An Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Propose a security framework for attack detection for VANETs;
- Define a hierarchy-based architecture that adapts each level roles and functions to their capabilities and needs;
- Compare multiple ML algorithms for attack detection;
- Use datasets available publicly, enabling the replication and verification of the results.
2. Background
2.1. Related Work
| Paper | Net Sim | Traffic Sim | Attacks | IDS Type | Detection Type | ML | Dataset | Placement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [22] | Own | Own | Malicious packets | Hierarchical | Anomaly | Learning Automata | From Simulation | Base Station |
| [23] | NS2 | N.A. | DoS | Hierarchical | Anomaly | Neural Networks | NS2 Trace file | Access Points |
| [24] | NS3 | SUMO | DoS, R2L, U2R, Probing | Hierarchical | Anomaly | Naive Bayes and Logistic Regression | TCPdump | Each cell and vehicle |
| [25] | NS3 | SUMO | Selective Forwarding, Black Hole, Packet duplication, Resource Exhaustion and Sybil attack | Hierarchical | Rule Based and Anomaly | SVM | NS3 Trace file | Vehicles and RSUs |
| [26] | — | — | DoS | Hierarchical | Misuse and Anomaly | Neural Networks | Kyoto Dataset | N.A. |
| [27] | Matlab | VANET Mobisim | packet dropping | Hierarchical | Watchdog and Anomaly | SVM | From Simulation | Vehicles |
| [28] | NetSim and Matlab | SUMO | Wormhole, Selective Forwarding, Packet Drop | Hierarchical | Anomaly | SVM | NS2 Trace file | Vehicles |
| [29] | N.A. | N.A. | DoS | Hierarchical | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. |
| [30] | - | - | Network Anomalies | Hierarchical | Anomaly | Logistic Regression | NSL-KDD | Vehicles |
| [31] | NS2 | SUMO | Network Anomalies | Hierarchical | N.A. | HGNG | From Simulation | Vehicles |
2.2. Datasets
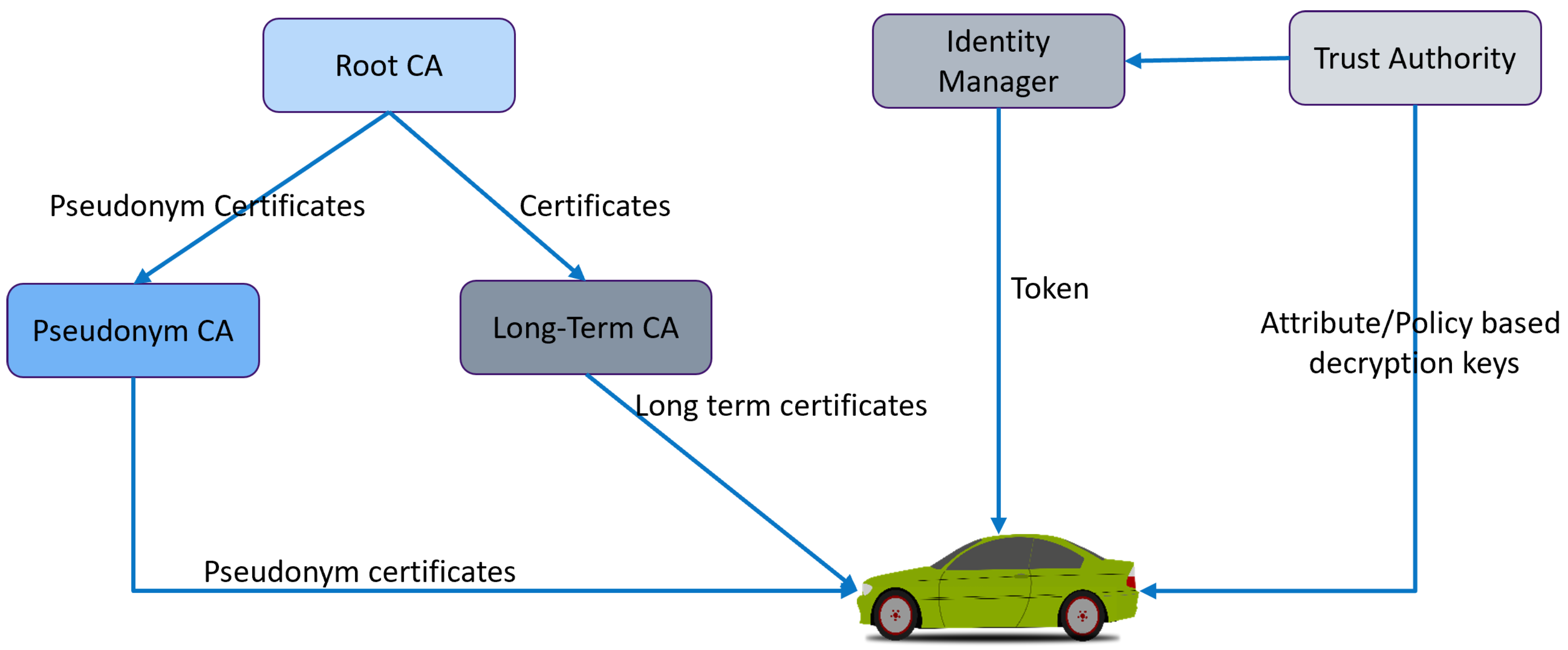
2.3. Securing Communications
3. Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs
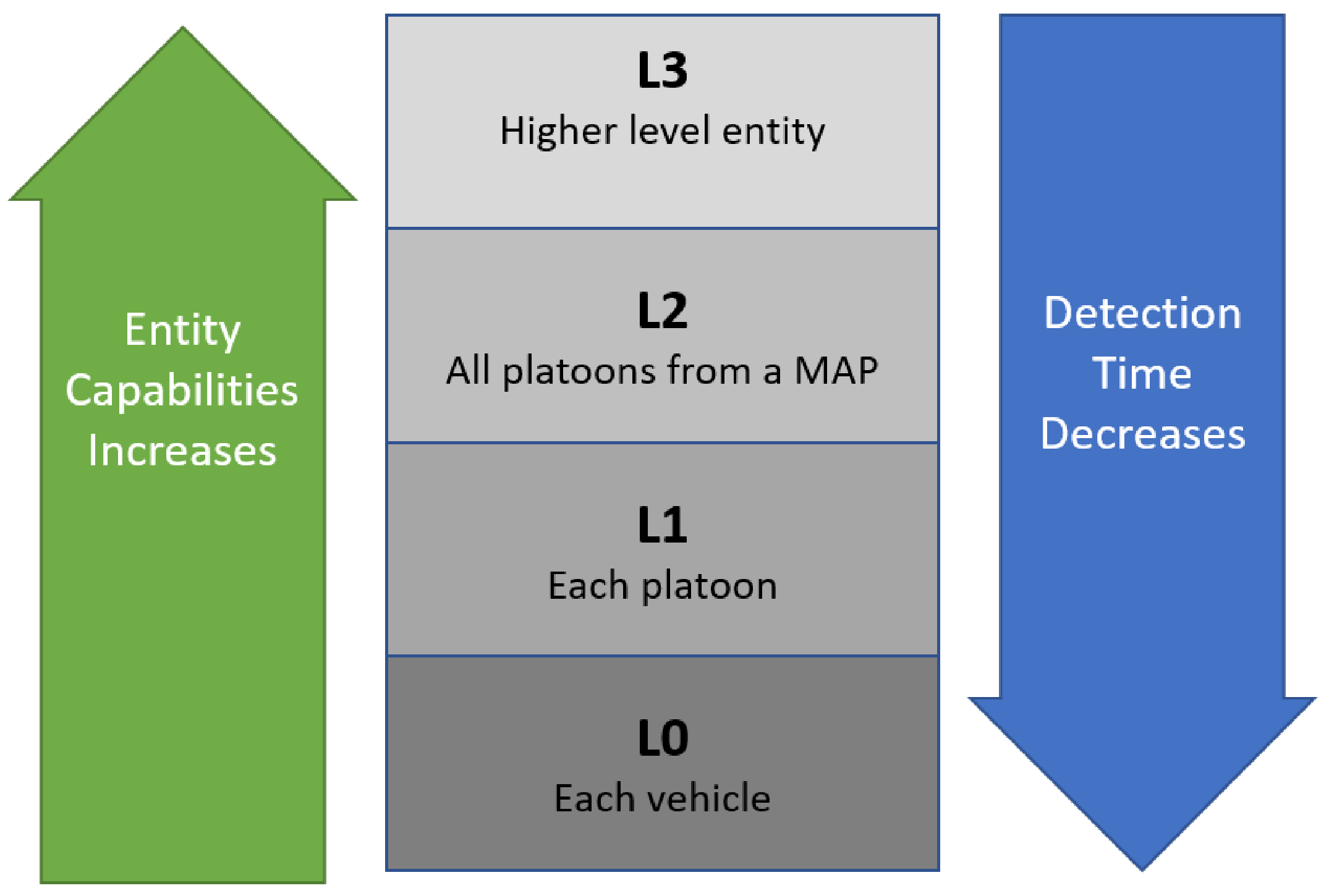
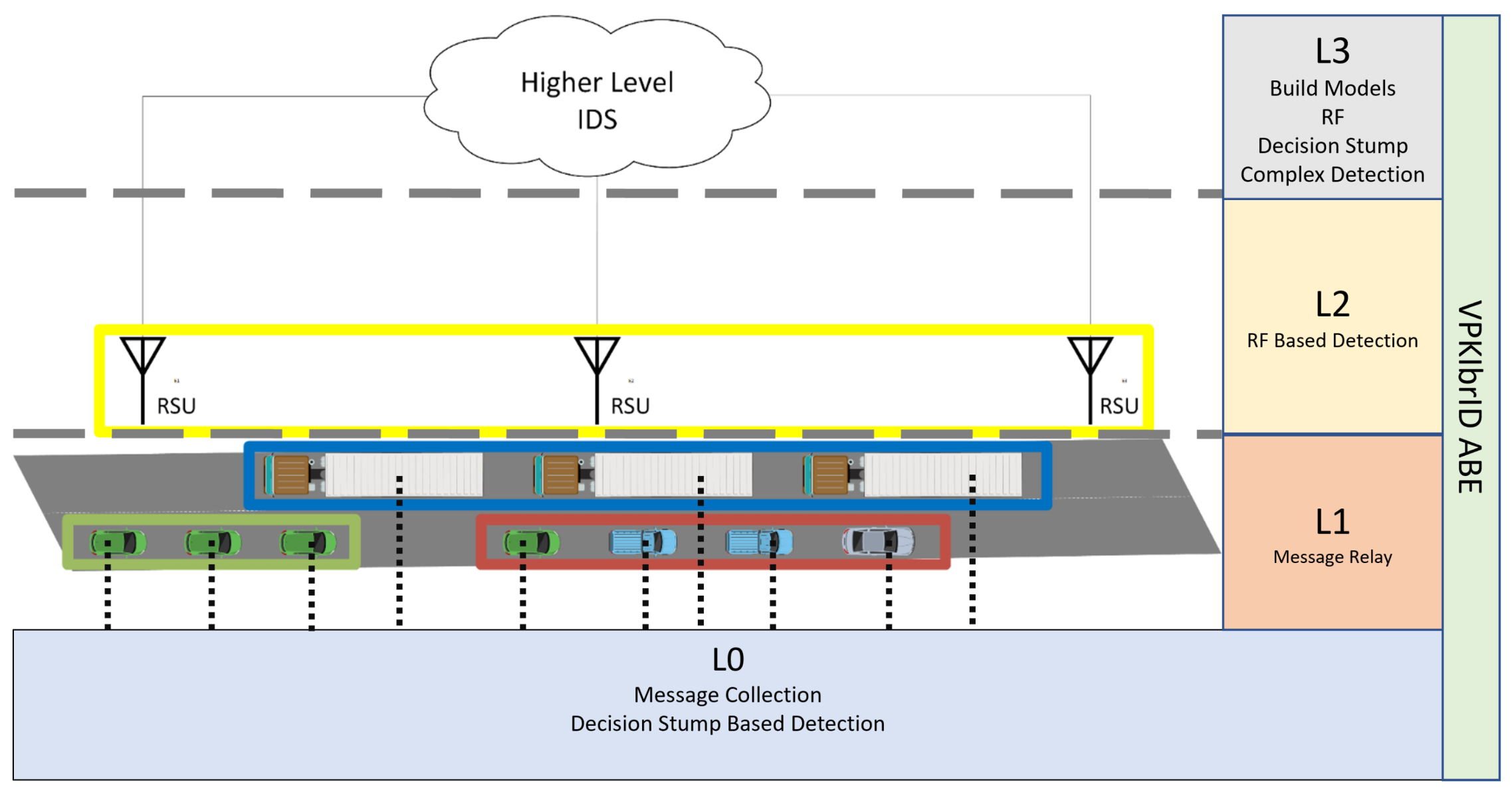
3.1. Architecture
- —Each vehicle on the map. These are the smallest cluster composed of only one entity
- —A group of vehicles organized into a single cluster;
- —All the vehicle clusters within a geographical region;
- —Cluster of all geographic maps;
3.2. Secure Communications
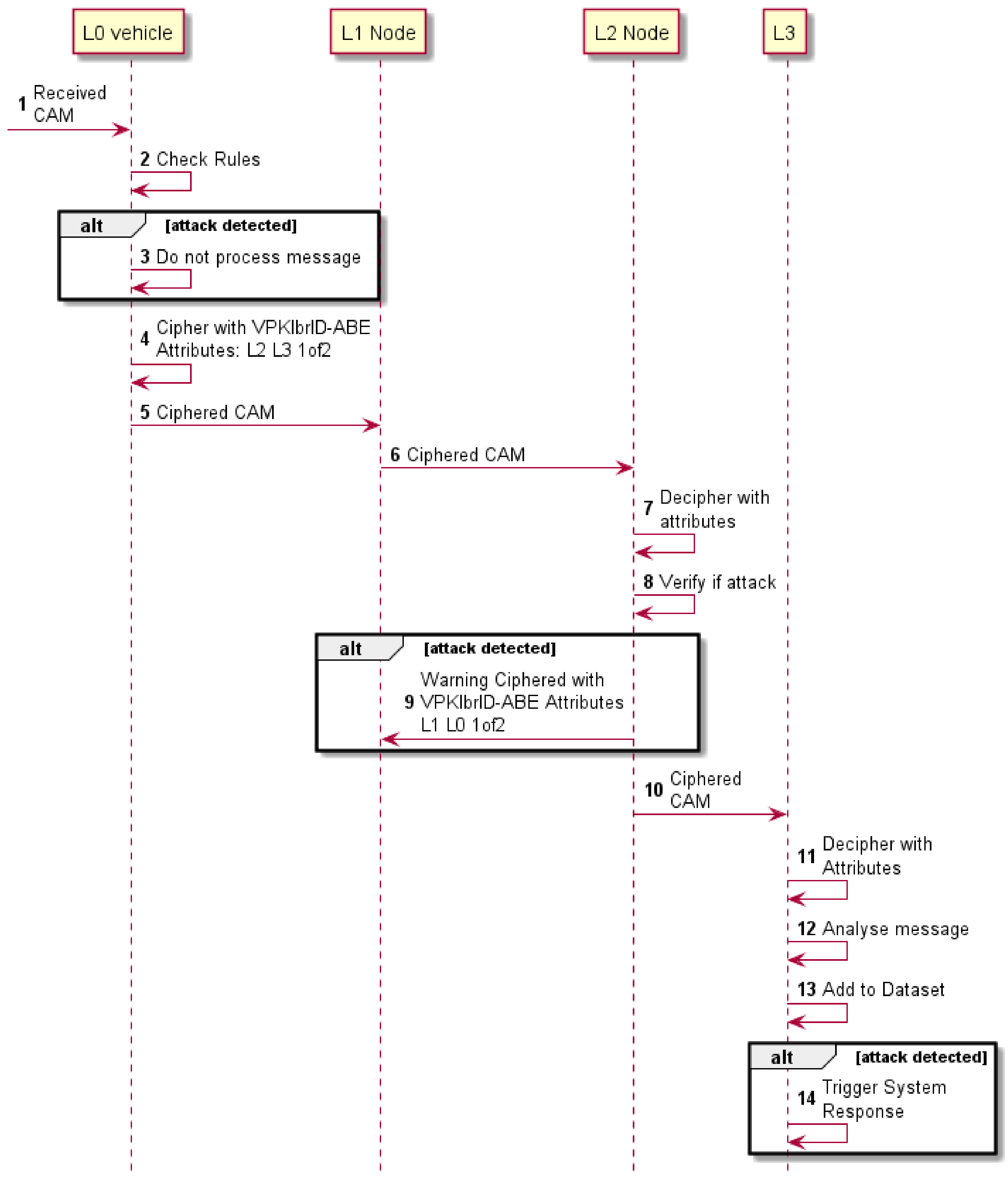
3.2.1. Upstream Communication
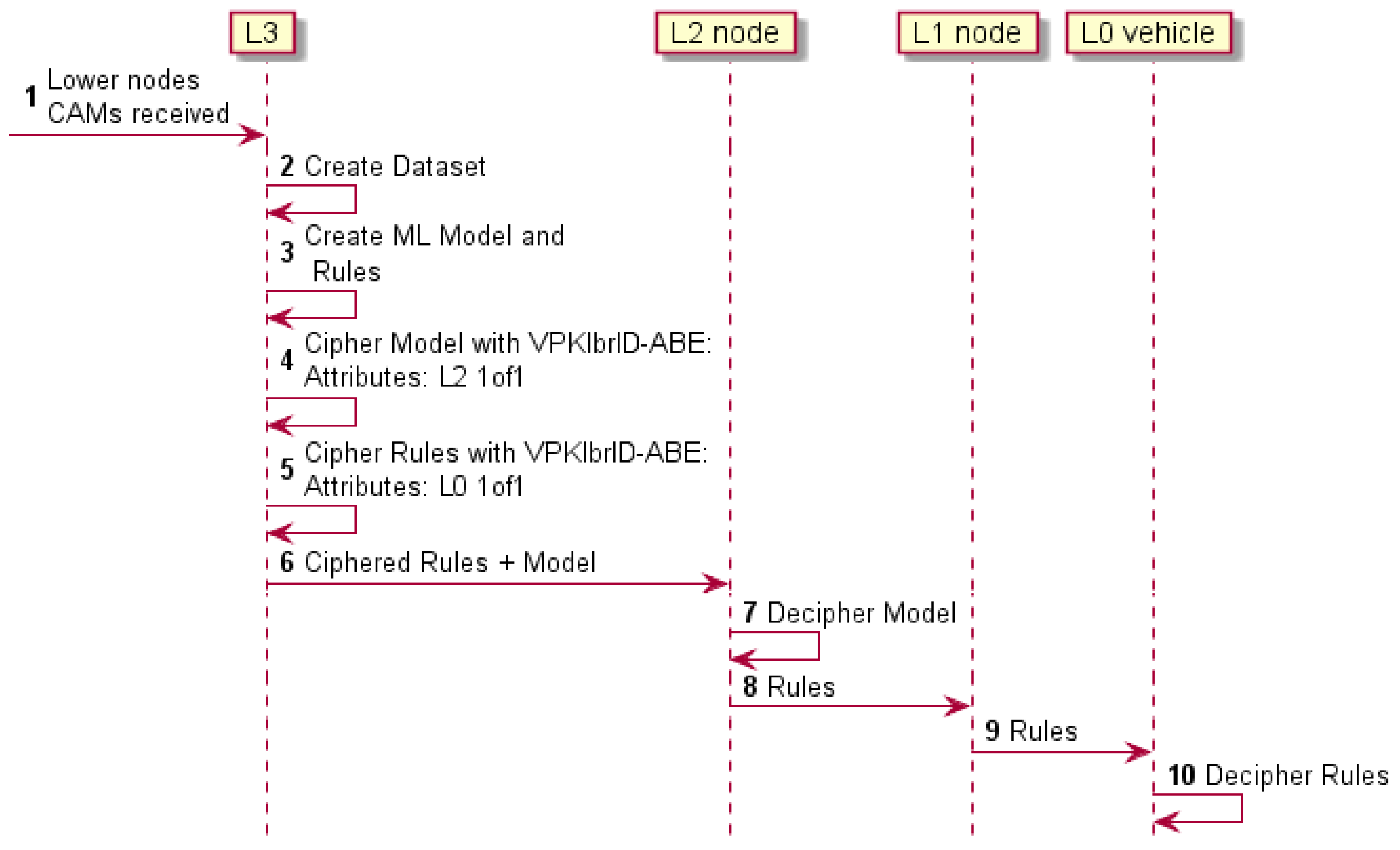
3.2.2. Downstream Communication
4. Clustering, Preprocessing and Analysis
4.1. Clustering
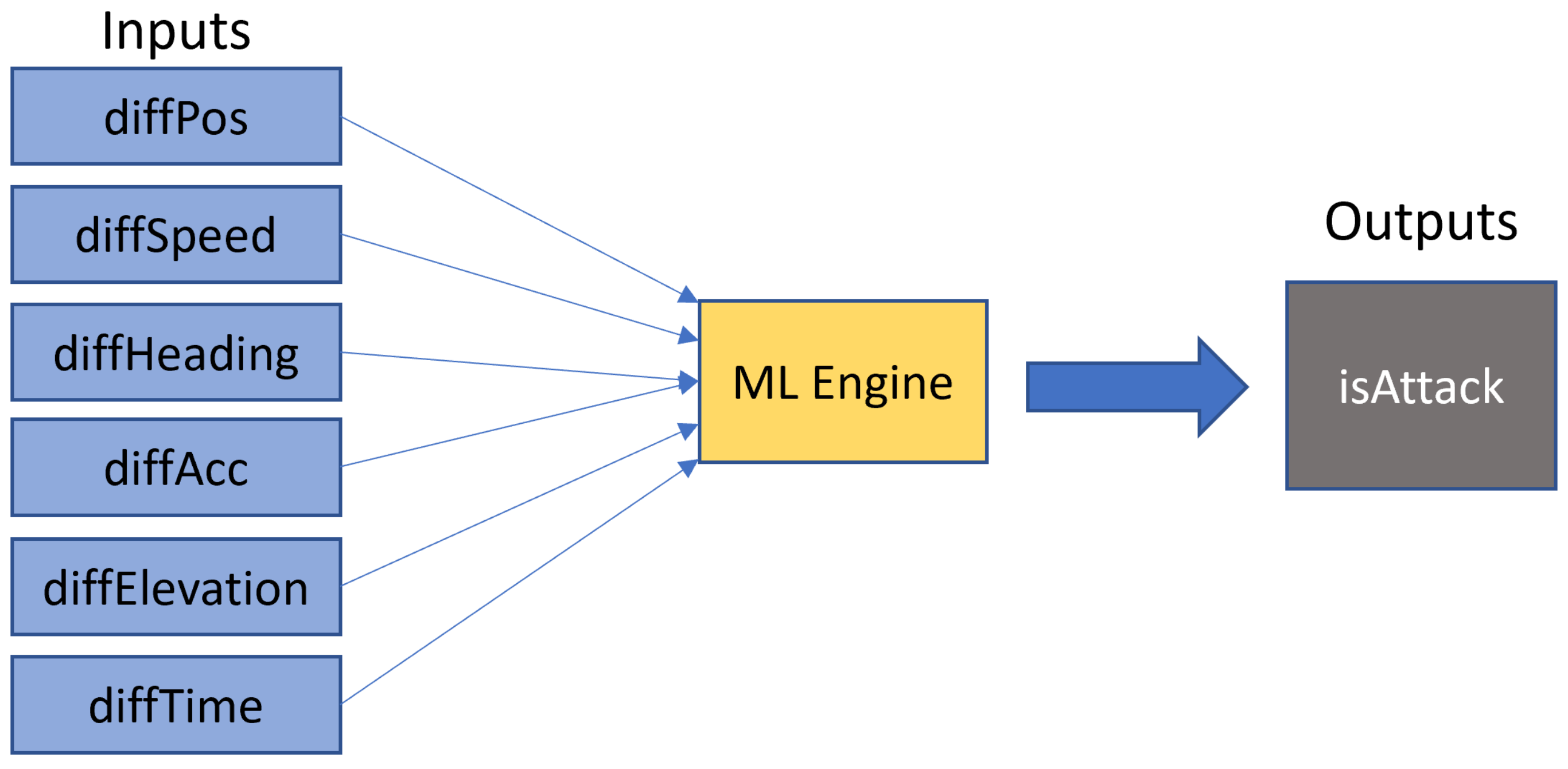
4.2. Methodology
5. Evaluation and Results
5.1. Evaluation Using Multiple ML Approaches
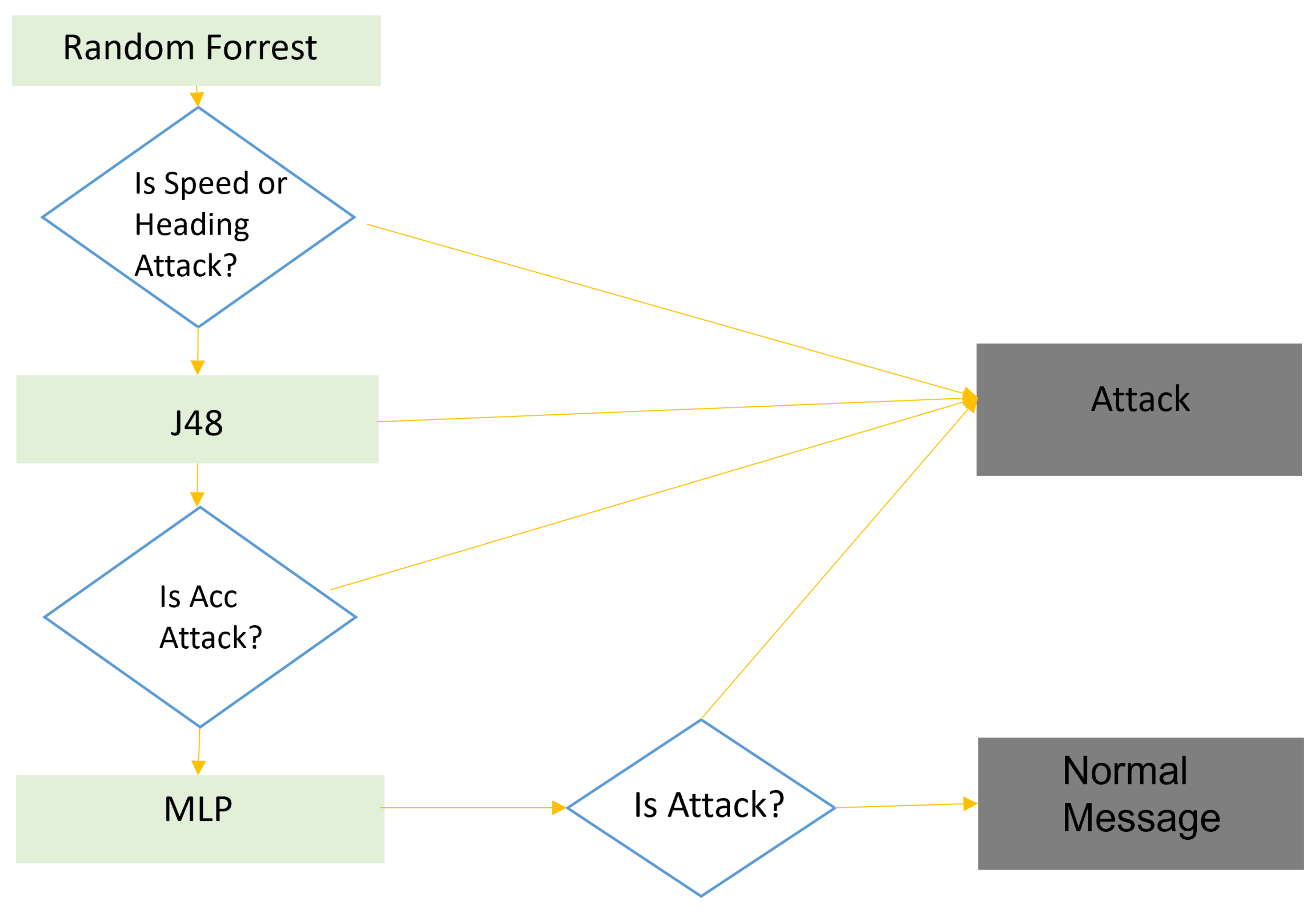
5.2. Ensemble-Based Evaluation
5.3. Rule-Based Evaluation
6. Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs Detection Algorithms and Use-Case
6.1. Detection
6.2. Detection
6.3. Detection
6.4. Detection
6.5. Hierarchical Intelligent IDS Architecture: Application Use-Case
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABE | Attribute-Based Encryption |
| CA | Certification Authority |
| CAM | Context Awareness Message |
| DCAITI | Daimler Center for Automotive IT Innovations |
| DoS | Denial of Service |
| DSRC | Dedicated Short Range Communications |
| FPR | False Positive Rate |
| IdM | Identity Manager |
| IDS | Intrusion Detection System |
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers |
| ITS | Intelligent Transportation Systems |
| LMT | Logistic Model Tree |
| LTC | Long-Term Certificate |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
| ns-3 | Network Simulator 3 |
| OBU | On-Board Unit |
| PC | Pseudonym Certificate |
| PKI | Public Key Infrastructure |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| RSU | Road Side Unit |
| SLR | Systematic Literature Review |
| SUMO | Simulation of Urban Mobility |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TA | Trusted Authority |
| TPR | True Positive Rate |
| VANET | Vehicular Ad hoc Network |
| V2V | Vehicle to Vehicle |
| VPKIbrID | Vehicular Ad hoc Network Public Key Infrastructure and Attribute-Based Encryption with Identity Manager Hybrid |
| VPKIbrID-ABE | VPKIbrID Attribute-Based Encryption |
| VPKIbrID-PKI | VPKIbrID Public Key Infrastructure |
| VSimRTI | V2X Simulation Runtime Infrastructure |
References
- Cseh, C. Architecture of the dedicated short-range communications (DSRC) protocol. In Proceedings of the VTC 98. 48th IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 21–21 May 1998; Volume 3, pp. 2095–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE. IEEE Standard for Information Technology—Local and Metropolitan Area Networks—Specific Requirements—Part 11: Wireless LAN Medium Access Control (MAC) and Physical Layer (PHY) Specifications Amendment 6: Wireless Access in Vehicular Environments; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, B.; Santos, A.; Costa, A.; Ribeiro, B.; Goncalves, F.; Macedo, J.; Nicolau, M.J.; Gama, O.; Sousa, S. Agnostic and Modular Architecture for the Development of Cooperative ITS Applications. J. Commun. Softw. Syst. 2018, 14, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engoulou, R.G.; Bellaiche, M.; Pierre, S.; Quintero, A. VANET security surveys. Comput. Commun. 2014, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, R.; Chen, I.R. A survey of intrusion detection in wireless network applications. Comput. Commun. 2014, 42, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2016; Chapter 7; pp. 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aburomman, A.A.; Reaz, M.B.I. Survey of learning methods in intrusion detection systems. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advances in Electrical, Electronic and Systems Engineering (ICAEES), Putrajaya, Malaysia, 14–16 November 2016; pp. 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, F.; Ribeiro, B.; Gama, O.; Santos, A.; Costa, A.; Dias, B.; Macedo, J.; Nicolau, M.J. A Systematic Review on Intelligent Intrusion Detection Systems for VANETs. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems and Workshops (ICUMT), Dublin, Ireland, 28–30 October 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, F.; Macedo, J.; Santos, A. Evaluation of VANET Datasets in context of an Intrusion Detection System. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks (SoftCOM 2021), Split, Croatia, 23–25 September 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Raya, M.; Hubaux, J.P. The security of VANETs. In Proceedings of the 2nd ACM international workshop on Vehicular ad hoc networks—VANET’05, Cologne, Germany, 2 September 2005; pp. 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesham, A.; Abdel-Hamid, A.; El-Nasr, M.A. A dynamic key distribution protocol for PKI-based VANETs. IFIP Wirel. Days 2011, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellur, B. Certificate Assignment Strategies for a PKI-Based Security Architecture in a Vehicular Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE GLOBECOM 2008—2008 IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, New Orleans, LA, USA, 30 November–4 December 2008; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wu, Q.; Yong, L. A hierarchical security architecture of VANET. Cyberspace Technol. 2013, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagan, A.A.; Mughal, B.M.; Hasbullah, H.; Iskandar, B.S. VANET Security Framework for Trusted Grouping using TPM Hardware. In Proceedings of the 2010 Second International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, Singapore, 26–28 February 2010; pp. 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bariah, L.; Shehada, D.; Salahat, E.; Yeun, C.Y. Recent advances in VANET security: A survey. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 82nd Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC Fall 2015, Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 September 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gad, A.R.; Nashat, A.A.; Barkat, T.M. Intrusion Detection System Using Machine Learning for Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks Based on ToN-IoT Dataset. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 142206–142217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustafa, N. TON-IOT. Dataset. Available online: https://research.unsw.edu.au/projects/toniot-datasets (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Alsarhan, A.; Alauthman, M.; Alshdaifat, E.; Al-Ghuwairi, A.R.; Al-Dubai, A. Machine Learning-driven optimization for SVM-based intrusion detection system in vehicular ad hoc networks. J. Ambient. Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmanos, D.; Pappas, A.; Maglaras, L.; Moschoyiannis, S.; Aparicio-Navarro, F.J.; Argyriou, A.; Janicke, H. A novel Intrusion Detection System against spoofing attacks in connected Electric Vehicles. Array 2020, 5, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Takakura, H.; Okabe, Y.; Eto, M.; Inoue, D.; Nakao, K. Statistical analysis of honeypot data and building of Kyoto 2006+ dataset for NIDS evaluation. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Building Analysis Datasets and Gathering Experience Returns for Security—BADGERS ’11, Kyoto, Japan, 5 November 2011; pp. 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaee, M.; Bagheri, E.; Lu, W.; Ghorbani, A.A. A detailed analysis of the KDD CUP 99 data set. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications, CISDA 2009, CISDA’09, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8–10 July 2009; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Misra, S.; Krishna, P.V.; Abraham, K.I. A stochastic learning automata-based solution for intrusion detection in vehicular ad hoc networks. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2011, 4, 666–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G.; Yu, G. A vehicular ad hoc networks intrusion detection system based on BUSNet. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Future Computer and Communication, ICFCC 2010, Wuhan, China, 21–24 May 22010; Volume 1, pp. 1–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yan, G.; Rawat, D.B.; Deng, S. Data mining intrusion detection in vehicular ad hoc network. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 2014, E97-D, 1719–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sedjelmaci, H.; Senouci, S.M. An accurate and efficient collaborative intrusion detection framework to secure vehicular networks. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2015, 43, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Alheeti, K.M.; McDonald-Maier, K. Hybrid intrusion detection in connected self-driving vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2016 22nd International Conference on Automation and Computing, ICAC 2016: Tackling the New Challenges in Automation and Computing, Colchester, UK, 7–8 September 2016; pp. 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, O.A.; Mourad, A.; Otrok, H.; Bentahar, J. CEAP: SVM-based intelligent detection model for clustered vehicular ad hoc networks. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 50, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaul, A. Hybrid fuzzy multi-criteria decision making based multi cluster head dolphin swarm optimized IDS for VANET. Veh. Commun. 2018, 12, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Gui, Z.; Chung, I. A Secure and Efficient Certificateless Authentication Scheme With Unsupervised Anomaly Detection in VANETs. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 74260–74276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhu, Q. Distributed Privacy-Preserving Collaborative Intrusion Detection Systems for VANETs. IEEE Trans. Signal Inf. Process. Over Netw. 2018, 4, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoob, A.; Su, G.; Al, G. Hierarchical Growing Neural Gas Network (HGNG)-Based Semicooperative Feature Classifier for IDS in Vehicular Ad Hoc Network (VANET). J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2018, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, F.; Ribeiro, B.; Gama, Ó.; Santos, J.; Costa, A.; Dias, B.; Nicolau, M.J.; Macedo, J.; Santos, A. Synthesizing Datasets with Security Threats for Vehicular Ad-Hoc Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom 2020: 2020 IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM’2020), Taipei, Taiwan, 7–11 December 2020. [Google Scholar]
- DCAITI. VSimRTI. Available online: https://www.dcaiti.tu-berlin.de/research/simulation/ (accessed on 12 November 2020).
- ETSI. ETSI EN 302 637-2 V1.3.1 Intelligent Transport Systems (ITS); Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 2: Specification of Cooperative Awareness Basic Service; ETSI: Sophia, France, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, F.; Santos, A.; Costa, A.; Dias, B.; Ribeiro, B.; Macedo, J.; Nicolau, M.J.N.; Sousa, S.; Gama, O.; Barros, S.; et al. Hybrid Model for Secure Communications and Identity Management in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks. In Proceedings of the 9th International Congress on Ultra Modern Telecommunications and Control Systems (ICUMT’2017), Munich, Germany, 6–8 November 2017; pp. 414–422. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, B.; Gonçalves, F.; Hapanchak, V.; Gama, Ó.; Barros, S.; Araújo, P.; Costa, A.; Nicolau, M.J.; Dias, B.; Macedo, J.; et al. PlaSA-Platooning Service Architecture. In Proceedings of the 8th ACM Symposium on Design and Analysis of Intelligent Vehicular Networks and Applications, Montreal, QC, Canada, 28 October–2 November 2018; pp. 80–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gonçalves, F.; Ribeiro, B.; Hapanchak, V.; Barros, S.; Gama, O.; Araújo, P.; Nicolau, M.J.; Dias, B.; Macedo, J.; Costa, A.; et al. Secure Management of Autonomous Vehicle Platooning. In Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Symposium on QoS and Security for Wireless and Mobile Networks, Q2SWinet’18, Montreal, QC, Canada, 28 October–2 November 2018; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, B.; Gonçalves, F.; Santos, A.; Nicolau, M.; Dias, B.; Macedo, J.; Costa, A. Simulation and Testing of a Platooning Management Protocol Implementation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wired/Wireless Internet Communication, St. Petersburg, Russia, 21–23 June 2017; pp. 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonçalves, F.; Santos, A.; Macedo, J. V2X Security Threats for Cluser-Based Evaluation [Data Set]; Zenodo: Genève, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Max Interval | >1000 ms |
| Min Interval | <100 ms |
| Position Change | >4 m |
| Heading Change | >4.0 degress |
| Velocity Change | >0.5 m/s |
| Map 1 | Platoon 1.1 | v_0, v_1, v_2, v_3, v_4 |
| Platoon 1.2 | v_14, v_15, v_17, v_21 | |
| Platoon 1.3 | v_16, v_18, v_20, v_23, v_26 | |
| Map 2 | Platoon 2.1 | v_0, v_6, v_12, v_18, v_24 |
| Platoon 2.2 | v_1, v_7, v_13, v_19, v_25, v_23, v_26 | |
| Platoon 2.3 | v_32, v_35, v_37, v_40, v_43 | |
| Platoon 2.4 | v_38, v_41, v_44, v_45, v_46, v_47, v_50 | |
| Platoon 2.5 | v_49, v_52, v_54, v_56, v_59 | |
| Platoon 2.6 | v_48, v_51, v_53, v_55 | |
| Map 3 | Platoon 3.1 | v_1, v_3, v_7, v_10, v_12 |
| Platoon 3.2 | v_13, v_15, v_17, v_18, v_19 | |
| Map 4 | Platoon 4.1 | v_4, v_5, v_7, v_10, v_11 |
| Platoon 4.2 | v_18, v_20, v_23, v_25 | |
| Platoon 4.3 | v_32, v_25, v_27, v_40, v_43 | |
| Platoon 4.4 | v_38, v_41, v_44, v_45, v_46, v_47, v_50 | |
| Platoon 4.5 | v_49, v_52, v_54, v_56, v_59 | |
| Platoon 4.6 | v_48, v_51, v_53, v_55 | |
| Map 5 | Platoon 5.1 | v_2, v_3, v_5, v_7 |
| Platoon 5.2 | v_10, v_12, v_14 | |
| Platoon 5.3 | v_19, v_21, v_23, v_25, v_26 | |
| Map 6 | Platoon 6.1 | v_0, v_1, v_2, v_3, v_4, v_6, v_8 |
| Platoon 6.2 | v_14, v_15, v_17, v_19, v_21, v_24, v_27 | |
| Platoon 6.3 | v_16, v_18, v_20, v_23 |
| Training | Test | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Value | % of Total | Value | % of Total |
| Messages (Total) | 2,491,271 | 100.00 | 17,237,722 | 100.00 |
| Non-Attack | 1,508,873 | 60.57 | 9,062,023 | 52.57 |
| DoS | 912,875 | 36.64 | 7,756,817 | 45.00 |
| Fab. Speed | 30,002 | 1.20 | 172,892 | 1.00 |
| Fab. Acc | 23,819 | 0.95 | 62,686 | 0.36 |
| Fab. Heading | 15,702 | 0.63 | 183,304 | 1.06 |
| Normal | DoS | Speed | Acc | Heading | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | Accuracy | MAE | RMSE | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | Avg TPR | Avg FPR |
| Random Forest | 0.98 | 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.98 | 0.02 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.77 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.88 | 0.01 |
| MLP | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.09 | 1.00 | 0.05 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.47 | 0.06 |
| J48 | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.97 | 0.02 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.78 | 0.01 | 0.89 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 0.01 |
| REP Tree | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.97 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0,71 | 0.01 | 0.62 | 0.01 | 0.87 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 0.01 |
| LMT | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.98 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 0.00 | 0.89 | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.01 |
| Random Tree | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.69 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.86 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.01 |
| Hoeffding Tree | 0.96 | 0.05 | 0.12 | 0.98 | 0.06 | 0.97 | 0.00 | 0.64 | 0.00 | 0.28 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.01 |
| Logistic | 0.95 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 0.09 | 0.96 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.39 | 0.02 |
| OneR | 0.94 | 0.03 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.92 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.03 |
| Decision Stump | 0.94 | 0.04 | 0.16 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.92 | 0.01 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.02 |
| SMO | 0.92 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.91 | 0.05 | 1.00 | 0.10 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.02 |
| PART | 0.97 | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.97 | 0,02 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.63 | 0.01 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.01 |
| Naive Bayes | 0.85 | 0.06 | 0.24 | 0.74 | 0.03 | 0.99 | 0.21 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.01 | 0.53 | 0.01 | 0.65 | 0.06 |
| Decision Table | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 0.71 | 0.31 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.26 | 0.14 |
| Algorithm | Train Time (s) | Test Time (s) | Size (KB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LMT | 21,879 | 23 | 1225 |
| Decision Table | 4514 | 169 | 29,684 |
| PART | 3128 | 281 | 4860 |
| Random Forrest | 3014 | 476 | 54,497 |
| SMO | 2688 | 23 | 10 |
| MLP | 1176 | 25 | 16 |
| J48 | 335 | 31 | 1024 |
| Logistic | 139 | 30 | 9 |
| REPTree | 123 | 19 | 791 |
| HoeffdingTree | 10 | 77 | 512 |
| Decision Stump | 7 | 15 | 3 |
| OneR | 7 | 29 | 17 |
| Naive Bayes | 4 | 79 | 5 |
| MLP | RF | J48 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| batchSize | 100 | batchSize | 100 | batchSize | 100 | |||
| numDecimalPlaces | 2 | numDecimalPlaces | 2 | numDecimalPlaces | 2 | |||
| hiddenLayers | a | bagSizePercent | 100 | confidenceFactor | 0.25 | |||
| learningRate | 0.3 | maxDepth | 0 | minNumObj | 2 | |||
| momentum | 0.2 | numExecutionSlots | 1 | numFolds | 3 | |||
| seed | 0 | numFeatures | 0 | seed | 1 | |||
| trainingTime | 500 | numIterations | 100 | |||||
| validationSetSize | 0 | seed | 1 | |||||
| validationThreshold | 20 | |||||||
| Normal | DoS | Speed | Acc | Heading | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ensemble | Accuracy | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR | Avg TPR | Avg FPR |
| Stacking Custom | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.89 | 0.00 |
| Stacking | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.02 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.79 | 0.00 | 0.67 | 0.00 | 0.90 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.00 |
| Vote Major | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 0.00 | 0.72 | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.00 | 0.87 | 0.00 |
| Vote Average | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.02 | 0.99 | 0.00 | 0.75 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.00 | 0.88 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.00 |
| Vote Maximum | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.01 |
| Vote Product | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.00 | 0.76 | 0.01 | 0.84 | 0.00 | 0.86 | 0.01 |
| Vote Minimum | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.00 | 0.77 | 0.01 | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.82 | 0.01 |
| Normal | Attack | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Attack Type | TPR | FPR | TPR | FPR |
| DoS | 0.99 | 0.1 | 0.94 | 0.01 |
| Speed | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.47 | 0.00 |
| Acceleration | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Heading | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.47 | 0.00 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gonçalves, F.; Macedo, J.; Santos, A. An Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs. Information 2021, 12, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12110455
Gonçalves F, Macedo J, Santos A. An Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs. Information. 2021; 12(11):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12110455
Chicago/Turabian StyleGonçalves, Fábio, Joaquim Macedo, and Alexandre Santos. 2021. "An Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs" Information 12, no. 11: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12110455
APA StyleGonçalves, F., Macedo, J., & Santos, A. (2021). An Intelligent Hierarchical Security Framework for VANETs. Information, 12(11), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/info12110455







