Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Finite-Time Extended State Observer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formation
2.1. Dynamic Model of Land Manipulator
2.2. Hydrodynamic Model and Analysis
- This study focuses solely on the self-motion of the manipulator under water, specifically its hydrodynamic modeling in a hydrostatic environment;
- The underwater manipulator is modeled as a regular cylinder with a uniform mass distribution. It has no airfoil structure and is unaffected by lift, that is, ;
- The center of mass of the underwater manipulator and its center of buoyancy can be aligned, and the weight of the manipulator is assumed to exceed the buoyant force;
- Fluid is considered incompressible;
- External disturbances acting on the underwater manipulator are bounded.
2.2.1. Analysis of Water Resistance
2.2.2. Analysis of Additional Mass Force
2.2.3. Analysis of Equivalent Gravity
3. Design of FTESO−GFTSMC
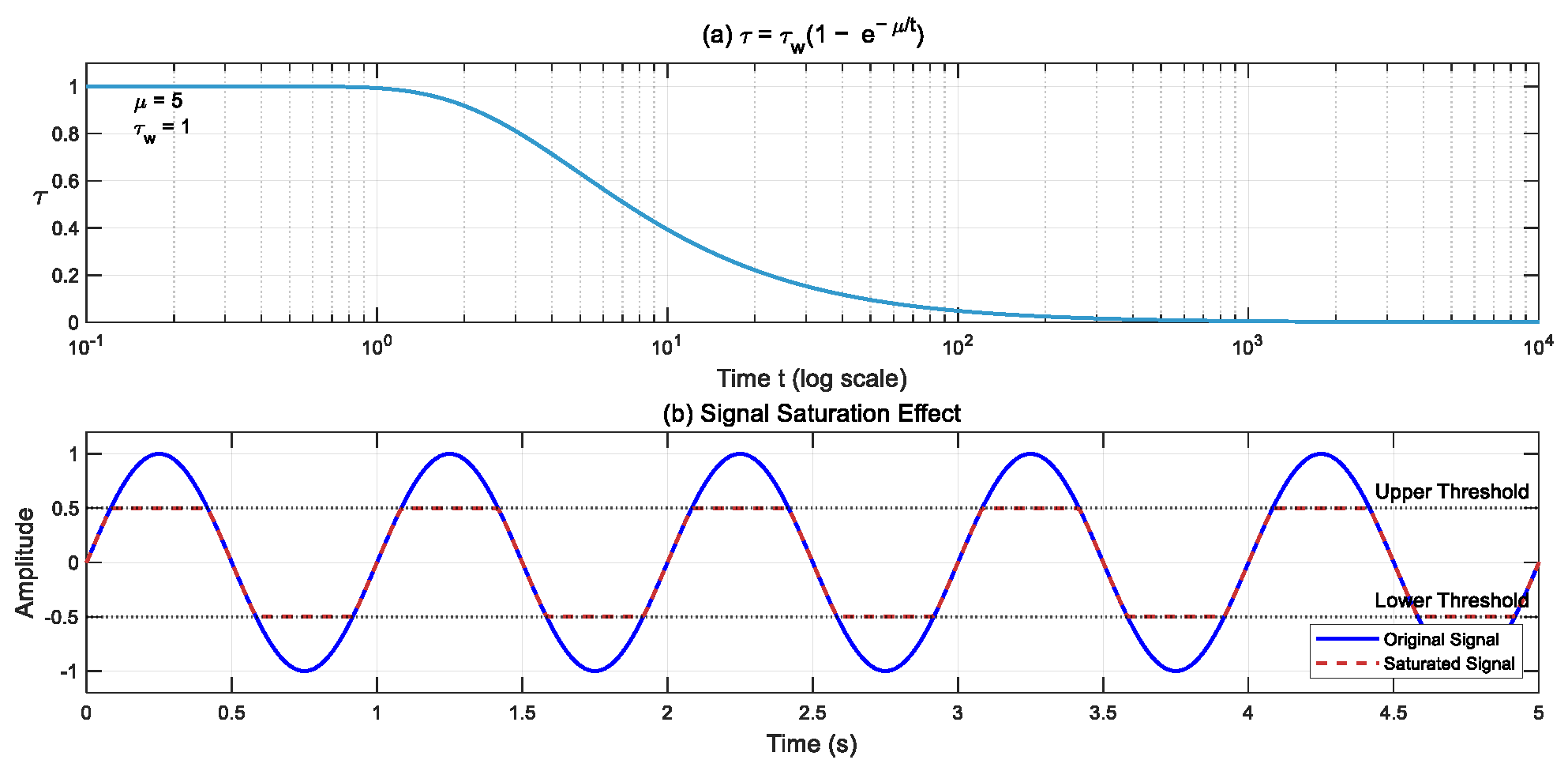
3.1. Design of Finite-Time Extended State Observer
3.2. Design of Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control
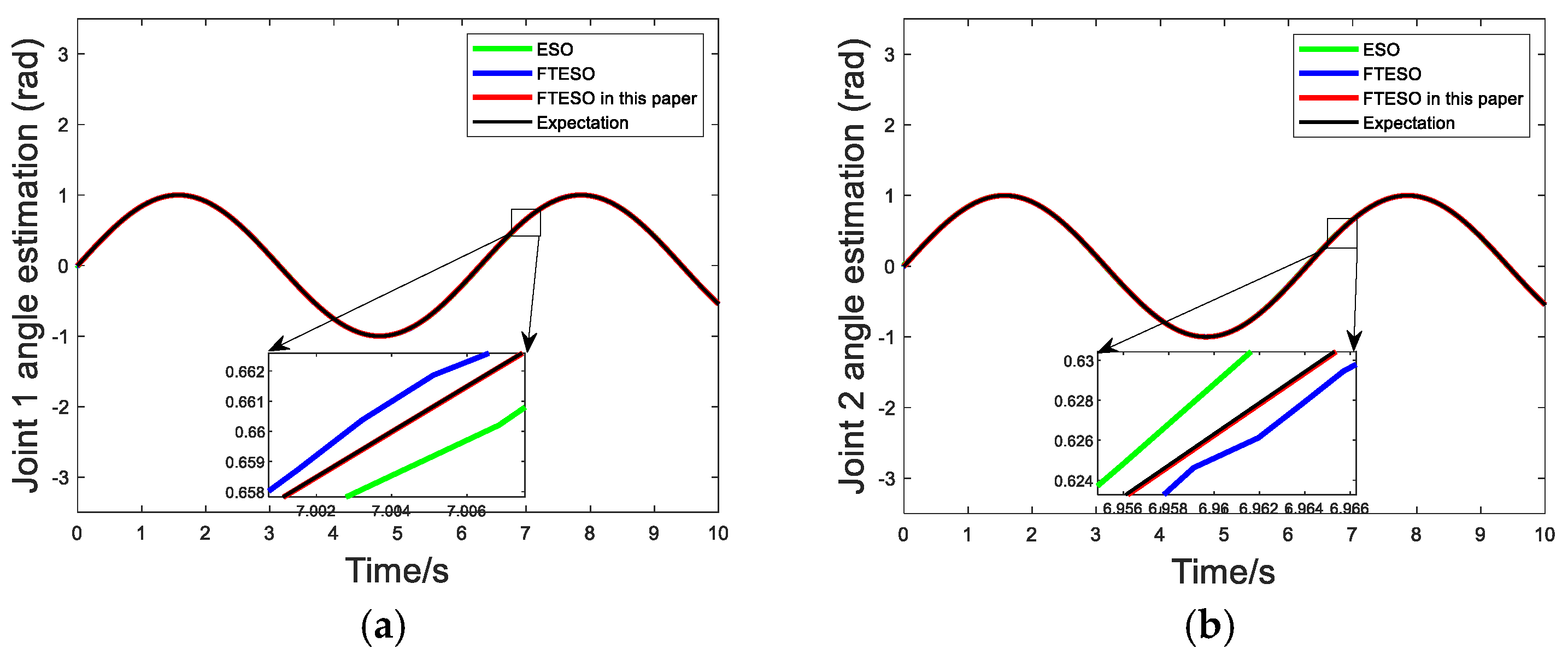
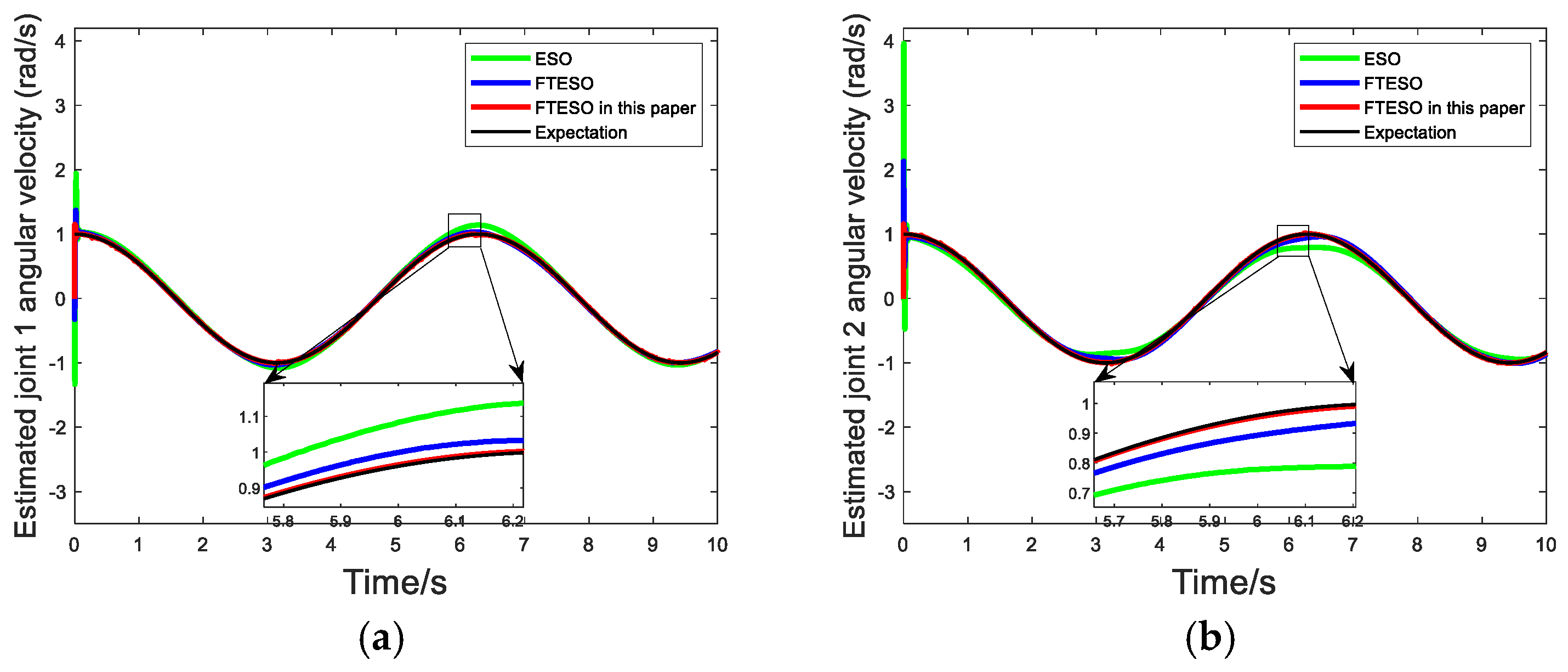
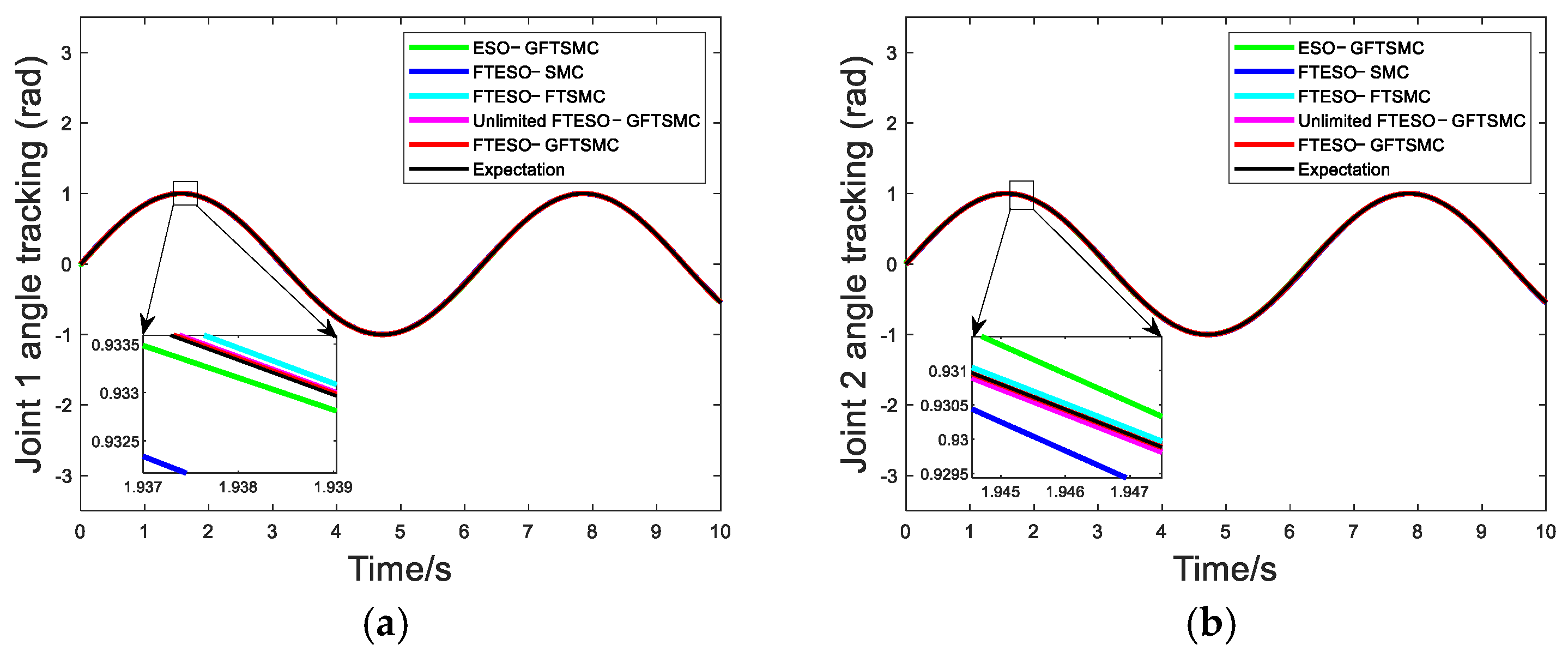
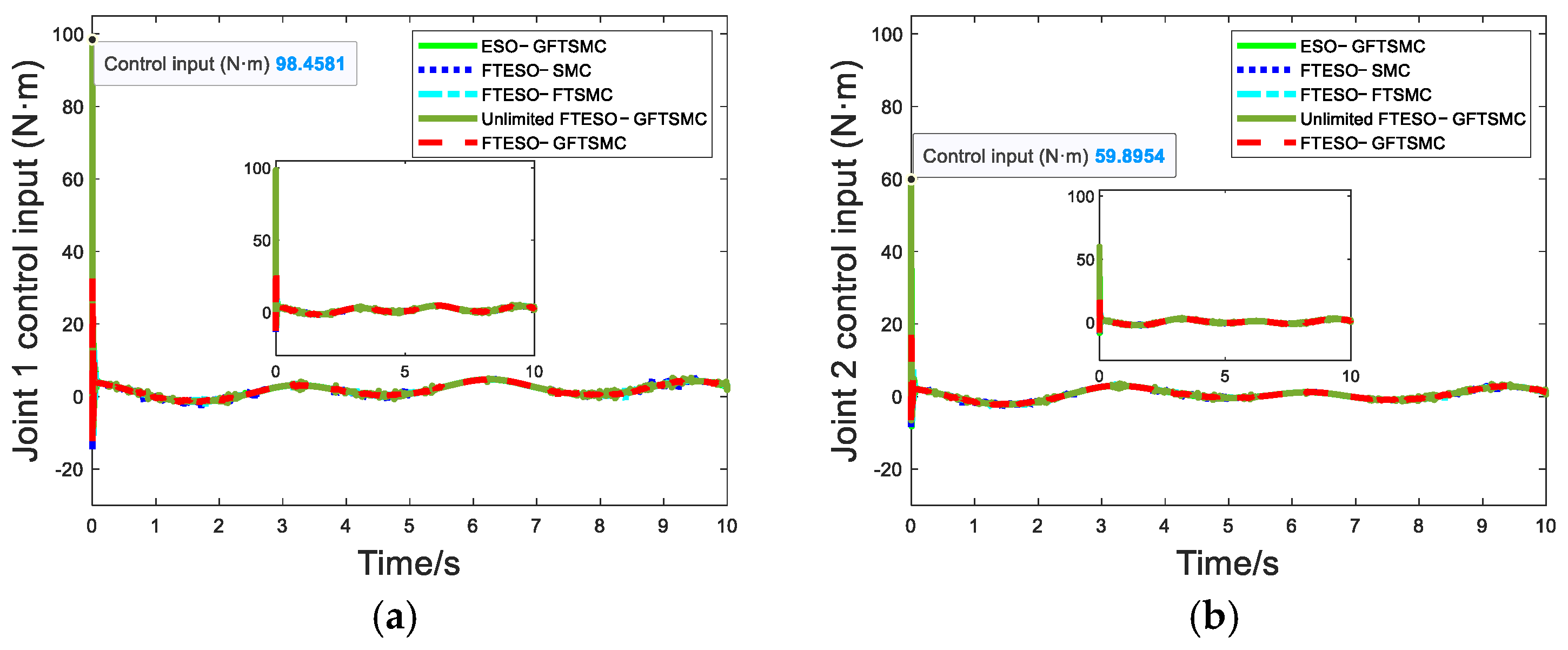
4. Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Martin, S.C.; Whitcomb, L.L. Nonlinear Model-Based Tracking Control of Underwater Vehicles with Three Degree-of-Freedom Fully Coupled Dynamical Plant Models: Theory and Experimental Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2018, 26, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivcev, S.; Coleman, J.; Omerdic, E.; Dooly, G.; Toal, D. Underwater Manipulators: A Review. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistone, A.; Ludovico, D.; Casareto, L.D.V.M.; Leggieri, S.; Canali, C.; Caldwell, D.G. Modelling and Control of Manipulators for Inspection and Maintenance in Challenging Environments: A Literature Review. Annu. Rev. Control 2024, 57, 100949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Huang, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bai, D.; Lv, Y. Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Underwater Manipulators Based on Extended State Observer Compensation. In Proceedings of the OCEANS 2024—Singapore, Singapore, 14–17 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataramanan, K.; Arun, M.; Jha, S.; Sharma, A. Analyzing Stability and Structural Aspects of Embedded Fuzzy Type 2 PID Controller for Robot Manipulators. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2024, 46, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Batista, J.; Souza, D.; Lima, A.; dos Reis, L.; Barbosa, A. Control and Identification of Parameters of a Joint of a Manipulator Based on PID, PID 2-DOF, and Least Squares. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2023, 45, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; He, X.; Shao, F.; Zhang, X. Research on the Optimization of the PID Control Method for an EOD Robotic Manipulator Using the PSO Algorithm for BP Neural Networks. Actuators 2024, 13, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, B.; Jiang, B.; Han, J.; Wen, C.-Y. Disturbance Observer-Based Model Predictive Control for an Unmanned Underwater Vehicle. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Null, W.D.; Edwards, W.; Jeong, D.; Tchalakov, T.; Menezes, J.; Hauser, K. Automatically-Tuned Model Predictive Control for an Underwater Soft Robot. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, H. Adaptive Model Predictive Control for Underwater Manipulators Using Gaussian Process Regression. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, F. Dynamic Modeling and Adaptive Fuzzy Sliding Mode Control for Multi-Link Underwater Manipulators. Ocean Eng. 2019, 187, 106202. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Tang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Yu, M. A Chattering-Suppression Sliding Mode Controller for an Underwater Manipulator Using Time Delay Estimation. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaare, S.; Soltanpour, M.R. Uncertainty and Velocity Observer-Based Predefined-Time Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode Control of the Underwater Robot Manipulators. Eur. J. Control 2024, 75, 100939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Song, G.; Hao, S.; Zhang, M.; Song, A. Development of a Lightweight Underwater Manipulator for Delicate Structural Repair Operations. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 6563–6570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, D.; Wang, G.; Ge, J.; Xiang, B.; You, Y.; Feng, A. Trajectory Tracking Control of Two-Joint Underwater Manipulator in Ocean-Wave Environment. Ocean Eng. 2024, 292, 116329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.; Gao, L.; Ngwa, M.; Zhang, D.; Du, J.; Li, B. Adaptive Super-Twisting Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Mechanical Leg with Extended State Observer. Actuators 2023, 12, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borlaug, I.L.G.; Gravdahl, J.T.; Sverdrup-Thygeson, J.; Pettersen, K.Y.; Loria, A. Trajectory Tracking for Underwater Swimming Manipulators Using a Super Twisting Algorithm. Asian J. Control 2019, 21, 208–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, Y.; Li, H. Observer-Based Finite-Time Sliding-Mode Control of Robotic Manipulator with Flexible Joint Using Partial States. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2023, 2023, 8859892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Sun, L.; Bai, X.; Zhao, Y.; Hui, X.; Wang, Y. Trajectory Tracking Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Adaptive Arctangent Nonsingular Terminal Sliding Mode. Control Decis. 2025, 40, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, H.; Huang, J. Dynamic Modeling and Vibration Control of Underwater Soft-Link Manipulators Undergoing Planar Motions. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 2022, 181, 109540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wen, H.; Huang, J.; Sun, B.; Chen, J.; Chen, W.; Feng, Y.; Duan, X. Adaptive Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Nonlinear Dynamics Model Compensation. J. Tsinghua Univ. (Sci. Technol.) 2023, 63, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.; Wang, Z. Research on Robust Fuzzy Logic Sliding Mode Control of Two-DOF Intelligent Underwater Manipulators. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2023, 20, 16279–16303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Tang, G.; Huang, H.; Han, L.; Xu, R. Adaptive Nonsingular Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Underwater Manipulator Robotics with Asymmetric Saturation Actuators. Control Theory Technol. 2020, 18, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chao, Z.-Q.; Huang, L.-B.; Li, H.-Y.; Zhang, C.-Q. Trajectory Tracking Control of Robot Manipulator Based on RBF Neural Network and Fuzzy Sliding Mode. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 5799–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Yang, S.X.; Biglarbegian, M. A Fuzzy Logic-Based Cascade Control without Actuator Saturation for the Unmanned Underwater Vehicle Trajectory Tracking. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. 2022, 106, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, P.N.; Dang, N.T.; Nguyen, T.L.; Dinh, G.K. Finite-Time Sliding Mode Control Strategies for Perturbed Input-Constrained Nonlinear Bilateral Teleoperation Systems with Variable-Time Communication Delays. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2025, 18, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, T.; Cao, D.; Yang, J. Bilateral Continuous Terminal Sliding Mode Control for Teleoperation Systems with High-Order Disturbances. Nonlinear Dyn. 2023, 111, 5345–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wei, C.; Shan, Z.; Shan, Z.; Liu, Y. Trajectory Tracking Control of Unmanned Vehicles with Odometer Positioning Compensation Based on Extended State Observer. Chin. J. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 45, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhu, Z.; Qin, H.; Deng, Z.; Sun, Y. Finite-Time Extended State Observer-Based Exact Tracking Control of an Unmanned Surface Vehicle. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2021, 31, 1704–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perruquetti, W.; Floquet, T.; Moulay, E. Finite−Time Observers: Application to Secure Communication. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2008, 53, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, S.P.; Bernstein, D.S. Geometric Homogeneity with Applications to Finite−Time Stability. Math. Control Signals Syst. 2005, 17, 101–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Lin, X.; Sheng, C.; Zhang, Z.; Song, S. Finite-Time Output Feedback Path Following Control of Underactuated MSV Based on FTESO. Ocean Eng. 2021, 224, 108660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, G.H.; Littlewood, J.E.; Pólya, G. Inequalities (Cambridge Mathematical Library); Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1934. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.; Li, H.; Sun, K. Finite−time control for nonlinear spacecraft attitude based on terminal sliding mode technique. ISA Trans. 2013, 53, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, M.Y.; Wang, Q.S. Safety−Guaranteed, Robust, Nonlinear, Path−Following Control of the Underactuated Hovercraft Based on FTESO. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Parameter | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| 0.14 | m | |
| 0.26 | m | |
| 1 | kg | |
| 2 | kg | |
| 0.06 | m | |
| 0.1 | m | |
| 1000 | kg/m3 | |
| 1680 | kg/m3 | |
| 9.8 | m/s2 |
| Design Elements | ESO in [28] | FTESO in [29] | FTESO in This Article |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input signal | actual measurement output | actual measurement output | actual measurement output |
| Disturbance compensation logic | direct output estimates | estimated output after filtering | output estimation after variable parameter filtering |
| Anti-noise ability | weaker | relatively strong | strong |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 180 | 0.1 | ||
| 16,880 | 0.0001 | ||
| 30,000 | 0.0001 | ||
| 0.7 | 0.0001 | ||
| 0.4 |
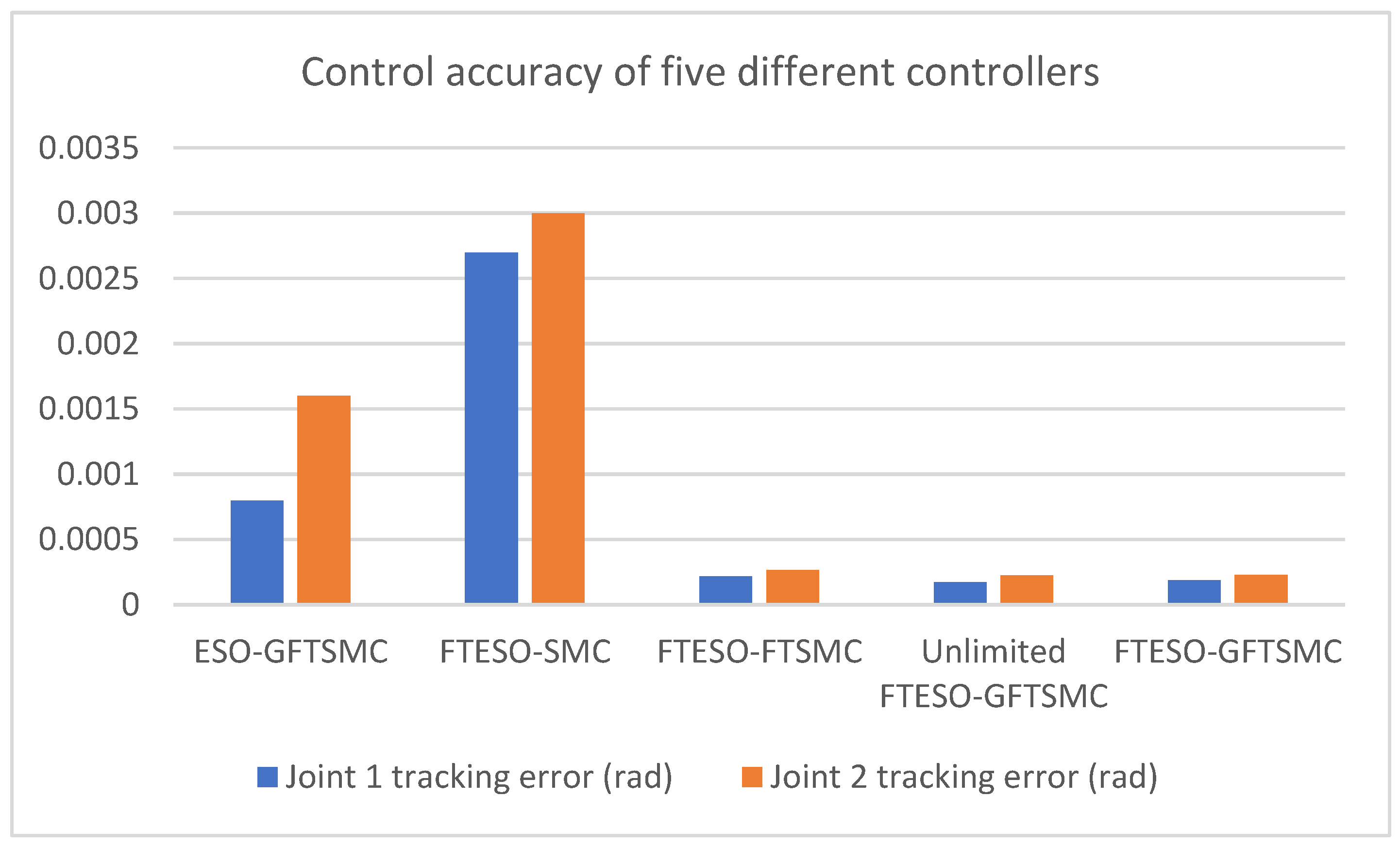
| Controller | Joint 1 Tracking Error (Rad) | Joint 2 Tracking Error (Rad) |
|---|---|---|
| ESO−GFTSMC | 7.98 × 10−4 | 1.6 × 10−3 |
| FTESO−SMC | 2.7 × 10−3 | 3 × 10−3 |
| FTESO−FTSMC | 2.18 × 10−4 | 2.67 × 10−4 |
| Unlimited FTESO−GFTSMC | 1.74 × 10−4 | 2.25 × 10−4 |
| FTESO−GFTSMC | 1.87 × 10−4 | 2.31 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Finite-Time Extended State Observer. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061038
Wang R, Huang W, Wu J, Wang H, Li J. Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Finite-Time Extended State Observer. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061038
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ran, Weiquan Huang, Junyu Wu, He Wang, and Jixiang Li. 2025. "Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Finite-Time Extended State Observer" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061038
APA StyleWang, R., Huang, W., Wu, J., Wang, H., & Li, J. (2025). Global Fast Terminal Sliding Mode Control of Underwater Manipulator Based on Finite-Time Extended State Observer. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061038







