Numerical Simulation on Anchored Load-Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caisson for Floating Offshore Wind Power
Abstract
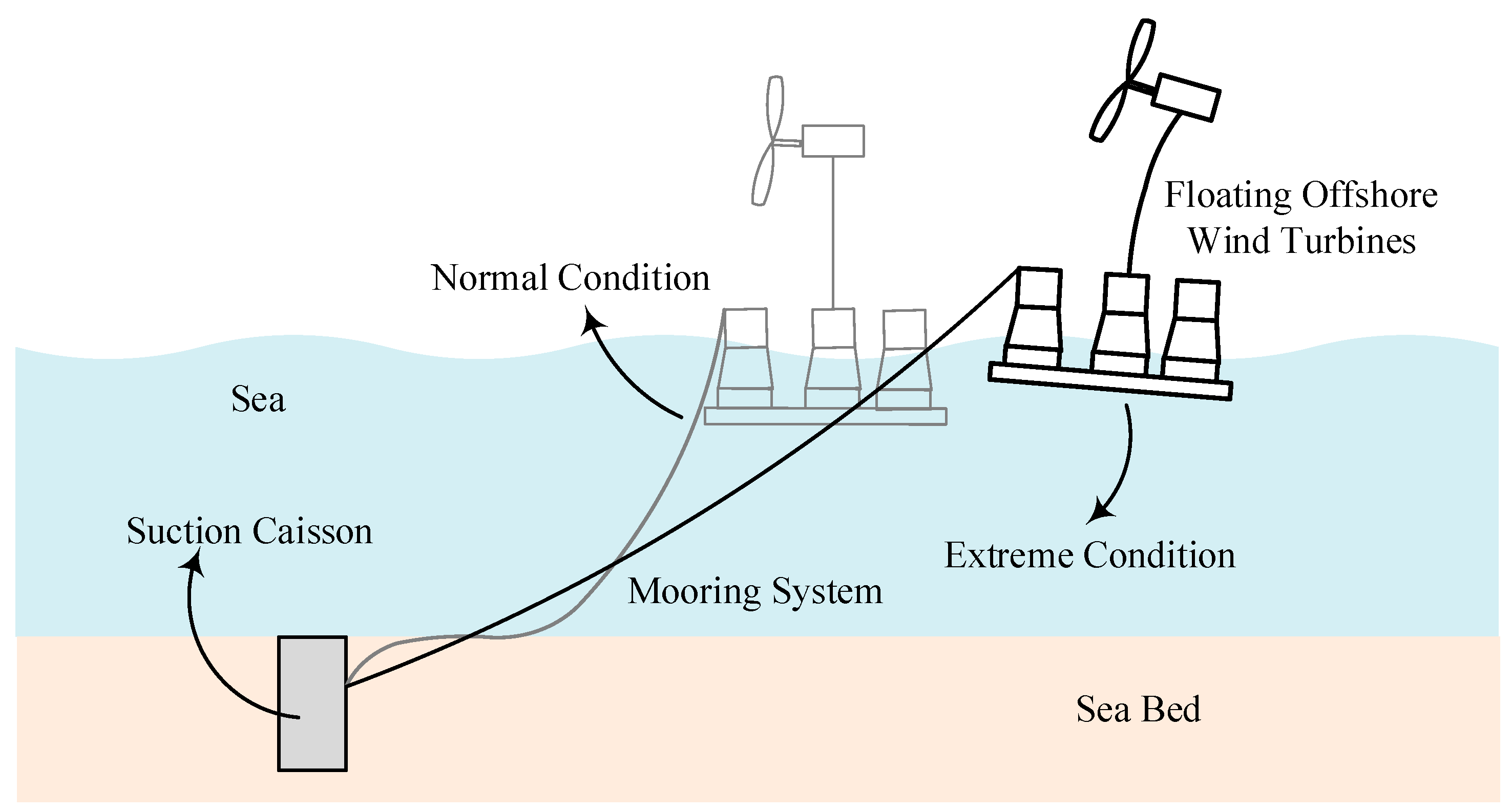
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Establishment of Finite Element Model for Suction Caisson Anchor Foundation
2.2. Finite Element Simulation Conditions for Suction Caisson Anchor Foundation
3. Analysis of Anchor Pull Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caisson Anchor Foundation
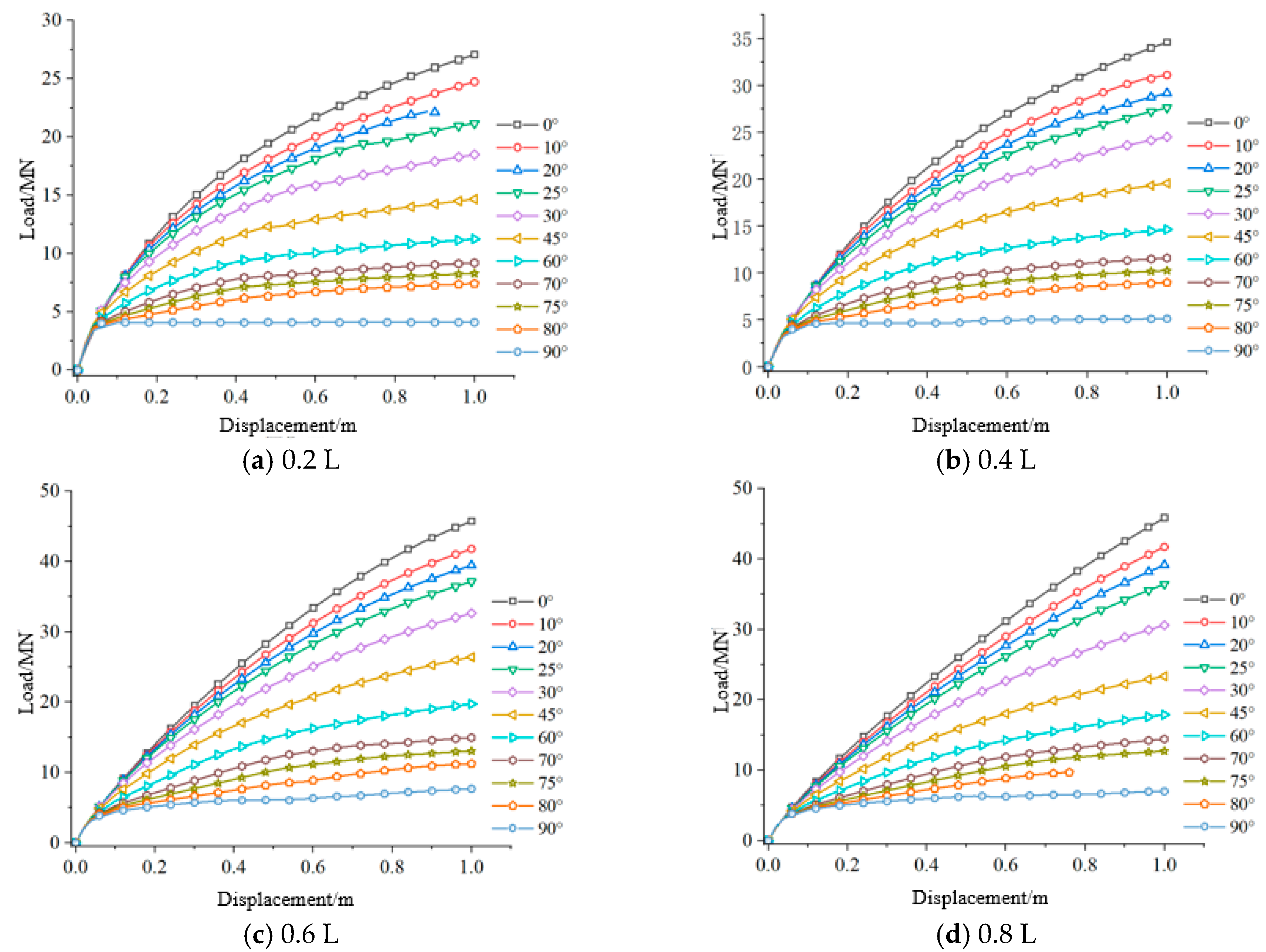
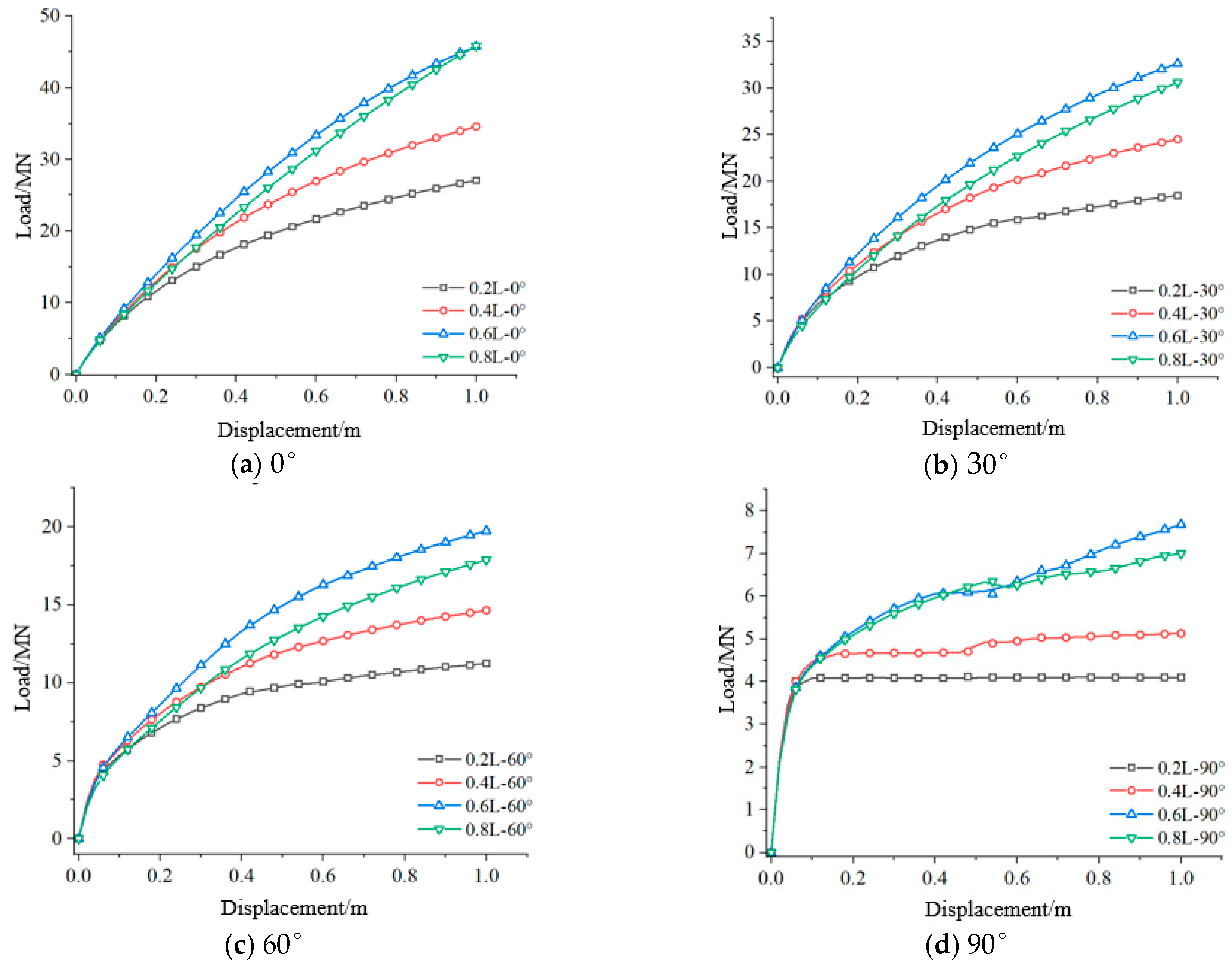
3.1. Analysis of Anchor Pull Load–Displacement Performance Curve
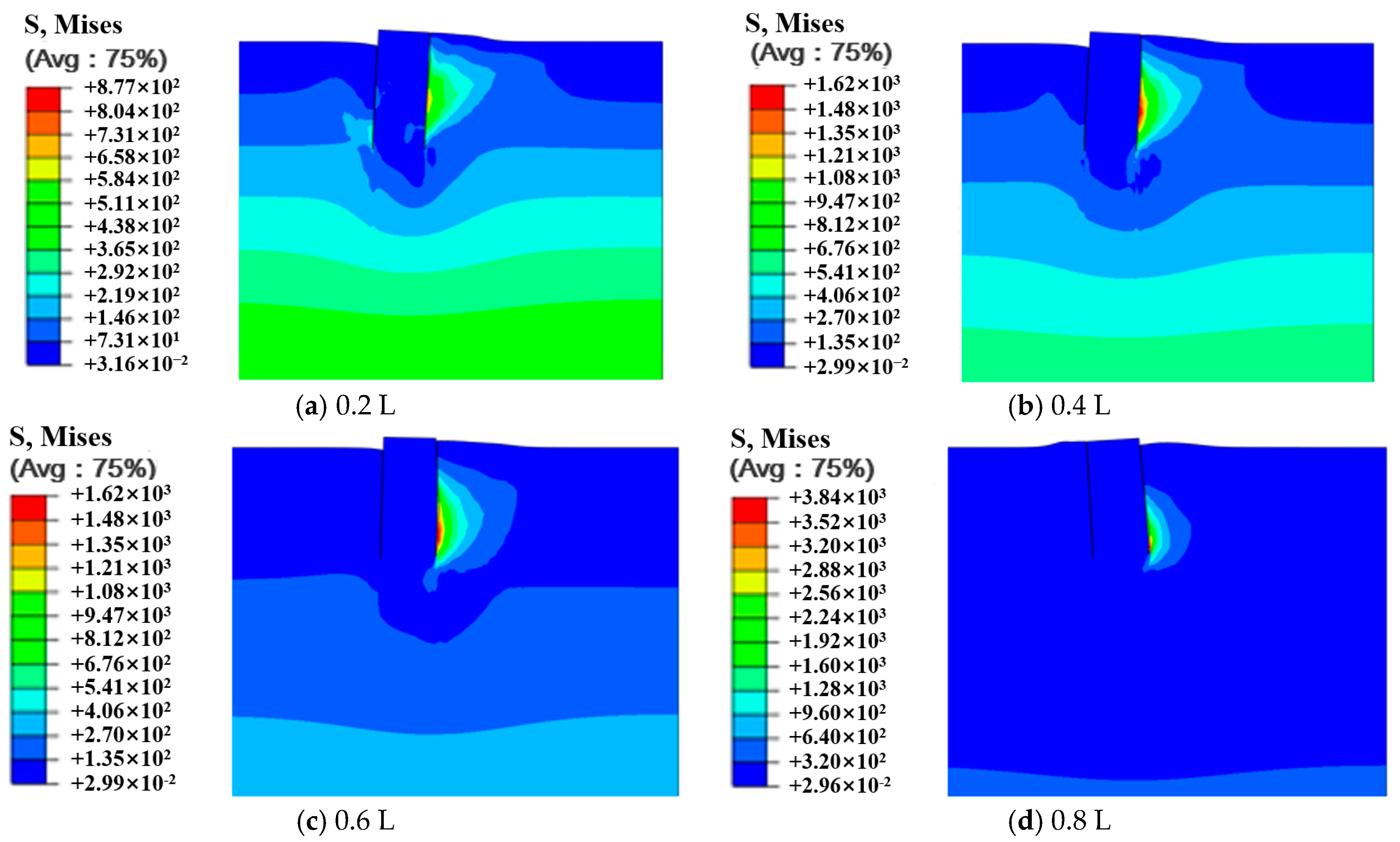
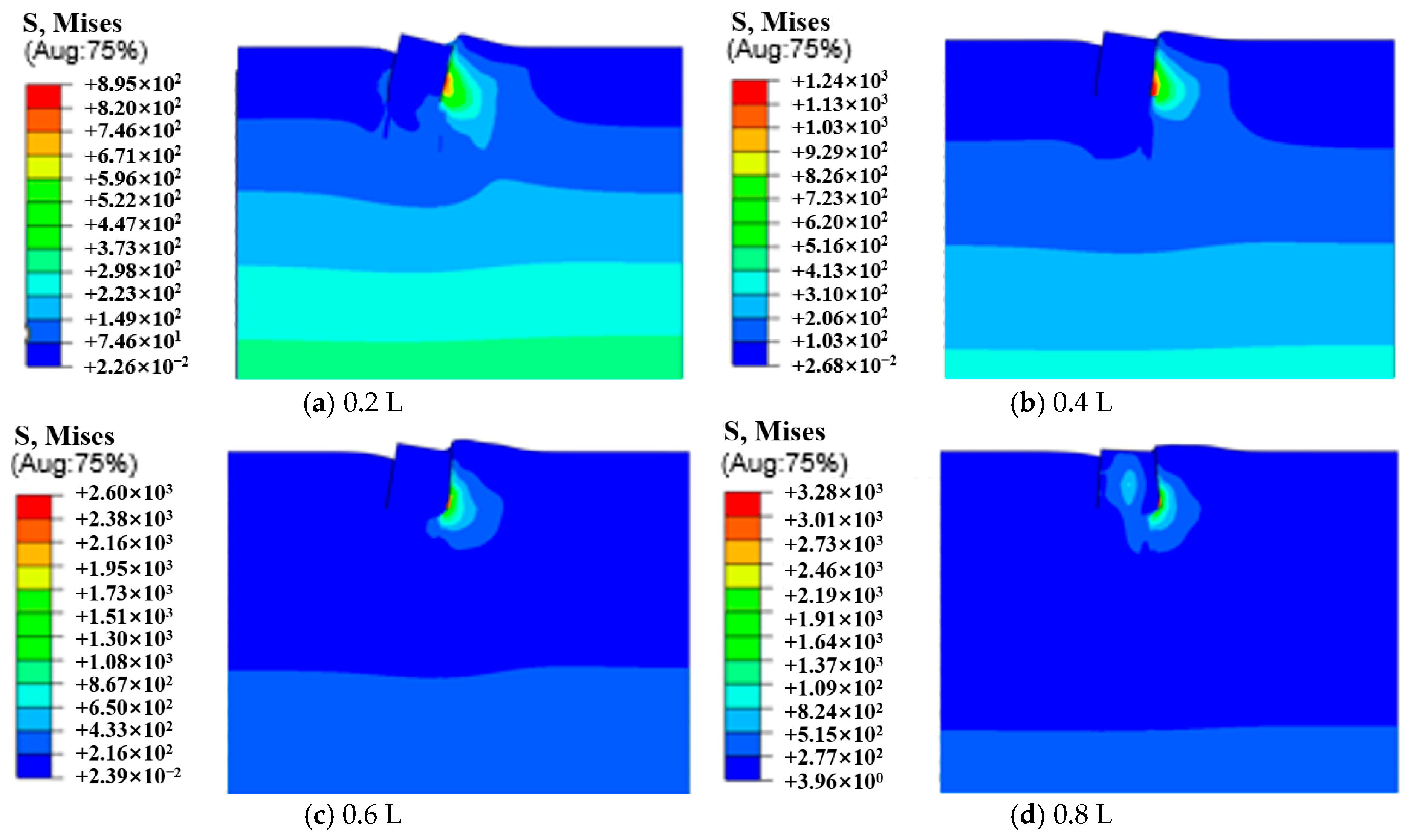
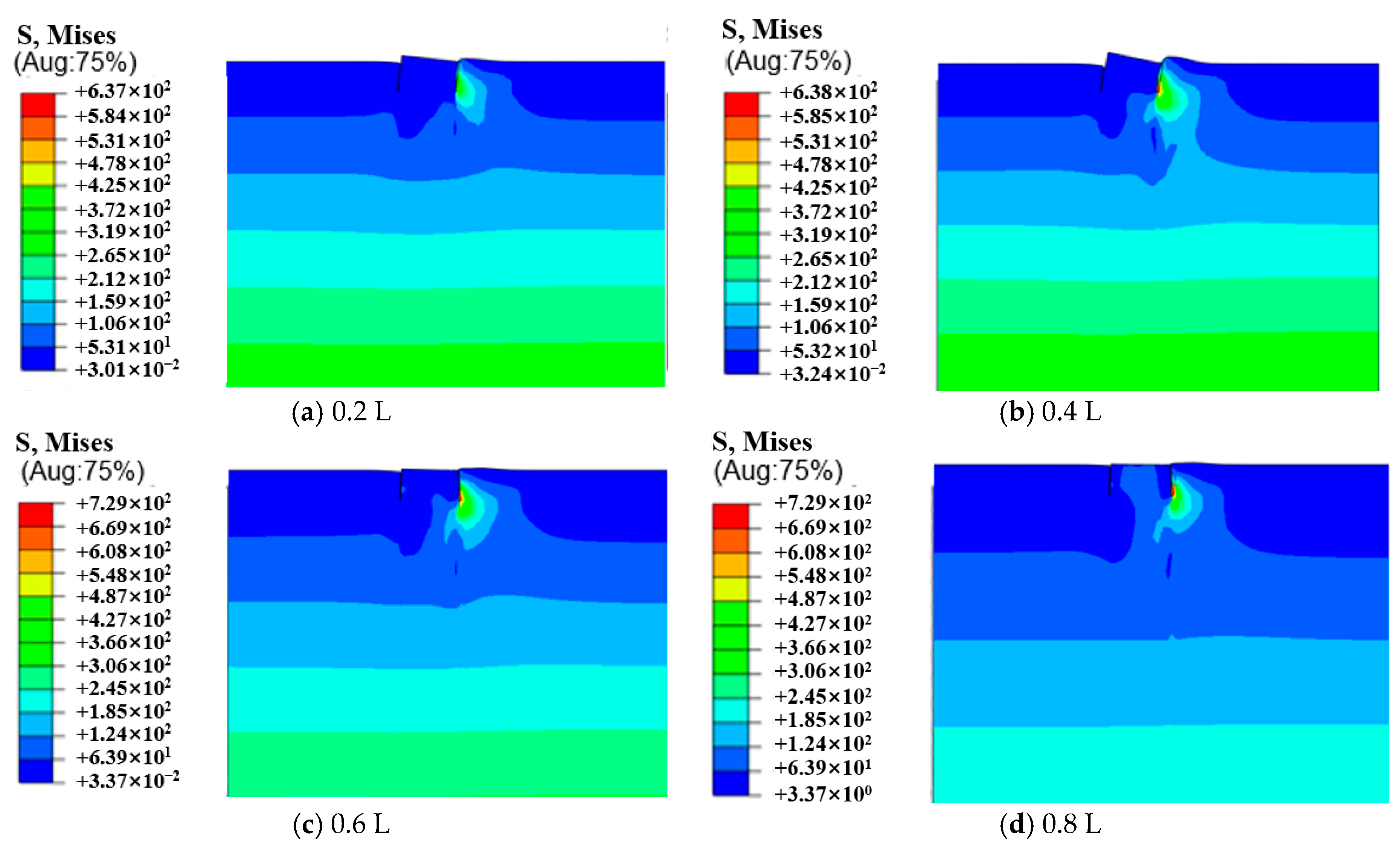
3.2. Analysis of Suction Caisson Foundation–Soil Interaction
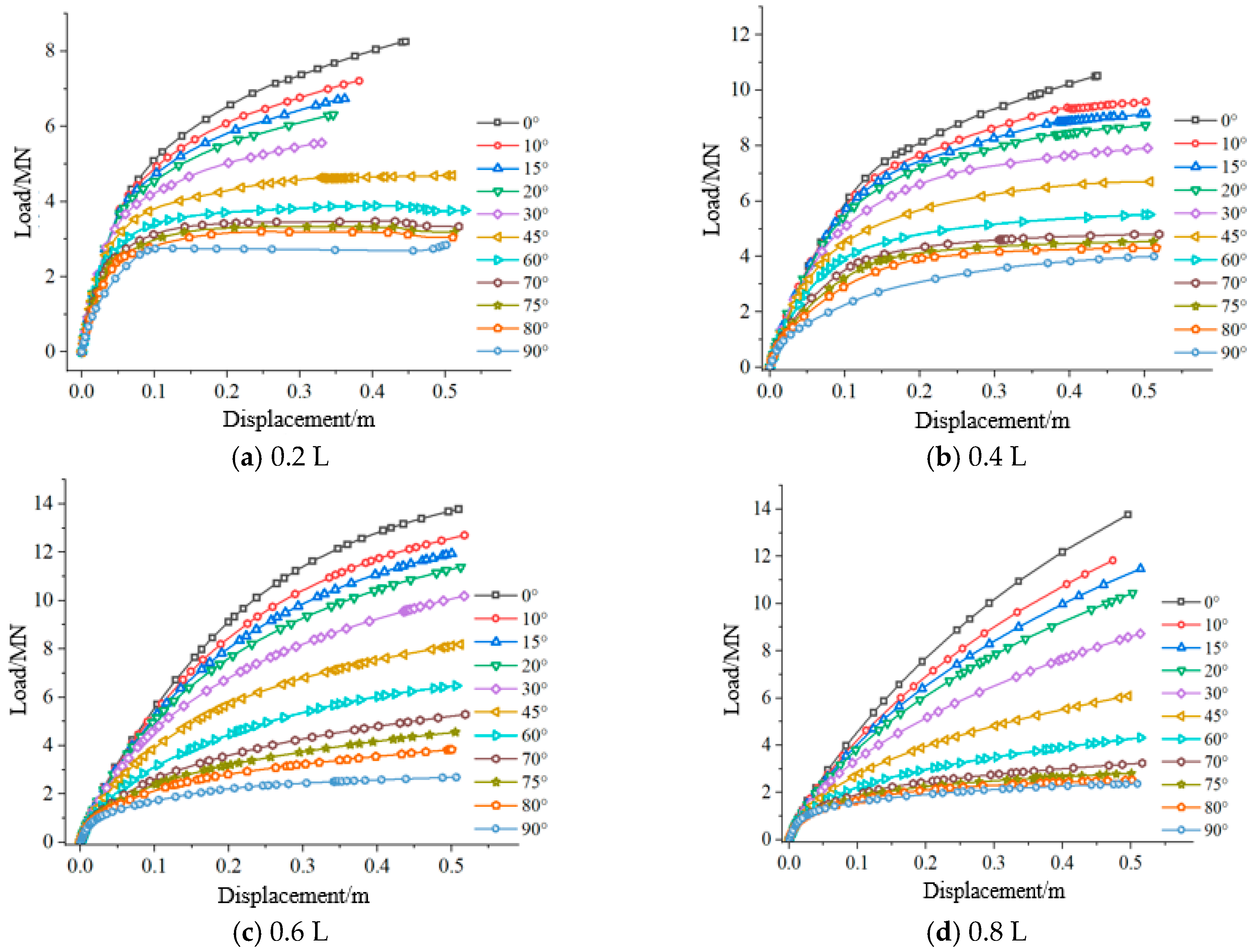
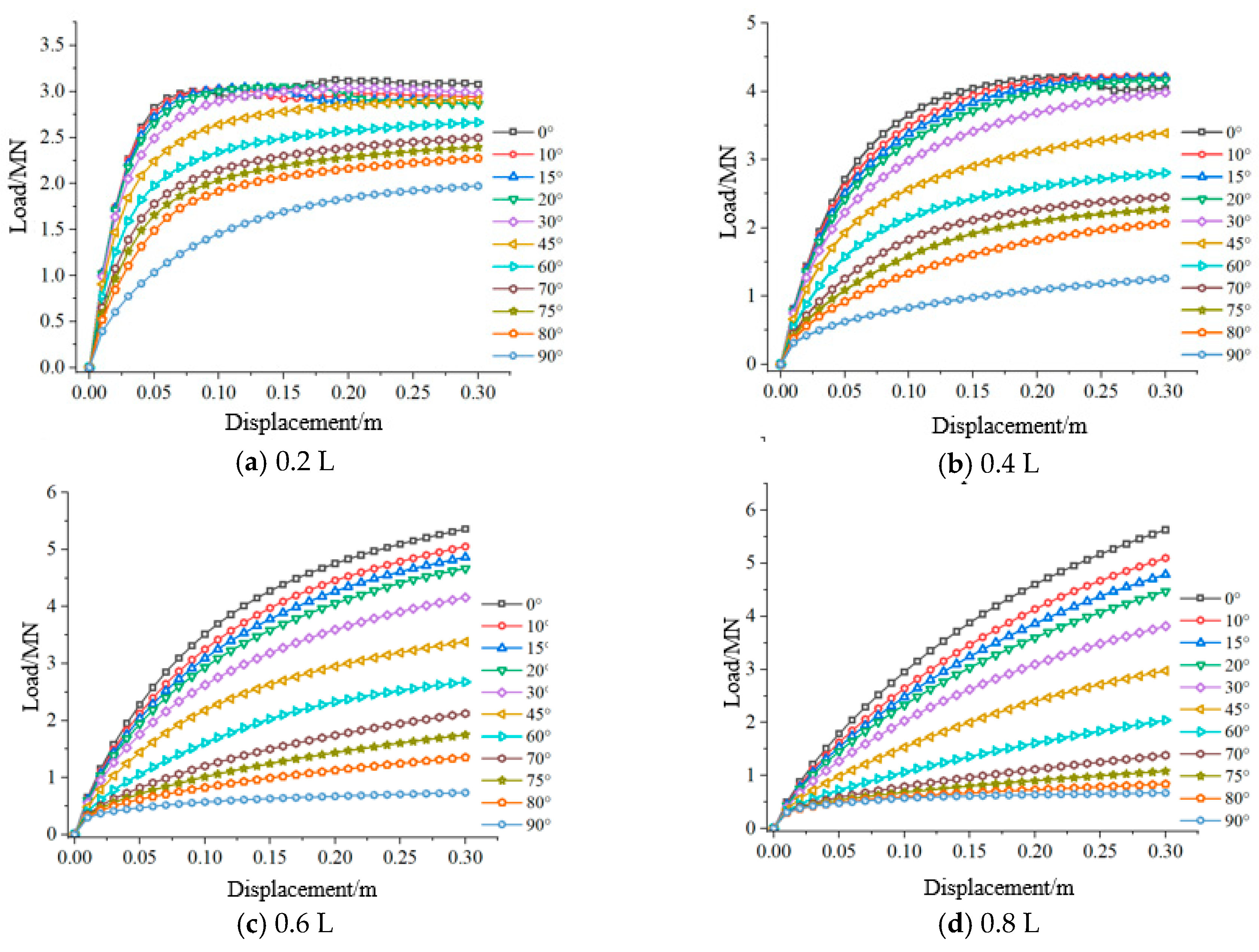
3.3. Analysis of the Influence of Length-to-Diameter Ratio on the Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caissons
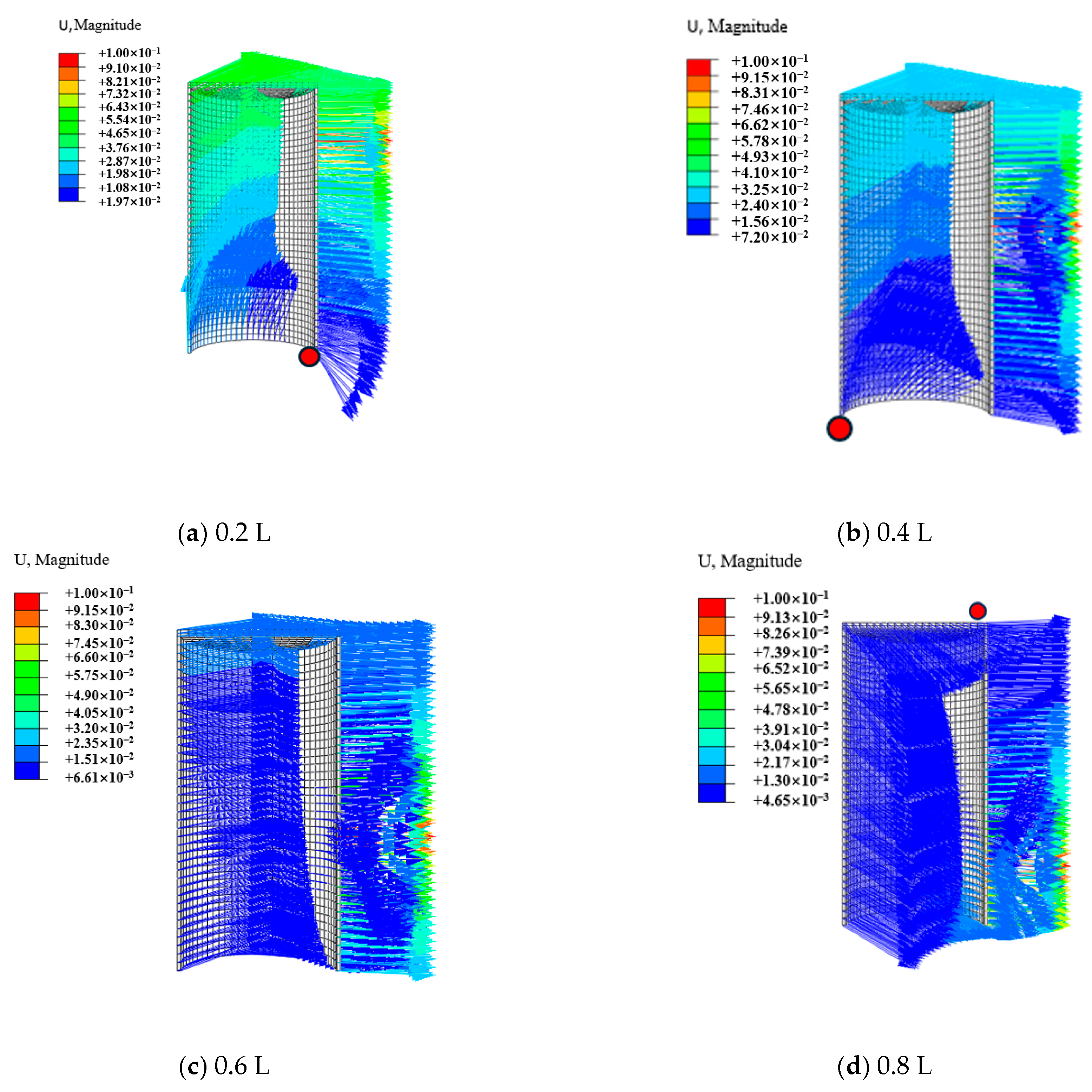
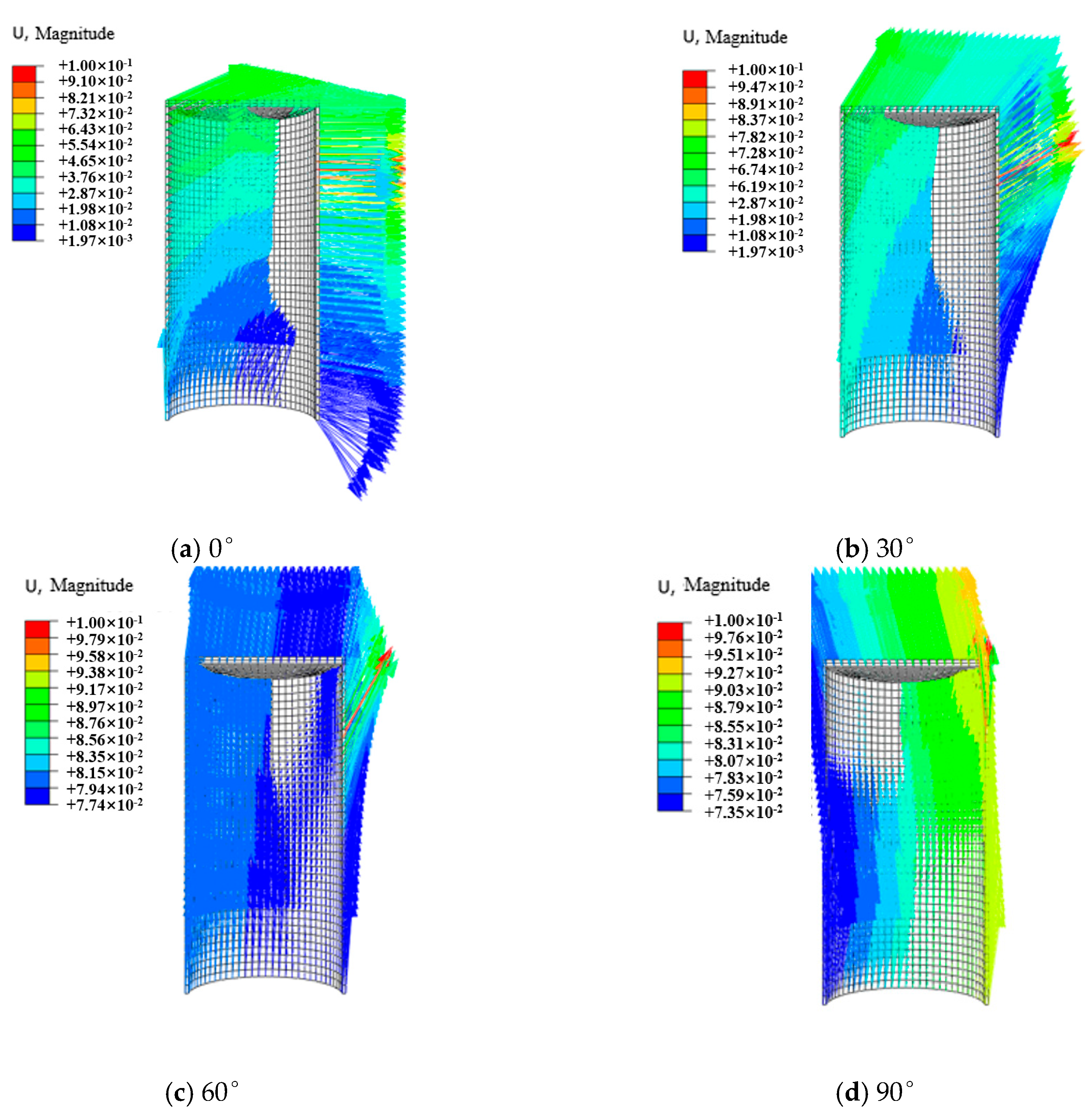
3.4. Analysis of Motion Failure Modes of Suction Anchors
4. Bearing Capacity Analysis of Suction Caisson Anchor Foundation
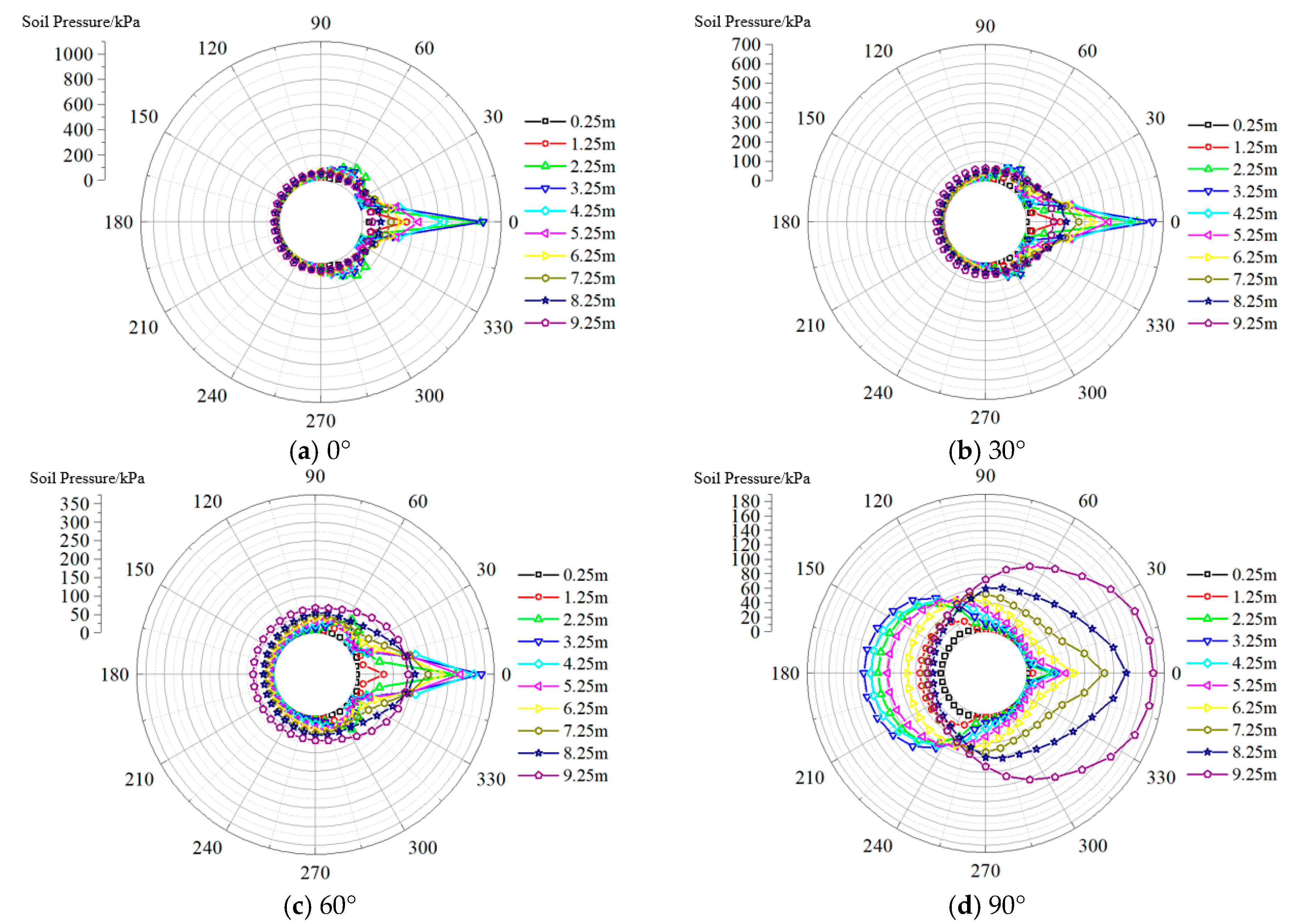
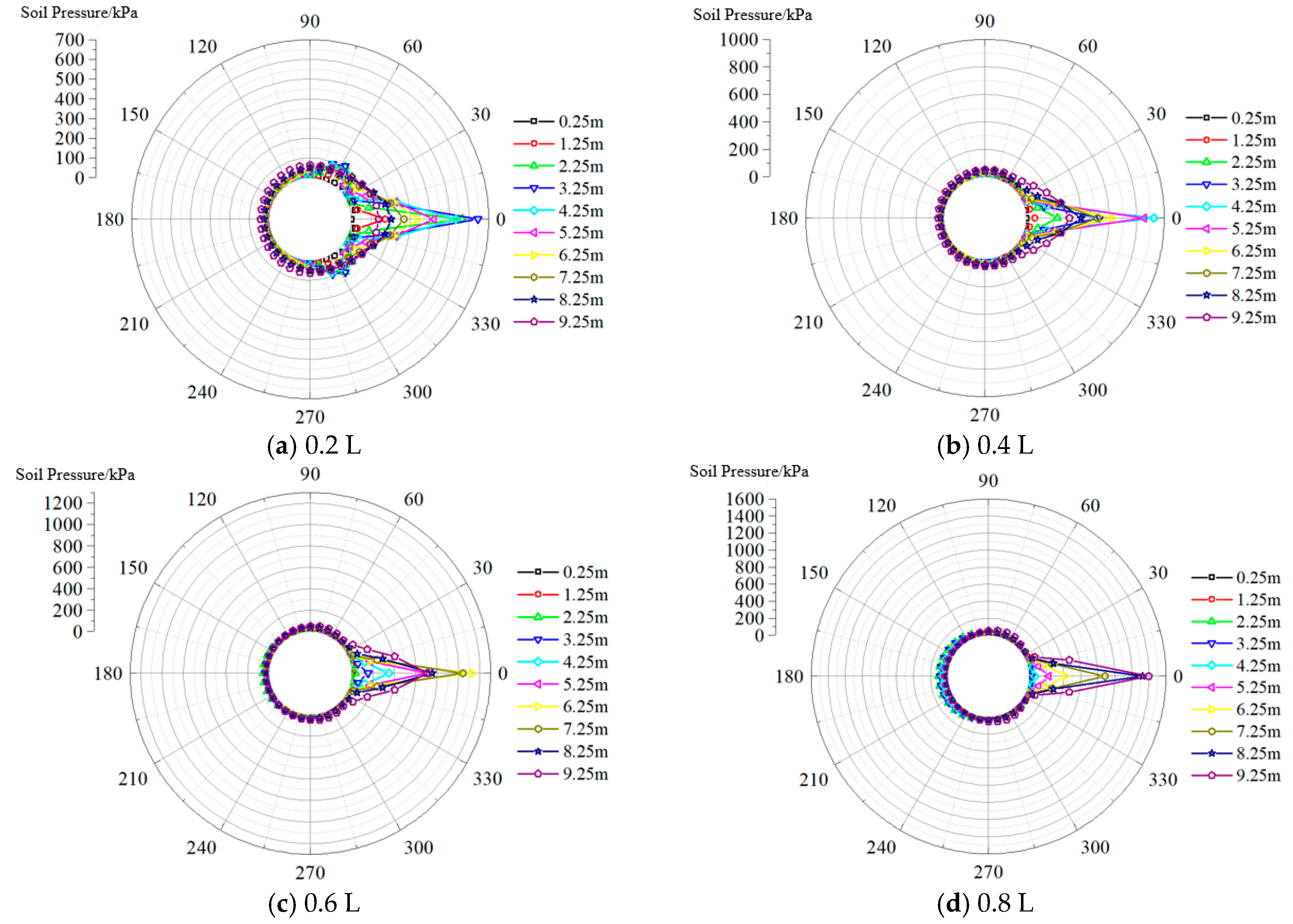
4.1. Analysis of Circumferential Soil Pressure
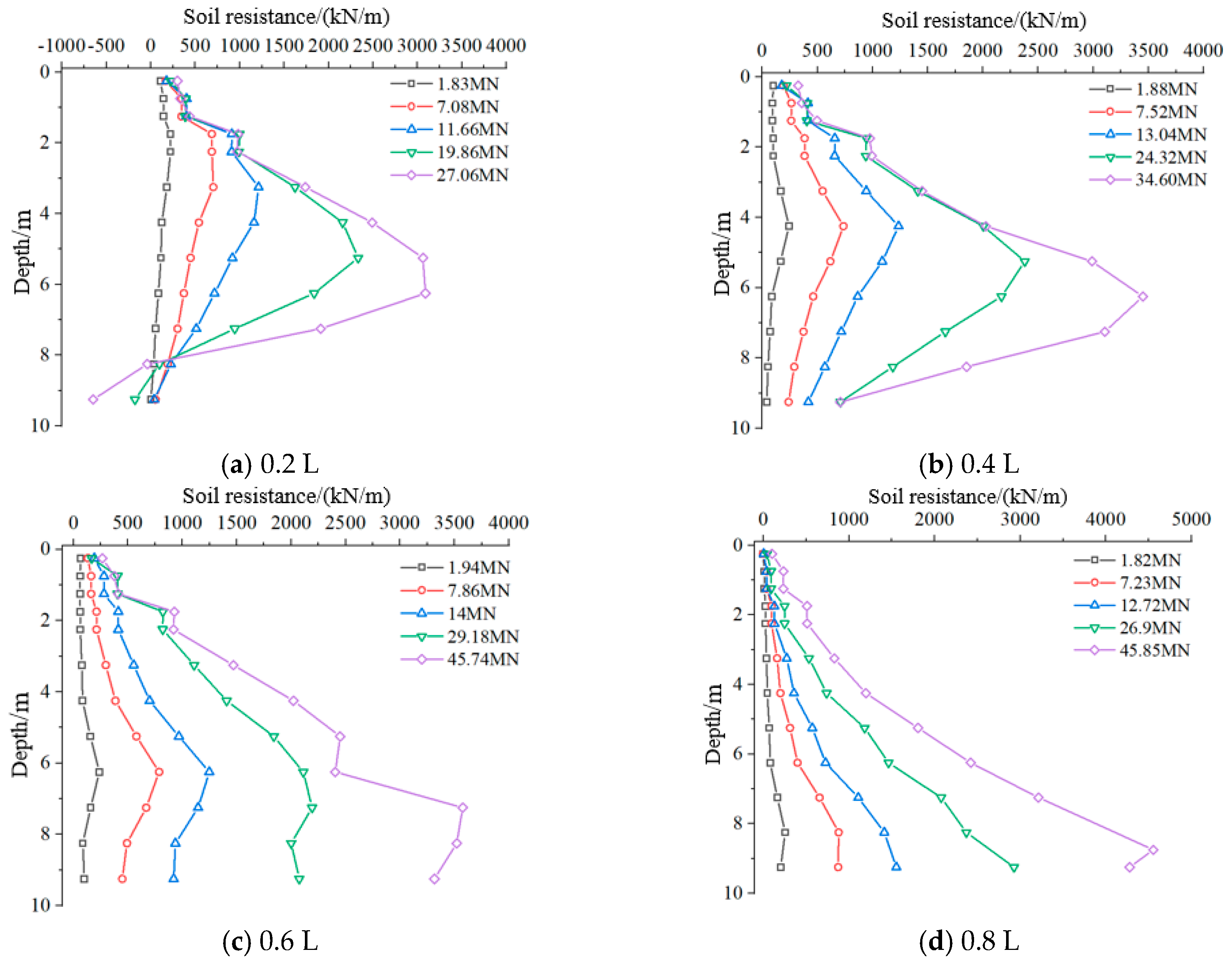
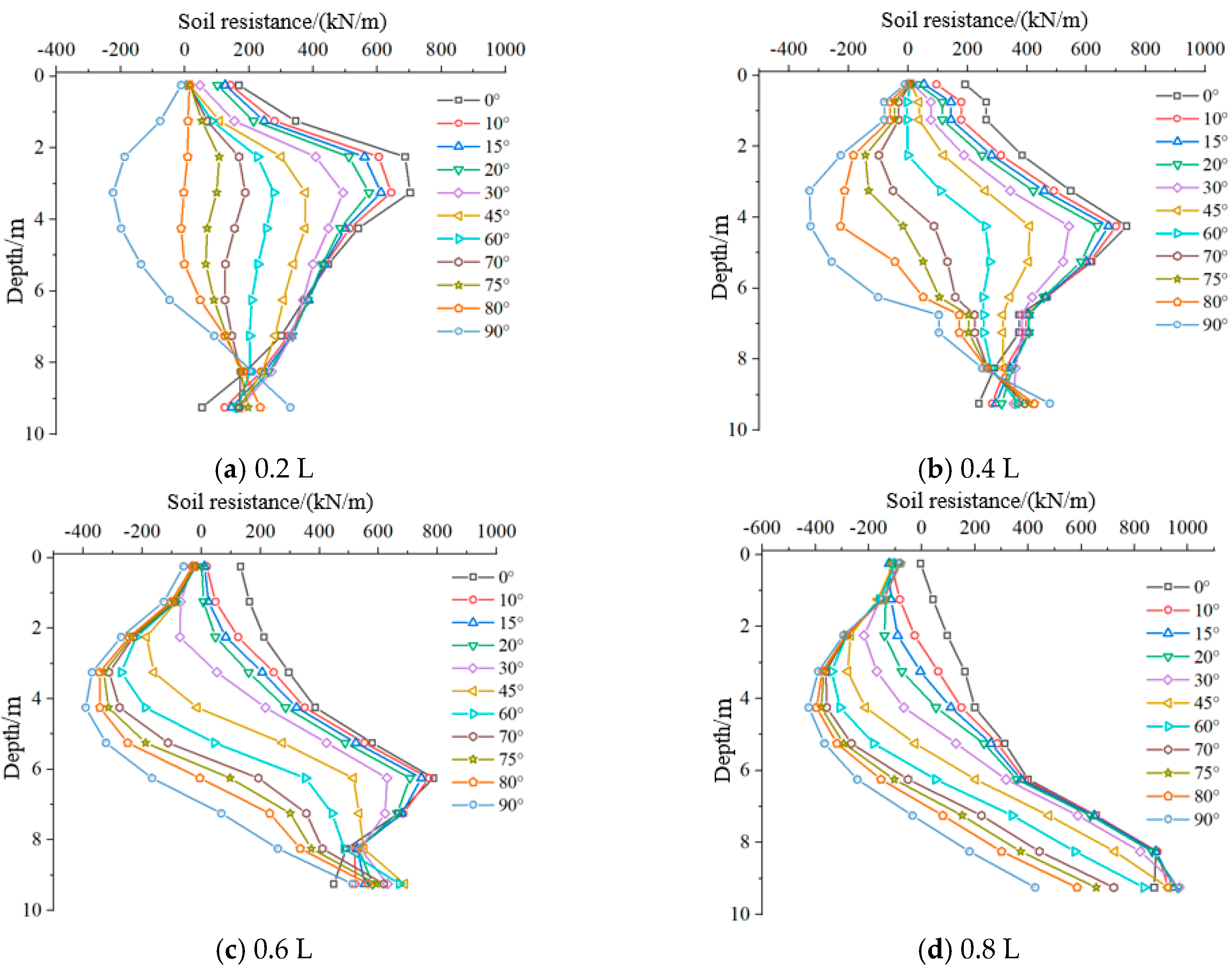
4.2. Analysis of Horizontal Soil Resistance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- The bearing capacity of the suction caisson is significantly correlated with the loading angle and the depth of the loading point. The bearing capacity is maximized when the loading angle is 0°, and it decreases as the loading angle increases, a pattern that is independent of the loading point depth. The bearing performance of the foundation initially increases and then decreases with increasing loading point depth, with the optimal loading point depth ranging between 0.6 L and 0.8 L. At this depth, when a horizontal load is applied, the foundation undergoes pure translation without rotation.
- The bearing capacity of the suction caisson anchor foundations is closely linked to its motion mode. During shallow loading (0.2 L–0.4 L), the foundation undergoes clockwise rotation, and the bearing capacity gradually increases with increasing loading depth. When the loading depth reaches 0.6 L, the overall motion mode of the foundation almost fully transitions to pure translation, with the bearing capacity reaching its peak. As the loading depth enters the deep range, the motion mode gradually shifts from translation to counterclockwise rotation, and the bearing capacity exhibits a decreasing trend compared to that at 0.6 L. Additionally, the loading angle of the suction caisson also influences the overall motion mode.
- Under varying length-to-diameter ratios, the bearing capacity of suction caisson anchor foundations follows similar trends with respect to loading angle and depth. However, as the length-to-diameter ratio decreases, the movement amplitude becomes less pronounced, affecting the optimal loading point position.
- The circumferential soil pressure distribution around suction caisson anchor foundations primarily exhibits two patterns. At the loading point, soil pressure is mainly concentrated within ±30°, peaking at 0° and decreasing toward both sides in a cosine function pattern. The overall circumferential soil pressure increases with loading point depth.
- The horizontal soil resistance distribution of suction caisson anchor foundations is significantly related to loading angle, loading point depth, and external load magnitude. Under horizontal loading, soil resistance exhibits a single-peak distribution along the depth, with the peak near the loading point. As the external load increases, the peak shifts downward below the loading point. Increasing loading angles induce a counterclockwise rotation mode, causing the soil resistance in the upper part of the foundation to transition to negative values.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allersma, H.G.B.; Kierstein, A.A.; Maes, D. Centrifuge modelling on suction piles under cyclic and long term vertical loading. In Proceedings of the ISOPE International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Seattle, WA, USA, 28 May 2000; p. ISOPE-I-00-159. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, H.; Xu, M.; Sun, D.; Rui, S. Calculation method for uplift capacity of suction caisson in sand considering different drainage conditions. Sustainability 2022, 15, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supachawarote, C. Inclined Load Capacity of Suction Caisson in Clay. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Q.L.; Wu, Y.P.; Ma, S.L.; Li, Y.C. A study on the bearing capacity of suction bucket foundations for offshore wind turbines on dense sand foundations. J. Basic Sci. Eng. 2021, 29, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Y.; Feng, L.Y.; Guo, Y.X.; Cao, L.X. Numerical analysis of horizontal bearing capacity of skirted suction foundation. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2013, 35, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Lü, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q. Large—Deformation finite element simulation of the penetration process of suction caisson foundation. Rock Soil Mech. 2015, 36, 3615–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, D.Y. Numerical analysis of influencing factors on the horizontal bearing capacity of skirted suction foundation. Port Eng. Technol. 2011, 48, 51–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.X. Study on Bearing Mechanism of Passive Piles Under Combined Loads. Ph.D. Thesis, Southeast University, Nanjing, China, 2016. Available online: https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=mV2q5OJ_OLwN8x4YyXJfKvkeqZcZxDroDWF2hc9wZkI26FragMair-qwbzOjxSiMPKXTEXVuxCqi6R282MXDHv0wAHqDmCdzMy0nGW6GvqhInPXiKz1D_Rmpn_k5GGj0Egpnv5khUoEUyG3DYbHkvY4p4KpWOhmJzgaRQpTVWlqIHSlkwpP6-PqFqPyBXR_zrlJxrqEVPHw=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS (accessed on 6 July 2025).
- Sun, L.Q.; Xing, X.J.; Zhai, X.L.; Wu, X.Z.; Wang, R. Study on undrained uplift bearing characteristics of suction bucket foundation under inclined load. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2020, 42, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, P.P. Ultimate Capacity of Suction Caisson in Normally and Lightly Overconsolidated Clays. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ukritchon, B.; Wongtoythong, P.; Keawsawasvong, S. New design equation for undrained pullout capacity of suction caissons considering combined effects of caisson aspect ratio, adhesion factor at interface, and linearly increasing strength. Appl. Ocean. Res. 2018, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourkoulis, R.S.; Lekkakis, P.C.; Gelagoti, F.M.; Kaynia, A.M. Suction caisson foundations for offshore wind turbines subjected to wave and earthquake loading: Effect of soil–foundation interface. Géotechnique 2014, 64, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Dai, G.; Zhang, F.; Gong, W. Energy-based analysis of laterally loaded caissons with large diameters under small-strain conditions. Int. J. Geomech. 2022, 22, 05022005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Ye, C.; Gao, J.; Dai, G.; Wang, D.; Dong, Y. Pore water pressure of clay soil around large-diameter open-ended thin-walled pile (LOTP) during impact penetration. Comput. Geotech. 2025, 180, 107065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Cai, S.; Dai, G.; Wang, D.; Chang, K. Soil resistance during driving of offshore large-diameter open-ended thin-wall pipe piles driven into clay by impact hammers. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 153, 105085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.; Preber, T.; Cho, Y.; Thomason, J.; Karnoski, S.R.; Taylor, R.J. Suction piles for mooring of mobile offshore bases. Mar. Struct. 2000, 13, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zhang, W.L.; Ying, P.P.; Chen, Y.M. Deflection-based bearing capacity of suction caisson foundations of offshore wind turbines. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulczykowski, M. Experimental investigation of skirted foundation in sand subjected to rapid uplift. Arch. Hydro-Eng. Environ. Mech. 2020, 67, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Qin, C.; Yang, Y.H.; Cheng, F.; Zhao, S.S. Field test study on uplift bearing characteristics of rock socketed piles in sandstone stratum. Soils Found. 2025, 65, 101598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basack, S.; Alkahtani, M.Q.; Islam, S. Analysis of single pile in two-layered soil subjected to uplift load. Geomech. Eng. 2025, 41, 583–596. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, S.; Li, S. Research on the Uplift Bearing Capacity of the Rock-socketed Pile and Failure Mechanism. ce/papers 2025, 8, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.B.; Houlsby, G.T.; Byrne, B.W. Transient vertical loading of model suction caissons in a pressure chamber. Géotechnique 2006, 56, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, B.W.; Houlsby, G.T. Experimental investigations of response of suction caissons to transient vertical loading. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2002, 128, 926–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mana, D.S.K.; Gourvenec, S.; Randolph, M.F. A numerical study of the vertical bearing capacity of skirted foundations. In Frontiers in Offshore Geotechnics II; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010; pp. 433–438. [Google Scholar]
- Mana, D.S.; Gourvenec, S.; Martin, C.M. Critical skirt spacing for shallow foundations under general loading. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 1554–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.A.; Bienen, B.; O’Loughlin, C.D. Pressure-Cycled Installation of Suction Buckets in Sand and Layered Soil Profiles. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2025, 151, 04024142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Jin, H.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, L.; Cai, Y. Experimental and Numerical Investigation of the Performance of Suction Buckets Subjected to Extreme Cyclic Tensile Loading in Sand. Int. J. Geomech. 2025, 25, 04025062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, J.; Juan, L. Study on Follower Structural Strenght Analysis Method for Suction Pile Penetration Using Hydraulic Hammering. In Proceedings of the ISOPE International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 1–6 June 2025; p. ISOPE-I-25-182. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.G.; Liu, F.C. Numerical analysis of bearing capacity of suction bucket foundation for offshore wind turbines. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2010, 15, 76–81. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Z.; Cui, H.; Huang, M.; Shen, K.; Wang, B. Inferred Winkler model for stiffness of suction caisson foundation under combined loading in non-homogeneous and layered soil. Acta Geotech. 2025, 20, 1069–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H. Analysis of laterally loaded bucket foundation with external skirt in sand using a Winkler model approach. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 147, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Feng, H.; Shi, Z.; Shen, K.; Wang, B. Inferred Winkler model for uplift response of suction caisson in undrained clays. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Gao, J.; Chang, K.; Dai, G.; Wei, H. Set-up effect of large-diameter open-ended thin-walled pipe piles driven in clay. Comput. Geotech. 2023, 159, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OuYang, H.; Dai, G.; Qin, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, W.; Gong, W. Experimental study on the mechanical behaviors and particle breakage characteristics of calcareous sand from South China Sea under repeated one-dimensional impacts. Acta Geotech. 2022, 17, 3927–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
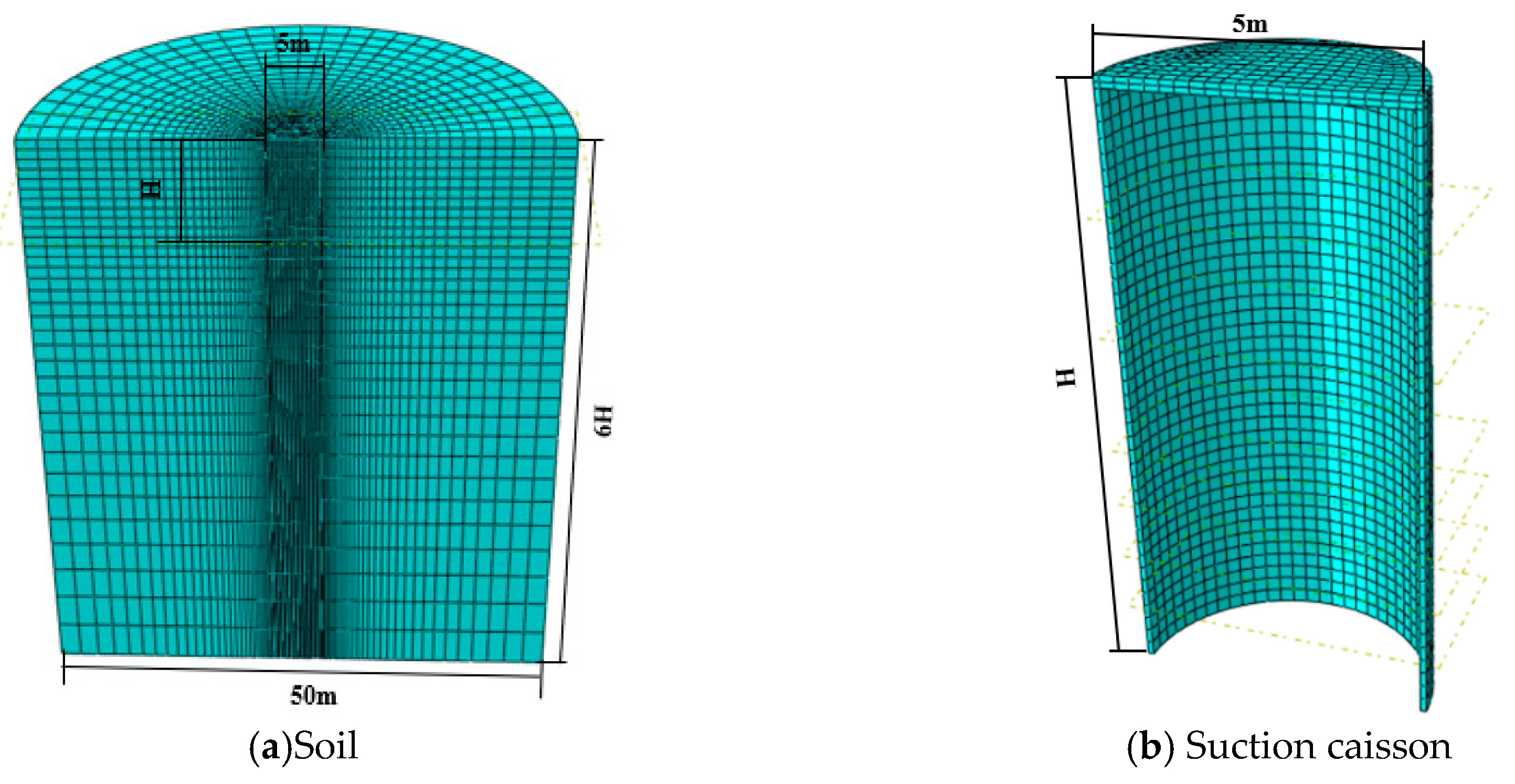
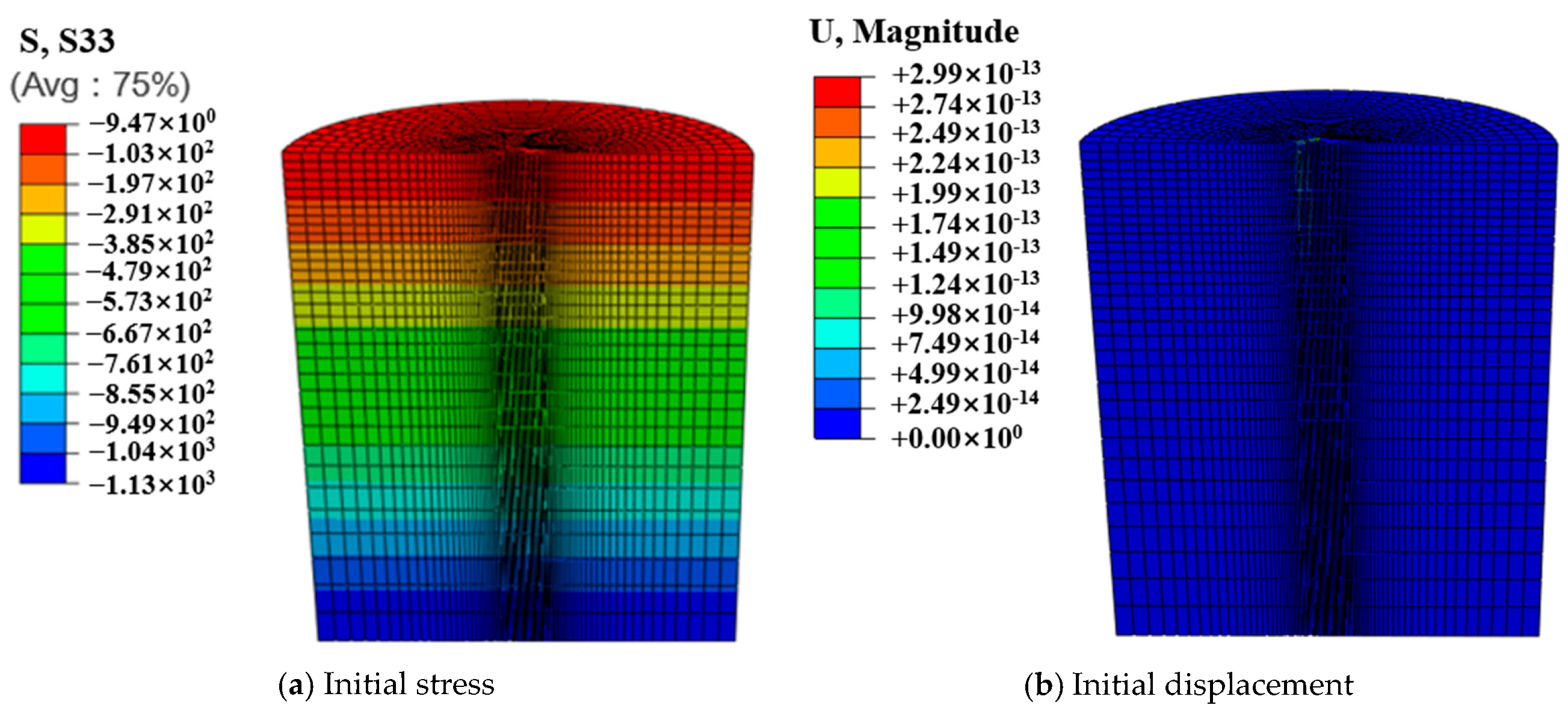

| Material | Elastic Modulus/Mpa | Effective Heavy/(kN·m−3) | Cohesion/kPa | Internal Friction Angle/(°) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Silty sand | 33 | 20.0 | 2 | 33.7 | 0.3 |
| Steel | 210,000 | 78.5 | - | - | 0.3 |
| Number | Caisson Length (m) | Caisson Body Loading Point | Loading Angle |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 0.2 L | Load at 11 angles: 0°, 10°, 15°, 20°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 70°, 75°, 80°, and 90°. |
| 2 | 0.4 L | ||
| 3 | 0.6 L | ||
| 4 | 0.8 L | ||
| 5 | 5 | 0.2 L | |
| 6 | 0.4 L | ||
| 7 | 0.6 L | ||
| 8 | 0.8 L | ||
| 9 | 2.5 | 0.2 L | |
| 10 | 0.4 L | ||
| 11 | 0.6 L | ||
| 12 | 0.8 L |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, S.; Sun, C.; Liu, B.; Huang, L.; Deng, H.; Zhu, M.; Li, X.; Dai, G. Numerical Simulation on Anchored Load-Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caisson for Floating Offshore Wind Power. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091653
Xie S, Sun C, Liu B, Huang L, Deng H, Zhu M, Li X, Dai G. Numerical Simulation on Anchored Load-Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caisson for Floating Offshore Wind Power. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091653
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Shangle, Chaoyi Sun, Bo Liu, Liji Huang, Huiyuan Deng, Mingxing Zhu, Xiaojuan Li, and Guoliang Dai. 2025. "Numerical Simulation on Anchored Load-Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caisson for Floating Offshore Wind Power" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091653
APA StyleXie, S., Sun, C., Liu, B., Huang, L., Deng, H., Zhu, M., Li, X., & Dai, G. (2025). Numerical Simulation on Anchored Load-Bearing Characteristics of Suction Caisson for Floating Offshore Wind Power. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1653. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091653






