Flow, Sediment, and Morpho-Dynamics of River Confluence in Tidal and Non-Tidal Environments
Abstract
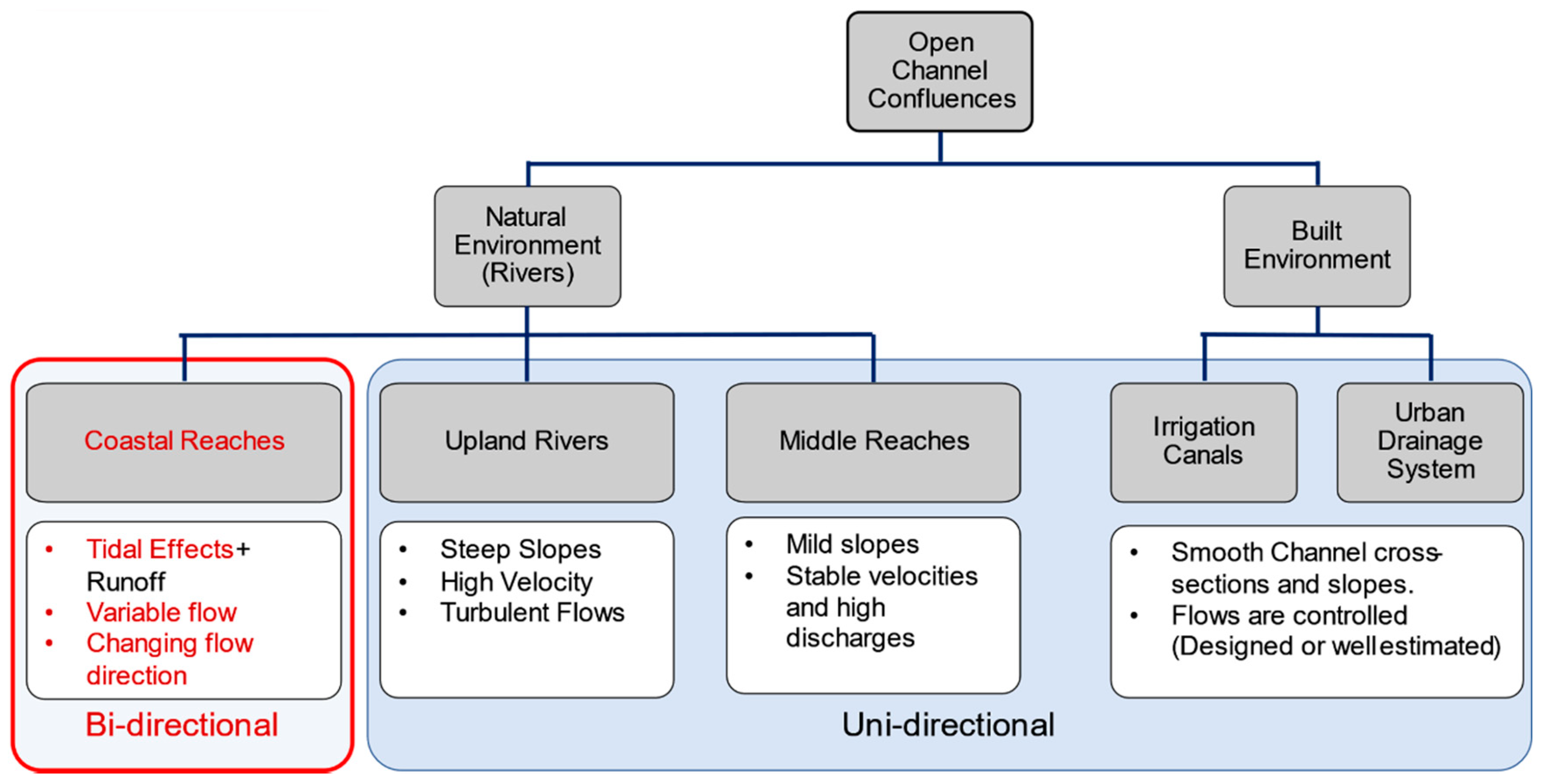
:1. Introduction
2. Hydrodynamics of River Confluences
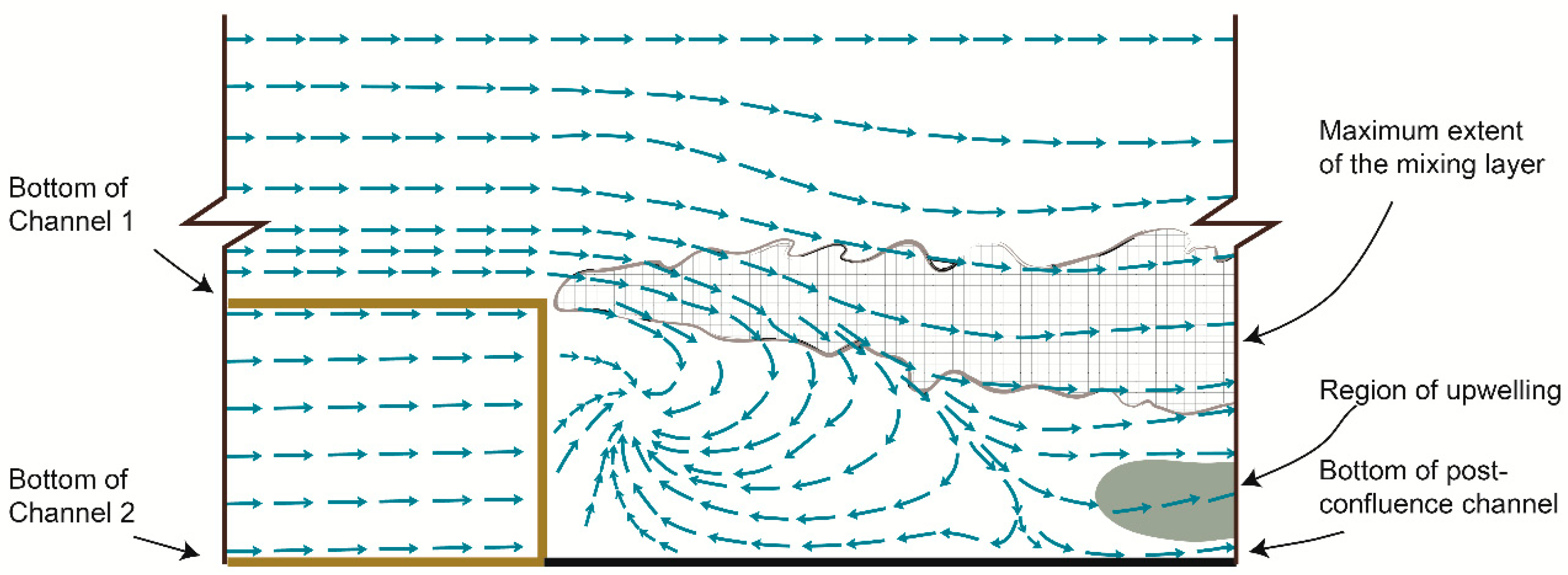
2.1. Mixing Zone and Shear Layer
2.2. Flow Stagnation
2.3. Flow Separation
2.4. Flow Acceleration and Recovery
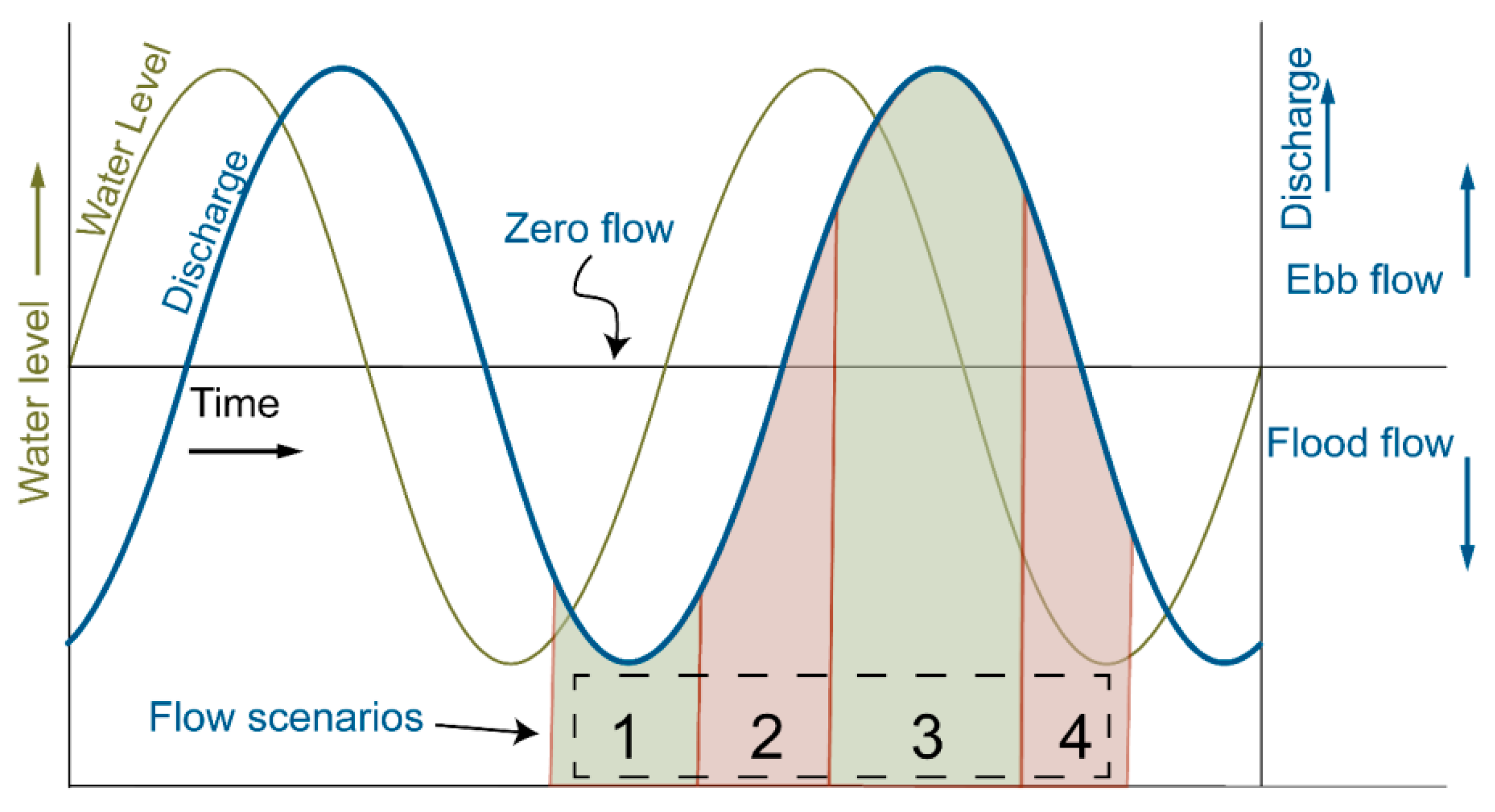
2.5. Tidal Flow Pattens
3. Sediment Transport and Morphology
3.1. Sediment Transport
3.2. Morphological Characteristics
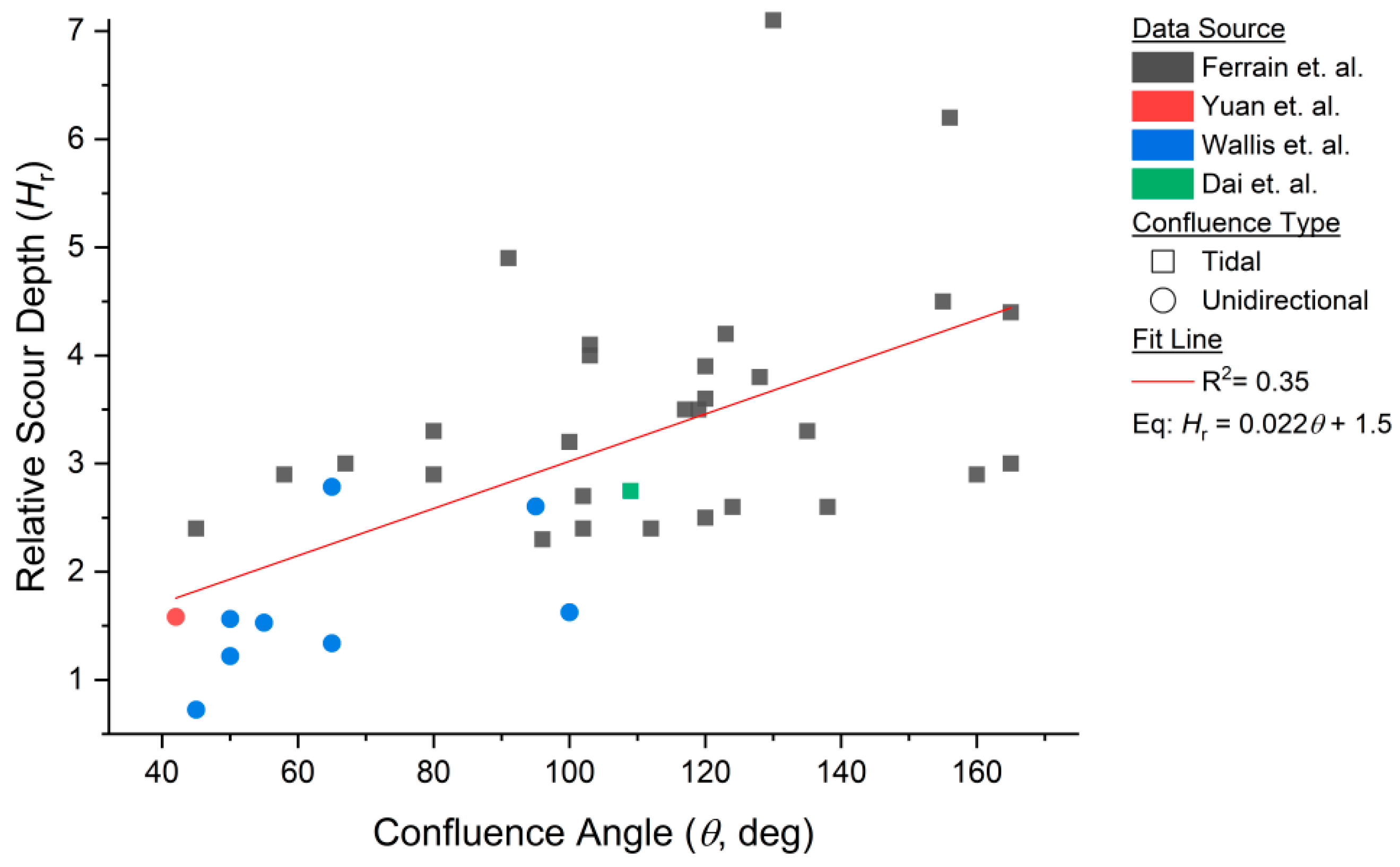
3.2.1. Scour-Hole
3.2.2. Mid-Channel Bars
3.2.3. Bank-Attached Bars
4. Key Factors Affecting the Morpho-Dynamics
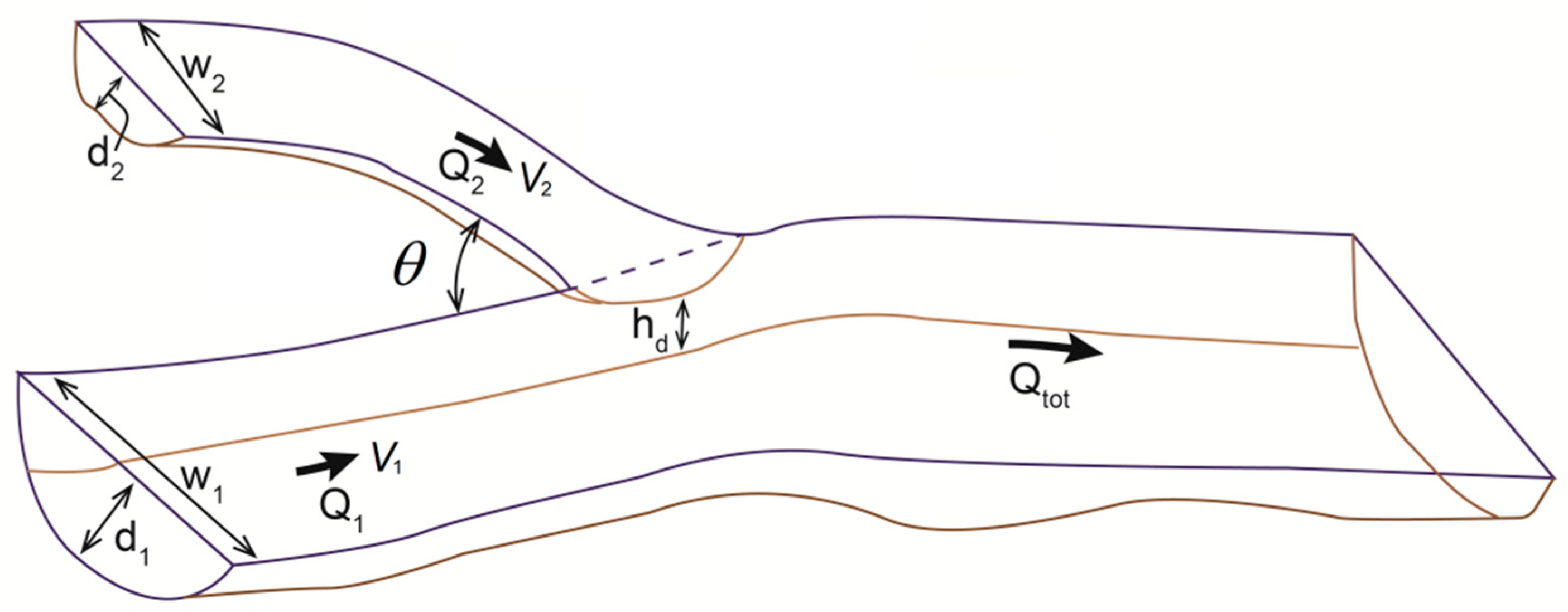
4.1. Confluence Planform
4.2. Ratio of Velocity, Discharge, and Momentum
4.3. Bed Discordance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taylor, E.H. Flow characteristics at rectangular open-channel junctions. Trans. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1944, 109, 893–902. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.P. High Mountain Streams: Effects of Geology on Channel Characteristics and Bed Material; State Bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology: Socorro, NM, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Mosley, M.P. An experimental study of channel confluences. J. Geol. 1976, 84, 535–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L. Flow Dynamics and Sediment Transport at River Channel Confluences. Ph.D. Thesis, University of London, London, UK, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.L. Sediment transport and bed morphology at river channel confluences. Sedimentology 1988, 35, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Tang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xia, Y. Water flow and sediment transport at open-channel confluences: An experimental study. J. Hydraul. Res. 2018, 56, 333–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Smith, G.H.S.; Best, J.L.; Nicholas, A.P.; Bull, J.M.; Vardy, M.E.; Sarker, M.H.; Goodbred, S. The planform mobility of river channel confluences: Insights from analysis of remotely sensed imagery. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2018, 176, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Rhoads, B.L.; Greenberg, J.A. Use of multispectral satellite remote sensing to assess mixing of suspended sediment downstream of large river confluences. J. Hyd. 2018, 556, 325–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanzoni, S. Long-term evolution and morphodynamic equilibrium of tidal channels. JGR 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seminara, G.; Lanzoni, S.; Tambroni, N.; Toffolon, M. How long are tidal channels? JFM 2010, 643, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leeder, M.R. On the interactions between turbulent flow, sediment transport and bedform mechanics in channelized flows. In Modern and Ancient Fluvial Systems; Collinson, J.D., Lewin, J., Eds.; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Oxford, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashworth, P.J.; Ferguson, R.I. Interrelationships of channel processes, changes and sediments in a proglacial braided river. Geogr. Ann. Ser. A Phys. Geogr. 1986, 68, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittaluga, M.B.; Tambroni, N.; Canestrelli, A.; Slingerland, R.; Lanzoni, S.; Seminara, G. Where river and tide meet: The morphodynamic equilibrium of alluvial estuaries. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 75–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Yang, J.; Lundström, S.; Dai, W. Understanding morphodynamic changes of a tidal river confluence through field measurements and numerical modeling. Water 2018, 10, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Coco, G.; Townend, I.; Olabarrieta, M.; van der Wegen, M.; Gong, Z.; D’Alpaos, A.; Gao, S.; Jaffe, B.E.; Gelfenbaum, G.; et al. Is “Morphodynamic Equilibrium” an oxymoron? Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 165, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolfram, P.J.; Fringer, O.B.; Monsen, N.E.; Gleichauf, K.T.; Fong, D.A.; Monismith, S.G. Modeling intrajunction dispersion at a well-mixed tidal river junction. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142, 04016019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gleichauf, K.; Wolfram, P.; Monsen, N.; Fringer, O.; Monismith, S. Dispersion mechanisms of a tidal river junction in the sacramento–san joaquin delta, california. San Fr. Estuary Watershed Sci. 2014, 12, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginsberg, S.S.; Perillo, G.M.E. Deep-scour holes at tidal channel junctions, Bahia Blanca Estuary, Argentina. Mar. Geol. 1999, 160, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginsberg, S.S.; Perillo, G.M.E. Characteristics of tidal channels in a mesotidal Estuary of Argentina. J. Coast. Res. 2004, 20, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, B.; Cui, Y.; Kettner, A.J.; Peacock, D.H.; Syvitski, J.P.M. Simulating changes to the sediment transport regime of the Waipaoa River, New Zealand, driven by climate change in the twenty-first century. GPC 2009, 67, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Madricardo, F.; Rizzetto, F.; Kiver, W.M.; Bellafiore, D.; Umgiesser, G.; Kruss, A.; Zaggia, L.; Foglini, F.; Ceregato, A.; et al. Geomorphology of scour holes at tidal channel confluences. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2018, 123, 1386–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P.E.; Ferguson, R.I.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Ashworth, P.J.; Paola, C. Secondary flow in anabranch confluences of a braided, gravel-bed stream. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1992, 17, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L.; Rhoads, B.L. Sediment Transport, Bed Morphology and the Sedimentology of River Channel Confluences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 45–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswal, S.K.; Mohapatra, P.K.; Muralidhar, K. Flow separation at an open channel confluence. ISH J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canelas, O.B.; Ferreira, R.M.L.; Guillén-Ludeña, S.; Alegria, F.C.; Cardoso, A.H. Three-dimensional flow structure at fixed 70° open-channel confluence with bed discordance. J. Hydraul. Res. 2019, 58, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.M.; Robson, C.; Lapointe, M.F.; Gaskin, S.J. Comparing different methods of bed shear stress estimates in simple and complex flow fields. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2004, 29, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, G.; Miyawaki, S.; Rhoads, B.; Sukhodolov, A.; Kirkil, G. Structure of turbulent flow at a river confluence with momentum and velocity ratios close to 1: Insight provided by an eddy-resolving numerical simulation. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Bilal, A.; Xie, Q.; Ahmad, I.; Joshi, I. Numerical modeling for hydrodynamics and near-surface flow patterns of a tidal confluence. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 36, 295–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Yang, J.; Lundström, T.S. Field studies and 3D modelling of morphodynamics in a meandering river reach dominated by tides and suspended load. Fluids 2019, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dordevic, D. Numerical study of 3D flow at right-angled confluences with and without upstream planform curvature. J. Hydroinformatics 2013, 15, 1073–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbrook, K.F. Numerical, Field and Laboratory Studies of Three-Dimensional Flow Structures at River Channel Confluences. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Best, J.L. The morphology of river channel confluences. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 1986, 10, 157–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, J.R. Lateral mixing of the Liard and Mackenzie rivers downstream from their confluence. CaJES 1970, 7, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L.; Roy, A.G. Mixing-layer distortion at the confluence of channels of different depth. Nature 1991, 350, 411–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, S.N.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L.; Orfeo, O.; Kostaschuk, R.A.; Hardy, R.J. Causes of rapid mixing at a junction of two large rivers: Río Paraná and Río Paraguay, Argentina. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2008, 113, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L.; Lane, S.N.; Kostaschuk, R.A.; Hardy, R.J.; Orfeo, O.; Amsler, M.L.; Szupiany, R.N. Large river channel confluences. In River Confluences, Tributaries and the Fluvial Network; Rice, S.P., Roy, A.G., Rhoads, B.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 73–91. [Google Scholar]
- Sukhodolov, A.N.; Schnauder, I.; Uijttewaal, W.S.J. Dynamics of shallow lateral shear layers: Experimental study in a river with a sandy bed. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vermaas, D.A.; Uijttewaal, W.S.J.; Hoitink, A.J.F. Lateral transfer of streamwise momentum caused by a roughness transition across a shallow channel. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén-Ludeña, S.; Franca, M.J.; Alegria, F.; Schleiss, A.J.; Cardoso, A.H. Hydromorphodynamic effects of the width ratio and local tributary widening on discordant confluences. Geomorphology 2017, 293, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijttewaal, W.S.J.; Booij, R. Effects of shallowness on the development of free-surface mixing layers. Phys. Fluids 2000, 12, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, S. Hydrodynamics and contaminant transport on a degraded bed at a 90-degree channel confluence. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2017, 18, 443–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.M.; Ramamurthy, A.S.; Han, S. Three-dimensional numerical modeling of mixing at river confluences. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2004, 130, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchez, J.; Lajeunesse, E.; Gaillardet, J.; France-Lanord, C.; Dutra-Maia, P.; Maurice, L. Turbulent mixing in the Amazon River: The isotopic memory of confluences. Eearth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2010, 290, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Kenworthy, S.T. Flow structure at an asymmetrical stream confluence. Geomorphology 1995, 11, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.M.; Lane, S.N. Modelling Hydraulics and Sediment Transport at River Confluences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyer, C.; Roy, A.G.; Best, J.L. Dynamics of a river channel confluence with discordant beds: Flow turbulence, bed load sediment transport, and bed morphology. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2006, 111, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Sukhodolov, A.N. Lateral momentum flux and the spatial evolution of flow within a confluence mixing interface. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Kenworthy, S.T. Time-averaged flow structure in the central region of a stream confluence. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1998, 23, 171–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Sukhodolov, A.N. Spatial and temporal structure of shear layer turbulence at a stream confluence. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Sukhodolov, A.N. Field investigation of three-dimensional flow structure at stream confluences: 1. Thermal mixing and time-averaged velocities. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2393–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.M.; Richer, A.; Kirkbride, A.D.; Roy, A.G.; Han, S. Spatial patterns of water surface topography at a river confluence. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2002, 27, 913–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J.L.; Reid, I. Separation zone at open-channel junctions. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1984, 110, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Larry, J.W.; Yong, G.L. Three-dimensional numerical study of flows in open-channel junctions. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2002, 128, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unde, M.G.; Dhakal, S. Sediment characteristics at river confluences: A case study of the Mula-Kas confluence, Maharashtra, India. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2009, 33, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.M.; Roy, A.G.; Best, J.L.; Boyer, C.J. Bed morphology and sedimentology at the confluence of unequal depth channels. Geomorphology 1993, 8, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbrook, K.F.; Lane, S.N.; Richards, K.S.; Biron, P.M.; Roy, A.G. Role of bed discordance at asymmetrical river confluences. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Serres, B.; Roy, A.G.; Biron, P.M.; Best, J.L. Three-dimensional structure of flow at a confluence of river channels with discordant beds. Geomorphology 1999, 26, 313–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.; Best, J.L.; André, G.R. Effects of bed discordance on flow dynamics at open channel confluences. J. Hydraul. Eng. 1996, 122, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoads, B.L.; Riley, J.D.; Mayer, D.R. Response of bed morphology and bed material texture to hydrological conditions at an asymmetrical stream confluence. Geomorphology 2009, 109, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szupiany, R.N.; Amsler, M.L.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L. Morphology, flow structure, and suspended bed sediment transport at two large braid-bar confluences. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wallis, E.; Nally, R.M.; Lake, P.S. A Bayesian analysis of physical habitat changes at tributary confluences in cobble-bed upland streams of the Acheron River basin, Australia. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cushman-Roisin, B.; Constantinescu, G.S. Dynamical adjustment of two streams past their confluence. J. Hydraul. Res. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, L. Confluence environments at the scale of river networks. In River Confluences, Tributaries and the Fluvial Network; Rice, S.P., Roy, A.G., Rhoads, B.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008; p. 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, R.; Hoey, T. Effects of Tributaries on Main-Channel Geomorphology; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.P. Which tributaries disrupt downstream fining along gravel-bed rivers? Geomorphology 1998, 22, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.P.; Kiffney, P.; Greene, C.; Pess, G.R. The Ecological Importance of Tributaries and Confluences; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 209–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, S.P.; Rhoads, B.L.; Roy, A.G. Introduction: River Confluences, Tributaries and the Fluvial Network; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benda, L.; Veldhuisen, C.; Black, J. Debris flows as agents of morphological heterogeneity at low-order confluences, Olympic Mountains, Washington. GSAMB 2003, 115, 1110–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, K.E.; Renshaw, C.E.; Magilligan, F.J.; Dade, W.B. Temporal and spatial scales of geomorphic adjustments to reduced competency following flow regulation in bedload-dominated systems. Geomorphology 2010, 118, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musselman, Z.A. The localized role of base level lowering on channel adjustment of tributary streams in the Trinity River basin downstream of Livingston Dam, Texas, USA. Geomorphology 2011, 128, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, P.; Roy, A.G.; Best, J.L. Turbulent flow structure at concordant and discordant open-channel confluences. Exp. Fluids 1996, 21, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridge, J.S.; Gabel, S.L. Flow and sediment dynamics in a low sinuosity, braided river: Calamus River, Nebraska Sandhills. Sedimentology 1992, 39, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradbrook, K.F.; Biron, P.M.; Lane, S.N.; Richards, K.S.; Roy, A.G. Investigation of controls on secondary circulation in a simple confluence geometry using a three-dimensional numerical model. Hydrol. Process. 1998, 12, 1371–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Bilal, A.; Xie, Q.; Zhai, Y. Numerical Simulation of a Deep-Scour Hole in a Tidal River Confluence Using Delft 3D. In Proceedings of the 37th IAHR World Congress, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 13–18 August 2017; pp. 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Gaucherel, C.; Frelat, R.; Salomon, L.; Rouy, B.; Pandey, N.; Cudennec, C. Regional watershed characterization and classification with river network analyses. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2017, 42, 2068–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.; Marpu, P.R.; Ouarda, T. Impact of river network type on the time of concentration. Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Schmidt, A.R. Application of Gibbs’ model to urban drainage networks: A case study in southwestern Chicago, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P.E.; Parker, G. Confluence scour in coarse braided streams. Water Resour. Res. 1983, 19, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Best, J.L. Flow dynamics at river channel confluences: Implications for sediment transport and bed morphology. In Recent Developments in Fluvial Sedimentology; Ethridge, F.G., Flores, R.M., Harvey, M.D., Eds.; SEPM Society for Sedimentary Geology: Tulsa, OK, USA, 1987; Volume 39, p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Q. Field Measurements and Numerical Simulations of Sediment Transport in a Tidal River. Ph.D. Thesis, Luleå University of Technology, Luleå, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Guillén-Ludeña, S. Hydro-Morphodynamics of Open-Channel Confluences with Low Discharge Ratio and Dominant Tributary Sediment Supply; EPFL: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Guillen-Ludena, S.; Franca, M.J.; Cardoso, A.H.; Schleiss, A.J. Evolution of the hydromorphodynamics of mountain river confluences for varying discharge ratios and junction angles. Geomorphology 2016, 255, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Ribeiro, M.; Blanckaert, K.; Roy, A.G.; Schleiss, A.J. Flow and sediment dynamics in channel confluences. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukhodolov, A.N.; Rhoads, B.L. Field investigation of three-dimensional flow structure at stream confluences: 2. Turbulence. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 2411–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmore, P.E.; Gardner, J.T. Unconfined Confluences in Braided Rivers; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2008; pp. 119–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.G.; Bergeron, N. Flow and particle paths at a natural river confluence with coarse bed material. Geomorphology 1990, 3, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancock, M.J. The Dynamics of Upland River Confluences. Ph.D. Thesis, Durham University, Durham, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoldi, W.; Zanoni, W.L.; Tubino, M. Assessment of morphological changes induced by flow and flood pulses in a gravel bed braided river: The Tagliamento River (Italy). Geomorphology 2010, 114, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, S.T.; Underwood, E.F.; Frueh, W.T. Sediment reservoirs at mountain stream confluences: Dynamics and effects of tributaries dominated by debris-flow and fluvial processes. GSAMB 2010, 122, 1775–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjerfve, B.; Shao, C.-C.; Stapor, F.W. Formation of deep scour holes at the junction of tidal creeks: An hypothesis. Mar. Geol. 1979, 33, M9–M14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambrook-Smith, G.H.; Ashworth, P.J.; Best, J.L.; Woodward, J.; Simpson, C.J. The morphology and facies of sandy braided rivers: Some considerations of scale invariance. In Fluvial Sedimentology VII; Blum, M.D., Marriott, S.B., Leclair, S.F., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfeo, O.; Parsons, D.R.; Best, J.L.; Lane, S.N.; Hardy, R.J.; Kostaschuk, R.A.; Szupiany, R.N.; Amsler, M.L. Morphology and flow structures in a large confluence-diffluence. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Fluvial Hydraulics, Lisbon, Purtagal, 6–8 September 2006; pp. 1277–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Bradbrook, K.F.; Lane, S.N.; Richards, K.S. Numerical simulation of three-dimensional, time-averaged flow structure at river channel confluences. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2731–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bradbrook, K.F.; Lane, S.N.; Richards, K.S.; Biron, P.M.; Roy, A.G. Large Eddy Simulation of periodic flow characteristics at river channel confluences. J. Hydraul. Res. 2000, 38, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penna, N.; De Marchis, M.; Canelas, O.; Napoli, E.; Cardoso, A.; Gaudio, R. Effect of the junction angle on turbulent flow at a hydraulic confluence. Water 2018, 10, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riley, J.D.; Rhoads, B.L.; Parsons, D.R.; Johnson, K.K. Influence of junction angle on three-dimensional flow structure and bed morphology at confluent meander bends during different hydrological conditions. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2015, 40, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, R.B.; Kuhn, N.J. Hydraulic conditions in experimental rill confluences and scour in erodible soils. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, G.; Miyawaki, S.; Rhoads, B.; Sukhodolov, A. Numerical analysis of the effect of momentum ratio on the dynamics and sediment-entrainment capacity of coherent flow structures at a stream confluence. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2012, 117, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, C.J.; Croke, J.C.; Purvis-Smith, D. Floodplain sediment disconnectivity at a tributary junction and valley constriction site in the Fitzroy River basin, Queensland, Australia. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindfessel, L.; Creelle, S.; De Mulder, T. Flow patterns in an open channel confluence with increasingly dominant tributary inflow. Water 2015, 7, 4724–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudet, J.M.; Roy, A.G. Effect of bed morphology on flow mixing length at river confluences. Nature 1995, 373, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludeña, S.G.; Cheng, Z.; Constantinescu, G.; Franca, M.J. Hydrodynamics of mountain-river confluences and its relationship to sediment transport. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 901–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhodolov, A.N.; Krick, J.; Sukhodolova, T.A.; Cheng, Z.; Rhoads, B.L.; Constantinescu, G.S. Turbulent flow structure at a discordant river confluence: Asymmetric jet dynamics with implications for channel morphology. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2017, 122, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Items | Non-Tidal Confluence | Tide-Driven Confluence |
|---|---|---|
| Flow volume timescale | daily/seasonal | hours |
| Main sediment forcing | river run-off (fresh-water) | tides (salty-water) |
| Sediment concentration timescale | days–weeks | hours |
| Sediment transport direction | unidirectional | bidirectional |
| Morphodynamic adaption time scale | months–years | weeks–months/years |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilal, A.; Xie, Q.; Zhai, Y. Flow, Sediment, and Morpho-Dynamics of River Confluence in Tidal and Non-Tidal Environments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080591
Bilal A, Xie Q, Zhai Y. Flow, Sediment, and Morpho-Dynamics of River Confluence in Tidal and Non-Tidal Environments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(8):591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080591
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilal, Ahmed, Qiancheng Xie, and Yanyan Zhai. 2020. "Flow, Sediment, and Morpho-Dynamics of River Confluence in Tidal and Non-Tidal Environments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 8: 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080591
APA StyleBilal, A., Xie, Q., & Zhai, Y. (2020). Flow, Sediment, and Morpho-Dynamics of River Confluence in Tidal and Non-Tidal Environments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(8), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8080591






