Abstract
A laboratory experiment investigates the influence of salinity on the characteristics of bubble clouds in varying saline solutions. Bubble clouds were generated with a water jet. Salinity, surface tension, and water temperature were monitored. Measured bubble cloud parameters include the number of bubbles, the void fraction, the penetration depth, and the cloud shape. The number of large (above 0.5 mm diameter) bubbles within a cloud increases by a factor of three from fresh to saline water of 20 psu (practical salinity units), and attains a maximum value for salinity of 12–25 psu. The void fraction also has maximum value in the range 12–25 psu. The results thus show that both the number of bubbles and the void fraction vary nonmonotonically with increasing salinity. The lateral shape of the bubble cloud does not change with increasing salinity; however, the lowest point of the cloud penetrates deeper as smaller bubbles are generated.
1. Introduction
Bubble clouds arising from waves breaking at the ocean surface play an important role in the transport of momentum and scalars between the atmosphere and the ocean [1,2]. The dynamics of bubble clouds is understood relatively well and allows the calculation of cloud integral characteristics such as length, depth, and shape [3,4,5]. Less is known about the kinematics of bubble clouds, as it is a complex interaction of wave and buoyancy forcing, with salinity and surface tension also playing influential roles. Buoyancy forcing arises from the presence of air bubbles entrained during the wave breaking process [6]. Parameters to characterize bubble clouds include the bubble size distribution [6,7,8] and the void fraction [4].
Previously, we have reported laboratory results on the bubble cloud characteristics under varying wind conditions in fresh water at fixed temperature [9]. Here, we continue our investigation by focusing on bubble cloud characteristics in saline water. Data from both laboratory and field experiments show a lack of consensus regarding the effect of salinity on bubble cloud characteristics when data are collected in either seawater or fresh water [5]. This paper reports the results of laboratory measurements of void fraction from an experiment where the salinity S has been varied systematically over a wide range from 1 to 38 psu (practical salinity units). Our data show that the void fraction varies nonmonotonically with salinity: it increases for values of S up to 20 psu, but decreases for higher S values. We suggest that recognition of the nonmonotonic salinity dependence of the void fraction can help to resolve the disagreement between the results of previous studies.
In addition, our concurrent measurements of surface tension can lead to clarification of how salinity impacts void fraction. This study of the effects of salinity on bubble clouds beneath breaking waves complements our study of salinity influence on large individual bubbles comprising whitecaps floating on water surface [10]. Each study provides insights on a different pathway through which salinity could affect oceanic whitecap longevity (persistence) [11]. Specifically, in [10], we addressed the whitecap persistence due to the surface lifetime of bubbles within whitecaps on the ocean surface. The current study helps to understand the whitecap persistence due to variations of bubble size distribution in the water column caused by salinity.
2. Background
An immediate outcome of wave breaking is entrainment of air; this leads to the formation of bubble clouds [1]. Bubble size distribution N(r) (where r is the bubble radius) is the most representative quantity for bubble populations because it can be related to other bubble cloud characteristics. For example, both void fraction α (defined as the volume occupied by air in a volume of an air-water mixture) and penetration depth z can be evaluated from measurements of N(r) and its variations in the water column. Integrating the volume of the bubbles comprising N(r) provides α [12]. Breaking waves at different scales yield bubble clouds with different z as varying bubble sizes stratify the entrainment of bubbles in water depth [13]. The universal use of N(r) to characterize bubble populations is the reason most experiments aim to measure the bubble size distribution.
Turbulence and buoyancy, associated with wave breaking, dictate the specific size distribution N(r) of the bubbles within the clouds [14]. Physicochemical processes—such as bubble coalescence and bubble coating by surface film—governed by the chemical composition of the water, including its salinity and the presence of organics or surface active materials (surfactants), also affect bubble size distributions and their evolution [15,16,17]. Early experiments on the effect of salinity have shown the formation of more bubbles of all sizes in more saline waters [15,18,19]. Observations have also shown narrowing of the bubble size spectrum towards small sizes as the mean bubble radius decreases from fresh to more saline waters [20,21,22]. Summary of recent results [23] confirms that the peak of the bubble size distribution shifts toward smaller bubble sizes with increasing salinity. As the volume of the large bubbles dominates α due to a r3 factor in the definition of the void fraction, a decrease of the number of large bubbles in bubble size distribution can affect α strongly. However, noting that previous experiments have shown at least an order of magnitude increase of the number of small bubbles relative to the number of large bubbles with increasing salinity [20,21], it is possible that the relative contribution of small and large bubbles to α can change.
The problem is that N(r) cannot always be measured reliably. It is known that bubbles exist in the ocean in two populations. Bubbles in equilibrium, with diameters 2r less than 0.5 mm, form a layer of persistent background population about 1 m thick [24,25]. This background bubble population is constantly interacted upon by intermittent and relatively short-lived bubble clouds (plumes), representing the transient bubble population. Biological processes are the major source of the background population. Oceanic whitecaps indicate the formation of the transient bubble population by wave breaking [24]. Bubbles formed during the initial (active) stages of the wave breaking show a wide range of sizes with prevalence of large ones (larger than 0.5 mm in diameter) [6,14]. The initial bubble clouds quickly decay and transition to a mature (residual) phase through rising of the largest and dissolving of the smallest bubbles [25]. Most previous studies have focused on the more stable, equilibrated phase of the bubble population [11] (their Chapter 4.4). Fewer have investigated the transient bubble population because of the challenge of resolving densely packed bubbles [6,12]. However, variations of bubble cloud characteristics during the active phase of wave breaking are of interest when studying gas exchange or turbulence and energy dissipation in the upper ocean [1,2,3,13,26]. In absence of reliable measurements of N(r), measuring the shape (including z) and void fraction α of a bubble cloud as a whole is a viable alternative [1,9]. For this reason, our approach in this study is to measure the characteristics of bubbles en masse—i.e., the integral characteristics of bubble clouds.
Salinity affects the characteristics of bubble clouds by changing the ionic strength of a solution (a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution) and the surface tension γ at air-water interfaces. Here we briefly introduce the physicochemical terminology and processes related to effects influenced by surface tension [27,28]. Generally, bubbles are easily created in aqueous solutions when γ is lower than its value in pure water γ0, i.e., γ < γ0. The surface tension of an aqueous solution can become lower when water temperature increases or simple organics or surfactants are added; Appendices B and C in [10] give details and schematics of such variations of γ. At a fixed water temperature (i.e., isothermal conditions), adding inorganic salts [e.g., sodium chloride (NaCl)] to water may either increase or decrease γ depending on the purity of the water. When adding salt to pure water (without organics and/or surfactants), the increase of salt concentration causes an increase of the surface tension γ above γ0. This is termed negative adsorption because the concentration of the salt at the free surface and at the bubble walls becomes smaller than in the bulk solution; excessive surface tension γ > γ0 produces negative surface film pressure ∆γ = γ0 − γ < 0. Because higher γ values (or, equivalently, negative film pressure ∆γ) hinder the formation of bubbles, the added salts act as antifoaming agents.
Organics and/or surfactants present in the water cause a decrease of the surface tension γ below γ0. This is termed positive adsorption because the concentration of an organic additive at any interface becomes higher than its concentration in the bulk solution. The addition of salts in aqueous solutions with organic additives enhances the positive adsorption already created by the organics. The lowered surface tension γ < γ0 produces positive surface film pressure ∆γ = γ0 − γ > 0. Because lower γ values (or, equivalently, positive film pressure ∆γ) facilitate bubble formation, the added salt now acts as a foaming agent. Moreover, positive ∆γ enhances the stabilization of bubbles against bursting (details in Appendix C of [10]). The antifoaming role of the salts therefore changes to that of foaming agents in contaminated aqueous solutions because salts start to contribute to both bubble formation and stabilization. We can evaluate the effect of S on bubble clouds by monitoring γ and using the strong connection between salinity and surface tension.
3. Experiment
3.1. Bubble Cloud Formation
Small scale laboratory experiments cannot simulate oceanic bubble clouds exactly as it is difficult to meet the requirements of Reynolds, Froude and Weber number scaling. Thus bubble clouds have been simulated with different experimental systems. For example, pouring of water in a tank with a tipping trough or bucket [20,21], or collision of two water waves in a tank [29] simulate intermittent breaking events and episodic (discrete) formation of bubble clouds. In contrast, experimental setups using injection of air through porous media such as glass frits or an aquarium diffuser, vertical or inclined plunging water jets, and weirs (in water jet or waterfall configurations) [15,30,31,32,33,34], simulate continuous (steady) formation of bubble clouds.
The limitations of the laboratory simulations vary with the experimental system. For the case of episodic production mechanisms, once the large bubbles rise to the surface, the remaining, smaller bubbles are free to rise at their slow velocities and persist within the cloud. In contrast, a steady plunging jet continuously introduces large bubbles into the tank, which, while rising, can scavenge smaller, slowly moving bubbles. Thus, bubble clouds produced by episodic mechanisms may contain relatively larger numbers of smaller bubbles than steady, plunging jets. Another concern regarding the use of plunging jets is that the resulting bubble population may reflect the scales of the jet [30].
There is a lack of consensus on the optimal experimental configuration for simulating oceanic bubble clouds. A reviewer suggests that mechanisms such as wave–wave collisions or tipping troughs entrain large air cavities, which shatter into bubble clouds in a manner similar to that of air entrapped by a plunging breaking wave in the ocean. A comparative study of air entrainment methods, however, has shown that a steady plunging jet impinging on large water volume at high jet speed V successfully simulates oceanic bubble size distributions [32]. A recent review of studies of air entrainment created by plunging jets from a nozzle and a breaking wave has shown “qualitatively different types of impact” [31].
We utilize a steady plunging jet to produce bubble clouds because we are interested in the underwater bubble population rather than the impact of the jet on the water or the mechanism of air entrapment. Our focus concerns the initial, transient bubble population, which forms immediately after wave breaking and contains large bubbles predominantly (Section 2). Figure 1 shows our experimental setup. The water jet, fed by a “supply” tank (121.9 cm L × 32.4 cm W × 39.0 cm H) with water depth of 33 cm, generated bubble clouds in a “receiving” tank (39.5 cm L × 39.5 cm W × 106 cm H, water depth of 59 cm); here L, W, and H stand for the length, width, and height of the tanks. The receiving tank had dimensions much larger than the bubble clouds to avoid wall effects. The height difference (or differential head) h between the water level in the supply tank and the end of the hose holding a nozzle over the receiving tank was 40.3 cm. The Bernoulli relation V = (2gh)½ gave an impact speed of the jet V = 2.84 m s−1. This value is within the range of the previously reported jet impact velocity of 1–7 m s−1 [15,35,36]. Note that estimating V from the Bernoulli equation is an upper bound as this estimate ignores losses from entrance, bend, and friction. The precise velocity is not critical, however, as the setup is the same for all experimental runs in varying saline solutions. The jet speed remained constant for the duration of the video records (1 min) because of the large volume of water in the supply tank. The water in the receiving tank was maintained at a constant level by collecting the overflow from a circular opening on the side wall at a height of 61 cm from the bottom.
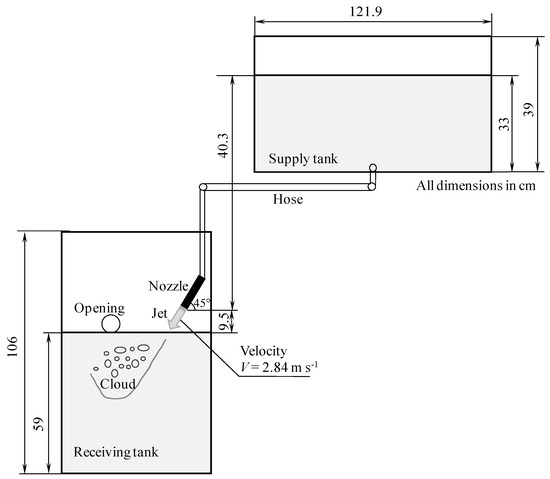
Figure 1.
Schematic of the experimental setup. The differential head is h = 40.3 cm; jet impacts the water from a distance l = 9.5 cm. All measures are in cm.
A nozzle with an inner diameter of 4.44 mm formed a jet plunging into the water of the receiving tank from a distance l of 9.5 cm. The jet impinged on the water surface under an angle θ = 45°. Our laboratory observations of breaking wind waves [9] and geometric considerations of the overturning of a breaking wave [37] informed the choice of 45° for θ. This θ value is in the middle of the range (approximately 30°–60°) of observed critical angles θc beyond which no bubble plumes formed for given nozzle size and impact velocity V [31,33,35].
3.2. Cloud Records and Image Processing
Side views of the bubble clouds in a transparent plastic tank were recorded for 1 min at each salinity value. A standard video camera (Burle TC355AC series) was positioned perpendicular to the tank wall and below the water level. The camera features CCD (charge-coupled device) black and white sensor with 768 × 494 pxl (pixels). The camera settings were: focus length of 12.5 mm, aperture 5.6, and shutter speed of 1 ms. The bubble clouds in the middle of the tank were in focus at working distance of 27.5 cm from the camera to the tank wall. The horizontal and vertical scales were 0.296 mm pxl−1 and 0.698 mm pxl−1. With these scales, the smallest bubbles within bubble clouds that we resolved have projected-area equivalent diameter [10] of ≈ 0.5 mm. Our system is thus suitable to study the large-size end of the bubble size spectrum formed during active wave breaking (Section 2).
For each salinity value, a sequence of 30 images of bubble clouds was constructed by digitizing every 60th frame, time interval of 2 s, in the 1-min video records. The digitizing window was 664 pxl × 192 pxl, which represented a part of the whole field of view (19.65 cm × 13.4 cm). The images were analyzed with image processing software (4MIP, EPIX, Inc., Buffalo Grove, IL, USA) to determine three bubble cloud characteristics—the bubble cloud shape, numbers of bubbles, and void fractions of bubble clouds. The respective processing procedures are described below.
The steps of the procedure to determine the bubble cloud shapes and depths of penetration are illustrated in Figure 2 for salinity S = 13 psu. First, an initial field of view without bubble clouds was subtracted from the raw images (Figure 2a) in order to remove the background lighting [9]; this improved the contrast of the images (Figure 2b). Then, all 30 images of bubble clouds were averaged and the silhouette of the cloud determined in the resultant image (Figure 2c). Gradient edge detection (from the 4MIP software) applied to this image helped to delineate the wedge-like boundary of the cloud (Figure 2d). Finally, the x and y coordinates of several points on this boundary were extracted for further analysis.
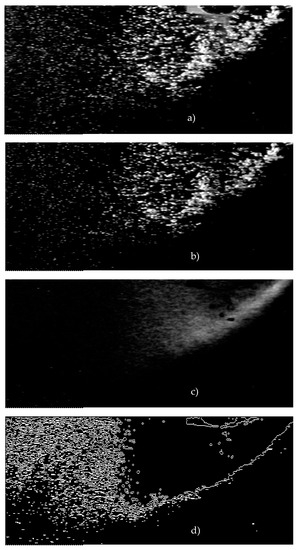
Figure 2.
Processing steps for bubble cloud characteristics: (a) Raw image; (b) image with subtracted background; (c) bubble cloud silhouette (result of averaging of 30 clouds); (d) edge detection reveals the cloud boundary. These and all other images are 590 × 180 pxl with horizontal and vertical scales of 0.296 mm pxl−1 and 0.698 mm pxl−1, respectively (see Section 3.2 for details).
The number of bubbles N within a bubble cloud was determined from the images with subtracted background (Figure 2b); the lowest intensity in these high-contrast images was 2 units (with 0 being black). All bright spots in these images thus represent air bubbles. The grayscale images were converted to binary images using intensity threshold. This conversion clearly separated different shapes in the images. BLOB (binary large object) analysis, available from the image processing software, was then applied to the binary images to count the bubbles; BLOB analysis refers to a group of connected pixels in a binary image. The largest bright blobs resulting from bubble overlapping or coalescence (especially for fresh and low-salinity water) were excluded by restricting the size of the bright spots to be counted. We effectively discarded blobs strongly deviating from circular or elliptical shapes by imposing maximum blob size of 20 pxl in any or both directions (x and y). This process excluded elongated shapes with sizes above ≈ 14 mm in one direction or ≈ 9 mm in both directions. Previous measurements [14,21] show few bubbles with such diameters. The BLOB analysis was performed twice on binary images formed with different intensity thresholds of 2 and 20 units to evaluate the effect of the threshold choice on the bubble count. As expected, more bubbles were counted for the lower threshold. However, the relative changes in the number of bubbles at different salinities, rather than the absolute number, are of interest. The results reported here are from BLOB analysis using an intensity threshold of 20 units. The BLOB analysis was applied to all 30 images taken at each salinity step, and an average value reported.
Estimates of void fraction α were calculated as ratio of the bright pixels (representing air) counted within the cloud volume to all pixels (representing air-water mixture) in the same volume [9]. The thickness of the slice over which α is calculated is around 5 cm; this is also the depth of the field at the camera settings. The slice is located at the middle of the laterally symmetric bubble cloud emanating from the jet. Fuzzy, out-of-focus bubbles outside of the slice were discarded. The cross-section of the cloud volume was delineated with a freehand drawing with the imaging software. Once again, an intensity threshold was used to separate bright pixels from the “mixture” pixels. This procedure was applied to all 30 images taken at each salinity step, and an average value reported.
3.3. Experimental Conditions
Both supply and receiving tanks (Figure 1) were filled with filtered tap water. We used filtered tap water to remove or minimize the presence of organic compounds. The experimental parameters changed and monitored during the experiment include salinity S, surface tension γ, and water temperature T. Table 1 summarizes the experimental conditions.

Table 1.
Summary of the controlled parameters: salinity S, water temperature T, calculated surface tension of pure NaCl solution γ0 (calculated for each S and T following [10] (their Appendix B)), measured surface tension γ, standard deviation of the measured surface tension σγ, surface film pressure ∆γ (calculated as ∆γ = γ0 − γ).
Salinity changed between 1 and 38 psu in steps of ∆S = 5–7 psu by adding an appropriate amount of laboratory grade NaCl to the water volumes, consistent with the procedures used in [10]. The salinity was measured with a handheld refractometer. The amount of salt added into the receiving tank was slightly augmented compared to the nominal ∆S estimates to eliminate salinity differences from the previous experiment. The next measurement started only when the salinity values in all volumes (the receiving tank, the supply tank, and the hose) were equal. Our experimental setup does not monitor for the influences of different fluid properties (e.g., density, viscosity, surface tension) on air entrainment [30] as salt is added. However, Chanson et al. [36] have shown that such influences are “negligibly small.” Experimental evidence also points to almost identical volumes of air entrained by breaking waves in fresh and saline waters [4,5,21]. We therefore assume that our plunging jet configuration provides the same energy input for each salinity step.
The water temperature was maintained constant within ∆T = ±0.1 °C between different salinity steps. Following [10] (see their Appendix B), such temperature change would affect the surface tension by ∆γ(∆T) = 0.014 mN m−1 at a given salinity. In comparison, a variation of salinity by 5 psu (change of S at our smallest step), would change the surface tension by ∆γ(∆S) = 0.11 mN m−1. We, therefore, consider all γ variations in our experiment to be caused by salinity.
Surface tension was measured with a tensiometer based on Wilhelmy plate method [10]. One reading of the surface tension was made for four salinity steps to avoid water contamination. Two γ readings were taken for S = 1, 25, and 38 psu. For each pair of data, the respective percent difference (PD) is 3.4%, 2.1%, and 9.9% (average 5.1%). Using these PDs as relative measuring error σγ/γ (where σγ is the standard deviation (SD) for surface tension), we estimate σγ = 3.6 mN m−1 on average. This estimate is comparable to the average σγ = 4.1 mN m−1 obtained from 10 samples in filtered water during a separate set of experiments characterizing individual bubbles [10]. Because this similarity lends confidence to the σγ estimates from the PDs of two readings, we use them as the measuring uncertainty for our bubble cloud experiment (Table 1).
4. Results
We often utilize the physicochemical terminology introduced in Section 2 when presenting and discussing our results below. Recall that a saline solution without organic additives exhibits negative adsorption and has negative surface film pressure ∆γ = γ0 − γ < 0 when its surface tension γ is higher than that of pure water, i.e., γ > γ0. Because higher γ values hinder the formation of bubbles, such a saline solutions acts as an antifoaming agent. Conversely, a saline solution which contains organic additives exhibits positive adsorption and has positive surface film pressure ∆γ > 0 because its surface tension γ is lower than that of pure water, i.e., γ < γ0. Because lower γ values facilitate both the formation and stabilization of bubbles, such a saline solution acts as a foaming agent.
4.1. Surface Tension Dependence on Salinity
To establish a baseline of behavior of the surface tension as a function of salinity γ(S) in different saline solutions, we measured γ as we changed S of small 150 mL water samples of distilled, filtered, tap, and contaminated waters. The contaminated water was a mixture of tap water with a drop of silicone oil, which acts as a surfactant. Figure 3a,b (solid symbols) show that the values of surface tension of distilled and filtered water at salinity of 1–2 psu are higher than the value γ0 for pure water (Section 2). As expected (see Appendix C in [10]), γ increases with salinity. We note from the different slopes in Figure 3a,b that the effect of S on γ is stronger for purer water.
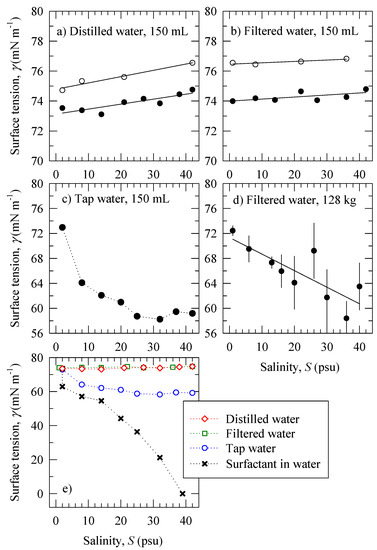
Figure 3.
Trend of the surface tension γ as a function of salinity S for water with different quality in 150 mL volume: (a) distilled; (b) filtered; (c) tap; (d) filtered (large volume), error bars are ±95% CI; (e) data from panels (a–c) (open symbols) are compared to data for silicone oil (a surfactant) mixed in water (crosses); the legend lists all symbols in panel (e). Solid lines are linear fits to data. Dotted lines connect the data points. The solid and open symbols in panels (a,b) are for two different measurements of γ at same salinity values. (Note in panel d 128 kg = 128 × 103 mL.).
The decreasing slope of γ(S) in Figure 3c confirms that the presence of either impurities in the added NaCl or various chemical compounds (nonorganic and organic) in tap water change the salinity effect as compared to that in pure water. The asymptotic trend (leveling off) at higher salinity in Figure 3c is consistent with predictions of the Gibbs adsorption equation for higher concentrations of inclusions (e.g., Appendix C in [10]). With the progression of the experiment to higher salinity, we observe: (i) enhanced suppression of γ by organic inclusions as ionic strength increases; or (ii) stronger suppression of γ by accumulation of additional inclusions. The decrease of γ by various inclusions in tap water is ∆γ ≅ 14 mN m−1 over the salinity range.
While a large water volume in the receiving tank is desirable to avoid wall effects (Section 3.1), it is difficult to keep the water free of contaminants [10]. This is demonstrated with the comparison of Figure 3d to Figure 3b: the decreasing γ(S) slope in Figure 3d is opposite to that of γ(S) in Figure 3b. Both measurements are in filtered water, but the water volumes are different. No leveling off at high salinity is observed (as in Figure 3c) suggesting that the contamination is not strong. The positive film pressure ∆γ could be caused by additional contamination.
Figure 3e compares the surface tension data from Figure 3a–c (open symbols) to the surface tension of water mixed with silicone oil (crosses). Adding silicone oil to fresh water (S = 2 psu) causes a drop of the surface tension from 73.53 mN m−1 to lower value of 62.92 mN m−1, a positive surface film pressure ∆γ of 10.6 mN m−1. Holding the silicone oil concentration constant but adding more salt (up to S = 14 psu) gradually suppresses the surface tension by an additional ∆γ = 8.6 mN m−1. The surface tension decreases much more for S > 14 psu and reaches a value of ∆γ ≅ 55 mN m−1. This contrasts with the positive ∆γ seen in Figure 3c,d. We thus infer that the positive ∆γ of tap water can be considered an upper limit against which we can assess possible contamination due to surfactants.
The specific γ(S) trends seen in Figure 3 can serve as indicators for the water quality during our experiment. These trends can also help to deduce the mechanisms through which different salinities affect the bubbles. The trends of Figure 3 are summarized as follows. Increasing trends (like those in Figure 3a,b) suggest that the salinity acts as an antifoaming agent and hinders the formation and stabilization of the bubbles. The decreasing trend with magnitude ∆γ up to 15 mN m−1 evident in Figure 3c would indicate the presence of contaminants, but not necessarily of surfactants. A leveling off for high salinity (like that in Figure 3c) at a fixed concentration of contaminants suggests that the bubble films become brittle; such a behavior is associated with the Gibbs effect [10] (their Appendix C). Monotonically decreasing trends (like that in Figure 3d) suggest initial but limited contamination. The presence of surface tension gradient (slope), which such cases exemplify, is consistent with bubble stabilization either by the Marangoni effect at low S (diluted solutions) or by film elasticity sustained by Gibbs effect at higher S values.
4.2. Bubble Cloud Characteritics
Figure 4 shows that the surface tension γ for our experiment in filtered water is above or close to the expected (high) γ0 values (dashed red line) over the salinity range; the corresponding surface excess (adsorption) values ∆γ are given in Table 1. The error bars show the measuring uncertainty (as defined in Section 3.3).
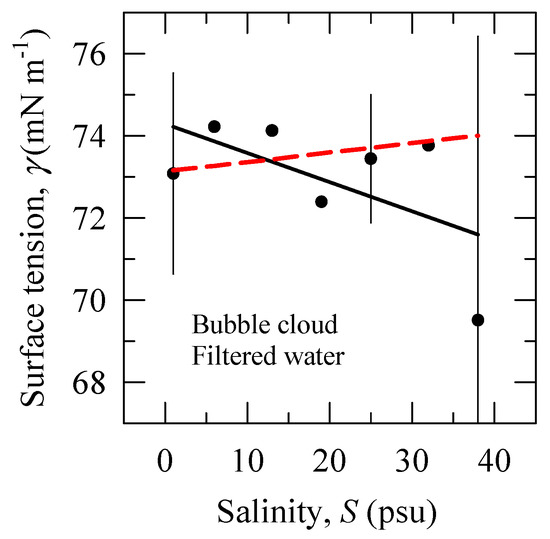
Figure 4.
Surface tension γ as a function of salinity S. Solid line is a linear regression fit to the data. Dashed line is expected surface tension of pure NaCl solutions γ0 (Table 1). The error bars are obtained as percent differences (PD) of two measured samples. We discussed the use of the PD values as the measuring uncertainty in Section 3.3.
The uncertainty (error bars) seen in Figure 4 makes it difficult to identify the physicochemical conditions during the experiment. Negative adsorptions at S of 6 and 13 psu suggest that the antifoaming action of salinity might have been observed in these solutions to some degree. Such inference is supported by a statistical significance test which shows that the γ0(S) trend—associated with the antifoaming action of the salinity (Figure 3a,b)—is not statistically different from the measured surface tension values (p > 0.05 for black symbols and dashed red line). The γ(S) trend (solid black line), though slightly decreasing over the range of salinity (by ≈ 6%), also does not differ statistically from the γ0(S) trend. Overall, recognizing the relatively high γ values (as compared to those in Figure 3), we deduce that our experiment provides useful information for the effect of the ionic strength on bubble cloud characteristics with minimal influence from organic contaminants.
The four panels of Figure 5 show images of bubble clouds in fresh water and water with salinity of 13, 25 and 38 psu. Evident in each panel is an inhomogeneous distribution of the bubble sizes: bubble sizes decrease with increasing distance from the energy source (i.e., horizontally from right to left). The bubble cloud in fresh water (Figure 5) comprises two parts: a part with many large bubbles near the source of bubble formation (i.e., jet), and another part with a few small bubbles further from the source. This observation is consistent with previous experiments, which also showed decreasing bubble sizes away from the air entrainment point [30,38,39]. Comparison of the left-hand sides of panels a, b, and c (fresh water and salinities of 13 and 25 psu) shows that the number of the small bubbles away from the source increases significantly with salinity. This is consistent with Scott’s [15] observations.
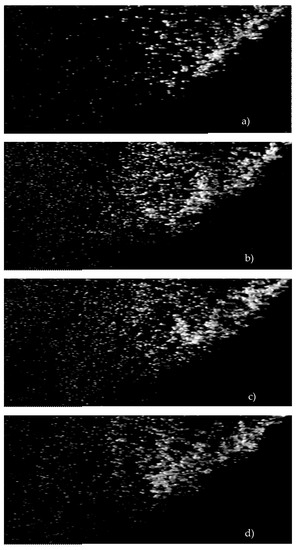
Figure 5.
Bubble clouds in fresh and saline water: (a) S = 2 psu; (b) S = 13 psu; (c) S = 25 psu; (d) S = 38 psu. Experimental conditions and monitored variables are given in Table 1 and Figure 4. The visualizations show that the overall shape of the envelope of the bubble cloud is the same for fresh or more saline water. Also evident is that there are fewer bubbles at the left-hand side for fresh water (panel (a)).
As the bubble size changes, so does the bubble penetration depth. The rapid rise of the large bubbles to the surface restricts their penetration depth (e.g., at the right side of the images in Figure 5); the smallest bubbles observed in our experiment are seen over the full depth on the images. This size-dependent deepening forms a bubble cloud with wedge-like shape, similar to the wind-driven bubble clouds [9]. The contours of bubble clouds for salinity of 19 and 31 psu are shown in Figure 6a; the contours for all other salinity values fall between them. The penetration depth for the large bubbles (close to the jet impact) is about 2 cm for all salinity values, whereas small bubbles can penetrate to 13 cm and beyond. Figure 6b shows the cloud shape for fresh water (solid line) together with its standard deviations (dotted lines). The similarity between the variations of the plume shape in Figure 6a (depicting variations with salinity) and Figure 6b (depicting statistical variations) suggests that the shape of the bubble cloud boundaries does not vary significantly with salinity.
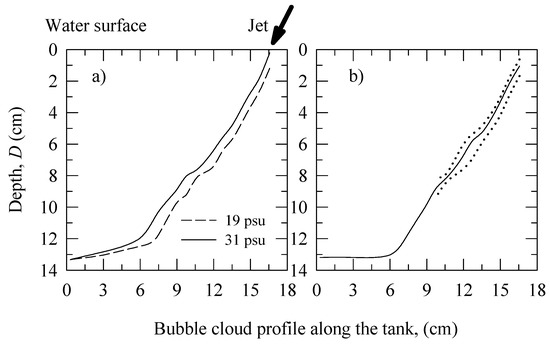
Figure 6.
Bubble cloud shape: (a) Bubble cloud contours for salinity of 19 and 31 psu; (b) Bubble cloud contour only for fresh water (solid line) together with the ± standard deviation (dotted lines).
Figure 7a shows the variation of the number of bubbles normalized by the maximum observed value Nn with salinity. The number of bubbles within the cloud increases with increasing salinity and attains a maximum in the range of 13–25 psu. The dependence of void fraction on salinity (Figure 7b) is similar to that of the number of bubbles; the void fraction increases with salinity to a maximum of 40% for 12–25 psu and then decreases to about 30% for the highest salinity. We compare our results in Figure 7b obtained with a continuous plunging jet to those of Monahan et al. [21] obtained with an episodic tipping trough. Monahan et al. [21] report maximum void fraction of 16% at S = 0 psu and of 20% at S = 20 psu; the void fraction increased from fresh to saline water by a factor of 1.25. From Figure 7b, we have a void fraction increase from fresh water to a solution of S = 19 psu by a factor of 1.9. The larger change of α observed in our experiment suggest that large bubbles contribute more to the void fraction than smaller bubbles. This explanation is reasonable considering that the continuous plunging jet may scavenge smaller bubbles (Section 3.1), and that our system reliably detects relatively large bubbles (Section 3.2). The emphasis on the contribution of small bubbles in [21] is likely compounded by the fact that the microscope system used in [21] to detect bubbles was positioned at 10 cm depth. According to our results (Figure 5 and Figure 6), small bubbles dominate the bubble population at such depth. We reiterate that our focus concerns the transient bubble population formed during active wave breaking when large bubbles dominate the dynamics.
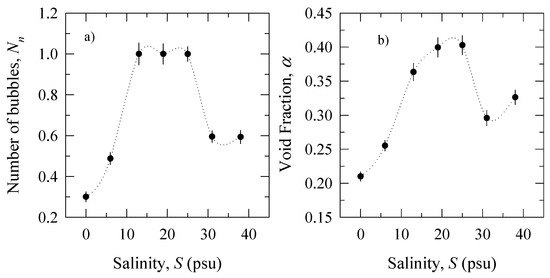
Figure 7.
Salinity dependence of the: (a) number of bubbles within the bubble cloud (normalized to the maximum observed value); (b) bubble cloud void fraction.
Blenkinsopp and Chaplin [4,5] discussed contrasting results in the literature for bubble cloud characteristics in fresh and saline waters: some investigations report significant differences in plume bubble size distributions, mean void fractions, and/or air entrainment volumes [20,21,29]; other investigations note lack of such differences (see [5] for references). These contrasting reports are based on measurements of bubble cloud characteristics in fresh versus saline waters. Our results, specifically the nonmonotonic dependence of number of bubbles Nn and void fraction α on salinity, give a possible explanation for such discrepancies. Figure 7b shows that the maximum difference for α (and by extension the bubble size distribution) is for fresh versus brackish waters (PD = 63%), not fresh water and seawater of 35 psu (PD = 38%). Such а trend implies that measuring the bubble cloud characteristics only at two points (fresh water and seawater) could give similar results and small differences.
Because our experimental setup (Section 3.1) simulates a breaker of one specific scale, we would suggest repeating our measurements for breakers with different scales in order to generalize the results. In our setup, a change of the angle θ and nozzle distance l (Figure 1) of the plunging jet could produce different bubble clouds thus simulating air entrainment from breakers at different scales (e.g., plunging, spilling, or in between). However, we do not expect the results presented here to change significantly for different setup configurations. Such expectation is based on previously reported results that the measured integral (mean) void fraction of bubble plumes is not dependent on breaker type and scale [4,38].
5. Discussion
5.1. Salinity Influence on Bubble Clouds
The two obvious effects of salinity on bubble clouds are a change of bubble sizes and a change of the number of formed bubbles (Figure 5). Our results of nonmonotonic changes with salinity in Figure 7 reflect the occurrence of both of these effects. Below we consider physicochemical processes, which bring about and explain these effects.
The increase of Nn and α in Figure 7 at low salinities arises as more bubbles (at any size) are generated in increasingly saline water (Section 2). The decrease of Nn and α for salinities above 25 psu can be explained by the narrowing of the bubble size spectrum with salinity. The same volume of entrained air (Section 3.3) is shattered into increasingly smaller bubbles as more salt is added; both the number of large bubbles and the observed maximum bubble size diminish with salinity (Section 2). Experiments with finer resolution of scales (less than 0.5 mm) than in our setup show negligible changes in the value of the void fraction. For example, a laboratory experiment with breaking waves has shown that differences in the contribution of small bubbles to the measured void fraction in freshwater, artificial seawater (≈34 psu), and natural seawater (≈27 psu) is barely detectable [5]. Experiments with a tipping trough showed a difference of only 4% in the void fractions measured in fresh water and brackish water (20 psu) when the number of small bubbles increased by more than an order of magnitude [20,21]. Our results in Figure 7 help to identify salinity value of around 25 psu as the threshold at which the salinity-enhanced production of bubbles smaller than 0.5 mm in diameter prevails; i.e., S ≈ 25 psu marks the salinity threshold at which the relevant contribution of small bubbles (with diameters below 0.5 mm) becomes dominant yielding lower void fraction values.
We speculate that the change of the bubble sizes is related to the change of the ionic strength (the abundance of ions) of the aqueous solutions. The addition of salt (NaCl in our experiment) to water increases the ionic strength of the aqueous solution as NaCl dissociates completely to Na+ and Cl− ions [27,28]. Thus, as salinity increases in our experiment, it changes not only the surface tension of the electrolyte solution (a solution containing ions), but also the electrical double layers (a charge accumulation and a charge separation that always occurs at interfaces within and of electrolyte solution) at the free air-sea interface and the bubble walls. The repulsive forces associated with the electrical double layers on air-water interfaces is likely to contribute to the formation of smaller bubbles. Further analytical consideration and collection of more data can help to improve our understanding.
The formation of large number of bubbles can be related also to the changes of the surface tension with salinity and thus the foaming ability of the saline solutions. To understand how the foaming ability of the solutions contributes to the nonmonotonic curves in Figure 7, we compare the trends in Figure 7a and Figure 4. This comparison shows apparent contradiction. The high surface tension γ and its weak variation over the salinity range γ(S) seen in Figure 4 do not foster bubble formation; this is because saline solutions with high γ values hinder the formation of bubbles and thus have antifoaming properties (Section 2 and Section 4.1). However, Figure 7a shows significant variations of Nn(S) for the weak γ(S) changes in Figure 4. We show below that we can reconcile the trends of Figure 4 and Figure 7a when we consider the foaming ability of the solutions. Our reasoning is as follows.
(a) The surface tension of fresh water at S = 1 psu (Figure 4) produces the lowest Nn value (Figure 7a), while a solution with S = 6 psu (Figure 4) increases Nn only modestly (Figure 7a). This is consistent with the antifoaming action of salinity at high surface tension in clean and dilute solutions in which surface films rupture easily.
(b) Figure 4 shows high γ value for S = 13 psu, which suggests antifoaming action of the solution at S = 13 psu. However, Figure 7a shows strong increase of Nn to its highest value; this deviates from the expected antifoaming action. Furthermore, the highest Nn values in Figure 7a are preserved for S = 13–25 psu, while the γ values in Figure 4 decrease only weakly. All these observations suggest that the decreasing γ(S) trend in Figure 4, though weak, is still able to facilitate the formation of more bubbles at S = 13–25 psu.
(c) The γ values for S > 25 psu in Figure 4 are associated with abrupt decrease of Nn and α in Figure 7. This suggests that, in addition to fewer large bubbles being formed (as explained in the beginning of this section), it is also possible that there is more efficient break-up of bubbles in stronger electrolyte solutions with high ionic strength. This is plausible because the weak γ(S) change occurs in solution with a minimal contamination (established from Figure 4). Such conditions inhibit bubble stabilization and are conducive to more bubble break-ups, thus contributing to the decrease of Nn and α.
5.2. Implications for Air-Sea Interaction Studies
The results of this laboratory experiment are for minimized effect of organics and surfactants in the water. It is clear, however, that the presence of organics and surfactants in saline solutions easily masks the sole effect of the salinity (Figure 3). The reported results reveal that, depending on the organic concentrations, salinity can hinder or enhance the effects of the organics in different solutions.
Bubble clouds in the ocean enhance the gas exchange across the air-sea interface [1]; the void fraction magnitude is important in this process [26]. Because the large bubbles predominantly determine α (Section 2), their decrease at higher S, as observed here, would affect the efficiency of the gas exchange in open ocean. Our results suggest that the influence of the salinity on the gas exchange would be most effective in brackish waters with S in the range of 12–25 psu. Estuaries, coastal zones, continental shelves, and small water bodies (e.g., Black, Caspian, and Baltic seas) with salinity in this range could thus contribute to gas exchange substantially. Considering that wave breaking in coastal zone and small seas is more frequent due to bottom topography, the gas exchange in brackish waters could be comparable to that in open ocean with S > 30 psu. While the contribution of large bubbles is dominant in transient bubble clouds, the smaller bubbles comprising the equilibrated, background bubble population likely dominate the gas exchange processes after the active wave breaking.
Our results show that salinity does not affect significantly the shape of the bubble clouds, but it brings notable changes in the bubble size distributions. This suggests that, at a given wind speed in the field, bubble clouds with similar shapes and lateral extent would form in waters with different salinity. It is known that the bubble clouds sustain and replenish the whitecaps on the surface through the degassing of the bubbles in the bubble plumes [9,13,24,25]. Therefore, the implication of our results is that varying salinity would not affect the horizontal extent of the whitecaps supported by similarly shaped underwater bubble clouds. However, different bubble size distributions in bubble clouds at different salinity would change the duration for which the underwater cloud shape supports the whitecaps. This would affect the whitecap lifetime on the surface. Our results thus suggest that the salinity influence on the persistence of oceanic whitecaps is not through geometric variations of the whitecap area but via the whitecap longevity.
The surface lifetime of the bubbles is another pathway that provides the whitecap longevity. Our laboratory results on individual large bubbles [10] suggested that, though present, the salinity effect on the surface lifetime of large bubbles is weak in field conditions; the effect of organics and surfactants on the surface lifetime is certainly stronger [17]. We thus surmise that the main pathway through which salinity affects the whitecap persistence is through changes of the bubble size distribution and the associated period of plume degassing.
6. Conclusions
We present the results of a laboratory experiment designed to observe and quantify the effect of salinity S over the range of 1–38 psu on the characteristics of bubble clouds comprising large bubbles (diameters above 0.5 mm). The experiment investigated the cloud shape and penetration depth, and the number of bubbles and void fraction of the bubble clouds. Concurrent measurements of surface tension γ during the experiments help to interpret the results in terms of physicochemical processes associated with the ionic strength of electrolyte solutions. The main conclusions of our study are:
(1) For the large end of the bubble size distribution, the number of bubbles generated within the cloud increases with the salinity and has maximum numbers over the range of salinity 12–25 psu (Figure 5 and Figure 7a). Further increase of salinity decreases the number of large bubbles in the cloud.
(2) The void fraction of the bubble cloud attains a maximum value of 40% over the range of salt concentrations 12–25 psu (Figure 7b). Thus, both the number of bubbles and the void fraction vary nonmonotonically with increasing salinity. Implication of this result is that bubble-mediated gas exchange could be more effective in waters with salinity below that of the open ocean (Section 5.2). This suggests that coastal zone and shallow seas could contribute to air-sea gas transfer substantially.
(3) Processes promoting maximum number of bubbles and void fraction at mid salinity values are (Section 5.1): (a) an enhanced formation of more bubbles with increasing salinity. (b) A shift of the bubble size peak toward smaller size end as salinity increases. (c) Salinity narrows the bubble size distribution on the large size end. (d) Interplay between the surface tension gradient due to organic additives and the ionic strength of solutions.
(4) The lateral shape of the bubble clouds does not change over the range of salinities used. Size dependence of the bubble penetration depth yields a wedge-like bubble clouds (Figure 5 and Figure 6). As salinity increases the number of smaller bubbles, the lowest point of the bubble cloud deepens.
(5) Invariant bubble cloud shape for different salinities, combined with varying bubble size distributions, suggests that the period of plume degassing is the primary mechanism through which salinity affects the whitecap persistence (Section 5.2).
The nonmonotonic variations of void fraction with salinity is an important result. It will be useful to corroborate this result with measurements in a different experimental configuration. Our results hint that salinity can affect the efficiency with which organics influence the characteristics of bubble clouds and individual bubbles. The intriguing interplay between salinity and organics deserves further investigation.
Acknowledgments
Part of this work is sponsored by the Office of Naval Research (NRL program element 61153N). Data for the experimental conditions and surface tension are given in tables in the text. More data are available from the first author upon request (maggie.anguelova@nrl.navy.mil).
Author Contributions
M.D.A. performed the experiments and analyzed the data; M.D.A. and P.H. interpreted the results and wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Thorpe, S.A. On the clouds of bubbles formed by breaking wind-waves in deep water, and their role in air-sea gas transfer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1982, A304, 155–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. Bubble clouds and the dynamics of the upper ocean. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1992, 118, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.A. Dynamical processes of transfer at the sea surface. Prog. Oceanogr. 1995, 35, 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Chaplin, J.R. Void fraction measurements in breaking waves. Proc. R. Soc. A 2007, 463, 3151–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Chaplin, J.R. Void fraction measurements and scale effects in breaking waves in freshwater and seawater. Coast. Eng. 2011, 58, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifer, I.; de Leeuw, G. Bubbles generated from wind-steepened breaking waves: 1. Bubble plume bubbles. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C06020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leifer, I.; Caulliez, G.; de Leeuw, G. Bubbles generated from wind steepened breaking waves: 2. Bubble plumes, bubbles, and wave characteristics. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, C06021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Bubbles in the near-surface ocean: A general description. J. Geophys. Res. 1988, 93, 587–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelova, M.D.; Huq, P. Characteristics of bubble clouds at various wind speeds. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, C03036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelova, M.D.; Huq, P. Effects of Salinity on Surface Lifetime of Large Individual Bubbles. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2017, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, E.R.; Schwartz, S.E. Sea Salt Aerosol Production: Mechanisms, Methods, Measurements and Models—A Critical Review; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Deane, G.B. Sound generation and air entrainment by breaking waves in the surf zone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1997, 102, 2671–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, A.H.; Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D. Laboratory air-entraining breaking waves: Imaging visible foam signatures to estimate energy dissipation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D. Scale dependence of bubble creation mechanisms in breaking waves. Nature 2002, 418, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.C. The role of salt in whitecap persistence. Deep Sea Res. 1975, 22, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struthwolf, M.; Blanchard, D.C. The residence time of air bubbles <400 µm diameter at the surface of distilled water and seawater. Tellus 1984, 36B, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, A.H.; Deane, G.B.; Stokes, M.D. Two regimes of laboratory Whitecap foam decay: Bubble-plume controlled and surfactant stabilized. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2013, 43, 1114–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.M. Sea Spray and Its Relationship to Low Elevation Wind Speed. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Cambridge, MA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Cartmill, J.; Su, M.-Y. Bubble-size distribution under salt-water and fresh-water breaking waves. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 1993, 20, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, W.M.; Fitzgerald, J.W.; Monahan, E.C.; Wang, Q. Measurement of the sound produced by a tipping trough with fresh and salt water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 3178–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wilson, M.B. Air entrainment by breaking waves: A laboratory assessment. AER Technol. 1994, 187, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, E.M. Comments on “Bubbles produced by salt breaking waves in fresh and water”. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2001, 31, 1931–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, G.; Andreas, E.L.; Anguelova, M.D.; Fairall, C.W.; Lewis, E.R.; O’Dowd, C.; Schulz, M.; Schwartz, S.E. Production flux of sea spray aerosol. Rev. Geophys. 2011, 49, RG2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monahan, E.C.; Lu, M. Acoustically relevant bubble assemblages and their dependence on meteorological parameters. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1990, 15, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Bubbles in the near-surface ocean: Their various structures. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 1955–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, T.G.; Landwehr, S.; Miller, S.D.; de Bruyn, W.J.; Callaghan, A.H.; Scanlon, B.; Ward, B.; Yang, M.; Saltzman, E.S. Estimation of bubble-mediated air-sea gas exchange from concurrent DMS and CO2 transfer velocities at intermediate-high wind speeds. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 9019–9033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattoraj, D.K.; Birdi, K.S. Adsorption and the Gibbs Surface Excess; Plenum Publishing Company: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemenz, P.C.; Rajagopalan, R. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 3rd ed.; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, E.M.; Zietlow, C.R. Laboratory comparisons of fresh-water and salt-water whitecaps. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 6961–6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, A.K. Gas entrainment by plunging liquid jets. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1993, 48, 3585–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiger, K.T.; Duncan, J.H. Air-Entrainment Mechanisms in Plunging Jets and Breaking Waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2012, 44, 563–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, E.; Coe, H.; Green, D.; de Leeuw, G.; McFiggans, G. Laboratory-generated primary marine aerosol via bubble-bursting and atomization. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M. Bubble entrainment in breaking wind waves. Tellus 1982, 34, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, M.E.; Nilsson, E.D.; Butcher, A.; Bilde, M. On the seawater temperature dependence of the sea spray aerosol generated by a continuous plunging jet. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9052–9072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detsch, R.; Sharma, R.N. The critical angle for gas bubble entrainment by plunging liquid jet. Chem. Eng. J. 1990, 44, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanson, H.; Aoki, S.; Maruyama, M. Unsteady air bubble entrainment and detrainment at a plunging breaker: Dominant time scales and similarity of water level variations. Coast. Eng. 2002, 46, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonmarin, P. Geometric properties of deep-water breaking waves. J. Fluid Mech. 1989, 209, 405–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blenkinsopp, C.E.; Chaplin, J.R. Bubble size measurements in breaking waves using optical fiber phase detection probes. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2010, 35, 388–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.A.; Poon, Y.-K.; Wu, J. Temperature effects on generation and entrainment of bubbles induced by a water jet. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1991, 21, 1602–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).