Effects of Ethinylestradiol (EE2) and an Organophosphorus Flame Retardant (TCPP) on Gonadal Maturation in the Sea Urchin, Paracentrotus lividus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sea Urchins
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Chemicals and Stock Solutions
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Mortality
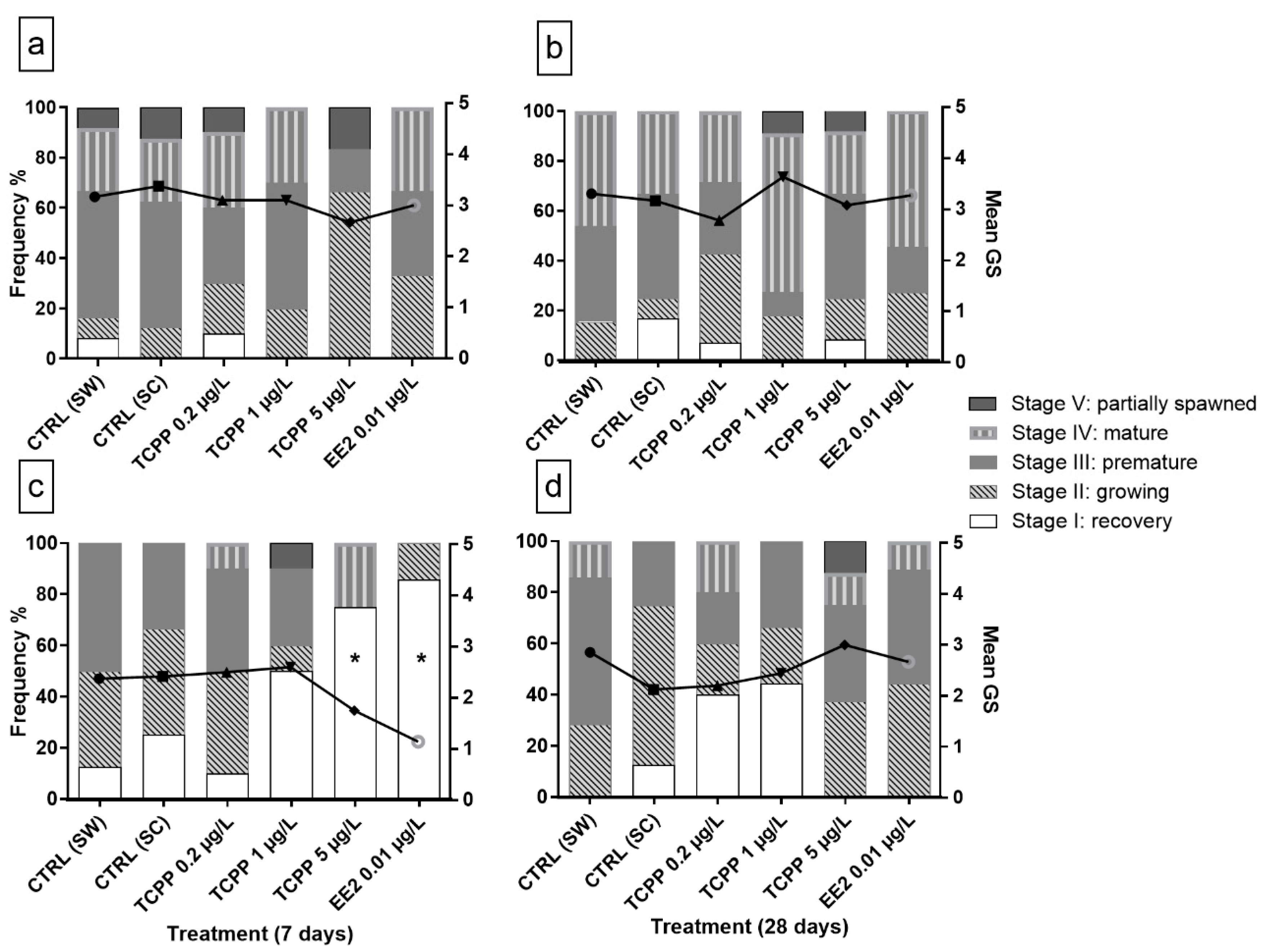
3.2. Sex and Gametogenic Stage
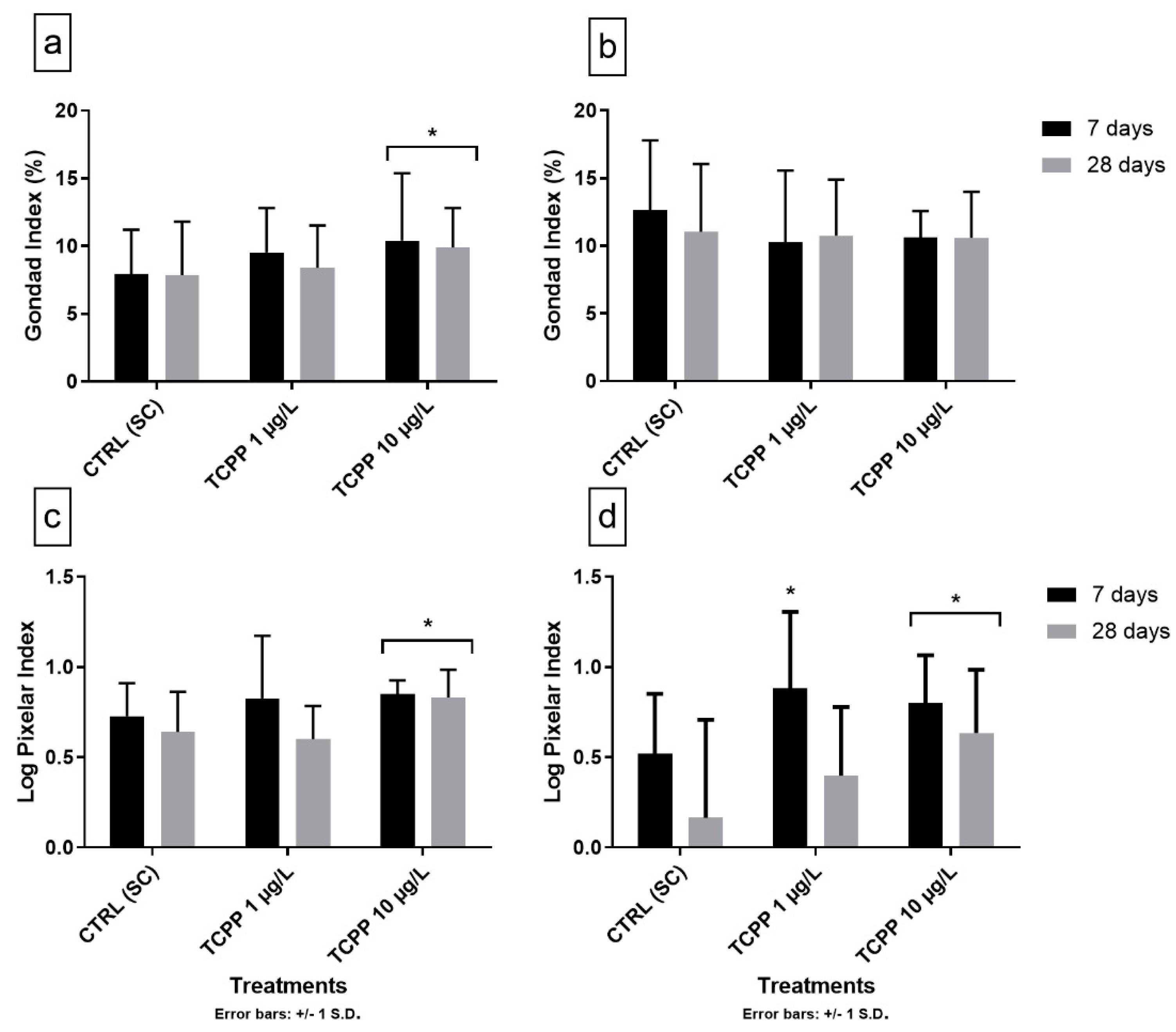
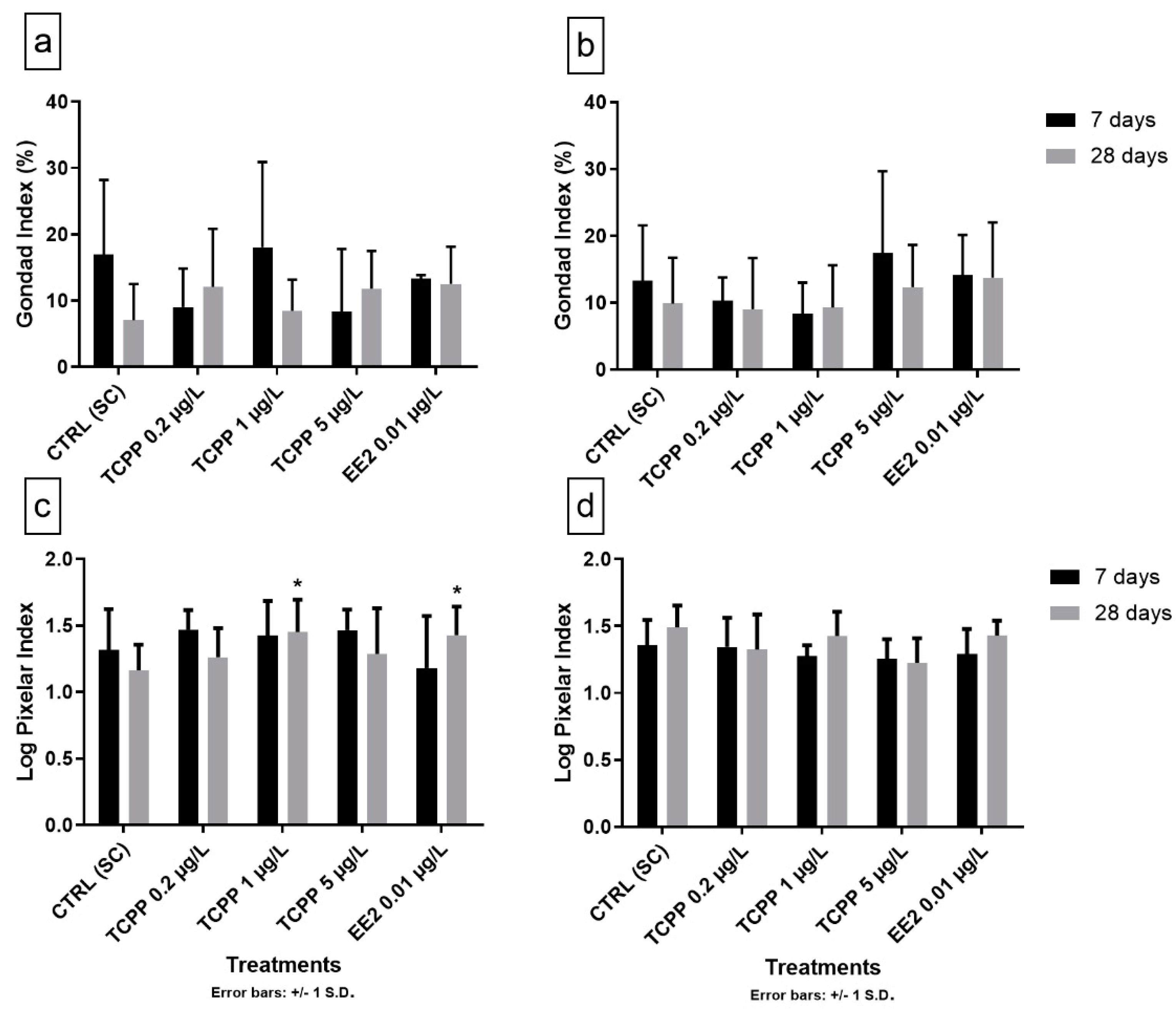
3.3. Gonad Growth and Pixelar Index
3.4. Natural and Anthropogenic Factors Affecting the Reproductive Cycle
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Commission. Environment. Endocrine Disruptors: Strategy. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/endocrine/strategy/index_en.htm (accessed on 10 February 2019).
- European Commission. Regulation (EC) No. 1907/2006 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 18 December 2006 concerning the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH), establishing a European Chemicals Agency, amending Directive 1999/45/EC and repealing Council Regulation (EEC) No. 793/93 and Commission Regulation (EC) No. 1488/94 as well as Council Directive 76/769/EEC and Commission Directives 91/155/EEC, 93/67/EEC, 93/105/EC and 2000/21/EC. Off. J. Eur. Union 2006, 396, 1–849. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Veen, I.; de Boer, J. Phosphorus flame retardants: Properties, production, environmental occurrence, toxicity and analysis. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1119–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regnery, J.; Püttmann, W. Occurrence and fate of organophosphorus flame retardants and plasticizers in urban and remote surface waters in Germany. Water Res. 2010, 44, 4097–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Syed, J.H.; Katsoyiannis, A.; Malik, R.N.; Farooqi, A.; Butt, A.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Cincinelli, A.; Jones, K.C. Legacy and emerging flame retardants (FRs) in the freshwater ecosystem: A review. Environ. Res. 2017, 152, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Concha-Graña, E.; López-Mahía, P.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Prada-Rodríguez, D. Emerging pollutants in sewage, surface and drinking water in Galicia (NW Spain). Chemosphere 2012, 86, 1040–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Cui, Q.; Wei, S.; Yu, H. Regional distribution of halogenated organophosphate flame retardants in seawater samples from three coastal cities in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lu, M.; Dong, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, W.; Zhao, M. Potential Estrogenic Effects of Phosphorus-Containing Flame Retardants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 6995–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ji, K.; Choi, K. Endocrine disruption potentials of organophosphate flame retardants and related mechanisms in H295R and MVLN cell lines and in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 114–115, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, B.; Shin, H.; Moon, H.-B.; Ji, K.; Kim, K.-T. Effects of tris (2-butoxyethyl) phosphate exposure on endocrine systems and reproduction of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jiang, L.; Liu, X.; Lv, J. Adsorption and aerobic biodegradation of four selected endocrine disrupting chemicals in soil–water system. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 76, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, C.; Boettcher, A.; Jones, A.G. Short-term exposure to a synthetic estrogen disrupts mating dynamics in a pipefish. Horm. Behav. 2010, 58, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, M.; O’Connor, W.; Dunstan, R.; MacFarlane, G. Exposure to 17α-ethynylestradiol causes dose and temporally dependent changes in intersex, females and vitellogenin production in the Sydney rock oyster. Ecotoxicology 2010, 19, 1440–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, G.-G.; Kookana, R.S.; Ru, Y.-J. Occurrence and fate of hormone steroids in the environment. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojana, G.; Gomiero, A.; Jonkers, N.; Marcomini, A. Natural and synthetic endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) in water, sediment and biota of a coastal lagoon. Environ. Int. 2007, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aris, A.Z.; Shamsuddin, A.S.; Praveena, S.M. Occurrence of 17α-ethynylestradiol (EE2) in the environment and effect on exposed biota: A review. Environ. Int. 2014, 69, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercurio, S.; Sugni, M.; Fernandes, D.; Porte, C.; Daniela, M.; Carnevali, C. Estrogen administration to the edible sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816). Zoosymposia 2012, 7, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugni, M.; Motta, D.; Tremolada, P.; Carnevali, M.D.C. Exploring endocrine regulation of sea urchin reproductive biology: Effects of 17ß-oestradiol. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2012, 92, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, K.M.; Gower, B.A.; Watts, S.A. Responses of ovaries and testes of Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) to dietary administration of estradiol, progesterone and testosterone. Mar. Biol. 2000, 137, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuma, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Akiyama, T. Effect of steroids on gonadal growth and gametogenesis in the juvenile red sea urchin Pseudocentrotus depressus. Biol. Bull. 1999, 196, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unuma, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Akiyama, T. Effects of oral administration of steroids on the growth of juvenile sea urchin, Pseudocentrotus depressus. Aquac. Sci. 1996, 44, 79–83. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, J.; Han, J.; Zhou, B.; Gong, Z.; Santos, E.M.; Huo, X.; Zheng, W.; Liu, H.; Yu, H.; Liu, C. Toxicogenomic Responses of Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae to Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) Phosphate (TDCPP) Reveal Possible Molecular Mechanisms of Developmental Toxicity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10574–10582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Li, R.; Zhao, J.; Wu, H. Determination and Prediction of the Binding Interaction between Organophosphate Flame Retardants and p53. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2014, 27, 1918–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noyes, P.D.; Haggard, D.E.; Gonnerman, G.D.; Tanguay, R.L. Advanced Morphological—Behavioral Test Platform Reveals Neurodevelopmental Defects in Embryonic Zebrafish Exposed to Comprehensive Suite of Halogenated and Organophosphate Flame Retardants. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 145, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lam, J.C.-W.; Man, Y.-C.; Lai, N.L.-S.; Kwok, K.Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Lam, P.K.-S.; Zhou, B. Bioconcentration, metabolism and neurotoxicity of the organophorous flame retardant 1,3-dichloro 2-propyl phosphate (TDCPP) to zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 158, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishaw, L.V.; Hunter, D.L.; Padnos, B.; Padilla, S.; Stapleton, H.M. Developmental Exposure to Organophosphate Flame Retardants Elicits Overt Toxicity and Alters Behavior in Early Life Stage Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 142, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, X.; Su, G.; Yu, L.; Letcher, R.J.; Hou, J.; Yu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Liu, C. Environmentally Relevant Concentrations of the Flame Retardant Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) Phosphate Inhibit Growth of Female Zebrafish and Decrease Fecundity. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14579–14587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wang, Q.; Fu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Gong, Z.; Wei, S.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; et al. Multiple bio-analytical methods to reveal possible molecular mechanisms of developmental toxicity in zebrafish embryos/larvae exposed to tris(2-butoxyethyl) phosphate. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 150, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Takeda, M.; Uchiyama, M. Toxicity, absorption and elimination of phosphoric acid triesters by killifish and goldfish. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1981, 27, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yin, H.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, F.; Deng, Y.; Lu, S. Preliminary ecotoxicity hazard evaluation of DOPO-HQ as a potential alternative to halogenated flame retardants. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekele, T.G.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Tan, F. Measurement and prediction of bioconcentration factors of organophosphate flame retardants in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 166, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Su, G.; Zou, M.; Yu, L.; Letcher, R.J.; Yu, H.; Giesy, J.P.; Zhou, B.; Liu, C. Effects of Tris(1,3-dichloro-2-propyl) Phosphate on Growth, Reproduction, and Gene Transcription of Daphnia magna at Environmentally Relevant Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12975–12983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavado, R.; Barbaglio, A.; Carnevali, M.D.C.; Porte, C. Steroid levels in crinoid echinoderms are altered by exposure to model endocrine disruptors. Steroids 2006, 71, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavado, R.; Sugni, M.; Candia Carnevali, M.D.; Porte, C. Triphenyltin alters androgen metabolism in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 79, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tato, T.; Salgueiro-González, N.; León, V.M.; González, S.; Beiras, R. Ecotoxicological evaluation of the risk posed by bisphenol A, triclosan, and 4-nonylphenol in coastal waters using early life stages of marine organisms (Isochrysis galbana, Mytilus galloprovincialis, Paracentrotus lividus, and Acartia clausi). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 232, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, A.; Montes, R.; Rodil, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Vidal-Liñán, L.; Beiras, R. Ecotoxicological Evaluation of the UV Filters Ethylhexyl Dimethyl p-Aminobenzoic Acid and Octocrylene Using Marine Organisms Isochrysis galbana, Mytilus galloprovincialis and Paracentrotus lividus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 72, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beiras, R.; Durán, I.; Bellas, J.; Sánches-Marín, P. Biological effects of contaminants: Paracentrotus lividus sea urchin embryo test with marine sediment elutriates. Ices Tech. Mar. Environ. Sci. 2012, 51, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Beiras, R.; Mariño-Balsa, J.C.; Fernández, N. Toxicity of Organic Compounds to Marine Invertebrate Embryos and Larvae: A Comparison Between the Sea Urchin Embryogenesis Bioassay and Alternative Test Species. Ecotoxicology 2005, 14, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novelli, A.A.; Argese, E.; Tagliapietra, D.; Bettiol, C.; Ghirardini, A.V. Toxicity of tributyltin and triphenyltin to early life-stages of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2002, 21, 859–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marín-Guirao, L.; Cesar, A.; Marin, A.; Lloret, J.; Vita, R. Establishing the ecological quality status of soft-bottom mining-impacted coastal water bodies in the scope of the Water Framework Directive. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasson, K.M.; Gower, B.A.; Hines, G.A.; Watts, S.A. Levels of progesterone, testosterone, and estradiol, and androstenedione metabolism in the gonads of Lytechinus variegatus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 2000, 126, 153–165. [Google Scholar]
- Wasson, K.M.; Watts, S.A. Chapter 5—Endocrine Regulation of Echinoid Reproduction. In Sea Urchins: Biology and Ecology, 3rd ed.; Lawrence, J.M., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 38, pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Barbaglio, A.; Sugni, M.; Di Benedetto, C.; Bonasoro, F.; Schnell, S.; Lavado, R.; Porte, C.; Candia Carnevali, D.M. Gametogenesis correlated with steroid levels during the gonadal cycle of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 147, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira-Pinto, E. Posible Efecto Tóxico de los Retardantes de Llama Organofosforados Sobre el Erizo de Mar Común (Paracentrotus lividus); University of Vigo: Vigo, Spain, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-González, L.E.; Diz, A.P.; Noche, G.G.; Lorenzo, S.M.; Beiras, R.; Sánchez-Marín, P. No evidence that vitellogenin protein expression is induced in marine mussels after exposure to an estrogenic chemical. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 137638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouréns, R.; Fernández, L.; Fernández-Boán, M.; Naya, I.; Freire, J. Reproductive dynamics of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus on the Galicia coast (NW Spain): Effects of habitat and population density. Mar. Biol. 2013, 160, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.L.; Battle, H.I. The gross and microscopic anatomy of the digestive tract of the oyster Crassostrea virginica (Gmelin). Can. J. Zool. 1957, 35, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, M. Annual reproductive cycles of the commercial sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus from an exposed intertidal and a sheltered subtidal habitat on the west coast of Ireland. Mar. Biol. 1990, 104, 275–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantilla-Aldana, L.; Campoy-López, P.; Pereira-Pinto, E.; Beiras, R. Pixelar index: A new quantitative approach for the assessment of reproductive condition in the purple sea urchin, Paracentrotus lividus, by image analysis. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirlet, C.; Grosjean, P.; Jangoux, M. Reproductive cycle of the echinoid Paracentrotus lividus: Analysis by means of the maturity index. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1998, 34, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, J.; Galera, J.; López, S.; Turon, X.; Palacín, C. Biological cycles and recruitment of Paracentrotus lividus (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) in two contrasting habitats. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1995, 122, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-España, A.I.; Martínez-Pita, I.; García, F.J. Gonadal growth and reproduction in the commercial sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck, 1816) (Echinodermata: Echinoidea) from southern Spain. Hydrobiologia 2004, 519, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Uz, S.; Carrasco, J.F.; Rodríguez, C. Temporal variability of spawning in the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus from northern Spain. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2018, 23, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catoira, J.L. Spatial and temporal evolution of the gonad index of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus (Lamarck) in Galicia, Spain. In Echinoderm Research; Emson, R., Smith, A., Campbell, A., Eds.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 295–298. [Google Scholar]
- Garmendia, J.M.; Menchaca, I.; Belzunce, M.J.; Franco, J.; Revilla, M. Seasonal variability in gonad development in the sea urchin (Paracentrotus lividus) on the Basque coast (Southeastern Bay of Biscay). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 61, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Irusta, J.M.; Goñi de Cerio, F.; Canteras, J.C. Reproductive cycle of the sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus in the Cantabrian Sea (northern Spain): Environmental effects. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. U. K. 2010, 90, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Osada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Mori, K. Changes in vitellin during oogenesis and effect of estradiol-17β on vitellogenesis in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas. Invertebr. Reprod. Dev. 1998, 33, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciocan, C.M.; Cubero-Leon, E.; Puinean, A.M.; Hill, E.M.; Minier, C.; Osada, M.; Fenlon, K.; Rotchell, J.M. Effects of estrogen exposure in mussels, Mytilus edulis, at different stages of gametogenesis. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 2977–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.A.; MacFarlane, G.R.; Kong, R.Y.C.; O’Connor, W.A.; Yu, R.M.K. Mechanistic insights into induction of vitellogenin gene expression by estrogens in Sydney rock oysters, Saccostrea glomerata. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 174, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.A.; MacFarlane, G.R.; Kong, R.Y.C.; Yu, R.M.K. Potential mechanisms underlying estrogen-induced expression of the molluscan estrogen receptor (ER) gene. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 179, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keay, J.; Bridgham, J.T.; Thornton, J.W. The Octopus vulgaris estrogen receptor is a constitutive transcriptional activator: Evolutionary and functional implications. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3861–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botticelli, C.R.; Hisaw, F.L.; Wotiz, H.H. Estrogens and Progesterone in the Sea Urchin (Strongylocentrotus franciscanus) and Pecten (Pecten hericius). Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1961, 106, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieleman, S.J.; Schoenmakers, H.J.N. Radioimmunoassays to determine the presence of progesterone and estrone in the starfish Asterias rubens. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1979, 39, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roast, S.D.; Benstead, R. Endocrine Disruption Horizon Scanning: Aquatic Invertebrates Review; SC030276/SR1; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2007.
- U.S. EPA. Flame Retardants Used in Flexible Polyurethane Foam: An Alternatives Assessment Update; EPA 744-R-15-002; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 612–615.

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campoy-López, P.; Pereira-Pinto, E.; Mantilla-Aldana, L.; Beiras, R. Effects of Ethinylestradiol (EE2) and an Organophosphorus Flame Retardant (TCPP) on Gonadal Maturation in the Sea Urchin, Paracentrotus lividus. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080611
Campoy-López P, Pereira-Pinto E, Mantilla-Aldana L, Beiras R. Effects of Ethinylestradiol (EE2) and an Organophosphorus Flame Retardant (TCPP) on Gonadal Maturation in the Sea Urchin, Paracentrotus lividus. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(8):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080611
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampoy-López, Pedro, Estefanía Pereira-Pinto, Leonardo Mantilla-Aldana, and Ricardo Beiras. 2020. "Effects of Ethinylestradiol (EE2) and an Organophosphorus Flame Retardant (TCPP) on Gonadal Maturation in the Sea Urchin, Paracentrotus lividus" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 8: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080611
APA StyleCampoy-López, P., Pereira-Pinto, E., Mantilla-Aldana, L., & Beiras, R. (2020). Effects of Ethinylestradiol (EE2) and an Organophosphorus Flame Retardant (TCPP) on Gonadal Maturation in the Sea Urchin, Paracentrotus lividus. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(8), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080611





