Estimation of Hydrodynamic Coefficients for the Underwater Robot P-SUROII via Constraint Recursive Least Squares Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Since the experimental data inherently include noise and bias, the CRLS approach was employed to achieve more robust parameter estimation.
- Although the CRLS method requires carefully defined constraints, the initial bounds were set using validated CFD results, and coefficient tuning was applied based on accumulated experience during the estimation process, which enhanced the accuracy of the parameter estimation.
2. System Overview and Modeling
2.1. P-SUROII Model
2.1.1. System Desciption
2.1.2. Vehicle Kinematics and Dynamics
2.1.3. Derivation of Nonlinear Dynamics
- P-SUROII is a low-speed UUV.
- P-SUROII has three planes of symmetry.
- The center of buoyancy of P-SUROII coincides with the body-fixed coordinate .
- The center of gravity is assumed to be at (0, 0, ), where is a non-zero value.
2.2. Thruster Model
2.3. Motion Sensor
2.3.1. IMU Measurement Correction
2.3.2. DVL Measurement Correction
3. Methodology
3.1. SI Methods
3.1.1. Related Works
3.1.2. Proposed Method
- The damping and added mass values are assumed to be greater than zero ( > 0).
- The initial values of the damping coefficients are set to the damping coefficients obtained from the CFD analysis.
- Since the P-SUROII is a larger system than the BlueROV2, the corresponding parameter values are set to be higher than those of the BlueROV2.
- The minimum and maximum bounds of each parameter are iteratively adjusted and optimized based on the experiments and simulation results.
| Algorithm 1 CRLS algorithm for Hydrodynamic Parameter Estimation |
|
3.2. Simulation Studies
| Algorithm 2 Synthetic data generation and CRLS-based parameter estimation for BlueROV2 | |
| Parameters: , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , | |
|
2: % Hydrodynamic coefficients and added mass terms | |
| % Step 1: Data Generation from the Dynamic Model | |
| 4: for to n do | |
| Generate control input | |
| 6: Simulate motion using BlueROV2 model: | |
| Add noise and bias: | % : noise and bias |
| 8: end for | |
| % Step 2: Constrained Recursive Least Squares Estimation | |
| 10: for to n do | |
| Define input–output structure of the dynamic system | |
| 12: Perform CRLS estimation with physical constraints | |
| Store or validate estimated parameters | |
| 14: end for | |
3.3. Experimental Studies
3.3.1. Data Acquisition
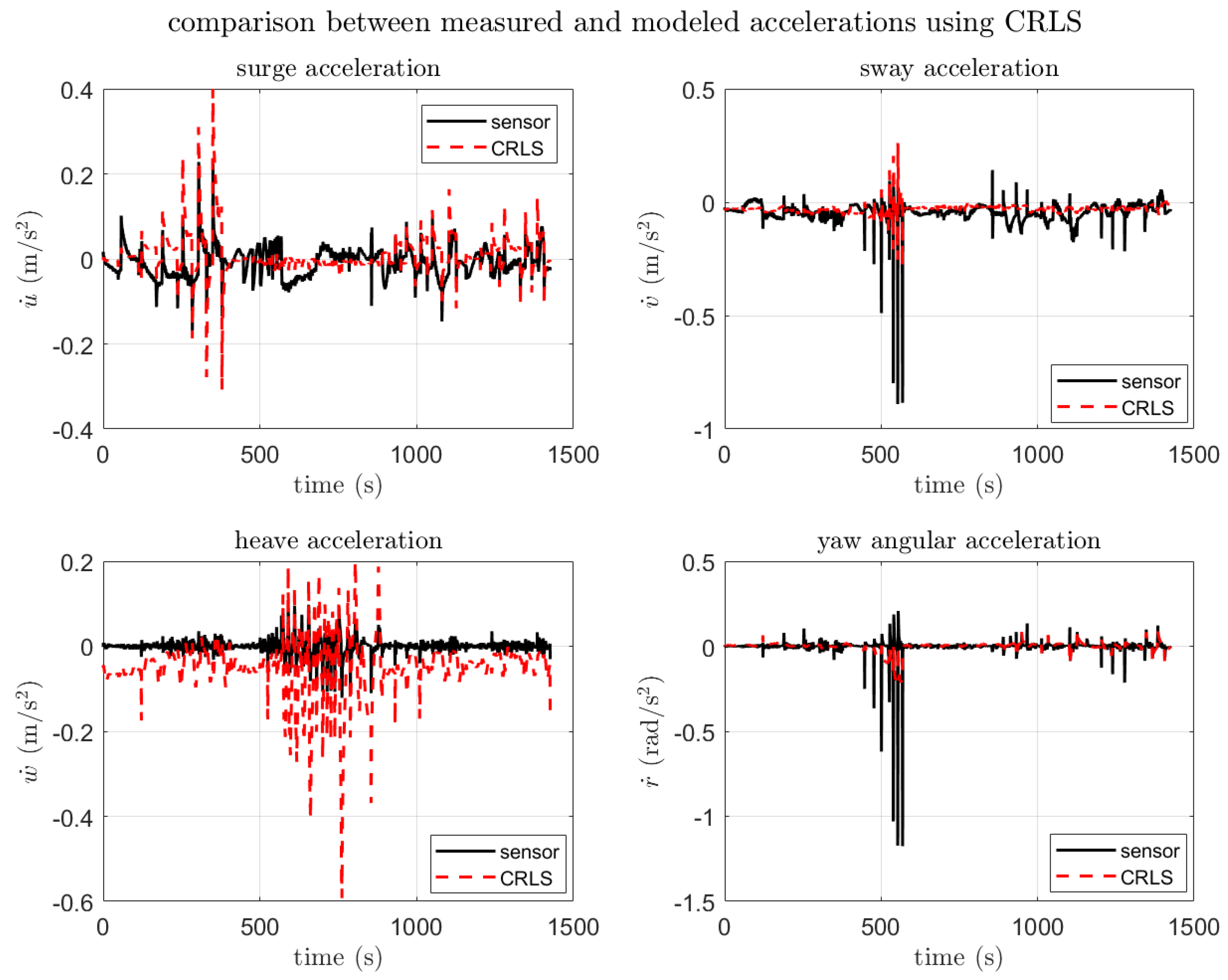
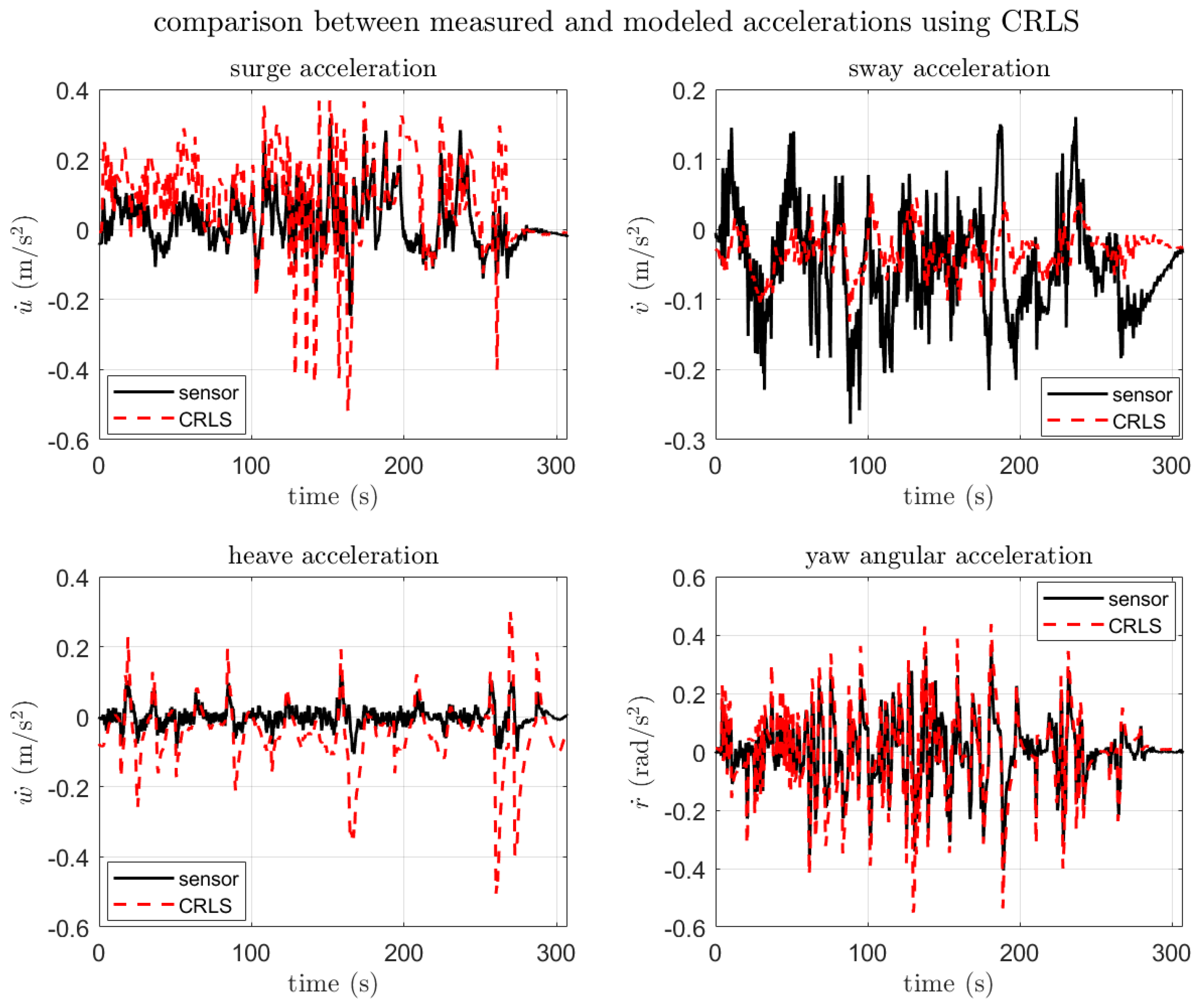
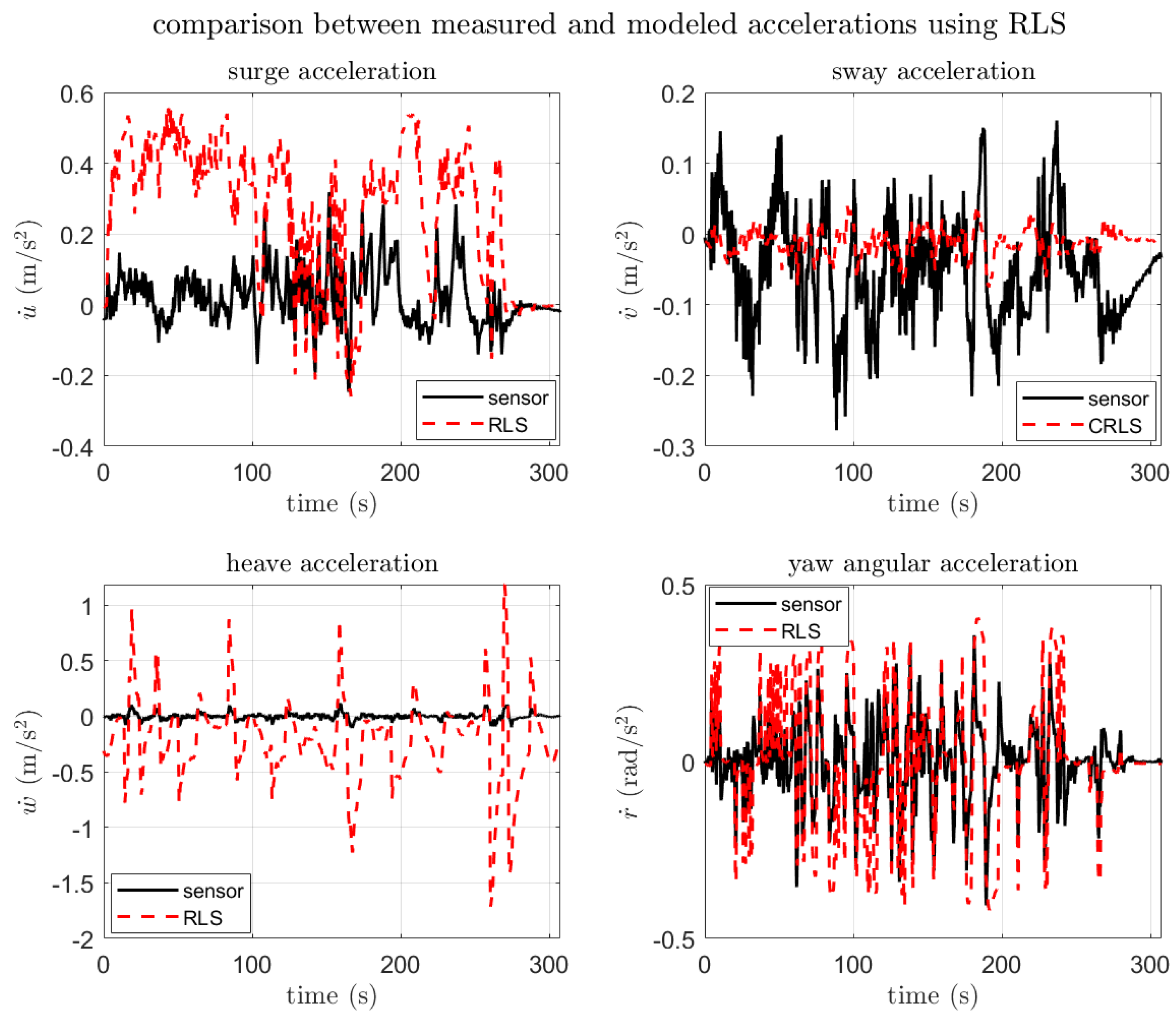
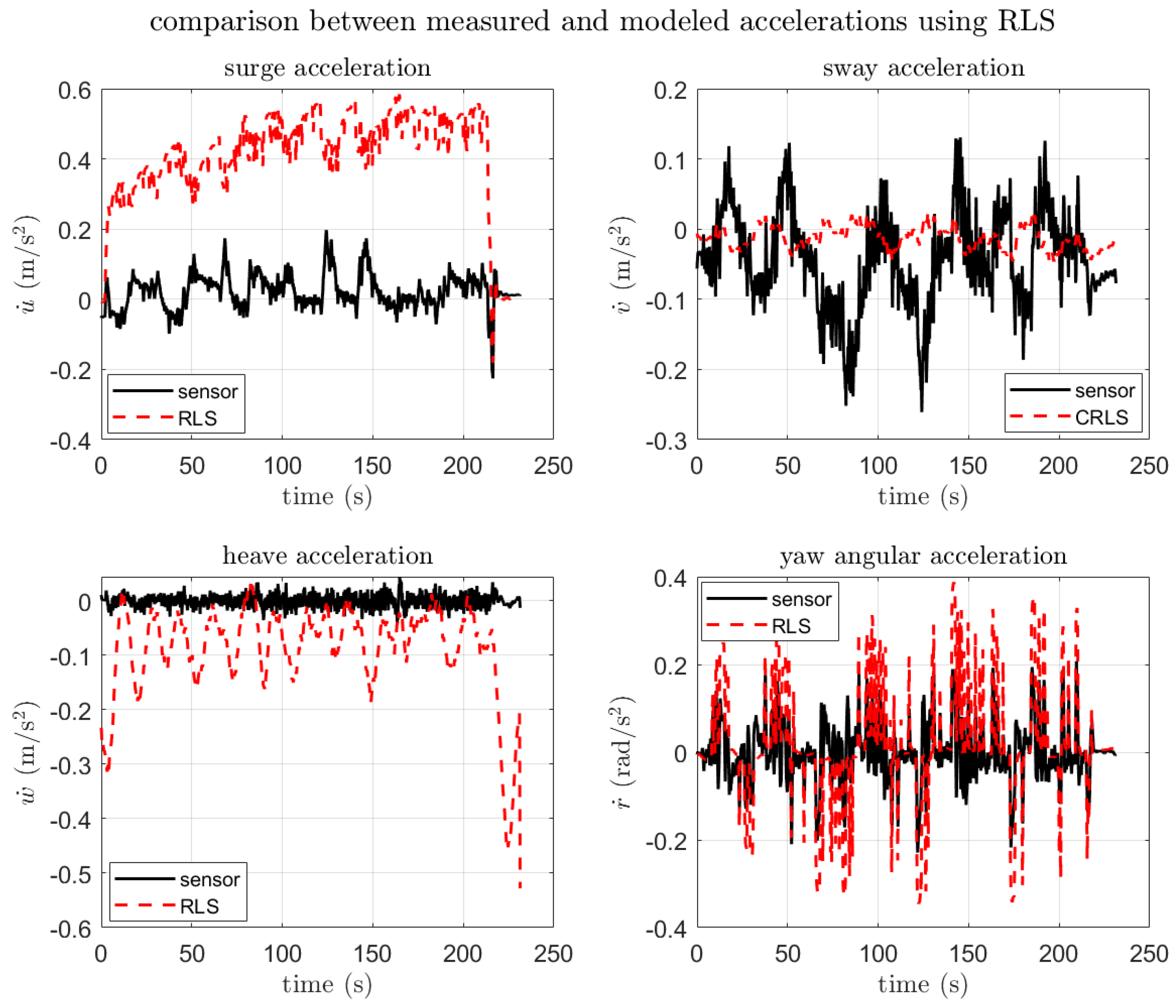
3.3.2. SI Result and Verification
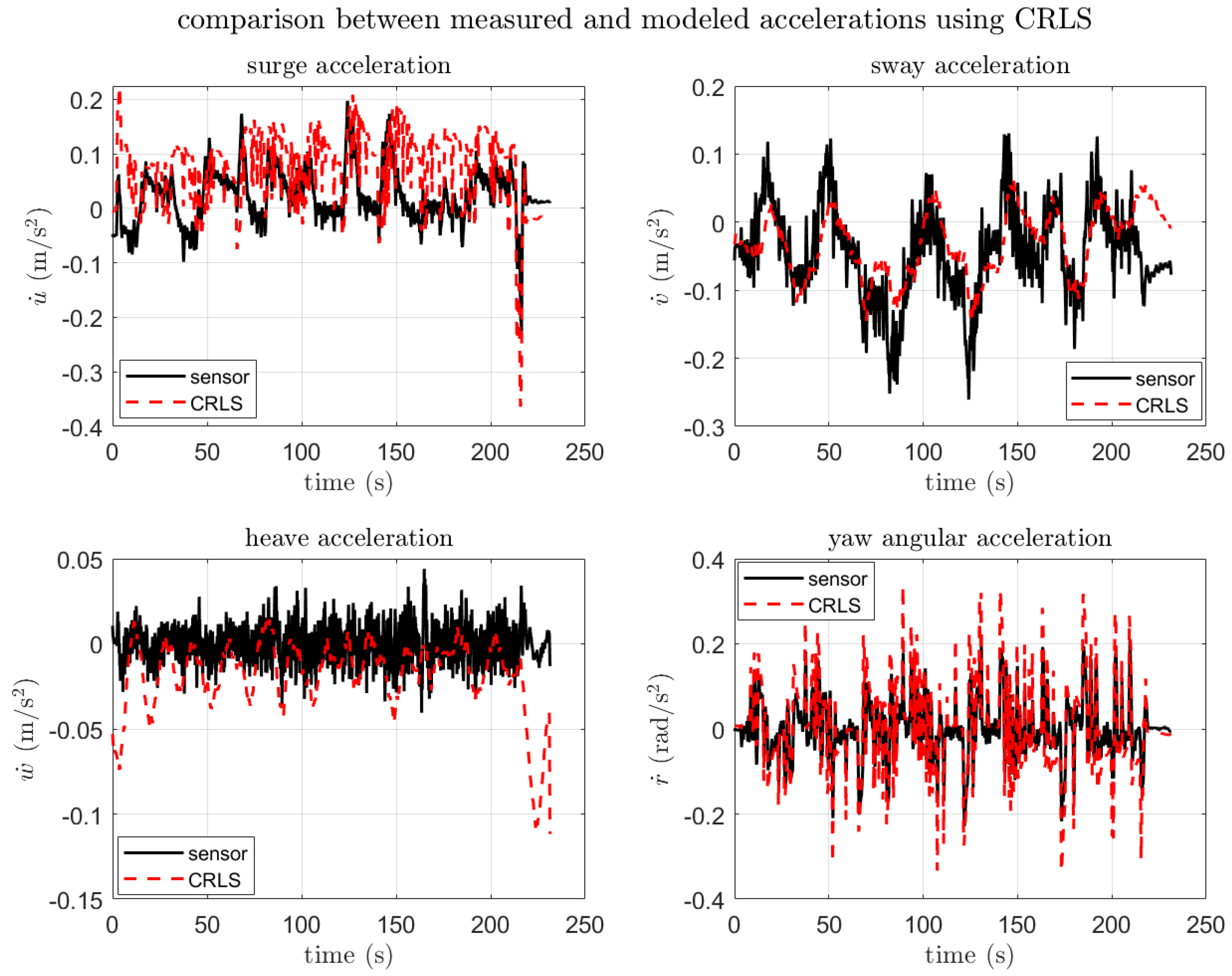
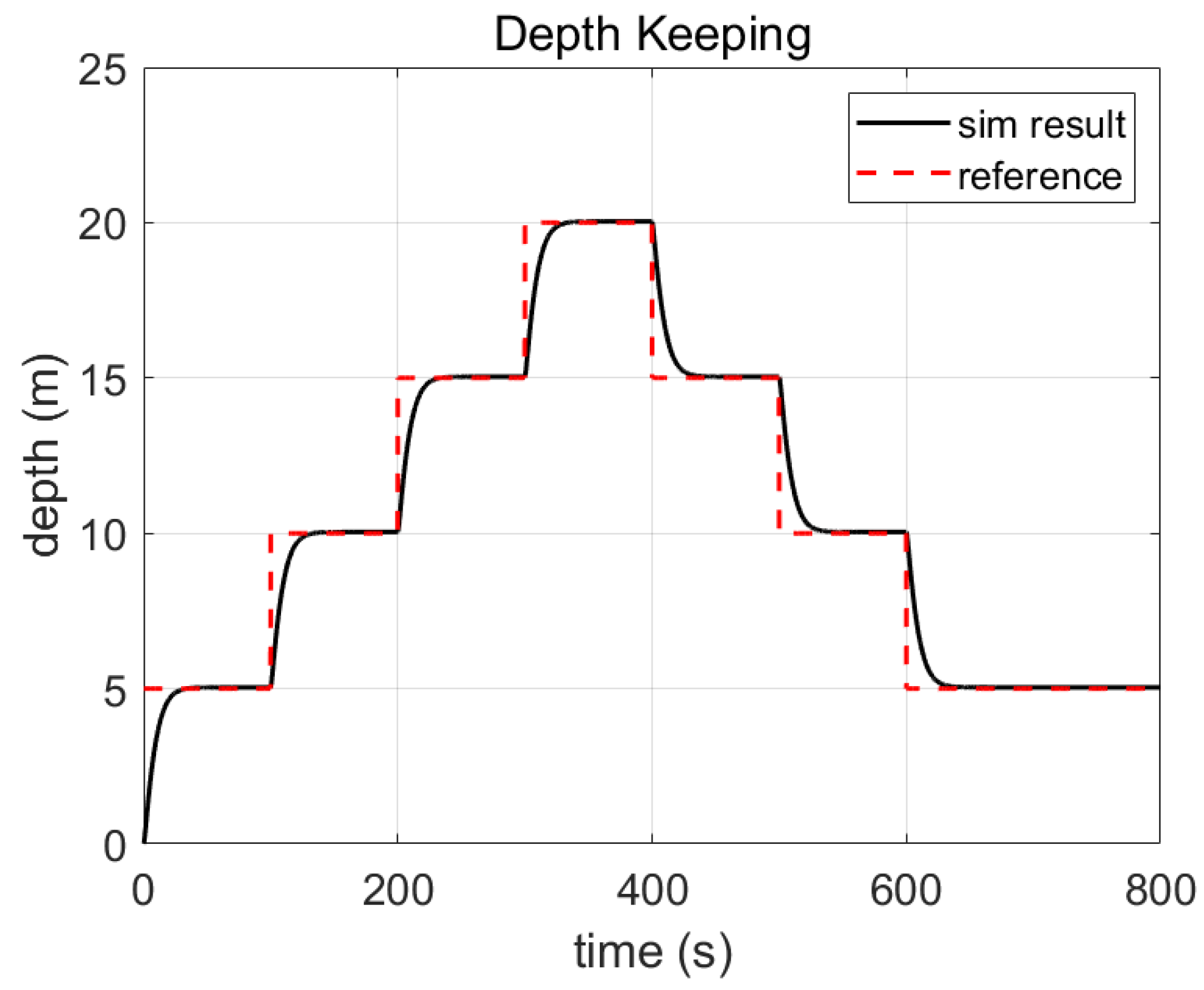
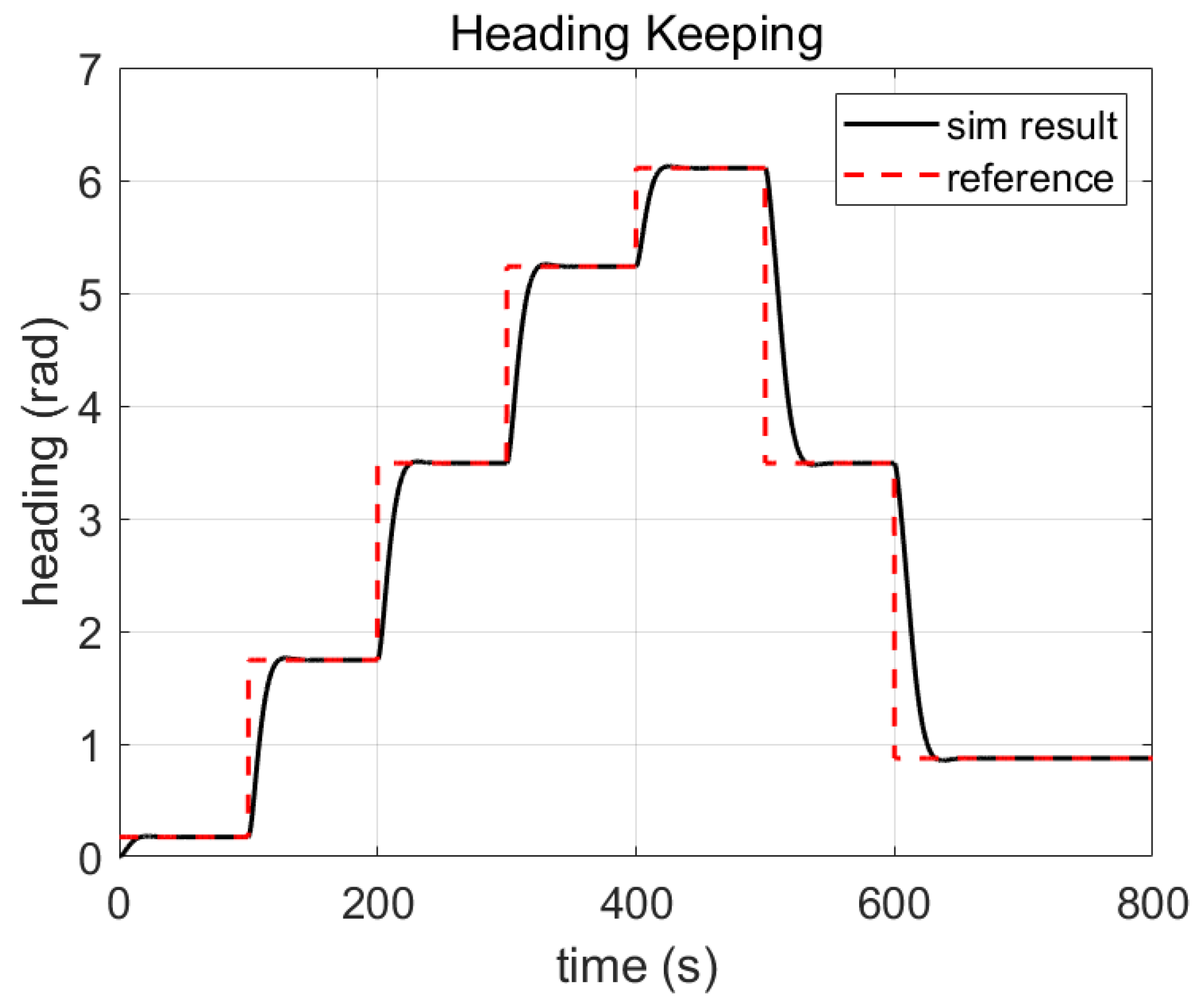
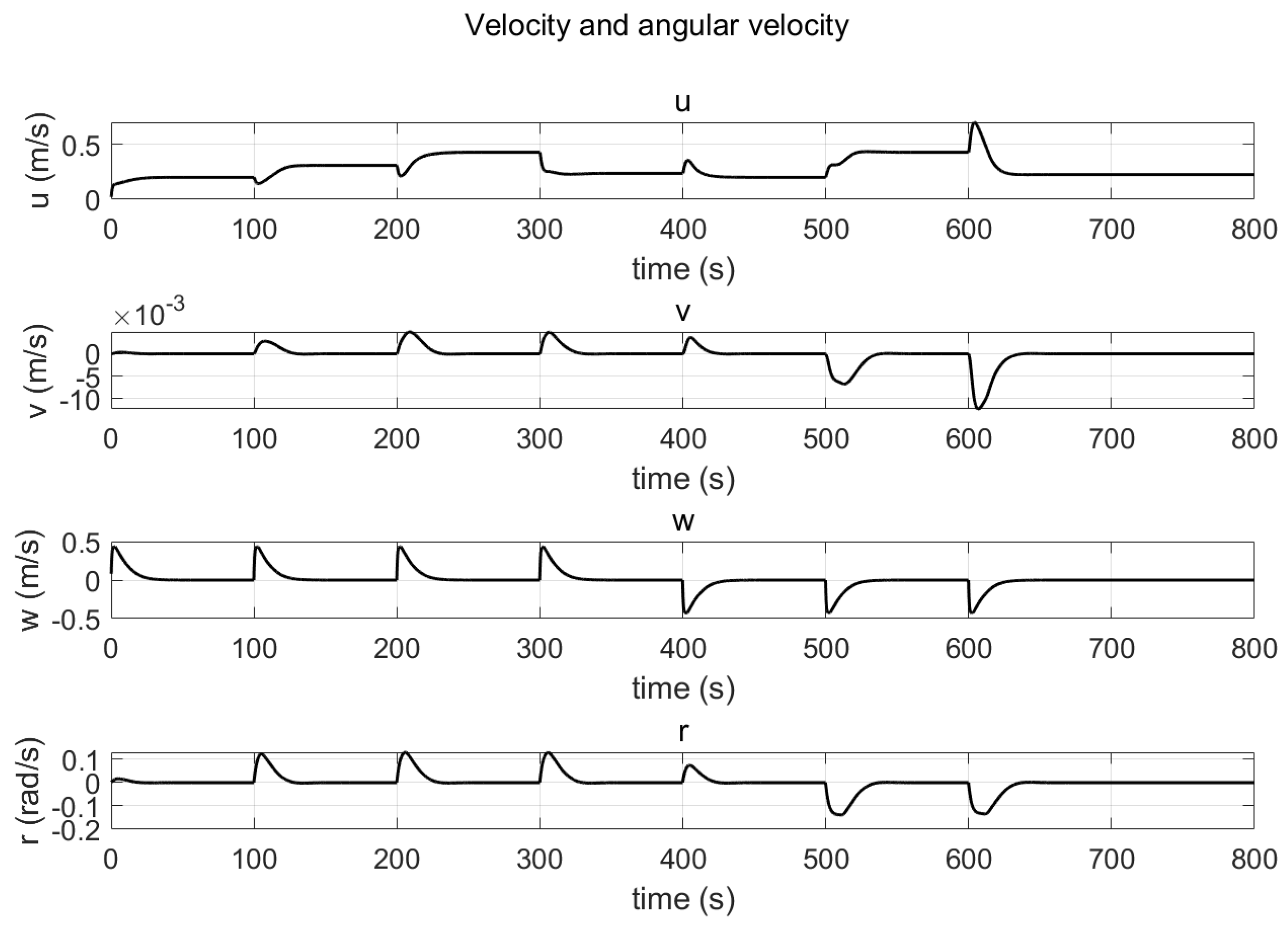
3.3.3. Simulation with PID Controller
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, G.R.; Kang, H.; Lee, M.J.; Li, J.H. Heading control of uri-t, an underwater cable burying rov: Theory and sea trial verification. J. Ocean Eng. Technol. 2019, 33, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Cho, G.R.; Kim, M.G.; Lee, M.J.; Li, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, H.; Lee, G. Mission management technique for multi-sensor-based AUV docking. J. Ocean Eng. Technol. 2022, 36, 81–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Zamora, J.J.; Camarillo-Gómez, K.A.; Pérez-Soto, G.I.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Morales-Hernández, L.A. Mini-AUV hydrodynamic parameters identification via CFD simulations and their application on control performance evaluation. Sensors 2021, 21, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Wang, R.; Zhai, Y.; Gu, H. Dynamic modeling of quadrotor AUV using a novel CFD simulation. Ocean Eng. 2021, 237, 109651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, G.; Ahn, H.T. Hydrodynamic derivative determination based on CFD and motion simulation for a tow-fish. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 82, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, F.; Rafeeyan, M.; Danesh, M. Estimation of hydrodynamic coefficients and simplification of the depth model of an AUV using CFD and sensitivity analysis. Ocean Eng. 2022, 263, 112369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.H.; Ok, J.H.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, S.K. Estimation of hydrodynamic derivatives and dynamic stability for submarine using captive model test. J. Navig. Port Res. 2015, 39, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.W.; Jeong, J.H.; Kim, I.G.; Lee, S.K. Estimation of hydrodynamic derivatives of submarine model by using VPMM test. J. Navig. Port Res. 2014, 38, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.J.; Lee, G.J.; Kwon, C.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Park, J.Y.; Jun, B.H. Added mass of submerged bodies obtained by forced oscillation tests and numerical calculations of potential flow. J. Soc. Nav. Archit. Korea 2022, 59, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardenas, P.; de Barros, E.A. Estimation of AUV hydrodynamic coefficients using analytical and system identification approaches. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2019, 45, 1157–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.A.; Clarke, D.B.; Brayshaw, I.B.; Barillon, J.L.; Anderson, B. The Calculation of Hydrodynamic Coefficients for Underwater Vehicles; Technical Report; Citeseer: University Park, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- De Barros, E.; Pascoal, A.; De Sa, E. Investigation of a method for predicting AUV derivatives. Ocean Eng. 2008, 35, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Faunt, L.M. [1] Parameter estimation by least-squares methods. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1992; Volume 210, pp. 1–37. [Google Scholar]
- Dinç, M.; Hajiyev, C. Identification of hydrodynamic coefficients of AUV in the presence of measurement biases. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2022, 236, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, P.C. Recursive least squares estimation. In Recursive Estimation and Time-Series Analysis: An Introduction for the Student and Practitioner; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 29–46. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, G.C.; Marantos, P.; Bechlioulis, C.P.; Kyriakopoulos, K.J. Unsupervised online system identification for underwater robotic vehicles. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 44, 642–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.B.; Weiss, H. Recursive prediction error methods for adaptive estimation. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. 1979, 9, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, H.; Mensler, M.; Richard, A. Continuous-time model identification from sampled data: Implementation issues and performance evaluation. Int. J. Control 2003, 76, 1337–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.J. 6-Dof Modelling and Control of a Remotely Operated Vehicle. Ph.D. Thesis, College of Science and Engineering, Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.H.; Lee, M.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, J.G.; Suh, J.H. Development of p-SURO II hybrid autonomous underwater vehicle and its experimental studies. J. Inst. Control. Robot. Syst. 2013, 19, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossen, T.I. Guidance and Control of Ocean Vehicles; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Chung, W.K. Accurate and practical thruster modeling for underwater vehicles. Ocean Eng. 2006, 33, 566–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Kim, M.G.; Kang, H.; Lee, M.J.; Cho, G.R. UUV Simulation Modeling and its Control Method: Simulation and Experimental Studies. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Kim, M.G.; Kang, H.; Lee, M.J.; Cho, G.R.; Kang, S. Initial alignment and position aiding time delay compensation for SDINS of deep sea underwater vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 American Control Conference (ACC), Atlanta, GA, USA, 8–10 June 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 3126–3131. [Google Scholar]
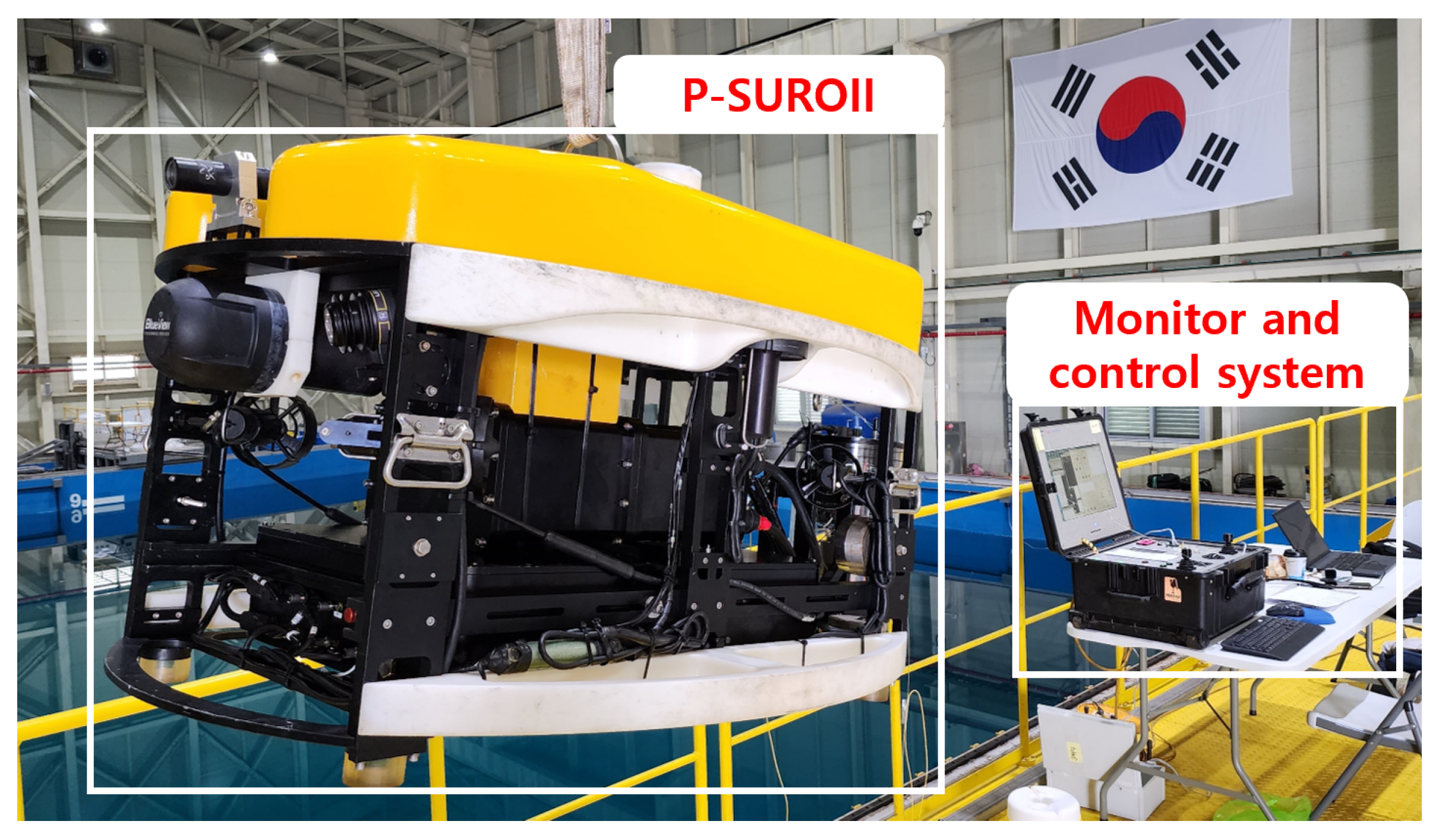
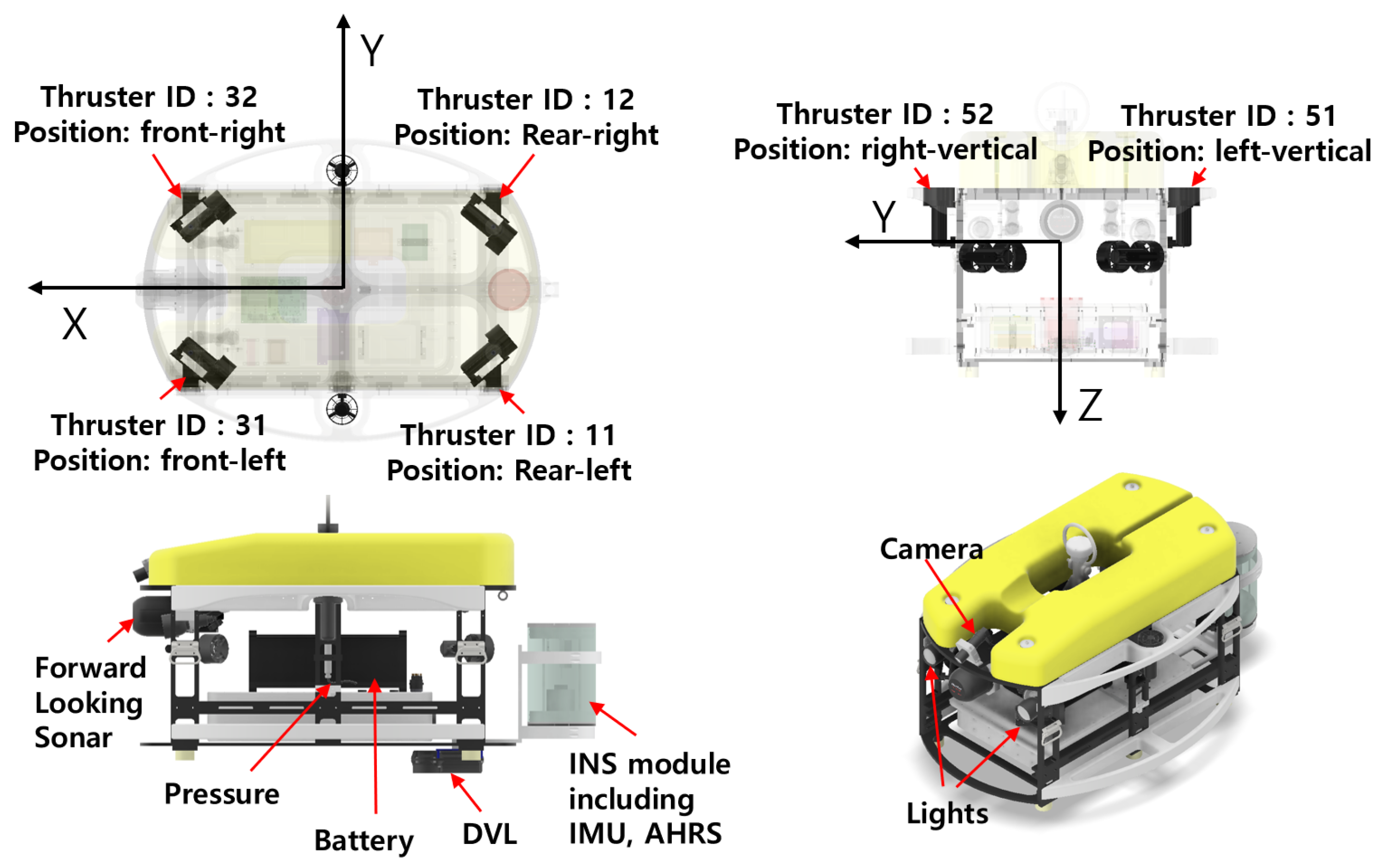
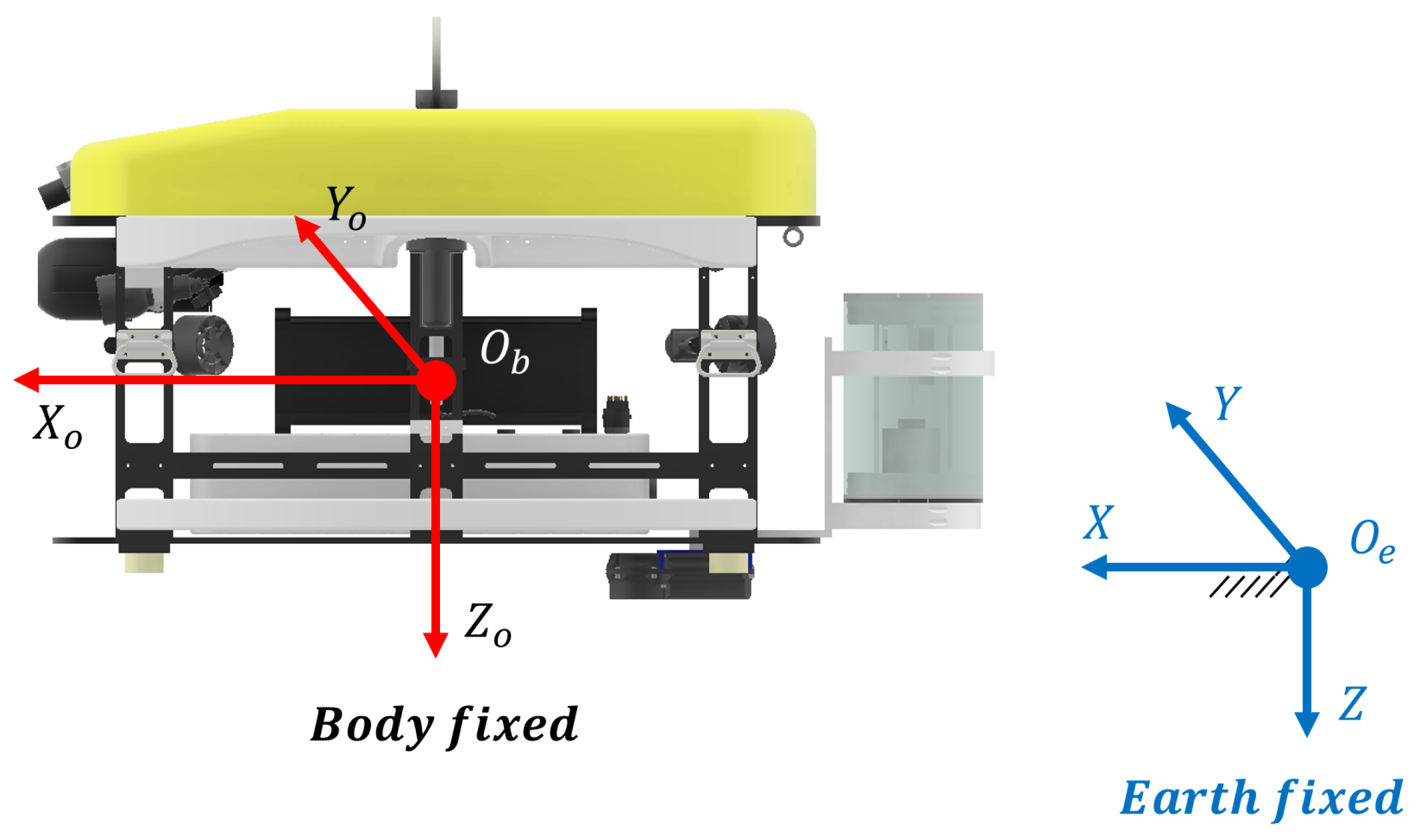
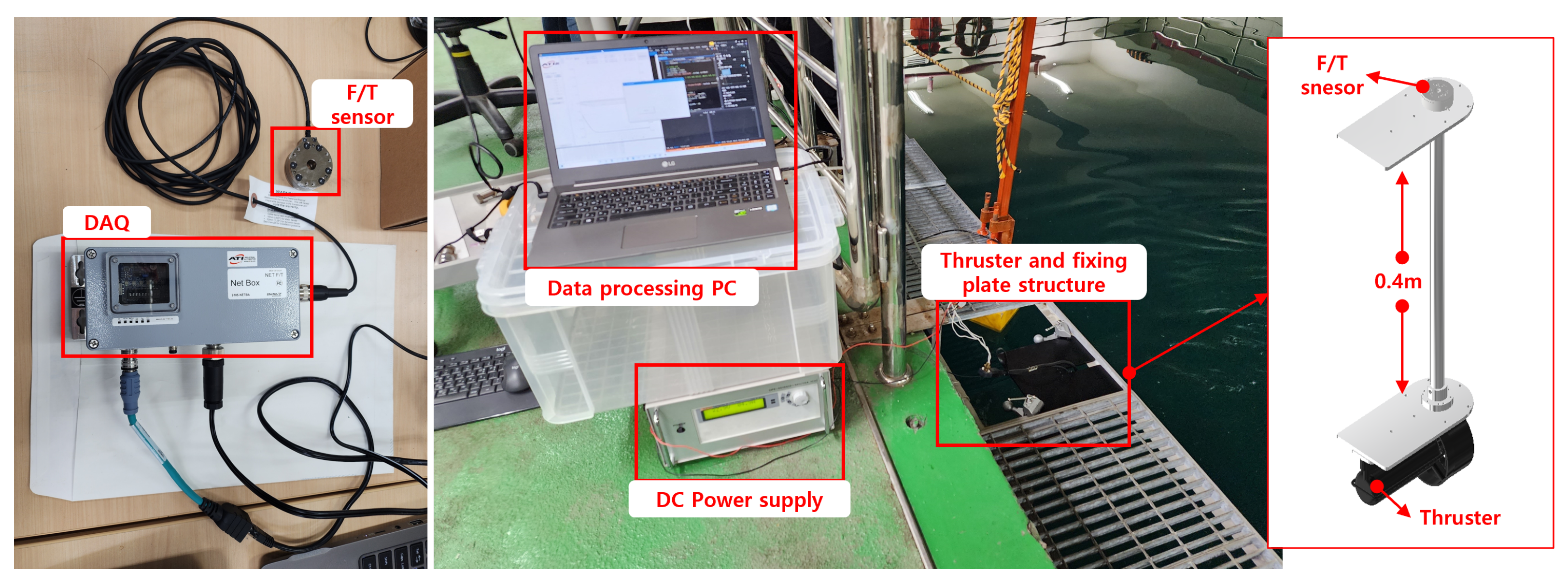
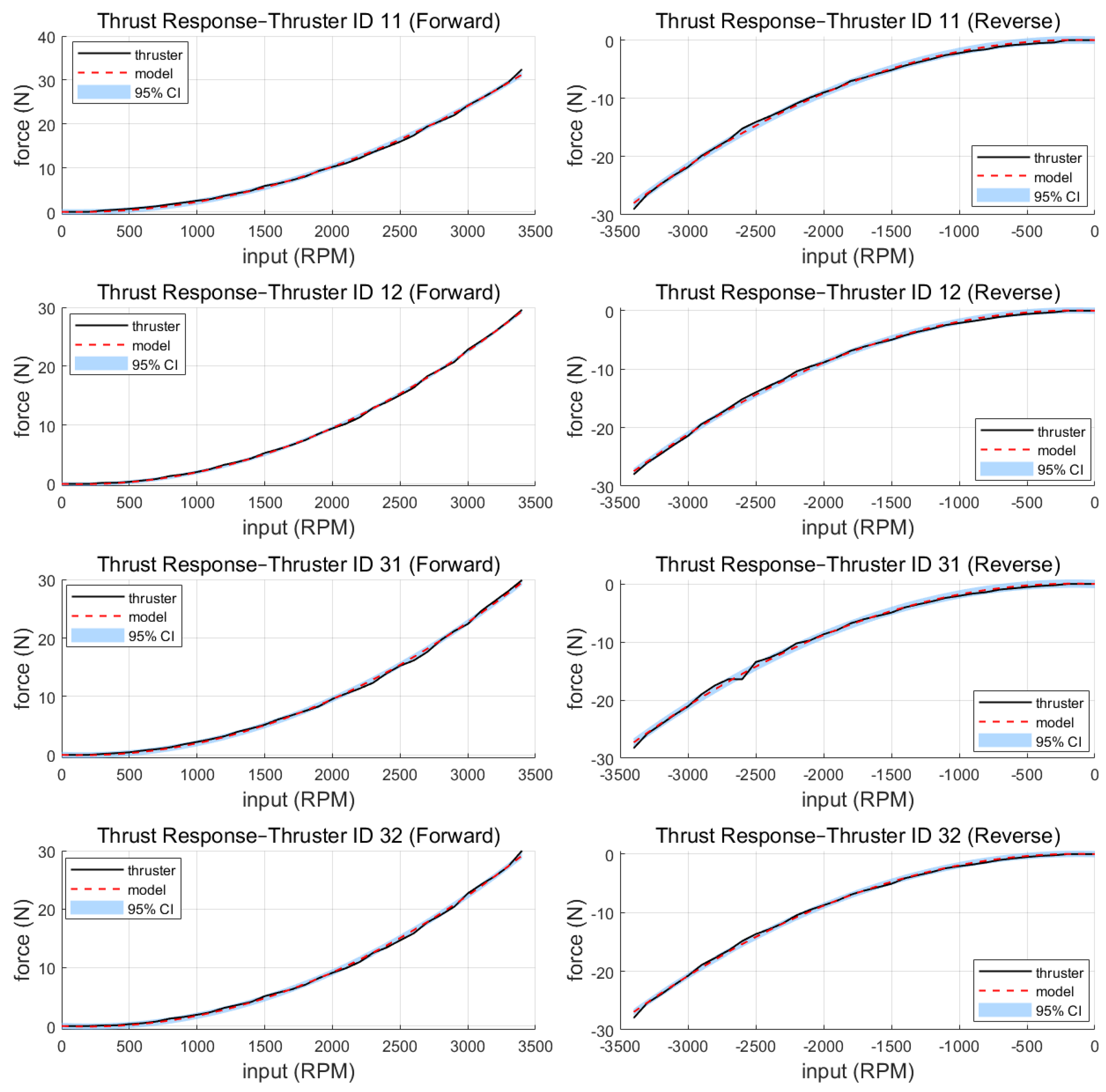
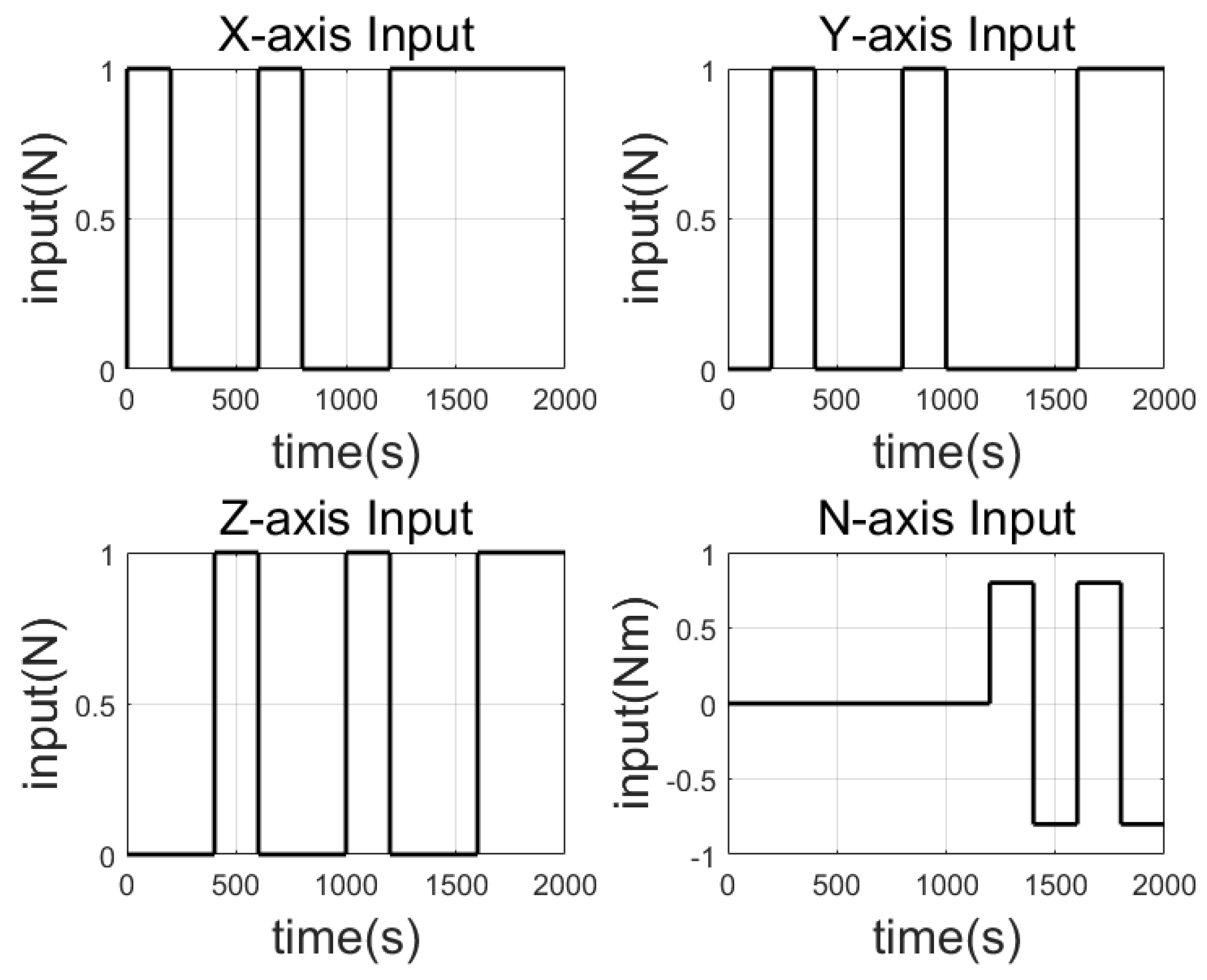
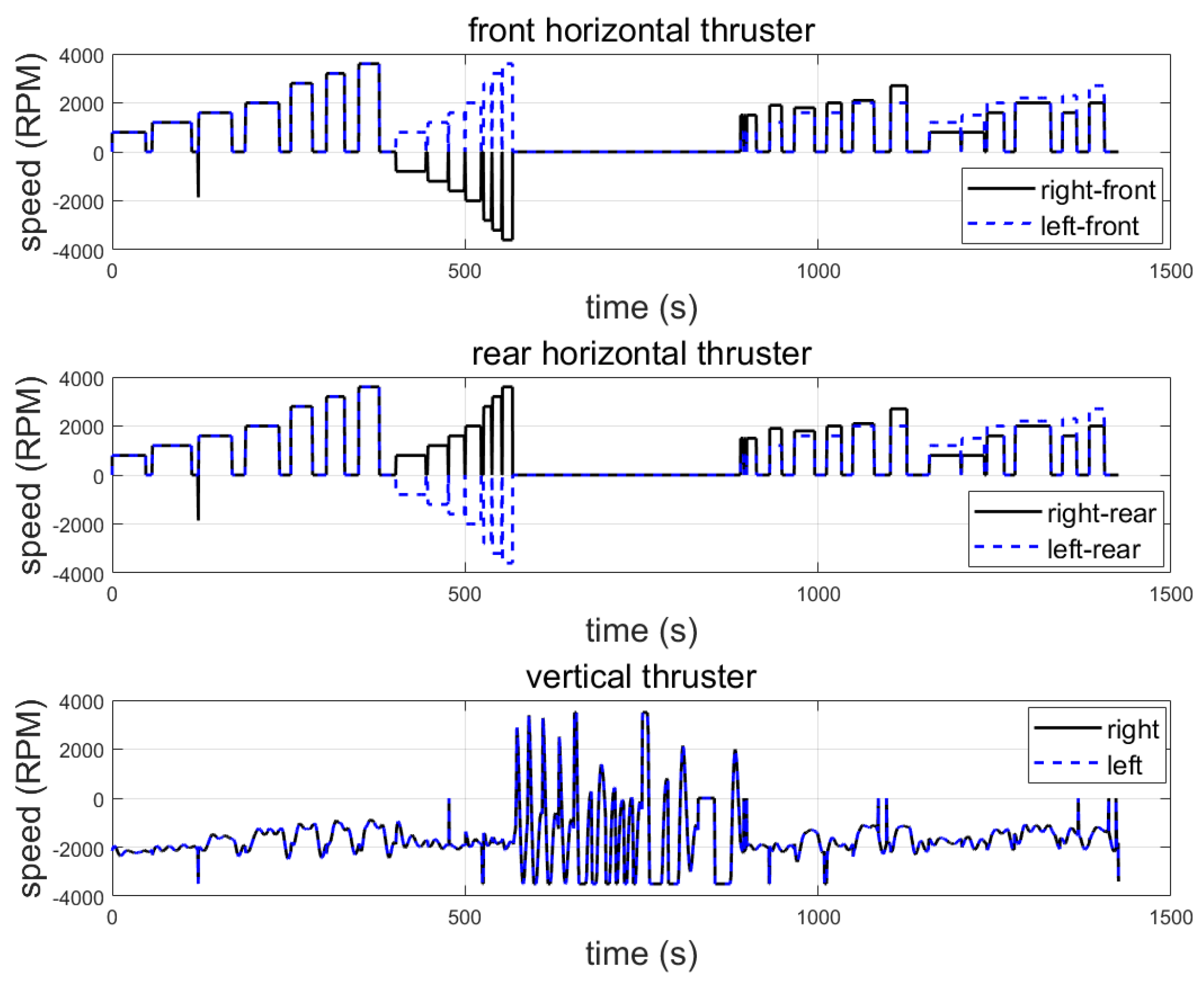
| Item | Spec |
|---|---|
| Size | 0.76 (H), 0.91 (W), 1.473 (L) (m) |
| Weight | 214.69 (kg) |
| Speed | Max. 0.5 (m/s) |
| Sensors | DVL (Teledyne, pathfiner) |
| IMU (Fiberpro, FI200P) | |
| AHRS (Microstrain, 3DM-GX5-25) | |
| Pressure (Keller, 36XW) | |
| Sonar (Blueview, P900) | |
| Thruster (Seabotix, HPDC1521/1513) |
| Thruster | (Forward) | (Forward) | (Reverse) | (Reverse) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID 11 | ||||
| ID 12 | ||||
| ID 31 | ||||
| ID 32 |
| Hydrodynamic Coefficients for Translational | Hydrodynamic Coefficients for Rotational | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Unit | CRLS | Reference | Error | Item | Unit | CRLS | Reference | Error |
| N·s/m | −3.8404 | −4.03 | −0.1896 | N·m·s/rad | 0 | −0.07 | −0.07 | ||
| N·s/m | −18.8662 | −18.18 | 0.6862 | N·m·s/rad | −1.2878 | −1.55 | −0.2622 | ||
| kg | −5.2189 | −5.5 | −0.2811 | kg·m | −0.1314 | −0.12 | 0.0114 | ||
| N·s/m | −6.4987 | −6.22 | 0.2787 | N·m·s/rad | 0 | −0.07 | −0.07 | ||
| N·s/m | −18.5199 | −21.66 | −3.1401 | N·m·s/rad | −2.9542 | −1.55 | 1.4042 | ||
| kg | −8.7398 | −12.7 | −3.9602 | kg·m | −0.1452 | −0.12 | 0.0252 | ||
| N·s/m | −6.2698 | −5.18 | 1.0898 | N·m·s/rad | −0.1 | −0.07 | 0.03 | ||
| N·s/m | −22.0082 | −36.99 | −14.9818 | N·m·s/rad | −1.3841 | −1.55 | −0.1659 | ||
| kg | −12.4941 | −14.57 | −2.0759 | kg·m | −0.094 | −0.12 | −0.026 | ||
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Total mass, m | |
| Center of gravity (CoG) | |
| Center of buoyancy (CoB) | |
| Moment of inertia, | |
| Moment of inertia, | |
| Moment of inertia, |
| Surge Direction | Sway Direction | Heave Direction | Yaw Direction | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Unit | Value | Item | Unit | Value | Item | Unit | Value | Item | Unit | Value |
| kg/s | 80.00 | kg/s | 175.77 | kg/s | 130.05 | kg·/s | 23.59 | ||||
| kg/m | 150.00 | kg/m | 255.38 | kg/m | 204.64 | kg·m | 22.42 | ||||
| kg | 25.50 | kg | 12.70 | kg | 99.50 | kg· | 34.22 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, H.; Li, J.-H.; Kim, M.-G.; Jin, H.; Lee, M.-J.; Cho, G.R.; Jin, S. Estimation of Hydrodynamic Coefficients for the Underwater Robot P-SUROII via Constraint Recursive Least Squares Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091610
Kang H, Li J-H, Kim M-G, Jin H, Lee M-J, Cho GR, Jin S. Estimation of Hydrodynamic Coefficients for the Underwater Robot P-SUROII via Constraint Recursive Least Squares Method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(9):1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091610
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Hyungjoo, Ji-Hong Li, Min-Gyu Kim, Hansol Jin, Mun-Jik Lee, Gun Rae Cho, and Sangrok Jin. 2025. "Estimation of Hydrodynamic Coefficients for the Underwater Robot P-SUROII via Constraint Recursive Least Squares Method" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 9: 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091610
APA StyleKang, H., Li, J.-H., Kim, M.-G., Jin, H., Lee, M.-J., Cho, G. R., & Jin, S. (2025). Estimation of Hydrodynamic Coefficients for the Underwater Robot P-SUROII via Constraint Recursive Least Squares Method. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(9), 1610. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13091610







