Application of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale to Assess Sand Dune Response to Tropical Storms
Abstract
1. Introduction
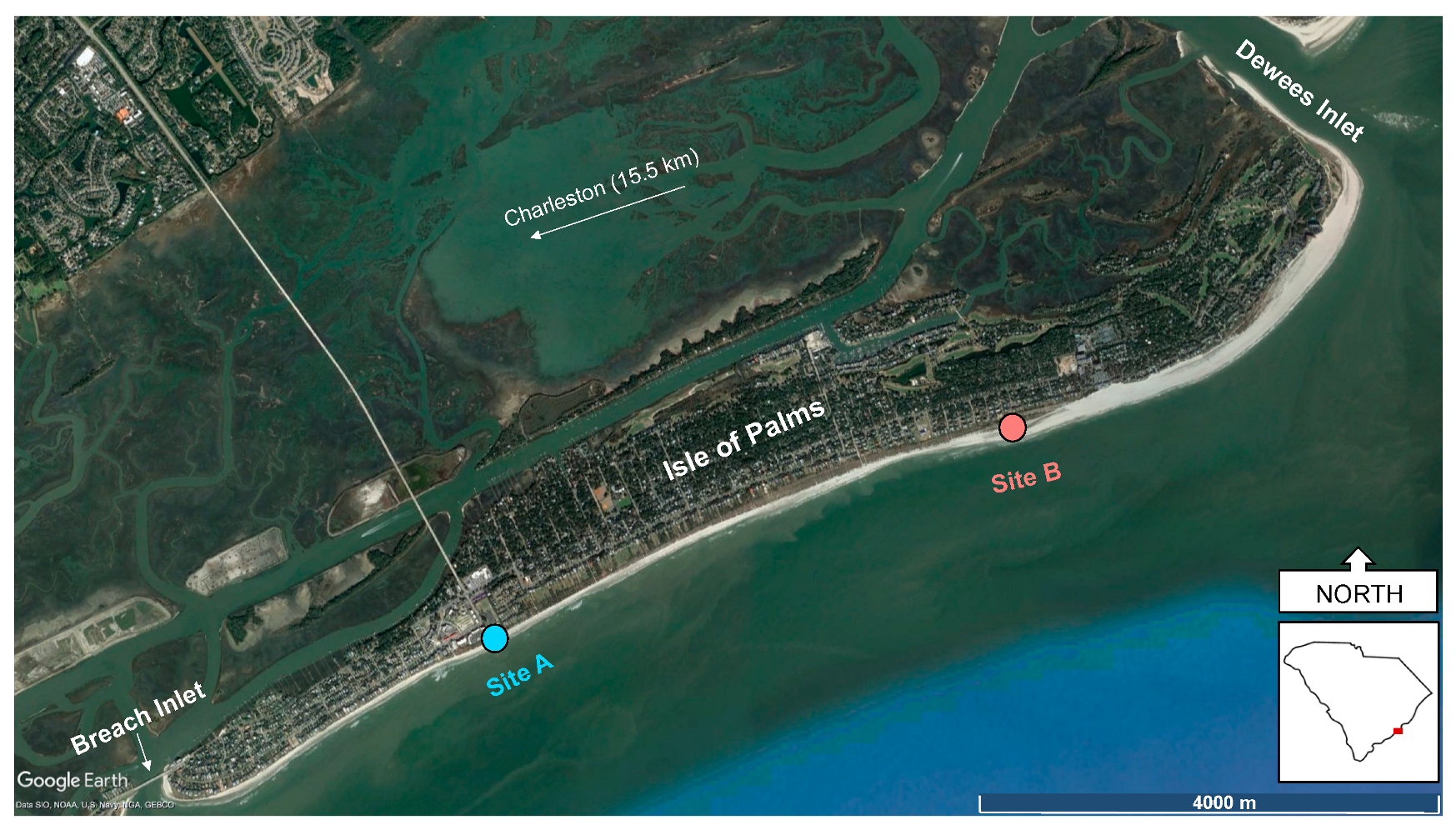
2. Study Area
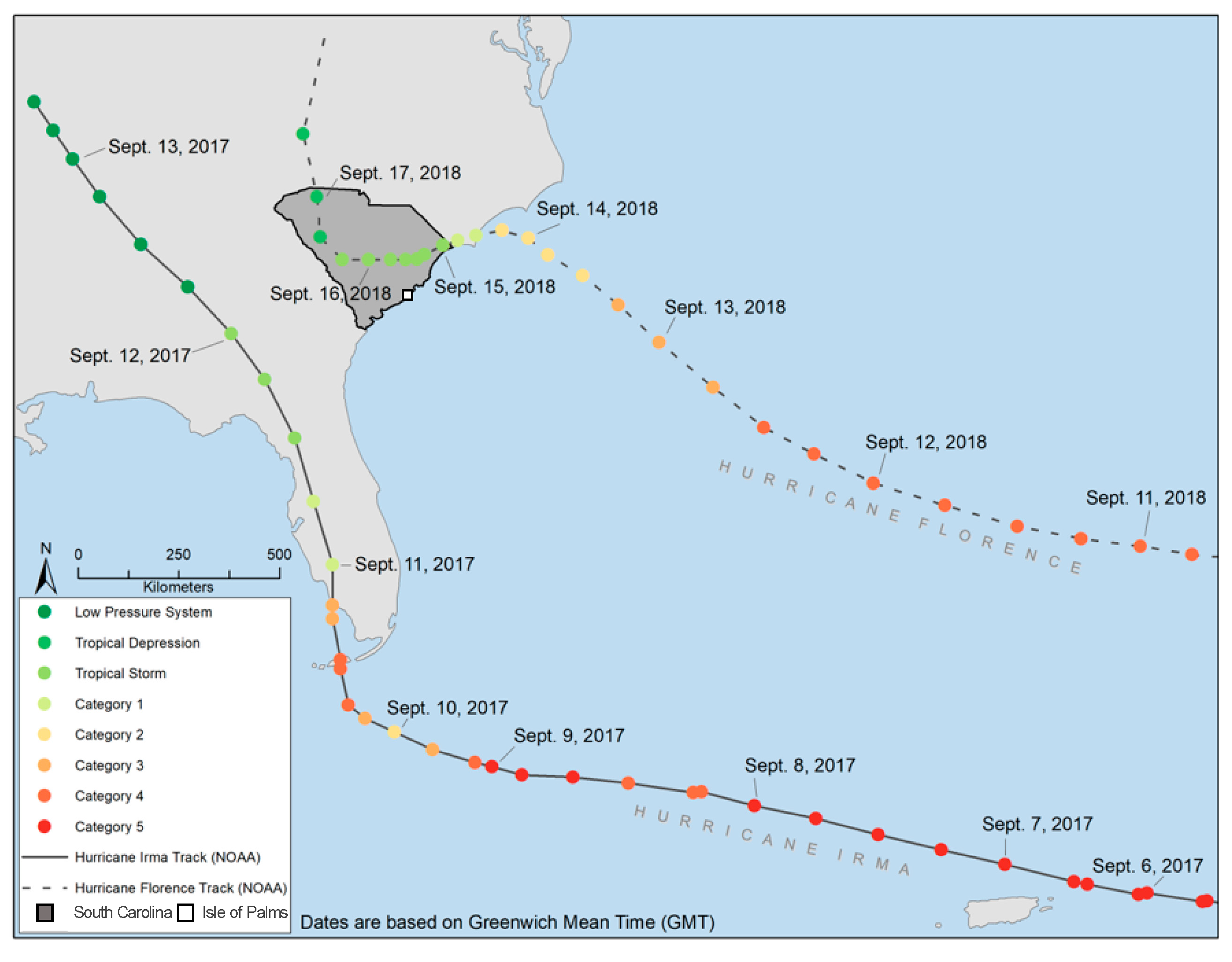
3. Hurricanes Irma and Florence
4. Assessing Dune Change
5. Results
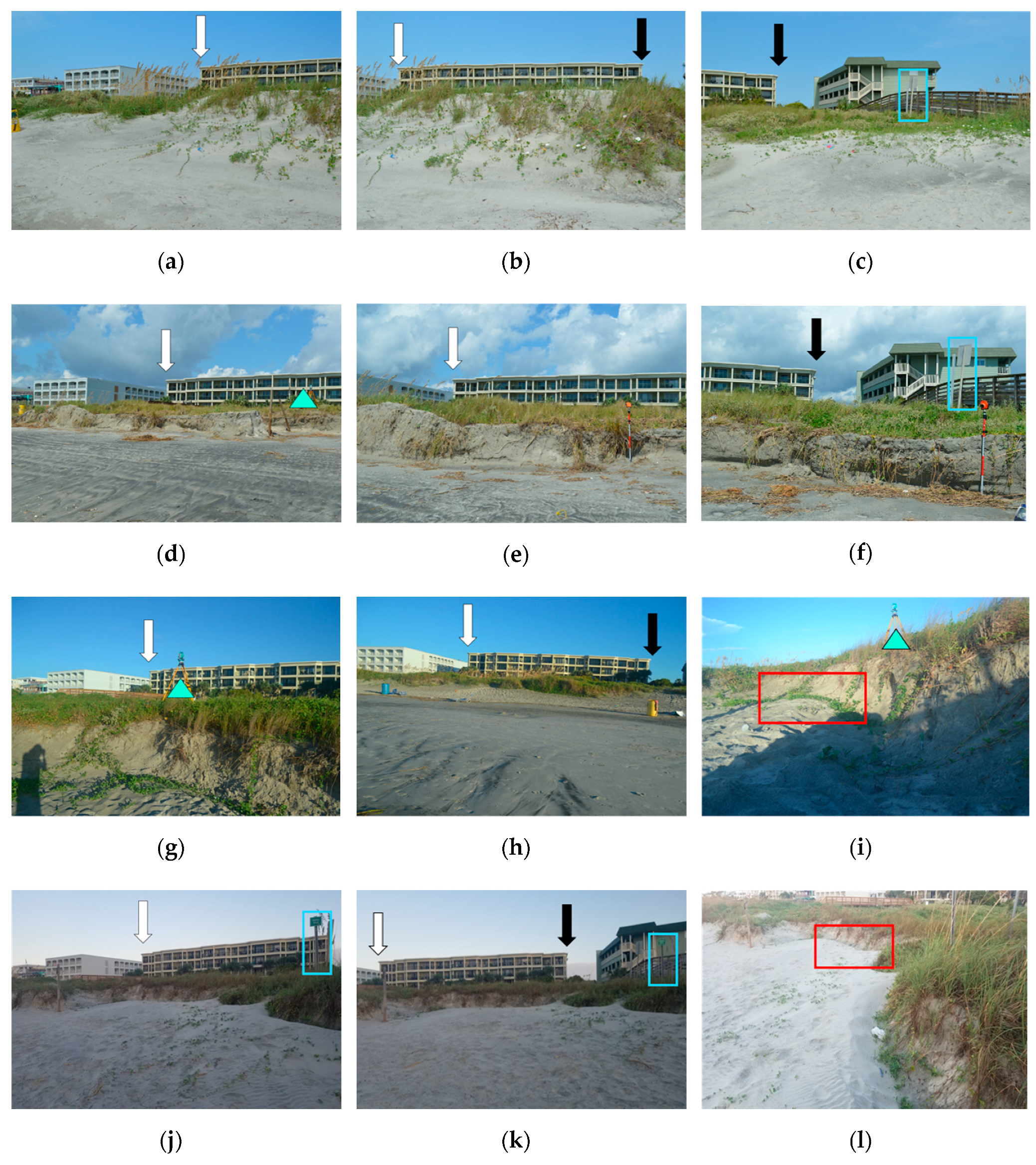
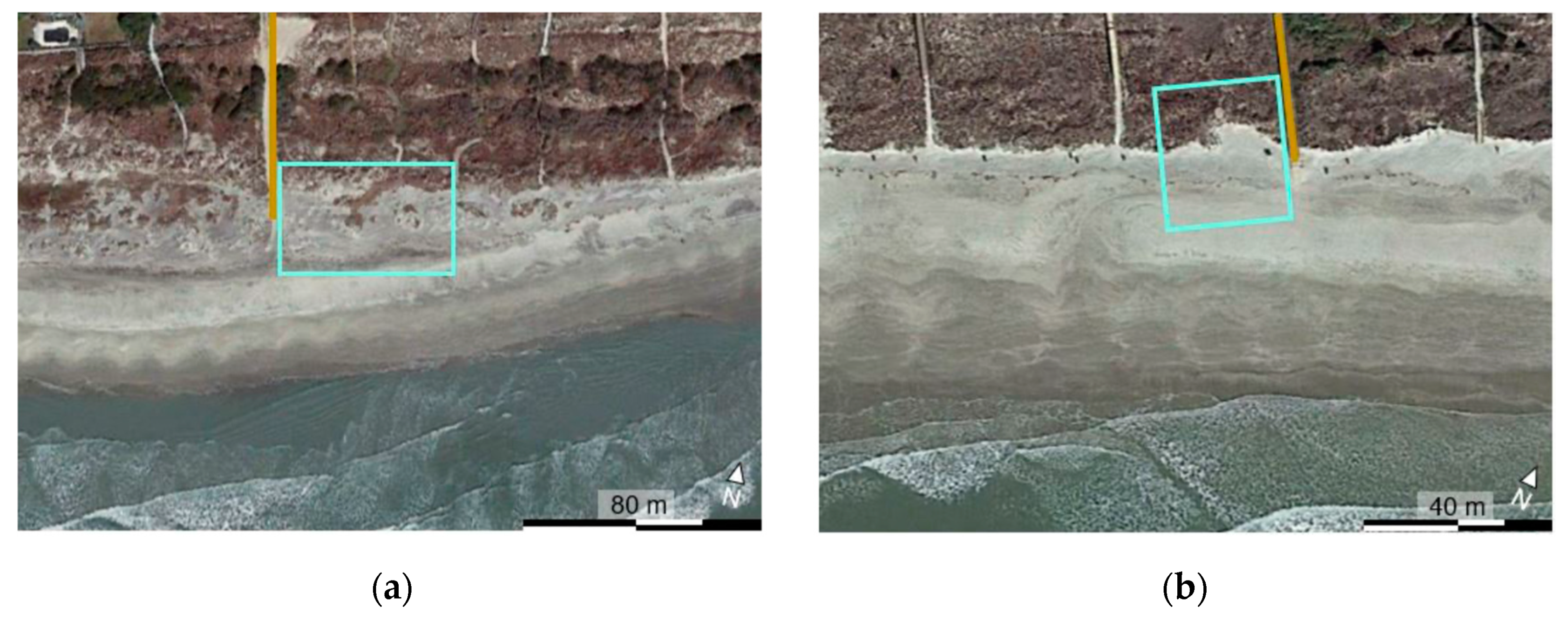
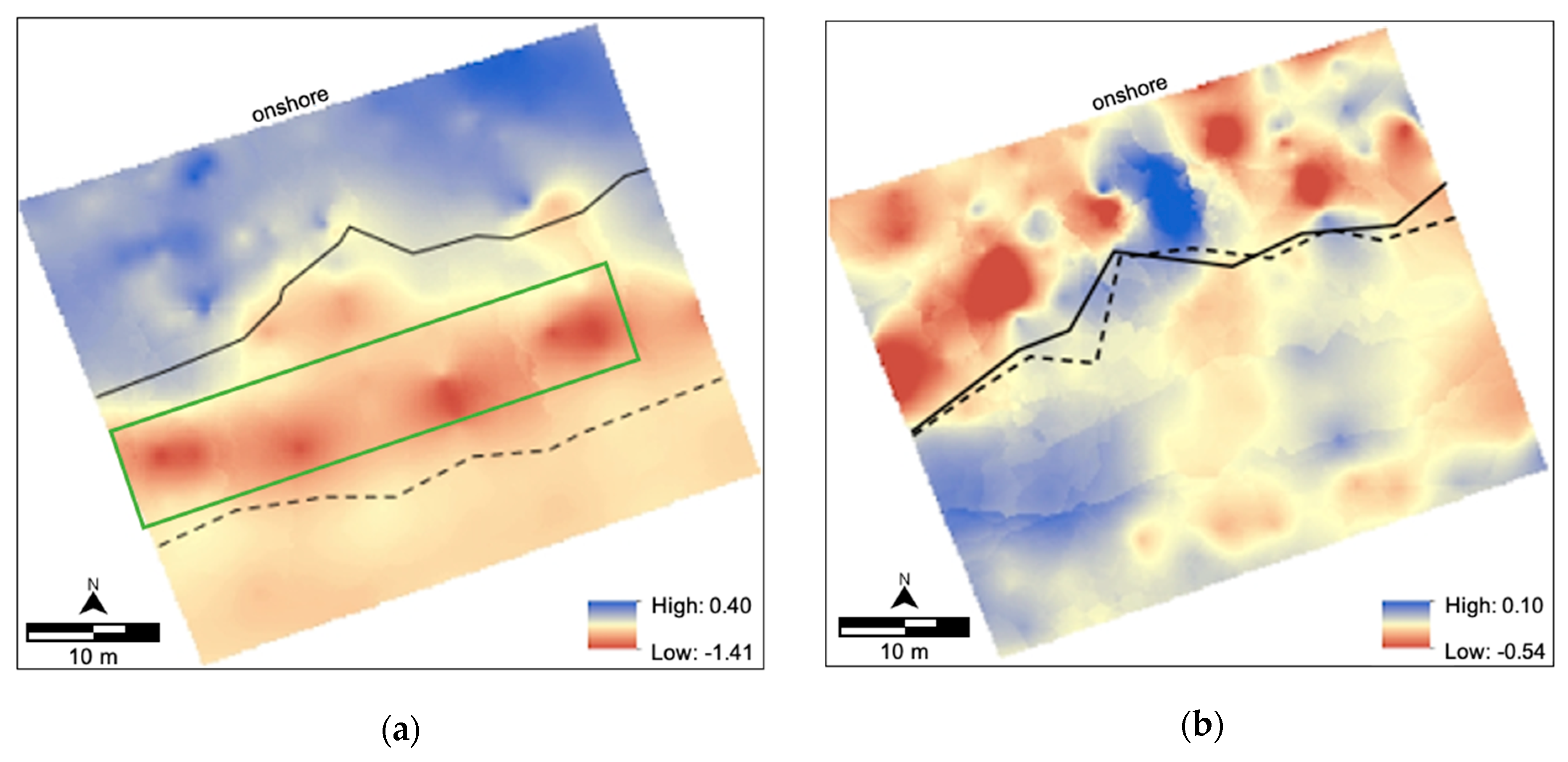
5.1. Site A Beach-Dune System
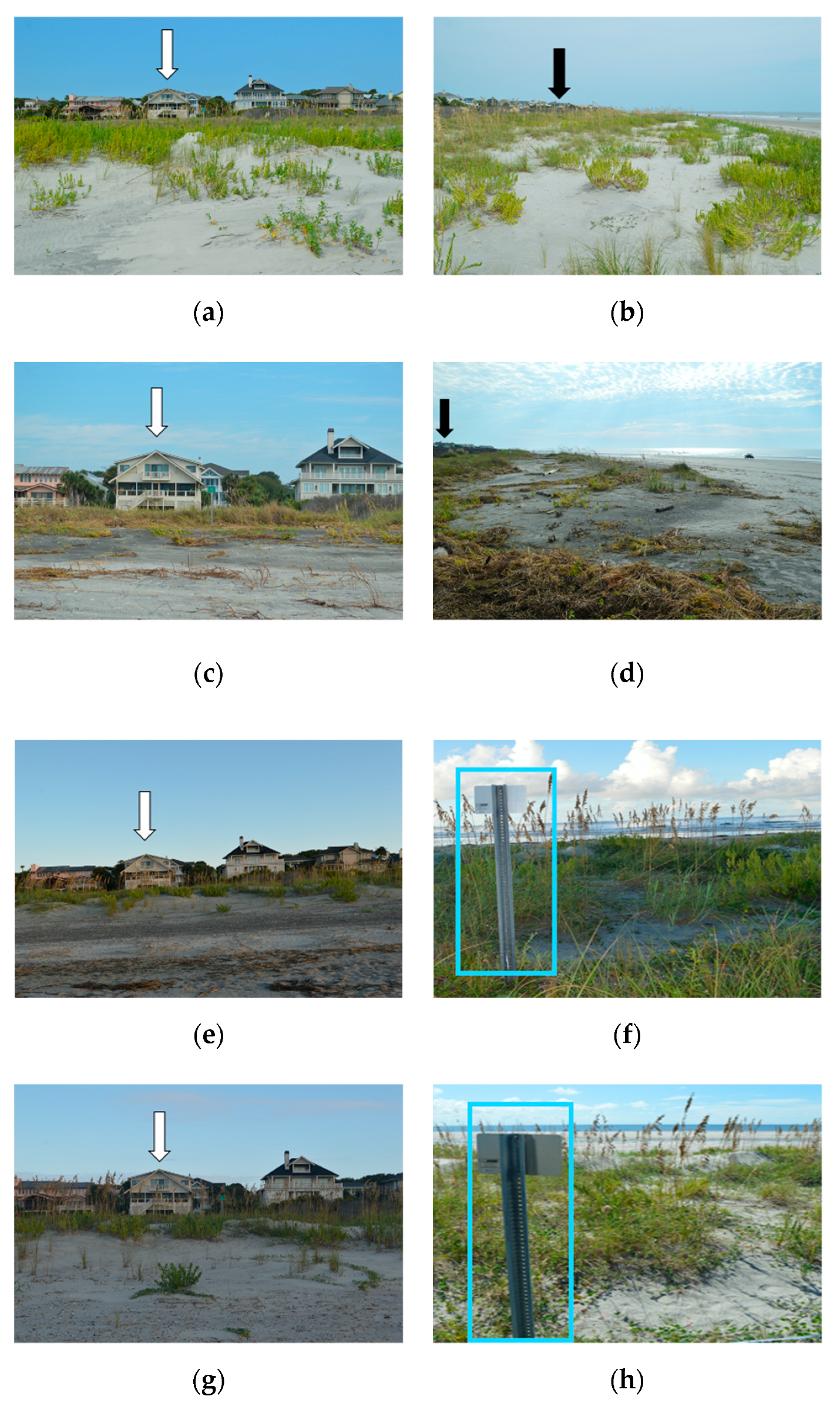
5.2. Site B Beach-Dune System
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Coastal Population Explosion. Available online: http://oceanservice.noaa.gov/websites/retiredsites/natdia_pdf/3hinrichsen.pdf (accessed on 8 September 2018).
- Nicholls, R.J. Planning for the impacts of sea level rise. Oceanography 2011, 24, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, M.D.; Ciavola, P. Managing local coastal inundation risk using real-time forecasts and artificial dune placements. Coast. Eng. 2013, 77, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.J.; Halsey, S.D. Comparison of overwash penetration from Hurricane Hugo and pre-storm erosion rates for Myrtle Beach and North Myrtle Beach, South Carolina, USA. J. Coast. Res. 1991, SI8, 229–235. [Google Scholar]
- Claudino-Sales, V.; Wang, P.; Horwitz, M.H. Factors controlling the survival of coastal dunes during multiple hurricane impacts in 2004 and 2005: Santa Rosa Barrier Island, Florida. Geomorphology 2008, 95, 295–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, N.G.; Stockdon, H.F. Probabilistic prediction of barrier-island response to hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Wernette, P.; Rentschlar, E.; Jones, H.; Hammond, B.; Trimble, S. Post-storm beach and dune recovery: Implications for barrier island resilience. Geomorphology 2015, 234, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coco, G.; Senechal, N.; Rejas, A.; Bryan, K.R.; Capo, S.; Parisot, J.P.; Brown, J.A.; MacMahan, J.H.M. Beach response to a sequence of extreme storms. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunarathna, H.; Pender, D.; Ranasinghe, R.; Short, A.D.; Reeve, D.E. The effects of storm clustering on beach profile variability. Mar. Geol. 2014, 348, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, P.; Brown, J.; Wisse, P.; Karunarathna, H. Effect of storm clustering on beach / dune erosion. J. Geol. 2015, 370, 63–75. [Google Scholar]
- Angnuureng, D.B.; Almar, R.; Senechal, N.; Castelle, B.; Addo, K.A.; Marieu, V.; Ranasinghe, R. Shoreline resilience to individual storms and storm clusters on a meso-macrotidal barred beach. Geomorphology 2017, 290, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, M.; Jones, J.; Watts, B. Have we neglected the societal importance of sand dunes? An ecosystem services perspective. Aquat. Conserv. 2010, 20, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Holland, G.J.; Curry, J.A.; Chang, H.R. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 2005, 5742, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Ellis, J. Morphodynamic systems: Beach and dune interaction. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Schroder, J., Sherman, D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 267–288. [Google Scholar]
- Román-Rivera, M.A. Innovative Approaches Using Multispectral Imagery to Detect Nearshore Bars and Elucidate Beach System Dynamics. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sallenger, A.H. Storm impact scale for barrier islands. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesp, P. Foredunes and blowouts: Initiation, geomorphology and dynamics. Geomorphology 2002, 48, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieler, E.R.; Young, R.S. Quantitative evaluation of coastal geomorphological changes in South Carolina after Hurricane Hugo. J. Coast. Res. Spec. Issue 1991, 8, 187–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, C.; Hapke, C.; Hamilton, S. Controls on coastal dune morphology, shoreline erosion and barrier island response to extreme storms. Geomorphology 2008, 100, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leatherman, S.P. Barrier island dynamics: Overwash processes and eolian transport. In Coastal Engineering 1976, Proceedings of the 15th International Conference; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1976; pp. 1958–1974. [Google Scholar]
- Leatherman, S.P. Barrier dune systems: A reassessment. Sediment. Geol. 1979, 24, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armon, J.W. Dune erosion and recovery on a northern barrier. In Coastal Zone ’80, Proceedings of the 2nd Symposium on Coastal and Ocean Management; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 1980; pp. 1233–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Psuty, N.P. Spatial variation in coastal foredune development. In Coastal Dunes: Geomorphology, Ecology and Management for Conservation; Carter, R.W.G., Curtis, T.G.F., Sheehy-Skeffington, M.J., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; pp. 3–13. [Google Scholar]
- Morton, R.A. Factors controlling storm impacts on coastal barriers and beaches—A preliminary basis for near real-time forecasting. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 18, 486–501. [Google Scholar]
- Priestas, A.M.; Fagherazzi, S. Morphological barrier island changes and recovery of dunes after Hurricane Dennis, St. George Island, Florida. Geomorphology 2010, 114, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claudino-Sales, V.; Wang, P.; Horwitz, M.H. Effect of Hurricane Ivan on coastal dunes of Santa Rosa Barrier Island, Florida: Characterized on the basis of pre- and poststorm LIDAR surveys. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Kirby, J.H.; Haber, J.D.; Horwitz, M.H.; Knorr, P.O.; Krock, J.R. Morphological and sedimentological impacts of Hurricane Ivan and immediate poststorm beach Recovery along the Northwestern Florida barrier-island coasts. J. Coast. Res. 2006, 226, 1382–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuna, M.P. The effect of Hurricane Hugo on the Isle of Palms, South Carolina: From destruction to recovery. J. Coast. Res. Spec. Issue 1991, 8, 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Coch, N.K.; Wolff, M.P. Effects of Hurricane Hugo storm surge in coastal South Carolina. J. Coast. Res. 1991, SI, 201–226. [Google Scholar]
- Saffir, H.S. Hurricane wind and storm surge. Military Eng. 1973, 423, 4–5. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, R.H. The hurricane disaster-potential scale. Weatherwise 1974, 27, 169–186. [Google Scholar]
- Kantha, L. Time to replace the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Scale? Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2006, 87, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, M.D.; Reinhold, T.A. Tropical cyclone destructive potential by integrated kinetic energy. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, E.J. Geomorphology storms, shoreface morphodynamics, sand supply, and the accretion and erosion of coastal dune barriers in the southern North Sea. Geomorphology 2013, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.O.; Moslow, T.F.; Hubbard, D.K. Beach Erosion in South Carolina; Coastal Research Division, Department of Geology, University of South Carolina: Colombia, SC, USA, 1978; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Tides & Currents: Isle of Palms Pier, SC–Station ID 8665494. Available online: https://tidesandcurrents.noaa.gov/stationhome.html?id=8665494 (accessed on 24 July 2020).
- Kana, T.W. Beach erosion during minor storms. J. Waterway Port Coast. Ocean Division 1977, 103, 505–518. [Google Scholar]
- CSC (Coastal Science & Engineering). Final Report 2018 Beach Restoration Project City of Isle of Palms; Technical Report #CSE–2453FR; CSE: Columbia, SC, USA, 2018; p. 57. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.T.; Román-Rivera, M.A. Assessing natural and mechanical dune performance in a post-hurricane environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, M.F.; Brown, P.J.; Fitzgerald, D.M.; Hubbard, M.K.; Hayes, M.O. Beach Erosion Inventory of Charleston County, South Carolina: A Preliminary Report; Technical Report No. 4; S.C.; Sea Grant: Charleston, SC, USA, 1975; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Fico, C. Influence of Wave Refraction on Coastal Geomorphology - Bull Island to Isle of Palms, South Carolina. Master’s Thesis, Coastal Research Division, Department of Geology, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA, 1978; p. 190. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.T.; Román-Rivera, M.A.; Harris, M.E.; Tereszkiewicz, P.A. Two years and two hurricanes later: Did the dunes recover? Shore & Beach 2020. (in print). [Google Scholar]
- South Carolina Department of Health and Environmental Control-Ocean & Coastal Management (SCDHEC-OCRM). SC Beachfront Jurisdictional Lines. Available online: https://gis.dhec.sc.gov/shoreline/ (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Cangialosi, J.P.; Latto, A.S.; Berg, R. National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Florence (AL112017). National Hurricane Center. 30 June 2018. p. 111. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/data/tcr/AL112017_Irma.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2019).
- Stewart, S.R.; Berg, R. National Hurricane Center Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Florence (AL062018). National Hurricane Center. 30 May 2019. 2019; p. 98. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/data/tcr/AL062018_Florence.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2019).
- National Hurricane Center and Central Pacific Hurricane Venter. NHC GIS Archive – Tropical Cyclone Best Track for AL 11207. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/gis/archive_besttrack_results.php?id=al11&year=2017&name=Hurricane%20IRMA (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- National Hurricane Center and Central Pacific Hurricane Venter. NHC GIS Archive – Tropical Cyclone Best Track for AL 062018. Available online: https://www.nhc.noaa.gov/gis/archive_besttrack_results.php?id=al06&year=2018&name=Hurricane%20FLORENCE (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Harris, M.E.; Ellis, J.T.; Barrineau, C.P. Evaluating the geomorphic response from sand fences on dunes impacted by hurricanes. Ocean Coast. Manage 2020. (in print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.; Leatherman, S.; The, S.; July, N.; Zhang, K.; Douglas, B.; Leatherman, S. Do storms cause long-term beach erosion along the U.S. east barrier coast? J. Geol. 2002, 110, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Weather Service (NWS). Tropical Storm Irma–September 10-11, 2017. Available online: https://www.weather.gov/chs/TropicalStormIrma-Sep2017f (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Masselink, G.; Hughes, M.G. Introduction to Coastal Geomorphology and Processes; Arnold: London, UK, 2003; p. 354. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, J.T.; Sherman, D.J. Fundamentals of aeolian sediment transport: Wind blown sand. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Schroder, J., Lancaster, N., Sherman, D.J., Baas, A.C.W., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 11, pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- USGS Coastal Change Hazards. Available online: https://marine.usgs.gov/coastalchangehazardsportal/ (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- Griffen, M.; Malsick, M.; Mizzell, H.; Moore, L. Historic rainfall and record-breaking flooding from Hurricane Florence in the Pee Dee Watershed. J. South Carolina Water Res. 2019, 6, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Irma | Florence | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SSHWS | Tropical storm | Tropical Storm | |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | Average | 7.3 * | 6.0 * |
| 2σ | 8.9 * | 7.2 * | |
| Wind Gust (m/s) | Average | 9.4 * | 7.6 * |
| 2σ | 11.5 * | 9.0 * | |
| Maximum | 30.1 * | 23.6 * | |
| Dominant Storm Wind Direction | NE * | SSW * | |
| Significant Wave Height (m) | Average | 1.8 * | 3.1 * |
| 2σ | 1.3 * | 1.4 * | |
| Storm Surge (m) MHHW | 1.28 ° | 0.45 # | |
| Storm Precipitation Total (mm) | 184.25 ° | 31.75 # |
| Irma | Florence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre- | Post- | Pre- | Post- | |
| SITE A | ||||
| Volume (m3) | 1762.2 | 1437.1 | 1488.9 | 1482.1 |
| nv | 1.00 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| SITE B | ||||
| Volume (m3) | 4934.6 | 2017.3 | 2953.5 | 2772.7 |
| nv | 1.00 | 0.41 | 1.00 | 0.94 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ellis, J.T.; Harris, M.E.; Román-Rivera, M.A.; Ferguson, J.B.; Tereszkiewicz, P.A.; McGill, S.P. Application of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale to Assess Sand Dune Response to Tropical Storms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090670
Ellis JT, Harris ME, Román-Rivera MA, Ferguson JB, Tereszkiewicz PA, McGill SP. Application of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale to Assess Sand Dune Response to Tropical Storms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(9):670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090670
Chicago/Turabian StyleEllis, Jean T., Michelle E. Harris, Mayra A. Román-Rivera, J. Brianna Ferguson, Peter A. Tereszkiewicz, and Sean P. McGill. 2020. "Application of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale to Assess Sand Dune Response to Tropical Storms" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 9: 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090670
APA StyleEllis, J. T., Harris, M. E., Román-Rivera, M. A., Ferguson, J. B., Tereszkiewicz, P. A., & McGill, S. P. (2020). Application of the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale to Assess Sand Dune Response to Tropical Storms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(9), 670. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8090670