Study on the Movement and Distribution Patterns of Sand Particles in a Vane-Type Multiphase Pump
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physical Model of Vane-Type Multiphase Pump
3. Discrete Phase Model
4. Boundary Conditions and Mesh Generation
4.1. Boundary Condition Setup
4.2. Mesh Generation
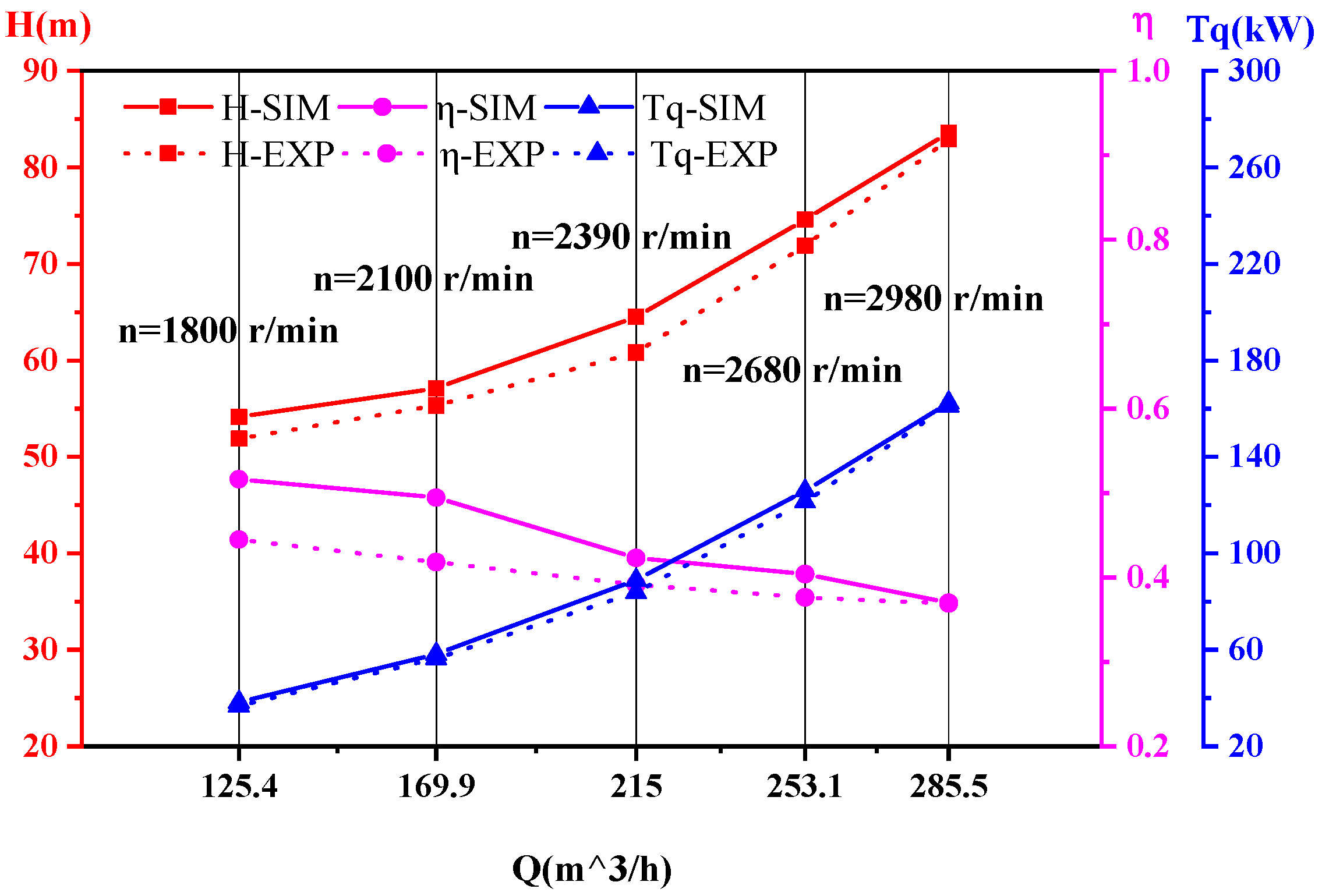
5. Experimental Study
6. Characteristics of Solid–Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Vane-Type Multiphase Pumps
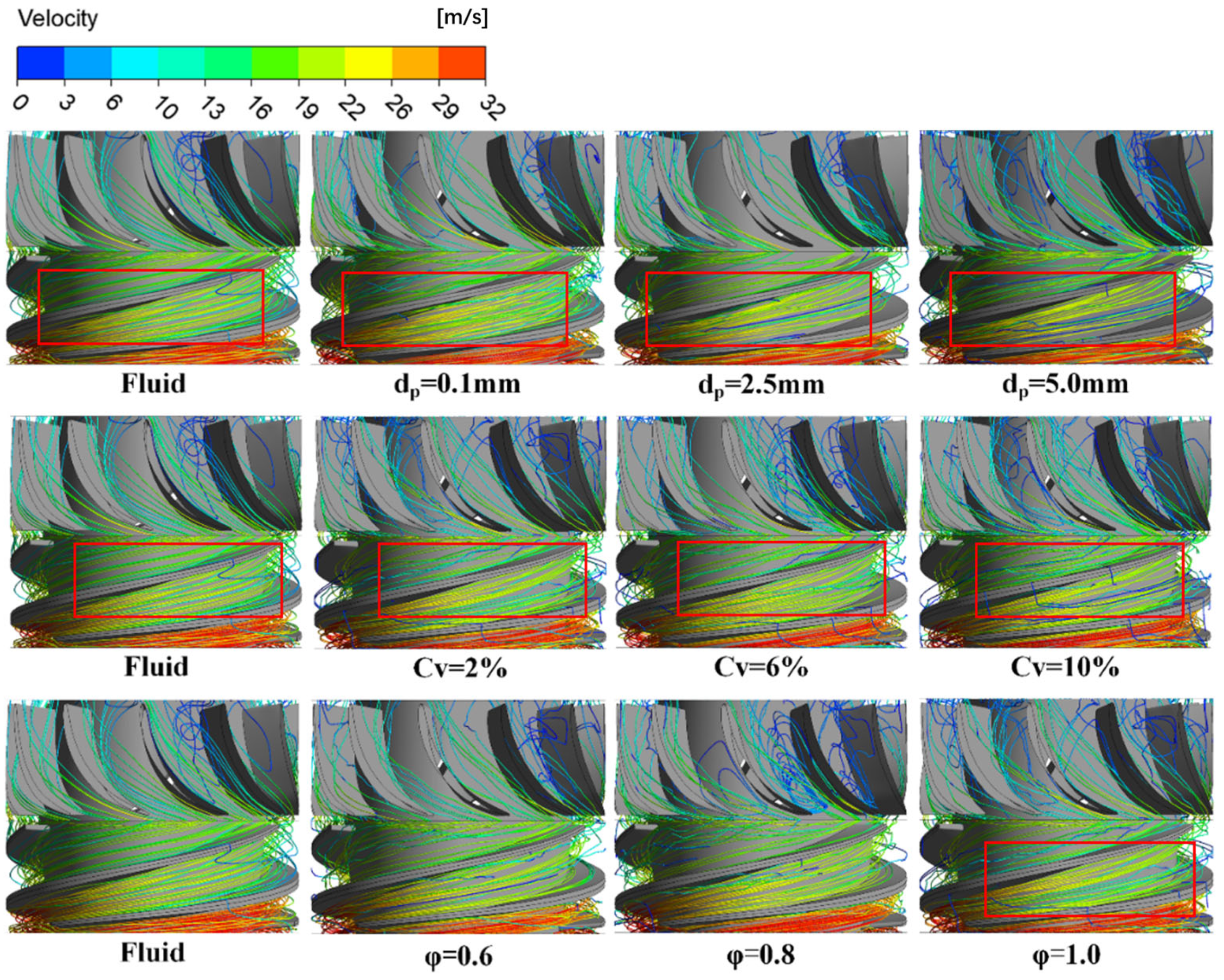
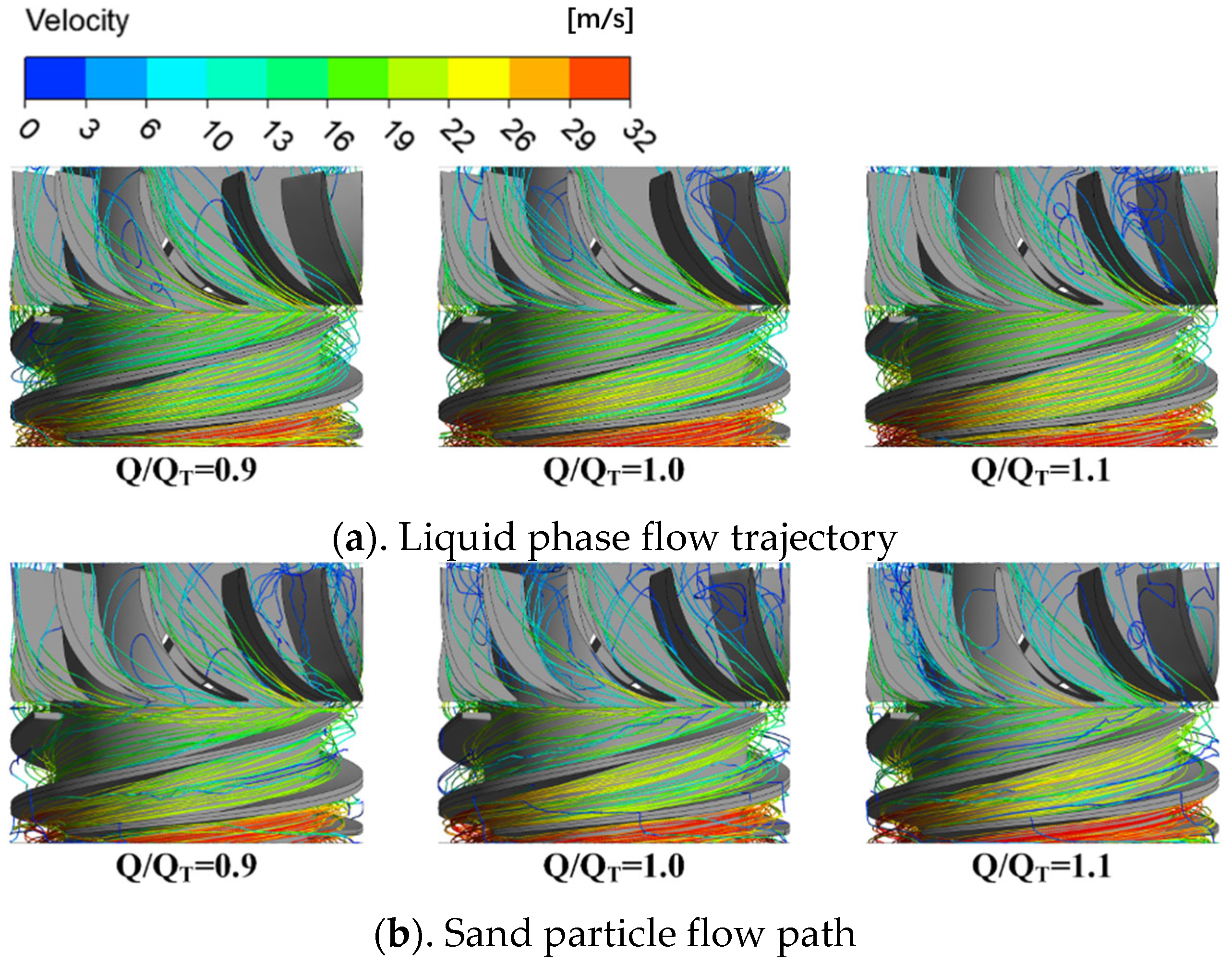
6.1. Solid–Liquid Two-Phase Trajectory
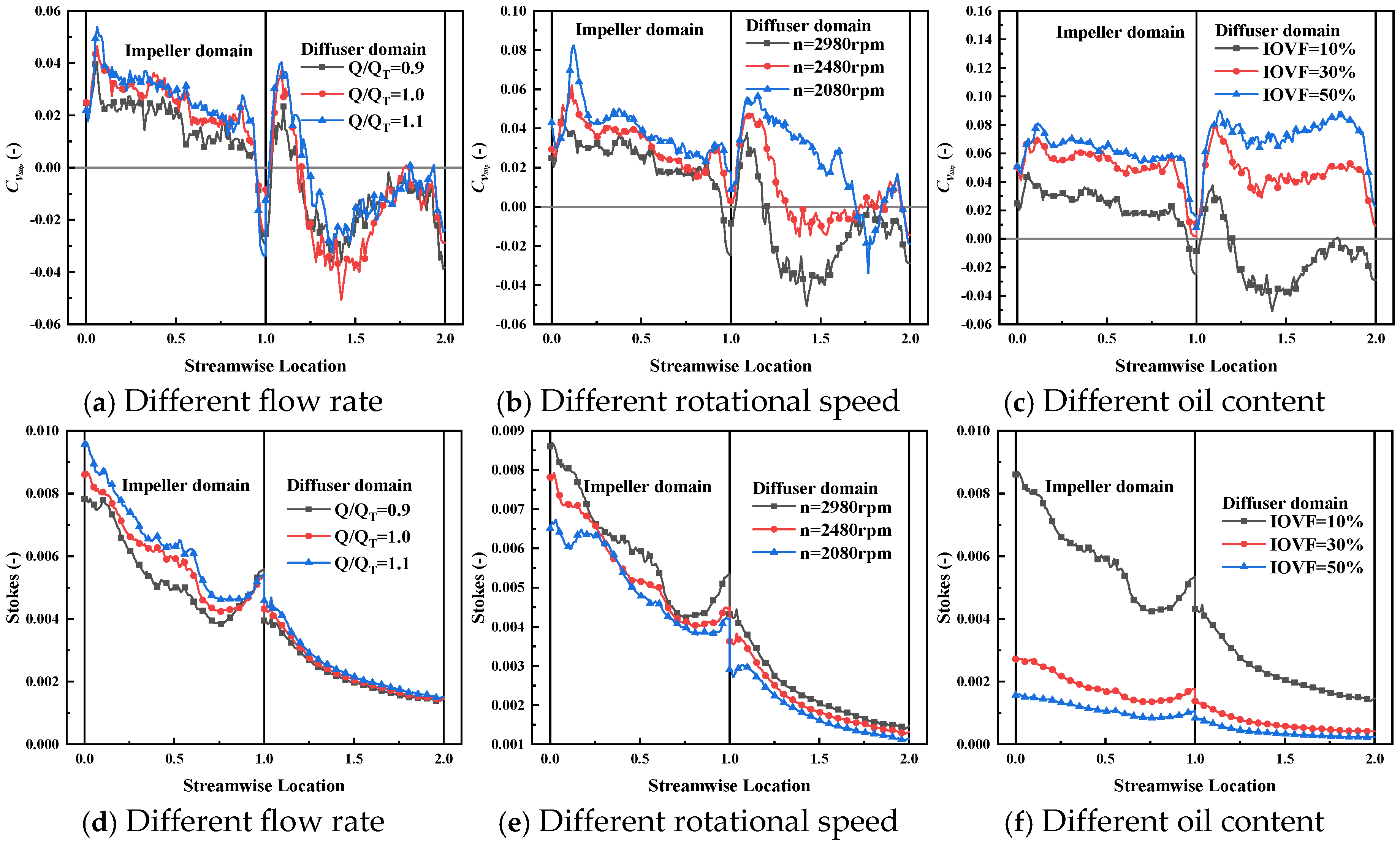
6.2. Sand Particle Motion Characteristics
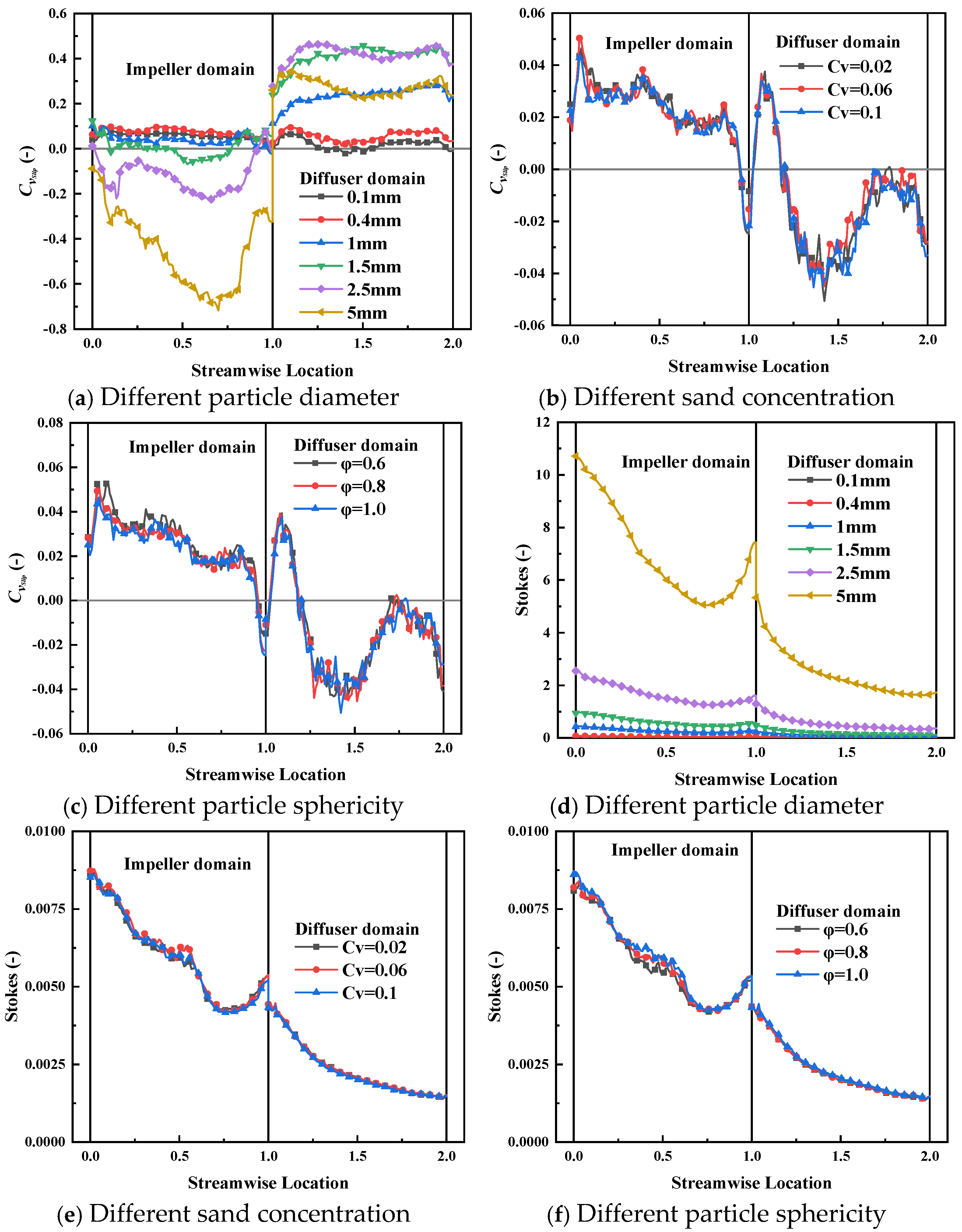
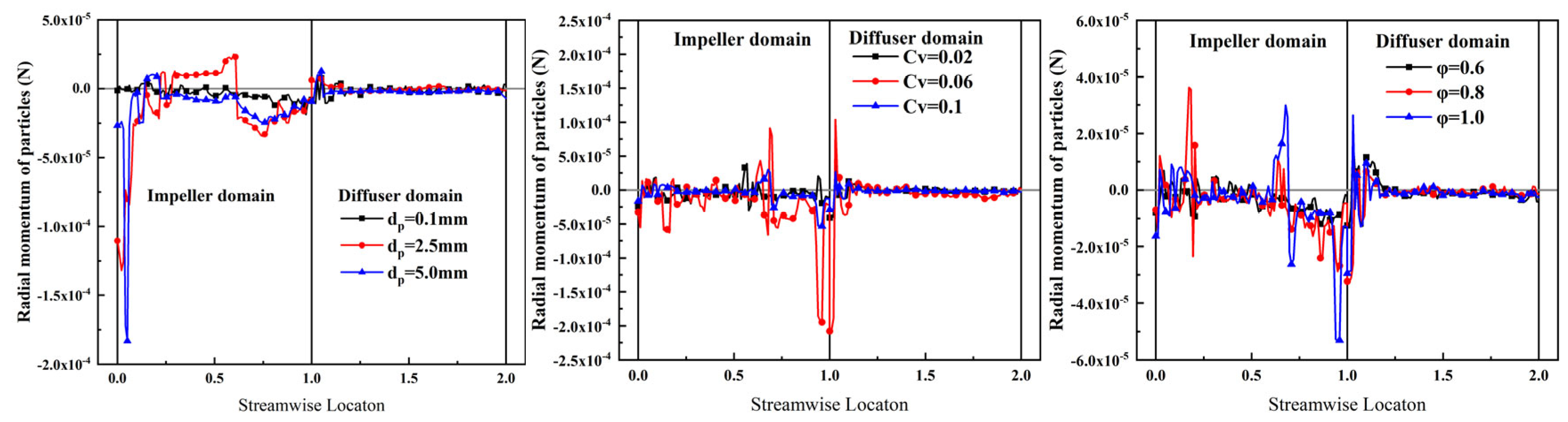
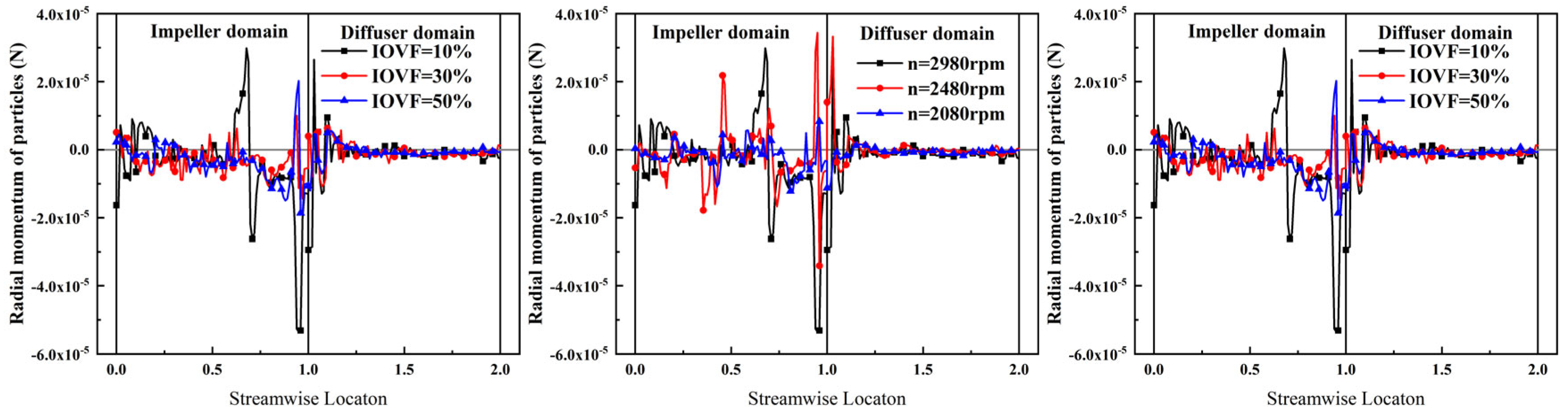
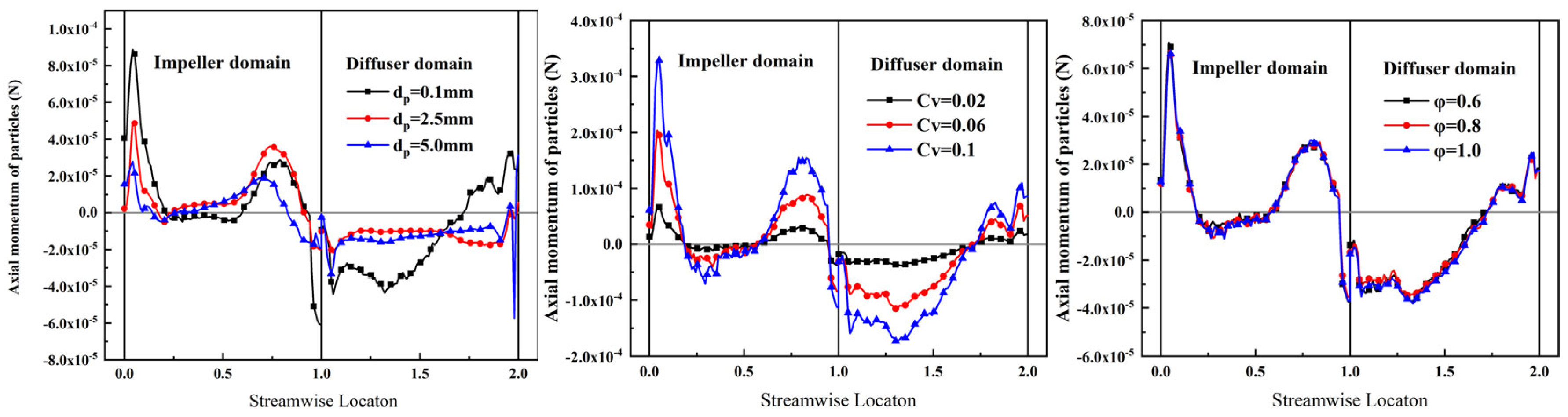
7. Sand Particle Momentum in Vane-Type Multiphase Pumps
7.1. Radial Momentum of Sand Particle Motion
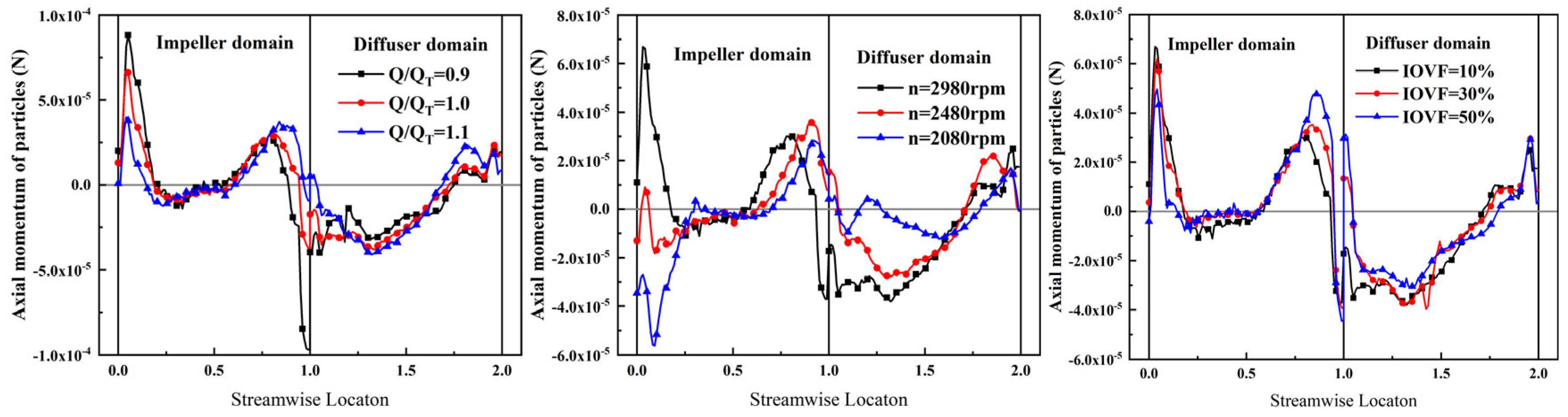
7.2. Axial Momentum of Sand Particle Motion
8. Characteristics of Sand Particle Distribution in Vane-Type Multiphase Pumps
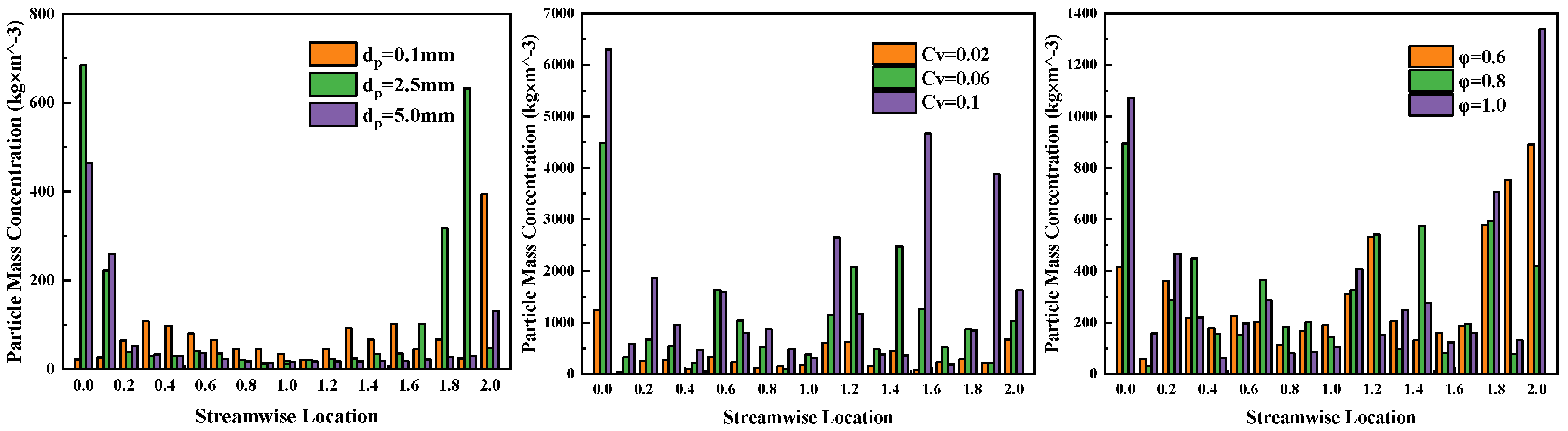
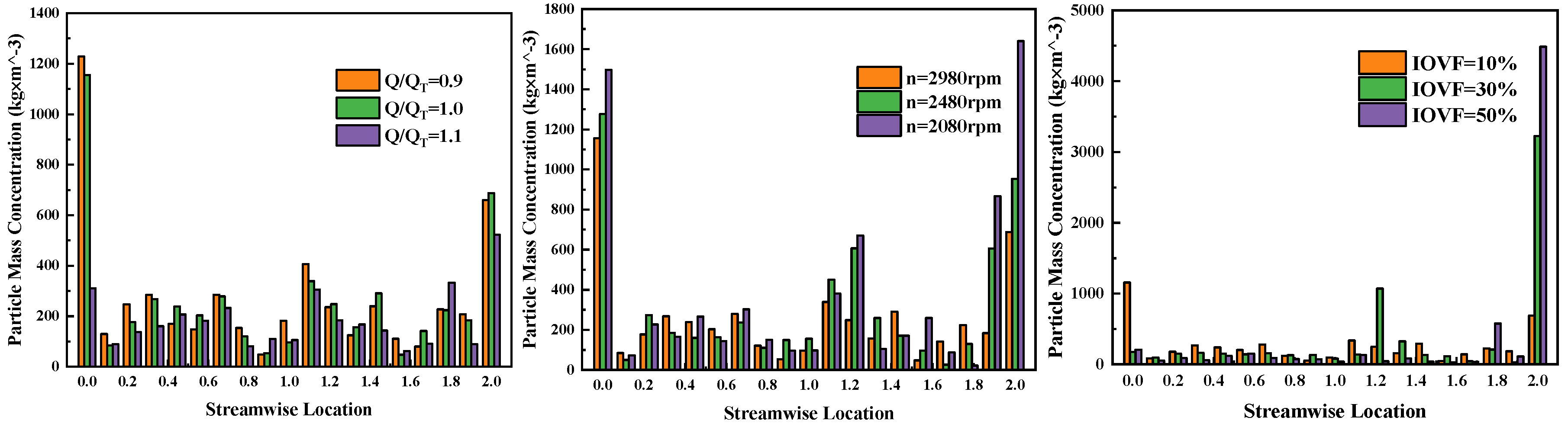
8.1. Sand Particle Mass Concentration Distribution in Flow Passage
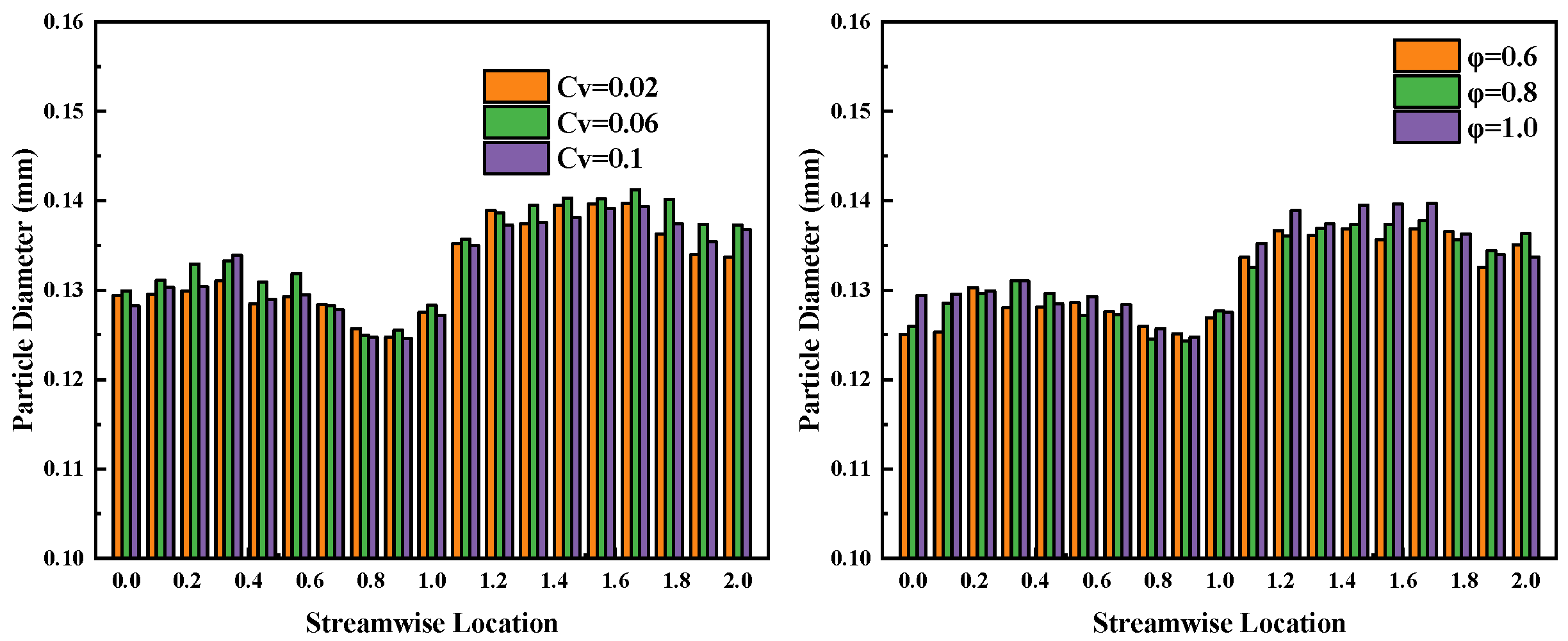
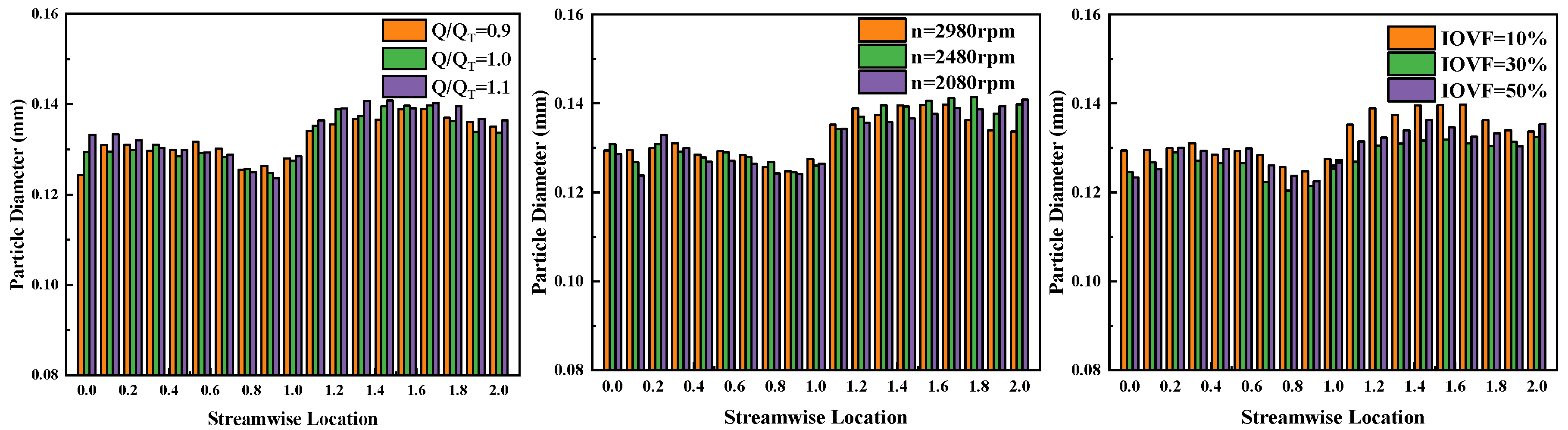
8.2. Distribution of Mean Sand Particle Diameter in Flow Passage
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajkumar, Y.; Shirazi, S.A.; Karimi, S. Effect of pipe size on erosion measurements and predictions in liquid-dominated multiphase flows for the elbows. Wear 2023, 523, 204797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othayq, M.M.; Bilal, F.S.; Sedrez, T.A.; Shirazi, S.A. Experimental and numerical assessments on solid particle erosion in upward vertical-horizontal and horizontal-vertical downward elbows for multiphase and gas-sand flows. Wear 2023, 524, 204812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza-Jara, A.; Walczak, M.; Brevis, W.; Messa, G.V. Erosion by turbulence: Discovering the counter-wise vortex events and their effect on wear. Wear 2023, 530–531, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Xue, K.; Pan, J.; Zhang, X.; Ying, R.; Wu, L.; Zhang, Y. Liquid/solid flow field in a centrifugal pump with different impeller blade types by PIV. Meas. Control 2021, 54, 1219–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Li, Q.; Li, M.; Teng, S. Deposition of solid particles exposed to the suction of dual pumps in the tank of a pumping station. Powder Technol. 2020, 361, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, L.; Lu, Z. Research on the Deposition Characteristics of Integrated Prefabricated Pumping Station. Symmetry 2020, 12, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, X.; Li, Y. Analysis of Flow and Wear Characteristics of Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow in Rotating Flow Channel. Processes 2020, 8, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xiong, H.; Cheng, H.; Yu, C.; Xie, J. Effect of particle motion on the hydraulic collection of coarse spherical particles. Acta Mech. Sin. 2020, 36, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, J.; Deng, L.; Kang, Y.; Liu, S. CFD-DEM Simulation of Backflow Blockage of Deep-Sea Multistage Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Hernández, J.W.; Sinatora, A.; de Melo, H.G.; Chaves, A.P.; Mano, E.S.; Filho, L.S.L.; Paiva, J.L.; Braga, A.S.; Pinto, T.C.S. Hydraulic convey of iron ore slurry: Pipeline wear and ore particle degradation in function of pumping time. Wear 2020, 450–451, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wydrych, J. Comparative analysis of the methods of simulation of flow in boiler dust systems. Chem. Process Eng. Inz. Chem. I Proces. 2010, 31, 603–623. [Google Scholar]
- Bukreev, F.; Raichle, F.; Nirschl, H.; Krause, M.J. Simulation of adsorption processes on moving particles based on an Euler-Euler description using a lattice Boltzmann discretization. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2023, 270, 118485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarodiya, R.; Gandhi, B.K. Numerical simulation of a centrifugal slurry pump handling solid-liquid mixture: Effect of solids on flow field and performance. Adv. Powder Technol. 2019, 30, 2225–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Huang, X.; Zhou, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhou, H. Solid-liquid two-phase flow and wear analysis in a large-scale centrifugal slurry pump. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2020, 114, 104602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, Y. Research of the Gas-solid Flow Character Based on the DEM Method. J. Therm. Sci. 2011, 20, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Luo, G.; Zhou, F.; Zhao, P.; Ma, L.; Chai, H.; Zhang, T. Numerical investigation of dust dispersion in a coal roadway with hybrid ventilation system. Powder Technol. 2017, 313, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, T.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Seames, W.S. Characterizing flame stability and radiative heat transfer in non-swirling oxy-coal flames using different multiphase modeling frameworks. Fuel 2019, 256, 115948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, B.; Prajapati, Y.K.; Sheth, P.N. CFD analysis of the downdraft gasifier using species-transport and discrete phase model. Fuel 2022, 328, 125302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, C.; Li, W.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H.; Xu, W. Numerical research on the particle transport and deposition in the impingement-film cooling passage. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 053302. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Lu, X. Investigation of particle size impact on dense particulate flows in a vertical pipe. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 073302. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.; Hu, X. Influence of Different Particle Parameters and Operating Conditions on Flow Characteristics and Performance of Deep-Sea Mining Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Qi, D.; Xu, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y. Numerical Simulation Prediction of Erosion Characteristics in a Double-Suction Centrifugal Pump. Processes 2021, 9, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno AH, S.; Solis, J.; Zhao, H.; Wang, C.; Simões, T.A.; Bryant, M.; Neville, A. Tribocorrosion evaluation of hydrogenated and silicon DLC coatings on carbon steel for use in valves, pistons and pumps in oil and gas industry. Wear 2018, 394, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Dular, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Effect of Coating Thickness on a Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow Centrifugal Pump under Water Medium. Stroj. Vestn.-J. Mech. Eng. 2019, 65, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Kim, Y.J. CFD-DEM Simulation for the Distribution and Motion Feature of Solid Particles in Single-Channel Pump. Energies 2020, 13, 4988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Liu, N.; Mou, J.; Zhou, P.; Qian, H.; Dai, D. Study on solid-liquid two-phase flow characteristics of centrifugal pump impeller with non-smooth surface. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2019, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Yan, M.; Yu, J.; Xia, K.; Ma, L.; Mou, J.; Wu, D.; Tang, J. Effect of the Bionic Circular Groove Non-Smooth Structure on the Anti-Wear Performance of the Two-Vane Pump. Lubricants 2022, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.L.; Chen, W.; Xu, C. Cavitation performance of multistage slurry pump in deep-sea mining. AIP Adv. 2019, 9, 105024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, S.; Yu, P. Numerical analysis of the effects of gas-phase properties on the internal characteristics and wear in a centrifugal pump. Aquac. Eng. 2020, 91, 102126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y. Influence of Blade Thickness on Solid-Liquid Two-Phase Flow and Impeller Wear in a Ceramic Centrifugal Slurry Pump. Processes 2021, 9, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Chen, Q.; Bai, L.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, L.; Huang, X. Wear mechanism investigation in a centrifugal slurry pump impeller by numerical simulation and experiments. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 128, 105637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, T.; Shen, Y.; Lei, W.; Xu, X.; Liang, L.; Waqar, H.S.; Lin, B.; Tian, Z.Q.; Shen, P.K. Reduced friction and wear enabled by arc-discharge method-prepared 3D graphene as oil additive under variable loads and speeds. Wear 2020, 462–463, 203495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meibohm, J.; Pistone, L.; Gustavsson, K.; Mehlig, B. Relative velocities in bidisperse turbulent suspensions. Phys. Rev. E 2017, 96, 061102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Impeller | Guide Vane | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Symbol | Value | Unit |
| Tip diameter | DS | 234 | DD | 234 | mm |
| Inlet hub diameter | Dh1 | 164 | Dh3 | 182 | mm |
| Outlet hub diameter | Dh2 | 182 | Dh4 | 164 | mm |
| Blade inlet angle | βh1/βs1 | 7.8/4.5 | βh3/βs3 | 0 | ° |
| Blade outlet angle | βh2/βs2 | 28/20 | βh4/βs4 | 35 | ° |
| Axial length | LI | 90 | LD | 92 | mm |
| Number of blades | BI | 3 | BD | 11 | — |
| Test Condition | Value | Test Condition | Value | Test Condition | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle diameter (dp) | 0.1 mm | Sand concentration (Cv) | 2% | Particle sphericity (φ) | 0.6 |
| 2.5 mm | 6% | 0.8 | |||
| 5.0 mm | 10% | 1.0 | |||
| Flow rate (Q/QT) | 0.9Q | Rotational speed (n) | 2080 rpm | Oil content (IOVF) | 10% |
| 1.0Q | 2480 rpm | 30% | |||
| 1.1Q | 2980 rpm | 50% |
| Item | Value/Method |
|---|---|
| Solver Type | Pressure-based |
| Inlet Boundary Condition | 2.54 m/s |
| Outlet Boundary Condition | 0.3 Mpa |
| Particle Size Distribution: Rosin-Rammler (RR) Distribution | : Fraction, d: Particle Diameter |
| Particle Velocity | 2.54 m/s |
| Inlet/Outlet Boundaries | Escape |
| Other Walls | Reflect |
| Pressure-Velocity Coupling Scheme | SIMPLE |
| Gradient | Green-Gauss cell-based |
| Pressure | PRESTO! |
| Density, Momentum, Turbulent Kinetic Energy, Turbulent Dissipation Rate | First-Order Upwind |
| GCI | 10−3 |
| Case No. | Impeller Mesh (Million) | Guide Vane Mesh (Million) | Total Mesh (Million) | Head (m) | Error Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.88 | 1.23 | 3.11 | 35.59 | 1 |
| 2 | 2.17 | 1.38 | 3.55 | 35.62 | 0.0843% |
| 3 | 2.36 | 1.49 | 3.85 | 35.65 | 0.169% |
| 4 | 2.64 | 1.55 | 4.19 | 35.72 | 0.365% |
| 5 | 2.74 | 1.67 | 4.41 | 35.53 | −0.169% |
| 6 | 2.93 | 1.72 | 4.65 | 35.61 | 0.0562% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Shi, G.; Liu, Y.; Wen, H.; Lv, W. Study on the Movement and Distribution Patterns of Sand Particles in a Vane-Type Multiphase Pump. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061034
Wang C, Shi G, Liu Y, Wen H, Lv W. Study on the Movement and Distribution Patterns of Sand Particles in a Vane-Type Multiphase Pump. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061034
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chenwei, Guangtai Shi, Yao Liu, Haigang Wen, and Wenjuan Lv. 2025. "Study on the Movement and Distribution Patterns of Sand Particles in a Vane-Type Multiphase Pump" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061034
APA StyleWang, C., Shi, G., Liu, Y., Wen, H., & Lv, W. (2025). Study on the Movement and Distribution Patterns of Sand Particles in a Vane-Type Multiphase Pump. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061034






