Field Measurements of a High-Energy Headland Deflection Rip Current: Tidal Modulation, Very Low Frequency Pulsation and Vertical Structure
Abstract
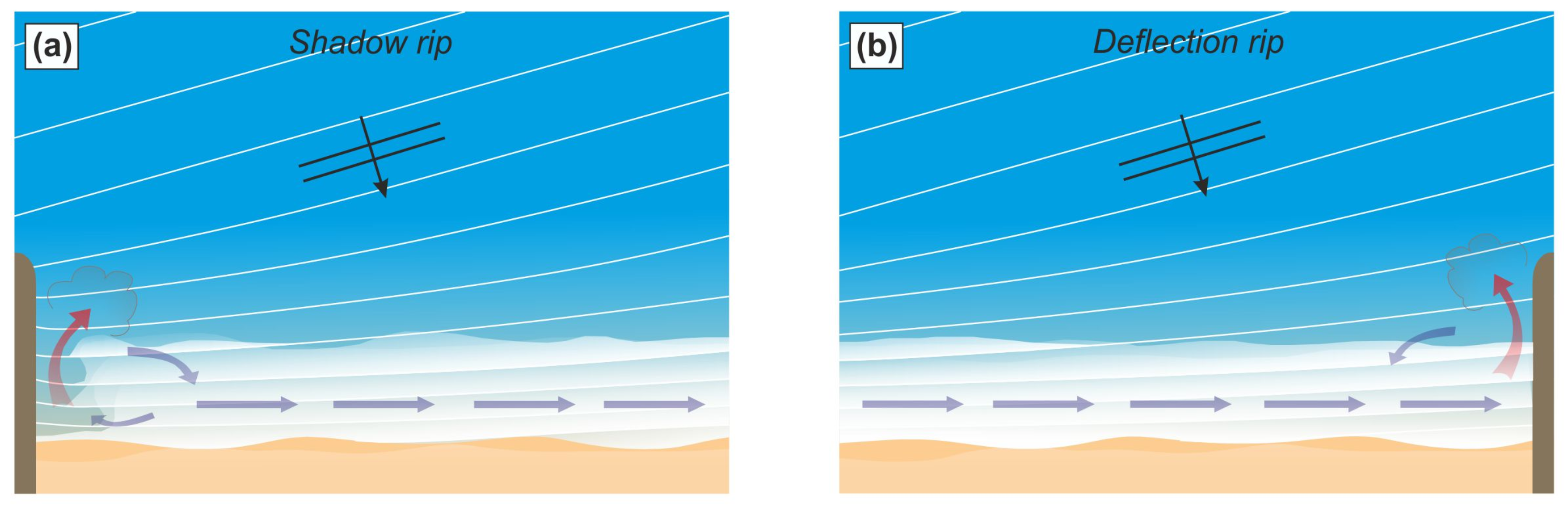
1. Introduction
2. Field Experiment
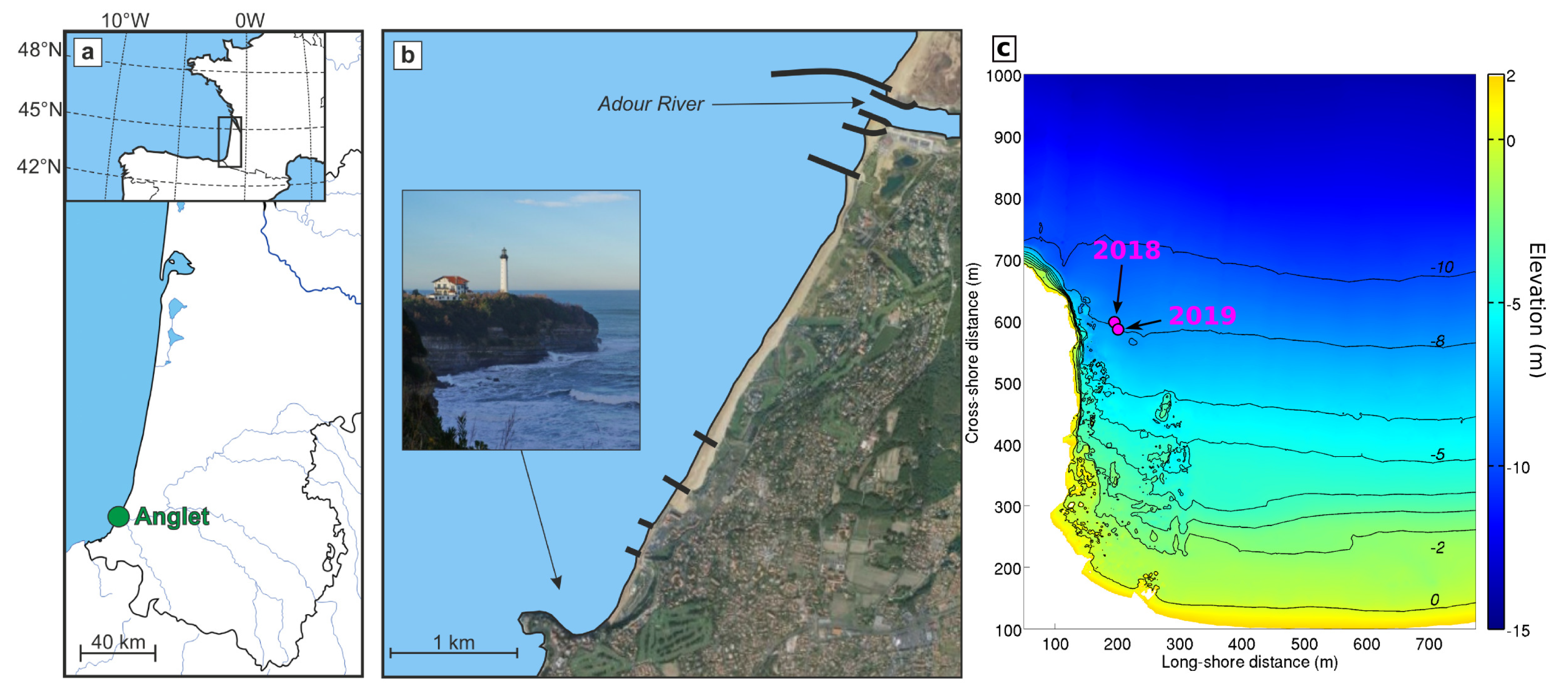
2.1. Field Site
2.2. Data and Methods
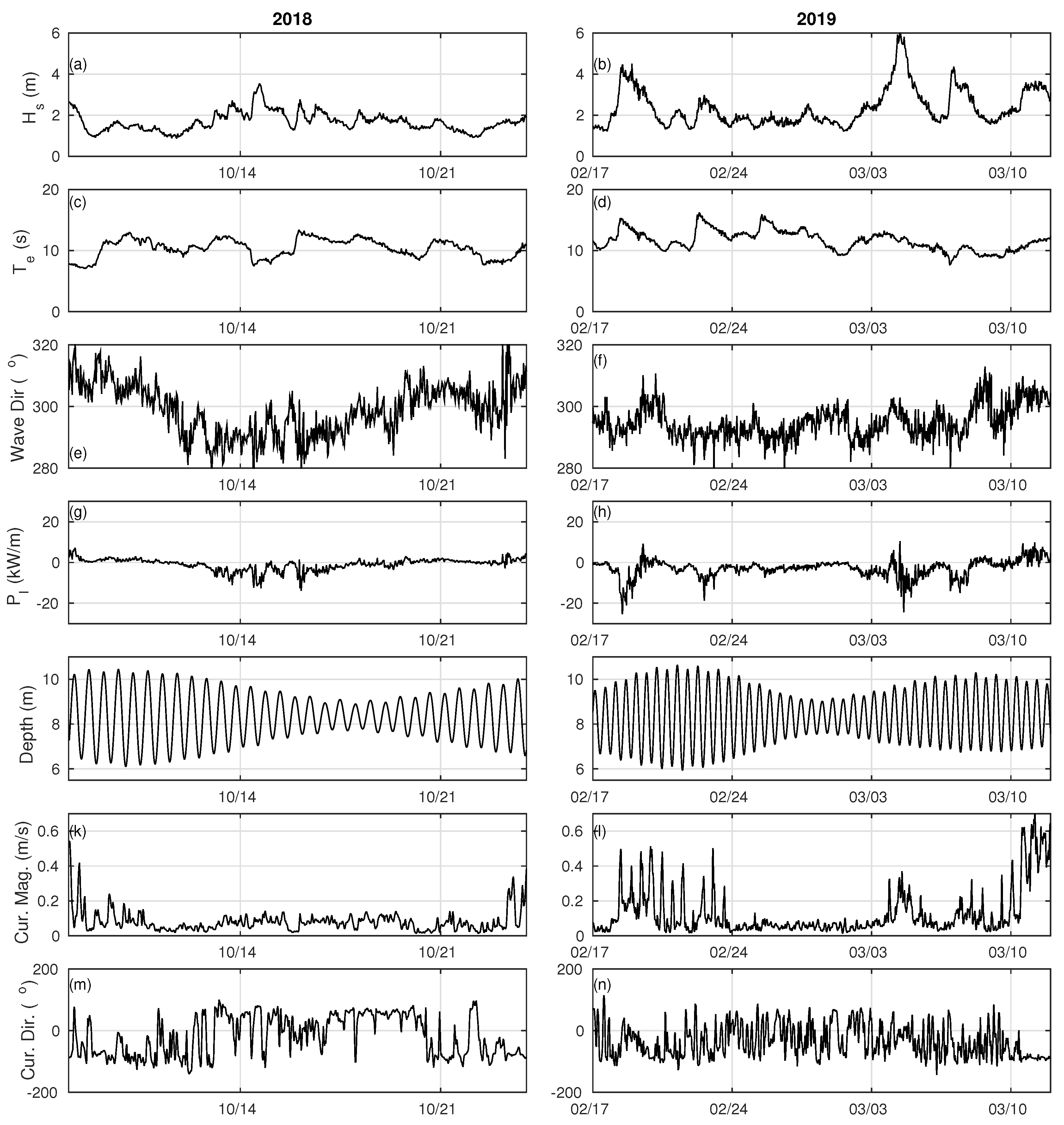
2.3. Field Conditions
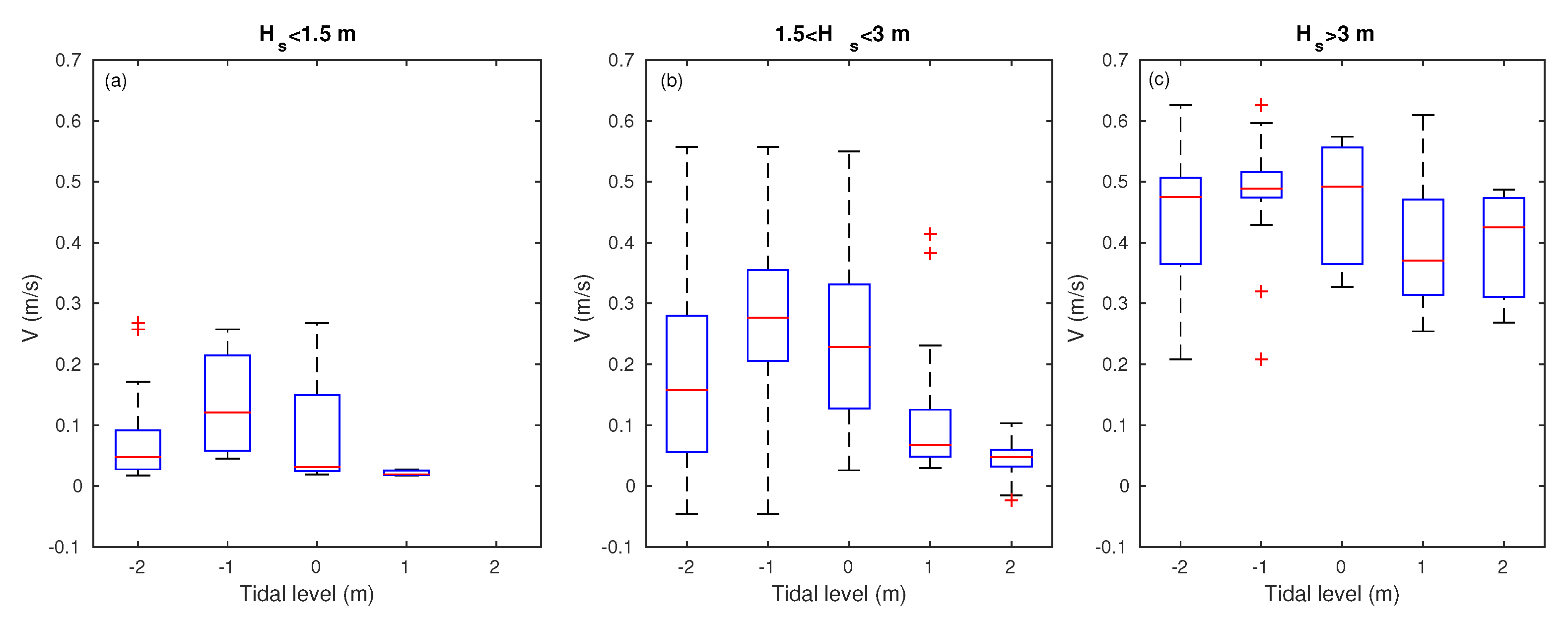
3. Results
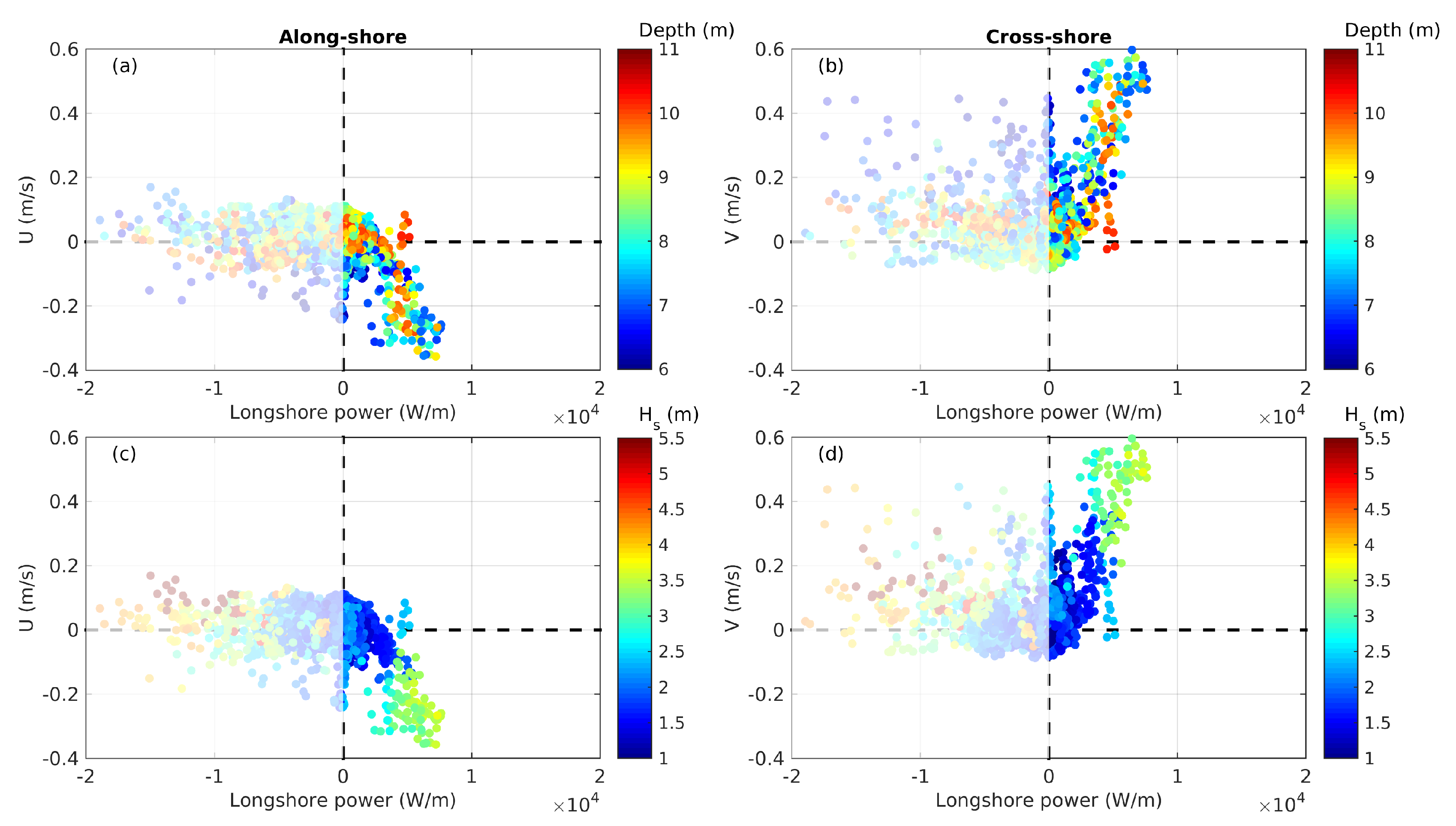
3.1. Headland Rip Flow
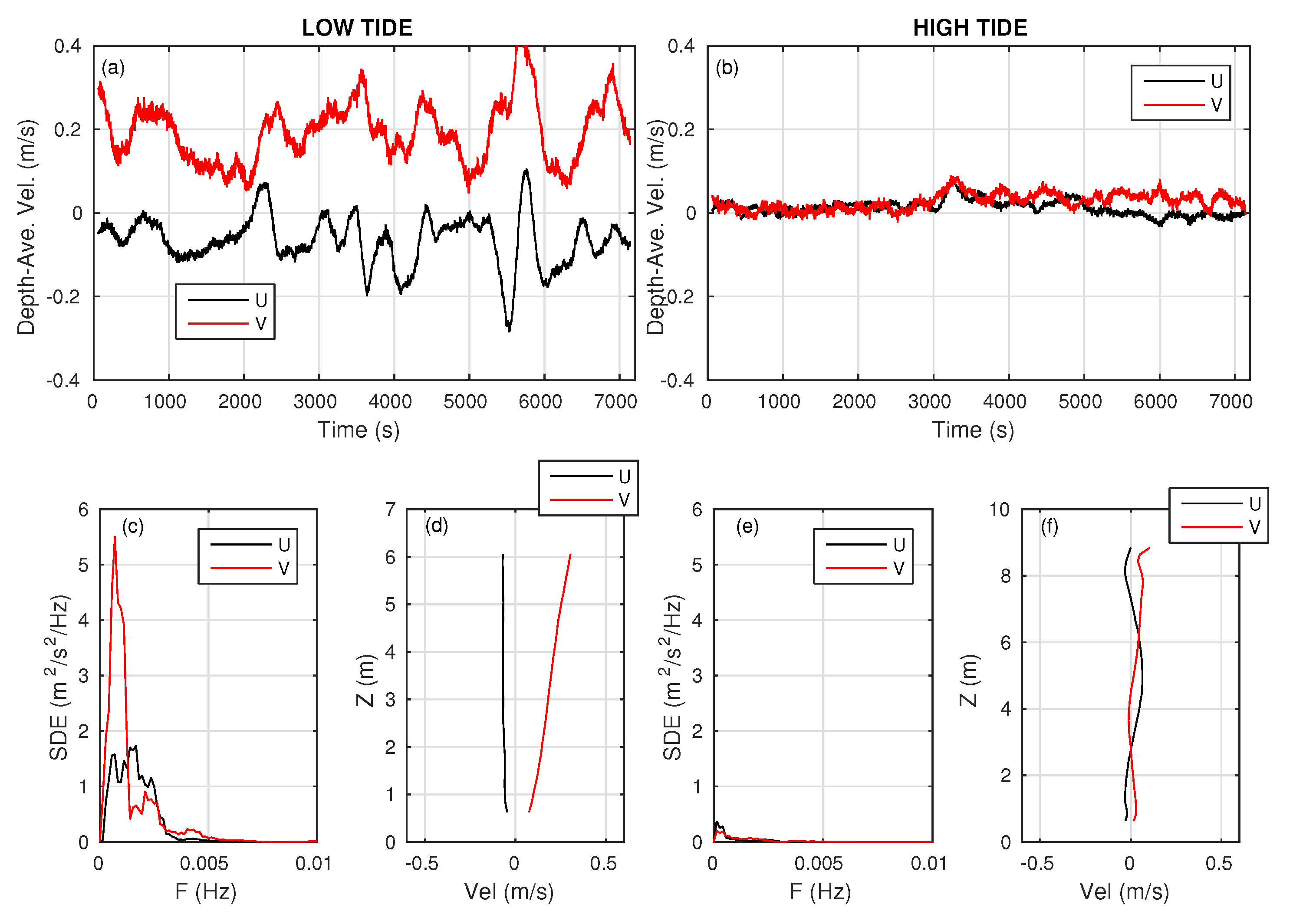
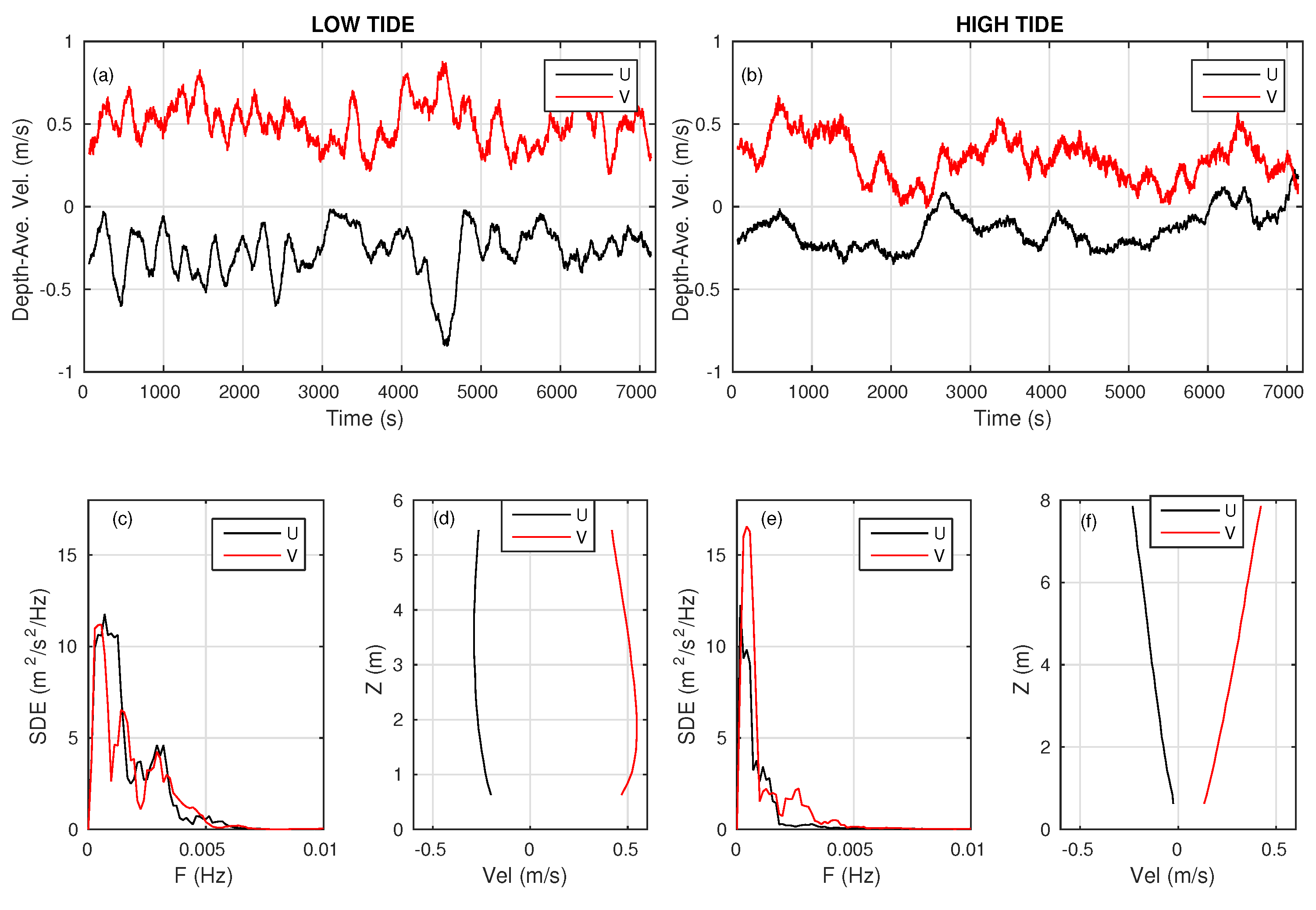
3.2. Representative Rip Flow Events
3.2.1. Moderate-Energy Deflection Rip
3.2.2. High-Energy Deflection Rip
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Short, A.D.; Masselink, G. Embayed and structurally controlled beaches. In Handbook of Beach and Shoreface Morphodynamics; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 230–250. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, R.; Baquerizo, A.; Ángel Losada, M.; Mendoza, E. Hydrodynamics of a headland-bay beach—Nearshore current circulation. Coast. Eng. 2010, 57, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, N.G.; McCarroll, R.J.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Wiggins, M. Multi-annual embayment sediment dynamics involving headland bypassing and sediment exchange across the depth of closure. Geomorphology 2019, 343, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallop, S.; Bryan, K.; Coco, G.; Stephens, S. Storm-driven changes in rip channel patterns on an embayed beach. Geomorphology 2011, 127, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Coco, G. The morphodynamics of rip channels on embayed beaches. Cont. Shelf Res. 2012, 43, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, M.D.; Turner, I.L.; Short, A.D. New insights into embayed beach rotation: The importance of wave exposure and cross-shore processes. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2015, 120, 1470–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinet, A.; Castelle, B.; Idier, D.; Harley, M.; Splinter, K. Controls of local geology and cross-shore/longshore processes on embayed beach shoreline variability. Mar. Geol. 2020, 422, 106118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, M.; Andriolo, U.; Armaroli, C.; Ciavola, P. Shoreline rotation and response to nourishment of a gravel embayed beach using a low-cost video monitoring technique: San Michele-Sassi Neri, Central Italy. J. Coast. Conserv. 2014, 18, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, G.; Pattiaratchi, C. Seasonal changes in beach morphology along the sheltered coastline of Perth, Western Australia. Mar. Geol. 2001, 172, 243–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.; Benedet, L.; Schumacher, D. Short-term beach rotation processes in distinct headland bay beach systems. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 18, 442–458. [Google Scholar]
- Ojeda, E.; Guillén, J. Shoreline dynamics and beach rotation of artificial embayed beaches. Mar. Geol. 2008, 253, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, R.; McLoughlin, R.; Short, A.; Symonds, G. The Southern Oscillation Index, wave climate, and beach rotation. Mar. Geol. 2004, 204, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, C.; Ferreira, O.; Cooper, J.A.G. Geologically constrained morphological variability and boundary effects on embayed beaches. Mar. Geol. 2012, 329–331, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turki, I.; Medina, R.; Coco, G.; Gonzalez, M. An equilibrium model to predict shoreline rotation of pocket beaches. Mar. Geol. 2013, 346, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratliff, K.M.; Murray, A.B. Modes and emergent time scales of embayed beach dynamics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 7270–7275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.; Austin, M.; Masselink, G.; Russell, P. Dynamics of rip currents associated with groynes—Field measurements, modelling and implications for beach safety. Coast. Eng. 2016, 107, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, R.J.; Brander, R.W.; Turner, I.L.; Power, H.E.; Mortlock, T.R. Lagrangian observations of circulation on an embayed beach with headland rip currents. Mar. Geol. 2014, 355, 173–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Scott, T.; Brander, R.; McCarroll, R. Rip current types, circulation and hazard. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 163, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, G.V.; Toldo, E.E.; da, F.; Klein, A.H.; Short, A.D.; Woodroffe, C.D. Headland sand bypassing—Quantification of net sediment transport in embayed beaches, Santa Catarina Island North Shore, Southern Brazil. Mar. Geol. 2016, 379, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, I.D.; Stables, M.A.; Olley, J.M. Wave climate, sand budget and shoreline alignment evolution of the Iluka–Woody Bay sand barrier, northern New South Wales, Australia, since 3000 yr BP. Mar. Geol. 2006, 226, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutts-Smith, A.J. The Significance of Mega-Rips Along an Embayed Coast. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sydney, Sydney, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple, R.A.; MacMahan, J.H.; Reniers, A.J.; Nelko, V. Rip Currents. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2011, 43, 551–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loureiro, C.; Ferreira, O.; Cooper, J.A.G. Extreme erosion on high-energy embayed beaches: Influence of megarips and storm grouping. Geomorphology 2012, 139–140, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, R.J.; Brander, R.W.; Turner, I.L.; Leeuwen, B.V. Shoreface storm morphodynamics and mega-rip evolution at an embayed beach: Bondi Beach, NSW, Australia. Cont. Shelf Res. 2016, 116, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarroll, R.J.; Masselink, G.; Valiente, N.G.; Scott, T.; King, E.V.; Conley, D. Wave and Tidal Controls on Embayment Circulation and Headland Bypassing for an Exposed, Macrotidal Site. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2018, 6, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, N.G.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T.; Conley, D.; McCarroll, R.J. Role of waves and tides on depth of closure and potential for headland bypassing. Mar. Geol. 2019, 407, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattiaratchi, C.; Olsson, D.; Hetzel, Y.; Lowe, R. Wave-driven circulation patterns in the lee of groynes. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1961–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallop, S.L.; Bryan, K.R.; Pitman, S.J.; Ranasinghe, R.; Sandwell, D.R.; Harrison, S.R. Rip current circulation and surf zone retention on a double barred beach. Mar. Geol. 2018, 405, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Coco, G. Surf zone flushing on embayed beaches. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wind, H.G.; Vreugdenhil, C.B. Rip-current generation near structures. J. Fluid Mech. 1986, 171, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouragues, A.; Bonneton, P.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; Barrett, A.; Bonneton, N.; Detand, G.; Martins, K.; McCarroll, R.; Morichon, D.; et al. Field observations of wave-induced headland rips. J. Coast. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brander, R.W.; Short, A.D. Flow kinematics of low-energy rip current systems. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 17, 468–481. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, M.; Scott, T.; Brown, J.; Brown, J.; MacMahan, J.; Masselink, G.; Russell, P. Temporal observations of rip current circulation on a macro-tidal beach. Cont. Shelf Res. 2010, 30, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, N.; Bonneton, P.; Castelle, B.; Pedreros, R. Modeling rip current circulations and vorticity in a high-energy meso-macrotidal environment. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelle, B.; Dodet, G.; Masselink, G.; Scott, T. A new climate index controlling winter wave activity along the Atlantic coast of Europe: The West Europe Pressure Anomaly. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadie, S.; Butel, R.; Dupuis, H.; Brière, C. Paramètres statistiques de la houle au large de la côte sud-aquitaine. C. R. Geosci. 2005, 337, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brière, C. Etude de l’hydrodynamique d’une zone côtière anthropisée: l’embouchure de l’Adour et les plages adjacentes d’Anglet. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Pau et des Pays de l’Adour, Pau, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huguet, J.R.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; Morichon, D.; de Santiago, I. Shoreline-Sandbar Dynamics at a High-Energy Embayed and Structurally-Engineered Sandy Beach: Anglet, SW France. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Padilla, I.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; Morichon, D. A Simple and Efficient Image Stabilization Method for Coastal Monitoring Video Systems. Remote Sens. 2019, 12, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouragues, A.; Bonneton, P.; Castelle, B.; Marieu, V.; McCarroll, R.; Scott, T.; Sous, D. New insights into high-energy surf zone currents and headland rips at a geologically-constrained mesotidal beach. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020. in revision. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, K.A.; Svendsen, I.A. Laboratory measurements of the vertical structure of rip currents. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2002, 107, 15-1–15-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahan, J.H.; Reniers, A.J.H.M.; Thornton, E.B.; Stanton, T.P. Surf zone eddies coupled with rip current morphology. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruneau, N.; Castelle, B.; Bonneton, P.; Pedreros, R.; Almar, R.; Bonneton, N.; Bretel, P.; Parisot, J.P.; Sénéchal, N. Field observations of an evolving rip current on a meso-macrotidal well-developed inner bar and rip morphology. Cont. Shelf Res. 2009, 29, 1650–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiman, J.D.; Kirby, J.T. Unforced Oscillation of Rip-Current Vortex Cells. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 477–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgar, S.; Raubenheimer, B.; Clark, D.B.; Moulton, M. Extremely Low Frequency (0.1 to 1.0 mHz) Surf Zone Currents. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2019, 46, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sous, D.; Tissier, M.; Rey, V.; Touboul, J.; Bouchette, F.; Devenon, J.L.; Chevalier, C.; Aucan, J. Wave transformation over barrier reefs. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sous, D.; Castelle, B.; Mouragues, A.; Bonneton, P. Field Measurements of a High-Energy Headland Deflection Rip Current: Tidal Modulation, Very Low Frequency Pulsation and Vertical Structure. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070534
Sous D, Castelle B, Mouragues A, Bonneton P. Field Measurements of a High-Energy Headland Deflection Rip Current: Tidal Modulation, Very Low Frequency Pulsation and Vertical Structure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(7):534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070534
Chicago/Turabian StyleSous, Damien, Bruno Castelle, Arthur Mouragues, and Philippe Bonneton. 2020. "Field Measurements of a High-Energy Headland Deflection Rip Current: Tidal Modulation, Very Low Frequency Pulsation and Vertical Structure" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 7: 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070534
APA StyleSous, D., Castelle, B., Mouragues, A., & Bonneton, P. (2020). Field Measurements of a High-Energy Headland Deflection Rip Current: Tidal Modulation, Very Low Frequency Pulsation and Vertical Structure. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(7), 534. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8070534




