Vulnerability Analysis of the Riumar Dune Field in El Garxal Coastal Wetland (Ebro Delta, Spain)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Set
2.3. Definition of Variables
2.3.1. Marine Influence (MI)
2.3.2. Human Pressure (HP)
2.3.3. Characteristics of the Vegetation Cover (VC)
2.3.4. Geomorphology of the Dune System (GD)
2.3.5. Geomorphology of the Beach (GB)
2.3.6. Aeolian Influence (AI)
| Variables | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | Source | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXP | MI | Waves Intensity (Hs) | <0.55 | 0.55–0.85 | 0.86–1.05 | 1.06–1.25 | >1.25 | [31] |
| Tidal range (m) | <2 | - | 2 to 4 | - | >4 | |||
| HP | Visitor pressure | Low | - | Moderate | - | High | Field/[32] | |
| Visitor frecuency | Low | - | Moderate | - | High | |||
| Access difficulty | High | - | Moderate | - | Low | |||
| SUS | VC | Average vegetation cover (m2) | >230 | <230 | <125 | <60 | <10 | Field/GIS |
| Percentage of the area with vegetation (Type II) | <5 | <15 | <30 | <60 | >60 | |||
| GD | Active dune system length (km) | >20 | >10 | >5 | >1 | >0.1 | GIS | |
| Active dune system width (km) | >2 | >1 | >0.5 | >0.1 | <0.1 | GIS | ||
| Average height of the coastal dune (m) | >2 | 1.5 to 2 | 1 to 1.5 | 0.5 to 1 | <0.5 | GIS | ||
| Particle size of the windward slope of the dune (Φ) | ≤−1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | Field/Lab | ||
| Relative surface with scarps (m2) | 0 | <5 | <20 | <50 | >50 | GIS | ||
| Modal beach state | Reflective | - | Intermediate | - | Dissipative | [31] | ||
| RS | GB | Number of sandy or rocky bars submerged or emerged | 0 | - | 1 | - | >1 | GIS |
| Beach width (m) | 0 | <10 | <25 | <75 | >75 | GIS | ||
| Particle size of the dry beach | <0 | - | 0 a 2 | - | >2 | [31] | ||
| Net Shoreline Movement (m) | <−40 | −10 to −40 | - | >0 to −10 | ≥0 | GIS | ||
| Beach surface variation | <−0.4 | −0.06 to −0.4 | - | <0 to −0.06 | ≥0 | GIS | ||
| AI | Sediment supply input | Low | - | Moderate | - | High | GIS | |
2.4. Dune Vulnerability Index (DVI)
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of the Variables
3.1.1. Marine Influence (MI)
3.1.2. Human Pressure (HP)
3.1.3. Characteristics of the Vegetation Cover (VC)
3.1.4. Geomorphology of the Dune System (GD)
3.1.5. Geomorphology of the Beach (GB)
3.1.6. Aeolian Influence (AI)
3.2. Dune Vulnerability Index Assessment (DVI)
4. Discussion
4.1. Exposure Assessment
4.2. Susceptibility Assessment
4.3. Resilience Assessment
4.4. DVI Assessment
4.5. Coastal Management Assessment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kjerfve, B. Coastal Lagoons. In Coastal Lagoon Processes; Kjerfve, B., Ed.; Elsevier Science Publishers: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1994; ISBN 0444882588. [Google Scholar]
- Otvos, E.G. Coastal barriers—Nomenclature, processes, and classification issues. Geomorphology 2012, 139, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Silva, J.; Alexandre, A.; Navarro, N.; Barrón, C.; Duarte, C. Ecosystem metabolism and carbon budget of tidal-dominated coastal lagoon. Estuaries 2004, 27, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christian, R.R.; Baird, D.; Bowen, R.E.; Clark, D.M.; DiGiacomo, P.M.; Jiménez, J.; Kineman, J.; Mazzilli, S.; Servin, G.; Viaroli, P.; et al. Coastal GTOS Draft Strategic Design and Phase 1 Implementation Plan; GTOS Report No. 36; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Reinson, G.E. Facies Models 14. Barrier Island Systems. Geoscience Canada, 6(2). 1979. Available online: https://journals.lib.unb.ca/index.php/GC/article/view/3154 (accessed on 2 March 2021).
- Rodríguez Santalla, I.; Sánchez, M.J.; Montoya, I.; Gómez, D.; Martín, T.; Serra, J. Internal structure of the aeolian sand dunes of El Fangar spit, Ebro Delta (Tarragona, Spain). Geomorphology 2009, 104, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, C.; Gallego, J.B.; Vidal, C. Manual de Restauración de Dunas Costeras; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente: Dirección General de Costas, Spain, 2007; p. 258.
- Bodéré, J.C.L.; Cribb, R.; Curr, R.C.F.; Davies, P.; Hallégouet, B.; Meur, C.; Pirou, N.; Williams, A.T.; Yoni, C. La gestion des milleux dunaires littoraux. Evaluation de leur vulnerabilité a partir d’une liste de controle. Etudes cas dans le sud de Pays de Galles et en Bretagne Occidentale. Norois 1991, 38, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Davies, P.; Curr, R.C.F.; Koh, A.; Bodéré, J.C.L.; Hallégouet, B.; Meur, C.; Yoni, C. A checklist assessment of dune vulnerability and protection in Devon and Cornwall, UK. In Coastal Zone’93; Magoon, O.T., Ed.; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1993; pp. 3394–3408. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.T.; Alveirinho-Dias, J.; García-Novo, F.; García-Mora, M.R.; Curr, R.; Pereira, A. Integrated coastal dune management: Checklist. Cont. Shelf Res. 2001, 21, 1937–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia Mora, M.R.; Gallego-Fernandez, J.B.; Williams, A.T.; García-Novo, F. A coastal dune vulnerability classification. A case study of the SW Iberian Peninsula. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 17, 802–811. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Vázquez, M.L.; Gallego, J.B.; García, J.; Moctezuma, C.; Jiménez, C.D. Assessment of coastal dune vulnerability to natural and anthropogenic disturbances along the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Conserv. 2006, 33, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracia Prieto, F.J.; Sanjaume, E.; Hernández, L.; Hernández, A.I.; Flor, G.; Gómez-Serrano, M.Á. Dunas marítimas y continentales. In VV.AA., Bases Ecológicas Preliminares Para La Conservación de Los Tipos de Hábitat de Interés Comunitario En España; Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, y Medio Rural y Marino: Madrid, Spain, 2009; p. 106. [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz, S.; Gallego, J.B.; Dellafiore, C.M. Dune Vulnerability in Relation to Tourism Pressure in Central Gulf of Cadiz (SW Spain), A Case study. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 243–251. [Google Scholar]
- Ciccarelli, D.; Pinna, M.S.; Alquini, F.; Cogoni, D.; Ruocco, M.; Bacchetta, G.; Sarti, G.; Fenu, G. Development of a coastal dune vulnerability index for Mediterranean ecosystems: A useful tool for coastal managers? Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 187, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Alonso, C.; Gallego-Fernández, J.B.; Hernández-Calvento, L.; Hernández-Cordero, A.I.; Ariza, E. Assessing the geomorphological vulnerability of arid beach-dune systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 635, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancho, F.; Oliveira, F.S.; Freire, P. Coastal dunes vulnerability indexes: A new proposal. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2012, 1, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, B.; Wandel, J. Adaptation, adaptive capacity and vulnerability. Glob. Environ. Change 2006, 16, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclaughlin, S.; Cooper, J.A. A multi-scale coastal vulnerability index: A tool for coastal managers? Environ. Hazards 2010, 9, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Cuesta, J.M.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Gracia, F.J.; Sánchez-García, M.J.; Barrio Parra, F. Analysis of recent geomorphological changes occurred in the Ebro River mouth by using changes detection techniques (period 1957–2013). Appl. Geog. 2016, 75, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Somoza, L. The Ebro River Delta. In The Spanish Coastal Systems—Dynamic Processes, Sediments and Management, 1st ed.; Morales, J.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 467–488. [Google Scholar]
- Maldonado, A. El Delta del Ebro. Estudio Sedimentológico y Estratigráfico. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad de Barcelona, Barcelona, Spain, 1972. Boletín de Estratigrafía Volume 1486. p. 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, J.A.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Valdemoro, H.I.; Gracia, V.; Nieto, F. Processes reshaping the Ebro delta. Mar. Geol. 1997, 144, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somoza, L.; Barnolas, A.; Arasa, A.; Maestro, A.; Rees, J.G.; Hernandez-Molina, F.J. Architectural stacking patterns of the Ebro delta controlled by Holocene high-frequency eustatic fluctuations, delta-lobe switching and subsidence processes. Sediment. Geol. 1998, 117, 11–32. [Google Scholar]
- Cearreta, A.; Benito, A.; Ibáñez, C.; Trobajo, R.; Giosan, L. Holocene palaeoenvironmental evolution of the Ebro Delta (Western Mediterranean Sea): Evidence for an early construction based on the benthic foraminiferal record. Holocene 2016, 26, 1438–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-García, M.J.; Montoya-Montes, I.; Casamayor, M.; Alonso, I.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I. Coastal Dunes in the Ebro Delta. In The Spanish Coastal Systems—Dynamic Processes, Sediments and Management, 1st ed.; Morales, J.A., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 1, pp. 611–630. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Triviño-Monozón, J. Determinación del cambio superficial y volumétrico en el periodo 2011–2016 del campo dunar de la playa de Riumar en la desembocadura del Río Ebro, por medio de datos LiDAR. X J. Geomorfol. Litoral 2019, 1, 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Montoya, I.; Sánchez, M.J.; Carreño, F. Geographic Information Systems applied to integrated coastal zone management. Geomorphology 2009, 107, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulton, M.A.B.; Hesp, P.A.; Miot da Silva, G.; Bouchez, C.; Lavy, M.; Fernandez, G.B. Changes in vegetation cover on the Younghusband Peninsula transgressive dune fields (Australia) 1949–2017. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2019, 44, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himmelstoss, E.; Henderson, R.; Kratzmann, M.; Farris, A. Digital Shoreline Analysis System (DSAS) Version 5.0 User Guide. U.S.; Geological Survey Open-File Report 2018–1179; USGS: Reston, VA, USA, 2018; p. 126. [CrossRef]
- Grases, A.; Gracia, V.; García-León, M.; Lin-Ye, J.; Sierra, J.P. Coastal Flooding and Erosion under a Changing Climate: Implications at a Low-Lying Coast (Ebro Delta). Water 2020, 12, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortells-Cabrera, V.; Querol-Gómez, A. El Parc Natural del Delta de l’Ebre: El Turismo Como Complemento Económico Sostenible; Servicio de Publicaciones Universidad de Almería: Almeria, Spain, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Piscioneri, N.; Smyth Thomas, A.G.; Hesp Patrick, A. Flow Dynamics over a Foredune Scarp. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 44, 1064–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Martín, R.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I. Detection of submerged sand bars in the Ebro delta using ASTER images. In New Frontiers in Engineering Geology and the Environment; Springer: Berlín/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Gómez-Ortiz, D.; Martín-Crespo, T.; Sánchez-García, M.J.; Montoya-Montes, I.; Martín-Velázquez, S.; Barrio, F.; Serra, J.; Ramírez-Cuesta, J.M.; Gracia, F.J. Study and Evolution of the Dune Field of La Banya Spit in Ebro Delta (Spain) Using LiDAR Data and GPR. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, J.P.; González del Río, J.; Flos, J.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Movellán, E.; Rodilla, M.; Mösso, C.; Martínez, R.; Falco, S.; Romero, I.; et al. Medición de parámetros físicos, biológicos y químicos en el tramo estuarino del río Ebro. Ingeniería 2001, 8, 459–468. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Arcilla, A.; Mösso, C.; Sierra, J.P.; Mestres, M.; Harzallah, A.; Senouci, M.; El Raey, M. Climatic drivers of potential hazards in Mediterranean coasts. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, M.; Gracia, F.J.; Peralta, G. Estuarine Mapping and Eco-Geomorphological Characterization for Potential Application in Conservation and Management: Three Study Cases along the Iberian Coast. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Mora, M.R.; Gallego-Fernández, J.B.; García-Novo, F. Plant functional types in coastal foredunes in relation to environmental stress and disturbance. J. Veg. Sci. 1999, 10, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, E.T.; Jiménez, J.A. Factors controlling vulnerability to storm impacts along the Catalonian coast. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Coastal Engineering, Lisbon, Portugal, 19–24 September 2004; pp. 3087–3099. [Google Scholar]
- Lorente, P.; Lin-Ye, J.; García-León, M.; Reyes, E.; Fernandes, M.; Sotillo, M.G.; Espino, M.; Ruiz, M.I.; Gracia, V.; Perez, S.; et al. On the Performance of High Frequency Radar in the Western Mediterranean during the Record-Breaking Storm Gloria. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 645762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartual, M.T.; Pareja, M. Procesos participativos de gestión para la sostenibilidad del desarrollo rural. El caso CETS (Carta Europea de Desarrollo Sostenible) en el Delta del Ebro, España. Rev. Interam. Ambient. Tur. 2015, 11, 16–30. [Google Scholar]
- Barrio-Parra, F.; Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Taborda, R.; Ribeiro, M. A modeling approach to assess the key factors in the evolution of coastal systems: The Ebro North Hemidelta case. Estuar. Coasts 2017, 40, 758–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, J.; Palanques, A. Short- and medium-term grain size changes in deltaic beaches (Ebro Delta, NW Mediterranean). Sediment. Geol. 1996, 101, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.; Valdemoro, H.; Bosom, E.; García, V. Storm-induced coastal hazards in the Ebro delta (NW Mediterranean). In The Proceedings of the Coastal Sediments; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011; pp. 1332–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Reed, D.J. Coastal biogeomorphology: An integrated approach to understanding the evolution, morphology, and sustainability of temperate coastal marshes. In Estuarine Science: A Synthetic Approach to Research and Practice; Hobbie, J.E., Ed.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2000; pp. 347–361. [Google Scholar]
- Cobani, M. Tunisia. In Mediterranean Coastal Lagoons: Sustainable Management and Interactions among Aquaculture, Capture Fisheries and the Environment; Stefano, C., Donatella, C., Fabio, M., Eds.; FAO Studies and Reviews: Rome, Italy, 2015; Volume 95, pp. 51–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Arcilla, A.; Jiménez, J.; Valdemoro, H. The Ebro Delta: Morphodynamics and Vulnerability. J. Coast. Res. 1998, 14, 754–772. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoch, L.; Day, J.W.; Ibáñez, C. Net primary productivity as an indicator of sustainability in the Ebro and Mississippi Deltas. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1044–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, A.; Carcavilla, L.; Díez-Herrero, A. Geomorphological Heritage and Conservation in Spain. In Landscapes and Landforms of Spain, 1st ed.; Gutiérrez, F., Gutiérrez, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 307–318. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, A.; Davies, P.; Dias, J.M.; Pereira, A.R.; Garcia-Mora, M.R.; Tejada, M. A re-evaluation of dune vulnerability checklist parameters. GAIA Rev. Geocienc. 1994, 8, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
- Oropeza-Orozco, O.; Sommer-Cervantes, I.; Carlos-Gómez, J.; Preciado-López, J.; Ortiz-Pérez, M.; López-Portillo, J. Assessment of Vulnerability and Integrated Management of Coastal Dunes in Veracruz, Mexico. Coast. Manag. 2011, 39, 492–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.T.; Davies, P. Coastal dunes of Wales; vulnerability and protection. J. Coast. Conserv. 2001, 7, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoni, D.; Sarti, G.; Alquini, F.; Ciccarelli, D. Implementing a coastal dune vulnerability index (CDVI) to support coastal management in different settings (Brazil and Italy). Ocean Coast. Manag. 2019, 180, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolini, S.; Mecocci, A.; Pozzebon, A.; Zoppetti, C.; Bertoni, D.; Sarti, G.; Caiti, A.; Costanzi, R.; Catani, F.; Ciampalini, A.; et al. Augmented virtuality for coastal management: A holistic use of in situ and remote sensing for large scale definition of coastal dynamics. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2018, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
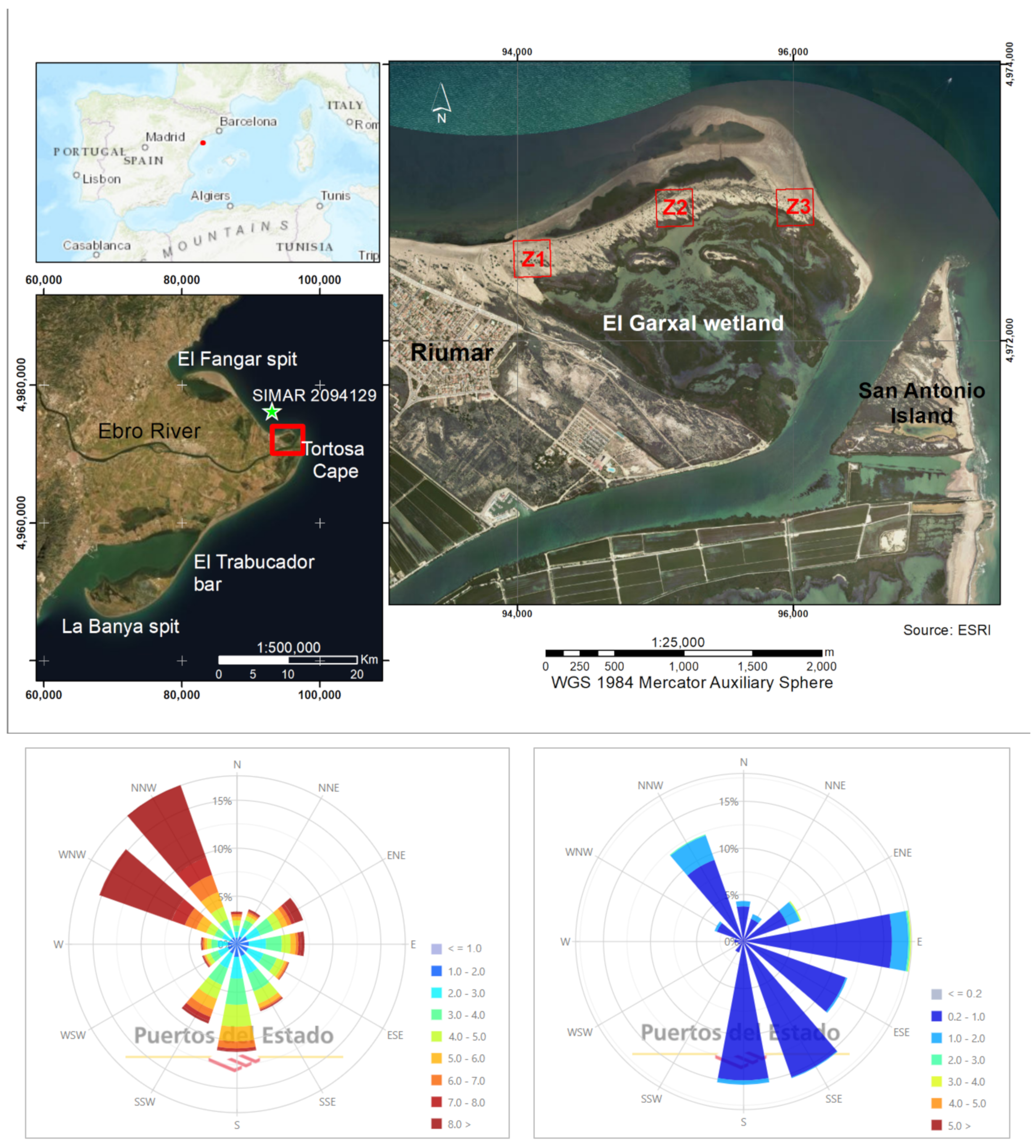
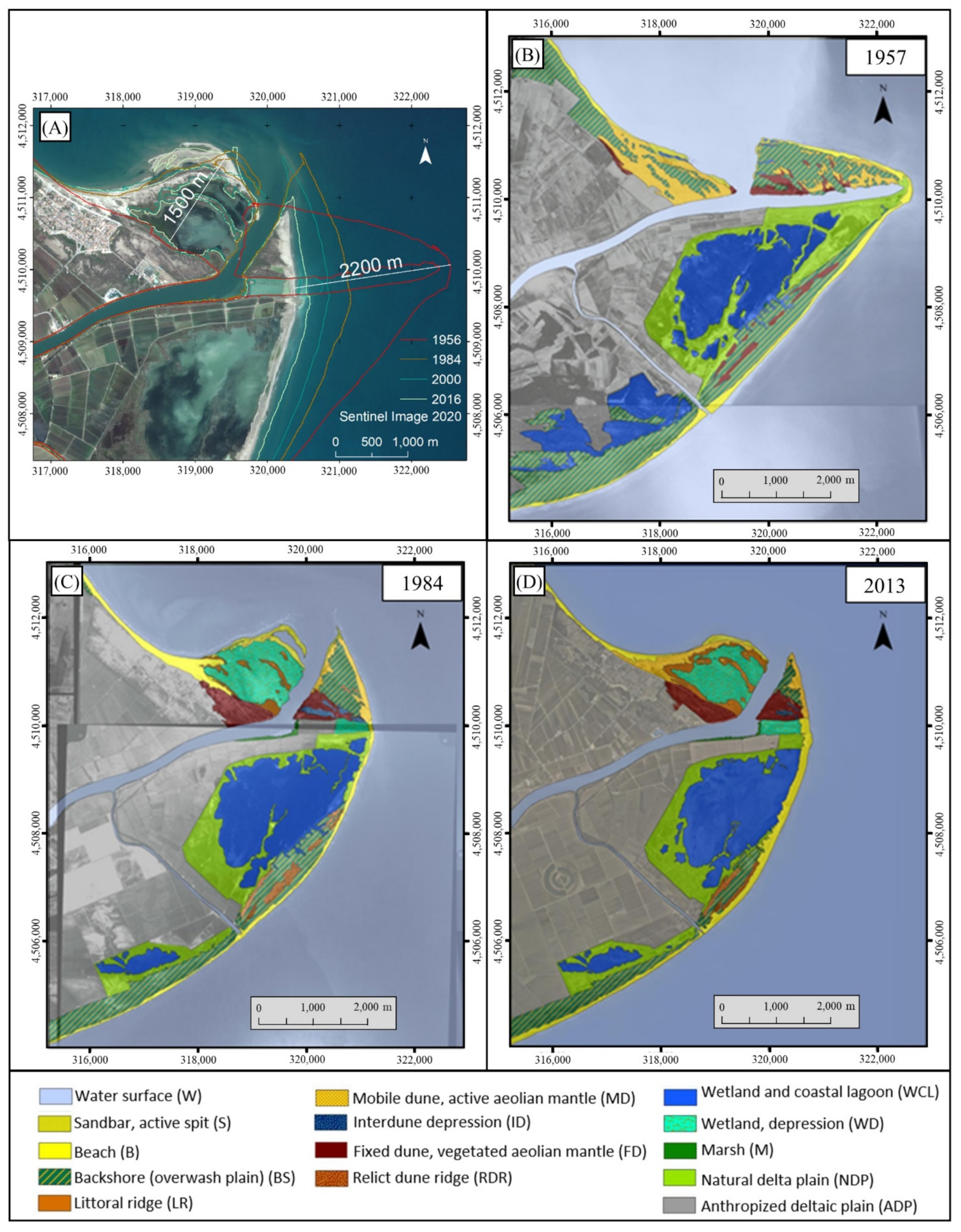
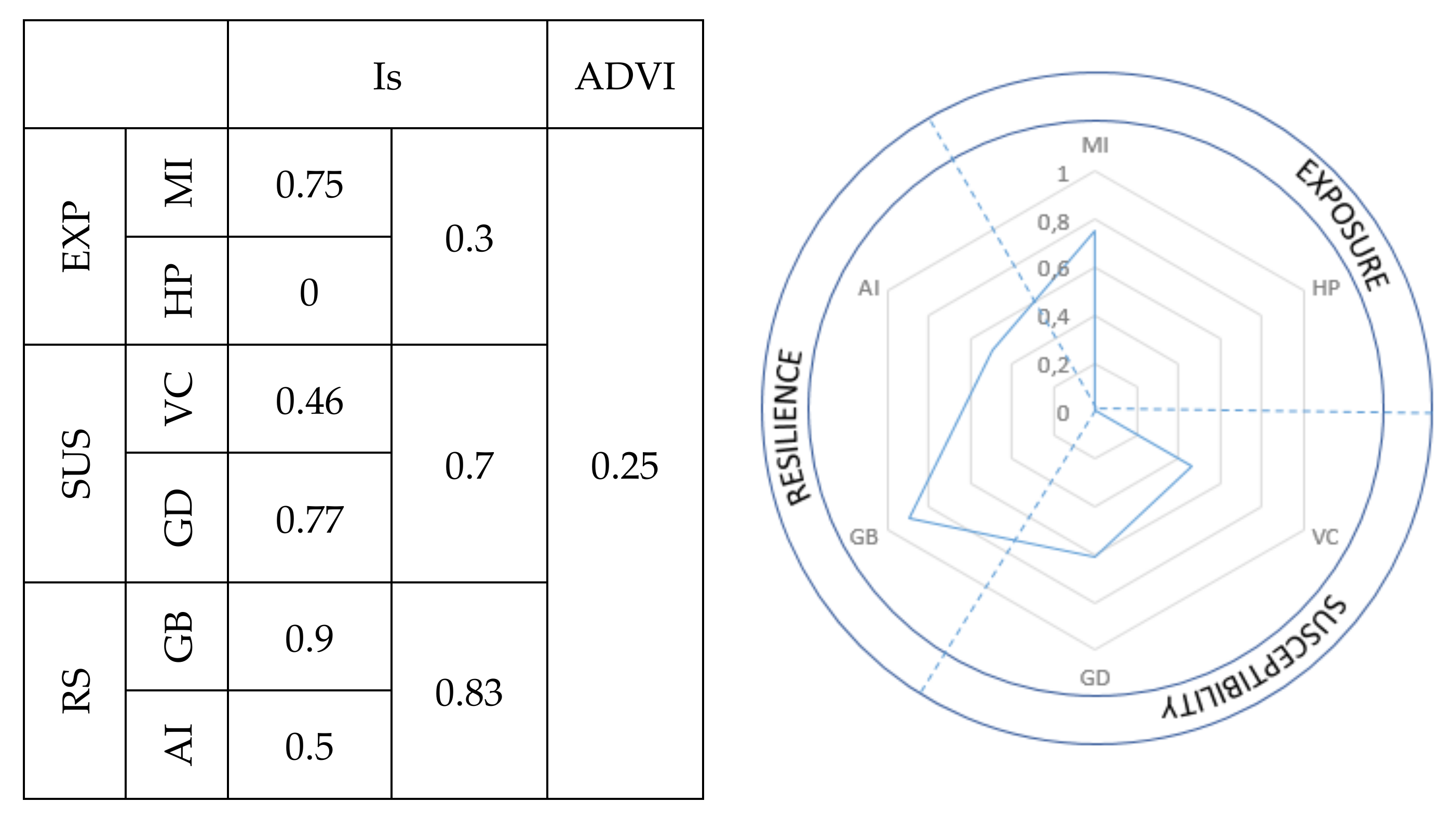
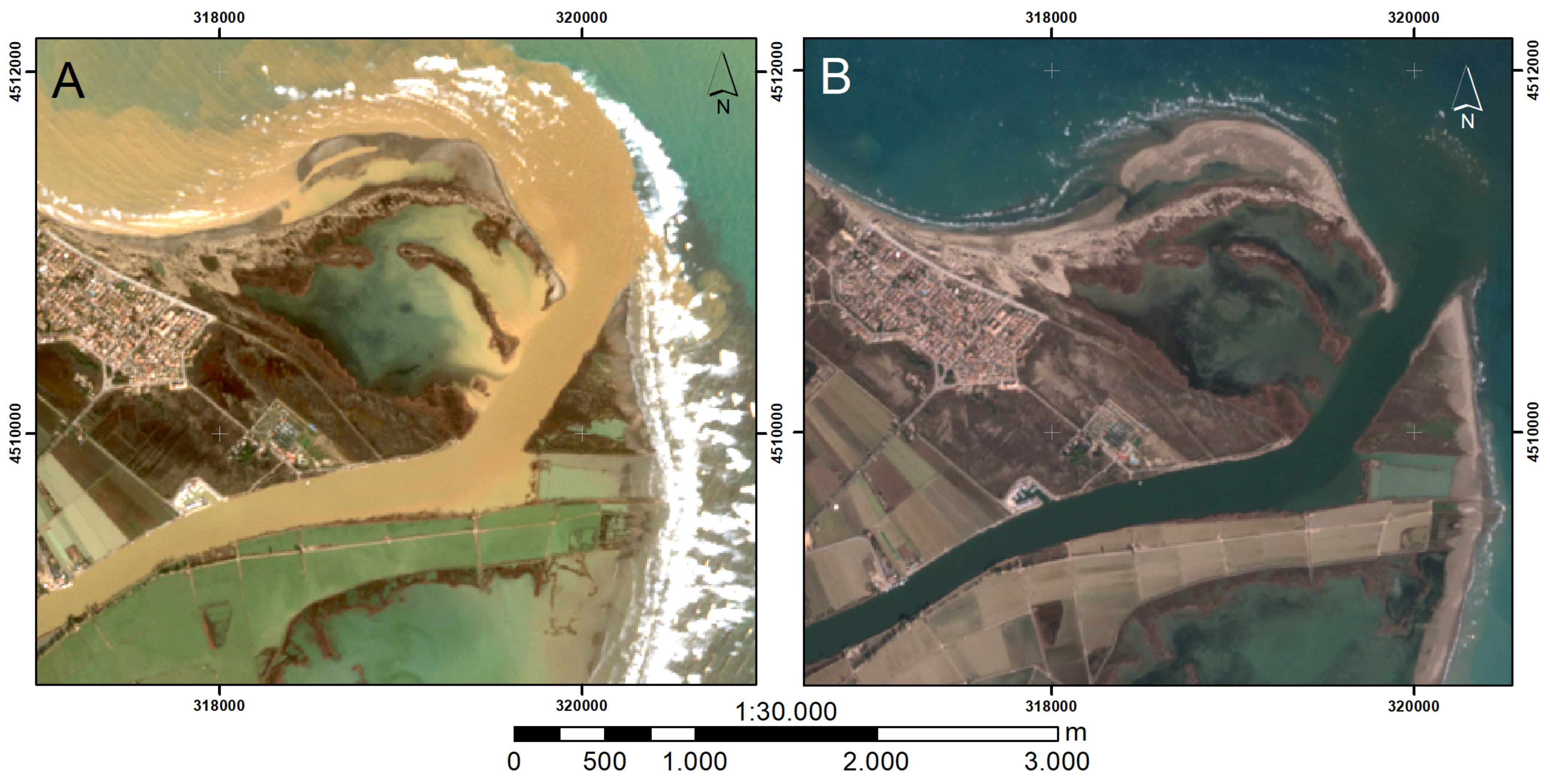
| Variables | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | Average | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXP | MI | Waves Intensity (Hs) | 4 | 4.00 | ||
| Tidal range (m) | 2 | 2.00 | ||||
| HP | Visitor pressure | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| Visitor frecuency | 0 | 0.00 | ||||
| Access difficulty | 0 | 0.00 | ||||
| SUS | VC | Average vegetation cover (m2) | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1.67 |
| Percentage of the area with vegetation (Type II) | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2.00 | ||
| GD | Active dune system length (km) | 3 | 3.00 | |||
| Active dune system width (km) | 3 | 3.00 | ||||
| Average height of the coastal dune (m) | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1.67 | ||
| Particle size of the windward slope of the dune (Φ) | 3 | 3.00 | ||||
| Relative surface with scarps (m2) | 4 | 4.00 | ||||
| Modal beach state | 4 | 4.00 | ||||
| RS | GB | Number of sandy or rocky bars submerged or emerged | 4 | 4.00 | ||
| Beach width (m) | 4 | 4.00 | ||||
| Particle size of the dry beach | 2 | 2.00 | ||||
| Net Shoreline Movement (m) | 4 | 4.00 | ||||
| Beach surface variation | 4 | 4.00 | ||||
| AI | Sediment input from the primary dune | 2 | 2.00 | |||
| Variables VC | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average vegetation cover (m2) | 54 | 192.77 | 179.22 |
| Percentage of the area with vegetation (Type II) | 11 | 39.31 | 27.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Santalla, I.; Díez-Martínez, A.; Navarro, N. Vulnerability Analysis of the Riumar Dune Field in El Garxal Coastal Wetland (Ebro Delta, Spain). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9060601
Rodríguez-Santalla I, Díez-Martínez A, Navarro N. Vulnerability Analysis of the Riumar Dune Field in El Garxal Coastal Wetland (Ebro Delta, Spain). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2021; 9(6):601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9060601
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Santalla, Inmaculada, Alejandro Díez-Martínez, and Nuria Navarro. 2021. "Vulnerability Analysis of the Riumar Dune Field in El Garxal Coastal Wetland (Ebro Delta, Spain)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 9, no. 6: 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9060601
APA StyleRodríguez-Santalla, I., Díez-Martínez, A., & Navarro, N. (2021). Vulnerability Analysis of the Riumar Dune Field in El Garxal Coastal Wetland (Ebro Delta, Spain). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 9(6), 601. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse9060601






