AGS-YOLO: An Efficient Underwater Small-Object Detection Network for Low-Resource Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
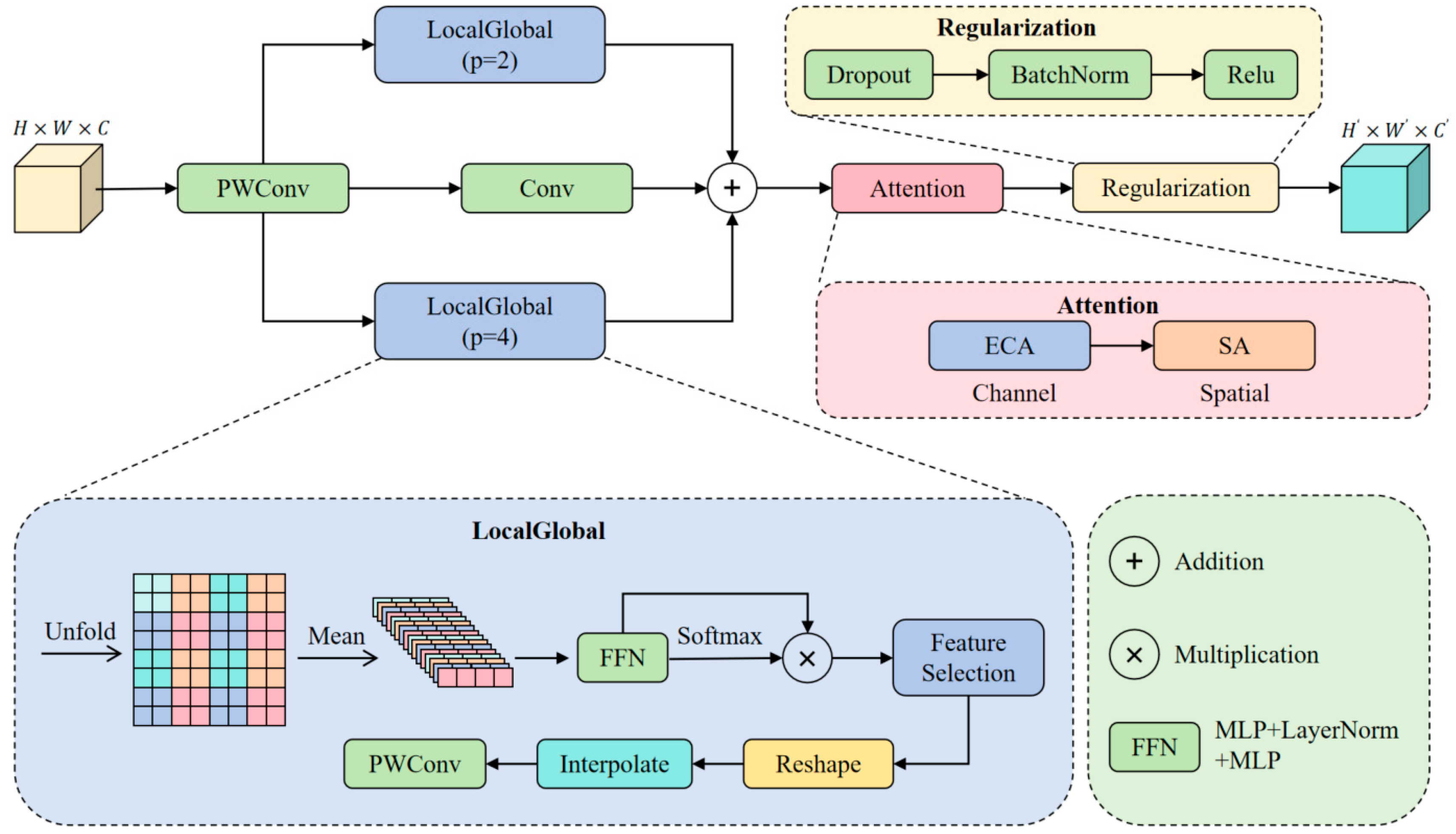
- Inspired by the idea of the PPA (Parallelized Patch-Aware Attention) module, the multi-scale aggregated attention module AMSA is proposed and integrated into the end of the C3k2 module. The AMSA module effectively enhances the model’s perception of tiny targets in complex underwater environments through multi-branch feature extraction, aggregating non-overlapping patches through a dual attention adaptive mechanism.
- (2)
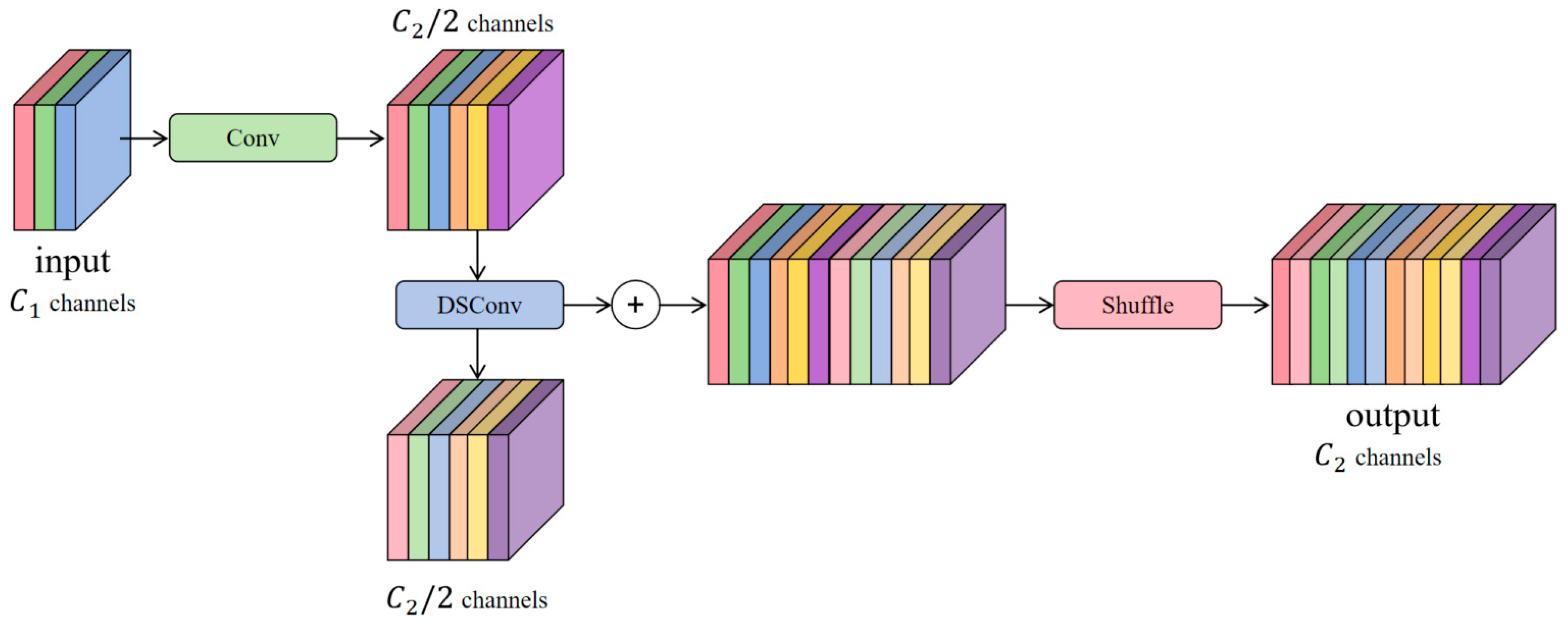
- In order to solve the problem of information loss during feature space compression and channel expansion of underwater optical images, the lightweight convolutional module GSconv is introduced, which adopts structural mixing and feature compensation strategies to decrease the model’s parameter count and computational complexity while ensuring the maximum retention of the hidden dependencies among channels.
- (3)
- Drawing on the idea of RT-DETR, a novel and efficient lightweight cross-scale connected neck network is designed, which introduces two types of convolutional unification channels, namely, lateral convolution and input projection, to decrease the number of model parameters and the computational complexity. The information interaction between features of different sizes is enhanced via the bidirectional feature fusion structure and cross-scale linking, allowing the model to efficiently capture multi-scale semantics and enhancing the detection accuracy for targets of varying sizes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. YOLO11
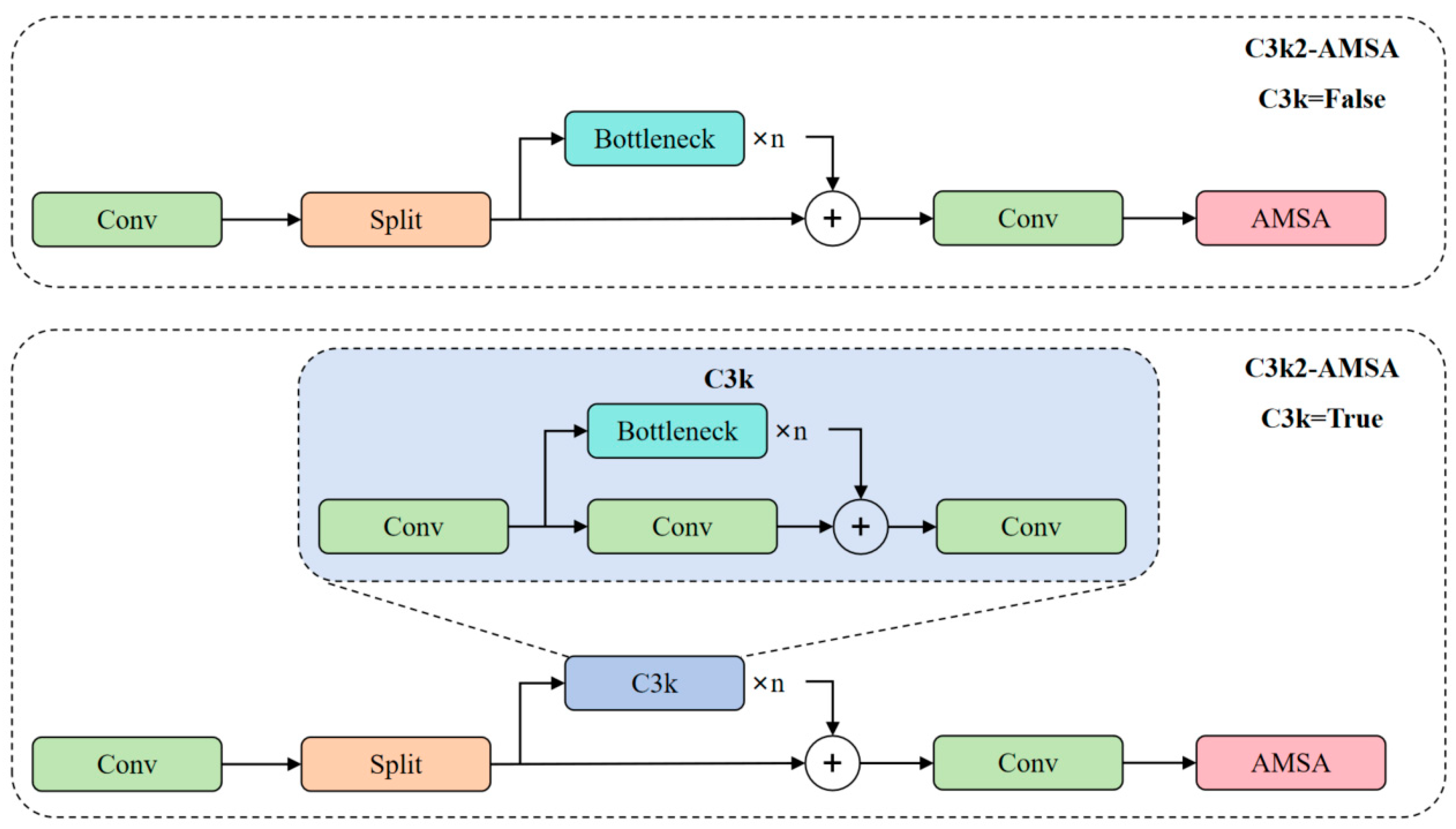
2.2. Proposed Model
2.2.1. AMSA
2.2.2. GSConv
2.2.3. CSFE
3. Experiments and Discussions
3.1. Experimental Environment and Configuration
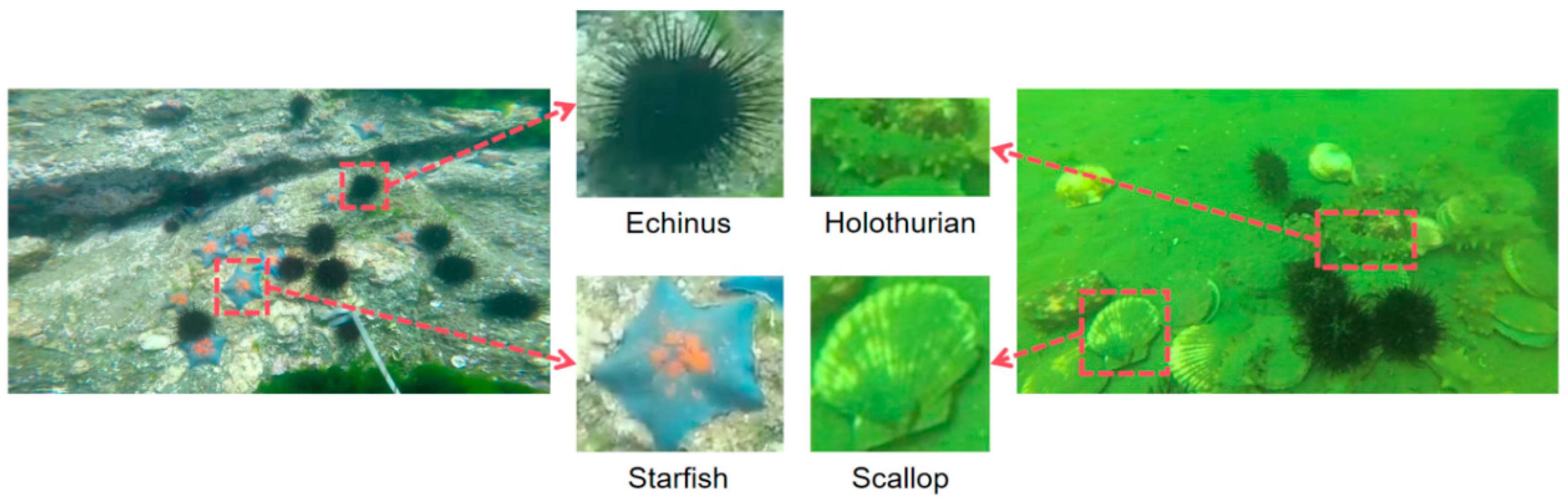
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Performance Evaluation
3.4. Ablation Experiments
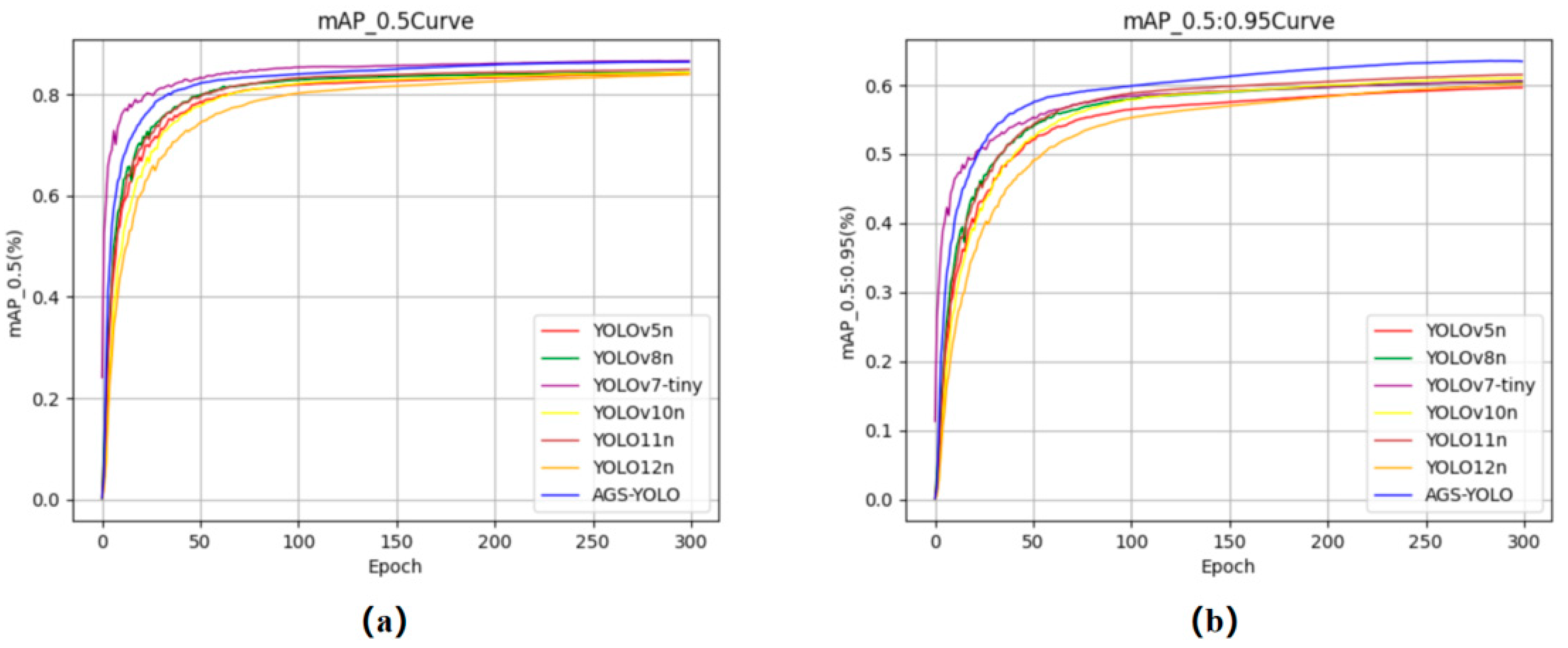
3.5. Comparison Experiments
3.5.1. Comparative Analyses on the DUO Dataset
3.5.2. Comparative Analyses on the RUOD Dataset
3.5.3. Comparison with Other Advanced Mainstream Models
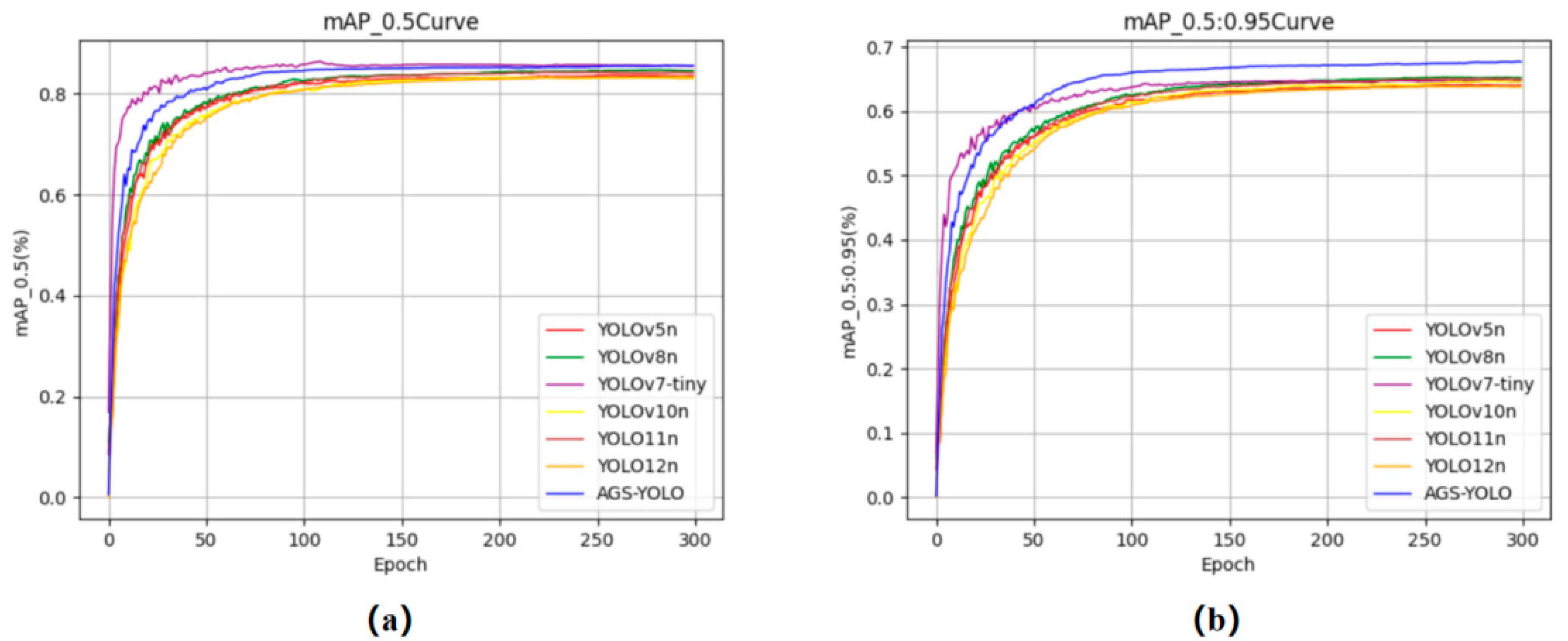
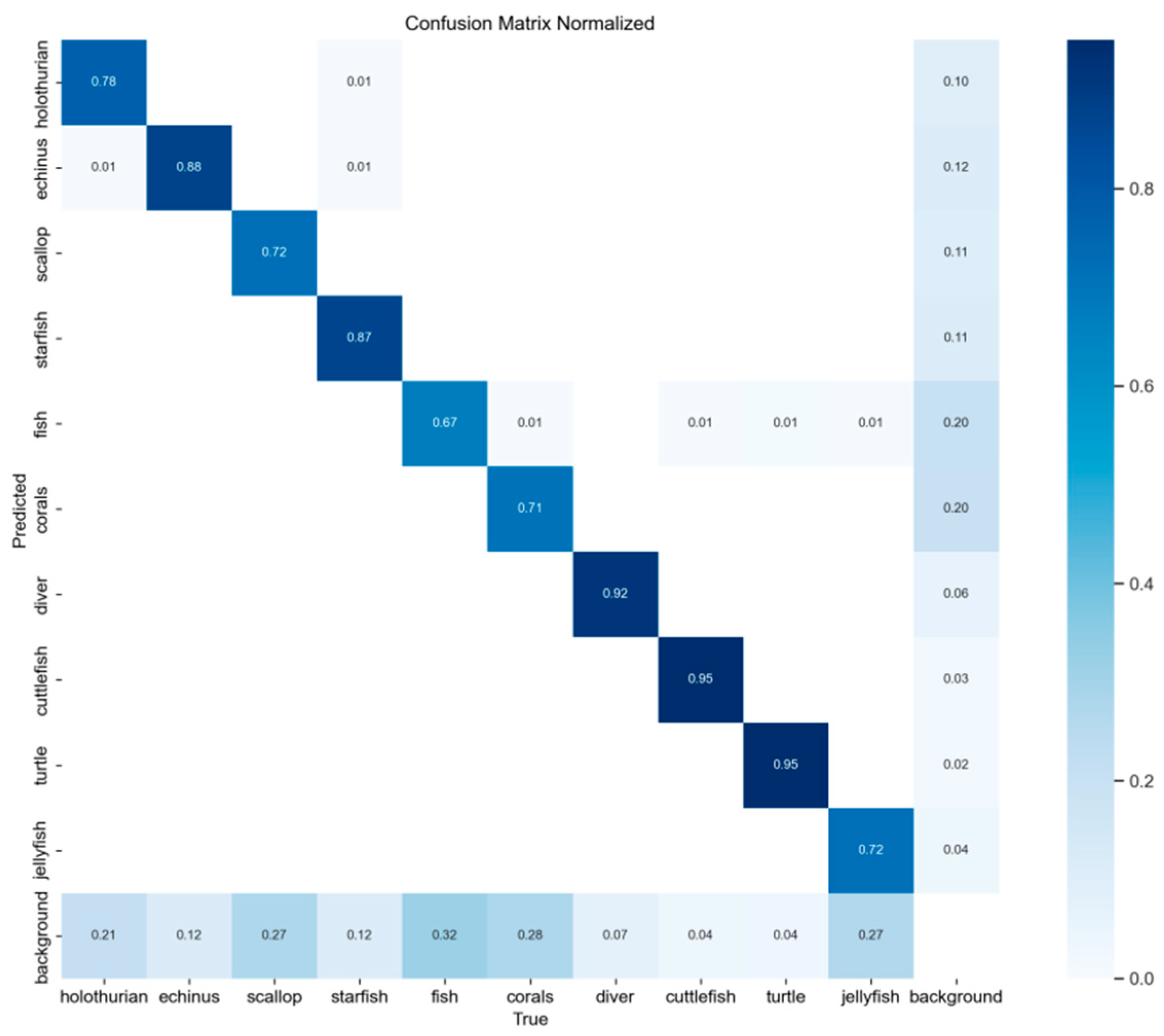
3.5.4. Statistical Significance Testing and Visualization
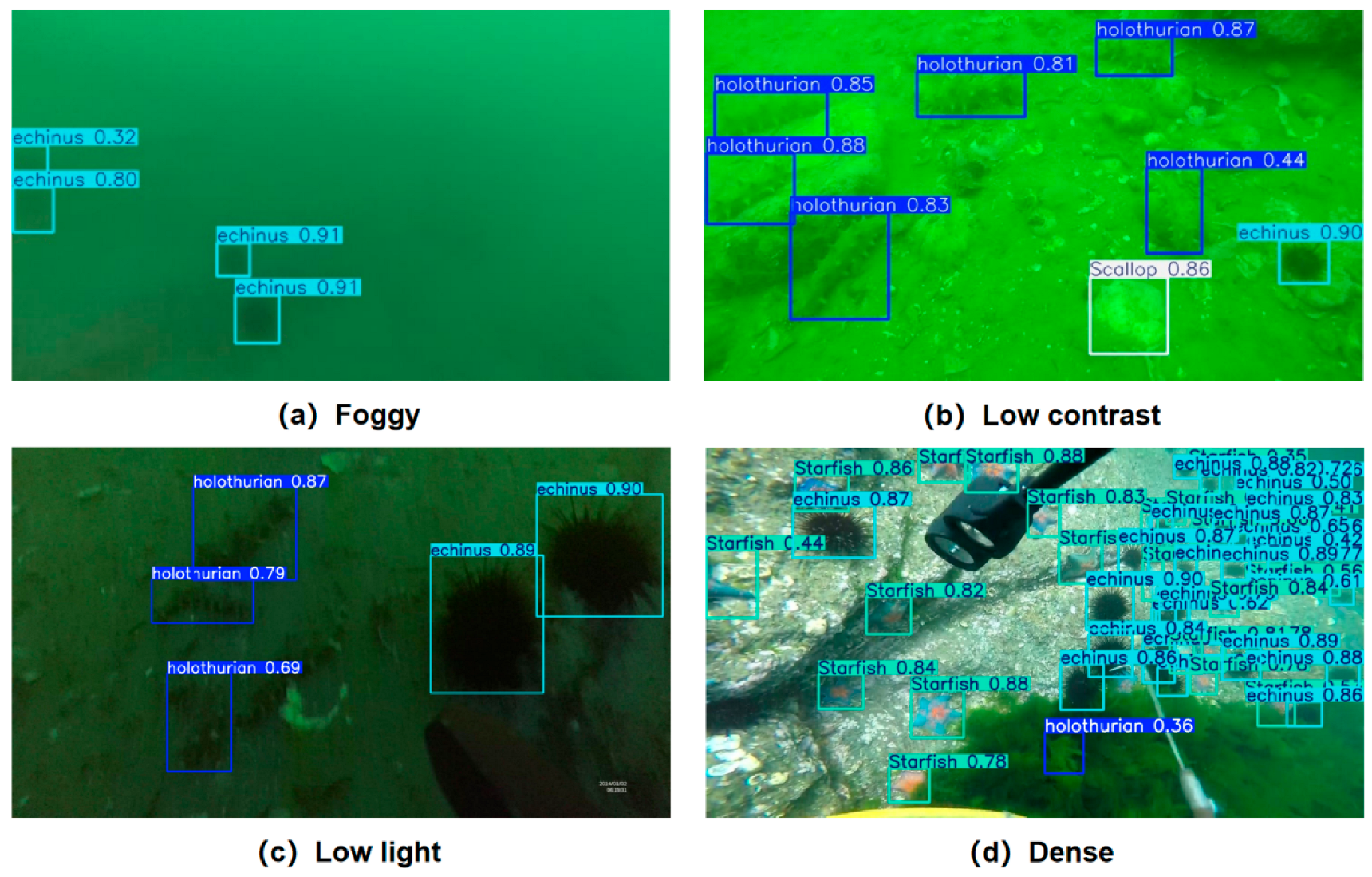
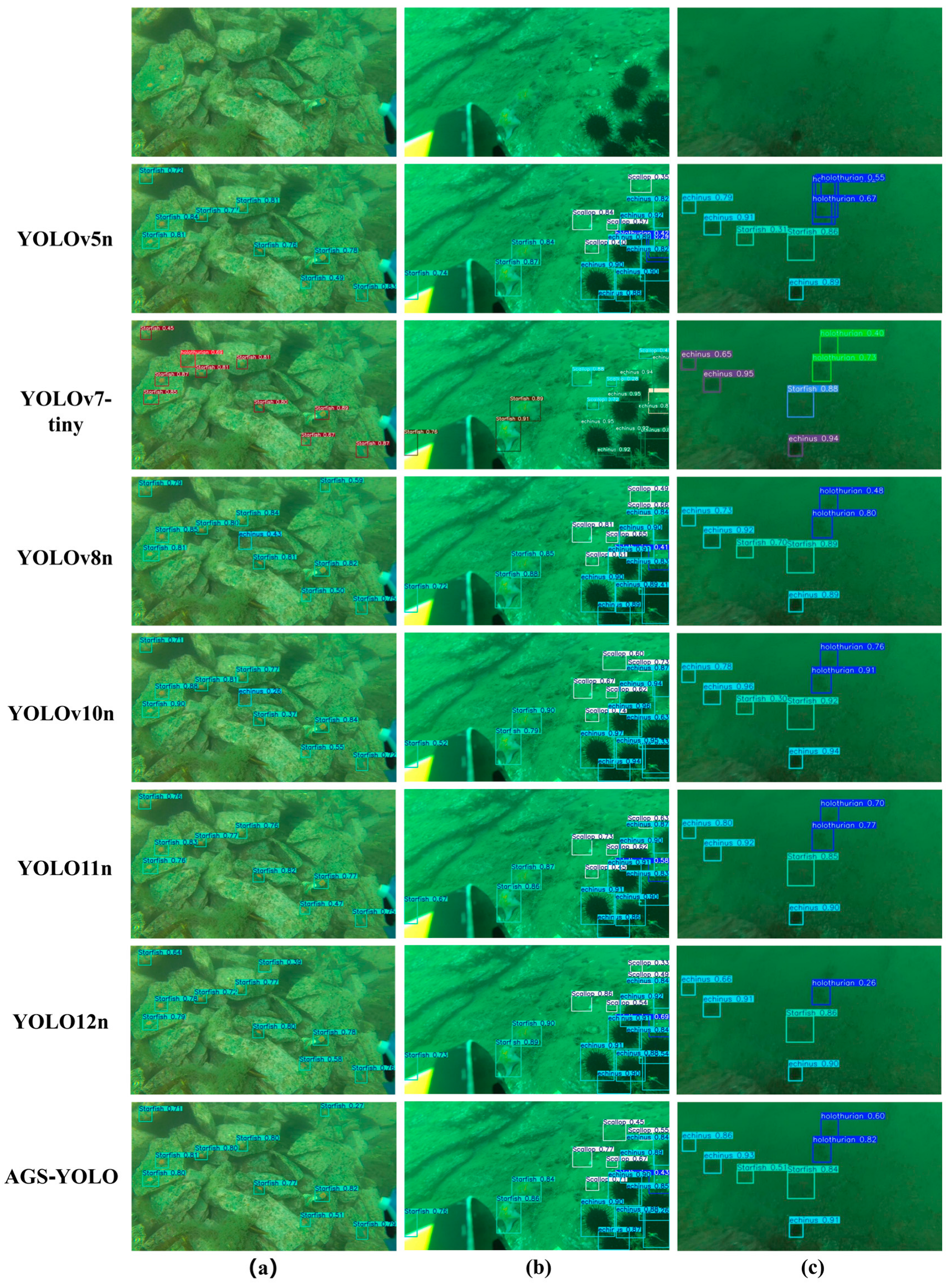
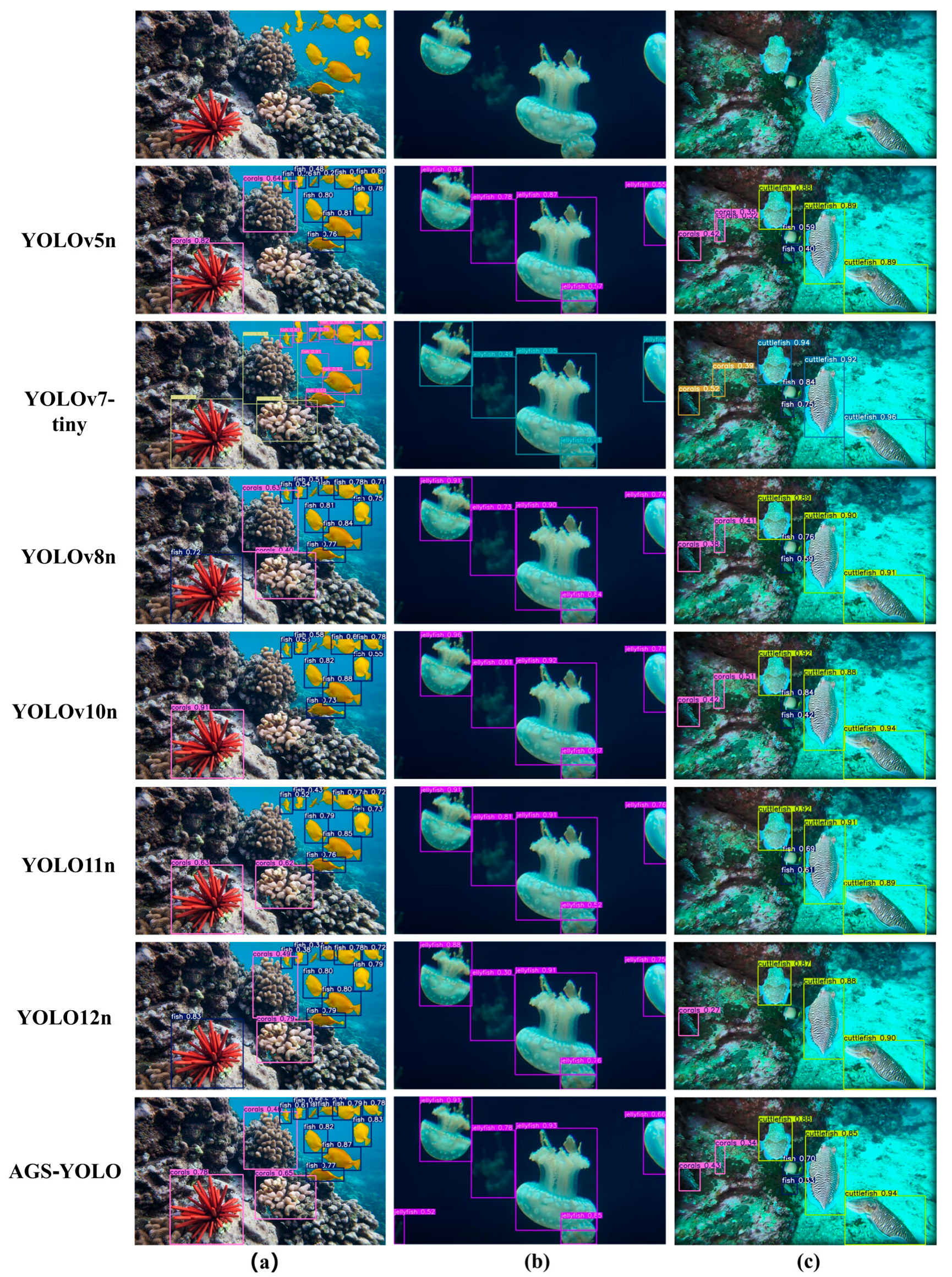
3.5.5. Visualization and Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, P.; Qian, W.; Wang, Y. YWnet: A Convolutional Block Attention-Based Fusion Deep Learning Method for Complex Underwater Small Target Detection. Ecol. Inform. 2024, 79, 102401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Fan, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Yao, H. Underwater Target Detection and Embedded Deployment Based on Lightweight YOLO_GN. J. Supercomput. 2024, 80, 14057–14084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, M.; Song, W.; Mei, H.; He, Q.; Liotta, A. A Systematic Review and Analysis of Deep Learning-Based Underwater Object Detection. Neurocomputing 2023, 527, 204–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.03762. [Google Scholar]
- Shahi, T.B.; Xu, C.-Y.; Neupane, A.; Guo, W. Recent Advances in Crop Disease Detection Using UAV and Deep Learning Techniques. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faster, R. Towards Real-Time Object Detection with Region Proposal Networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 9199, 2969239–2969250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhu, P.; Yu, J.; Li, S. Extraction of Visual Texture Features of Seabed Sediments Using an SVDD Approach. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 142, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Sun, B.; Zhu, D. Underwater Target Detection Based on Faster R-CNN and Adversarial Occlusion Network. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2021, 100, 104190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.-Y.; Berg, A.C. Ssd: Single Shot Multibox Detector. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016: 14th European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; Proceedings, Part I 14. Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 21–37. [Google Scholar]
- Al Muksit, A.; Hasan, F.; Emon, M.F.H.B.; Haque, M.R.; Anwary, A.R.; Shatabda, S. YOLO-Fish: A Robust Fish Detection Model to Detect Fish in Realistic Underwater Environment. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 72, 101847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Lyu, L.; Yan, P.; Zhang, J. MAD-YOLO: A Quantitative Detection Algorithm for Dense Small-Scale Marine Benthos. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Cai, R.; Su, J.; Hou, M.; Deng, R. U-YOLOv7: A Network for Underwater Organism Detection. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 75, 102108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. BGLE-YOLO: A Lightweight Model for Underwater Bio-Detection. Sensors 2025, 25, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carion, N.; Massa, F.; Synnaeve, G.; Usunier, N.; Kirillov, A.; Zagoruyko, S. End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Geng, X.; Tang, H.; Bhatti, U.A. PE-Transformer: Path Enhanced Transformer for Improving Underwater Object Detection. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 246, 123253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cao, W.; Gao, J.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Song, K.; Wang, H. Underwater Object Detection Algorithm Based on an Improved YOLOv8. JMSE 2024, 12, 1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Anwar, S.; Hou, J.; Cong, R.; Guo, C.; Ren, W. Underwater Image Enhancement via Medium Transmission-Guided Multi-Color Space Embedding. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 4985–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanam, R.; Hussain, M. Yolov11: An Overview of the Key Architectural Enhancements. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2410.17725. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Ye, Q.; Doermann, D. Yolov12: Attention-Centric Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.12524. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Zheng, S.; Xu, W.; Xu, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Teng, X.; Li, A.; Guo, L. HCF-Net: Hierarchical Context Fusion Network for Infrared Small Object Detection. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.10778. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, X.; Zhuang, L.; Dong, X.; Gao, L.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, K. FFN: Fountain Fusion Net for Arbitrary-Oriented Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2023, 61, 3276995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-Neck by GSConv: A Lightweight-Design for Real-Time Detector Architectures. J. Real-Time Image Proc. 2024, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.G.D.; Fawcett, R.; Prisacariu, V.A. Dsconv: Efficient Convolution Operator. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5148–5157. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Lv, W.; Xu, S.; Wei, J.; Wang, G.; Dang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. DETRs Beat YOLOs on Real-Time Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16 June 2024; pp. 16965–16974. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, M.; Shen, J.; Lin, Y.; Pantic, M. Dilated Convolutions with Lateral Inhibitions for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.03708. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, M.; Massaroli, S.; Nguyen, E.; Fu, D.Y.; Dao, T.; Baccus, S.; Bengio, Y.; Ermon, S.; Ré, C. Hyena Hierarchy: Towards Larger Convolutional Language Models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 28043–28078. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Zhu, M.; Wang, D.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z. A Dataset and Benchmark of Underwater Object Detection for Robot Picking. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), Shenzhen, China, 5–9 July 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, C.; Liu, R.; Fan, X.; Chen, P.; Fu, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhu, M.; Luo, Z. Rethinking General Underwater Object Detection: Datasets, Challenges, and Solutions. Neurocomputing 2023, 517, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-Cam: Visual Explanations from Deep Networks via Gradient-Based Localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Jocher, G.; Stoken, A.; Borovec, J.; Changyu, L.; Hogan, A.; Diaconu, L.; Poznanski, J.; Yu, L.; Rai, P.; Ferriday, R. Ultralytics/Yolov5: V3. 0. Zenodo; European Organization for Nuclear Research: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, G. Detection and Counting of Small Target Apples under Complicated Environments by Using Improved YOLOv7-Tiny. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohan, M.; Sai Ram, T.; Rami Reddy, C.V. A Review on Yolov8 and Its Advancements. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data Intelligence and Cognitive Informatics, Tirunelveli, India, 18–20 November 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 529–545. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Lin, Z.; Han, J. Yolov10: Real-Time End-to-End Object Detection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2024, 37, 107984–108011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, L. Ship Plate Detection Algorithm Based on Improved RT-DETR. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, C.; Zhang, W.; Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, K. Rtmdet: An Empirical Study of Designing Real-Time Object Detectors. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.07784. [Google Scholar]








| Training Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.01 |
| Image size | |
| Epochs | 300 |
| Batch | 32 |
| Workers | 4 |
| Optimizer | SGD |
| Cache | False |
| Weight Decay | 0.0005 |
| Model | AMSA | CSFE | GSConv | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Parameter/M | GFLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLO11n | × | × | × | 84.2 | 65.1 | 2.58 | 6.3 |
| √ | × | × | 85.3 | 67.4 | 3.8 | 10.8 | |
| √ | √ | × | 85.4 | 67.6 | 3.1 | 9.7 | |
| √ | √ | √ | 85.5 | 67.7 | 3.0 | 9.6 |
| Model | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Parameter/M | GFLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n [34] | 83.6 | 64.1 | 2.2 | 5.9 |
| YOLOv7-tiny [35] | 85.0 | 64.7 | 6.0 | 13.0 |
| YOLOv8n [36] | 84.6 | 65.3 | 2.7 | 6.9 |
| YOLOv10n [37] | 83.3 | 64.6 | 2.7 | 8.3 |
| YOLO11n | 84.2 | 65.1 | 2.6 | 6.3 |
| YOLO12n | 83.2 | 63.8 | 2.6 | 6.4 |
| AGS-YOLO | 85.5 | 67.7 | 3.0 | 9.6 |
| Model | mAP@0.5 | mAP@0.5:0.95 | Parameter/M | GFLOPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv5n | 84.1 | 59.7 | 2.2 | 5.9 |
| YOLOv7-tiny | 85.0 | 57.9 | 6.0 | 13.0 |
| YOLOv8n | 84.3 | 60.5 | 2.7 | 6.9 |
| YOLOv10n | 84.3 | 61.1 | 2.7 | 8.3 |
| YOLO11n | 84.9 | 61.5 | 2.6 | 6.3 |
| YOLO12n | 83.9 | 60.2 | 2.6 | 6.4 |
| AGS-YOLO | 86.4 | 63.5 | 3.0 | 9.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Hao, J.; Yao, Q.; Xi, H.; Wu, Y.; Xing, Z. AGS-YOLO: An Efficient Underwater Small-Object Detection Network for Low-Resource Environments. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081465
Sun W, Liu X, Hao J, Yao Q, Xi H, Wu Y, Xing Z. AGS-YOLO: An Efficient Underwater Small-Object Detection Network for Low-Resource Environments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(8):1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081465
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Weikai, Xiaoqun Liu, Juan Hao, Qiyou Yao, Hailin Xi, Yuwen Wu, and Zhaoye Xing. 2025. "AGS-YOLO: An Efficient Underwater Small-Object Detection Network for Low-Resource Environments" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 8: 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081465
APA StyleSun, W., Liu, X., Hao, J., Yao, Q., Xi, H., Wu, Y., & Xing, Z. (2025). AGS-YOLO: An Efficient Underwater Small-Object Detection Network for Low-Resource Environments. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(8), 1465. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13081465






