The Impact of Storm-Induced Breaches on Barrier Coast Systems Subject to Climate Change—A Stochastic Modelling Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How do storm-induced breaches affect existing inlets connecting to the same backbarrier basin and what are the interactions between them?
- What breach characteristics determine whether a breach evolves into an open inlet or closes?
- How are multiple-inlet systems affected by climate driven changes in the storm climate?
2. Methods
2.1. Idealized Barrier Coast Model
2.2. Stochastic Shell: Forcing Storm-Induced Breaches
- Step 1
- determines the number of storms that occur during the timestep,
- Step 2
- determines the number of breaches that occur (if ),
- Step 3
- determines the initial inlet cross-section and inlet location of each newly created breach (if ).
2.3. Design of Model Experiments
2.3.1. Outline of a Single Simulation
2.3.2. Monte Carlo Simulation
- the relative size of the breach ,
- the barrier coast saturation ,
- the distance of a breach to the nearest neighboring inlet .
3. Results
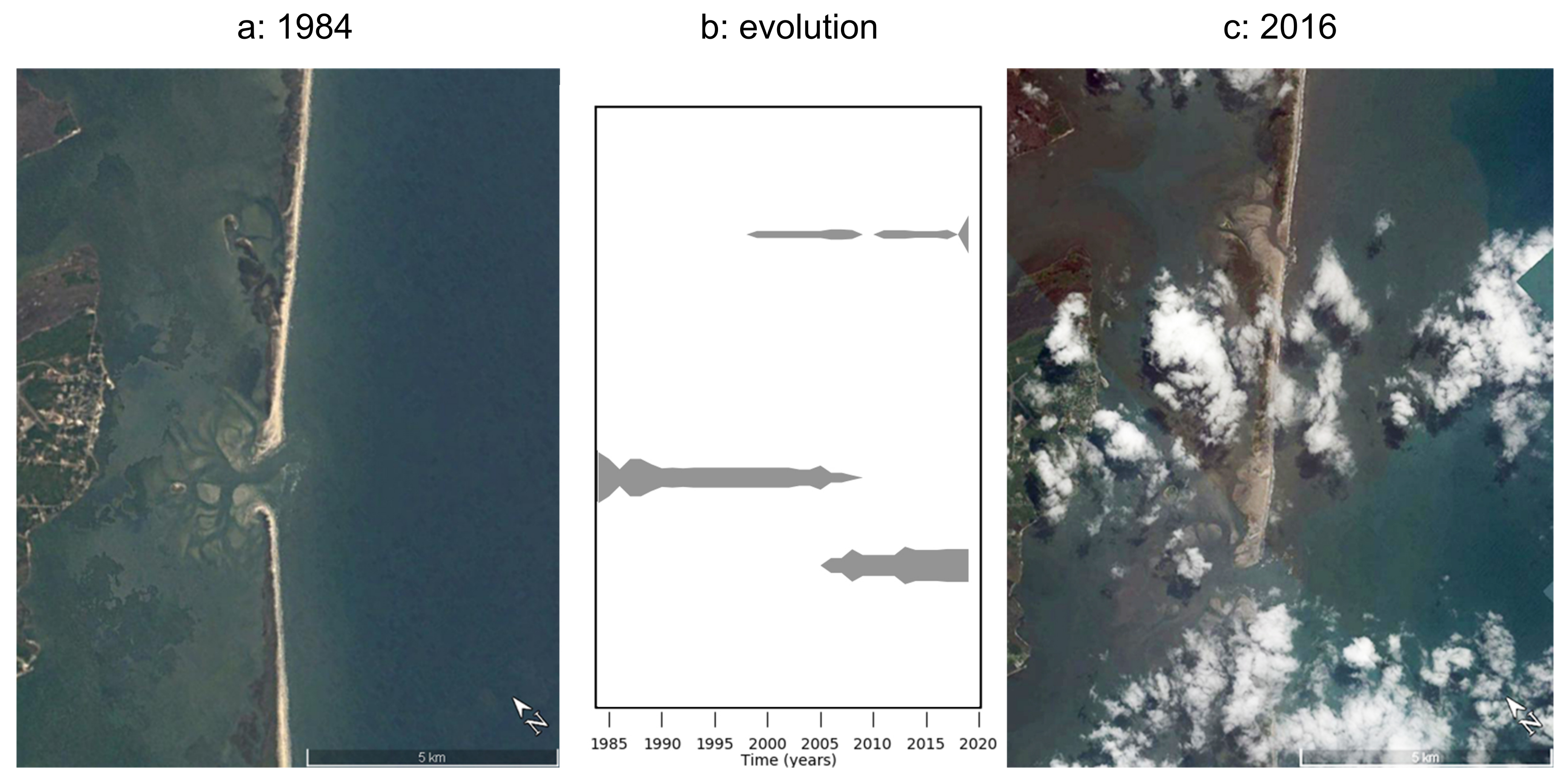
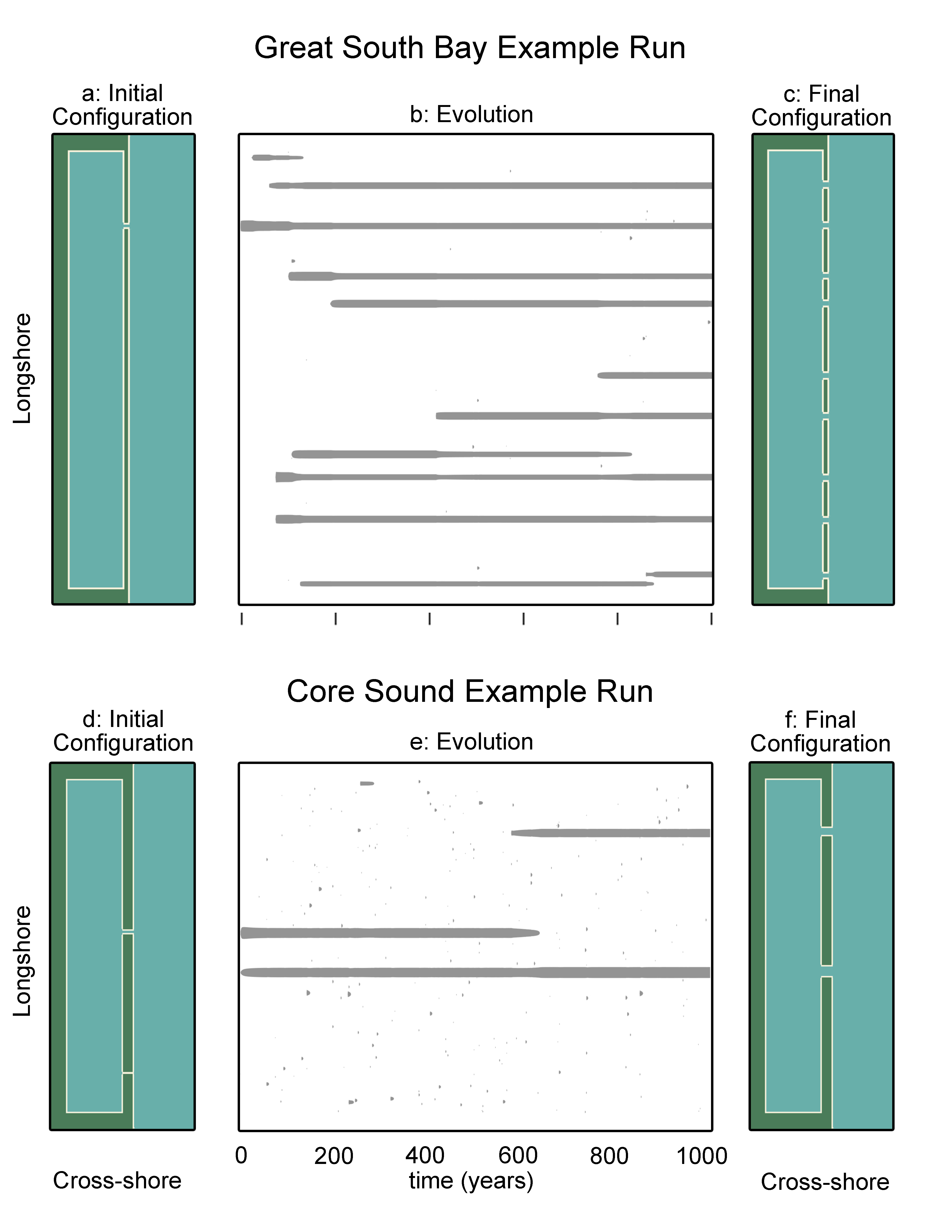
3.1. Example Model Run
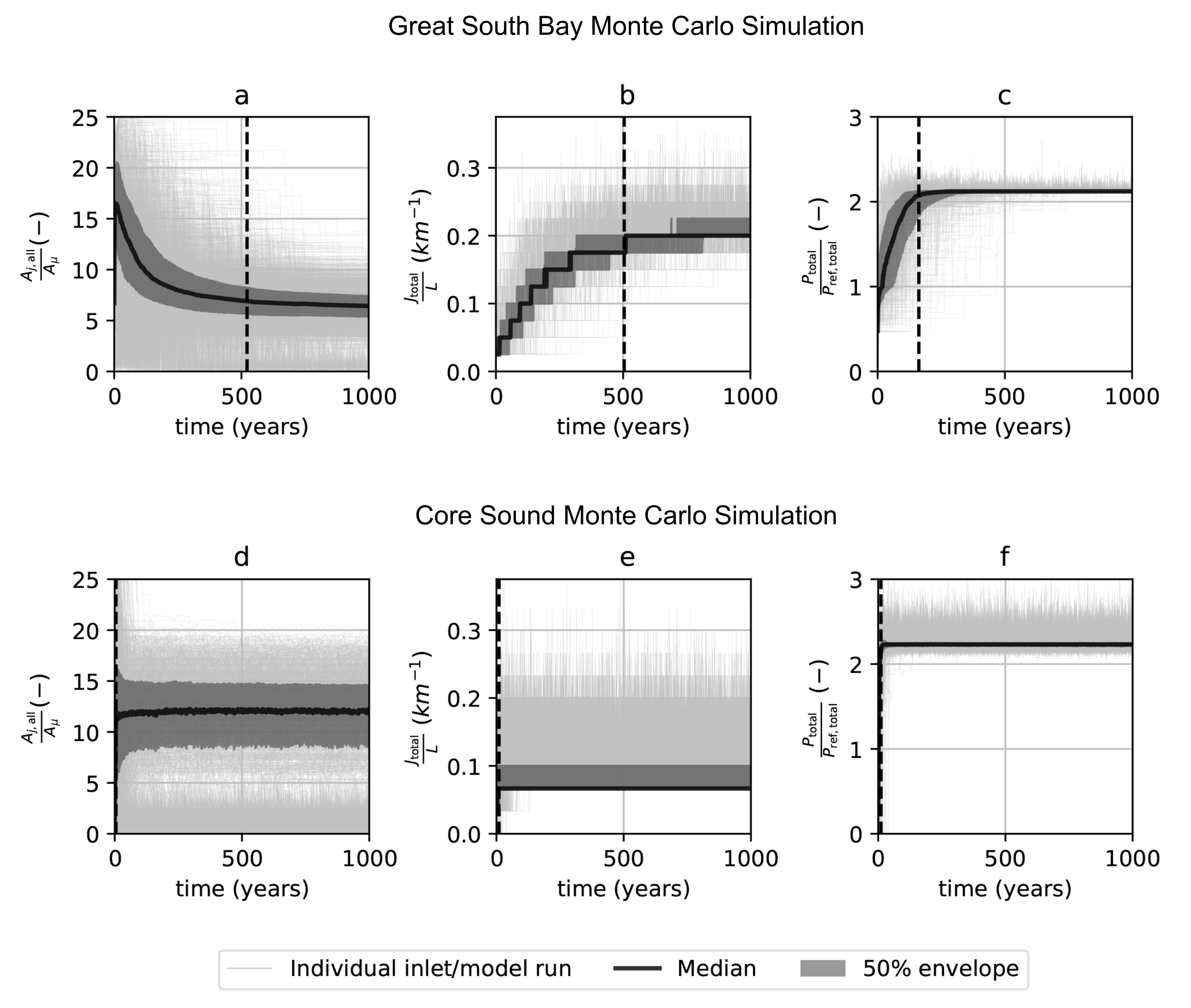
3.2. Monte Carlo Ensemble
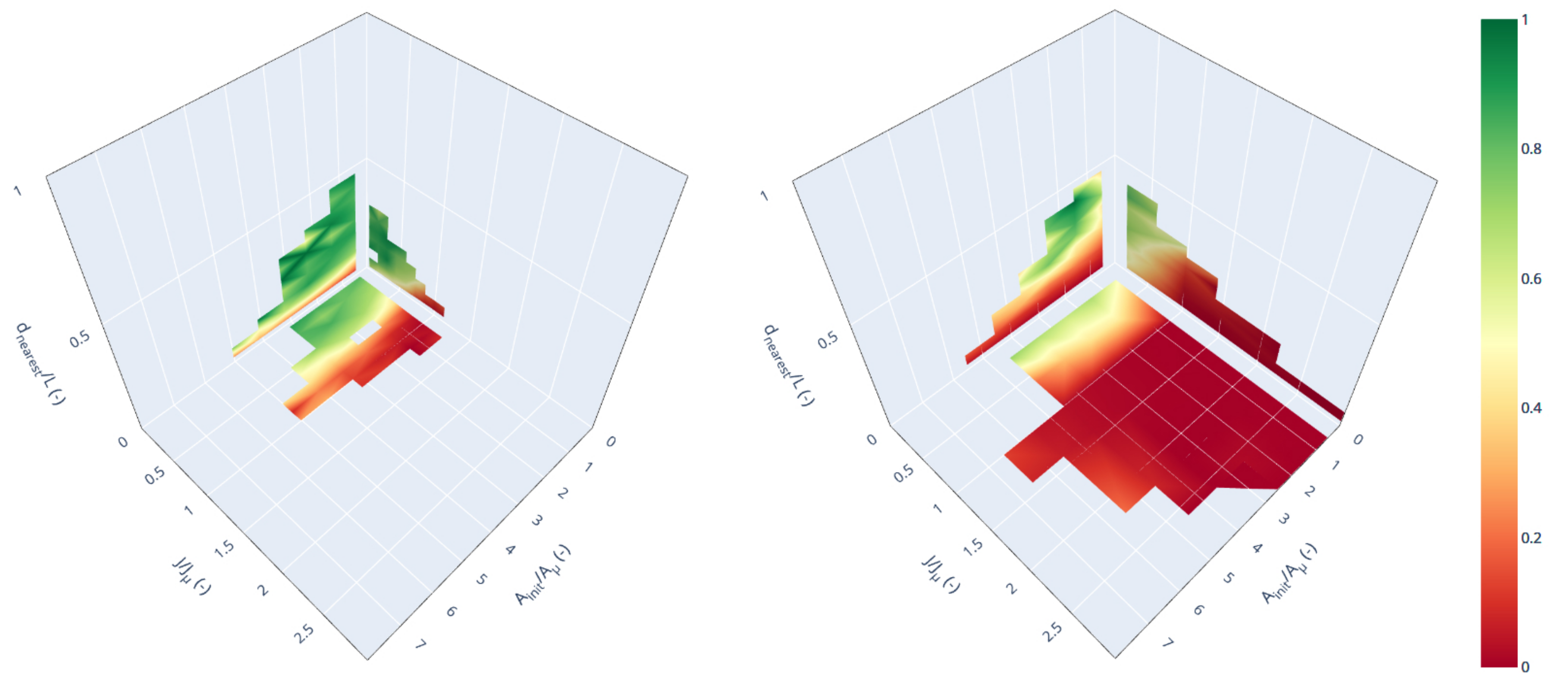
3.3. Breach Survival Chance
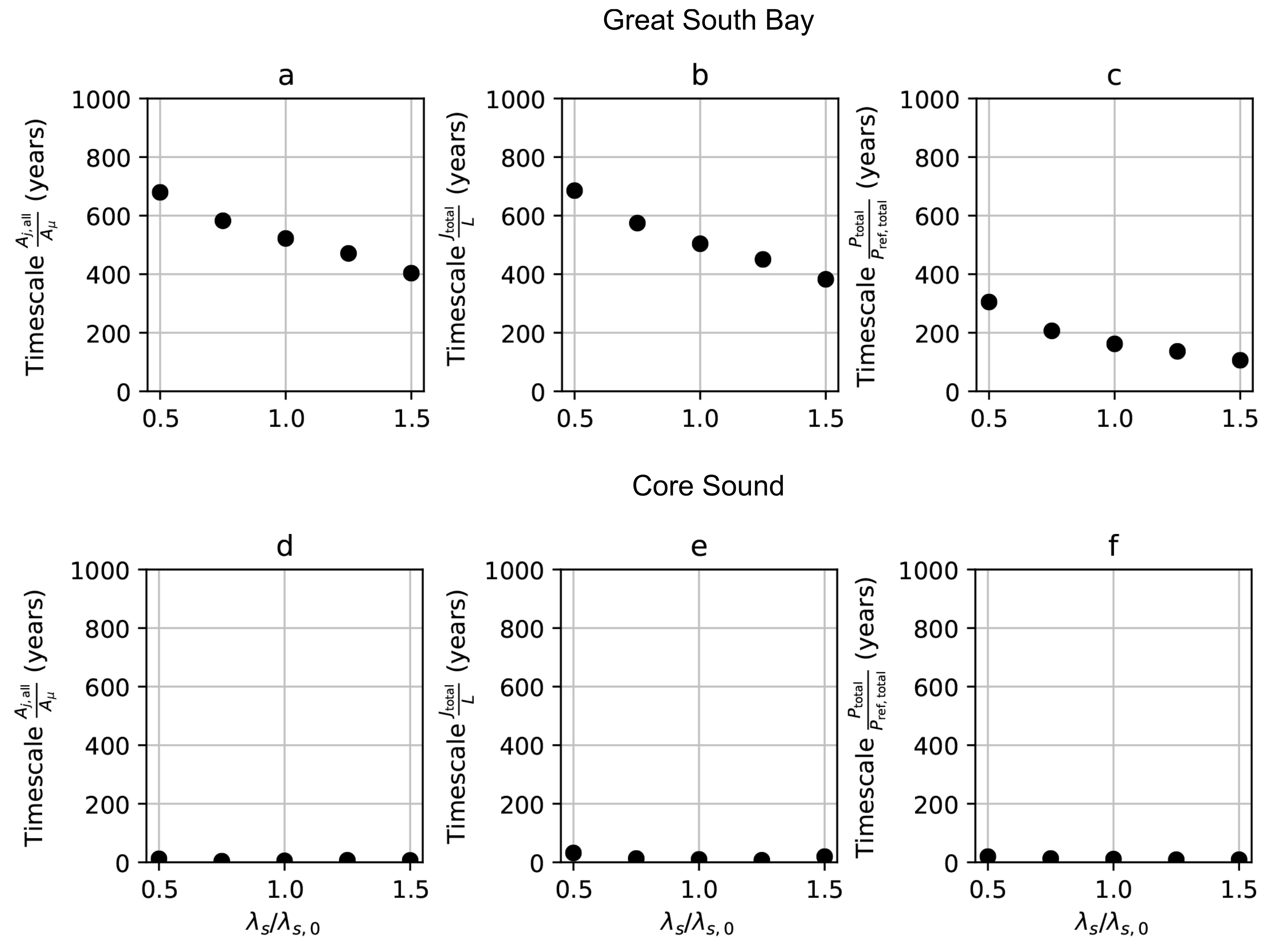
3.4. The Effects of Climate Change
4. Discussion
4.1. System-Wide Equilibrium
4.2. Survival of the Farthest
4.3. Model Validity & Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Glaeser, J.D. Global Distribution of Barrier Islands in Terms of Tectonic Setting. J. Geol. 1978, 86, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, M.L.; Pilkey, O.H. Open-ocean barrier islands: Global influence of climatic, oceanographic, and depositional settings. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 207–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oost, A.P.; Hoekstra, P.; Wiersma, A.; Flemming, B.; Lammerts, E.J.; Pejrup, M.; Hofstede, J.; van der Valk, B.; Kiden, P.; Bartholdy, J.; et al. Barrier island management: Lessons from the past and directions for the future. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2012, 68, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.B.; Hoekstra, P.; Burchard, H.; Ridderinkhof, H.; De Swart, H.E.; Stive, M.J.F. Morphodynamics of the Wadden Sea and its barrier island system. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2012, 68, 39–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Swart, H.E.; Zimmerman, J.T.F. Morphodynamics of Tidal Inlet Systems. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2009, 41, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.A.; Hayes, M.O. What is a Wave-Dominated Coast? Dev. Sedimentol. 1984, 39, 313–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoffier, E.F. The stability of tidal inlets. Shore Beach 1940, 8, 114–115. [Google Scholar]
- Salles, P.; Voulgaris, G.; Aubrey, D.G. Contribution of nonlinear mechanisms in the persistence of multiple tidal inlet systems. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 65, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Matute, M.; Gerkema, T.; De Boer, G.J.; Nauw, J.J.; Gräwe, U. Residual circulation and freshwater transport in the Dutch Wadden Sea: A numerical modelling study. Ocean. Sci. 2014, 10, 611–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, M.; Duran-Matute, M.; van Kessel, T.; Gerkema, T. Variability of residual fluxes of suspended sediment in a multiple tidal-inlet system: The Dutch Wadden Sea. Ocean. Dyn. 2015, 65, 1321–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, R.L.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Roos, P.C. Modelling the influence of spatially varying hydrodynamics on the cross-sectional stability of double inlet systems. Ocean. Dyn. 2013, 63, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roos, P.C.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Brouwer, R.L. Observations of barrier island length explained using an exploratory morphodynamic model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 4338–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reef, K.R.G.; Roos, P.C.; Schuttelaars, H.M.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Influence of backbarrier basin geometry on multiple tidal inlet systems: The roles of resonance and bottom friction. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallenger, A.H. Storm Impact Scale for Barrier Islands. J. Coast. Res. 2000, 16, 890–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraus, N.C.; Militello, A.; Todoroff, G. Barrier Beaching Processes and Barrier Spit Breach, Stone Lagoon, California. Shore Beach 2002, 70, 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Leatherman, S.P. Geomorphic and Stratigraphic Analysis of Fire Island, New York. Mar. Geol. 1985, 63, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallinson, D.J.; Smith, C.W.; Culver, S.J.; Riggs, S.R.; Ames, D. Geological characteristics and spatial distribution of paleo-inlet channels beneath the outer banks barrier islands, North Carolina, USA. Estuarine Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 88, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Concejo, A.; Matias, A.; Ferreira, Ó.; Duarte, C.; Dias, J. Recent Evolution of the Natural Inlets of a Barrier Island System in Southern Portugal. J. Coast. Res. 2002, 36, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kombiadou, K.; Matias, A.; Ferreira, Ó.; Carrasco, A.R.; Costas, S.; Plomaritis, T. Impacts of human interventions on the evolution of the Ria Formosa barrier island system (S. Portugal). Geomorphology 2019, 343, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, C.; Flagg, C.N.; Wilson, R.E. Great South Bay After Sandy: Changes in Circulation and Flushing due to New Inlet. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 2172–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wilson, R.E.; Flagg, C.N. A Hydraulic Model for Multiple-Bay-Inlet Systems on Barrier Islands. Estuaries Coasts 2018, 41, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FEMA. Hurricane Sandy in New Jersey and New York (FEMA P-942); Technical Report November; FEMA: Washington, DC, USA, 2013.
- Mallinson, J.; Culver, J.; Walsh, J.P.; Curtis, W. Past, Present and Future Inlets of the outer Banks Barrier Islands, North Carolina; Technical Report; East Carolina University: Greenville, NC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Van Goor, M.A.; Zitman, T.J.; Wang, Z.B.; Stive, M.J.F. Impact of sea-level rise on the morphological equilibrium state of tidal inlets. Mar. Geol. 2003, 202, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgheib, A.; Roelvink, J.A.; Wang, Z.B. Long-term process-based morphological modeling of the Marsdiep Tidal Basin. Mar. Geol. 2008, 256, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.R.; Marani, M.; Scaioni, M. Statistical Distribution Fits for Hurricanes Parameters in the Atlantic Basin; ASITA: Richmond, BC, USA, 2016; pp. 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- Keim, B.D.; Muller, R.A.; Stone, G.W. Spatiotemporal patterns and return periods of tropical storm and hurricane strikes from Texas to Maine. J. Clim. 2007, 20, 3498–3509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google. Map data: SIO, NOAA, U.S. Navy, NGA, GEBCO, TerraMetrics; Google: Menlo Park, CA, USA.
- Vogel, M.J.; Kana, T.W. Sedimentation Patterns in a Tidal Inlet System Moriches Inlet, New York; Coastal Engineering Proceedings; ASCE: Reston, VA, USA, 1984; pp. 3017–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacIvor, L.H.; Motivans, K. Impacts to Piping Plover and Seabeach Amaranth from Long-Term Sand Management Component; Technical Report; US Army Corps of Engineers: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Matias, A.; Ferreira, Ó.; Alveirinho-Dias, J.M. Preliminary results of the Cacela Peninsula (southern Portugal) replenishment. Bol. Inst. Esp. Oceanogr 1999, 15, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Cañizares, R.; Irish, J.L. Simulation of storm-induced barrier island morphodynamics and flooding. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 1089–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamsley, T.V.; Hathaway, K.K.; Wutkowski, M. Hatteras Breach, North Carolina; Technical Report; US Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Clinch, A.S.; Russ, E.R.; Oliver, R.C.; Mitasova, H.; Overton, M.F. Hurricane Irene and the Pea Island breach: Prestorm site characterization and storm surge estimation using geospatial technologies. Shore Beach 2012, 80, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Flagg, C.; Hinrichs, C.; Flood, R.; Wilson, R. Update on the Status of Old Inlet Breach; Stony Brook University, School of Marine and Atmospheric Science: Stony Brook, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Safak, I.; Warner, J.C.; List, J.H. Barrier island breach evolution: Alongshore transport and bay-ocean pressure gradient interactions. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2016, 121, 8720–8730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.; Kumar, K.K.; Aldria, E.; An, S.I.; Cavalcanti, I.; Castro, M.D.; Dong, W.; Goswami, P.; Hall, A.; Kanyanga, J.; et al. Climate Phenomena and their Relevance for Future Regional Climate Change Supplementary Material. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1011.1669v3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Concejo, A.; Matias, A.; Pacheco, A.; Ferreira, Ó.; Dias, J.A. Quantification of inlet-related hazards in barrier island systems. An example from the Ria Formosa (Portugal). Cont. Shelf Res. 2006, 26, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Kreeke, J.; Brouwer, R.L.; Zitman, T.J.; Schuttelaars, H.M. The effect of a topographic high on the morphological stability of a two-inlet bay system. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Swart, H.E.; Volp, N.D. Effects of hypsometry on the morphodynamic stability of single and multiple tidal inlet systems. J. Sea Res. 2012, 74, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kragtwijk, N.G.; Zitman, T.J.; Stive, M.J.F.; Wang, Z.B. Morphological response of tidal basins to human interventions. Coast. Eng. 2004, 51, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reef, K.R.G.; Lipari, G.; Roos, P.C.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Time-varying storm surges on Lorentz’s Wadden Sea networks. Ocean. Dyn. 2018, 68, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, D.M. Geomorphic Variability and Morphologic and Sedimentologic Controls on Tidal Inlets. J. Coast. Res. 1996, 47–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, E.P.L.; Van Der Spek, A.J.; Wang, Z.B.; De Ronde, J. Morphodynamic development and sediment budget of the Dutch Wadden Sea over the last century. Geol. Mijnbouw/Netherlands J. Geosci. 2012, 91, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Symbol (unit) | Great South Bay | Core Sound |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tidal Elevation Amplitude in sea | Z (m) | 0.5 | 0.325 |
| Tidal Frequency in sea | (rad/s) | ||
| Basin Depth | (m) | 1.3 | 2 |
| Basin Length | L (km) | 40 | 30 |
| Basin Width | B (km) | 5 | 5 |
| Drag Coefficient | (-) | ||
| Inlet Length | (km) | 0.5 | 1 |
| Mean Initial Inlet Cross Section | (m) | 281 | 281 |
| Inlet Shape Factor | (-) | 0.005 | 0.005 |
| Outer Sea Depth | (m) | 10 | 10 |
| Sediment Import | |||
| Mean number of Hurricanes per year | (year) | 1/35 | 1/5 |
| Morphodynamic Timestep | (year) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| # of Simulations in one Ensemble | n (-) | 500 | 500 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reef, K.R.G.; Roos, P.C.; Andringa, T.E.; Dastgheib, A.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. The Impact of Storm-Induced Breaches on Barrier Coast Systems Subject to Climate Change—A Stochastic Modelling Study. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040271
Reef KRG, Roos PC, Andringa TE, Dastgheib A, Hulscher SJMH. The Impact of Storm-Induced Breaches on Barrier Coast Systems Subject to Climate Change—A Stochastic Modelling Study. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2020; 8(4):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040271
Chicago/Turabian StyleReef, Koen R. G., Pieter C. Roos, Tessa E. Andringa, Ali Dastgheib, and Suzanne J. M. H. Hulscher. 2020. "The Impact of Storm-Induced Breaches on Barrier Coast Systems Subject to Climate Change—A Stochastic Modelling Study" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 8, no. 4: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040271
APA StyleReef, K. R. G., Roos, P. C., Andringa, T. E., Dastgheib, A., & Hulscher, S. J. M. H. (2020). The Impact of Storm-Induced Breaches on Barrier Coast Systems Subject to Climate Change—A Stochastic Modelling Study. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 8(4), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse8040271







