Historical Trends of Trace Metals in the Sepetiba Bay Sediments: Pollution Indexes, Fluxes and Inventories
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
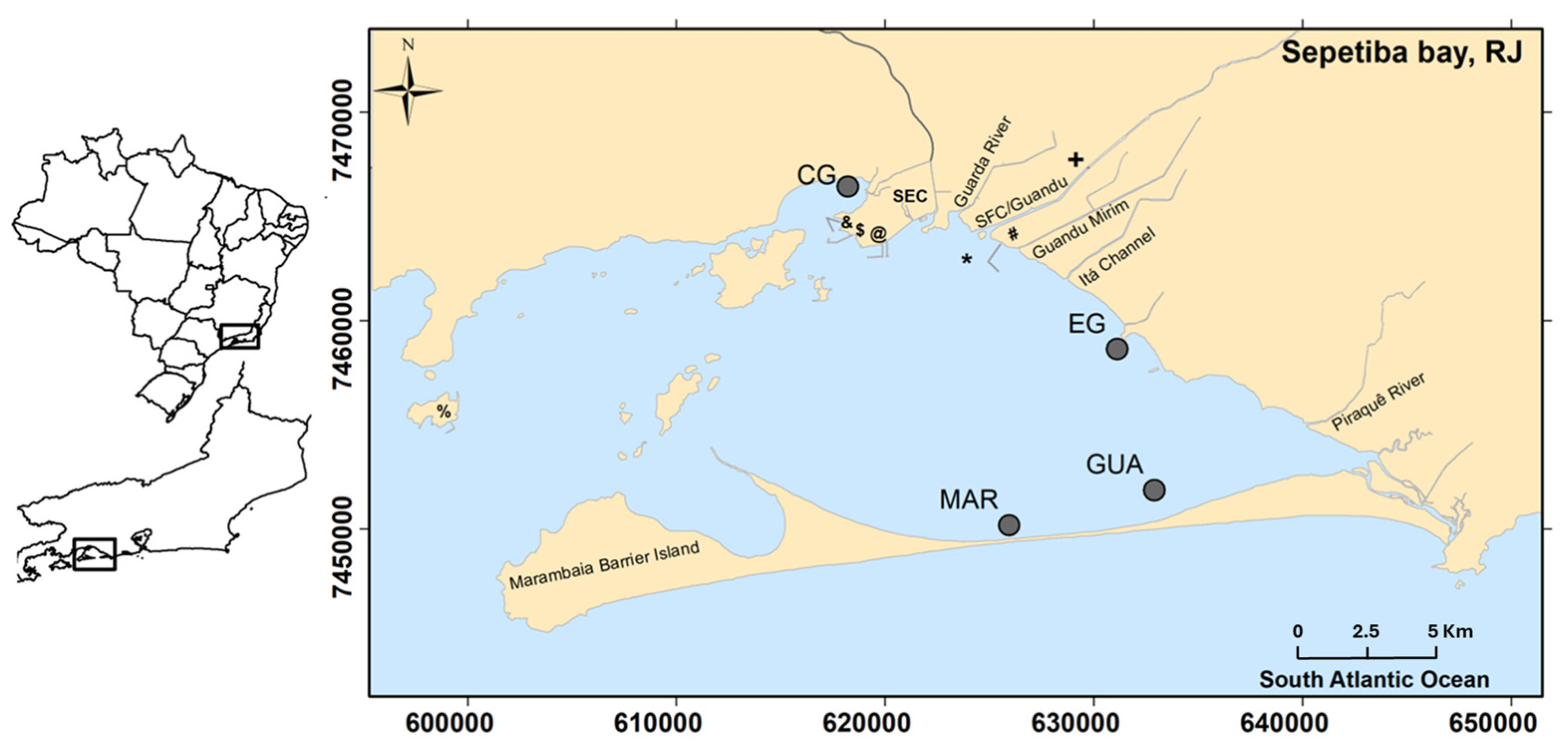
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Mass Accumulation Rates (MAR) and Metal Fluxes
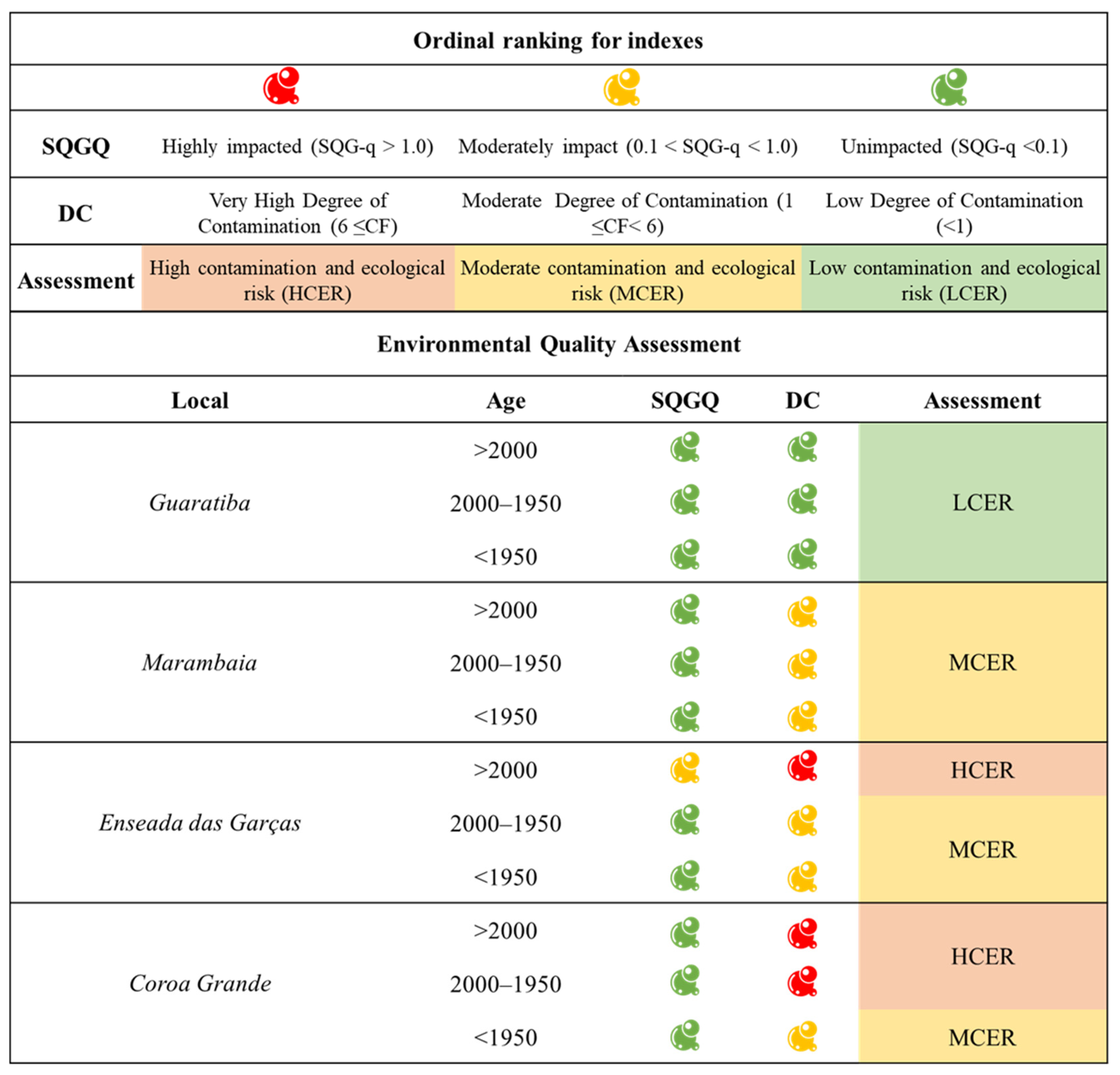
2.4. Pollution Indexes
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
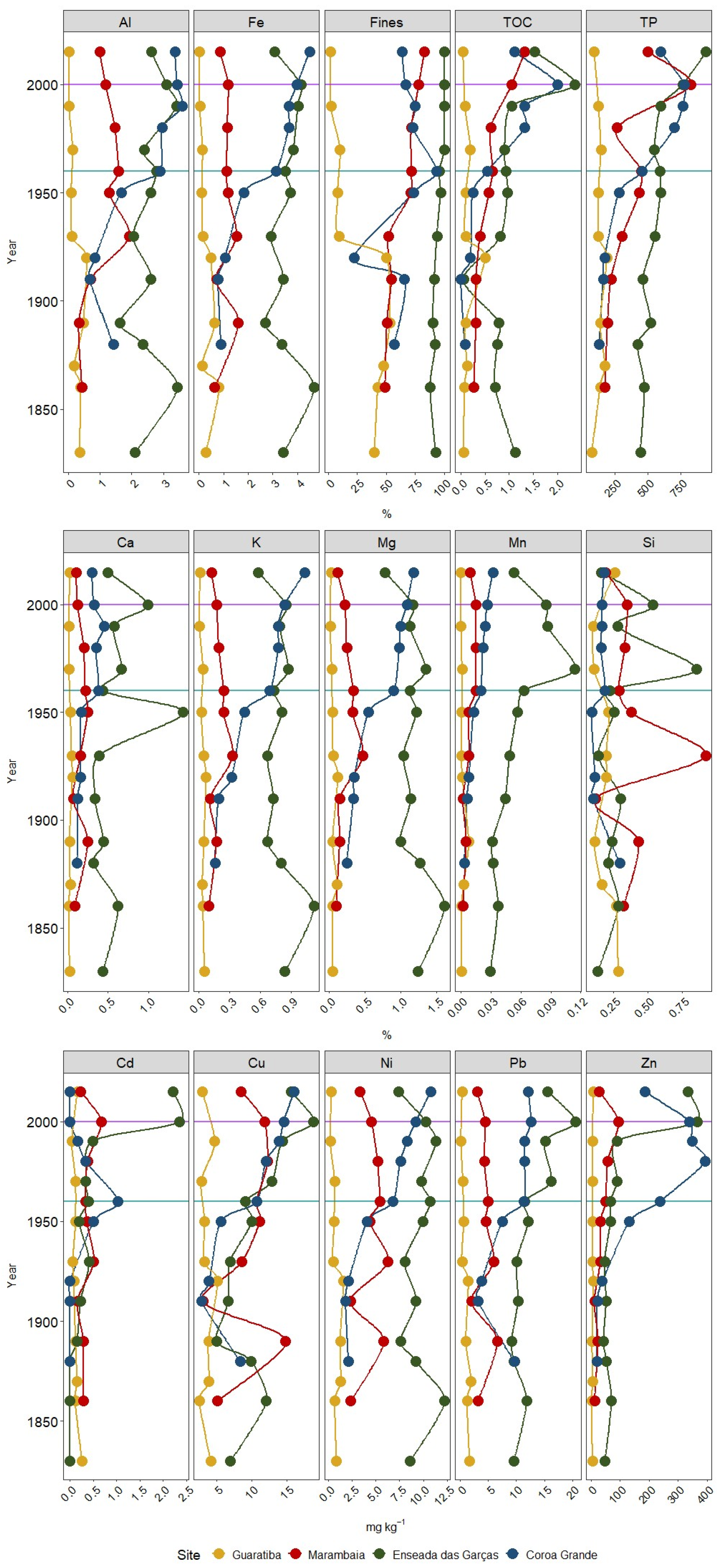
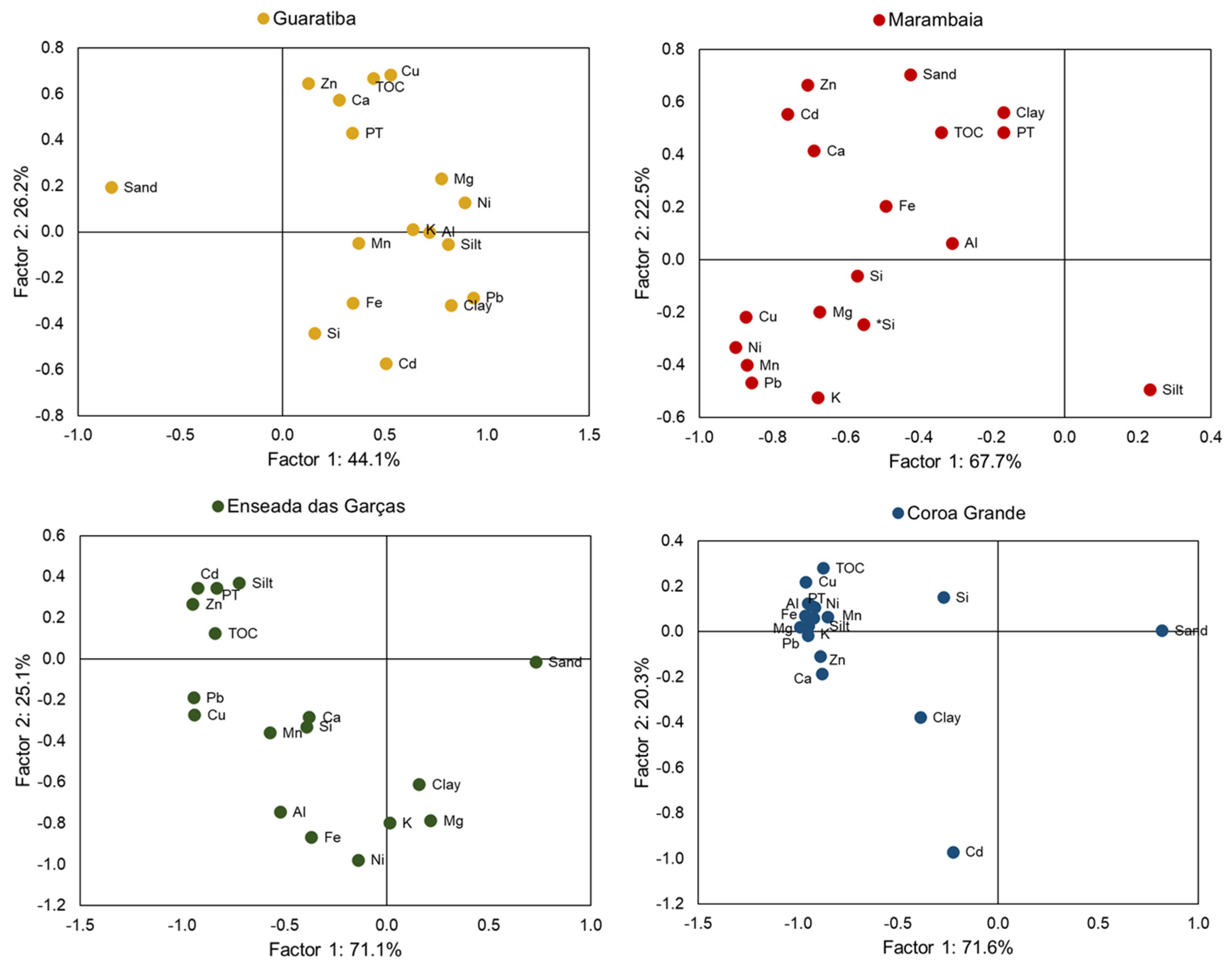
3.1. Granulometry, Total Organic Carbon, Phosphorous and Mineralogy
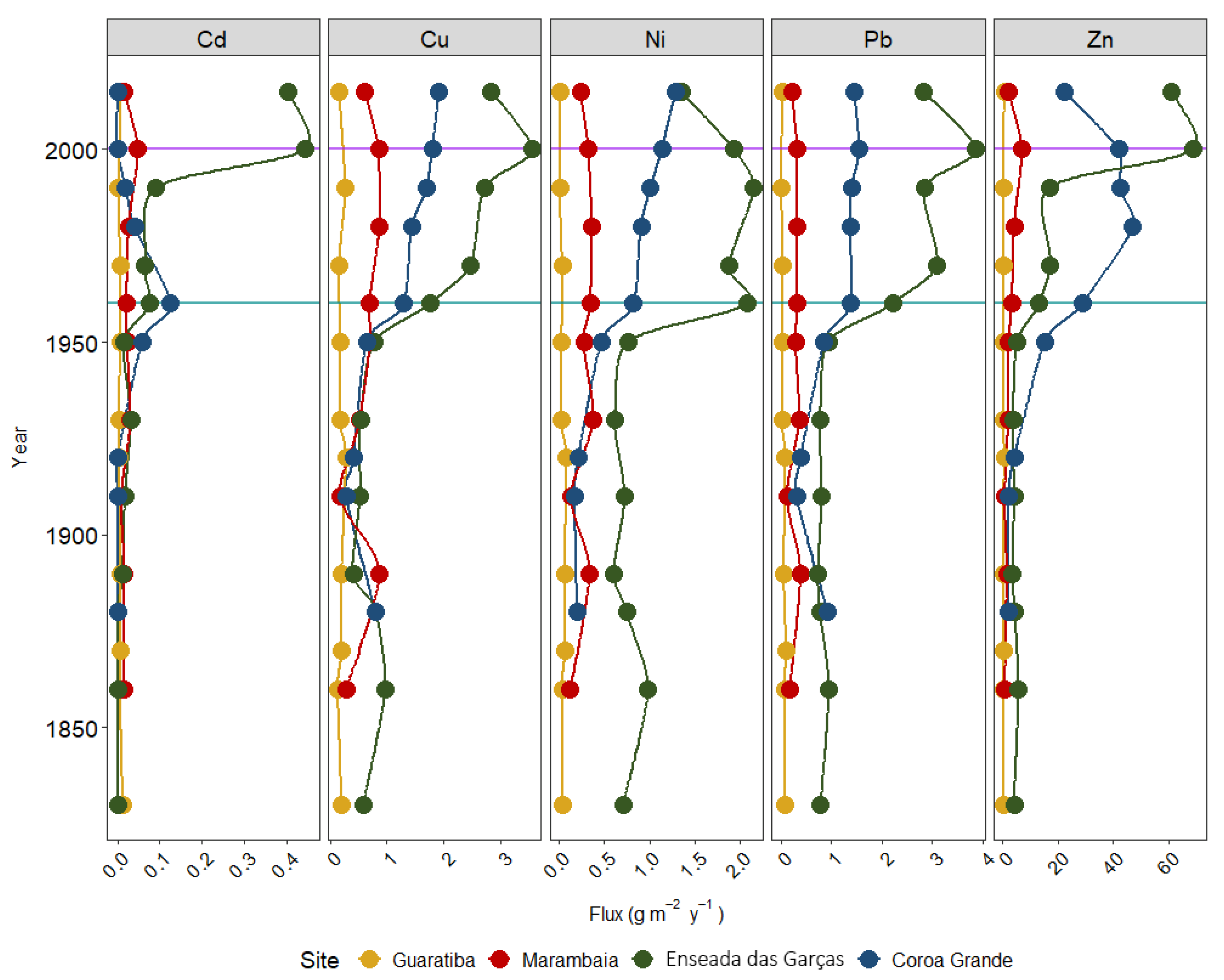
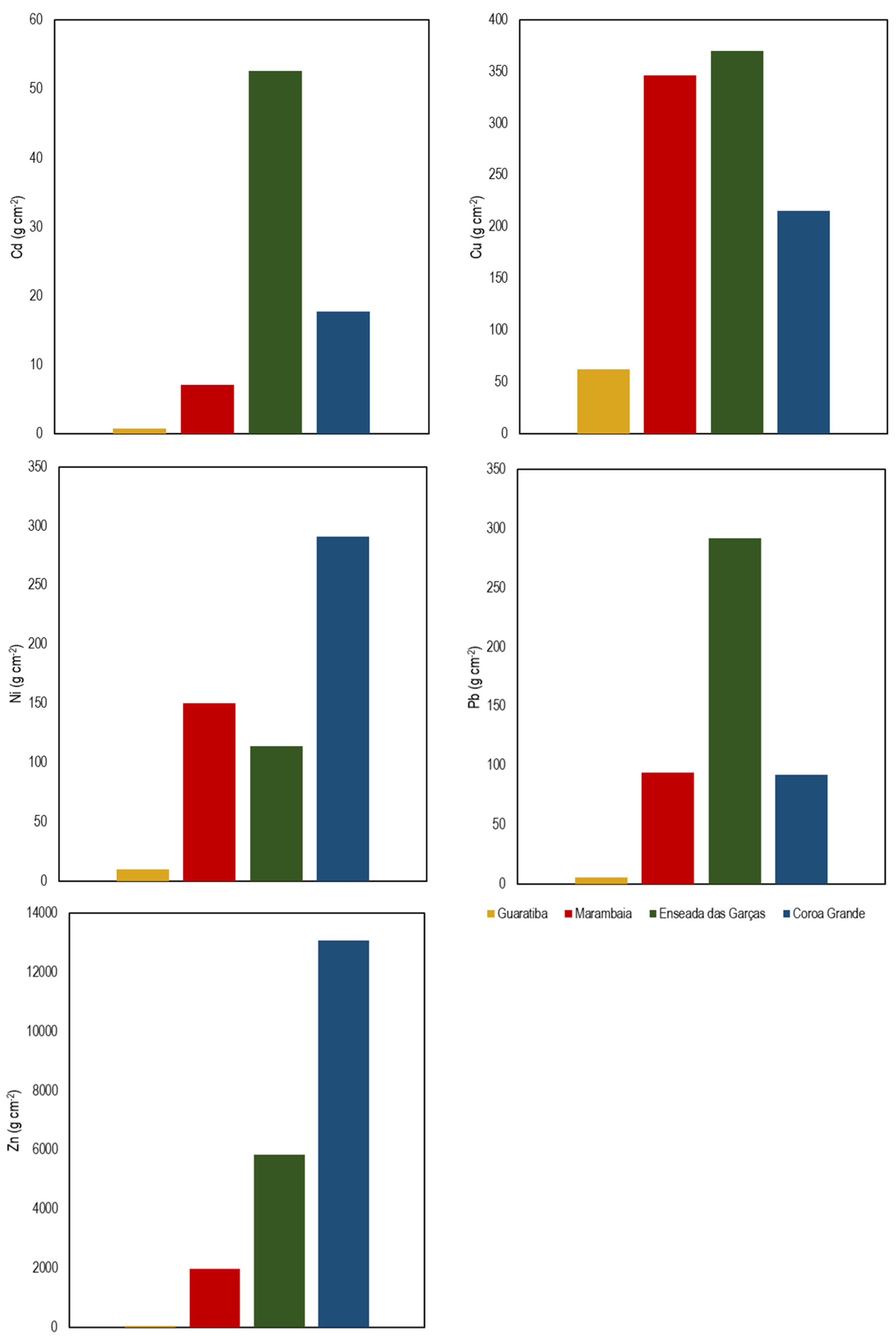
3.2. Trace Metals Concentrations Fluxes and Inventories
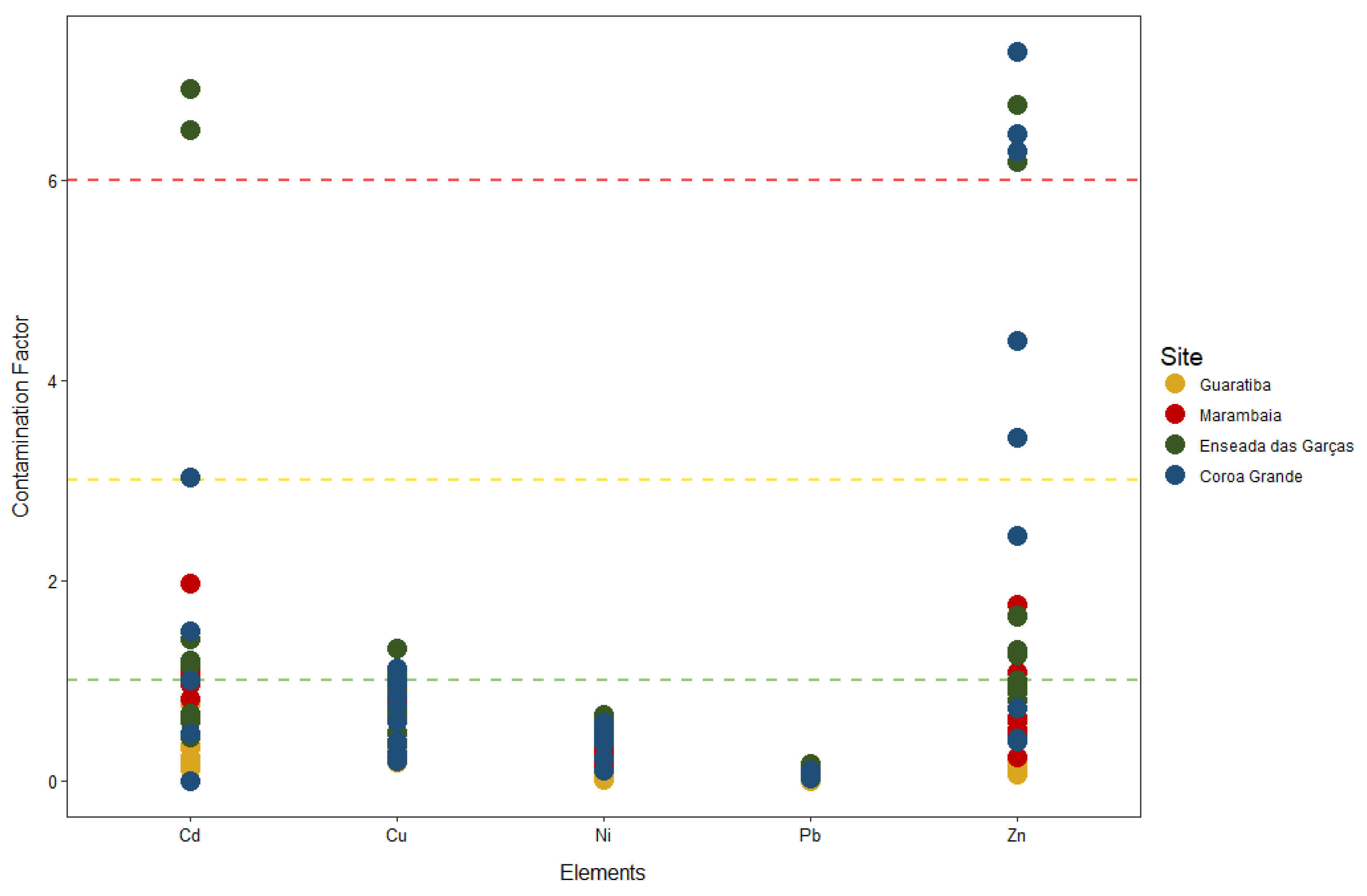
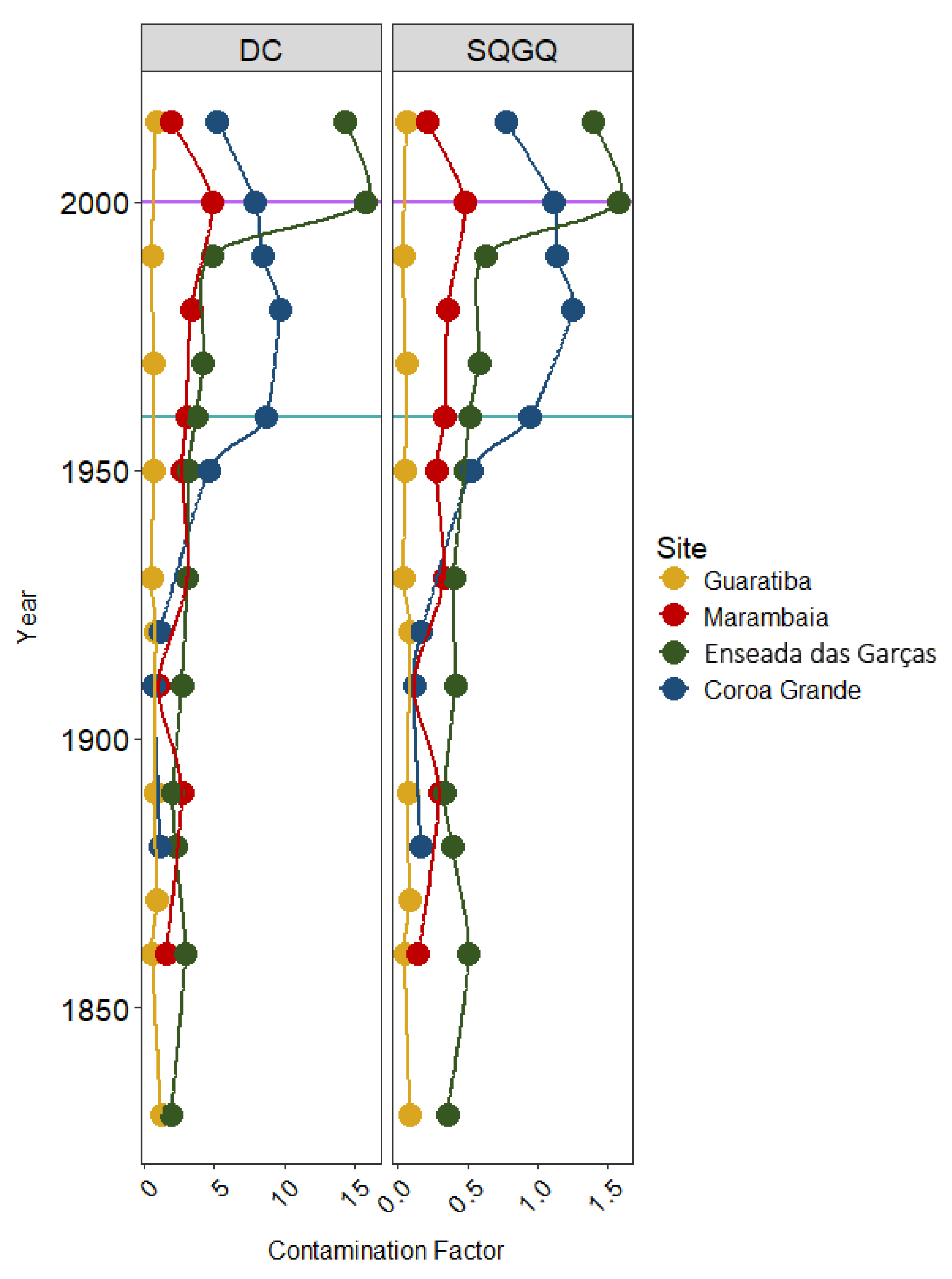
3.3. Pollution Indexes Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatial Distribution and Geochemical Behavior of Trace Metals
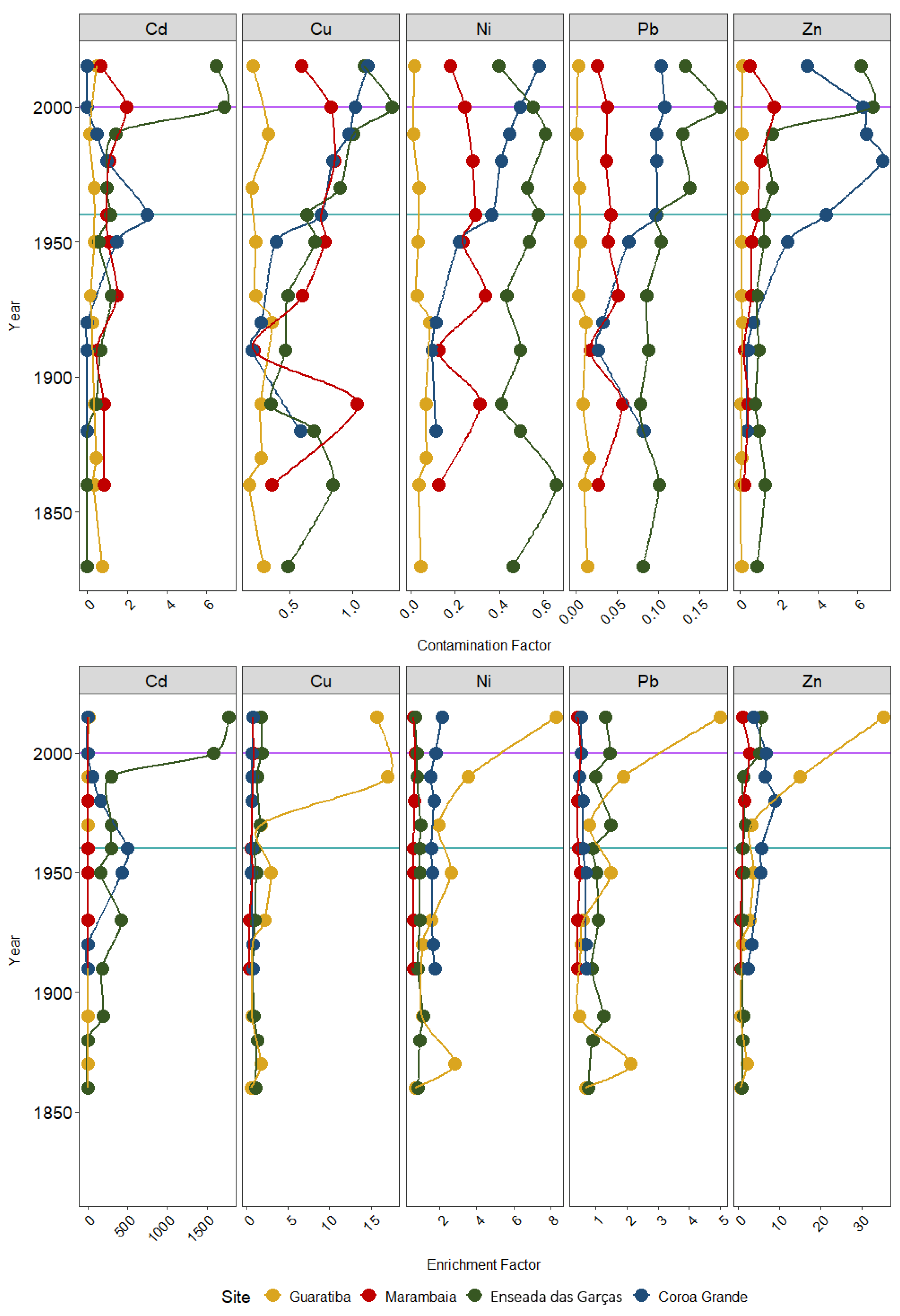
4.2. Historical Perspective on Trace Metal Fluxes and Inventories
4.3. Evaluation of Priority Metals and Areas of Concern with Results of Pollution Indexes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koiter, A.; Owens, P.; Petticrew, E.; Lobb, D. The behavioural characteristics of sediment properties and their implications for sediment fingerprinting as an approach for identifying sediment sources in river basins. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 125, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, R.C.; dos Santos, D.D.; Santelli, R.E., Jr.; Figueiredo, A.G.; Moreira, L.S.; Machado, W.T.V.; Meniconi, M.F.G. Bulk, isotopic, petrographic organic matter and mineral distribution as proxies of environmental process in Guanabara Bay, SE, Brazil. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2021, 41, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, R.; Monteiro, F.; Santelli, R.; Moreira, L.; Figueiredo, A.; Bidone, E.; Pereira, R.; Anjos, L.; Meniconi, M. Environmental and anthropic variabilities at Guanabara Bay (Brazil): A comparative perspective of metal depositions in different time scales during the last 5500 yrs. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzoli, F.; Smolders, S.; Eelkema, M.; Ysebaert, T.; Escaravage, V.; Temmerman, S.; Meire, P.; Herman, P.M.; Bouma, T.J. A modeling approach to assess coastal management effects on benthic habitat quality: A case study on coastal defense and navigability. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2017, 184, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Jin, P. Impact of human interventions on coastal and marine geological hazards: A review. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2018, 77, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, P.; Navarro, E.; Marcé, R.; Ordoñez, J.; Caputo, L.; Armengol, J. Elemental ratios in sediments as indicators of ecological processes in Spanish reservoirs. Limnetica 2006, 25, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, C.D.; Oliveira, D.F.C.; Frota, M.N.; Viana, C.A.S.; Gonçalves, R.A.; Godoy, J.M.O. Siltation Process and Metals Sediment Profile in a Hydroelectric Power Plant Reservoir Located in the Brazilian Most Industrialized Region, Paraíba Do Sul River Basin, Southeastern Brazil. Environ. Erath Sci. 2022, 81, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, L.C.; Martins, M.V.A.; Castelo, W.F.L.; Saibro, M.B.; Rangel, D.; Pereira, E.; Bergamaschi, S.; Sousa, S.H.M.; Varela, J.; Laut, L.; et al. Trace metals enrichment and potential ecological risk in sediments of the Sepetiba Bay (Rio de Janeiro, SE Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 177, 113485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.K.; Machado, W.; Guerra, J.V.; Geraldes, M.; Morales, S.; Vinzón, S.B. Changes in Cd and Zn distribution in sediments after closure of an electroplating industry, Sepetiba bay, Brazil. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.F.; Peres, L.G.; Yepez, S.; Mulholland, D.S.; Machado, W.; Tonhá, M.; Garnier, J. Assessing man-induced environmental changes in the Sepetiba Bay (Southeastern Brazil) with geochemical and satellite data. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2017, 349, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.; Machado, W.; Weiss, D.; Mulholland, D.S.; Boaventura, G.R.; Viers, J.; Garnier, J.; Dantas, E.L.; Babinski, M. A critical examination of the possible application of zinc stable isotope ratios in bivalve mollusks and suspended particulate matter to trace zinc pollution in a tropical estuary. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, S.K.; Abessa, D.M.; Rodrigues, A.P.d.C.; Soares-Gomes, A.; Freitas, C.B.; Santelli, R.E.; Freire, A.S.; Machado, W. Sediment quality in a metal-contaminated tropical bay assessed with a multiple lines of evidence approach. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 228, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, F.d.C.; Godoy, J.M.; Godoy, M.L.D.; de Carvalho, Z.L.; Lopes, R.T.; Sanchez-Cabeza, J.A.; de Lacerda, L.D.; Wasserman, J.C. Metal concentrations, fluxes, inventories and chronologies in sediments from Sepetiba and Ribeira Bays: A comparative study. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 59, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.D.; Marins, R.V.; Barcellos, C.; Molisani, M.M. Chapter 21: Sepetiba bay: A case study of the environmental geochemistry of heavy metals in a subtropical coastal lagoon. In Environmental Geochemistry in Tropical and Subtropical Environments; Lacerda, L.D., Santelli, R.E., Duursma, E.K., Abrao, J.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 293–318. ISBN 978-3-662-07060-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lacerda, L.; Molisani, M. Three decades of Cd and Zn contamination in Sepetiba Bay, SE Brazil: Evidence from the mangrove oyster Crassostraea rhizophorae. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 52, 969–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barcellos, C.; Lacerda, L.D. Cadmium and zinc source assessment in the Sepetiba Bay and basin region. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1994, 29, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda, L.D.; Pfeiffer, W.C.; Fiszman, M. Heavy metals distribution, availability and fate in the Sepetiba Bay (SE-Brazil). Sci. Total Environ. 1987, 65, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, C.N.; Rodrigues, A.P.C.; Cordeiro, R.C.; Freire, A.S.; Santelli, R.E.; Machado, W. Changes in Cd and Zn bioavailability upon an experimental resuspension of highly contaminated coastal sediments from a tropical estuary. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 1, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.; Figueiredo, A.M.G.; Dos Santos, J.O.; Dantas, E.; Cotrim, M.E.B.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Filho, E.V.S.; Wasserman, J.C. Combined SEM/AVS and attenuation of concentration models for the assessment of bioavailability and mobility of metals in sediments of Sepetiba Bay (SE Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 68, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.R.; Bidone, E.D.; Rolão-Araripe, D.; Keunecke, K.A.; Sabadini-Santos, E. Trace metal distribution in white shrimp (Litopenaeus schmitti) tissues from a Brazilian coastal area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, F.L.; Martins, M.V.A.; Santos, L.G.C.; Filho, J.G.M.; Hohenegger, J.; Reis, G.A.; Diaz, R.d.S.; Rebouças, R.C.; Senez-Mello, T.M.; Arruda, S.; et al. Assessment of potential ecological risk by metals in Ilha Grande Bay (Southeast Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 212, 117612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, F.L.; Martins, M.V.A.; Frontalini, F.; Pawlowski, J.; Cermakova, K.; Angeles, I.B.; Santos, L.G.C.; Filho, J.G.M.; Francescangeli, F.; Senez-Mello, T.M.; et al. Assessment of the ecological quality status of the Sepetiba Bay (SE Brazil): When metabarcoding meets morphology on foraminifera. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 195, 106340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damasceno, F.L.; Martins, M.V.A.; Senez-Mello, T.M.; Santos, L.G.C.; Filho, J.G.M.; Pereira, E.; Figueira, R.; Nascimento, C.A.D.; Arruda, S.; Castelo, W.F.L.; et al. Potential ecological risk by metals in Sepetiba bay (SE Brazil): Exporting metals to the oceanic region. J. South. Am. Earth Sci. 2024, 141, 104934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saibro, M.B.; Martins, M.V.A.; Guerra, J.V.; Figueira, R.C.L.; Simões, F.d.C.F.; Dadalto, T.P.; Trevizani, T.H.; Ferreira, P.A.d.L.; Silva, C.G.; Dos Reis, A.T.; et al. Transfer of industrial contaminants from the inner to the outer region of Sepetiba Bay (SE Brazil) by dredge spoil dumping activities: A temporal record. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Araújo, D.F.; Garnier, J.; Mulholland, D.; Machado, W.; Cunha, B.; Ponzevera, E. Copper and lead isotope records from an electroplating activity in sediments and biota from Sepetiba Bay (southeastern Brazil). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 190, 114848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonhá, M.S.; Araújo, D.F.; Araújo, R.; Cunha, B.C.; Machado, W.; Portela, J.F.; Souza, J.P.; Carvalho, H.K.; Dantas, E.L.; Roig, H.L.; et al. Trace metal dynamics in an industrialized Brazilian river: A combined application of Zn isotopes, geochemical partitioning, and multivariate statistics. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu, I.M.; Cordeiro, R.C.; Soares-Gomes, A.; Abessa, D.M.S.; Maranho, L.A.; Santelli, R.E. Ecological risk evaluation of sediment metals in a tropical Euthrophic Bay, Guanabara Bay, Southeast Atlantic. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marins, R.V.; Machado, W.; Paraquetti, H.H.M.; Bidone, E.D.; Lacerda, L.D.; Molisani, M.M. Environmental changes in Sepetiba Bay, SE Brazil. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2004, 4, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roncarati, H.; Carelli, S.G. Considerações sobre estado da arte dos processos geológicos cenozóicos atuantes na baía de Sepetiba. In Baía de Sepetiba: Estado da Arte; Rodrigues, M.A.C., Pereira, S.D., dos Santos, S.B., Eds.; FAPERJ: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012; pp. 12–36. [Google Scholar]
- Barcellos, C.; de Lacerda, L.D.; Ceradini, S. Sediment origin and budget in Sepetiba Bay (Brazil)—An approach based on multielemental analysis. Environ. Geol. 1997, 32, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Magalhães, V.F.; Pfeiffer, W.C. Arsenic concentration in sediments near a metallurgical plant (Sepetiba Bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). J. Geochem. Explor. 1995, 52, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CEIVAP—Committee for the Integration of the Paraíba do Sul River Basin. Environmental Impact Report—EIA for the Guandu Hydroelectric Project. Available online: https://www.ceivap.org.br/guandu/eia/CD%20FINAL/RIMA/01_Rima.pdf (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Castelo, W.F.L.; Martins, M.V.A.; Martínez-Colón, M.; Guerra, J.V.; Dadalto, T.P.; Terroso, D.; Soares, M.F.; Frontalini, F.; Duleba, W.; Socorro, O.A.A.; et al. Disentangling natural vs. anthropogenic induced environmental variability during the Holocene: Marambaia Cove, SW sector of the Sepetiba Bay (SE Brazil). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 22612–22640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.F.S.; Martins, M.V.A.; da Fonseca, M.C.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.C.; Nogueira, L.; Laut, L.L.M.; Pereira, E. Late holocene evolution of the northeast intertidal region of Sepetiba bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Sediment. Environ. 2016, 1, 50–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pinto, A.F.S.; Martins, M.V.A.; da Fonseca, M.C.M.; Pereira, E.; Terroso, D.L.; Rocha, F.; Rodrigues, M.A.D.C. Holocene closure of a barrier beach in sepetiba bay and its environmental impact (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). J. Sediment. Environ. 2017, 2, 50–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, H.V.; Nittrouer, C.A. Sediment accumulation in Sepetiba Bay (Brazil) during the Holocene: A Reflex of the human influence. J. Sediment. Environ. 2016, 1, 96–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patchineelam, S.M.; Sanders, C.J.; Smoak, J.M.; Zem, R.C.; Oliveira, G.; Patchineelam, S.R. A Historical Evaluation of Anthropogenic Impact in Coastal Ecosystems by Geochemical Signatures. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2010, 22, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.N., Jr.; Monna, F.; Silva Filho, E.V.; Fernex, F.E.; Simões Filho, F.L. Apparent discrepancy in contamination history of a sub-tropical estuary evaluated through 210Pb profile and chronostratigraphical markers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, S.J.D.; Guerra, J.V.; Nunes, M.A.D.S.; de Souza, A.M.; Geraldes, M.C. Evaluation of the environmental state of the western sector of Sepetiba Bay (Se Brazil): Trace metal contamination. J. Sediment. Environ. 2019, 4, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, R.L.; Ward, W.C. Brazos river bar: A study of significante of grain size parameters. J. Sediment. Pet. 1957, 27, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, M.G. SysGran: Um sistema de código aberto para análises granulométricas do sedimento. Rev. Bras. Geociências 2006, 36, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspila, K.I.; Agemian, H.; Chau, A.S.Y. A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 1976, 101, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Method 3050B: Acid Digestion of Sediments, Sludges and Soils. Revision 2; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Sutherland, R.A. Bed sediment-associated trace metals in an urban stream, Oahu, Hawaii. Environ. Geol. 2000, 39, 611–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairey, R.; Long, E.R.; Roberts, C.A.; Anderson, B.S.; Phillips, B.M.; Hunt, J.W.; Puckett, H.R.; Wilson, C.J. An evaluation of methods for calculating mean Sediment Quality Guideline Quotients as indicators of contamination and acute toxicity to amphipods by chemical mixtures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 2276–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, M. The importance of Enrichment Factor (EF) and Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo) to Evaluate the Soil Contamination. Geol. Geophys. 2016, volume 5, 1000237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrahim, G.M.S.; Parker, R.J. Assessment of heavy metal enrichment factors and the degree of contamination in marine sediments from Tamaki Estuary, Auckland, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 136, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uduma, A.U.; Jimoh, W.L.O. Aluminum as a Reference Element for the Elucidation of Pb Enrichment/Depletion in Selected Arable Soils of Nigeria. IOSR J. Eng. 2014, 4, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Wedepohl, K.H. The composition of the continental crust. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 1217–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CONAMA – National Council for the Environment. Resolution No. 454 of 2012. Establishes General Guidelines and Minimum Procedures for the Assessment of Material to Be Dredged in Brazilian Jurisdictional Waters, and Other Provisions. Official Gazette of the Federative Republic of Brazil, Brasília. Available online: https://conama.mma.gov.br/?option=com_sisconama&task=arquivo.download&id=667 (accessed on 12 April 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Posit team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. Posit Software, version 2024.04, PBC: Boston, MA, USA. 2023. Available online: https://www.posit.co/ (accessed on 30 September 2024).
- Moreira, L.B.; Choueri, R.B.; Abessa, D.M.d.S. A consensus-based approach for the development of Site-specific Sediment Quality Values in an SW Atlantic region (São Paulo State, Brazil). J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 7, 100142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar, V.M.; Bastos, A.C.; Quaresma, V.d.S.; Orlando, M.T.D.; Vedoato, F.; Cavichini, A.S.; Neto, J.A.B. Trace metals distribution along sediment profiles from the Doce River Continental Shelf (DRCS) 3 years after the biggest environmental disaster in Brazil, the collapse of the Fundão Dam. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2023, 63, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castelo, W.F.L.; Martins, M.V.A.; Ferreira, P.A.d.L.; Figueira, R.; da Costa, C.F.; da Fonseca, L.B.; Bergamashi, S.; Pereira, E.; Terroso, D.; Pinto, A.F.S.; et al. Long-term eutrophication and contamination of the central area of Sepetiba Bay (SW Brazil). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gaillardet, J.; Louvat, P.; Huon, S. Zn isotopes in the suspended load of the Seine River, France: Isotopic variations and source determination. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 4060–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenworthy, J.B.; Forstner, U.; Wittman, G.T.W. Metal Pollution in the Aquatic Environment. J. Ecol. 1981, 68, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sposito, G. The Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, L.S.; Wijesiri, B.; Ayoko, G.A.; Egodawatta, P.; Goonetilleke, A. Water-sediment interactions and mobility of heavy metals in aquatic environments. Water Res. 2021, 202, 117386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aşçı, Y.; Nurbaş, M.; Açıkel, Y.S. Investigation of sorption/desorption equilibria of heavy metal ions on/from quartz using rhamnolipid biosurfactant. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, F.F.; Cordeiro, R.C.; Santelli, R.E.; Machado, W.; Evangelista, H.; Villar, L.S.; Viana, L.C.A.; Bidone, E.D. Sedimentary geochemical record of historical anthropogenic activities affecting Guanabara Bay (Brazil) environmental quality. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 65, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Iglesias, P.; Rubio, B.; Vilas, F. Pollution in intertidal sediments of San Simon Bay (inner Ria de Vigo, NW of Spain). Total heavy metal concentration and speciation. Mar Pollut Bull 2003, 46, 491–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, G.D.; Rinklebe, J.; Vandecasteele, B.; Meers, E.; Tack, F. Trace metal behaviour in estuarine and riverine floodplain soils and sediments: A review. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 407, 3972–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Chen, C.A. Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of the coastal Bohai Bay. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1901–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Xi, B.; Yu, X.; Su, J.; Zan, F.; Zhao, G. Application of equilibrium partitioning approach to derive sediment quality criteria for heavy metals in a shallow eutrophic lake, Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2275–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayarathne, A.; Egodawatta, P.; Ayoko, G.A.; Goonetilleke, A. Assessment of ecological and human health risks of metals in urban road dust based on geochemical fractionation and potential bioavailability. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 635, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.; Oliveira, D.; Rezende, C.E.; Almeida, P.; Lacerda, L.; da Gama, B.; Godoy, J.M. Spatial and temporal effects of decommissioning a zinc smelter on the sediment quality of an estuary system: Sepetiba bay, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2020, 31, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazilian Navy–Directorate of Ports and Coasts. NORMAM-23: Standards of the Maritime Authority for the Control of Antifouling Systems on Vessels; Brazilian Navy–Directorate of Ports and Coasts: 2007. Available online: https://www.marinha.mil.br/dpc/normas-autoridade-maritima-brasileira (accessed on 20 May 2025).
- Turner, A. Marine pollution from antifouling paint particles. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Depth (cm) | SAR (cm y−1) | References | Estimated Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marambaia—Guaratiba | 0–30 | 0.1 | [30] | 1970–1997 |
| >30 | 0.4 | <1970 | ||
| Enseada das Garças | 0–60 | 1.2 | [30] | 1970–1997 |
| 60–175 | 0.49 | <1970 | ||
| Coroa Grande | 0–16.5 | 0.8 | [32] | 1980–1995 |
| >16.5 | 1.03 | <1980 |
| Index | Degree | Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Enrichment Factor | EF < 2 | Low enrichment; |
| 2≤ EF < 20 | Significant enrichment; | |
| EF > 20 | High enrichment; | |
| Contamination Factor/Degree | CF/DC < 1 | Low Degree of Contamination |
| 1 ≤ CF/DC < 6 | Significant Degree of Contamination | |
| 6 ≤ CF/DC | Very High Degree of Contamination | |
| Sediment Quality Guideline Quotient | SQGQ < 0.1 | Unimpacted |
| 0.1 < SQGQ < 1.0 | Significantly impacted | |
| SQGQ > 1 | Highly impacted |
| Local | Surface | Middle | Bottom |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guaratiba | Quartz > Goethite | Quartz > Goethite | Quartz > left > Goethite > Biotite > Magnetite > Pyrite |
| Marambaia | Quartz > Biotite > Magnetite | Quartz > Chloritoid > Biotite > Magnetite | Quartz > Chloritoid |
| Enseada das Garças | Kaolinite > Chloritoid > Quartz > Biotite > Pyrite > Magnetite | Quartz > Kaolinite > Chloritoid > Magnetite > Pyrite | Kaolinite > Quartz > Chloritoid > Biotite > Magnetite > Pyrite |
| Coroa Grande | Kaolinite > Quartz > Aragonite > Biotite > Gibbsite > Pyrite | Quartz > Nacrite > Gibbsite > Aragonite > Biotite > Magnetite | Nacrite > Quartz > Aragonite > Gibbsite > Magnetite |
| Cd | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Marambaia Barrier Island | ND | 2 | - | - | <500 | [37] |
| 0.1 | 7 | 7.7 | 17.7 | 27.6 | [33,56] | ||
| 0.01 | 2.49 | 4.1 | 17.67 | 27.6 | [8] | ||
| Marambaia | 0.16 | 3.08 | 2.32 | 2.09 | 12.6 | This study | |
| Guaratiba | ND | 2.63 | 0.2 | 0.22 | 3.35 | This study | |
| Enseada das Garças | ND | 5.1 | 7.4 | 9.2 | 43.8 | This study | |
| Guandú Channel Mouth | 0.34 | 8.09 | 8.32 | 20 | 54 | [13] | |
| 0.4 | 12 | 17 | 22 | 57 | [8] | ||
| Coroa Grande | ND | 2.9 | 1.8 | 3.2 | 20.9 | This study | |
| <0.2 | - | - | - | 69–103 | [38] | ||
| Guanabara Bay (Brazil) | 0.35 | 3.43 | 8.9 | 5.1 | 39.2 | [3] | |
| São Paulo State coast (Brazil) | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.31 | 0.83 | 1.65 | [54] | |
| Doce River Mouth (Brazil) | - | 2 | 3.57 | 2.76 | 24.51 | [55] | |
| Maximum | Marambaia Barrier Island | 0.3 | 5 | - | - | ~1600 | [37] |
| 2.1 | 27.6 | 22.8 | 60.6 | 433.7 | [33,56] | ||
| 3.1 | 27.61 | 22.8 | 73.53 | 577.8 | [8] | ||
| Marambaia | 0.67 | 14.84 | 6.25 | 6.59 | 94.9 | This study | |
| Guaratiba | 0.26 | 5.16 | 1.54 | 2 | 8.92 | This study | |
| Enseada das Garças | 2.4 | 18.8 | 12.2 | 20.4 | 364.7 | This study | |
| Guandú Channel Mouth | 4.9 | 42.5 | 27.1 | 55 | 779 | [13] | |
| 4.9 | 38 | 35 | 77 | 1067 | [8] | ||
| Coroa Grande | 1 | 16 | 10.8 | 12.6 | 393.1 | This study | |
| 1.6 | - | - | - | 878 | [38] | ||
| Guanabara Bay (Brazil) | 1.33 | 59 | 17.3 | 34.8 | 179 | [3] | |
| São Paulo State coast (Brazil) | 8.84 | 167.2 | 44.2 | 204.75 | 1077.33 | [54] | |
| Doce River Mouth (Brazil) | - | 44.92 | 52.41 | 43.41 | 75.53 | [55] | |
| Threshoulds | Level 1 | 1.2 | 34 | 20.9 | 46.7 | 150 | [51] |
| Level 2 | 7.2 | 270 | 51.6 | 218 | 410 |
| Guaratiba | |||
| Recent | Bottom | Excess | |
| Cd | 8 × 10−2 | 0.013 | 0.796 |
| Cu | 0.162 | 0.208 | 62.386 |
| Ni | 0.017 | 0.042 | 10.053 |
| Pb | 0.022 | 0.086 | 5.992 |
| Zn | 0.48 | 0.272 | 49.941 |
| Marambaia | |||
| Recent | Bottom | Excess | |
| Cd | 0.016 | 0.015 | 7.164 |
| Cu | 0.612 | 0.277 | 346.47 |
| Ni | 0.238 | 0.126 | 150.22 |
| Pb | 0.217 | 0.172 | 93.839 |
| Zn | 1.959 | 0.7 | 1976.327 |
| Coroa Grande | |||
| Recent | Bottom | Excess | |
| Cd | 1 × 10−4 | 9 × 10−5 | 17.707 |
| Cu | 1.916 | 0.802 | 215.078 |
| Ni | 1.29 | 0.202 | 290.864 |
| Pb | 1.452 | 0.923 | 92.407 |
| Zn | 22.128 | 2.001 | 13,078.959 |
| Enseada das Garças | |||
| Recent | Bottom | Excess | |
| Cd | 0.403 | 8 × 10−5 | 52.647 |
| Cu | 2.838 | 0.577 | 370.163 |
| Ni | 1.348 | 0.707 | 113.652 |
| Pb | 2.826 | 0.786 | 291.901 |
| Zn | 60.874 | 4.017 | 5841.952 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, S.K.; Machado, W.T.V.; Barreira, J.; Vinzón, S.B. Historical Trends of Trace Metals in the Sepetiba Bay Sediments: Pollution Indexes, Fluxes and Inventories. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061033
Rodrigues SK, Machado WTV, Barreira J, Vinzón SB. Historical Trends of Trace Metals in the Sepetiba Bay Sediments: Pollution Indexes, Fluxes and Inventories. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061033
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Sarah Karoline, Wilson Thadeu Valle Machado, João Barreira, and Susana Beatriz Vinzón. 2025. "Historical Trends of Trace Metals in the Sepetiba Bay Sediments: Pollution Indexes, Fluxes and Inventories" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061033
APA StyleRodrigues, S. K., Machado, W. T. V., Barreira, J., & Vinzón, S. B. (2025). Historical Trends of Trace Metals in the Sepetiba Bay Sediments: Pollution Indexes, Fluxes and Inventories. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061033






