. Segmentation of intra-retinal cysts from optical coherence tomography images using a fully convolutional neural network model. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 23, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadon, S. A survey of loss functions for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Viña del Mar, Chile, 27–29 October 2020; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, S. QU-net++: Image Quality Detection Framework for Segmentation of Medical 3D Image Stacks. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2110.14181. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Ren, X.; Wei, B. Segmentation of infected region in CT images of COVID-19 patients based on QC-HC U-net. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgari Taghanaki, S.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.P.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Sharifai, N.; Jiang, K.; Wang, F.; Teodoro, G.; Farris, A.B.; Kong, J. Artificial intelligence based liver portal tract region identification and quantification with transplant biopsy whole-slide images. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 150, 106089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Hong, Q.Q.; Teku, R.; Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.D. Transfer learning for medical images analyses: A survey. Neurocomputing 2022, 489, 230–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Shamma, O.; Zhang, J.; Santamaría, J.; Duan, Y.; R. Oleiwi, S. Towards a better understanding of transfer learning for medical imaging: A case study. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Model | Total Params | Trainable Params | Non-Trainable Params |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unet | 7,767,523 | 7,763,555 | 3968 |
| wUnet | 9,290,998 | 9,286,658 | 4340 |
| Unet++ | 9,045,507 | 9,043,587 | 1920 |
| NUMSnet | 11,713,943 | 11,711,843 | 2100 |
| NUMS-all | 14,526,368 | 14,524,268 | 2100 |
| Task | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUMSnet, Con | 82.06 | 65.86 | 57.43 | 61.25 |
| NUMSnet, GGO | 89.86 | 85.87 | 78.76 | 81.29 |
| NUMSnet, Lung | 97.35 | 94.96 | 92.94 | 95.9 |
| Unet, Con | 91.91 | 32.48 | 30.43 | 33.84 |
| Unet, GGO | 90.56 | 73.69 | 68.26 | 70.92 |
| Unet, Lung | 91.66 | 94.31 | 86.59 | 92.2 |
| wUnet, Con | 64.02 | 77.85 | 53.42 | 53.66 |
| wUnet, GGO | 81.92 | 95.29 | 78.33 | 80.43 |
| wUnet, Lung | 99.27 | 91.47 | 90.94 | 94.35 |
| Unet++, Con | 71.67 | 57.14 | 42.21 | 45.36 |
| Unet++, GGO | 92.87 | 71.54 | 68.06 | 71.18 |
| Unet++, Lung | 99.61 | 90.41 | 90.17 | 93.89 |
| Task | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUMSnet, Con | 68.22 | 79.1 | 57.08 | 59.42 |
| NUMSnet, GGO | 85.1 | 91.86 | 80.31 | 83.0 |
| NUMSnet, Lung | 99.36 | 93.29 | 92.76 | 95.22 |
| Unet, Con | 64.2 | 49.93 | 31.2 | 31.28 |
| Unet, GGO | 92.33 | 79.11 | 75.06 | 77.99 |
| Unet, Lung | 98.52 | 93.75 | 92.41 | 95.11 |
| wUnet, Con | 83.31 | 47.68 | 42.18 | 46.26 |
| wUnet, GGO | 89.41 | 86.61 | 79.4 | 81.99 |
| wUnet, Lung | 97.15 | 95.71 | 93.22 | 95.8 |
| Unet++, Con | 71.51 | 62.08 | 47.27 | 50.48 |
| Unet++, GGO | 94.14 | 71.92 | 69.83 | 73.03 |
| Unet++, Lung | 98.36 | 94.3 | 92.84 | 95.4 |
| Task | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data: | Lung-med | |||
| Initial, Seq, Con | 82.5 | 35.05 | 26.1 | 29.34 |
| Initial, Seq, GGO | 85.78 | 69.13 | 59.30 | 62.21 |
| Initial, Seq, Lung | 88.85 | 93.45 | 82.98 | 89.90 |
| Mid, Rand, Con | 60.38 | 96.52 | 57.97 | 57.97 |
| Mid, Rand, GGO | 70.15 | 99.46 | 69.75 | 69.75 |
| Mid Rand, Lung | 99.27 | 89.19 | 88.62 | 92.94 |
| Mid, Seq, Con | 60.37 | 97.32 | 58.91 | 58.91 |
| Mid, Seq, GGO | 70.15 | 93.17 | 68.01 | 68.01 |
| Mid, Seq, Lung | 98.73 | 89.28 | 88.27 | 92.59 |
| Data: | 10 Lung-rad | Stacks | ||
| Initial, Seq, Con | 87.74 | 44.24 | 38.94 | 43.13 |
| Initial, Seq, GGO | 92.23 | 75.69 | 72.46 | 75.19 |
| Initial, Seq, Lung | 95.44 | 96.74 | 92.87 | 95.79 |
| Mid, Rand, Con | 62.05 | 99.1 | 60.91 | 60.91 |
| Mid, Rand, GGO | 72.22 | 99.0 | 70.22 | 70.22 |
| Mid Rand, Lung | 99.79 | 91.74 | 91.6 | 94.57 |
| Mid, Seq, Con | 59.15 | 98.51 | 59.49 | 59.76 |
| Mid, Seq, GGO | 82.22 | 99.0 | 80.22 | 80.22 |
| Mid, Seq, Lung | 99.0 | 90.74 | 90.6 | 93.8 |
| Data | Lung-Med | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task | ||||
| NUMS-all, Con | 66.81 | 72.63 | 53.08 | 54.86 |
| NUMS-all, GGO | 83.11 | 91.06 | 78.09 | 81.02 |
| NUMS-all, Lung | 99.67 | 90.93 | 90.74 | 94.64 |
| Data | 10 Lung-rad | Stacks | ||
| NUMS-all, Con | 64.14 | 96.04 | 63.05 | 63.06 |
| NUMS-all, GGO | 86.97 | 92.34 | 81.82 | 84.34 |
| NUMS-all, Lung | 99.63 | 92.89 | 92.56 | 95.1 |
| Task | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NUMSnet, pix | 96.2 | 78.83 | 75.53 | 78.01 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 96.89 | 86.2 | 83.42 | 85.04 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 94.84 | 98.16 | 93.29 | 95 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 96.61 | 86.23 | 83.4 | 85.8 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 94.95 | 80.26 | 76.03 | 79.28 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 98.42 | 96.84 | 95.55 | 96.88 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 90.41 | 81.55 | 73.03 | 75.05 |
| Unet, pix | 95.01 | 79.17 | 75.48 | 79.3 |
| Unet, pix | 95.54 | 88.39 | 85.31 | 87.78 |
| Unet, pix | 94.8 | 95.08 | 91.06 | 93.34 |
| Unet, pix | 92.27 | 82.5 | 76.44 | 80.49 |
| Unet, pix | 90.09 | 83.1 | 74.84 | 79.23 |
| Unet, pix | 97.53 | 80.95 | 79.43 | 81.93 |
| Unet, pix | 88.1 | 46.81 | 44.01 | 46.81 |
| wUnet, pix | 95.93 | 75.18 | 72.37 | 76.02 |
| wUnet, pix | 94.64 | 91.75 | 87.37 | 89.96 |
| wUnet, pix | 94.42 | 95.05 | 90.73 | 93.11 |
| wUnet, pix | 89.27 | 64.52 | 57.46 | 61.54 |
| wUnet, pix | 90.93 | 80.84 | 72.93 | 77.22 |
| wUnet, pix | 95.3 | 88.77 | 84.91 | 87.99 |
| wUnet, pix | 84.37 | 69.65 | 60.09 | 62.74 |
| Unet++, pix | 96.11 | 67.93 | 65.01 | 68.82 |
| Unet++, pix | 94.69 | 88.92 | 84.59 | 86.91 |
| Unet++, pix | 97.06 | 92.21 | 89.93 | 92.46 |
| Unet++, pix | 88.46 | 73.42 | 63.44 | 67.36 |
| Unet++, pix | 94.21 | 73.17 | 69.7 | 73.09 |
| Unet++, pix | 96.07 | 88.15 | 85.06 | 86.96 |
| Unet++, pix | 65.06 | 99.95 | 65.07 | 65.07 |
| Data | Lung-Med | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task | ||||
| NUMSnet, Con | 70.48 | 71.34 | 51.14 | 53.1 |
| NUMSnet, GGO | 91.11 | 80.6 | 75.62 | 78.48 |
| NUMSnet, Lung | 99.61 | 90.55 | 90.24 | 93.99 |
| NUMSnet, Con | 66.82 | 86.12 | 58.86 | 60.3 |
| NUMSnet, GGO | 78.56 | 97.75 | 77.56 | 79.8 |
| NUMSnet, Lung | 98.5 | 92.61 | 91.38 | 94.61 |
| Data | 10 Lung-rad | Stacks | ||
| NUMSnet, Con | 67.66 | 75.28 | 51.86 | 53.67 |
| NUMSnet, GGO | 89.67 | 88.22 | 80.63 | 83.38 |
| NUMSnet, Lung | 99.51 | 93.16 | 92.72 | 95.2 |
| NUMSnet, Con | 68.42 | 75.53 | 53.51 | 55.35 |
| NUMSnet, GGO | 88.76 | 88.95 | 80.14 | 82.88 |
| NUMSnet, Lung | 99.52 | 93.42 | 93.0 | 95.36 |
| Data | Heart-CT | |||
| NUMSnet, pix | 97.38 | 67.21 | 65.51 | 68.85 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 94.92 | 88.71 | 84.42 | 86.03 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 97.29 | 94.56 | 92.34 | 94.31 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 90.03 | 87.87 | 78.95 | 82.43 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 90.9 | 75.95 | 68.3 | 71.9 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 97.91 | 87.58 | 85.82 | 87.43 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 89.96 | 75.67 | 68.12 | 70.17 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 96.63 | 78.18 | 75.65 | 78.36 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 95.9 | 83.1 | 80.24 | 81.93 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 97.44 | 90.48 | 88.44 | 90.33 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 94.49 | 78.9 | 74.98 | 77.97 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 93.76 | 76.93 | 71.15 | 74.16 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 98.52 | 90.13 | 88.84 | 90.19 |
| NUMSnet, pix | 89.07 | 86.02 | 76.42 | 78.34 |
| Method | Data | #Training Images | Metrics | Epochs/Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saood et al. (2D) [13] | Lung-med | 72 | [22.5–60]% | 160/25 min |
| Voulodimos (2D) [21] | Lung-med | 418 | [65–85] %(GGO) | ∼210 s |
| Roychowdhury (2D) [35] | Lung-med | 40 | 64% (GGO) | 40/∼70 s |
| NUMSnet (2D) | Lung-med | 82 | [61–96%] | 40/224 s |
| Payer et al. (3D) [22] | Heart-CT | 7831 | [84–93%] | 30,000/3–4 h |
| Wang et al. (3D) [15] | Heart-CT | 7831 | [64.82–90.44%] | 12,800/(Azure cloud) |
| Ye et al. (3D) [30] | Heart-CT | 7831 | [86–96%] | 60,000/∼2–4 h |
| NUMSnet (Ours) (2D) | Heart-CT | 363 | [75–97%] | 60/362 s |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roychowdhury, S. NUMSnet: Nested-U Multi-Class Segmentation Network for 3D Medical Image Stacks. Information 2023, 14, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14060333
Roychowdhury S. NUMSnet: Nested-U Multi-Class Segmentation Network for 3D Medical Image Stacks. Information. 2023; 14(6):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14060333
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoychowdhury, Sohini. 2023. "NUMSnet: Nested-U Multi-Class Segmentation Network for 3D Medical Image Stacks" Information 14, no. 6: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14060333
APA StyleRoychowdhury, S. (2023). NUMSnet: Nested-U Multi-Class Segmentation Network for 3D Medical Image Stacks. Information, 14(6), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/info14060333








