Experimental Study on the Sediment-Trapping Performance of Different Coastal Protection Structures in a High-Tidal Range Area
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
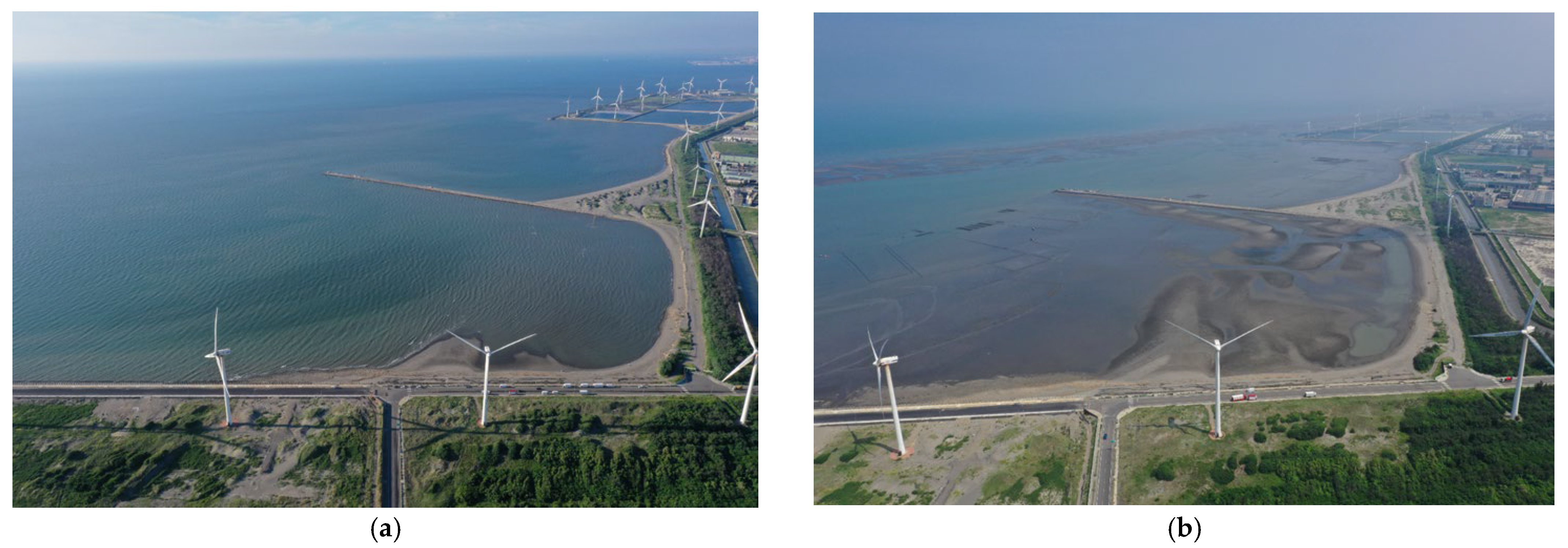
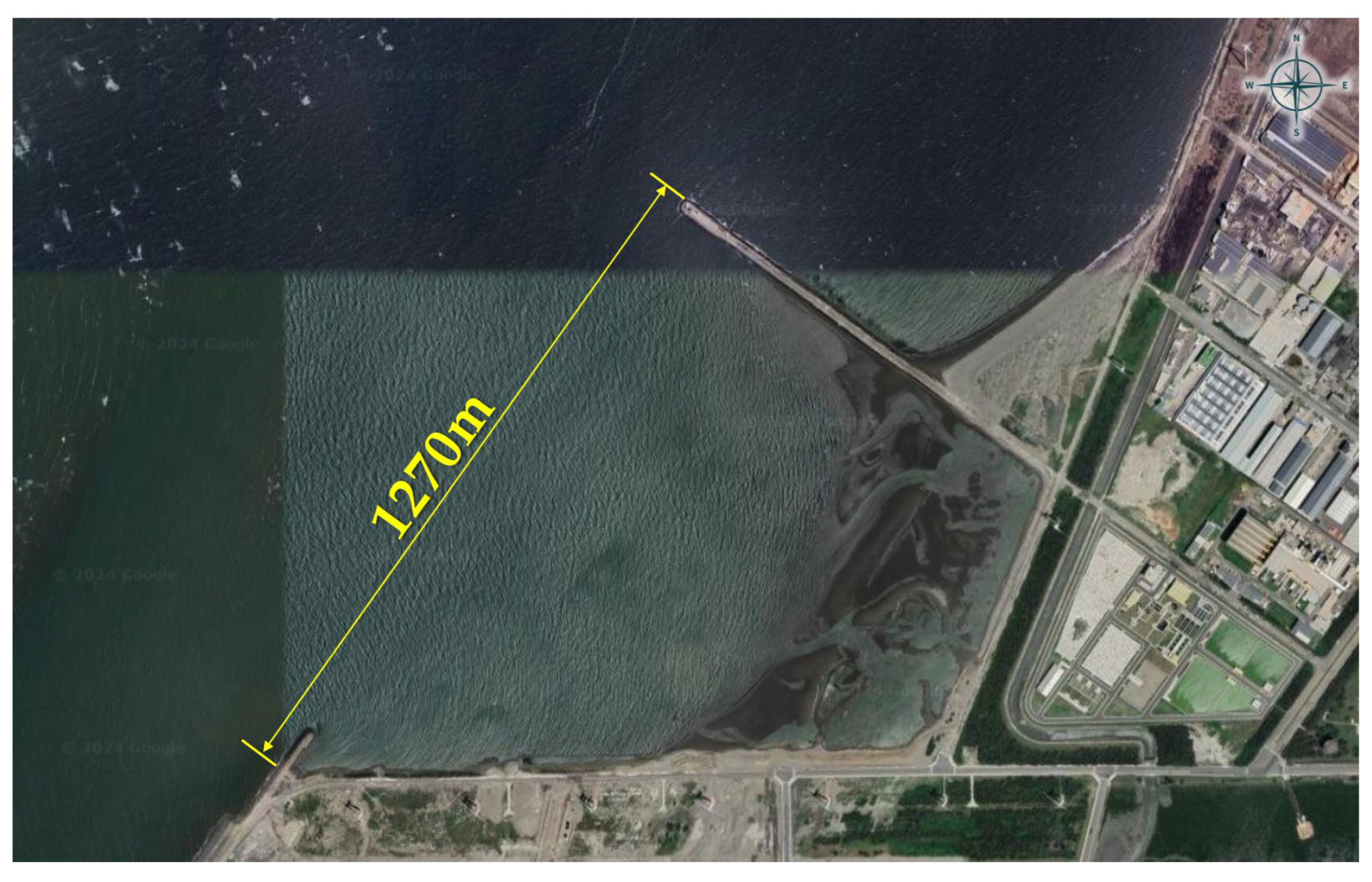
2.1. Overview of the Field Environment
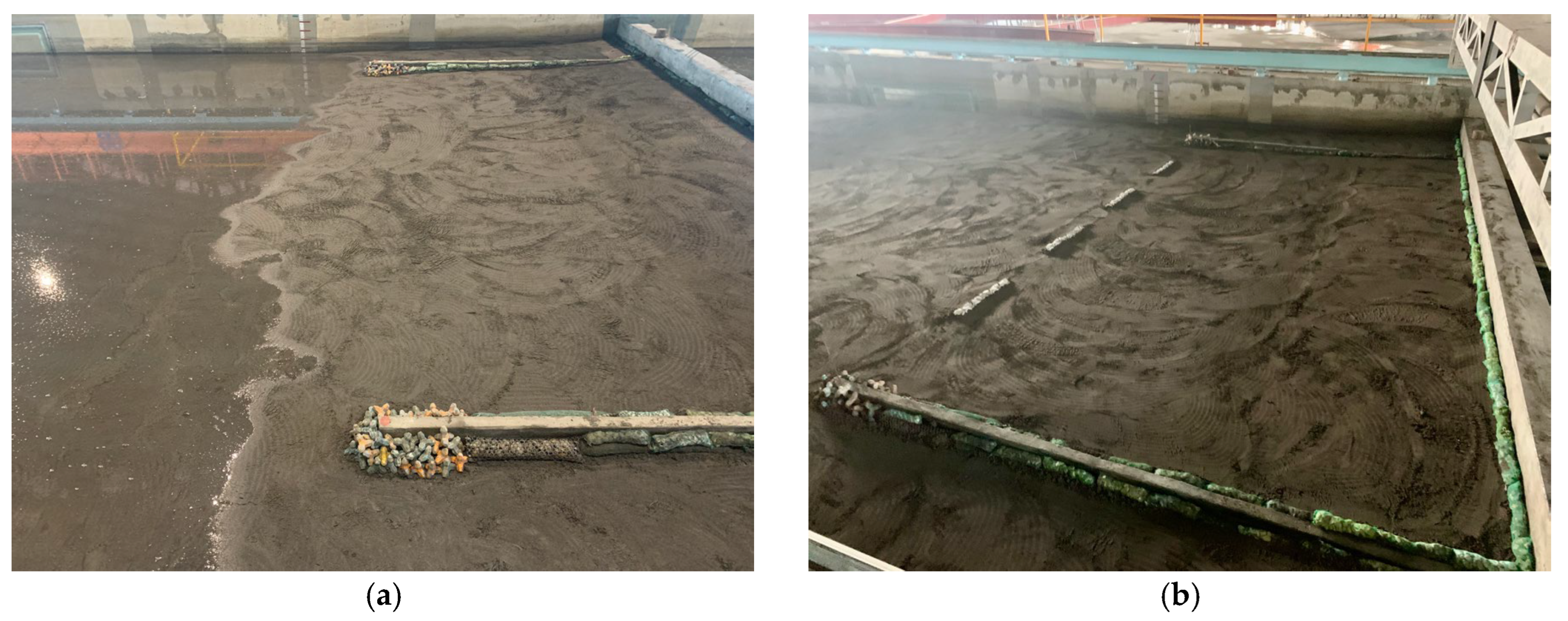
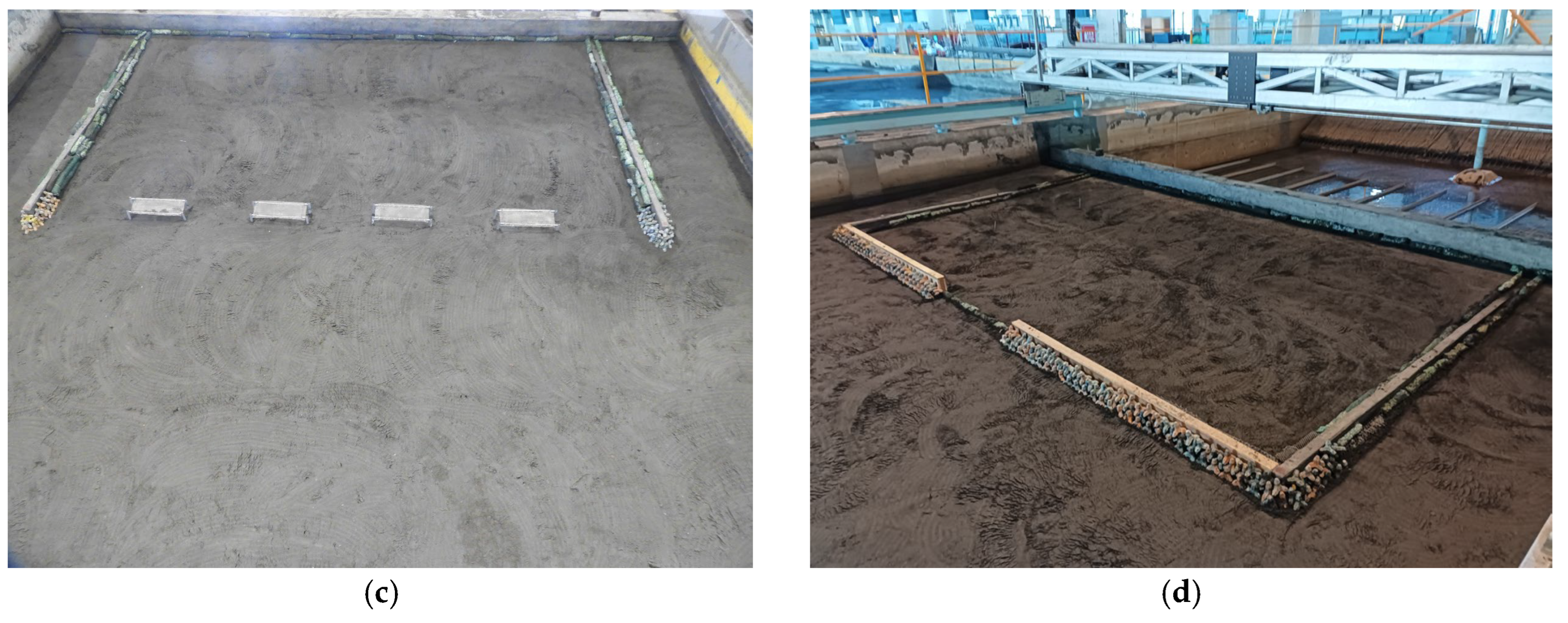
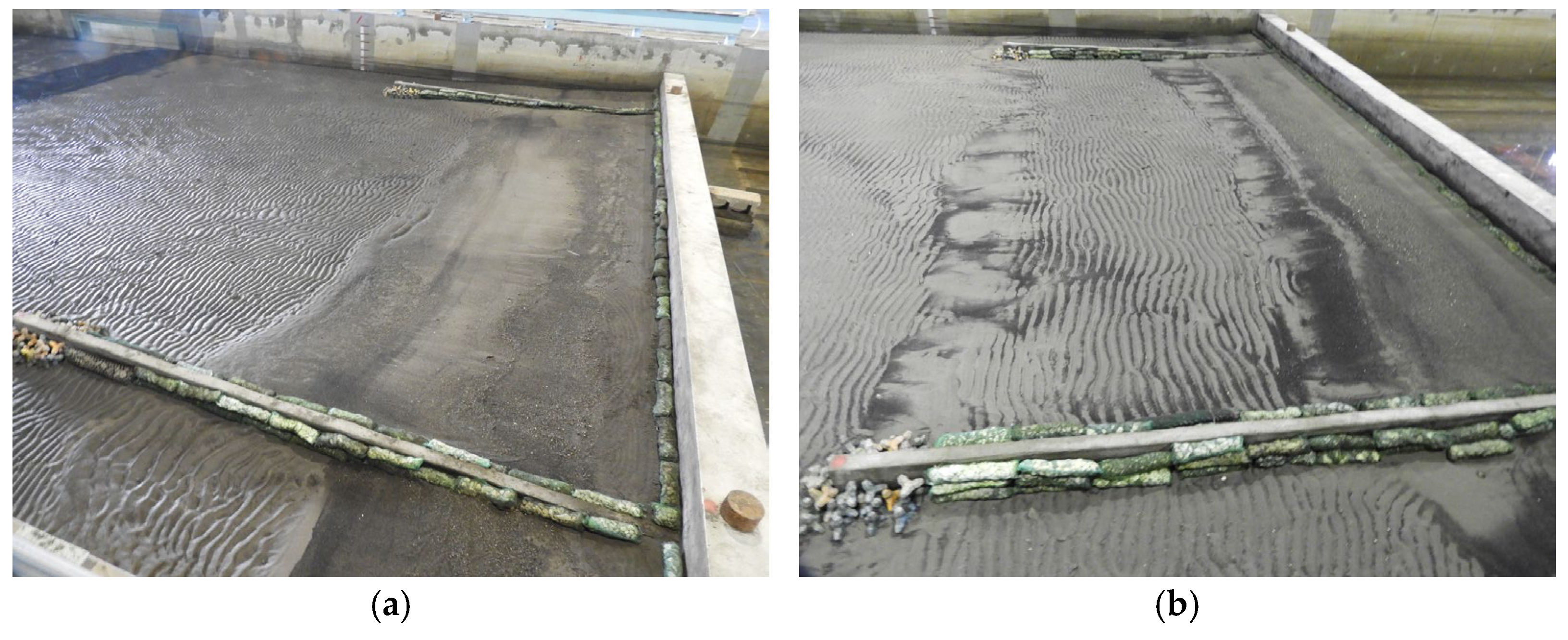
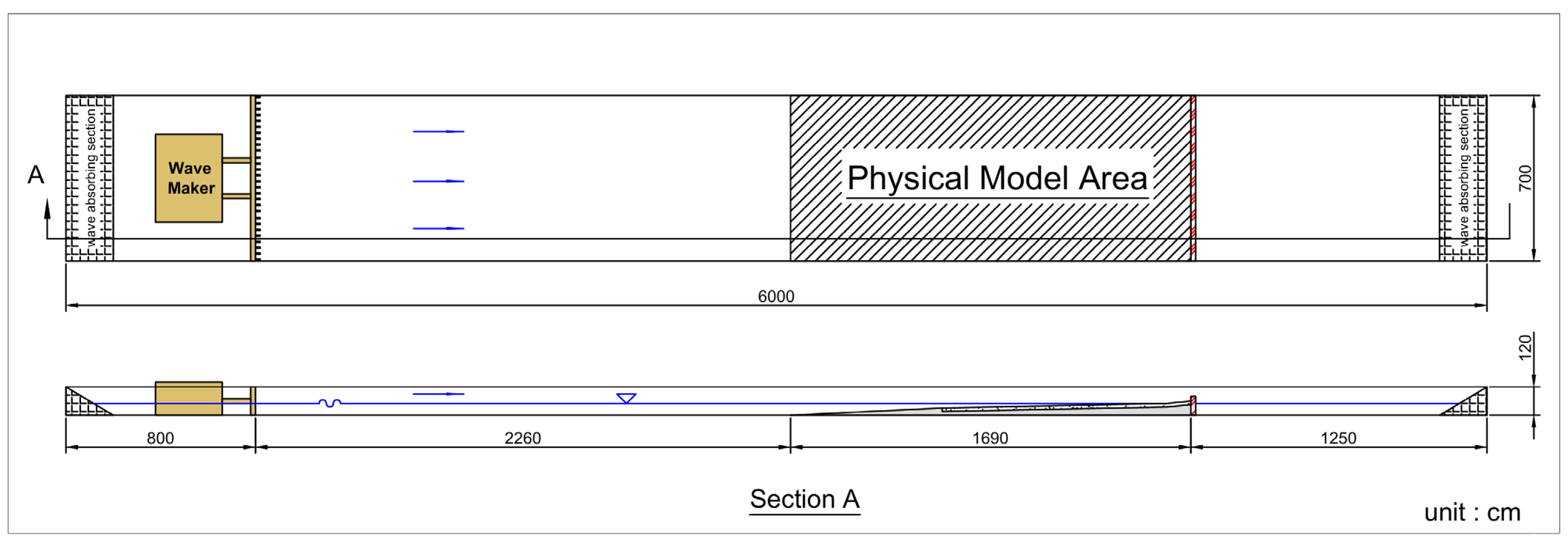
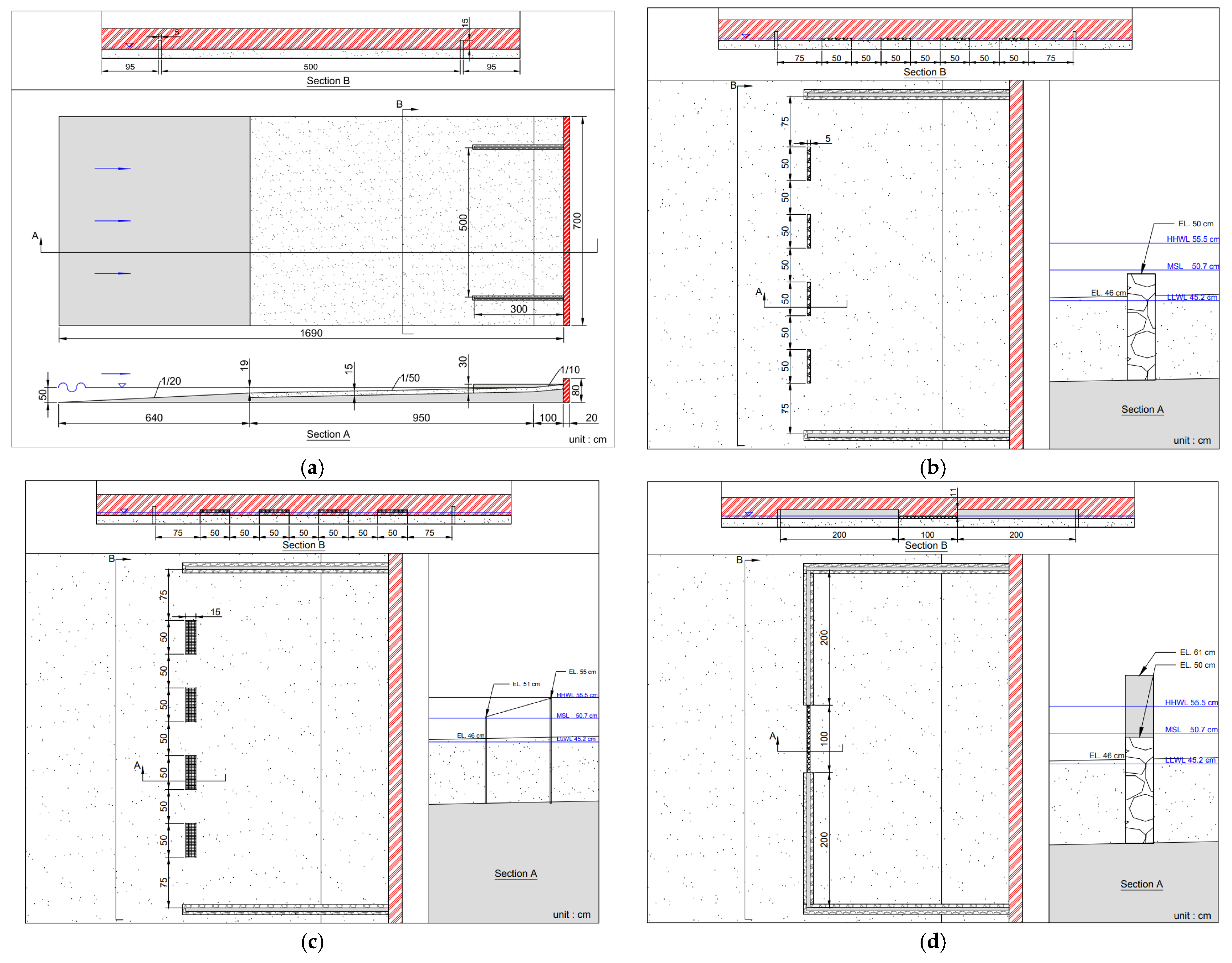
2.2. Physical Modelling of Hydraulic Experiments
3. Results
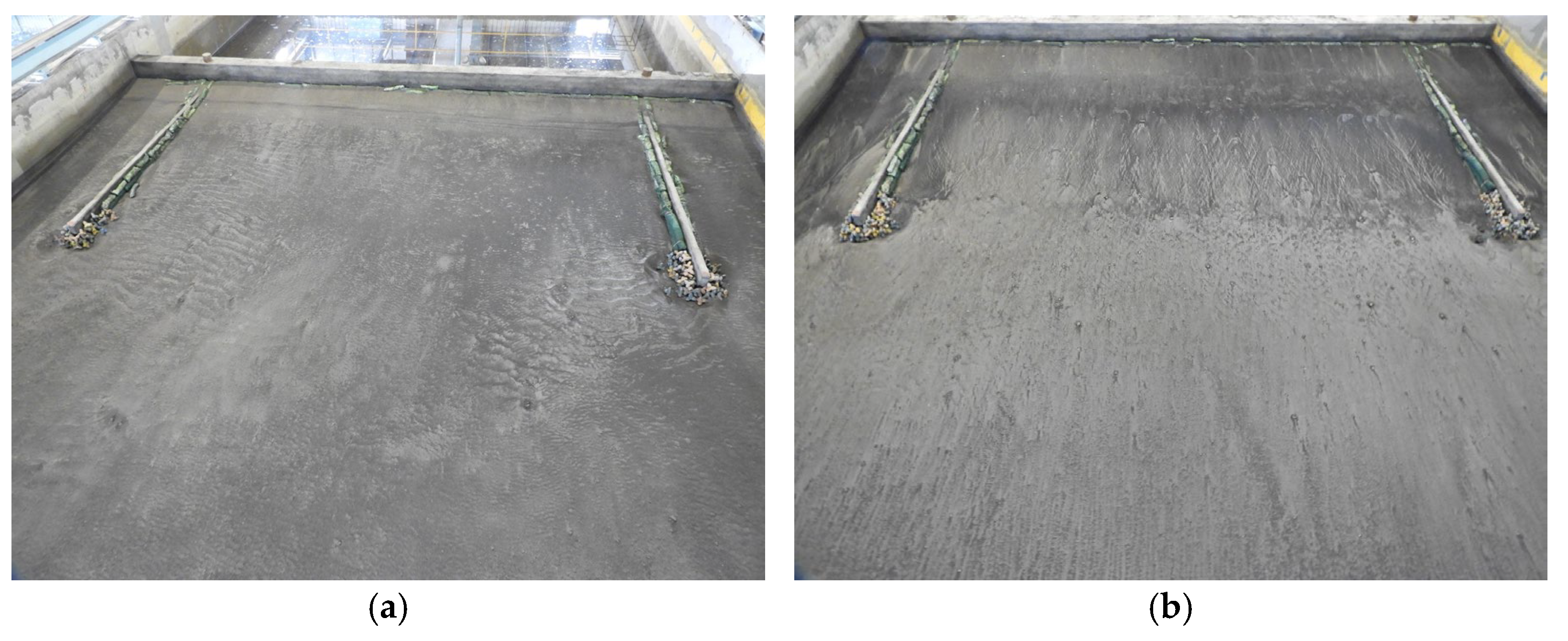
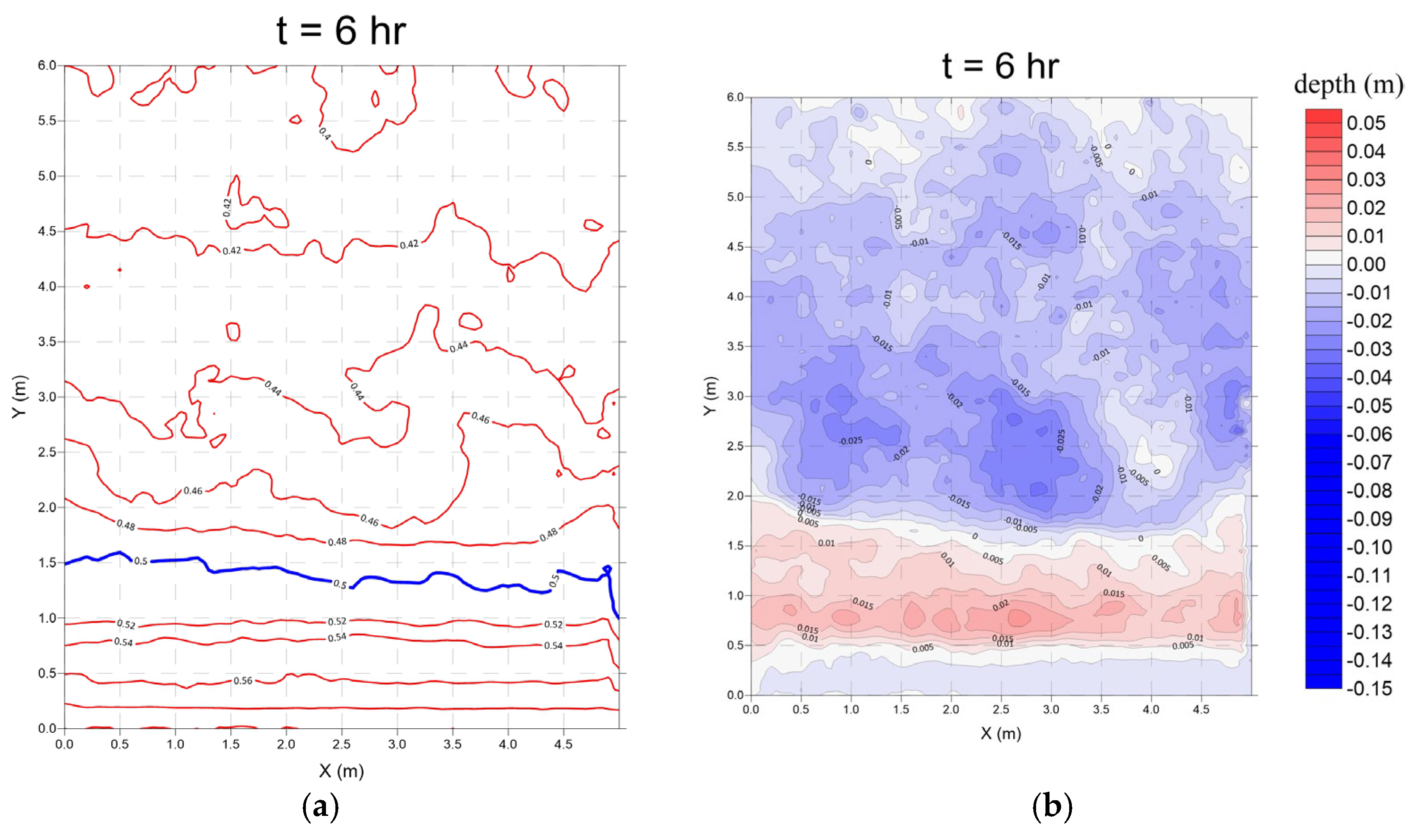
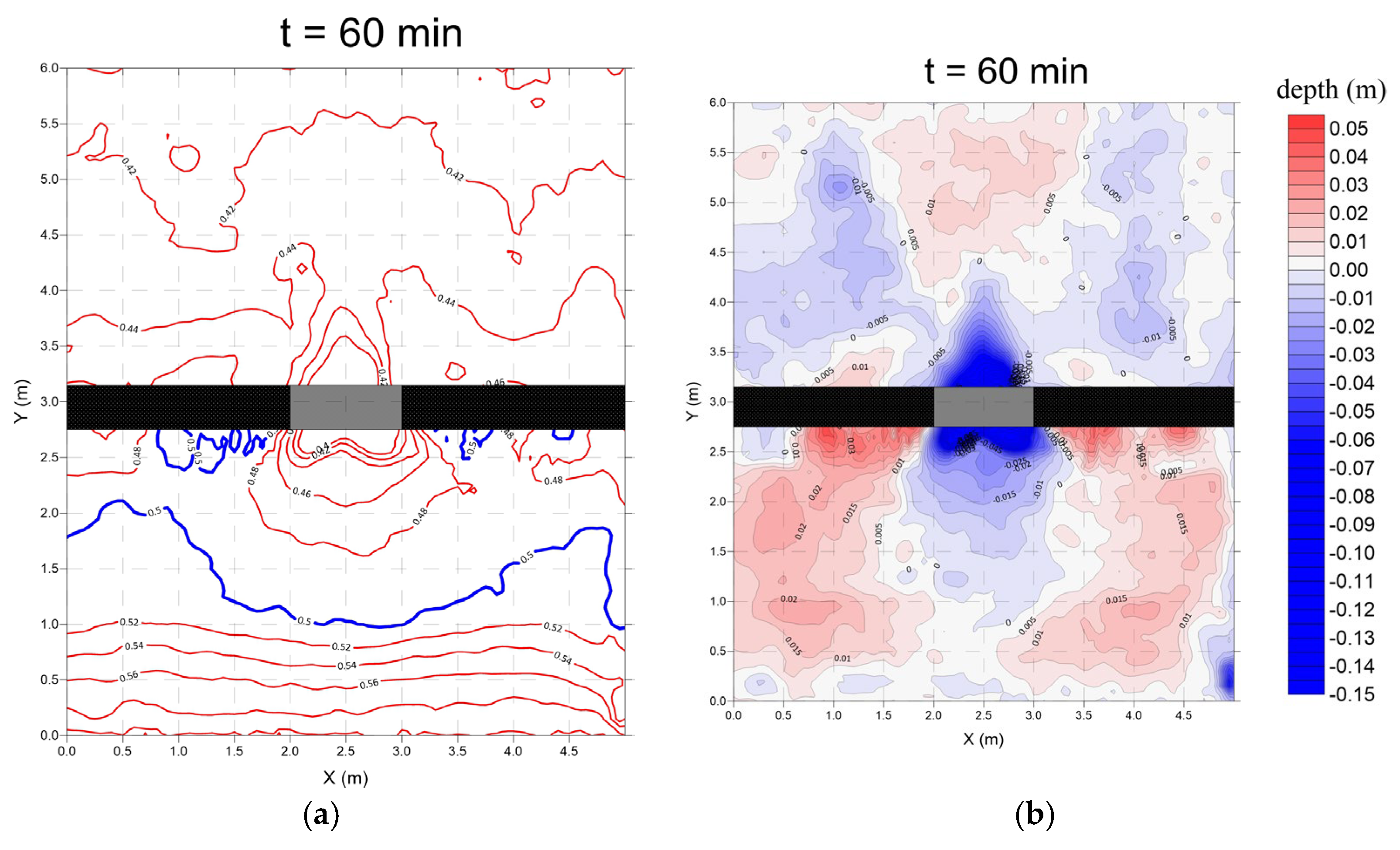
3.1. No Structure (Case 1)
- Monsoon wave
- 2.
- Typhoon wave
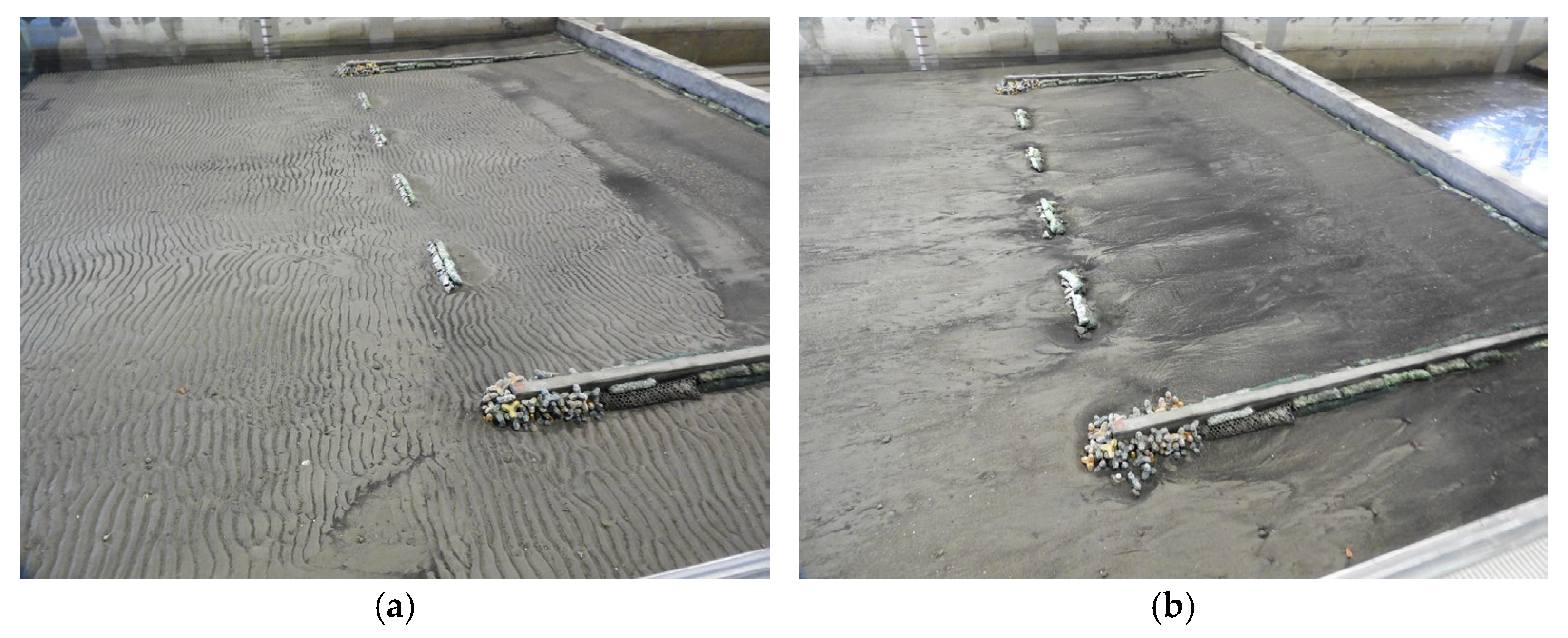
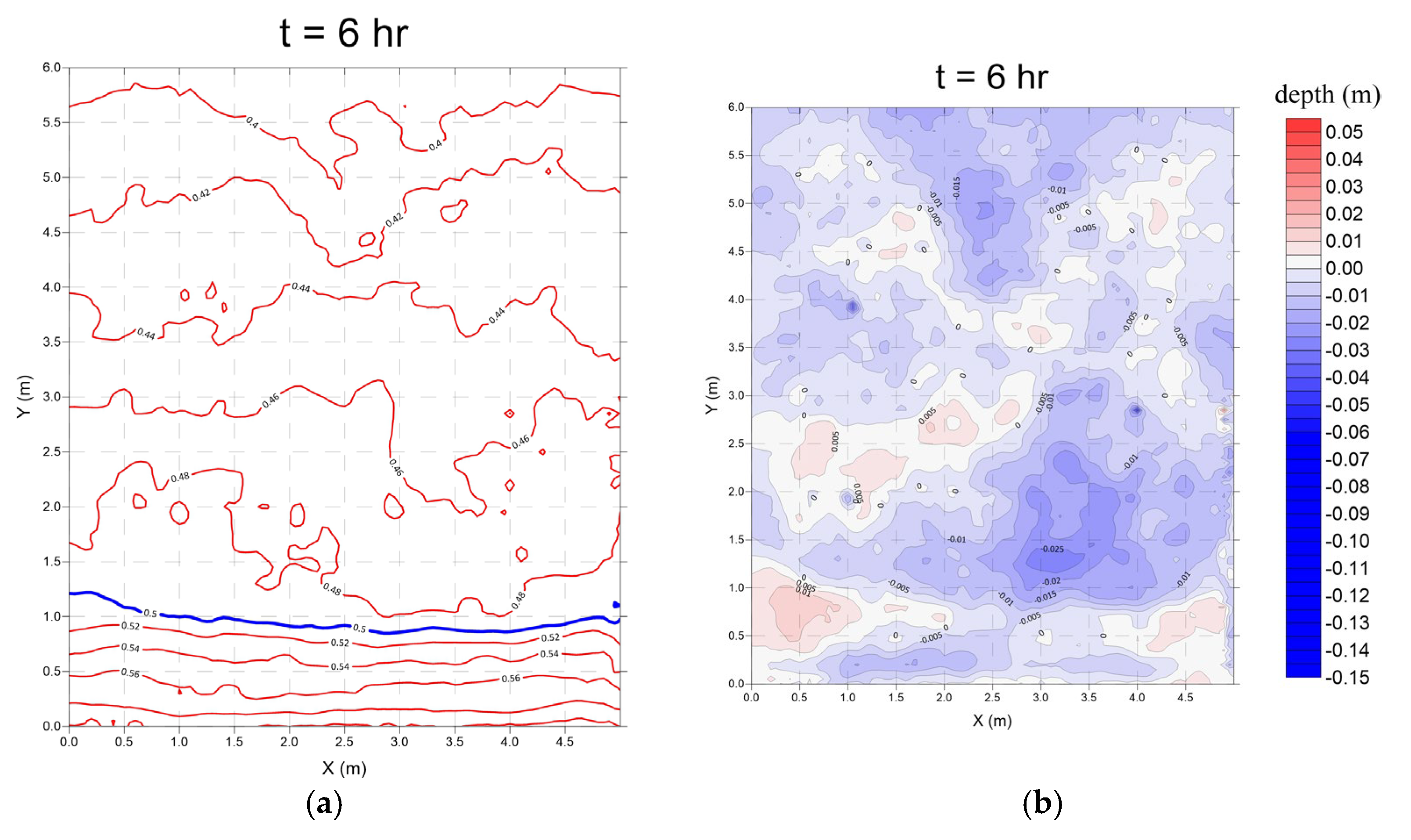
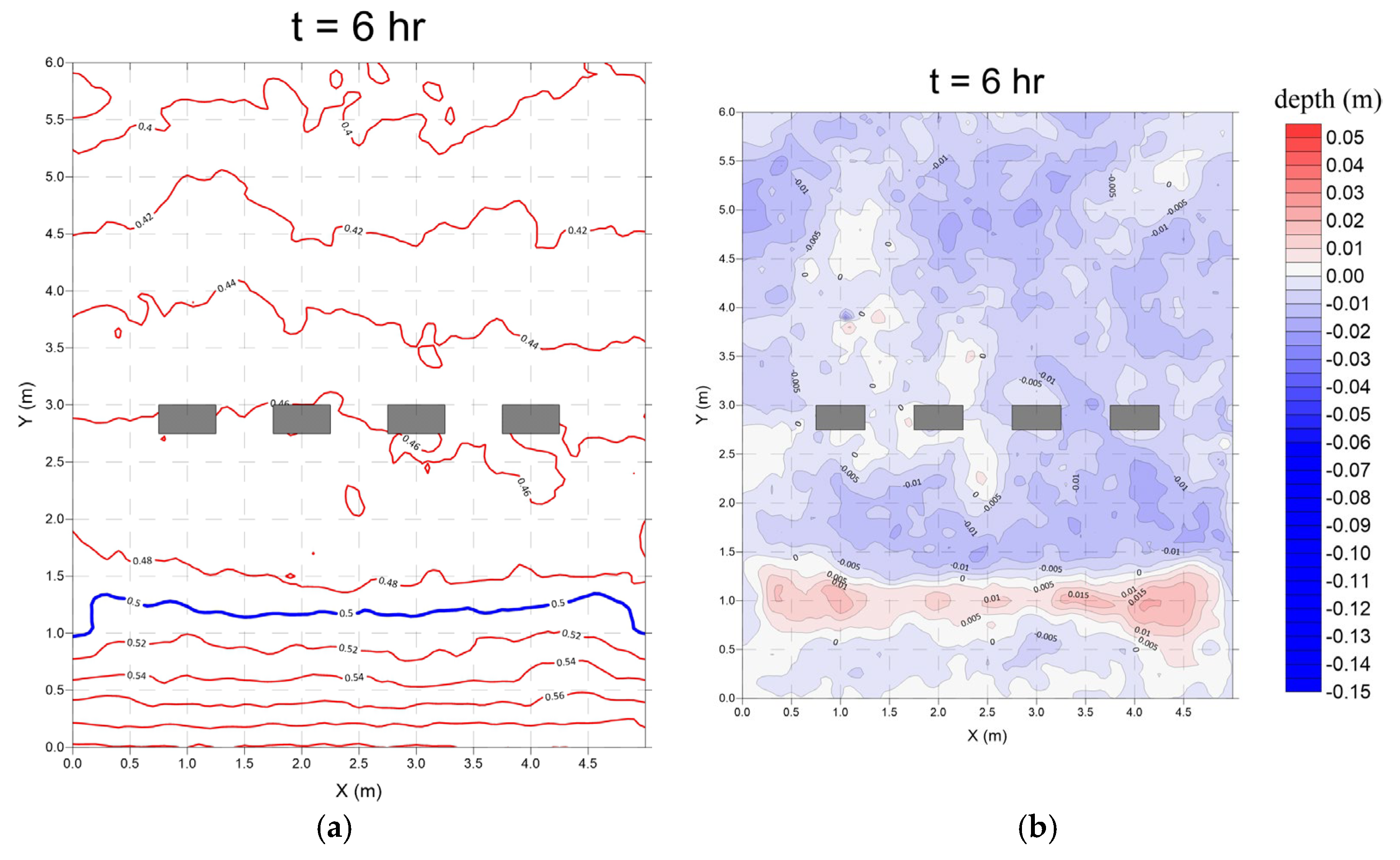
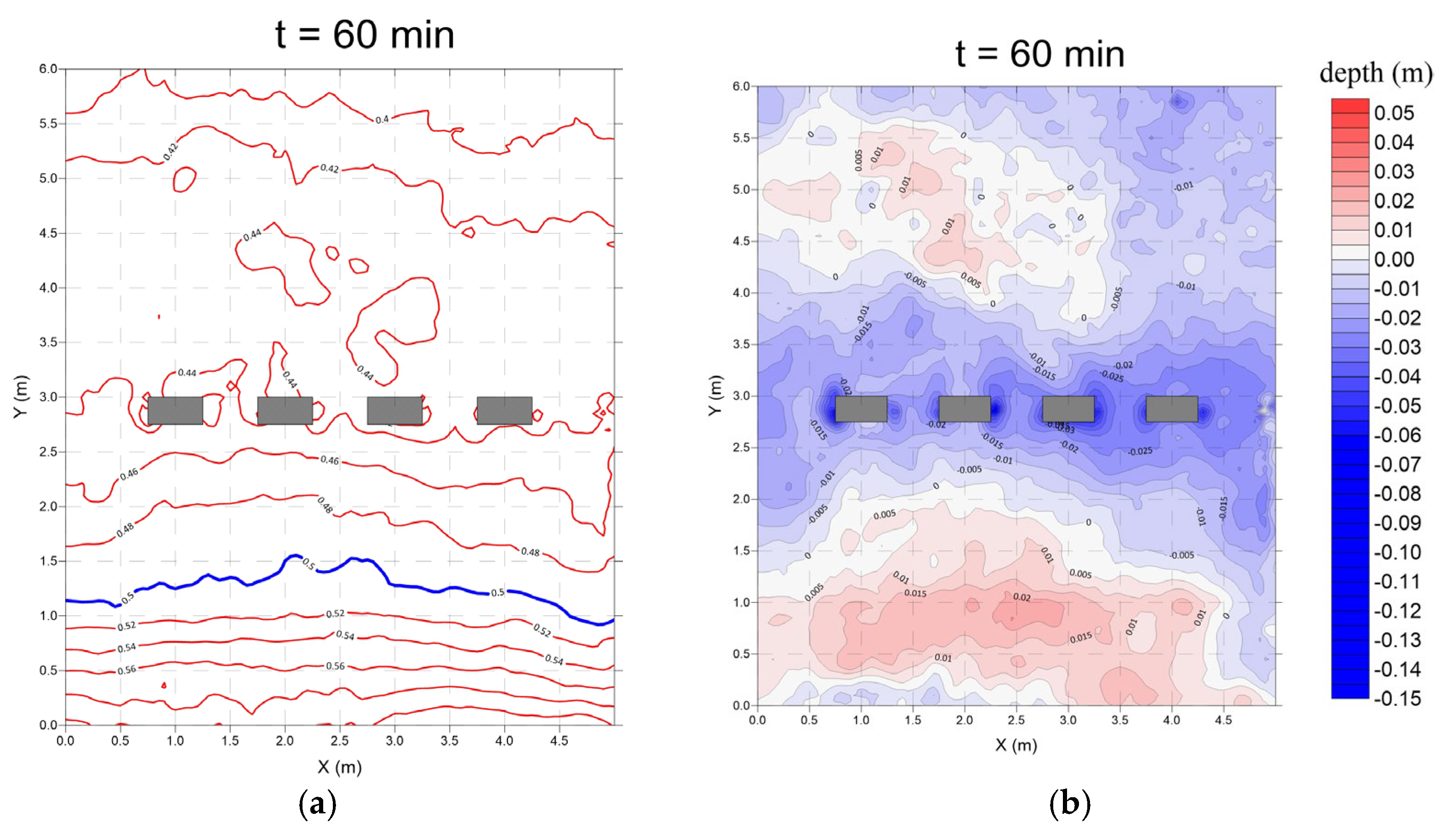
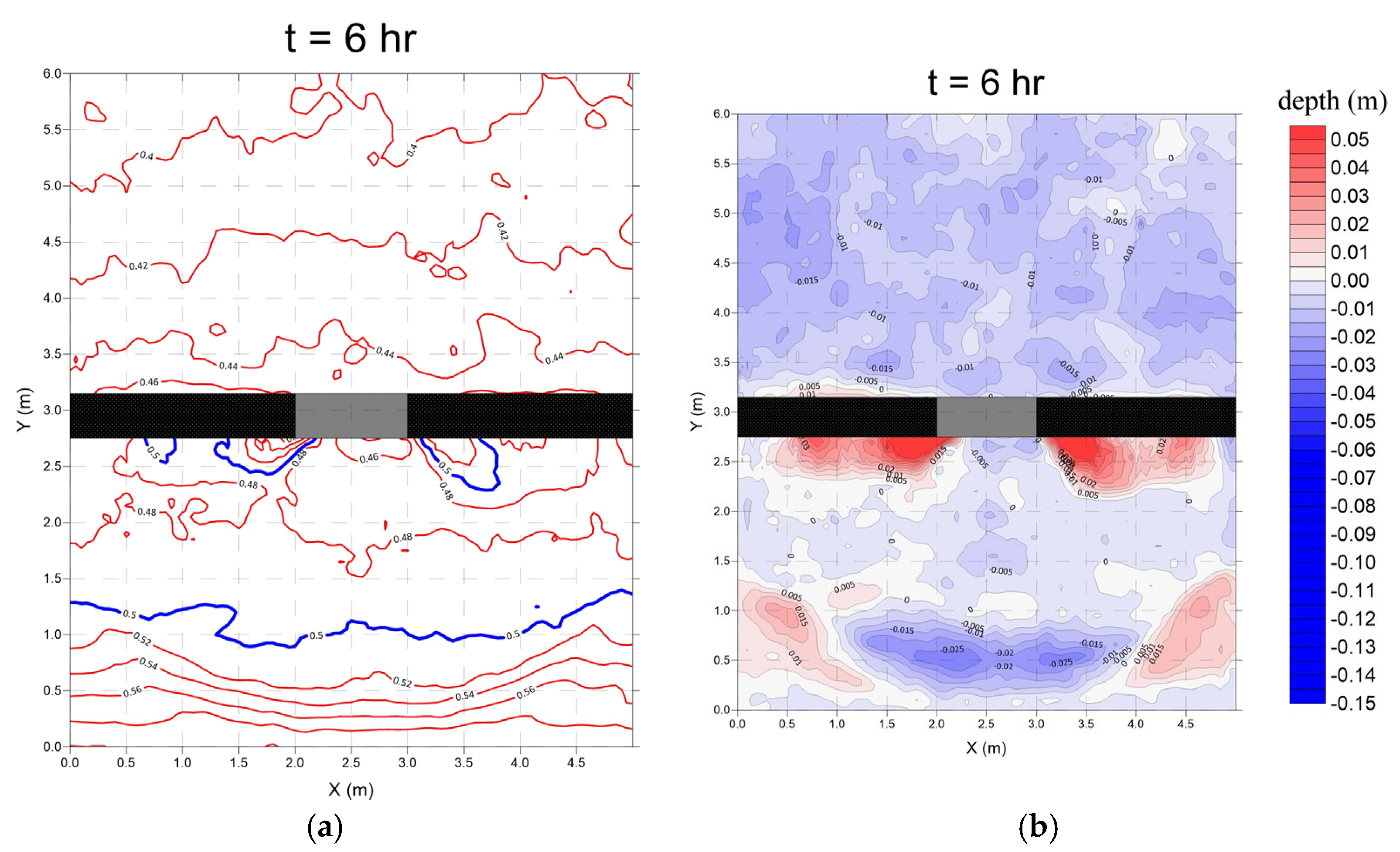
3.2. Submerged Breakwaters (Case 2)
- Monsoon wave
- 2.
- Typhoon wave
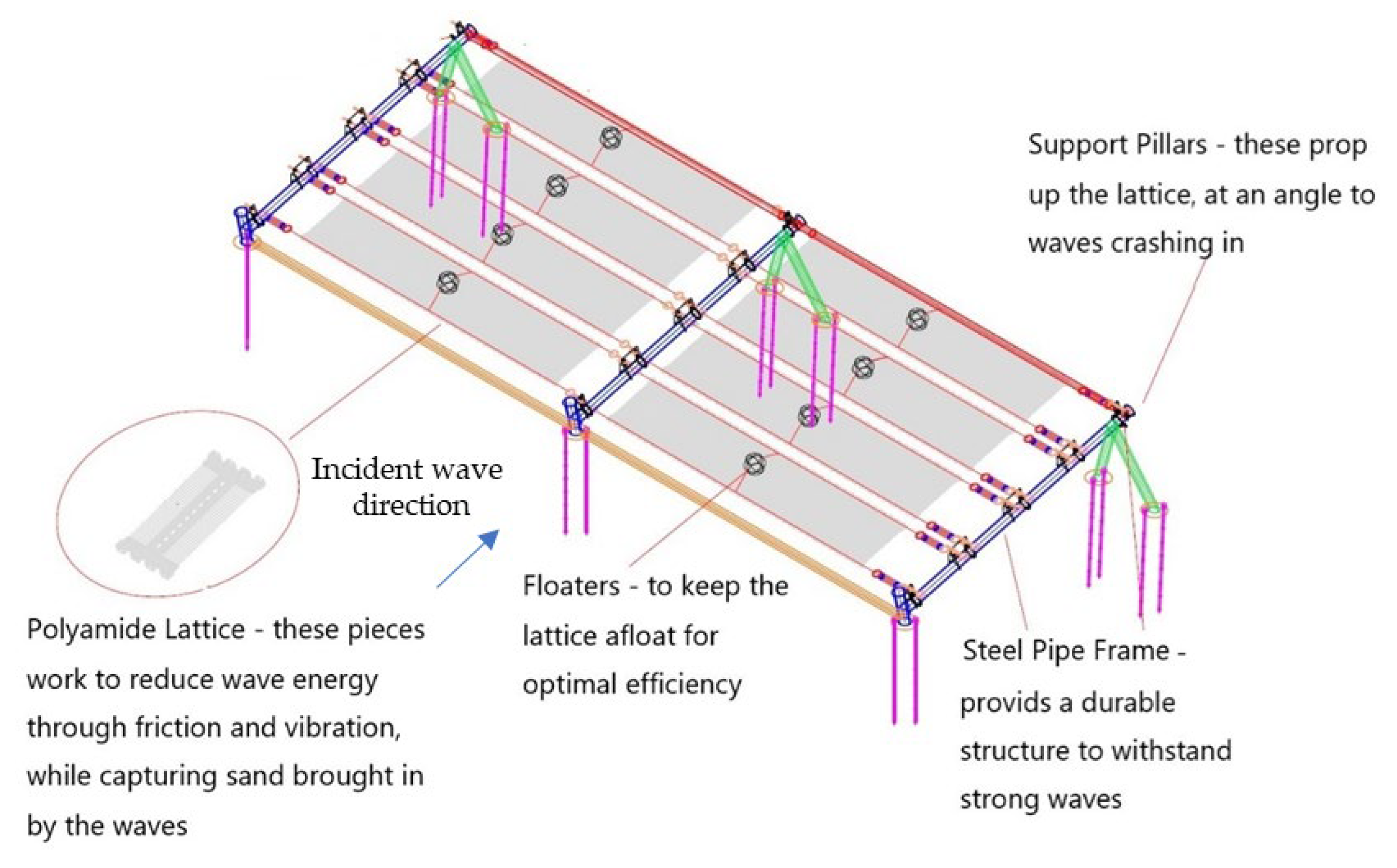
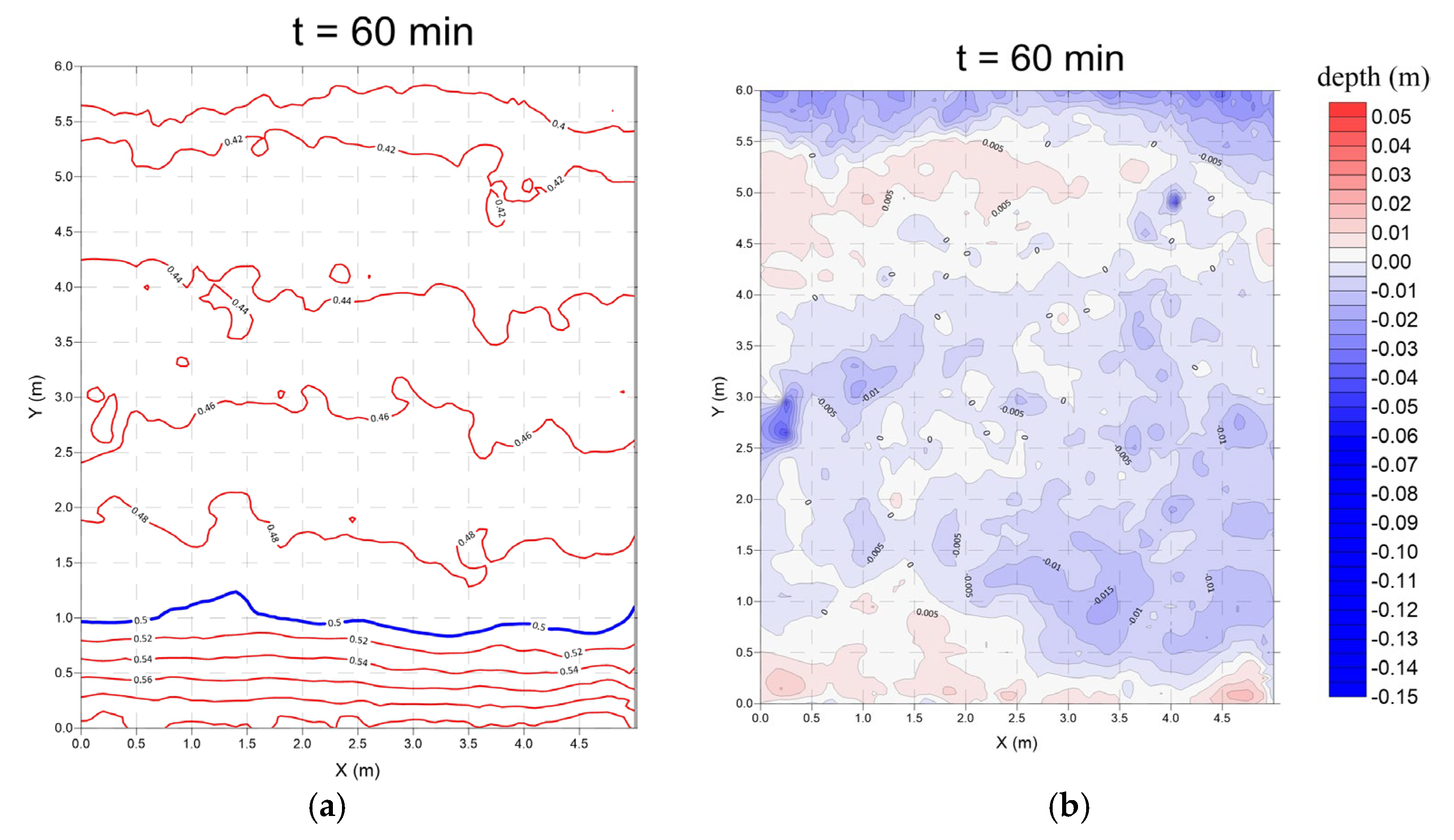
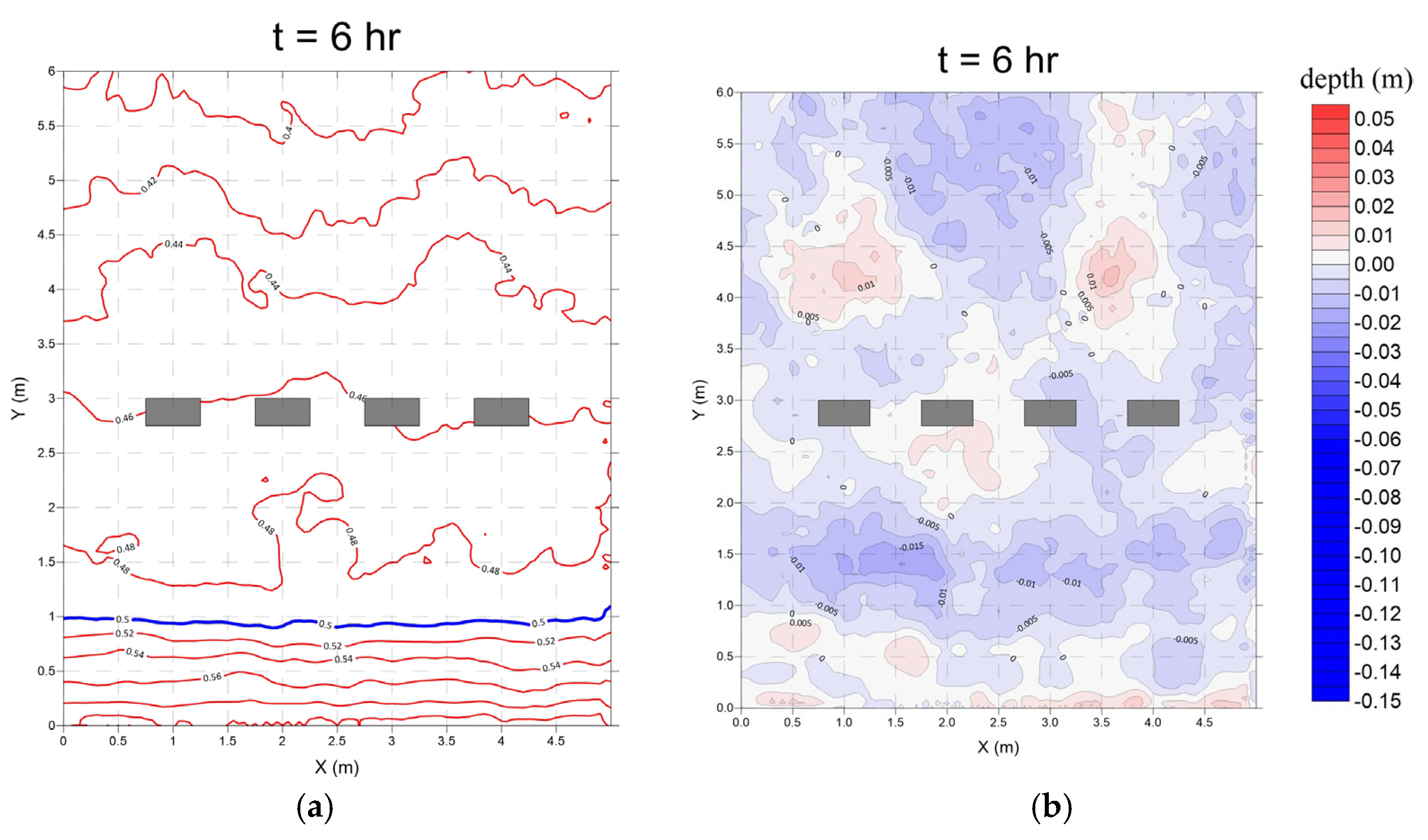
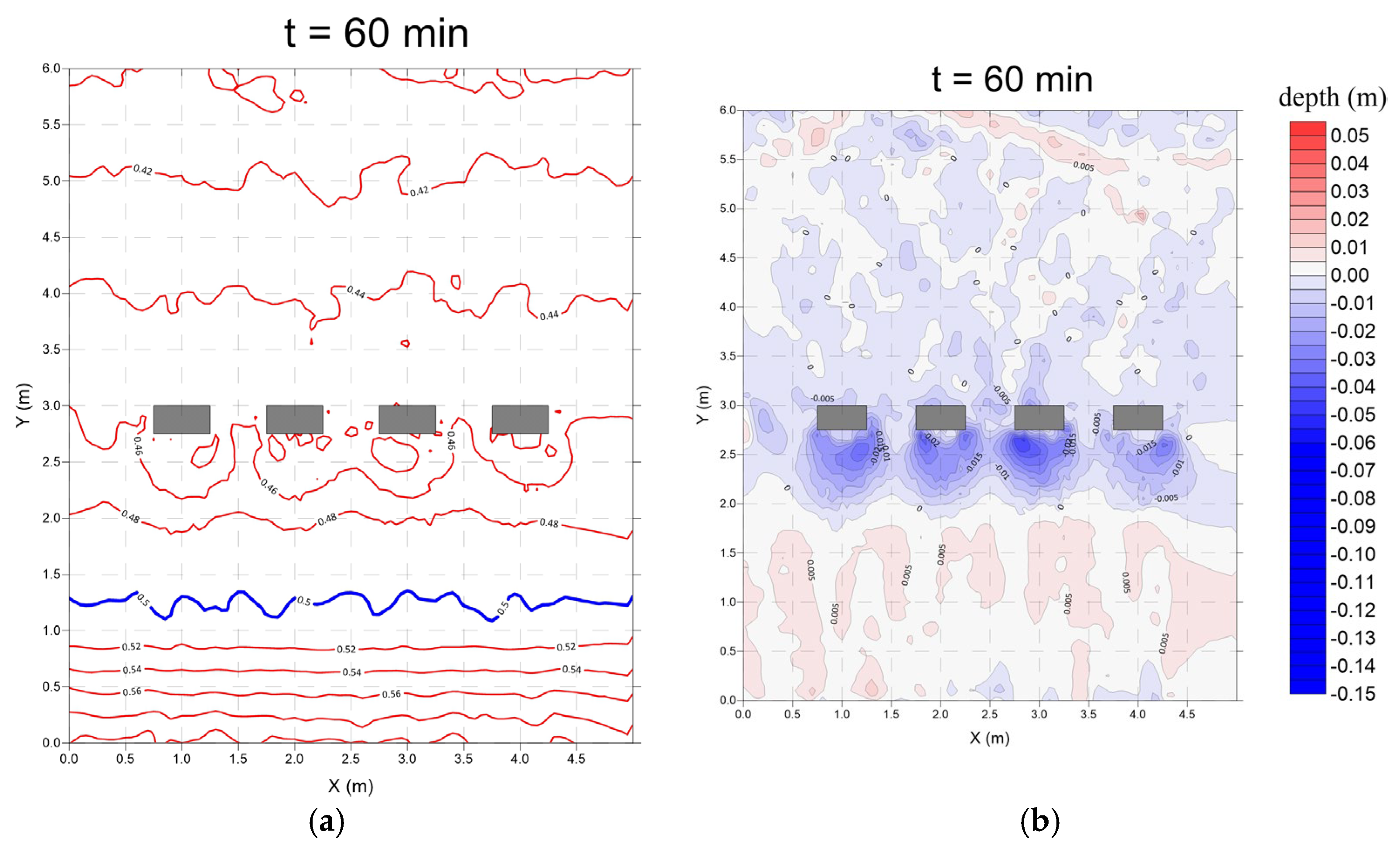
3.3. Derosion Lattices (Case 3)
- Monsoon wave
- 2.
- Typhoon wave
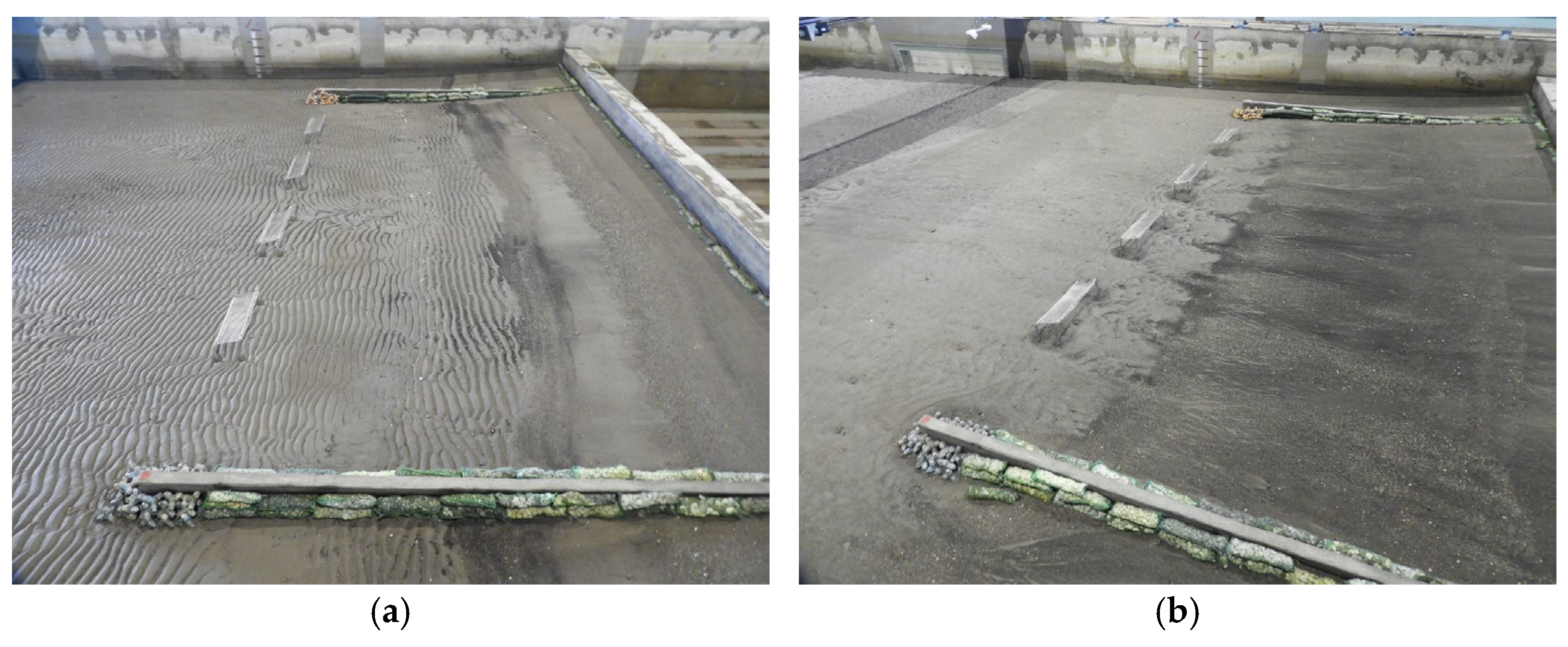
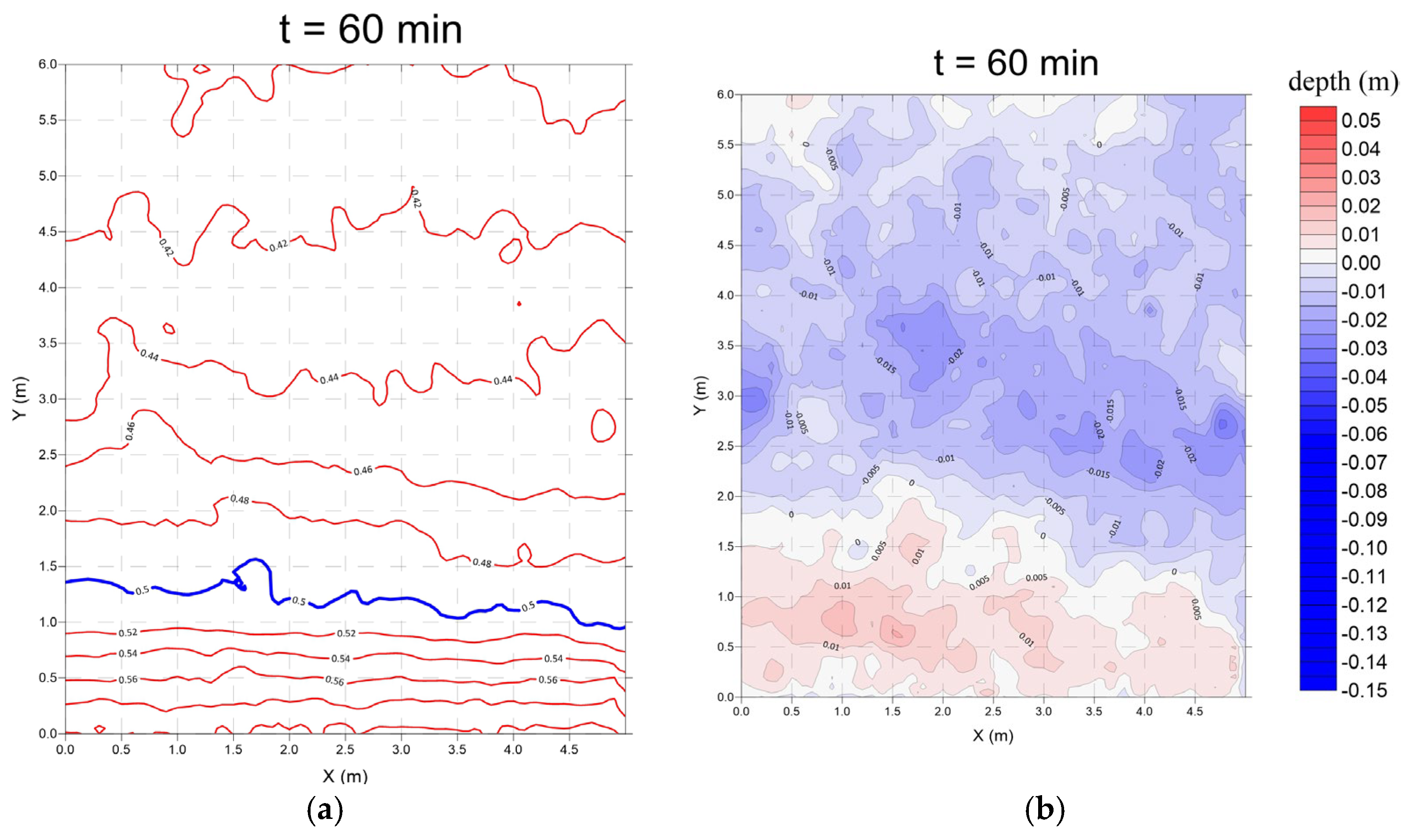
3.4. Seawall Combined with Submerged Breakwater (Case 4)
- Monsoon wave
- 2.
- Typhoon wave
4. Discussion on Sediment-Trapping Performance of Different Coastal Structures
5. Conclusions
- In the landward region, all three coastal protection structures showed significantly higher sediment retention compared to the no-structure case, under both conditions. The composite system exhibited the highest retention, submerged breakwaters ranked second, and derosion lattices had slightly lower retention;
- In the seaward region under typhoon wave conditions, all three structures showed notable improvements in sediment retention compared to the no-structure case, with the derosion lattice achieving the best performance. Under monsoon wave conditions, only the derosion lattice resulted in greater sediment retention than Case 1, while the other two structures performed worse than the no-structure case;
- Among the three structural types tested, the derosion lattice was the only configuration that achieved improved sediment retention on both the seaward and landward sides under all wave conditions, compared to the no-structure case. Considering its low construction cost, ease of installation, and consistent sediment-trapping performance, the derosion lattice serves as one viable option among modern coastal protection measures;
- In contrast to the findings of Lu [13], which reported reduced sediment-trapping performance and relative erosion on the seaward side of derosion lattices, this study demonstrates that the derosion lattices (Case 3) exhibited effective sediment-trapping performance even in the seaward region. This difference may be attributed to the use of variable water levels, a plan-view (3D) wave basin, and large-scale physical modeling in the present experiments;
- Under monsoon wave conditions, the submerged breakwaters and the composite system demonstrated relatively poor sediment retention on the seaward side. Although this was primarily caused by strong wave reflection commonly associated with hard engineering structures, differences in cross-sectional flow areas between structures may also have contributed. Due to limitations in the experimental design, the composite system tested in this study featured only a single and relatively narrow gap, resulting in the smallest flow cross-section among the three structures. Future studies are encouraged to examine modified composite systems with wider or multiple openings to enable a more balanced performance comparison;.
- In summary, the experimental results demonstrated that each coastal protection structure exhibited distinct performance characteristics depending on the wave conditions and spatial location. The derosion lattice showed relatively stable performance across both the seaward and landward regions, whereas the submerged breakwaters and the composite system performed well in the landward region but were affected by localized scour and wave reflection issues on the seaward side.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- LeMéhauté, B.; Oceanographic, L.P.; Tech, I.T. An Introduction to Hydrodynamics and Water Waves; Environmental Science Servies Administration: Boulder, CO, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.-C. The Effect of Coast Development on the Coastal Morphology; National Taiwan Ocean University: Keelung, Taiwan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.-Y. Effects of the Sediment Transport in Estuary on Coastal Topographic Changes; National Taiwan Ocean University: Keelung, Taiwan, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Water Resources Agency, MOEA. The Manual of Coastal Protection Facilities Planning and Design; Water Resources Agency, MOEA: Taichung, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, K.-T.; Kim, K.-H. A Study on the Effects of Morphological Changes Due to the Construction of Multiple Coastal Structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Qu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, M.; Liang, B. An experimental study on the evolution of beach profiles under different beach nourishment methods. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1381937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Kobayashi, N.; Cardenas, X.C. Comparison of Rock Seawall and Dune for Storm Damage Reduction. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2017, 1, sediment.31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.-R. Experimental Study of Morphological Evolution Due to Irregular Waves on a Gravel Beach; National Cheng Kung University: Tainan, Taiwan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vera-Cruz, D. Artificial Nourishment of Copacabana Beach. Coast. Eng. 1972, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunyakti, A. Beach Preservation by Means of Offshore Submerged Mound of Dredged Materials. In Proceedings of the Coastal Zone’87, Seattle, WA, USA, 26–29 May 1987; pp. 2461–2471. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, T.-H. An Experimental Field Study Using a Flexible High–Strength Net Breakwater for Shore Protection; National Cheng Kung University: Tainan, Taiwan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-Y. Experimental Study on the Shore Erosion and Deposition Evolution by Using Derosion Lattice; National Cheng Kung University: Tainan, Taiwan, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.-L. Experimental Study on the Effect of Shore Erosion and Deposition by Using Submerged Derosion Lattice; National Cheng Kung University: Tainan, Taiwan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau of Industrial Parks; Ministry of Economic Affairs. Final Report of the Annual Entrusted Planning and Feasibility Study Project: Integrated Development Plan and Technical Services for the Development of the Changhua Coastal Industrial Park; Sinotech Engineering Consultants, Ltd.: Taipei, Taiwan, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Unitech New Energy Engineering Co., Ltd. Environmental Impact Assessment Report for the Zhongneng Offshore Wind Farm Project; Commissioned by China Steel Power Corporation; Unitech New Energy Engineering Co., Ltd.: New Taipei, Taiwan, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ou, S.-H.; Hsu, T.-W. Similarity Laws for Coastal Movable Bed Models on Sloping Beaches. Harb. Technol. Q. 1985, 1, 33–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.-K. Coastal Engineering Hydraulic Model; Transportation Technology Research Center, MOTC: Taichung, Taiwan, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Yen, C.-C. Experimental Study of the Tide-Affecting Beach Profile Under Wave Action; National Sun Yat-sen University: Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zwamborn, J.A.; Fromme, G.A.W.; FitzPatrick, J.B. Underwater Mound for the Protection of Durban’s Beaches. Coast. Eng. 1970, 975–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, K. Nearshore Dynamics and Coastal Processes: Theory, Measurement, and Predictive Models; University of Tokyo Press: Tokyo, Japan, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sawaragi, T.; Deguchi, I.; Park, S.-K. Experimental Study on the Function of Submerged Breakwater to Control Cross-Shore Sediment Transport on Artificially Nourished Beaches. Coast. Eng. Jpn. 1988, 31, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.-T. Coastal Engineering; Chinese Institute of Civil and Hydraulic Engineering: Taipei, Taiwan, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Werf, I.; Van Gent, M.R.A. Gravel Beaches with Seawalls. Coast. Eng. Proc. 2011, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Return Period (Years) | Significant Wave Height, Hs (m) | Peak Period, Tp (s) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 3.65 | 8.02 |
| 25 | 6.32 | 10.56 |
| 50 | 7.35 | 11.39 |
| 100 | 8.32 | 12.12 |
| Highest High Water Level (m) | Highest Astronomical Tide (m) | Mean High Water Level (m) | Mean Sea Level (m) | Mean Low Water Level (m) | Lowest Astronomical Tide (m) | Lowest Low Water Level (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.728 | 2.563 | 1.839 | 0.343 | −1.194 | −2.150 | −2.379 |
| Category | Prototype | Model | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monsoon | Hs (m) | 2 | 0.0556 |
| Tp (s) | 7 | 1.17 | |
| Typhoon | Hs (m) | 7.35 | 0.2041 |
| Tp (s) | 11.39 | 1.90 | |
| Submerged unit weight (m) | 1.65 | 1.05 | |
| Median particle diameter (mm) | 0.24 | 0.15 | |
| Bed slope | 1/200 | 1/50 | |
| Monsoon time scale | 1 year | 6 hr | |
| Typhoon time scale | 7 hr | 1 hr | |
| Highest high water level | 2.728 m | 5.456 cm (55.5 cm) | |
| Mean sea level | 0.343 m | 0.686 cm (50.7 cm) | |
| Lowest low water level | −2.379 m | −4.758 cm (45.2 cm) | |
| Monsoon Wave | Seaward of the Structures (Y = 2.75~5.5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| deposition area (m2) | 2.62/19.05% | 1.14/8.29% | 4.67/33.96% | 1.06/7.71% |
| erosion area (m2) | 10.51/76.44% | 11.99/87.20% | 8.45/61.45% | 12.36/89.89% |
| unchanged area (m2) | 0.62/4.51% | 0.62/4.51% | 0.63/4.59% | 0.33/2.40% |
| deposition volume (m3) | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.016 |
| erosion volume (m3) | −0.062 | −0.089 | −0.042 | −0.143 |
| total volume S (m3) | −0.056 | −0.087 | −0.024 | −0.127 |
| Monsoon Wave | Landward of the Structures (Y = 0~2.75) | |||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| deposition area (m2) | 3.80/27.64% | 4.83/35.13% | 3.96/28.80% | 6.03/43.85% |
| erosion area (m2) | 9.33/67.85% | 8.30/60.36% | 9.16/66.62% | 7.12/51.78% |
| unchanged area (m2) | 0.62/4.51% | 0.62/4.51% | 0.63/4.58% | 0.60/4.37% |
| deposition volume (m3) | 0.017 | 0.028 | 0.012 | 0.062 |
| erosion volume (m3) | −0.092 | −0.060 | −0.053 | −0.042 |
| total volume L (m3) | −0.075 | −0.032 | −0.041 | 0.020 |
| total volume S+L (m3) | −0.131 | −0.119 | −0.065 | −0.107 |
| Typhoon Wave | Seaward of the Structures (Y = 2.75~5.5) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| deposition area (m2) | 0.07/0.51% | 3.76/27.35% | 4.99/36.29% | 5.12/37.24% |
| erosion area (m2) | 13.05/94.91% | 9.38/68.22% | 8.13/59.13% | 8.25/60.00% |
| unchanged area (m2) | 0.63/4.58% | 0.61/4.43% | 0.63/4.58% | 0.38/2.76% |
| deposition volume (m3) | 0.000 | 0.016 | 0.009 | 0.031 |
| erosion volume (m3) | −0.150 | −0.133 | −0.022 | −0.104 |
| total volume S (m3) | −0.150 | −0.117 | −0.013 | −0.073 |
| Typhoon Wave | Landward of the Structures (Y = 0~2.75) | |||
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 4 | |
| deposition area (m2) | 7.54/54.84% | 7.32/53.24% | 9.46/68.80% | 10.09/73.38% |
| erosion area (m2) | 5.58/40.58% | 5.79/42.11% | 3.68/26.76% | 3.07/22.33% |
| unchanged area (m2) | 0.63/4.58% | 0.64/4.65% | 0.61/4.44% | 0.59/4.29% |
| deposition volume (m3) | 0.053 | 0.071 | 0.040 | 0.117 |
| erosion volume (m3) | −0.059 | −0.071 | −0.041 | −0.040 |
| total volume L (m3) | −0.006 | 0.000 | −0.001 | 0.077 |
| total volume S+L (m3) | −0.156 | −0.117 | −0.014 | 0.004 |
| Wave Condition | Case | Seaward of the Structures | Landward of the Structures |
|---|---|---|---|
| monsoon | 2 | −55.36% | 57.33% |
| 3 | 57.14% | 45.33% | |
| 4 | −126.79% | 126.67% | |
| typhoon | 2 | 22.00% | 100.00% |
| 3 | 91.33% | 83.33% | |
| 4 | 51.33% | 1383.33% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, H.-N.; Chen, H.-H.; Yang, R.-Y. Experimental Study on the Sediment-Trapping Performance of Different Coastal Protection Structures in a High-Tidal Range Area. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061022
Hung H-N, Chen H-H, Yang R-Y. Experimental Study on the Sediment-Trapping Performance of Different Coastal Protection Structures in a High-Tidal Range Area. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(6):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061022
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Hao-Nan, Hsin-Hung Chen, and Ray-Yeng Yang. 2025. "Experimental Study on the Sediment-Trapping Performance of Different Coastal Protection Structures in a High-Tidal Range Area" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 6: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061022
APA StyleHung, H.-N., Chen, H.-H., & Yang, R.-Y. (2025). Experimental Study on the Sediment-Trapping Performance of Different Coastal Protection Structures in a High-Tidal Range Area. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(6), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13061022










