Multilingual Open Information Extraction: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Open Information Extraction
Open IE with Different Languages
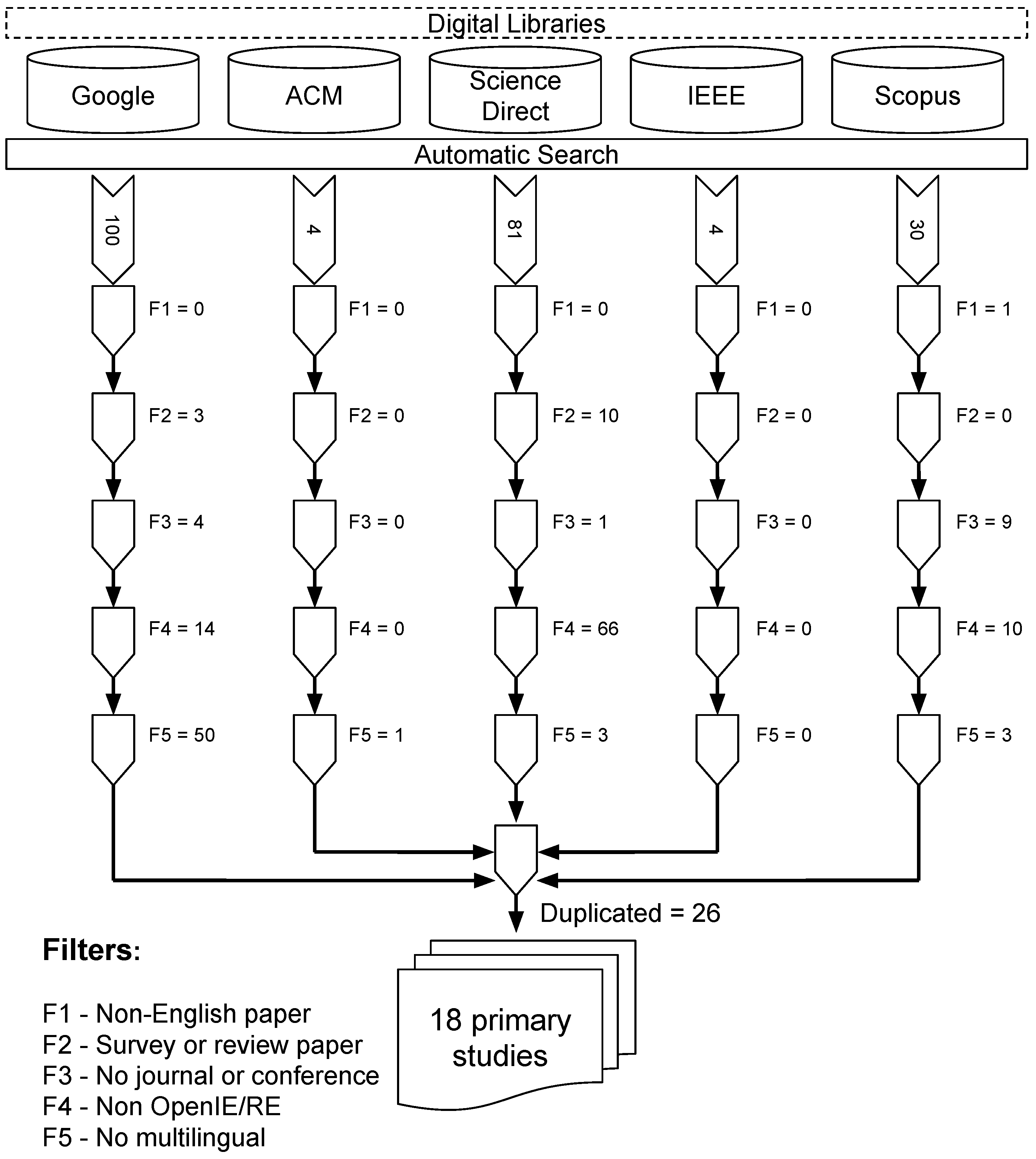
3. Multilingual Open IE: A Systematic Mapping Study
- Main Research Question (MRQ): What is the state of the art of Multilingual Open Information Extraction?
- RQ1: What are the sources of publications in the area of Multilingual Open IE ?
- RQ2: What are the types of contributions made by Multilingual Open IE studies?
- RQ3: What are the types of applications made for Multilingual Open IE studies?
- RQ4: What are the available Multilingual Open IE datasets?
- RQ5: What are the tools used in Multilingual Open IE systems?
- RQ6: How are Multilingual Open IE systems evaluated?
- “multi lingual” OR “crosslingual” OR “multilingual” OR “multi-lingual”,
- “open information extraction”,
- “relation extraction”.
- F1: Remove non-English written paper.
- F2: Remove survey or review paper.
- F3: Remove paper not published in journals or conferences.
- F4: Remove paper that has some “openie” or “relation extraction” terms, but do not deal with this topic.
- F5: Remove the non-multilingual paper.
- Duplicated: Remove one of the duplicate occurrences.
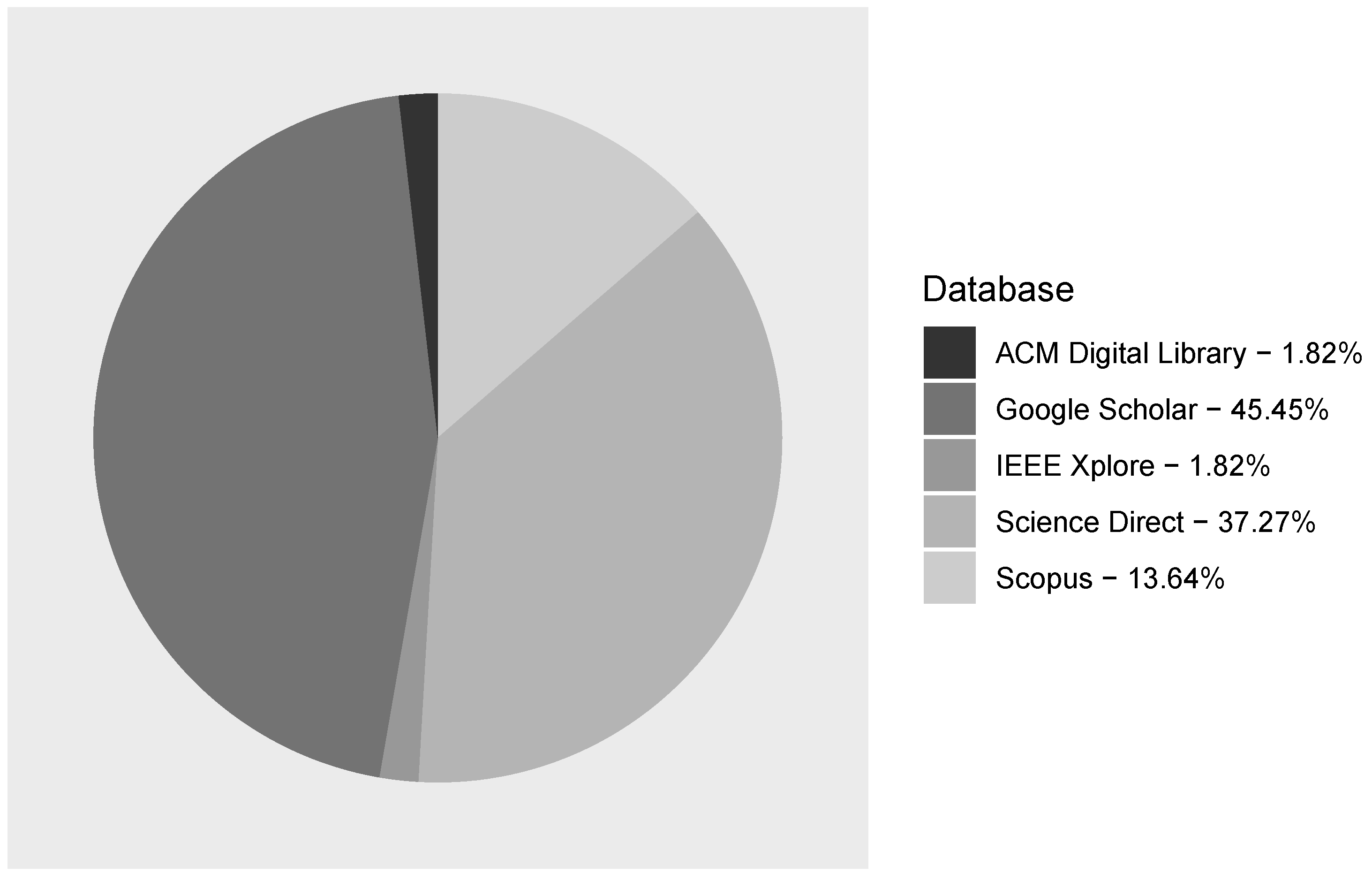
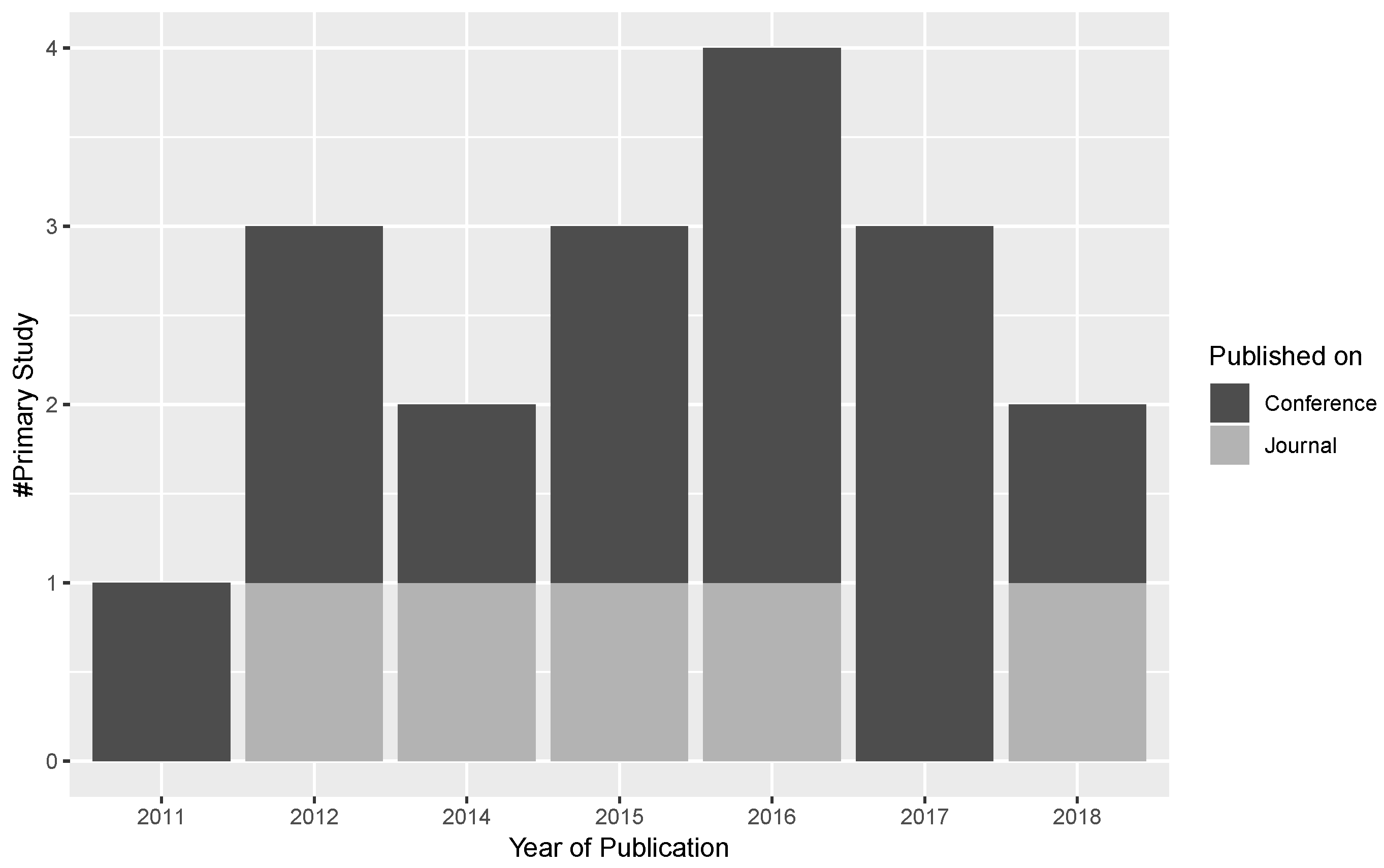
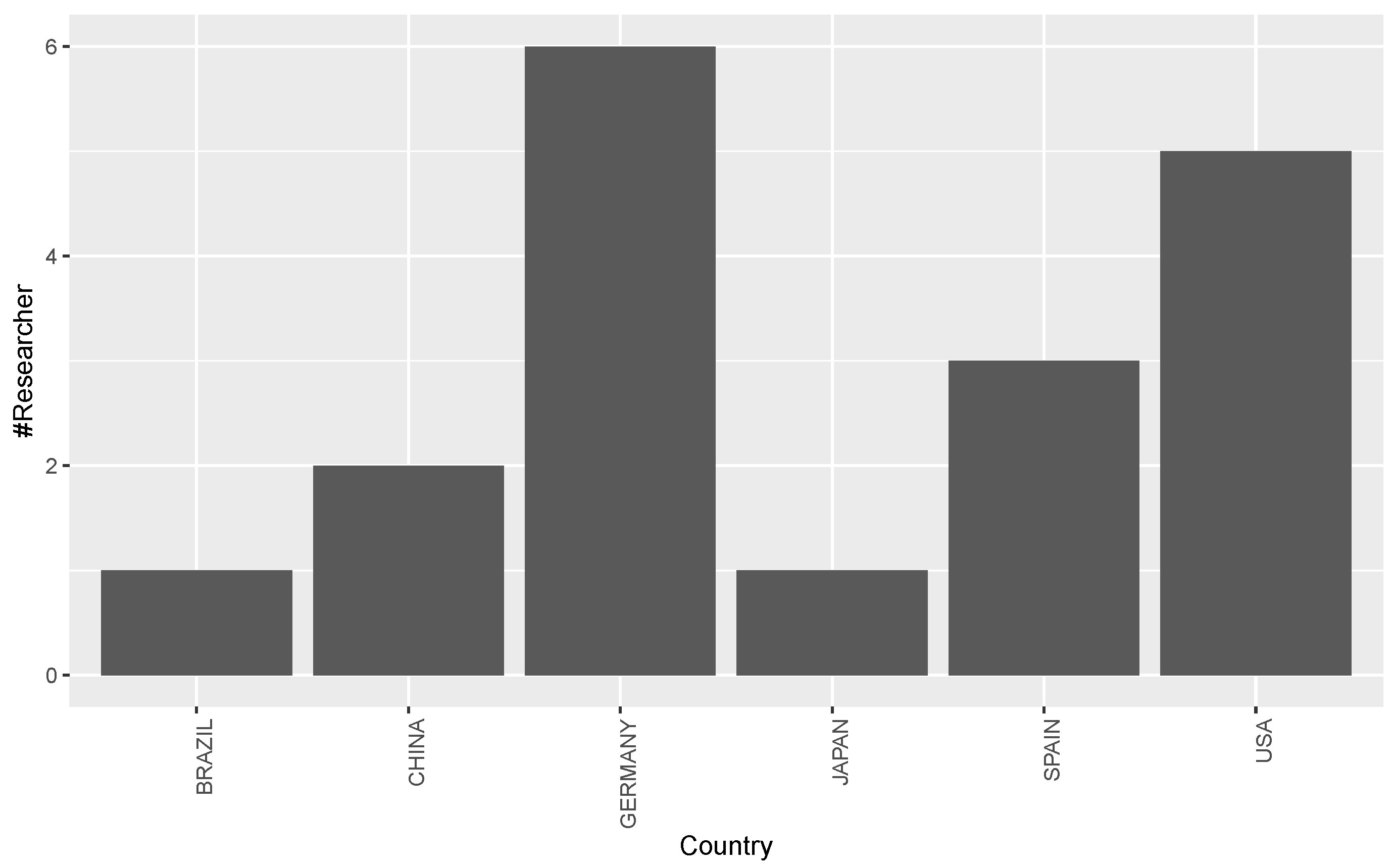
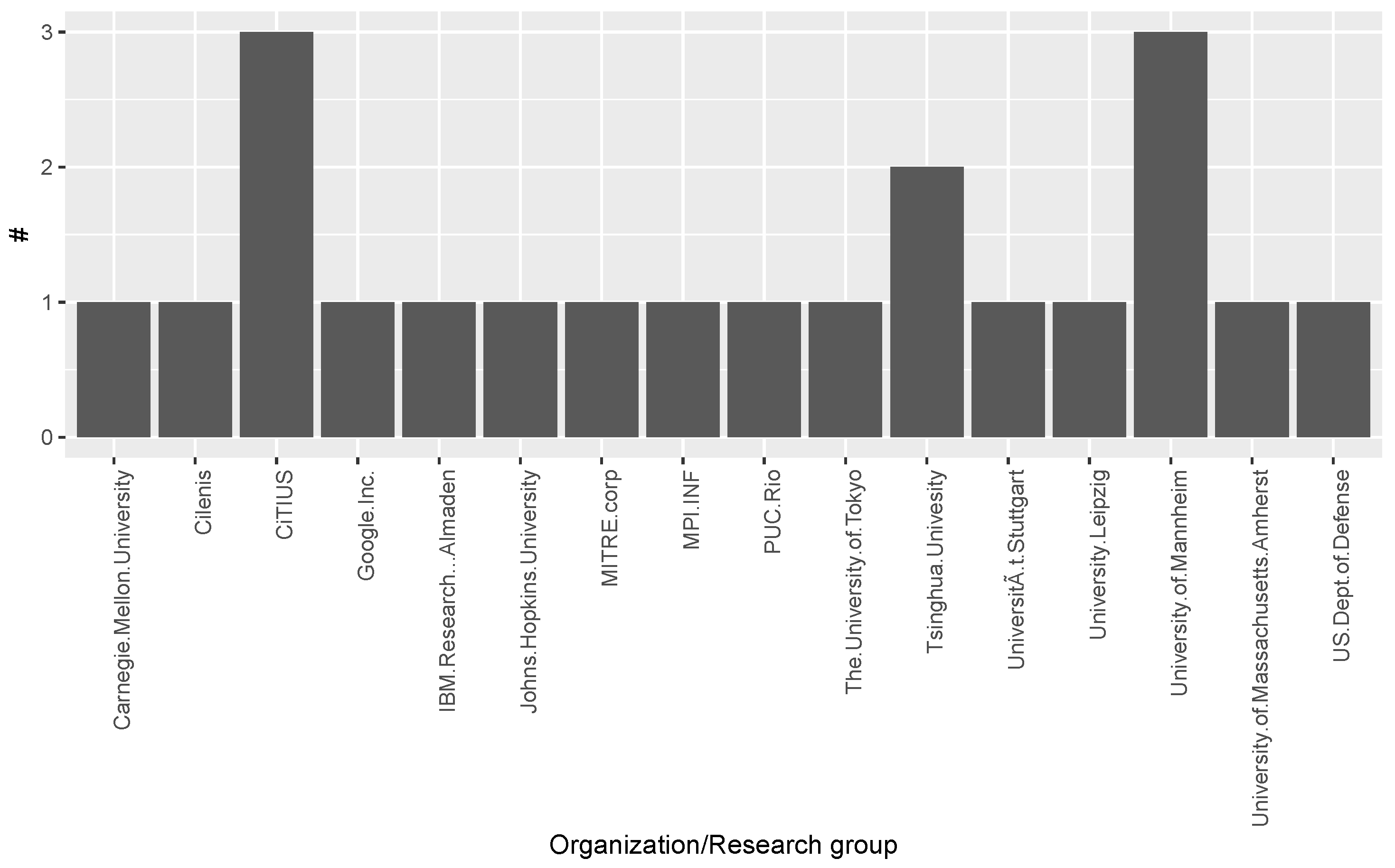
3.1. Answer to RQ1: What Are the Sources of Publications in Multilingual Open IE Area?
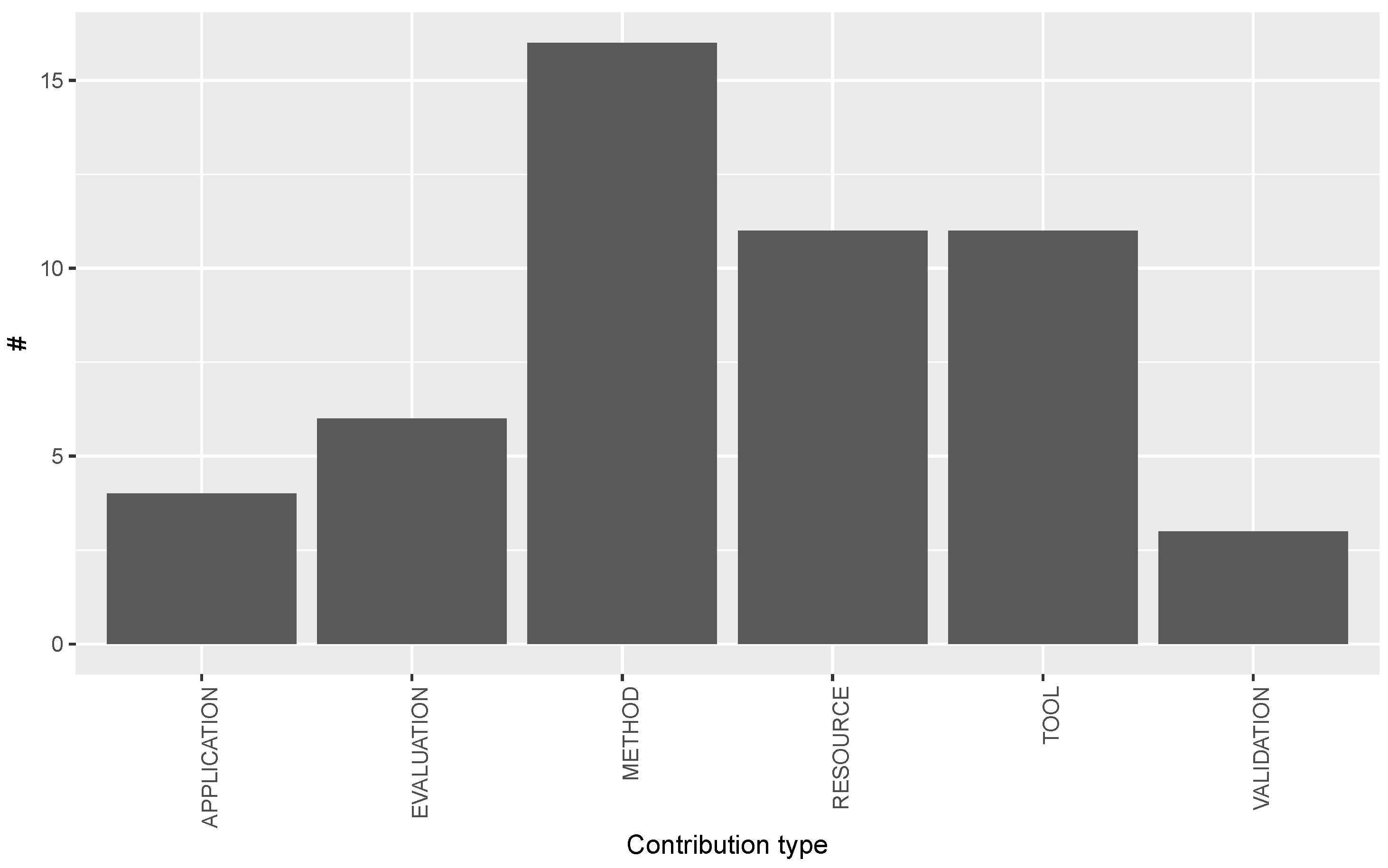
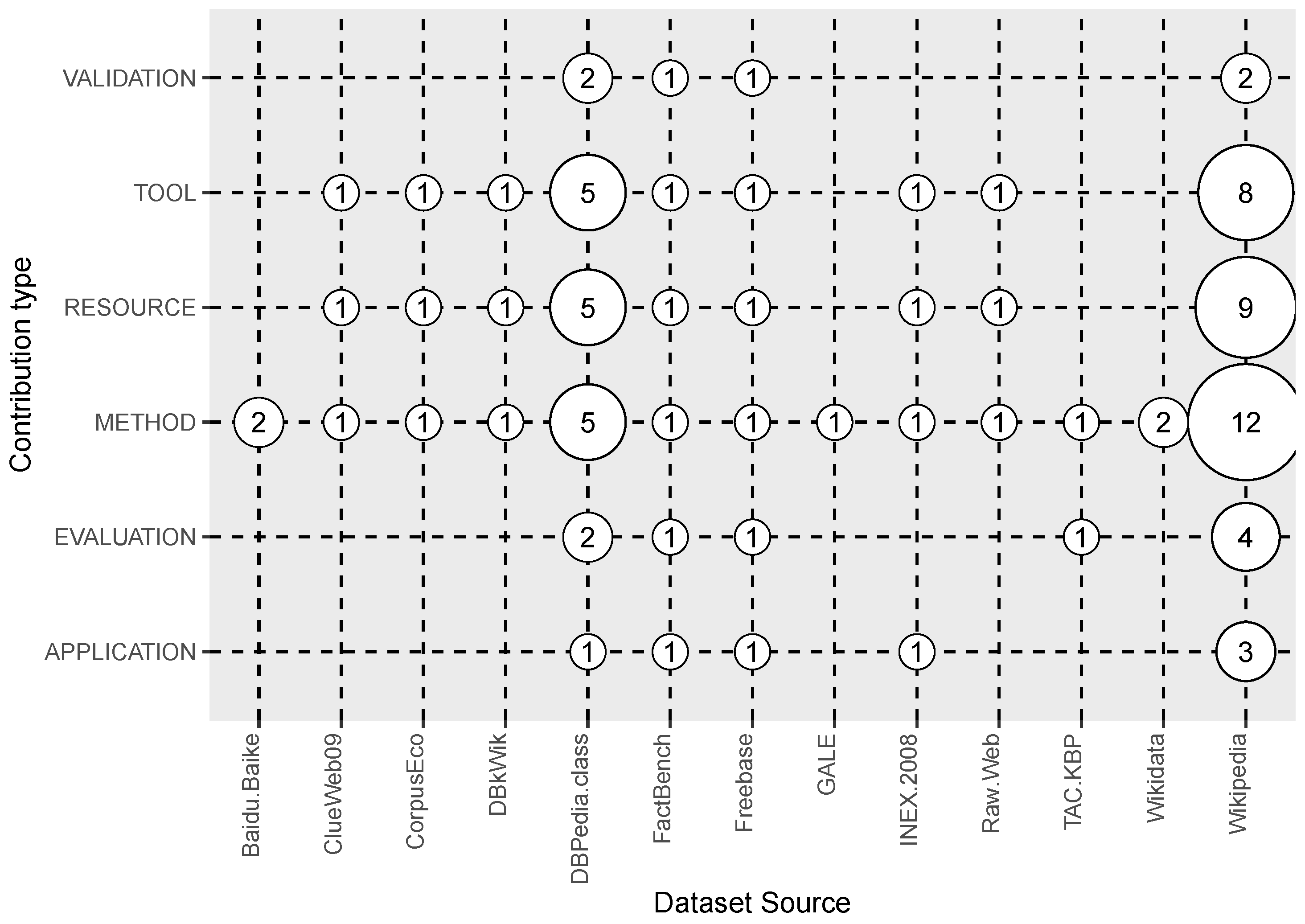
3.2. Answer to RQ2: What Are the Types of Contributions by Multilingual Open IE Studies?
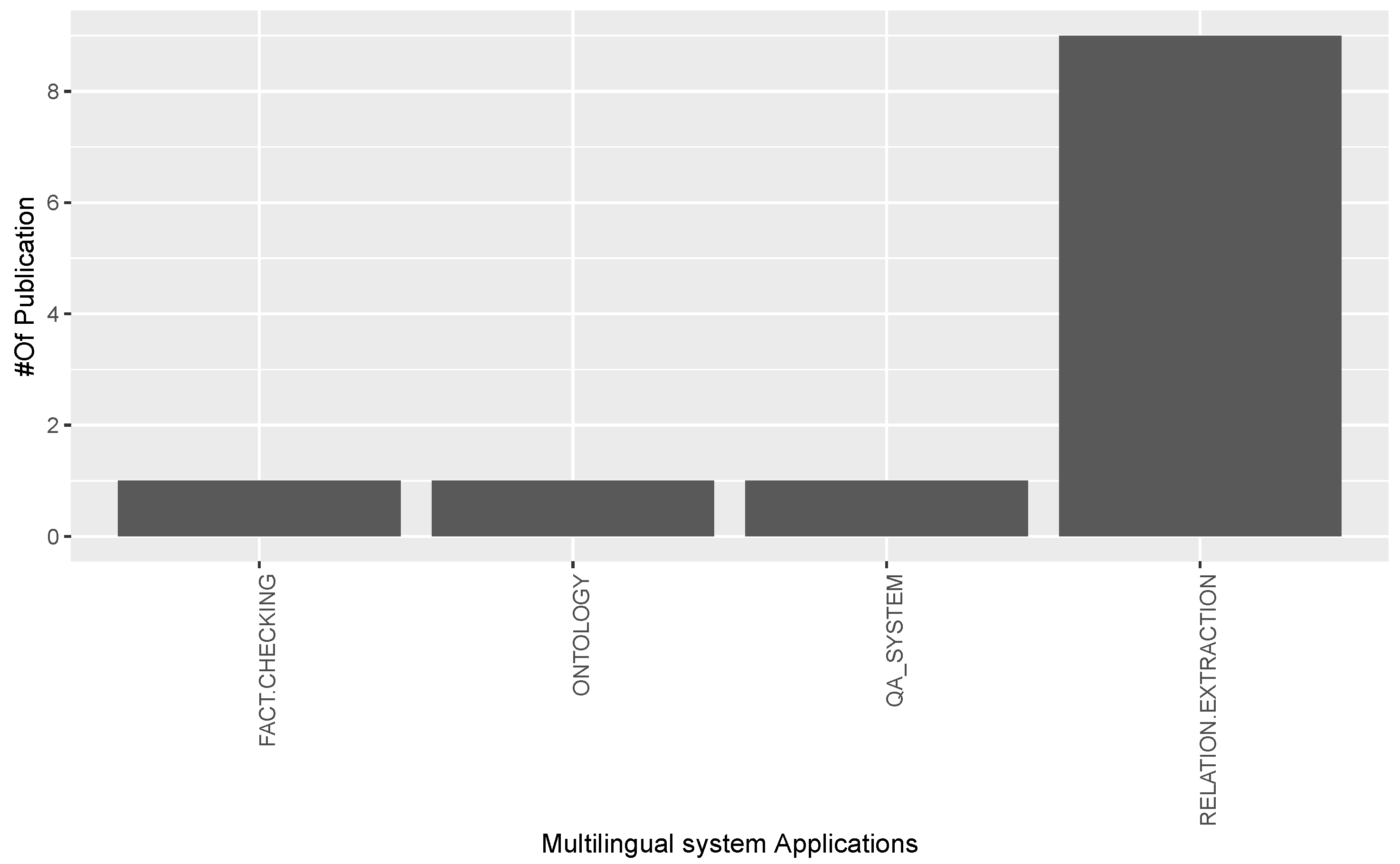
3.3. Answer to RQ3: What Are the Types of Applications Made by Multilingual Open IE Studies?
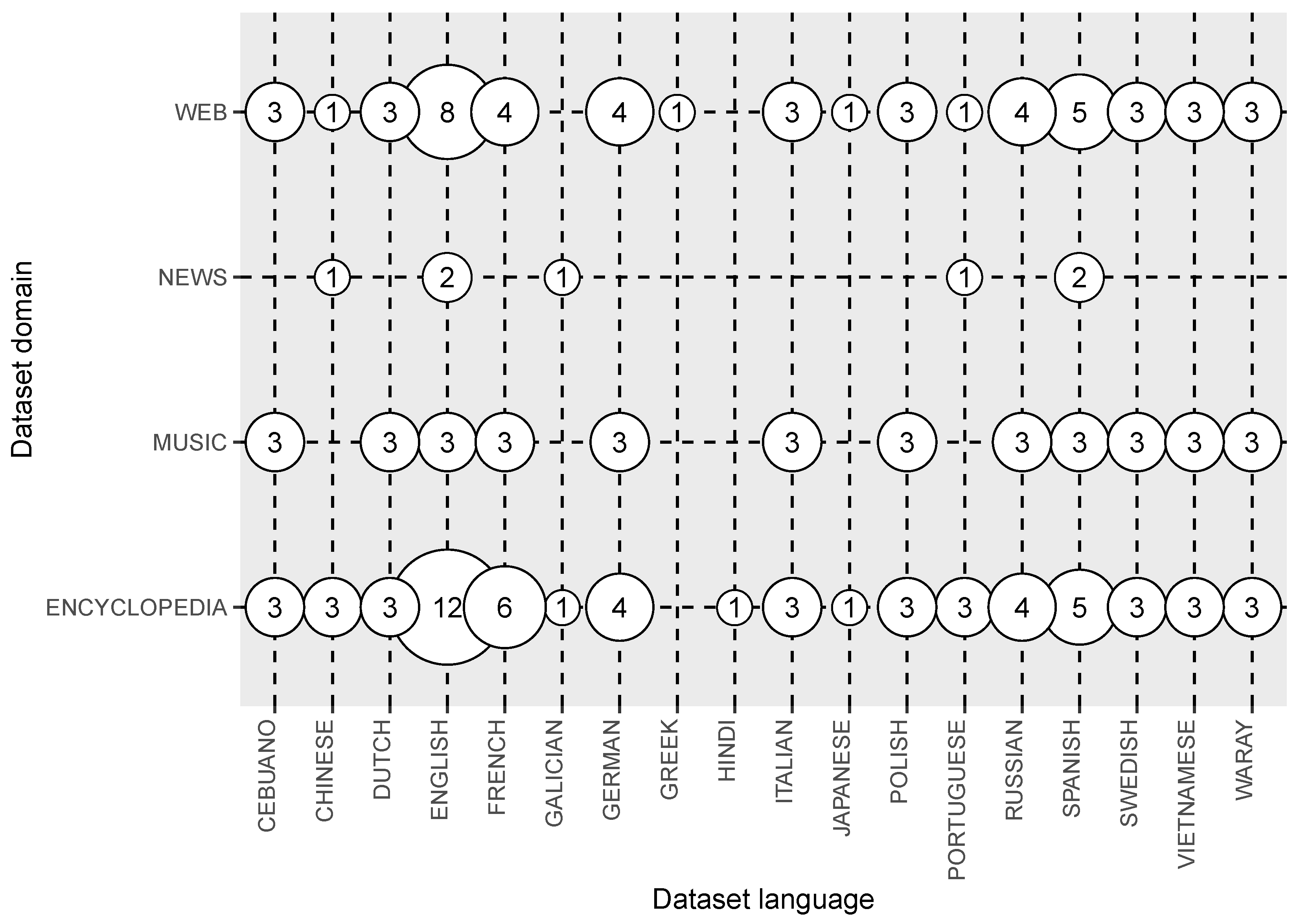
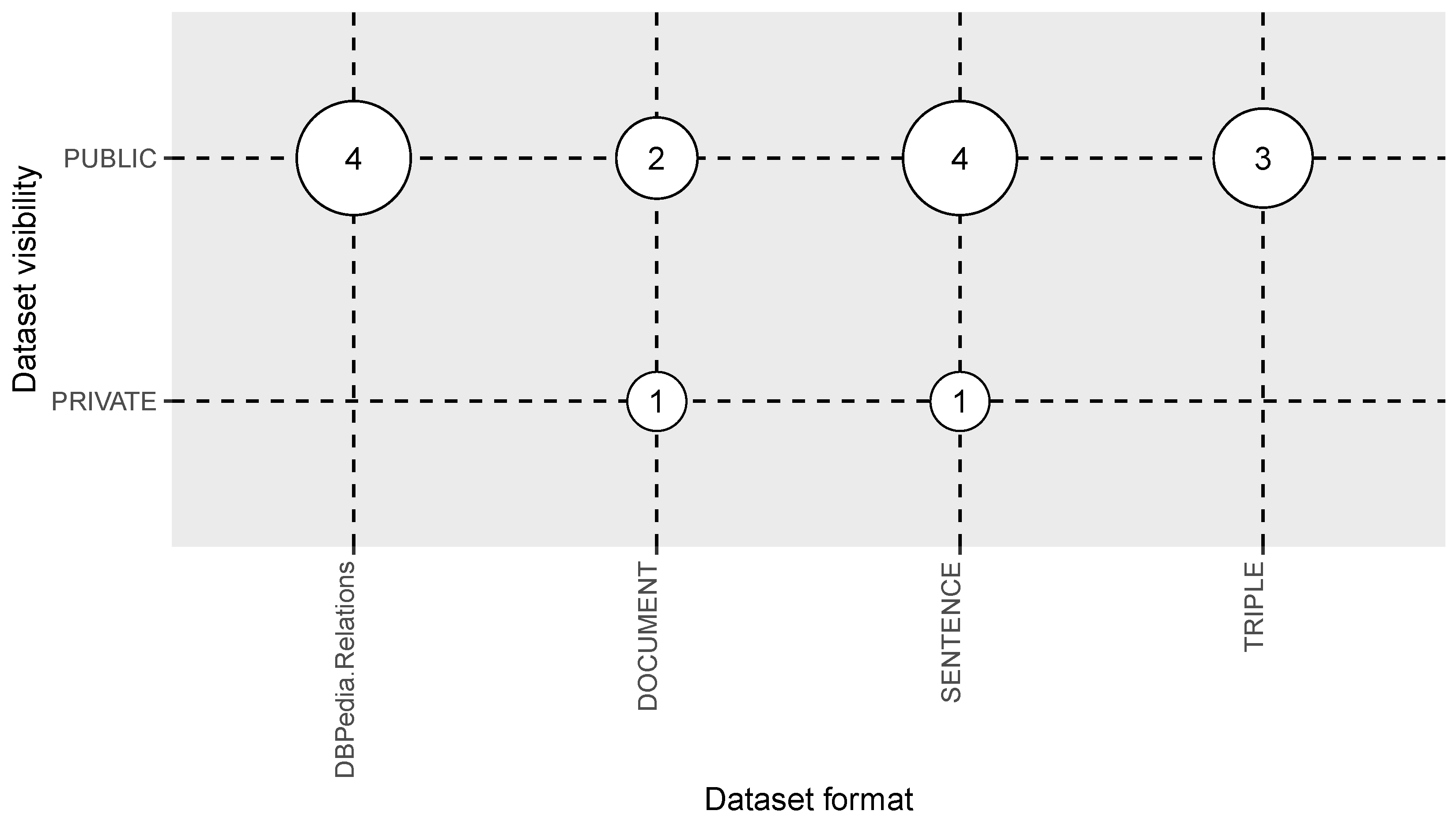
3.4. Answer to RQ4: What Are the Available Multilingual Open IE Datasets?
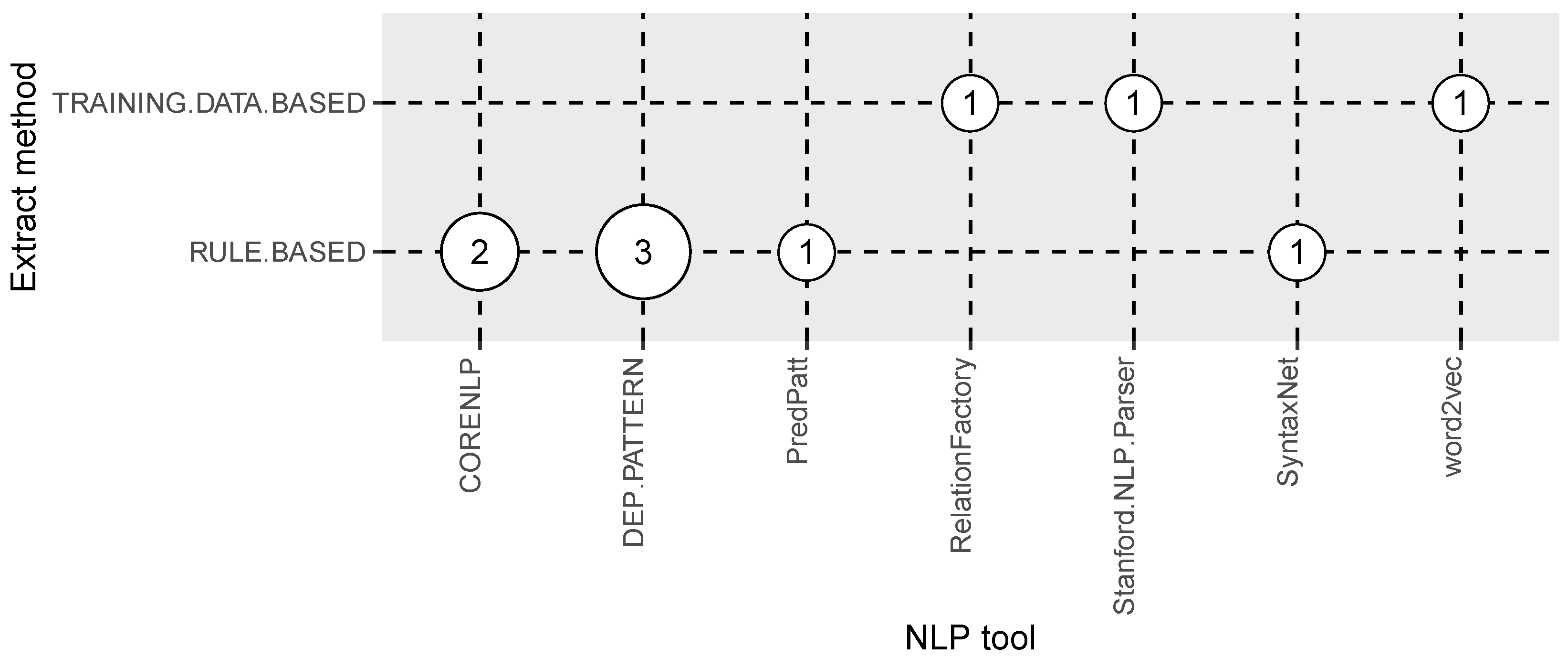
3.5. Answer to RQ5: What Are the Tools Used in Multilingual Open IE Systems?
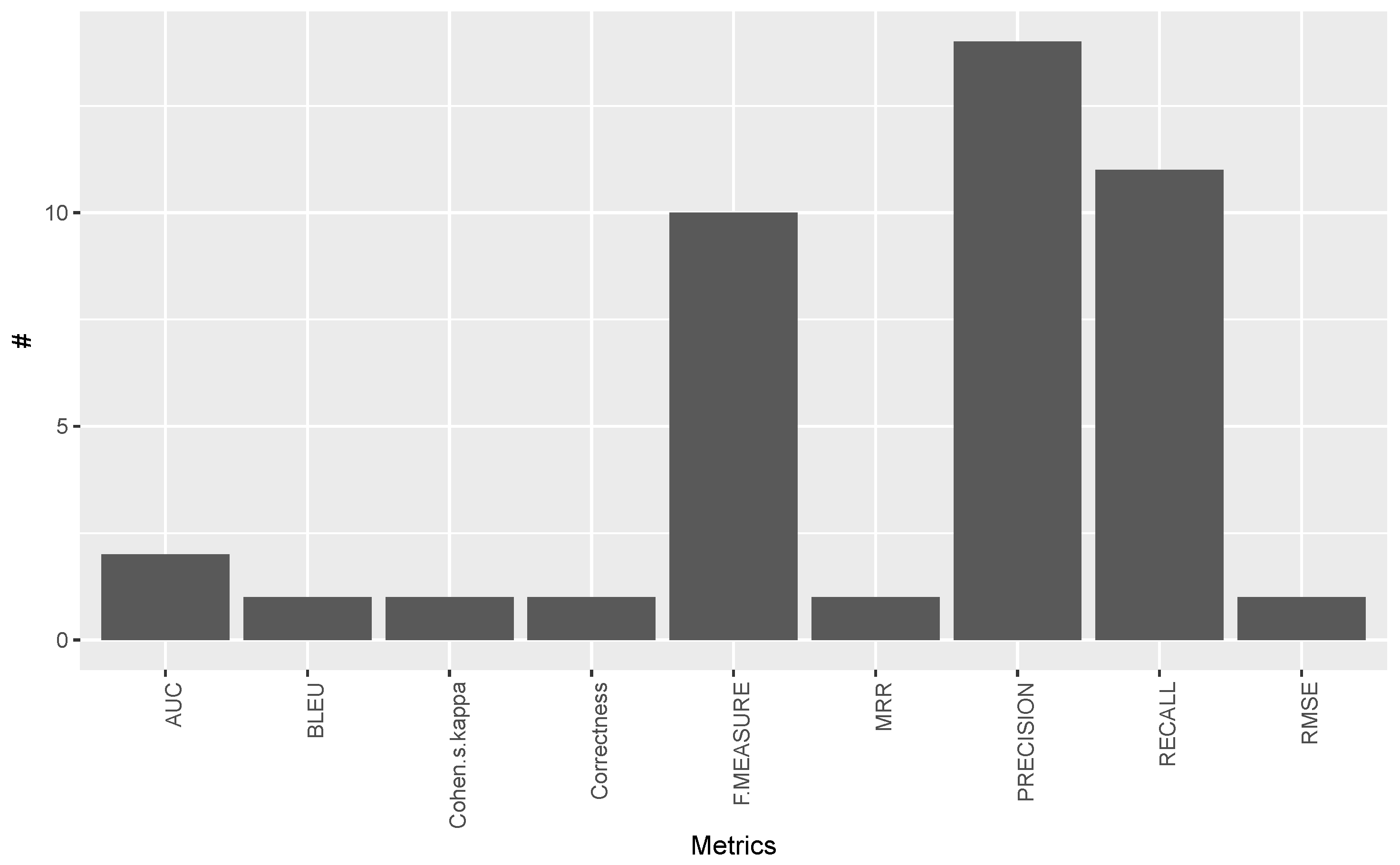
3.6. Answer to RQ6: How Are Multilingual Open IE Systems Evaluated?
4. Some Experiments on Transferable Knowledge in Multilingual Open IE
4.1. Dataset
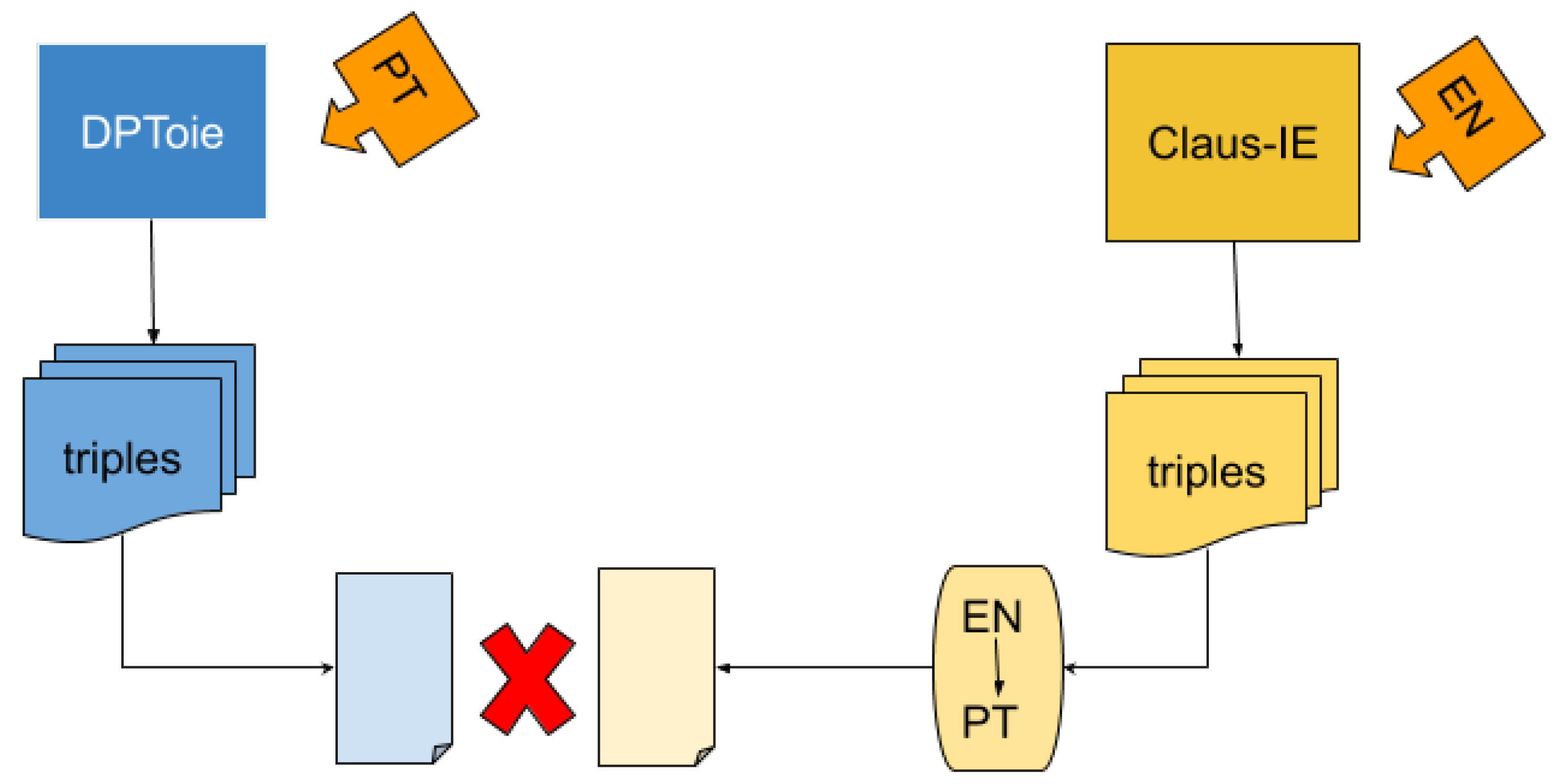
4.2. Experiment: Analyzing Cross-Lingual Extraction Complementarity
which have the pronoun ‘it’ as subject, can be translated to:“It is naturally important that food can also flow freely”,
containing as a main verb ‘é’ (is)—in this context, an impersonal verb—and, thus, does not contain a subject. Naturally, the related extraction from the English (‘it’, ‘is’, ‘important naturally that food can also flow freely’) cannot be properly translated into Portuguese.“É naturalmente importante que os produtos alimentares possam também circular livremente.”
is aligned with“The report proposes twelve representatives for the board of the new Food Authority, two of whom would be representatives of the food industry.”
“O senhor deputado propõe para o Conselho de Administração da Autoridade Alimentar Europeia doze representantes, dois dos quais em representação da indústria alimentar.” (“The deputy proposes for the Administrative Council of the European Food Authority twelve representatives, two of which representing the food industry.”)
the pronoun ‘you’ has been translated into ‘V. Exa.’ (Your Excellency), while, in the Portuguese corpus, the same sentence describes ’o senhor comissário’ (commissioner) as subject of the verb ‘afirmou’ (said), generating the extractions (‘V. Exa.’, ‘afirmou’, …) and (‘o senhor’, ‘afirmou’, …).“Commissioner, you have said on many occasions…”
Claus-IE extracted the triple (‘Mr Whitehead’, ‘has managed’, ‘in a balanced report to combine the many opinions expertly’), while DPToie extracted the triple (‘Phillip Whitehead’, ‘conseguiu’, ‘reunir de forma magistral em um relatório equilibrado as muitas opiniões existentes en o nosso Parlamento’) ((‘Phillip Whitehead’, ‘has managed’, ‘to expertly combine in a balanced report the many opinions which are around in our Parliament’).).“Mr Whitehead has managed, in a balanced report, to expertly combine the many opinions which are around in our Parliament on the establishment of a food authority.”
Similarly, DPToie was able to extract several triples for which Claus-IE made no corresponding extraction. We believe this is evidence for our idea that the difference in linguistic structure in the sentences in different languages may help a multilingual system to extract more valid information from a sentence, since, in each language, it privileges a certain structuring of the information in the sentence.“For example, Article 5 should clearly define the objectives of food legislation and …”
5. Challenges and Opportunities
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OIE | Open Information Extraction |
| IE | Information Extraction |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| POS Tagger | Part-of-Speech Tagger |
| SMS | Systematic Mapping Study |
| MRQ | Main Research Question |
| RQ | Research Question |
| QA | Querying Answering |
| RDF | Resource Definition Framework |
| DP | Dependency Parser |
| SRL | Semantic Role Labeling |
| NER | Named Entity Recognition |
References
- Berners-Lee, T.; Hendler, J.; Lassila, O. The semantic web. Sci. Am. 2001, 284, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizer, C.; Heath, T.; Berners-Lee, T. Linked data: The story so far. In Semantic Services, Interoperability and Web Applications: Emerging Concepts; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 205–227. [Google Scholar]
- Fader, A.; Soderland, S.; Etzioni, O. Identifying relations for open information extraction. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 1535–1545. [Google Scholar]
- Etzioni, O.; Fader, A.; Christensen, J.; Soderland, S.; Mausam, M. Open information extraction: The second generation. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Second International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence; AAAI Press: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 3–10. [Google Scholar]
- Mintz, M.; Bills, S.; Snow, R.; Jurafsky, D. Distant supervision for relation extraction without labeled data. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference of the 47th Annual Meeting of the ACL and the 4th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing of the AFNLP: Volume 2-Volume 2; Association for Computational Linguistics: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 2009; pp. 1003–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Grishman, R. Employing word representations and regularization for domain adaptation of relation extraction. In Proceedings of the 52nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Baltimore, MD, USA, 22–27 June 2014; pp. 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bollacker, K.; Evans, C.; Paritosh, P.; Sturge, T.; Taylor, J. Freebase: A collaboratively created graph database for structuring human knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2008 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–12 June 2008; pp. 1247–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Vrandečić, D.; Krötzsch, M. Wikidata: A Free Collaborative Knowledge Base. Available online: https://ai.google/research/pubs/pub42240.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2019).
- Riedel, S.; Yao, L.; McCallum, A. Modeling relations and their mentions without labeled text. In Joint European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 148–163. [Google Scholar]
- Surdeanu, M.; Tibshirani, J.; Nallapati, R.; Manning, C.D. Multi-instance multi-label learning for relation extraction. In Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning, Jeju Island, Korea, 12–14 July 2012; pp. 455–465. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, S.; Li, H.; Uszkoreit, H.; Xu, F. Large-scale learning of relation-extraction rules with distant supervision from the web. In International Semantic Web Conference; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 263–278. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.V.T.; Moschitti, A. End-to-end relation extraction using distant supervision from external semantic repositories. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Short Papers-Volume 2, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 June 2011; pp. 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Banko, M.; Cafarella, M.J.; Soderland, S.; Broadhead, M.; Etzioni, O. Open Information Extraction from the Web. In Proceedings of the 20th International Joint Conference on Artifical Intelligence (IJCAI’07), Hyderabad, India, 6–12 January 2007; pp. 2670–2676. [Google Scholar]
- Kilgarriff, A.; Grefenstette, G. Web as corpus. In Proceedings of the Corpus Linguistics 2001, Lancaster, UK, 29 March–2 April 2001; pp. 342–344. [Google Scholar]
- Yangarber, R.; Grishman, R.; Tapanainen, P.; Huttunen, S. Automatic acquisition of domain knowledge for information extraction. In Proceedings of the 18th conference on Computational linguistics-Volume 2, Saarbrücken, Germany, 31 July–4 August 2000; pp. 940–946. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, R.J.; Bunescu, R. Mining knowledge from text using information extraction. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2005, 7, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socher, R.; Chen, D.; Manning, C.D.; Ng, A. Reasoning with neural tensor networks for knowledge base completion. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Lake Tahoe, NV, USA, 5–10 December 2013; pp. 926–934. [Google Scholar]
- Plank, B.; Moschitti, A. Embedding semantic similarity in tree kernels for domain adaptation of relation extraction. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Sofia, Bulgaria, 4–9 August 2013; pp. 1498–1507. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Grishman, R. Relation extraction: Perspective from convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Vector Space Modeling for Natural Language Processing, Denver, CO, USA, 5 June 2015; pp. 39–48. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y.; Courville, A.; Vincent, P. Representation learning: A review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 35, 1798–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Bollegala, D.; Matsuo, Y.; Ishizuka, M. Using graph based method to improve bootstrapping relation extraction. In Computational Linguistics and Intelligent Text Processing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; Volume 2, pp. 127–138. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, C.C.; de Lima, V.L.S.; Souza, M. Open information extraction based on lexical semantics. J. Braz. Comput. Soc. 2015, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Weld, D.S. Open Information Extraction Using Wikipedia. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Uppsala, Sweden, 11–16 July 2010; pp. 118–127. [Google Scholar]
- Faruqui, M.; Kumar, S. Multilingual Open Relation Extraction Using Cross-lingual Projection. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberger, R. A survey of methods to ease the development of highly multilingual text mining applications. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2012, 46, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehn, P. Europarl: A parallel corpus for statistical machine translation. In Proceedings of the Tenth Machine Translation Summit, Phuket, Thailand, 12–16 September 2005; pp. 79–86. [Google Scholar]
- Eisele, A.; Chen, Y. MultiUN: A Multilingual Corpus from United Nation Documents; LREC: Stockholm, Sweeden, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberger, R.; Pouliquen, B.; Widiger, A.; Ignat, C.; Erjavec, T.; Tufis, D.; Varga, D. The JRC-Acquis: A Multilingual Aligned Parallel Corpus with 20+ Languages. arXiv 2006, arXiv:cs/0609058. [Google Scholar]
- Déjean, H.; Gaussier, É.; Sadat, F. An approach based on multilingual thesauri and model combination for bilingual lexicon extraction. In Proceedings of the 19th international conference on Computational linguistics-Volume 1, Taipei, Taiwan, 24 August–1 September 2002; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.C.; Luk, J. Automatic generation of English/Chinese thesaurus based on a parallel corpus in laws. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2003, 54, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Weischedel, R.; Nguyen, C. Evaluating a probabilistic model for cross-lingual information retrieval. In Proceedings of the 24th Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–12 September 2001; pp. 105–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrández, S.; Toral, A.; Ferrández, O.; Ferrández, A.; Munoz, R. Applying Wikipedia’s multilingual knowledge to cross–lingual question answering. In International Conference on Application of Natural Language to Information Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 352–363. [Google Scholar]
- Mihalcea, R.; Simard, M. Parallel texts. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2005, 11, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarowsky, D.; Ngai, G.; Wicentowski, R. Inducing multilingual text analysis tools via robust projection across aligned corpora. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Human Language Technology Research, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–21 March 2001; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Bentivogli, L.; Pianta, E. Exploiting parallel texts in the creation of multilingual semantically annotated resources: The MultiSemCor Corpus. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2005, 11, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, R.; Resnik, P.; Weinberg, A.; Cabezas, C.; Kolak, O. Bootstrapping parsers via syntactic projection across parallel texts. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2005, 11, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bel, N.; Koster, C.H.; Villegas, M. Cross-lingual text categorization. In International Conference on Theory and Practice of Digital Libraries; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2003; pp. 126–139. [Google Scholar]
- Bering, C.; Drozdzynski, W.; Erbach, G.; Guasch, C.; Homola, P.; Lehmann, S.; Li, H.; Krieger, H.U.; Piskorski, J.; Schäfer, U.; et al. Corpora and evaluation tools for multilingual named entity grammar development. In Proceedings of the Multilingual Corpora Workshop at Corpus Linguistics, Lancaste, UK, 28–31 May 2003; pp. 42–52. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd-Graber, J.; Blei, D.M. Multilingual topic models for unaligned text. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 18–21 June 2009; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, S.; Mihalcea, R. Cross-lingual semantic relatedness using encyclopedic knowledge. In Proceedings of the 2009 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Singapore, 6–7 August 2009; pp. 1192–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Rfou, R.; Perozzi, B.; Skiena, S. Polyglot: Distributed Word Representations for Multilingual Nlp. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1307.1662. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Neural relation extraction with multi-lingual attention. In Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Verga, P.; Belanger, D.; Strubell, E.; Roth, B.; McCallum, A. Multilingual relation extraction using compositional universal schema. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1511.06396. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Duh, K.; Van Durme, B. Mt/ie: Cross-lingual open information extraction with neural sequence-to-sequence models. In Proceedings of the 15th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Volume 2, Short Papers; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Han, X.; Lin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. Adversarial multi-lingual neural relation extraction. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Computational Linguistics; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2018; pp. 1156–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Gamallo, P.; Garcia, M.; Fernandez-Lanza, S. Dependency-based Open Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the Joint Workshop on Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Learning in NLP; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, E.N.P.; Claro, D.B. Extração de Relações utilizando Features Diferenciadas para Português. Linguamática 2014, 6, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Etzioni, O.; Banko, M.; Soderland, S.; Weld, D.S. Open information extraction from the web. Commun. ACM 2008, 51, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, M.; Bart, R.; Soderland, S.; Etzioni, O. Open Language Learning for Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning, Jeju Island, Korea, 12–14 July 2012; pp. 523–534. [Google Scholar]
- Del Corro, L.; Gemulla, R. ClausIE: Clause-based Open Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the 22Nd International Conference on World Wide Web, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 13–17 May 2013; pp. 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bast, H.; Haussmann, E. Open information extraction via contextual sentence decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Seventh International Conference on Semantic Computing, Irvine, CA, USA, 16–18 September 2013; pp. 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Bast, H.; Haussmann, E. More Informative Open Information Extraction via Simple Inference. In Proceedings of the 36th European Conference on IR Research on Advances in Information Retrieval—Volume 8416; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashteovski, K.; Gemulla, R.; Del Corro, L. MinIE: Minimizing Facts in Open Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 2630–2640. [Google Scholar]
- Gamallo, P.; Garcia, M. Multilingual Open Information Extraction. In Progress in Artificial Intelligence: 17th Portuguese Conference on Artificial Intelligence, EPIA 2015, Coimbra, Portugal, 8–11 September 2015; Pereira, F., Machado, P., Costa, E., Cardoso, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xavier, C.C.; de Lima, V.L.S.; Souza, M. Open Information Extraction based on lexical-syntactic patterns. In Proceedings of the 2013 Brazilian Conference on Intelligent Systems (BRACIS), Fortaleza, Brazil, 19–24 October 2013; pp. 189–194. [Google Scholar]
- Sena, C.F.L.; Glauber, R.; Claro, D.B. Inference Approach to Enhance a Portuguese Open Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems—Volume 1: ICEIS; INSTICC, ScitePress: Porto, Portugal, 2017; pp. 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, C.F.L.; Claro, D.B. InferPortOIE: A Portuguese Open Information Extraction system with inferences. Nat. Lang. Eng. 2019, 25, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.S.; Glauber, R.; Claro, D.B. DependentIE: An Open Information Extraction system on Portuguese by a Dependence Analysis. In Proceedings of the Encontro Nacional de Inteligência Artificial e Computacional, Uberlândia, Brasil, 2–5 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- de Oliveira, L.S.; Claro, D.B. DptOIE: A Portuguese Open Information Extraction system based on Dependency Analysis. Comput. Speech Lang. 2019. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Lee, L.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Liao, B.S.; Liu, M.J.; Chen, H.H.; Etzioni, O.; Fader, A. Chinese open relation extraction for knowledge acquisition. In Proceedings of the 14th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Gothenburg, Sweden, 26–30 April 2014; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, L.; Zhang, Y. ZORE: A Syntax-based System for Chinese Open Relation Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP); Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2014; pp. 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Gan, L.; Deng, L.; Wang, J.; Yan, Z. Dependency parsing based Chinese open relation extraction. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Computer Science and Network Technology (ICCSNT), Harbin, China, 19–20 December 2015; Volume 1, pp. 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, G.; Tian, F.; Nan, Y.; Ma, J. GCORE: A Gravitation-Based Approach for Chinese Open Relation. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Science and Mechanical Automation (CSMA), Hangzhou, China, 23–25 October 2015; pp. 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, B. The CRFs-Based Chinese Open Entity Relation Extraction. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Second International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC), Shenzhen, China, 26–29 June 2017; pp. 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassa, A.; Kroll, M.; Kern, R. GerIE-An Open Information Extraction System for the German Language. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 2018, 24, 2–24. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, D.; Vo, D.T.; Nguyen, U.T. Vietnamese Open Information Extraction. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Symposium on Information and Communication Technology, Singapore, 15–18 May 2017; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, K.; Feldt, R.; Mujtaba, S.; Mattsson, M. Systematic Mapping Studies in Software Engineering. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering; BCS Learning & Development Ltd.: Swindon, UK, 2008; pp. 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Petersen, K.; Vakkalanka, S.; Kuzniarz, L. Guidelines for conducting systematic mapping studies in software engineering: An update. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2015, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glauber, R.; Claro, D.B. A Systematic Mapping Study on Open Information Extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, E.M.; Friedman, B. Data Statements for Natural Language Processing: Toward Mitigating System Bias and Enabling Better Science. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2018, 6, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.; Gamallo, P. Entity-centric coreference resolution of person entities for open information extraction. Proces. Leng. Nat. 2014, 53, 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, T.; Schwabe, D. Building Distant Supervised Relation Extractors. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Semantic Computing, Newport Beach, CA, USA, 16–18 June 2014; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Akbik, A.; Danilevsky, M.; Kbrom, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, H. Multilingual information extraction with PolyglotIE. In Proceedings of the COLING 2016, the 26th International Conference on Computational Linguistics: System Demonstrations, Osaka, Japan, 11–16 December 2016; pp. 268–272. [Google Scholar]
- Duc, N.T.; Bollegala, D.; Ishizuka, M. Cross-language latent relational search between japanese and english languages using a web corpus. ACM Trans. Asian Lang. Inf. Process. 2012, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vulić, I.; Moens, M.F. Monolingual and cross-lingual information retrieval models based on (bilingual) word embeddings. In Proceedings of the 38th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Santiago, Chile, 9–13 August 2015; pp. 363–372. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyay, S.; Faruqui, M.; Dyer, C.; Roth, D. Cross-lingual models of word embeddings: An empirical comparison. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1604.00425. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Guo, Y. Distributed word representation learning for cross-lingual dependency parsing. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning, Baltimore, MD, USA, 26–27 June 2014; pp. 119–129. [Google Scholar]
- Täckström, O.; McDonald, R.; Uszkoreit, J. Cross-lingual word clusters for direct transfer of linguistic structure. In Proceedings of the 2012 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Montreal, QC, Canada, 3–8 June 2012; pp. 477–487. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Salakhutdinov, R.; Cohen, W. Multi-Task Cross-Lingual Sequence Tagging from Scratch. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.06270. [Google Scholar]
- de Abreu, S.C.; Vieira, R. Relp: Portuguese open relation extraction. KO KNOWLEDGE ORGANIZATION 2017, 44, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falke, T.; Stanovsky, G.; Gurevych, I.; Dagan, I. Porting an open information extraction system from english to german. In Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Austin, TX, USA, 1–4 November 2016; pp. 892–898. [Google Scholar]


| Sentence | Uninformative Extraction |
|---|---|
| “After the defense of Bahia rebound, Maurinho kicked and scored.” | (defense of Bahia, rebound, Maurinho) |
| “The star symbol of (PT) will frame the scenario of the candidate’s programs Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva.” | (PT, will frame, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva) |
| Data Item | Value | RQ |
|---|---|---|
| General study ID | Integer | |
| Article Title | Title of the Article | |
| Author list | List of the Author’s name | |
| Year of publication | Calendar year | RQ1 |
| Research center | Author’s affiliation | RQ1 |
| Country | Country of the Research Centre or Organization | RQ1 |
| Affiliation | Affiliation of the authors | RQ1 |
| Publication | Source of publication: conference or journal | RQ1 |
| Dataset visibility | Public or Private | RQ4 |
| Dataset language | English, Chinese, Portuguese... | RQ4 |
| Dataset source | Corpus name employed to create the dataset | RQ5 |
| Dataset format | Sentence, document, triple, ... | RQ4 |
| Dataset domain | Domain of the Corpus | RQ4 |
| Evaluation | Evaluation measures used in the study | RQ6 |
| Contribution type | Tool, Resource, Method, Application, Validation or Evaluation | RQ2 |
| NLP task | NLP tasks employed in the study | RQ5 |
| NLP tool | NLP tools employed in the study | RQ5 |
| Other tool | Other tools employed in the study | RQ5 |
| Extract method | Training data or handcrafted rules based | RQ5 |
| Application | Construction of ontology, text summarization... | RQ3 |
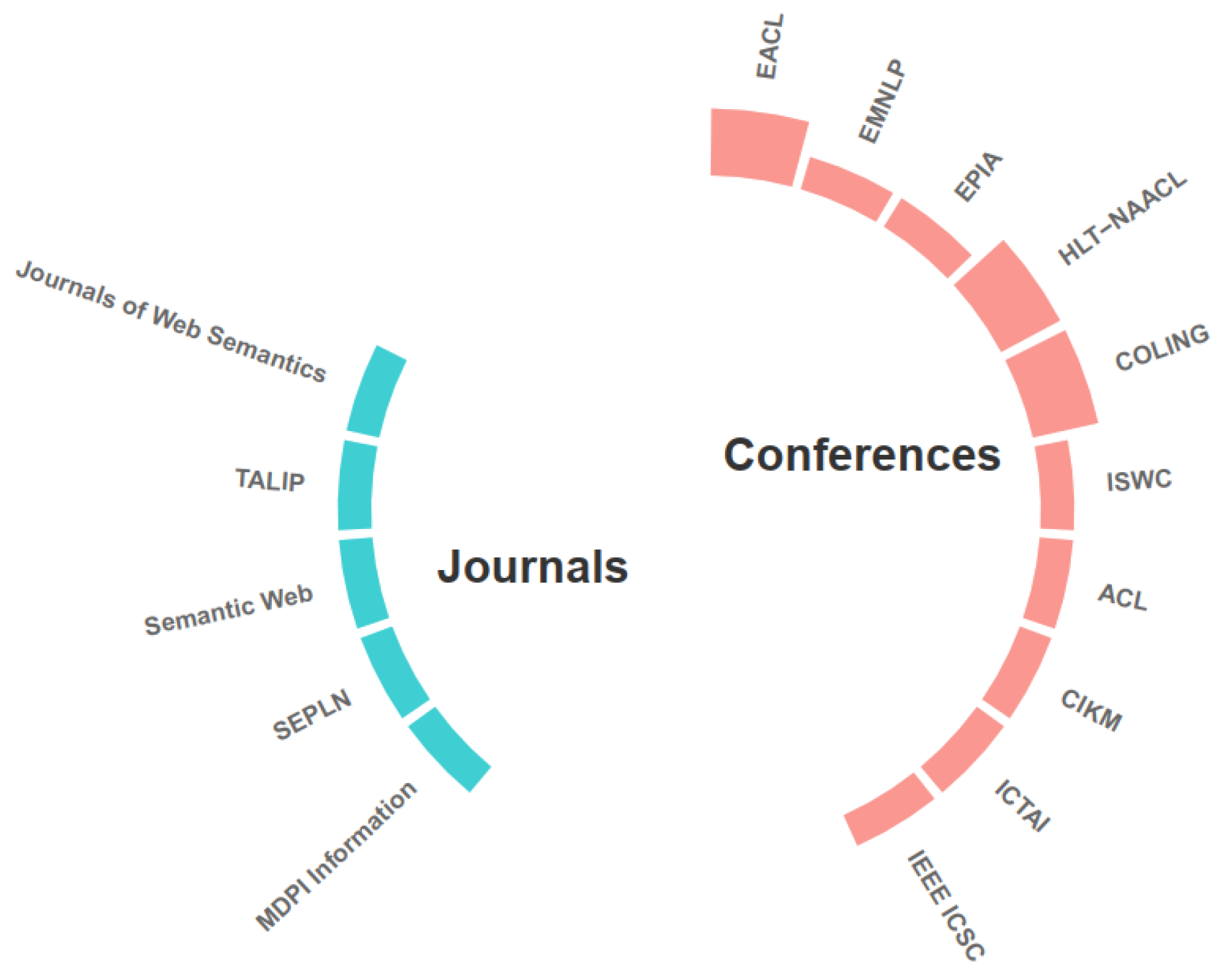
| Acronym | Conference and Journal Names |
|---|---|
| EACL | European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics |
| EMNLP | Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing |
| EPIA | Portuguese Conference on Artificial Intelligence |
| HLT-NAACL | Human Language Technology Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics |
| COLING | International Conference on Computational Linguistics |
| ISWC | International Semantic Web Conference |
| ACL | Association for Computational Linguistics |
| CIKM | Conference on Information and Knowledge Management |
| ICTAI | International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence |
| IEEE ICSC | IEEE International Conference on Semantic Computing |
| TALIP | ACM Transactions on Asian Language Information Processing |
| SEPLN | Spanish Society for Natural Language Processing |
| MDPI Information | Information Journal |
| Semantic Web | The Semantic Web Journal |
| − | Journal of Web Semantics |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Claro, D.B.; Souza, M.; Castellã Xavier, C.; Oliveira, L. Multilingual Open Information Extraction: Challenges and Opportunities. Information 2019, 10, 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10070228
Claro DB, Souza M, Castellã Xavier C, Oliveira L. Multilingual Open Information Extraction: Challenges and Opportunities. Information. 2019; 10(7):228. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10070228
Chicago/Turabian StyleClaro, Daniela Barreiro, Marlo Souza, Clarissa Castellã Xavier, and Leandro Oliveira. 2019. "Multilingual Open Information Extraction: Challenges and Opportunities" Information 10, no. 7: 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10070228
APA StyleClaro, D. B., Souza, M., Castellã Xavier, C., & Oliveira, L. (2019). Multilingual Open Information Extraction: Challenges and Opportunities. Information, 10(7), 228. https://doi.org/10.3390/info10070228





