5G-IPAKA: An Improved Primary Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for 5G Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- By analyzing the latest version of the 5G AKA protocol, we point out that the protocol still has seven shortcomings;
- We propose a new 5G-IPAKA protocol by improving the latest version of the 5G AKA protocol from four aspects;
- We formally analyze the security of the 5G-IPAKA protocol in the mixed strand space model for mixed protocols [28]. As a result, the 5G-IPAKA protocol is secure in the mixed strand space model;
- Through discussion and analysis, we are able to overcome the above shortcomings of the latest version of the 5G AKA protocol;
- Through discussion and a comparative analysis, we show that the new 5G-IPAKA protocol is better than the recently improved 5G AKA protocols in overcoming the various shortcomings, and is efficient and backward-compatible.
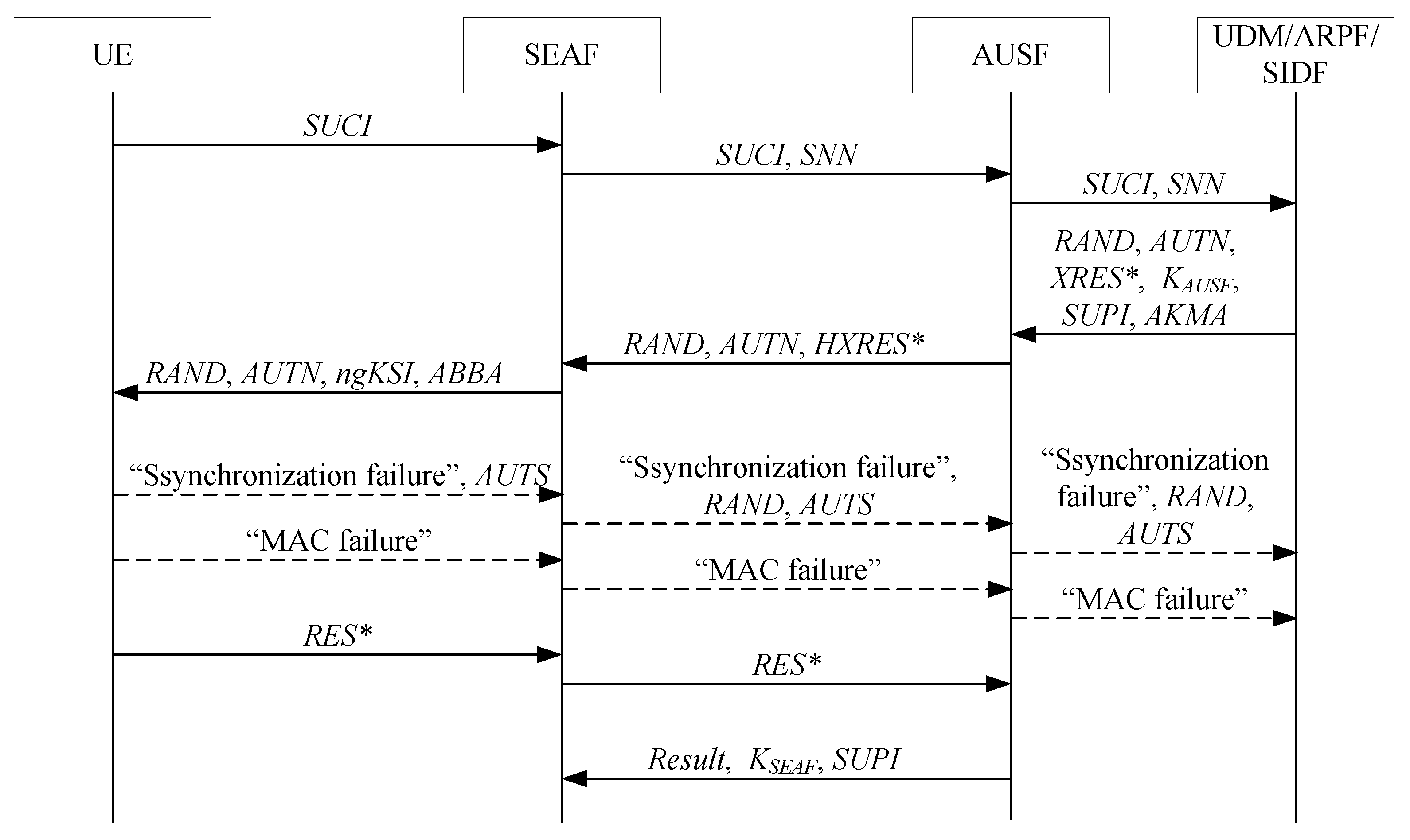
2. Overview of the 5G AKA Protocol
- When the SEAF initiates an authentication with the UE, the UE sends to the SEAF, where the UE includes the ME and the USIM. denotes a SUCI of the UE and , where denotes the subscription permanent identifier (SUPI) of the UE, and are an ephemeral public–private key pair of the UE for Diffie–Hellman exchange, and are the ephemeral public–private key pair of the HN for Diffie–Hellman exchange, and , is an encryption key, is an initial counter block (ICB), is a message authentication code (MAC) key, is a MAC of the UE, is a key derivation function, and is a hash function for computing MAC;
- Upon receiving , the SEAF sends and to the AUSF. denotes the serving network name (SNN) of the SN;
- If the SEAF is entitled to use , then the AUSF stores the receiving and sends and to the UDM;
- The UDM invokes the SIDF regardless of whether is received. Then, the SIDF de-conceals to gain before the UDM can process the request. Based on , the UDM/ARPF chooses the authentication method;
- When 5G AKA is selected, the UDM/ARPF generates , calculates and , and derives , and then creates a 5G home environment authentication vector (5G HE AV) from , , , and . is an unpredictable challenge of the HN. is an authentication token of the HN and , where is a fresh sequence number generated by the HN, is an anonymity key and , is the authentication management field (AMF) and the separation bit of the AMF is set 1, is a MAC of the HN and , is a long-term key between the UE and the HN, is a message authentication function, and is a key-generating function. Here, , where is a cipher key and , is an integrity key and , is an expected response and , is a message authentication function, and and are two key-generating functions. is a key derived from and , and ;
- The UDM sends the 5G HE AV to the AUSF together with . When an authentication and key management for applications (AKMA) subscription is used, the UDM also sends to the AUSF. denotes the AKMA indication and routing indicator;
- The AUSF stores the temporarily together with the received ;
- The AUSF generates a 5G AV from the 5G HE AV received from the UDM/ARPF by computing from , computing from , replacing with , and replacing with in the 5G HE AV, where , , and is a hash function;
- The ASUF creates a 5G serving environment authentication vector (5G SE AV) by removing from the 5G AV, then sends the 5G SE AV (i.e., , , and ) to the SEAF;
- The SEAF stores , and then sends , , , and to the UE. Here, is used by the UE and the access and mobility management function (AMF) to identify the and the partial native security context that is created if the authentication is successful. denotes the anti-bidding down between architectures (ABBA) parameter;
- In the UE, the ME forwards and to the USIM. Upon receipt of and , the USIM first computes the anonymity key and retrieves the sequence number . Next, the USIM computes and compares this with , which is included in . Then, the USIM verifies that the received is in the correct range. If is the same as and is in the correct range, then the USIM computes a response , , and , and then returns , , and to the ME. The ME then computes , , and ;
- The UE sends to the SEAF;
- The SEAF computes and compares this with . If they coincide, then the SEAF considers the authentication successful from the serving network point of view; if not, then the SEAF considers the authentication unsuccessful;
- The SEAF sends the received to the AUSF;
- The AUSF compares the received with the stored . If and are equal, then the AUSF considers the authentication successful from the home network point of view. Then, the AUSF informs the UDM about the authentication result;
- The AUSF indicates to the SEAF whether the authentication was successful or not from the home network point of view (i.e., ). If the authentication was successful, then the ASUF also sends and to the SEAF.
3. Shortcomings of the 5G AKA Protocol
- can be replayed without being found. The HN cannot find out whether is a replayed message because does not contain the challenge of the HN. Similarly, the UE cannot find out whether is a replayed message because does not contain the challenge of the UE (i.e., ), which is included in generated by the UE;
- Mutual authentication between the UE and the SN cannot be established. The UE cannot authenticate the SN because does not contain . Similarly, the SN cannot authenticate the UE for the following three reasons. Firstly, the SN does not verify , , , , and . Secondly, the second received message of the SN does not contain to match with in the first received message of the SN. Finally, the last received message of the SN does not contain , meaning that in the last received message of the SN cannot match with the UE identity in and , which are included in the second received message of the SN;
- cannot reach an agreement. The last received message of the SN does not contain , so this message can be a replayed message, meaning that on the SN is not equal to on the HN. As a result, on the SN is not equal to on the UE;
- The location privacy of the UE can be compromised. Because does not contain the challenge of the UE (i.e., ), the first received message of the UE can be a replayed message. If is in the correct range, then the location of the UE can be compromised by reidentifying . If is not in the correct range, then the location privacy of the UE can be compromised by identifying the “synchronization failure” indication; that is to say, when the first received message of the UE is replayed, the legitimate UE response is or a “synchronization failure” indication, but any other UE response is a “MAC failure” indication. As a result, the location privacy of the legitimate UE can be compromised;
- DoS attacks against the SN can be formed. Because the received messages of the SN does not contain the challenge of the SN, these messages can be replayed messages. As a result, the penetrator can impersonate the UE and the HN to complete the entire 5G AKA protocol with the SN, forming DoS attacks against the SN;
- Attacks based on MAC failure can be performed. Firstly, the penetrator can forge or tamper with the first received message of the UE to make the UE respond to a “MAC failure” indication, resulting in authentication failure. Secondly, the penetrator can directly send a “MAC failure” indication to the SN to cause authentication failure. Finally, the penetrator can also replay a “MAC failure” indication between the SN and the HN to cause authentication failure;
- Perfect forward secrecy cannot be provided. In the latest version of the 5G AKA protocol, if is leaked, then the penetrator can calculate and based on those messages transmitted in the past run of the protocol. As a result, the penetrator can decrypt those encrypted communication messages transmitted in the past run of the protocol. Therefore, the latest version of the 5G AKA protocol cannot provide perfect forward secrecy.
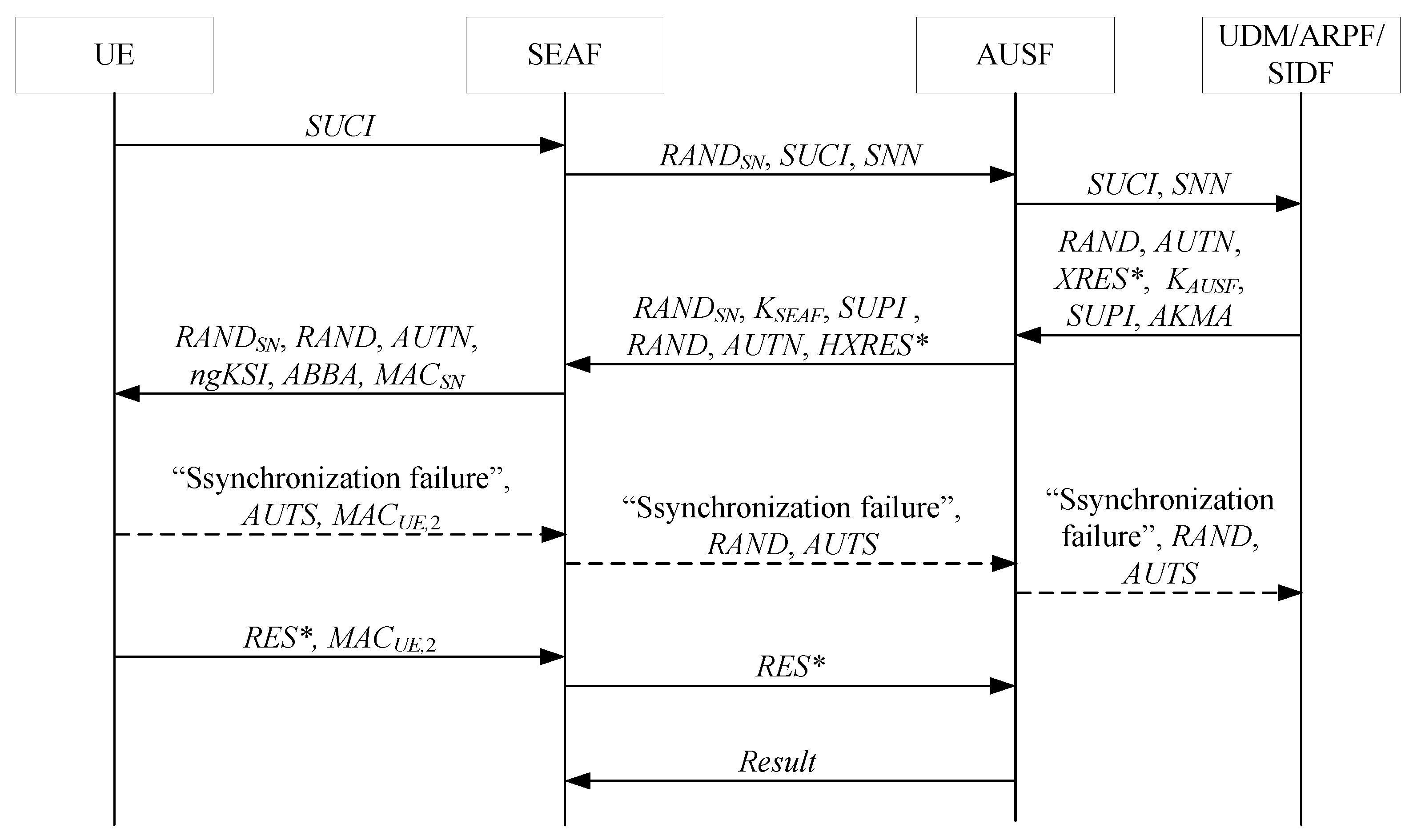
4. Our Proposed 5G-IPAKA Protocol
- When the SEAF initiates an authentication with the UE, the UE sends to the SEAF;
- Upon receiving , the SEAF generates and then sends , , and to the AUSF, where is an unpredictable challenge of the SEAF;
- If the SEAF is entitled to use , then the AUSF stores the receiving and sends and to the UDM;
- The UDM invokes the SIDF whether is received or not. Then, the SIDF de-conceals to gain before the UDM can process the request. Based on , the UDM/ARPF chooses the authentication method;
- When 5G-IPAKA is selected, the UDM/ARPF generates , calculates and , and derives , and then creates a 5G HE AV from , , , and , where , , , , , , , , and ;
- The UDM sends the 5G HE AV to the AUSF together with . When an AKMA subscription is used, the UDM also sends to the AUSF;
- The AUSF stores the temporarily together with the received ;
- The AUSF generates a 5G AV from the 5G HE AV received from the UDM/ARPF by computing from , computing from , replacing with , and replacing with in the 5G HE AV;
- The ASUF creates a 5G SE AV by adding to the 5G AV, then sends the 5G SE AV (i.e., , , , , and ) together with to the SEAF;
- The SEAF stores , computes , and then sends , , , , , and to the UE, where is a MAC of the SEAF and ;
- In the UE, the ME forwards and to the USIM. Upon receipt of and , the USIM first computes and the anonymity key and retrieves the sequence number . Next, the USIM computes and compares this with which is included in . Then, the USIM verifies that the received is in the correct range. If is the same as and is in the correct range, then the USIM computes a response , , and , and then returns , , and to the ME. The ME then computes , , and . Finally, the ME verifies using . If the verification fails, then the ME aborts;
- The UE computes , and then sends and to the SEAF, where is another MAC of the UE;
- The SEAF verifies . If the verification fails, then the SEAF aborts. Otherwise, the SEAF computes and compares this with . If they coincide, then the SEAF considers the authentication as successful from the serving network point of view. If not, then the SEAF considers the authentication as unsuccessful;
- The SEAF sends the received to the AUSF;
- The AUSF compares the received with the stored . If and are equal, then the AUSF considers the authentication as successful from the home network point of view. Then, the AUSF informs the UDM about the authentication result;
- The AUSF indicates to the SEAF whether the authentication was successful or not from the home network point of view (i.e., ).
- Replace the pre-shared key between the UE and the HN with a derivation key of the pre-shared key. In detail, is replaced with on the UE and the HN;
- Add the challenge-response mechanism for the SN. Firstly, is added to the first send message of the SEAF as a challenge and is added to the second received message of the SEAF as a response. Then, is added to the second send message of the SEAF as a challenge and is added to the third received message of the SEAF as a response (i.e., in );
- Add the mutual authentication and key confirmation between the UE and the SN. Firstly, and are moved to the second sent message of the AUSF from the last sent message of the AUSF. Then, the UE and the SN perform a mutual authentication and key confirmation process based on and , which are generated by using ;
- Replace the MAC failure procedure with the timeout mechanism on the HN. If in the received and calculated locally by the UE are different, then the UE directly discards the first received message of the UE without responding to a “MAC failure” indication, so the HN will initiate a new authentication procedure towards the UE when the HN does not receive an authentication response message or a synchronization failure message within a certain period of time.
5. Formal Verification of the 5G-IPAKA Protocol
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : .
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : ;
- : .
6. Discussion
6.1. Security of the 5G-IPAKA Protocol
6.2. Performance of the 5G-IPAKA Protocol
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, S.; Gan, Z. Review and trends of 5G security technology. Radio Commun. Technol. 2020, 46, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- 3GPP TS 33.102: 3G Security. Security Architecture. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/33102.htm (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- 3GPP TS 33.401: 3GPP System Architecture Evolution (SAE). Security Architecture. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/33401.htm (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- 3GPP TS 33.501: 3GPP System Architecture Evolution (SAE). Security Architecture. Available online: https://www.3gpp.org/DynaReport/33501.htm (accessed on 26 January 2022).
- Ferrag, M.A.; Maglaras, L.; Argyriou, A.; Kosmano, D.; Janicke, H. Security for 4G and 5G cellular networks: A survey of existing authentication and privacy-preserving schemes. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2018, 101, 55–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jover, R.P.; Marojevic, V. Security and protocol exploit analysis of the 5G specifications. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 24956–24963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Shahabuddin, S.; Kumar, T.; Okwuibe, J.; Ylianttila, M. Security for 5G and beyond. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 21, 3682–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.; Kumar, P.; Jayakody, D.N.K.; Liyanage, M. A survey on security and privacy of 5G technologies: Potential solutions, recent advancements, and future directions. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019, 22, 196–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, S.R.; Echeverria, M.; Karim, I.; Chowdhury, O.; Berino, E. 5GReasoner: A property-directed security and privacy analysis framework for 5G cellular network protocol. In Proceedings of the 2019 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, London, UK, 11–15 November 2019; pp. 669–684. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.R.; Echeverria, M.; Chowdhury, O.; Li, N.; Bertino, E. Privacy attacks to the 4G and 5G cellular paging protocols using side channel information. In Proceedings of the 26th Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 February 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, H.; Martin, K.M. A survey of subscription privacy on the 5G radio interface-the past, present and future. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2020, 53, 102537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnel-Wild, M.; Cremers, C. Security Vulnerability in 5G-AKA Draft; Department of Computer Science, University of Oxford: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meier, S.; Schmidt, B.; Cremers, C.; Basin, D. The Tamarin prover for the symbolic analysis of security protocols. In Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Computer Aided Verification, Saint Petersburg, Russia, 13–19 July 2013; pp. 696–701. [Google Scholar]
- Basin, D.; Dreier, J.; Hirschi, L.; Radomirovic, S.; Sasse, R.; Stettler, V. A formal analysis of 5G authentication. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 October 2018; pp. 1383–1396. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Peng, J.; Zuo, M. Toward a secure access to 5G network. In Proceedings of the 2018 17th IEEE International Conference on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and Communications/12th IEEE International Conference on Big Data Science and Engineering (TrustCom/BigDataSE), New York, NY, USA, 1–3 August 2018; pp. 1121–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Borgaonkar, R.; Hirschi, L.; Park, S.; Shaik, A. New privacy threat on 3G, 4G, and upcoming 5G AKA Protocols. Proc. Priv. Enhancing Technol. 2019, 3, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cremers, C.; Dehnel-Wild, M. Component-based formal analysis of 5G-AKA: Channel assumptions and session confusion. In Proceedings of the 26th Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS), San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 February 2019; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsos, A. The 5G-AKA authentication protocol privacy. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE European Symposium on Security and Privacy (EuroS&P), Stockholm, Sweden, 17–19 June 2019; pp. 464–479. [Google Scholar]
- Bana, G.; Comon-Lundh, H. Towards unconditional soundness: Computationally complete symbolic attacker. In Proceedings of the First international conference on Principles of Security and Trust (ETAPS), Tallinn, Estonia, 24 March–1 April 2012; pp. 189–208. [Google Scholar]
- Bana, G.; Comon-Lundh, H. A computationally complete symbolic attacker for equivalence properties. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 3–7 November 2014; pp. 609–620. [Google Scholar]
- Braeken, A.; Liyanage, M.; Kumar, P.; Murphy, J. Novel 5G authentication protocol to improve the resistance against active attacks and malicious serving networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 64040–64052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharsallah, I.; Smaoui, S.; Zarai, F. A secure efficient and lightweight authentication protocol for 5G cellular networks: SEL-AKA. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Wireless Communications & Mobile Computing Conference (IWCMC), Tangier, Morocco, 24–28 June 2019; pp. 1311–1316. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Cheng, X. A security enhanced 5G authentication scheme for insecure channel. Trans. Inf. Syst. 2020, 103, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, S.; Li, J.; Cheng, X. A vulnerability in 5G authentication protocols and its Countermeasure. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2020, 103, 1806–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edris, E.K.K.; Aiash, M.; Loo, J.K. Formal verification and analysis of primary authentication based on 5G-AKA protocol. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Software Defined Systems (SDS), Paris, France, 20–23 April 2020; pp. 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- Ouaissa, M.; Ouaissa, M. An improved privacy authentication protocol for 5G mobile networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication & Materials (ICACCM), Dehradun, India, 21–22 August 2020; pp. 136–143. [Google Scholar]
- Parne, B.L.; Gupta, S.; Gandhi, K.; Meena, S. PPSE: Privacy preservation and security efficient AKA protocol for 5G communication networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Networks and Telecommunications Systems (ANTS), New Delhi, India, 14–17 December 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fábrega, F.J.T.; Herzog, J.C.; Guttman, J.D. Mixed strand spaces. In Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Computer Security Foundations Workshop, Mordano, Italy, 30 June 1999; pp. 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Fábrega, F.J.T.; Herzog, J.C.; Guttman, J.D. Strand space: Proving security protocols correct. J. Comput. Secur. 1999, 7, 191–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, J.C. The Diffie-Hellman key-agreement scheme in the strand-space model. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE Computer Security Foundation Workshop, Pacific Grove, CA, USA, 30 June–2 July 2003; pp. 234–247. [Google Scholar]
| Shortcomings | 5G AKA | [23] | [24] | [26] | [27] | 5G-IPAKA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| can be replayed without being found | Yes | No | Yes | No | No | No |
| Mutual authentication between the UE and the SN cannot be established | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| cannot reach an agreement | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| The location privacy of the UE can be compromised | Yes | No | No | No | No | No |
| DoS attacks against the SN can be formed | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Attacks based on MAC failure can be performed | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Perfect forward secrecy cannot be provided | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Protocols | The Number of Messages | The Amount of Calculation | Backward Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5G AKA | 11 | 1ECDH+1ED+12F+2XOR | - |
| [23] | 11 | 4PED+1ED+10F+2XOR | No |
| [24] | 11 | 2PED+1ECDH+1ED+13F+1XOR | No |
| [26] | 9 | 1ECDH+1ED+12F | No |
| [27] | 7 | 1ED+15F+1LRCS+6XOR | No |
| 5G-IPAKA | 9 | 1ECDH+1ED+16F+2XOR | Yes |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiao, Y.; Wu, Y. 5G-IPAKA: An Improved Primary Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for 5G Networks. Information 2022, 13, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030125
Xiao Y, Wu Y. 5G-IPAKA: An Improved Primary Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for 5G Networks. Information. 2022; 13(3):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiao, Yuelei, and Yang Wu. 2022. "5G-IPAKA: An Improved Primary Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for 5G Networks" Information 13, no. 3: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030125
APA StyleXiao, Y., & Wu, Y. (2022). 5G-IPAKA: An Improved Primary Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for 5G Networks. Information, 13(3), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/info13030125






