Measurement of Poly(ADP-ribose) Level with Enhanced Slot Blot Assay with Crosslinking
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
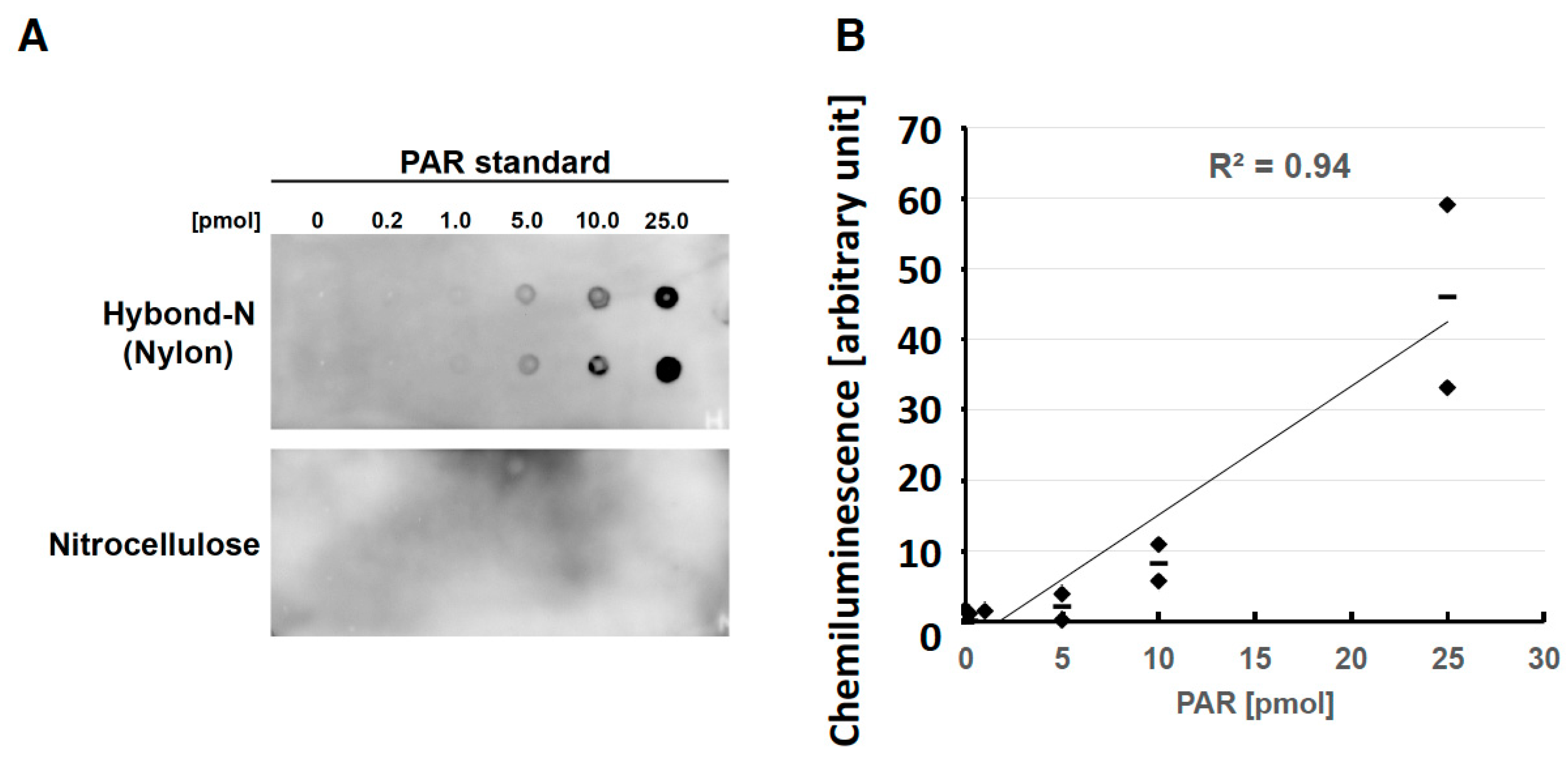
2.1. Optimization of Slot Blot Assay of PAR Using Crosslinking
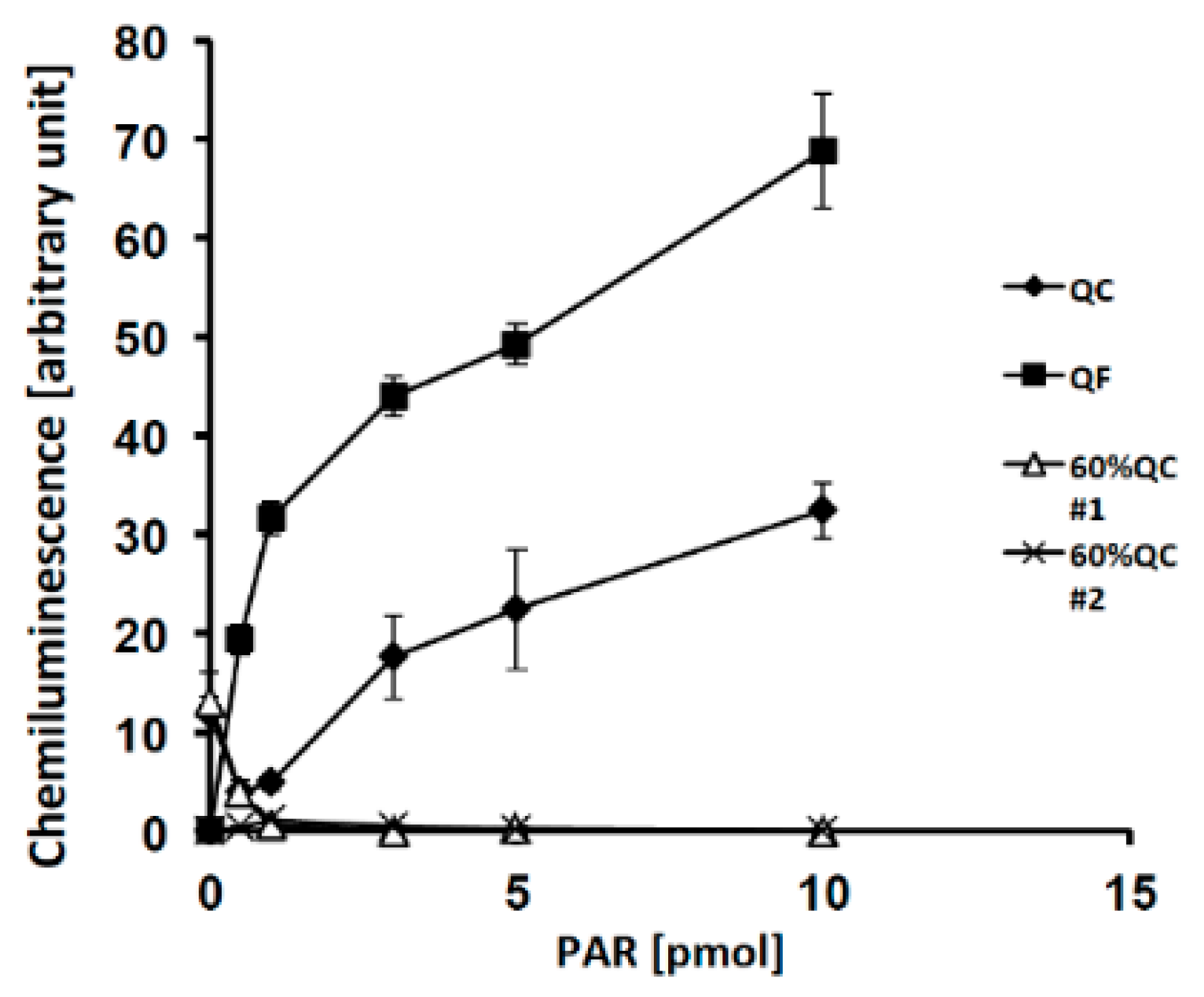
2.2. Effects of PAR Length on Detection with Slot Blot Assay of PAR
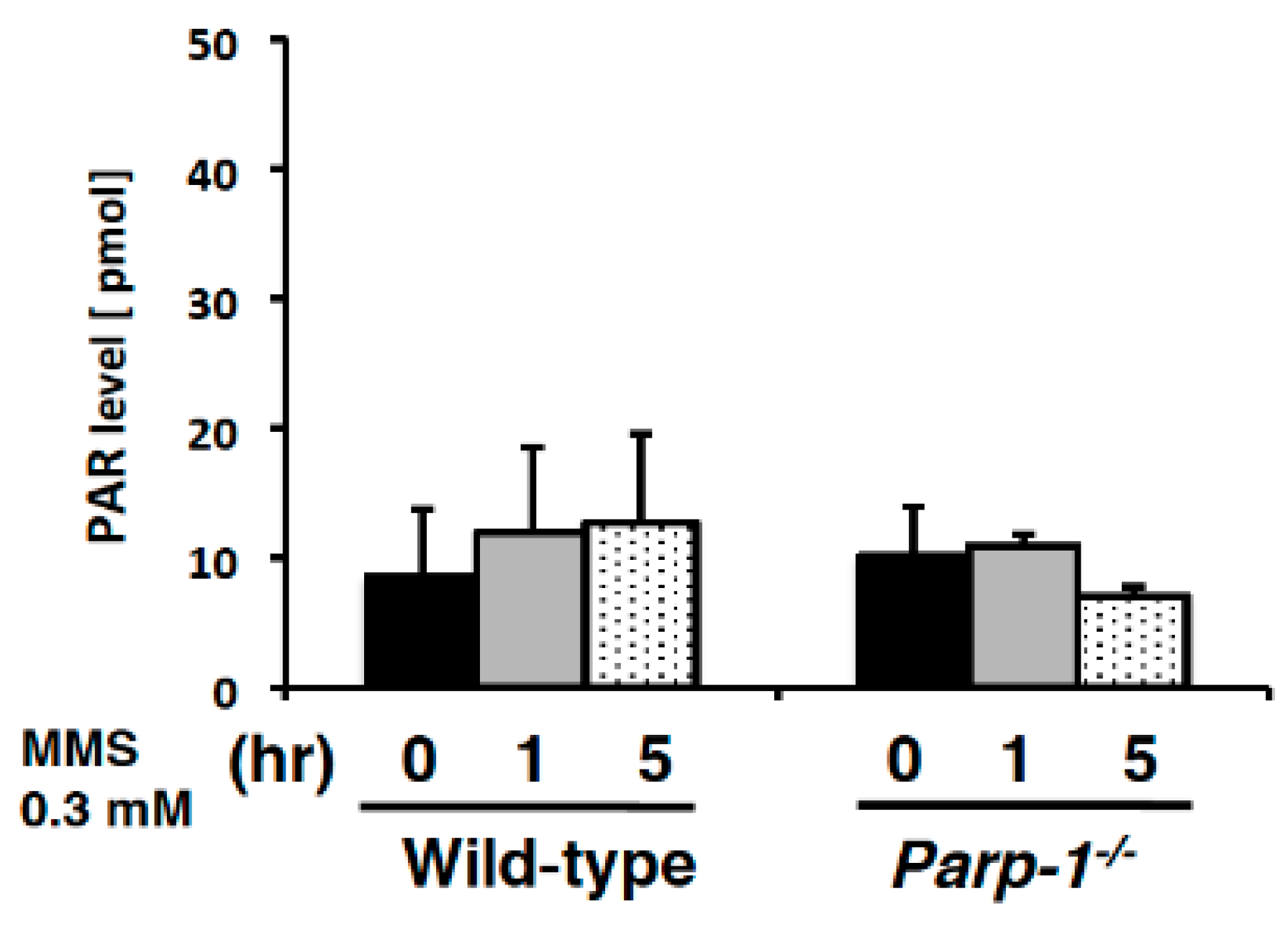
2.3. Detection of PAR Level Changes with Slot Blot Assay in Cultured Cells
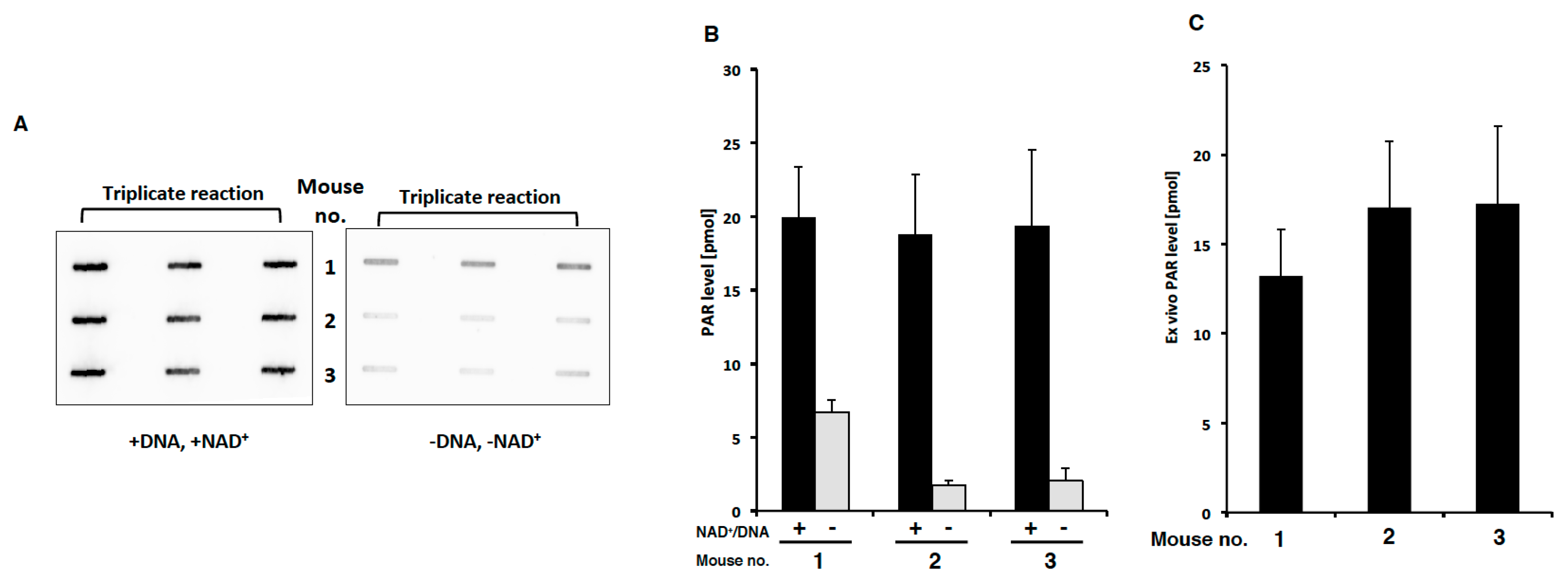
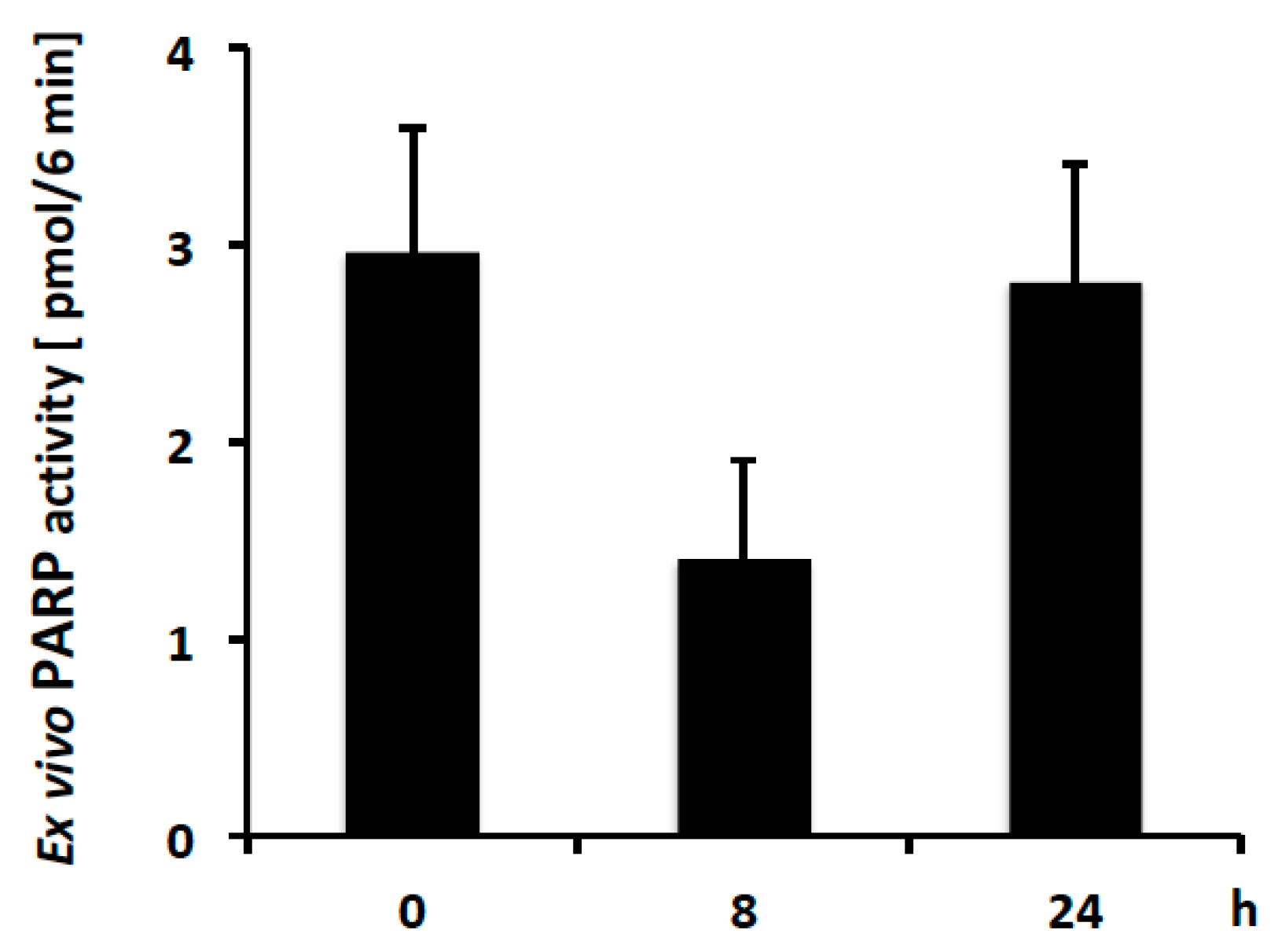
2.4. PAR Levels in Mouse PBMCs Detected with Ex Vivo PARP Assay
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of PAR Using Recombinant PARP-1
4.2. Slot Bot Assay of PAR
4.3. Ex Vivo Assay of PARP Activity
4.4. Extraction of PBMC from Mice
4.5. UV Crosslinking
4.6. Chemical Crosslinking
4.7. Culture of Mouse Wild-Type ES Cells
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schreiber, V.; Dantzer, F.; Ame, J.C.; de Murcia, G. Poly(adp-ribose): Novel functions for an old molecule. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y.; Kawaminami, Y.; Miwa, M.; Matsushima, T.; Sugimura, T. Naturally-occurring antibodies to poly(adp-ribose) in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nature 1977, 265, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y.; Sugimura, T. Comparative studies on antibodies to poly(adp-ribose) in rabbits and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Immunology 1981, 43, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanai, Y. Overview on poly(adp-ribose) immuno-biomedicine and future prospects. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2016, 92, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamitsu, H.; Hoshino, H.; Okada, H.; Miwa, M.; Momoi, H.; Sugimura, T. Monoclonal antibodies to poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) recognize different structures. Biochemistry 1984, 23, 3771–3777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, E.R.; Middleton, M.R.; Jones, C.; Olsen, A.; Hickson, I.; McHugh, P.; Margison, G.P.; McGown, G.; Thorncroft, M.; Watson, A.J.; et al. Temozolomide pharmacodynamics in patients with metastatic melanoma: Dna damage and activity of repair enzymes o6-alkylguanine alkyltransferase and poly(adp-ribose) polymerase-1. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3402–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, N.J. Parp inhibitors for cancer therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2005, 7, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisay, M.; Edessa, D. Parp inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for various cancers: Focus on niraparib and its first global approval for maintenance therapy of gynecologic cancers. Gynecol. Oncol. Res. Pract. 2017, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, H.E.; Schultz, N.; Thomas, H.D.; Parker, K.M.; Flower, D.; Lopez, E.; Kyle, S.; Meuth, M.; Curtin, N.J.; Helleday, T. Specific killing of brca2-deficient tumours with inhibitors of poly(adp-ribose) polymerase. Nature 2005, 434, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, H.; McCabe, N.; Lord, C.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Johnson, D.A.; Richardson, T.B.; Santarosa, M.; Dillon, K.J.; Hickson, I.; Knights, C.; et al. Targeting the DNA repair defect in brca mutant cells as a therapeutic strategy. Nature 2005, 434, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, N.; Turner, N.C.; Lord, C.J.; Kluzek, K.; Bialkowska, A.; Swift, S.; Giavara, S.; O’Connor, M.J.; Tutt, A.N.; Zdzienicka, M.Z.; et al. Deficiency in the repair of DNA damage by homologous recombination and sensitivity to poly(adp-ribose) polymerase inhibition. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8109–8115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ding, Q.; Fujimori, H.; Motegi, A.; Miki, Y.; Masutani, M. Loss of ctip disturbs homologous recombination repair and sensitizes breast cancer cells to parp inhibitors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7701–7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N.D.C. Available online: http://dctd.Cancer.Gov/researchresources/biomarkers/polyadenosylribose.htm (accessed on 20 June 2018).
- Kalachikov, S.M.; Adarichev, B.A.; Dymshits, G.M. Immobilization of DNA on microporous membranes using uv-irradiation. Bioorg. Khim. 1992, 18, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shimokawa, T.; Ogino, H.; Maeda, D.; Nakagama, H.; Sugimura, T.; Masutani, M. Poly(adp-ribose) preparation using anion-exchange column chromatography. Org. Chem. Insights 2009, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Shirai, H.; Poetsch, A.R.; Gunji, A.; Maeda, D.; Fujimori, H.; Fujihara, H.; Yoshida, T.; Ogino, H.; Masutani, M. Parg dysfunction enhances DNA double strand break formation in s-phase after alkylation DNA damage and augments different cell death pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, M.; Saikawa, N.; Yamaizumi, Z.; Nishimura, S.; Sugimura, T. Structure of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose): Identification of 2′-[1″-ribosyl-2″-(or 3″-)(1‴-ribosyl)]adenosine-5′,5″,5‴-tris(phosphate) as a branch linkage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veskimae, K.; Staff, S.; Gronholm, A.; Pesu, M.; Laaksonen, M.; Nykter, M.; Isola, J.; Maenpaa, J. Assessment of parp protein expression in epithelial ovarian cancer by elisa pharmacodynamic assay and immunohistochemistry. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 11991–11999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ida, C.; Yamashita, S.; Tsukada, M.; Sato, T.; Eguchi, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ogata, S.; Fujii, T.; Nishi, Y.; Ikegami, S.; et al. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay-based system for determining the physiological level of poly(adp-ribose) in cultured cells. Anal. Biochem. 2016, 494, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, R.; Pluim, D.; van Triest, B.; van den Heuvel, M.; Peulen, H.; van Berlo, D.; George, J.; Verheij, M.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Vens, C. Improved pharmacodynamic (pd) assessment of low dose parp inhibitor pd activity for radiotherapy and chemotherapy combination trials. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 126, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, J.; Huang, S.Y.; Das, B.B.; Renaud, A.; Zhang, Y.; Doroshow, J.H.; Ji, J.; Takeda, S.; Pommier, Y. Trapping of parp1 and parp2 by clinical parp inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5588–5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affar, E.B.; Duriez, P.J.; Shah, R.G.; Sallmann, F.R.; Bourassa, S.; Kupper, J.H.; Burkle, A.; Poirier, G.G. Immunodot blot method for the detection of poly(adp-ribose) synthesized in vitro and in vivo. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 259, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiffer, R.; Brabeck, C.; Burkle, A. Quantitative nonisotopic immuno-dot-blot method for the assessment of cellular poly(adp-ribosyl) ation capacity. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 275, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneke, S.; Scherr, A.L.; Ponath, V.; Popp, O.; Burkle, A. Enzyme characteristics of recombinant poly(adp-ribose) polymerases-1 of rat and human origin mirror the correlation between cellular poly(adp-ribosyl) ation capacity and species-specific life span. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2010, 131, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubel, T.; Martello, R.; Burkle, A.; Mangerich, A. Quantitation of poly(adp-ribose) by isotope dilution mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1608, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burinaru, T.A.; Avram, M.; Avram, A.; Marculescu, C.; Tincu, B.; Tucureanu, V.; Matei, A.; Militaru, M. Detection of circulating tumor cells using microfluidics. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 107–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okajima, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Fujimori, H.; Wang, J.; Harada, H.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Masutani, M. Rapid degradation of poly(adp-ribose) after injection into the mouse bloodstream. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senra, J.M.; Telfer, B.A.; Cherry, K.E.; McCrudden, C.M.; Hirst, D.G.; O’Connor, M.J.; Wedge, S.R.; Stratford, I.J. Inhibition of parp-1 by olaparib (azd2281) increases the radiosensitivity of a lung tumor xenograft. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, H.; Ogino, H.; Maeda, D.; Shirai, H.; Nozaki, T.; Kamada, N.; Jishage, K.; Tanuma, S.; Takato, T.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Poly(Adp-ribose) Glycohydrolase Deficiency Sensitizes mouse ES Cells to DNA Damaging Agents. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozaki, T.; Masutani, M.; Watanabe, M.; Ochiya, T.; Hasegawa, F.; Nakagama, H.; Suzuki, H.; Sugimura, T. Syncytiotrophoblastic giant cells in teratocarcinoma-like tumors derived from parp-disrupted mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 13345–13350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kudo, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Onodera, T.; Hashimoto, J.; Nozaki, T.; Tamura, K.; Watanabe, M.; Masutani, M. Measurement of Poly(ADP-ribose) Level with Enhanced Slot Blot Assay with Crosslinking. Challenges 2018, 9, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe9020027
Kudo Y, Sasaki Y, Onodera T, Hashimoto J, Nozaki T, Tamura K, Watanabe M, Masutani M. Measurement of Poly(ADP-ribose) Level with Enhanced Slot Blot Assay with Crosslinking. Challenges. 2018; 9(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe9020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleKudo, Yuko, Yuka Sasaki, Takae Onodera, Jun Hashimoto, Tadashige Nozaki, Kenji Tamura, Masatoshi Watanabe, and Mitsuko Masutani. 2018. "Measurement of Poly(ADP-ribose) Level with Enhanced Slot Blot Assay with Crosslinking" Challenges 9, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe9020027
APA StyleKudo, Y., Sasaki, Y., Onodera, T., Hashimoto, J., Nozaki, T., Tamura, K., Watanabe, M., & Masutani, M. (2018). Measurement of Poly(ADP-ribose) Level with Enhanced Slot Blot Assay with Crosslinking. Challenges, 9(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/challe9020027





