Energy Minimization for Underwater Multipath Time-Delay Estimation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Correlation Function Modeling for Multipath Propagation
3. Multipath Time-Delay Estimation
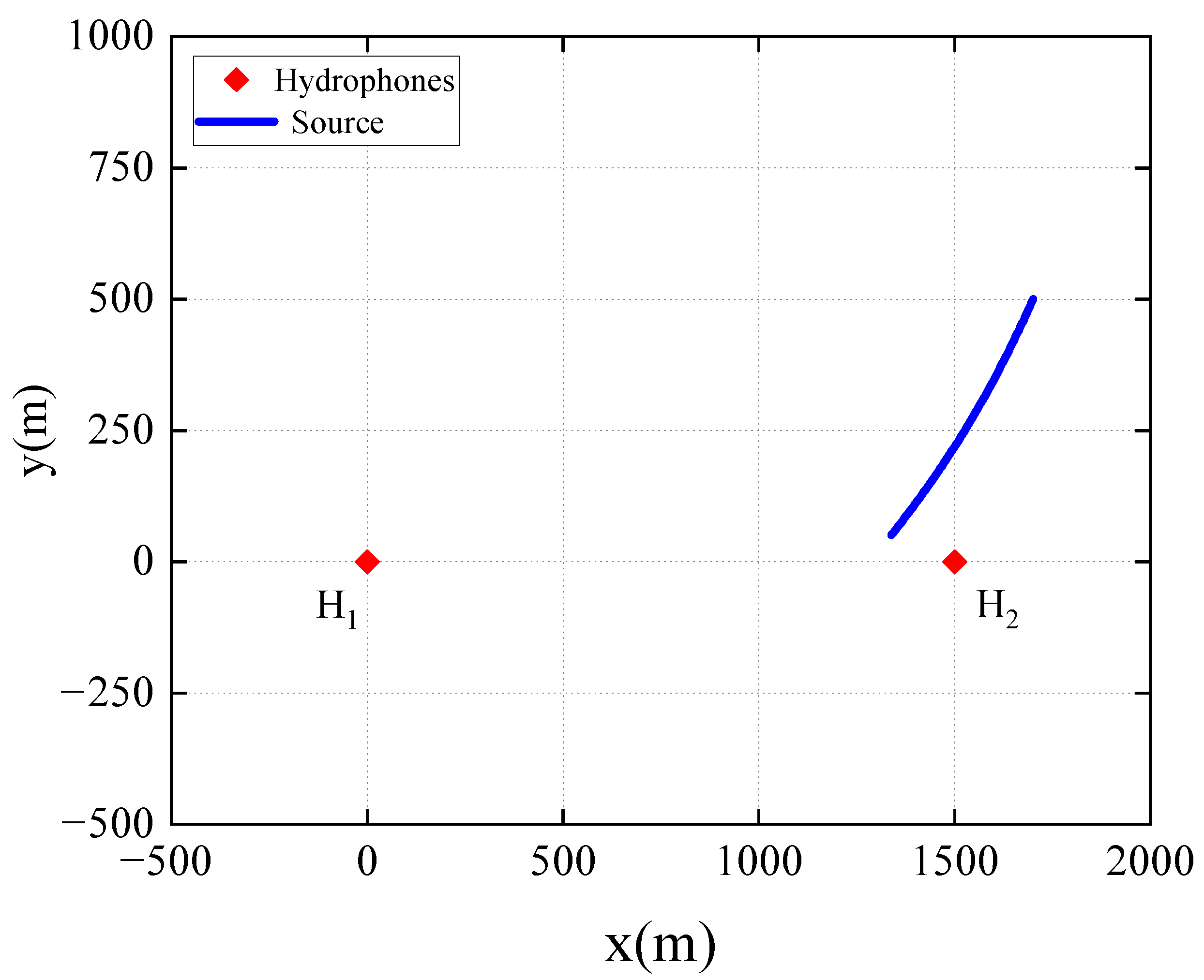
3.1. Problem Statement
3.2. Energy Function
- 1.
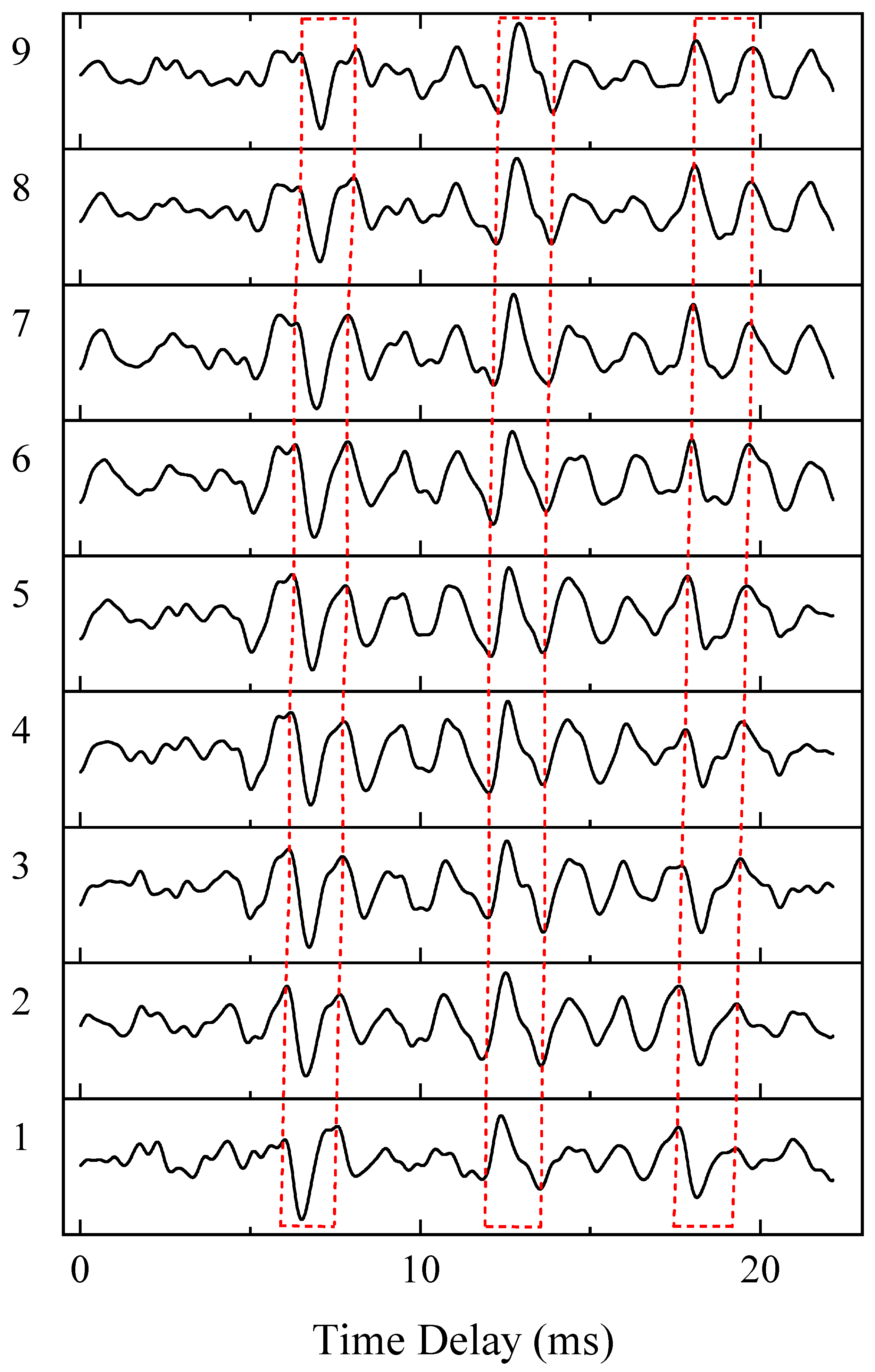
- Similarity. Due to channel effects, the cross-correlation pulses from different propagation paths exhibit distinct deformations compared to the autocorrelation pulse of the source signal. However, pulses corresponding to the same propagation path tend to remain similar across different time frames, as illustrated in Figure 1. Specifically, for the same path indices k and l in Equation (5), shows strong similarity in both polarity and shape. This property facilitates the association of cross-correlation pulses originating from the same path. To quantify pulse similarity, we employ the Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM), defined as follows:where and are the mean of the amplitude vectors and , and are their variance, and denotes the covariance term. and are small constants introduced in the SSIM to avoid instability when the denominator approaches zero. The SSIM is computed for every pair of pulses of , and their average is used as the overall similarity score. The energy contribution from pulse similarity is defined as follows:where is the total number of , as described in Table 1.
- 2.
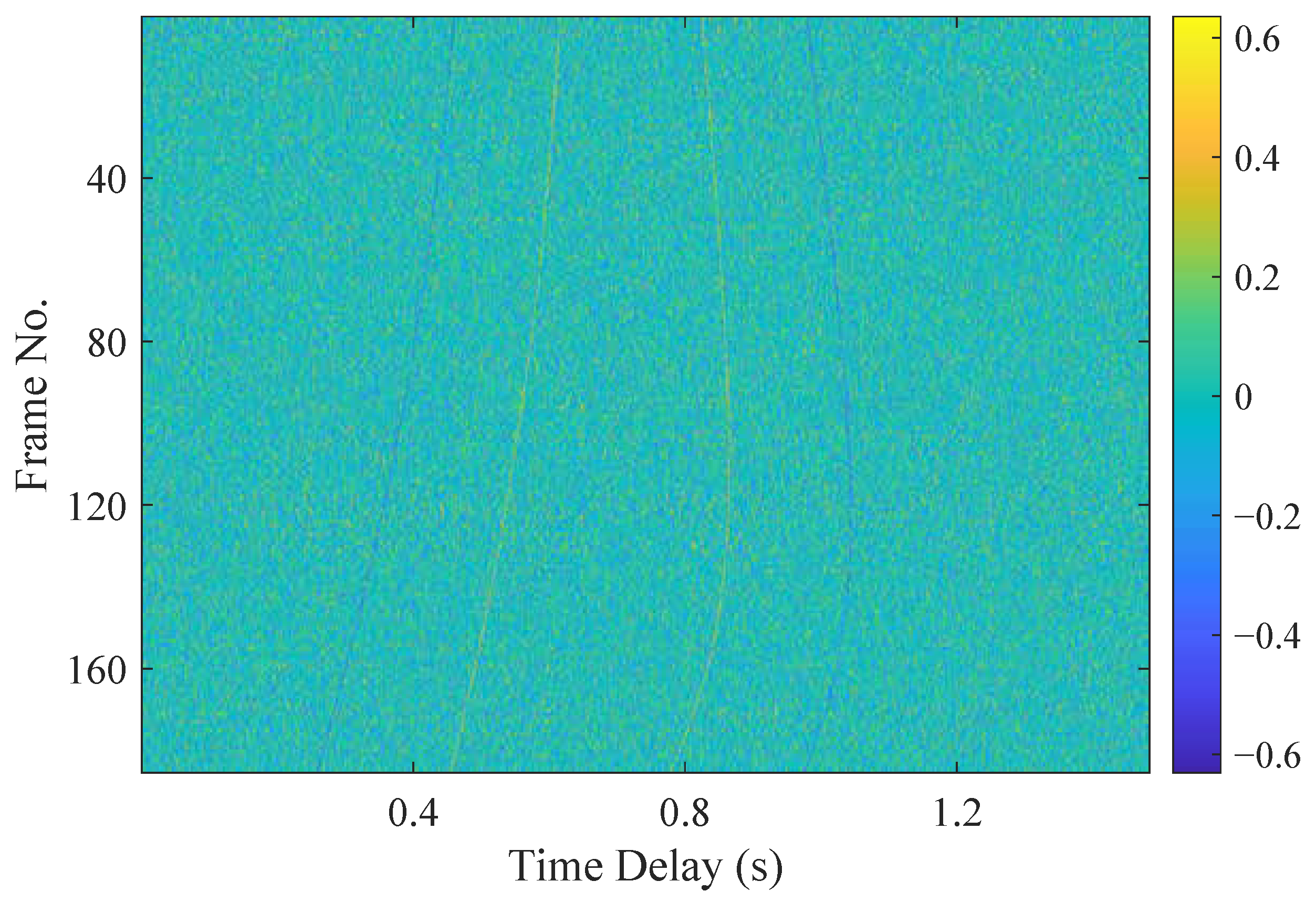
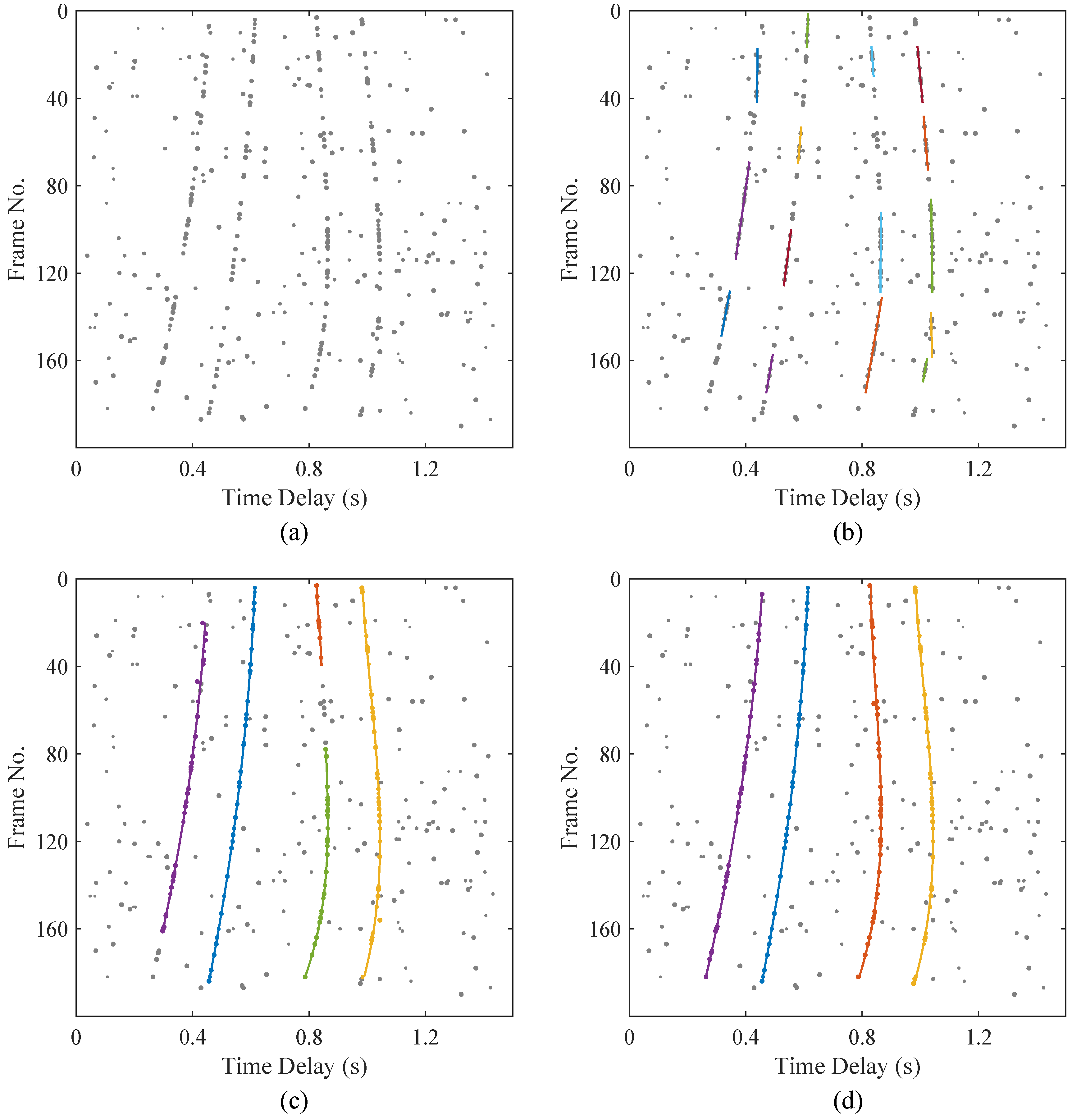
- Data term. Multipath delays vary with the relative motion of the source and hydrophones. Since the movement of the source is continuous, the corresponding delay trajectories are also continuous. The weighted cubic spline interpolation provides an effective means of fitting these delay trajectories by capturing their natural evolution.Figure 2 is a schematic diagram of weighted cubic spline fitting. The observed time delays associated with the n-th trajectory are used to perform trajectory fitting, where the independent variable is the discrete frame index . The fitted trajectory is likewise a function of t, and we denote by the fitted value at frame t.The data term evaluates the accuracy of trajectory fitting by measuring the Euclidean distance between the observations and the estimated trajectory:where represents the weight assigned to each observation, which is correlated with its peak amplitude. The start time and the end time correspond to the indices of the first and last observations in trajectory n, respectively. If an observation does not belong to any trajectory, it is classified as an outlier, ⌀, and assigned a constant cost, . The final formulation of the data term is given by the following equation:The outlier weight is set to a small constant to ensure numerical stability, and the outlier cost is set proportional to the average inlier fitting error.
- 3.
- Dynamics. The fitted trajectory reflects the motion characteristics of the target over time and is constrained by real-world physical limitations. The constant velocity model is widely used to describe the motion characteristics of targets because it supports linear paths, thereby reducing target identity switches. However, this approach also limits the flexibility of target motion. In this study, constraints are primarily imposed on the cubic coefficients of the spline, as they directly influence the maximum velocity of the target:where represents the maximum value among the cubic spline coefficients of trajectory . is a scaling factor that is introduced to balance the contribution of the trajectory smoothness term and the data fidelity term. In our implementation, is tuned empirically within the range of , and the final value is chosen via cross-validation on synthetic data.
- 4.
- Trajectory Persistence. The proposed method imposes no strict requirements on the start or end points of a target trajectory; it does not necessarily need to begin at the first frame or terminate at the last frame. However, longer trajectories are encouraged. Due to the influence of random noise and other strong interferences, correlation pulses may be completely submerged or become indistinguishable at certain moments or over short time intervals, leading to the disappearance of the targets. In such cases, multiple disconnected short trajectories are often formed, which is not conducive to tracking the trajectories. Assigning a higher cost to short trajectories helps reconnect fragmented tracks and prevents unnecessary identity switches. is used to adjust the importance of trajectory persistence to the energy function, usually taken as a fixed constant (0.5 in our experiments), which reflects encouragement for long trajectories and punishment for short trajectories:
- 5.
- High-order data fidelity. Equation (11) defines the requirement for trajectories to approximate the observations as closely as possible. Nevertheless, considering that targets may be intermittently obscured by noise, it is not mandatory for each frame within a trajectory duration to include a corresponding observation. To mitigate potential errors in trajectory fitting and the merging of short tracks, a constraint on the maximum permissible gap between successive observations is imposed:where denotes the maximum number of consecutive frames in which no observation is associated with the trajectory . The scaling factor is introduced to penalize long gaps and is set as a constant (empirically chosen in the range of ).
- 6.
- Regularization. The individual cost terms comprising the energy function are mutually constrained. For example, reducing the number of trajectories N tends to lower the energy associated with the , , and terms. However, an overly small N may result in many observations being left unassigned and labeled as outliers, thereby increasing the data term energy . In practice, without proper constraints on the number of targets, the model tends to generate a large number of short trajectories. To avoid overfitting, a higher penalty should be imposed for introducing additional targets.
3.3. Optimization
| Algorithm 1 Optimization |
Input: Initial observation set Output: Optimized trajectory set
|
- Initialization Strategy
- Hypothesis Space Expansion
- Computational Complexity
4. Results
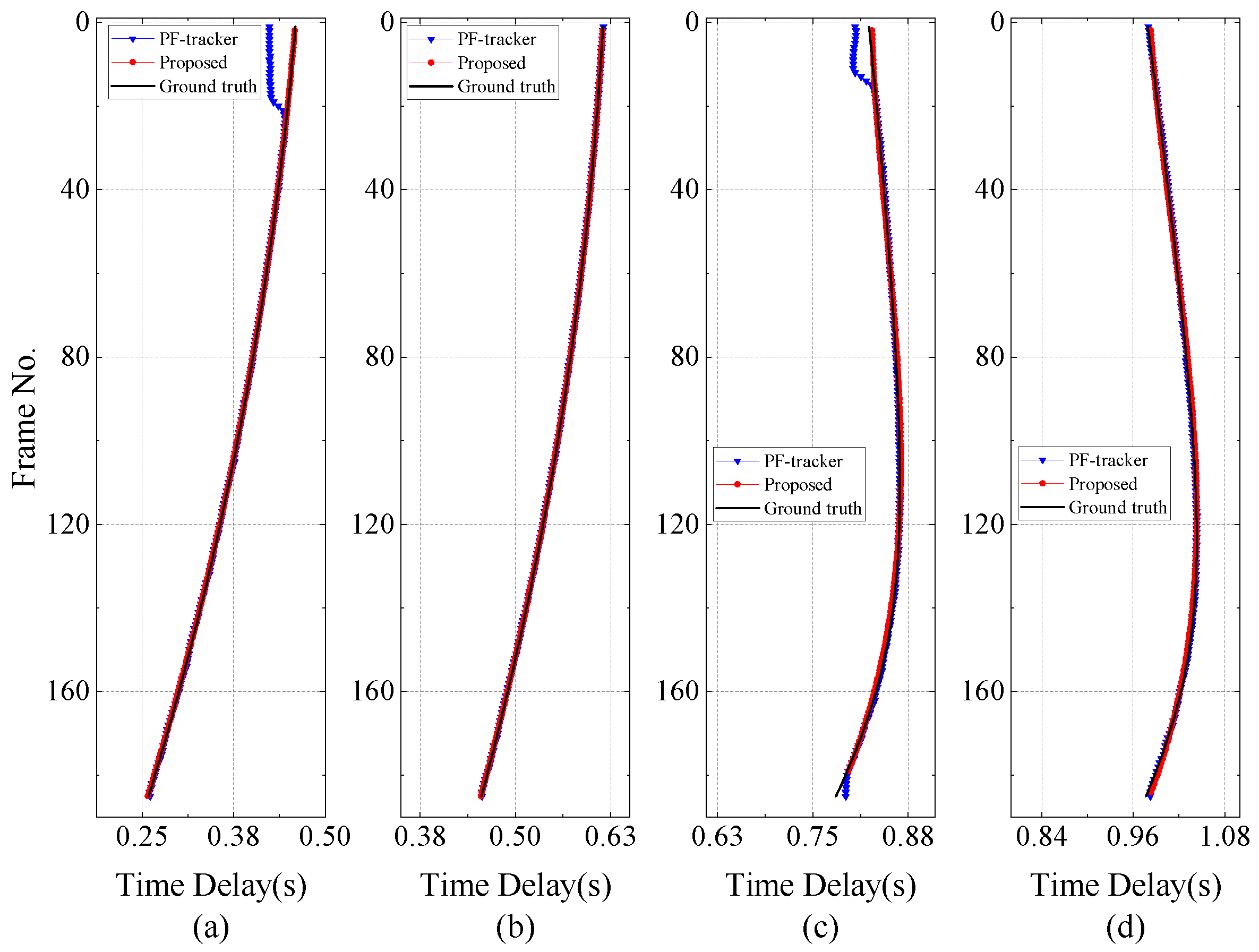
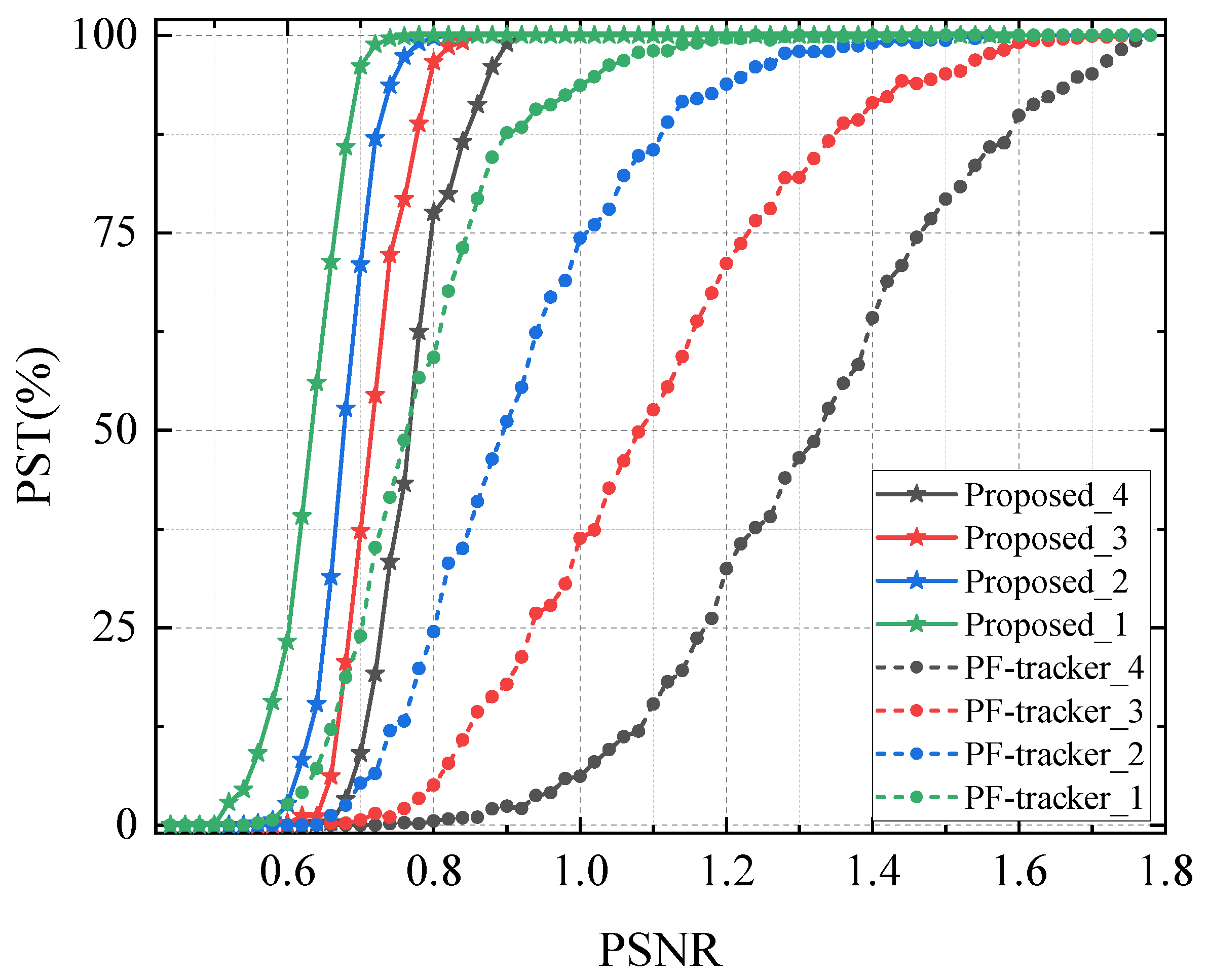
4.1. Numerical Simulation
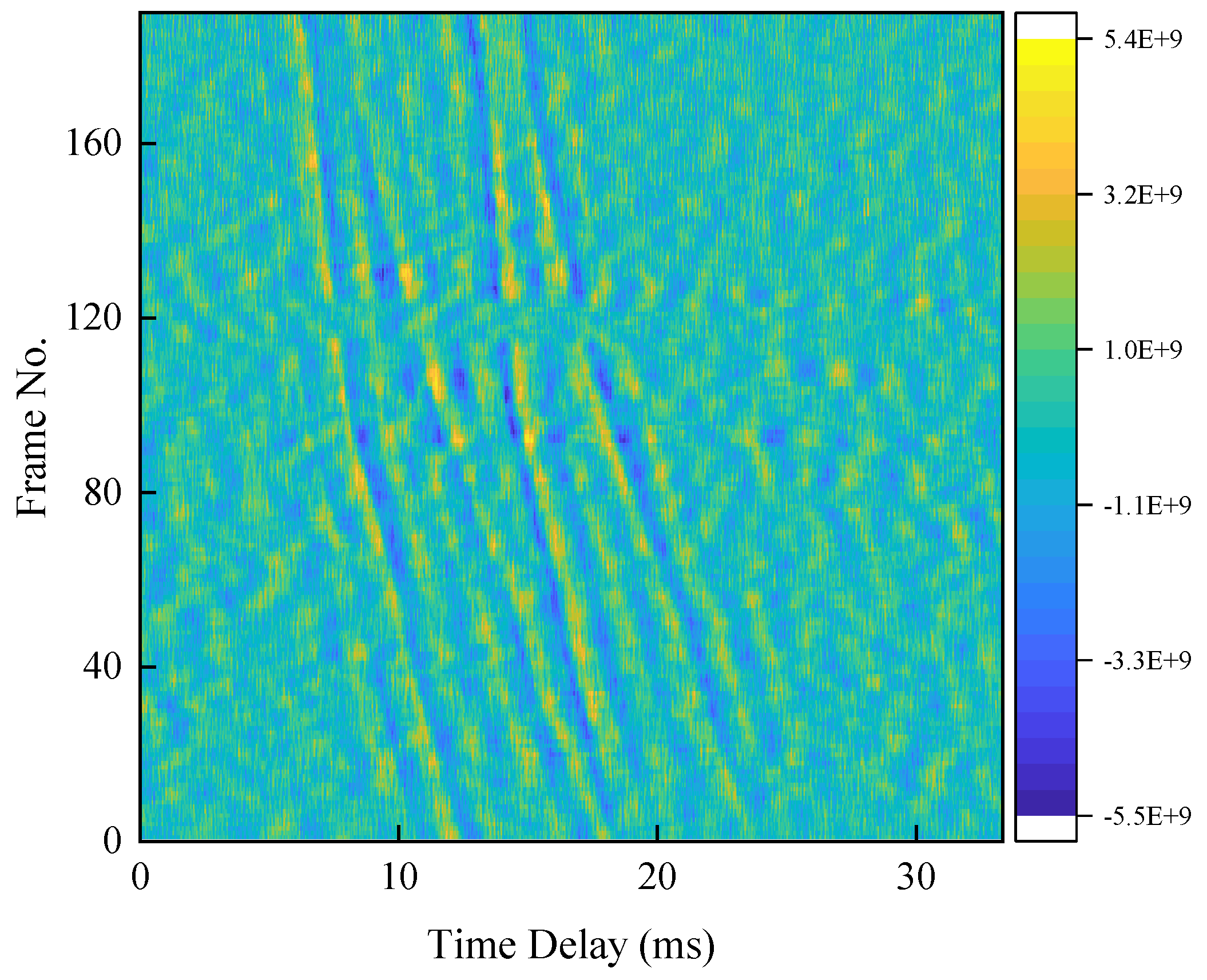
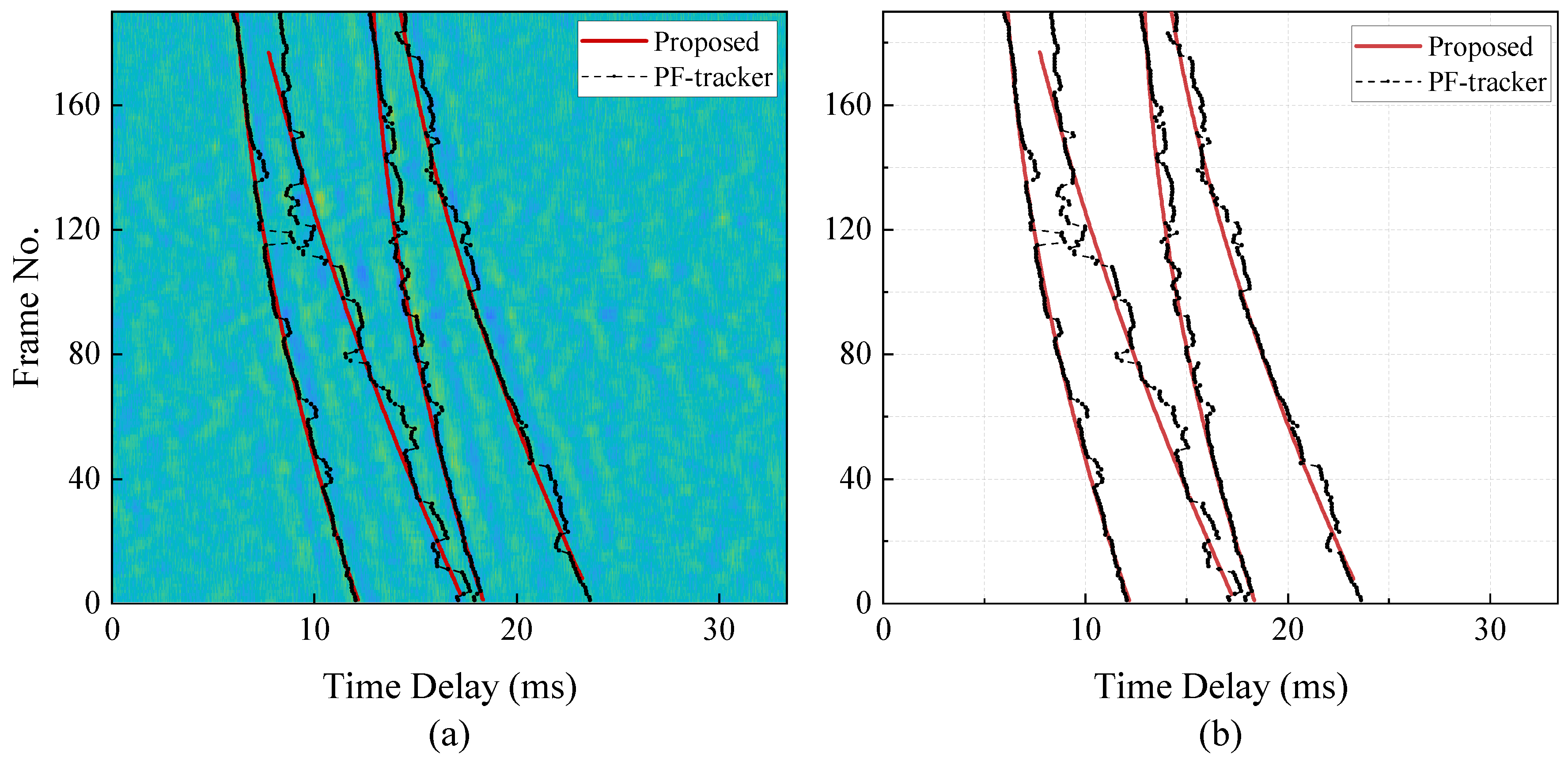
4.2. Experimental Validation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
- (3.b) CA-CFAR (cell-averaging CFAR). Using the same reference set , define
References
- Vaccaro, R. The past, present, and the future of underwater acoustic signal processing. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 1998, 15, 21–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, D.; Conti, A.; Ferner, U.; Giorgetti, A.; Win, M.Z. Ranging With Ultrawide Bandwidth Signals in Multipath Environments. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 404–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.R.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhou, S. Application of compressive sensing to sparse channel estimation. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2010, 48, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchendu, N.; Muggleton, J.M.; White, P.R. Acoustic leak localisation based on multipath identification. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 602, 118970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Xie, Z.; Pan, Y.; Ji, G.; Lü, X. Research on multipath performance of acoustic spread-spectrum signals based on artificial multipath experiments in an anechoic chamber. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 218, 109893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, M.; Catipovic, J.; Proakis, J. Phase-Coherent Digital-Communications for Underwater Acoustic Channels. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1994, 19, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhuo, J.; Sun, C. Imaging Seafloor Features Using Multipath Arrival Structures. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.J.; Jiang, X.; So, H.C. Sparse-representation algorithms for blind estimation of acoustic-multipath channels. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 133, 2191–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Yang, X.; Tong, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, T. A Low-Complexity Underwater Acoustic Coherent Communication System for Small AUV. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Preisig, J.C. Estimation of rapidly time-varying sparse channels. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2007, 32, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.R.; Zhou, S.; Preisig, J.C.; Willett, P. Sparse Channel Estimation for Multicarrier Underwater Acoustic Communication: From Subspace Methods to Compressed Sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2010, 58, 1708–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Q.; Li, H. Moving source localization with a single hydrophone using multipath time delays in the deep ocean. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, EL159–EL165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Z.; Yang, K.; Ma, Y. Passive localization in the deep ocean based on cross-correlation function matching. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 139, EL196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Han, G.; Guizani, M.; Yan, L.; Shu, L. Peak Extraction Passive Source Localization Using a Single Hydrophone in Shallow Water. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 3412–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Duan, R.; Yang, K. Formulas for three-dimensional source localization using multipath time delays measured by asynchronous distributed sensors in deep water. Ocean Eng. 2023, 286, 115499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Guo, L. Analysis of multipath time delay difference in deep sea convergence zone and its application in source range estimation. J. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 43, 237–251. [Google Scholar]
- Tiemann, C.O.; Thode, A.M.; Straley, J.; O’Connell, V.; Folkert, K. Three-dimensional localization of sperm whales using a single hydrophone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 2355–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Michalopoulou, Z.H. A particle filtering approach for spatial arrival time tracking in ocean acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, EL236–EL241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, K.; Duan, R. Robust Multipath Time-Delay Estimation of Broadband Source Using a Vertical Line Array in Deep Water. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2020, 27, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalopoulou, Z.H.; Jain, R. Particle filtering for arrival time tracking in space and source localization. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3041–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolfe, K.F.; Sabra, K.G.; Kuperman, W.A. Optimized extraction of coherent arrivals from ambient noise correlations in a rapidly fluctuating medium. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, EL375–EL381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebbie, J.; Siderius, M.; McCargar, R.; Allen, J.S., III; Pusey, G. Localization of a noisy broadband surface target using time differences of multipath arrivals. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, EL77–EL83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebbie, J.; Siderius, M.; Allen, J.S. A two-hydrophone range and bearing localization algorithm with performance analysis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 137, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Yang, K.; Wu, F.; Ma, Y. Particle filter for multipath time delay tracking from correlation functions in deep water. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 144, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Fang, S.; Zhu, C.; An, L.; Gu, Z.; Cao, W.; Cao, H. A TDOA sequence estimation method of underwater sound source based on hidden Markov model. Appl. Acoust. 2025, 227, 110238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milan, A.; Roth, S.; Schindler, K. Continuous Energy Minimization for Multitarget Tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 36, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, W. Near-Online Multi-target Tracking with Aggregated Local Flow Descriptor. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 3029–3037. [Google Scholar]
- Andriyenko, A.; Schindler, K.; Roth, S. Discrete-continuous optimization for multi-target tracking. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 1926–1933. [Google Scholar]
- Kochańska, I.; Nissen, I.; Marszal, J. A method for testing the wide-sense stationary uncorrelated scattering assumption fulfillment for an underwater acoustic channel. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, EL116–EL120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochanska, I. Assessment of Wide-Sense Stationarity of an Underwater Acoustic Channel Based on a Pseudo-Random Binary Sequence Probe Signal. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xerri, B.; Cavassilas, J.F.; Borloz, B. Passive tracking in underwater acoustic. Signal Process. 2002, 82, 1067–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, N.; Gupta, A.S.; Gupta, A. Underwater acoustic channel estimation via CS with prior information. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2017—Aberd, Aberdeen, UK, 19–22 June 2017; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Boykov, Y.; Kolmogorov, V. An Experimental Comparison of Min-Cut/Max-Flow Algorithms for Energy Minimization in Vision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2004, 26, 1124–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boykov, Y.; Veksler, O.; Zabih, R. Fast approximate energy minimization via graph cuts. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 1222–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolmogorov, V.; Zabih, R. What energy functions can be minimized via graph cuts? IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Machine Intell. 2004, 26, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delong, A.; Osokin, A.; Isack, H.N.; Boykov, Y. Fast Approximate Energy Minimization with Label Costs. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–18 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Isack, H.; Boykov, Y. Energy-Based Geometric Multi-model Fitting. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2012, 97, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Symbol | Description |
|---|---|
| observations (correlation pulses) | |
| the total number of observations in the tth frame | |
| target trajectories | |
| observations associated with trajectory | |
| the total number of | |
| the start and end time of trajectory | |
| ⌀ | observations considered as outliers |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, M.; Fang, S.; An, L.; Zhu, C.; Huang, S.; Fan, Q.; Zhou, Y. Energy Minimization for Underwater Multipath Time-Delay Estimation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091764
Feng M, Fang S, An L, Zhu C, Huang S, Fan Q, Zhou Y. Energy Minimization for Underwater Multipath Time-Delay Estimation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091764
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Miao, Shiliang Fang, Liang An, Chuanqi Zhu, Shuxia Huang, Qing Fan, and Yifan Zhou. 2025. "Energy Minimization for Underwater Multipath Time-Delay Estimation" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091764
APA StyleFeng, M., Fang, S., An, L., Zhu, C., Huang, S., Fan, Q., & Zhou, Y. (2025). Energy Minimization for Underwater Multipath Time-Delay Estimation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1764. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091764







