Granulometric Analysis of Shallow Vents Sediments at Banderas Bay (Mexico)
Abstract
1. Introduction
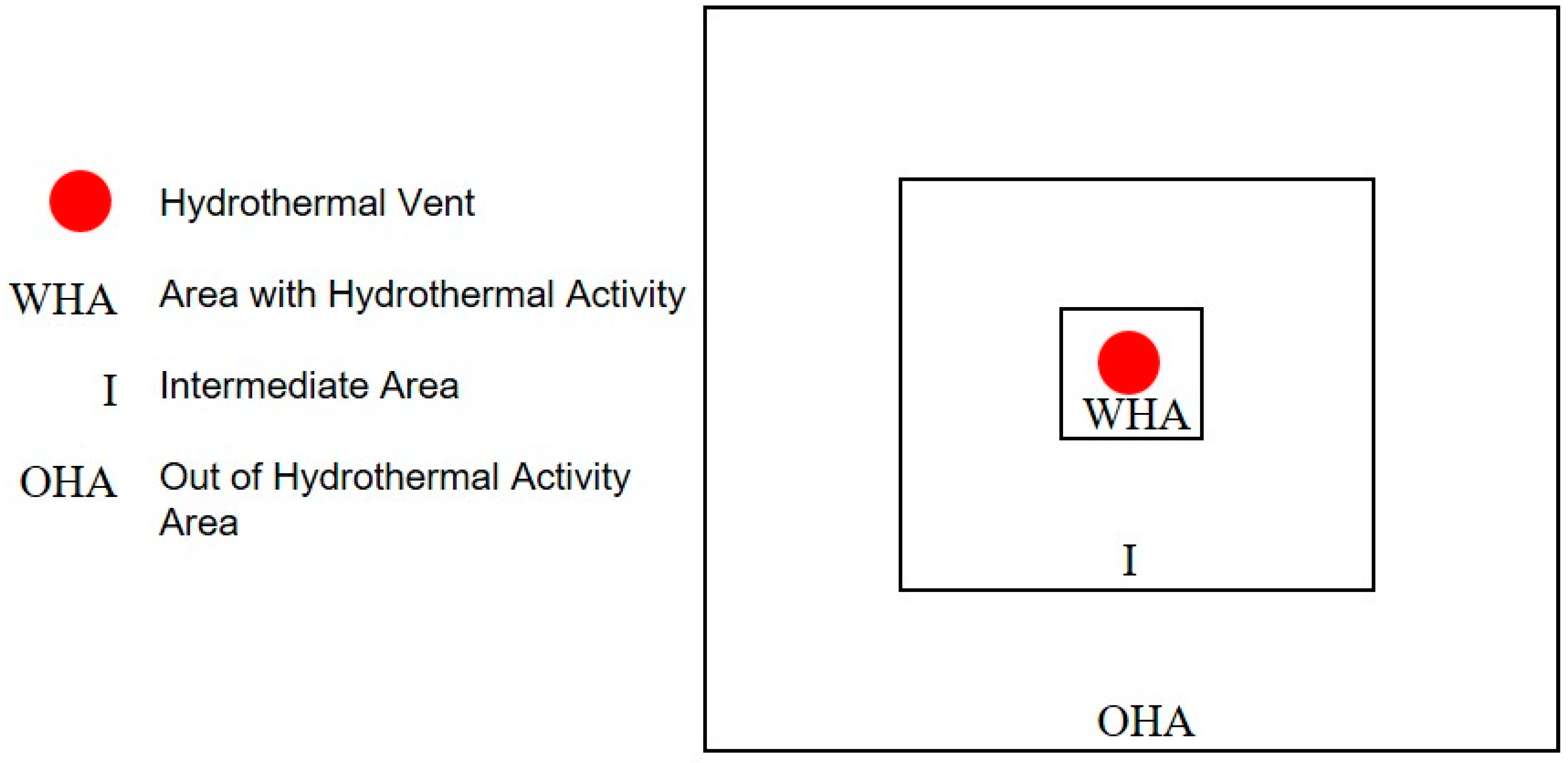
2. Materials and Methods
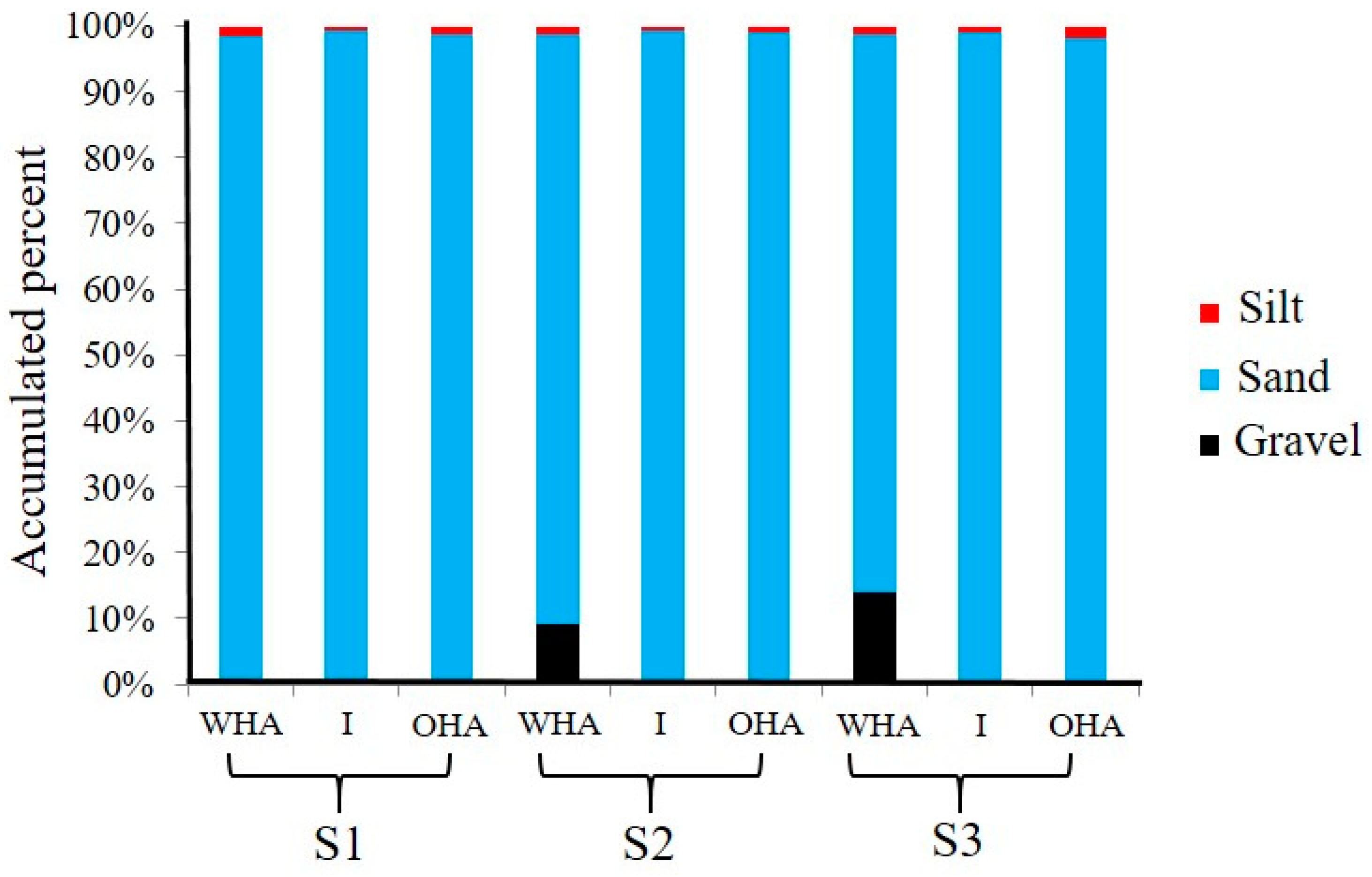
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Núñez-Cornú, F.J.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Cupul-Magaña, A.; Suárez-Plascencia, C. Near shore submarine hydrothermal activity in Bahia Banderas, western Mexico. Geofis. Int. 2000, 39, 171–178. [Google Scholar]
- Canet, C.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M. Procesos de mineralización en manantiales hidrotermales submarinos someros. Ejemplos en México. Boletín la Soc. Geológica Mex. 2006, 58, 83–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, V.G.; Gebruk, A.V.; Mironov, A.N.; Moskalev, L.I. Deep-sea and shallow-water hydrothermal vent communities: Two different phenomena? Chem. Geol. 2005, 224, 5–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Canet, C.; Villanueva-Estrada, R.E.; Ortega-Osorio, A. Morphology of pyrite in particulate matter from shallow submarine hydrothermal vents. Am. Mineral. 2010, 95, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, C.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Melgarejo, J.C. El sistema hidrotermal de Punta Mita (México): Un ejemplo de depósito exhalativo submarino actual. Cad. Lab. Xeolóxico Laxe 2000, 25, 325–327. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Uribe, M.C.; Núñez-Cornú, F.J.; Chávez-Dagostino, R.M. Contribuciones al estudio de los sistemas hidrotermales subamrinos someros en México. Biblio3W. Rev. Bibliográfica Geogr. y Ciencias Soc. 2018, 23, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Canet, C.; Tolson, G.; García-Palomo, A.; Miller, R.; Rubio, M.A.; Torres-de León, R.; Huicochea-Alejo, J.S. Basaltic Volcanism and Submarine Hydrothermal Activity in Punta Mita, Nayarit, Mexico. In Proceedings of the Geologic transects across Cordilleran Mexico, Guidebook for the field trips of the 99th Geological Society of America Cordilleran Section Annual Meeting, Puerto Vallarta, Jalisco, Mexico, 30–31 March 2003; pp. 169–182. [Google Scholar]
- de la Vega-Márquez, T.F.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M. Imágenes landsat TM y modelo digital de elevación para la identificación de lineamientos y mapeo litológico en punta mita (México). Bol. la Soc. Geol. Mex. 2011, 63, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Uribe, M.C.; Chávez-Dagostino, R.M.; Del Moral-Flores, L.F.; Bravo-Olivas, M.L. First record of amphioxus branchiostoma californiense (Amphioxiformes: Branchiostomatidae) adjacent to a shallow submarine hydrothermal system at Banderas bay (Mexico). Diversity 2019, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, C.; Prol-Ledesma, R.M.; Melgarejo, J.C.; Reyes, A. Methane-related carbonates formed at submarine hydrothermal springs: A new setting for microbially-derived carbonates? Mar. Geol. 2003, 199, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiermann, F.; Akoumianaki, I.; Hughes, J.A.; Giere, O. Benthic fauna of a shallow-water gaseohydrothermal vent area in the Aegean Sea (Milos, Greece). Mar. Biol. 1997, 128, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melwani, A.R.; Kim, S.L. Benthic infaunal distributions in shallow hydrothermal vent sediments. Acta Oecologica 2008, 33, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupul-Magaña, L.A.; Mösso-Aranda, C.; Sierra, J.P.; Martí, E.; Ferman-Almada, J.L.; Rodilla, M.; González del Río, J.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A. Caracterización y patrones de distribución de los sedimentos superficiales en Bahía Cullera, España. Ciencias Mar. 2006, 32, 617–629. [Google Scholar]
- Blott, S.J.; Pye, K. Gradistat: A grain size distribution and statistics package for the analysis of unconsolidated sediments. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2001, 26, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos River Bar: A study in the significance of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, G.M. Differences in size distributions of populations of particles among sands of various origins: Addendum to IAS Presidential Address. Sedimentology 1979, 26, 859–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, E.N.; Mazzullo, J.M.; Wilding, L.P. Using quartz grain size and shape analysis to distinguish between aeolian and fluvial deposits in the Dallol Bosso of Niger (West Africa). Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 1989, 14, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.; Choumiline, E.; Estela lópez-Ortiz, B.; Aguíñiga, S.; Sánchez-Vargas, L.; Romero-Guadarrama, A.; Rodríguez-Meza, D. Patrón de transporte de sedimento en bahía magdalena, baja california sur, méxico, inferido del análisis de tendencias granulométricas. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2010, 38, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, D.L. Practical Sedimentology, 1st ed.; Hutchinson Ross Publishing: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 1984; ISBN 0879334436. [Google Scholar]
- Udden, J.A. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America. Mechanical Composition Composition of Clastic Sediments. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1914, 25, 655–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, C.K. A Scale of Grade and Class Terms for Clastic Sediments. J. Geol. 1922, 30, 377–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbein, W.C. Size Frequency Distributions of Sediments and the Normal Phi Curve. SEPM J. Sediment. Res. 1938, 8, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, G.M.; Johnson, K.G. Exercises in Sedimentology; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1982; ISBN 0471874531. [Google Scholar]
- Gower, J.C. Some Distance Properties of Latent Root and Vector Methods Used in Multivariate Analysis. Biometrika 1966, 53, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.; Gorley, R.N.; Clarke, K.R. PERMANOVA + for PRIMER User Manual; PRIMER-E Ltd: Plymouth, UK, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Fuentes-Hernández, M. Algunas Características Sedimentológicas Del Puerto Pesquero Internacional De Güiria Y Sus Alrededores, Estado Sucre, Venezuela. SABER. Rev. Multidiscip. del Cons. Investig. la Univ. Oriente 2006, 18, 197–206. [Google Scholar]
- Baux, N.; Murat, A.; Faivre, Q.; Lesourd, S.; Poizot, E.; Méar, Y.; Brasselet, S.; Dauvin, J.C. Sediment dynamic equilibrium, a key for assessing a coastal anthropogenic disturbance using geochemical tracers: Application to the eastern part of the Bay of Seine. Cont. Shelf Res. 2019, 175, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, J.C. Scientific Method in Analysis of Sediments; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]




| Statistical Moment | Formulae |
|---|---|
| Mean | |
| Standard deviation | |
| Skewness | |
| Kurtosis |
| Site | Area | Gravel | Sand | Silt | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Very fine [−2,−1] phi | Very Coarse [−1,0] phi | Coarse [0,1] phi | Medium [1,2] phi | Fine [2,3] phi | Very Fine [3,4] phi | Very Coarse >4 phi | ||
| S1 | WHA | 0 ± 0 | 0.38 ± 0.009 | 2.26 ± 0.013 | 2.79 ± 0.061 | 22.76 ± 0.8 | 70.66 ± 0.164 | 1.15 ± 0.45 |
| I | 0 ± 0 | 0.18 ± 0.05 | 0.97 ± 0.03 | 1.8 ± 0.15 | 24.24 ± 1.08 | 72.02 ± 0.94 | 0.8 ± 0.01 | |
| OHA | 0 ± 0 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 1.26 ± 0.01 | 1.56 ± 0.02 | 18.9 ± 1.4 | 76.86 ± 1.3 | 1.3 ± 0.13 | |
| S2 | WHA | 9 ± 0.13 | 7.66 ± 0.62 | 14.79 ± 1.04 | 4.45 ± 0.17 | 20.24 ± 0.51 | 42.77 ± 1.2 | 1.28 ± 0.01 |
| I | 0 ± 0 | 0.03 ± 0.01 | 0.17 ± 0.00 | 0.71 ± 0.02 | 23.82 ± 2.31 | 74.61 ± 2.23 | 0.67 ± 0.04 | |
| OHA | 0 ± 0 | 0.11 ± 0.11 | 0.37 ± 0.01 | 1.39 ± 0.01 | 27.87 ± 0.74 | 69.32 ± 0.60 | 0.94 ± 0.03 | |
| S3 | WHA | 14 ± 1.21 | 13.52 ± 2.89 | 20.93 ± 0.94 | 5.68 ± 0.42 | 11.08 ± 1.15 | 33.44 ± 1.49 | 1.36 ± 0.10 |
| I | 0 ± 0 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.27 ± 0.03 | 17.40 ± 0.58 | 81.18 ± 0.62 | 1.04 ± 0.08 | |
| OHA | 0 ± 0 | 0.01 ± 0.01 | 0.15 ± 0.03 | 0.33 ± 0.01 | 15.88 ± 0.84 | 81.79 ± 0.62 | 1.83 ± 0.17 | |
| Site | Area | Statistical Moments | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | WHA | 3.14 ± 0.001 | 0.69 ± 0.000 | −2.25 ± 0.017 | 8.91 ± 0.09 |
| I | 3.19 ± 0.009 | 0.58 ± 0.004 | −2.15 ± 0.005 | 9.29 ± 0.24 | |
| OHA | 3.24 ± 0.015 | 0.57 ± 0.005 | −2.55 ± 0.128 | 11.18 ± 0.781 | |
| S2 | WHA | 2.02 ± 0.048 | 1.72 ± 0.006 | −0.81 ± 0.069 | 2.25 ± 0.116 |
| I | 3.24 ± 0.022 | 0.47 ± 0.009 | −1.64 ± 0.209 | 6.15 ± 1.124 | |
| OHA | 3.18 ± 0.003 | 0.53 ± 0.010 | −1.63 ± 0.240 | 6.81 ± 1.804 | |
| S3 | WHA | 1.41 ± 0.128 | 1.88 ± 0.031 | −0.17 ± 0.114 | 1.55 ± 0.075 |
| I | 3.32 ± 0.004 | 0.41 ± 0.003 | −1.93 ± 0.089 | 6.65 ± 0.519 | |
| OHA | 3.34 ± 0.008 | 0.41 ± 0.001 | −2.16 ± 0.189 | 8.78 ± 1.673 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Uribe, M.C.; Núñez-Cornú, F.J.; Chávez-Dagostino, R.M.; Trejo-Gómez, E. Granulometric Analysis of Shallow Vents Sediments at Banderas Bay (Mexico). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8050342
Rodríguez-Uribe MC, Núñez-Cornú FJ, Chávez-Dagostino RM, Trejo-Gómez E. Granulometric Analysis of Shallow Vents Sediments at Banderas Bay (Mexico). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(5):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8050342
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Uribe, María Carolina, Francisco Javier Núñez-Cornú, Rosa María Chávez-Dagostino, and Elizabeth Trejo-Gómez. 2020. "Granulometric Analysis of Shallow Vents Sediments at Banderas Bay (Mexico)" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 5: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8050342
APA StyleRodríguez-Uribe, M. C., Núñez-Cornú, F. J., Chávez-Dagostino, R. M., & Trejo-Gómez, E. (2020). Granulometric Analysis of Shallow Vents Sediments at Banderas Bay (Mexico). Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(5), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8050342





