A Saturation Adaptive Nonlinear Integral Sliding Mode Controller for Ship Permanent Magnet Propulsion Motors
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Enhanced Sliding Mode Control Design:
- It proposes a nonlinear sliding mode surface function combined with an adaptive saturation-index reaching law.
- It effectively suppresses control chattering while improving the response speed of traditional SMCs.
- It incorporates adaptive mechanisms to enhance load variation robustness, significantly reducing load disturbance impacts.
- (2)
- Experimental Validation:
- It demonstrates the SANI-SMC’s effectiveness through the experimental platform for ship electric propulsion.
- It verifies the SANI-SMC’s superior performance over conventional PI controllers and SMCs in precision speed tracking, disturbance rejection capability, and overall system stability.
2. Mathematical Modeling of PMSM Electric Propulsion System
2.1. PMSM Model
2.2. Novel Adaptive Gain Saturation Exponential Approaching Rate
2.3. Integral Nonlinear Sliding Mode Surface
3. Novel Sliding Mode Speed Control
3.1. Design of the SANI-SMC Controller
3.2. Design of Novel Sliding Mode Control
4. Experimental Verification of the Control Strategy
4.1. Experimental Setup
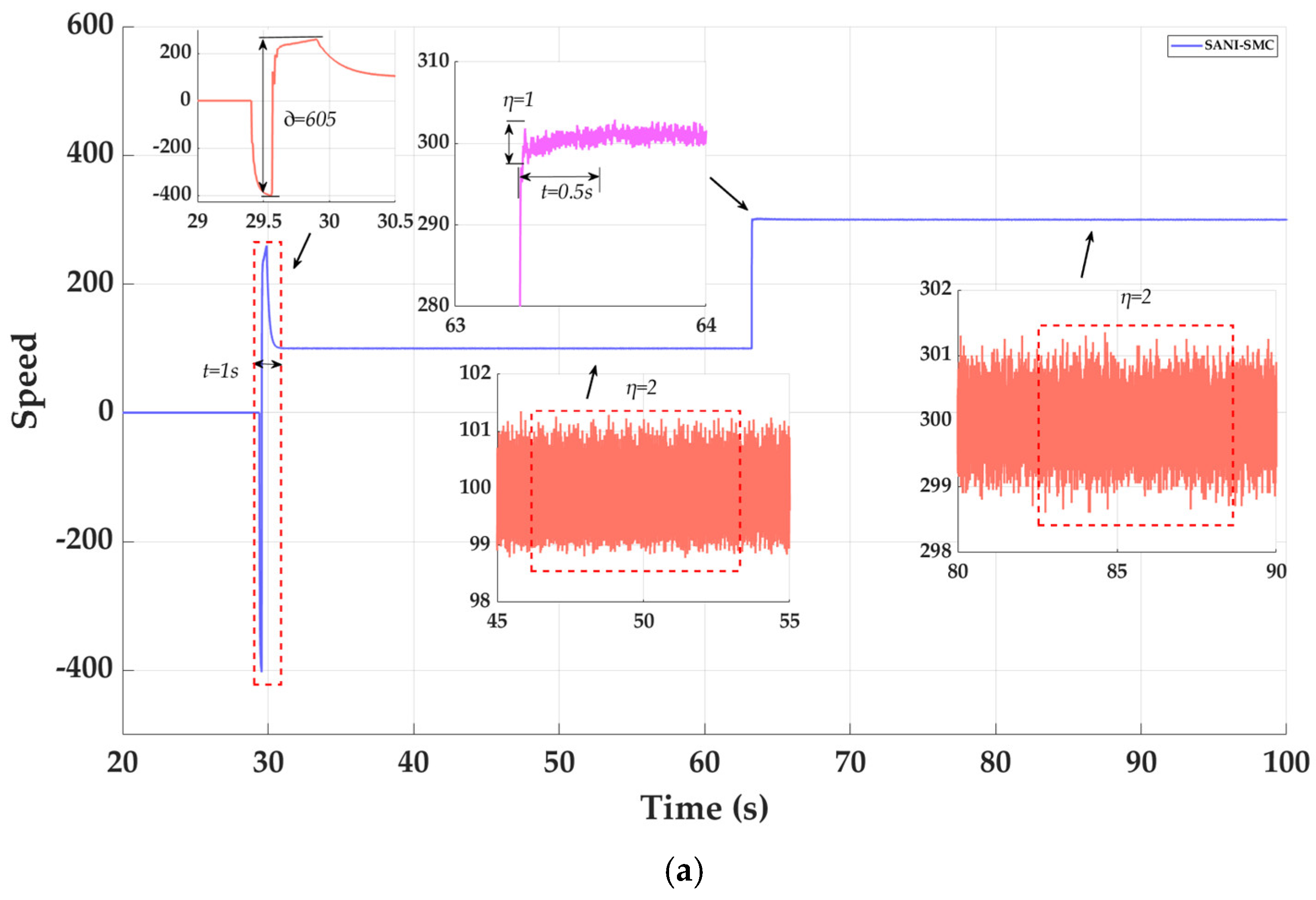
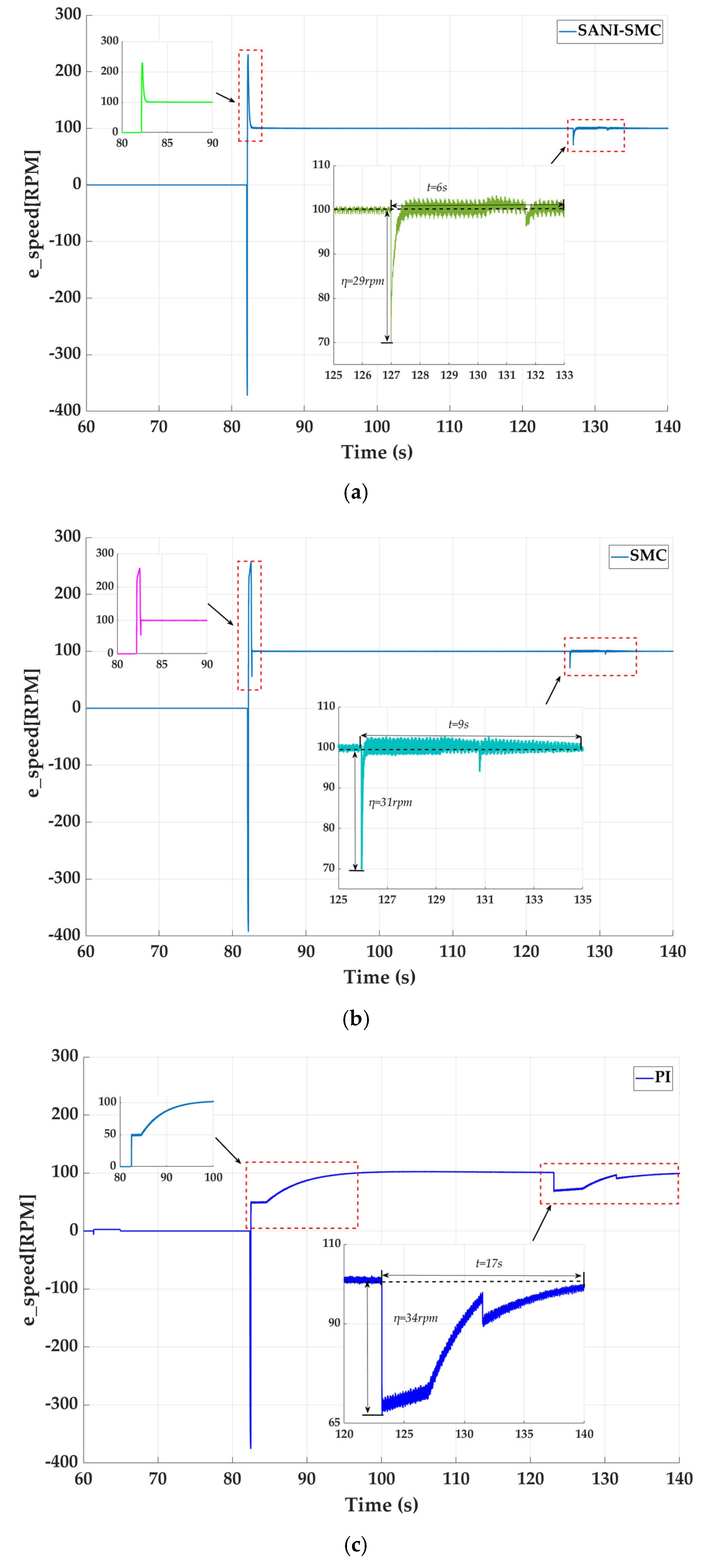
4.2. Comparison of Speed Tracking Performance for Three Controllers
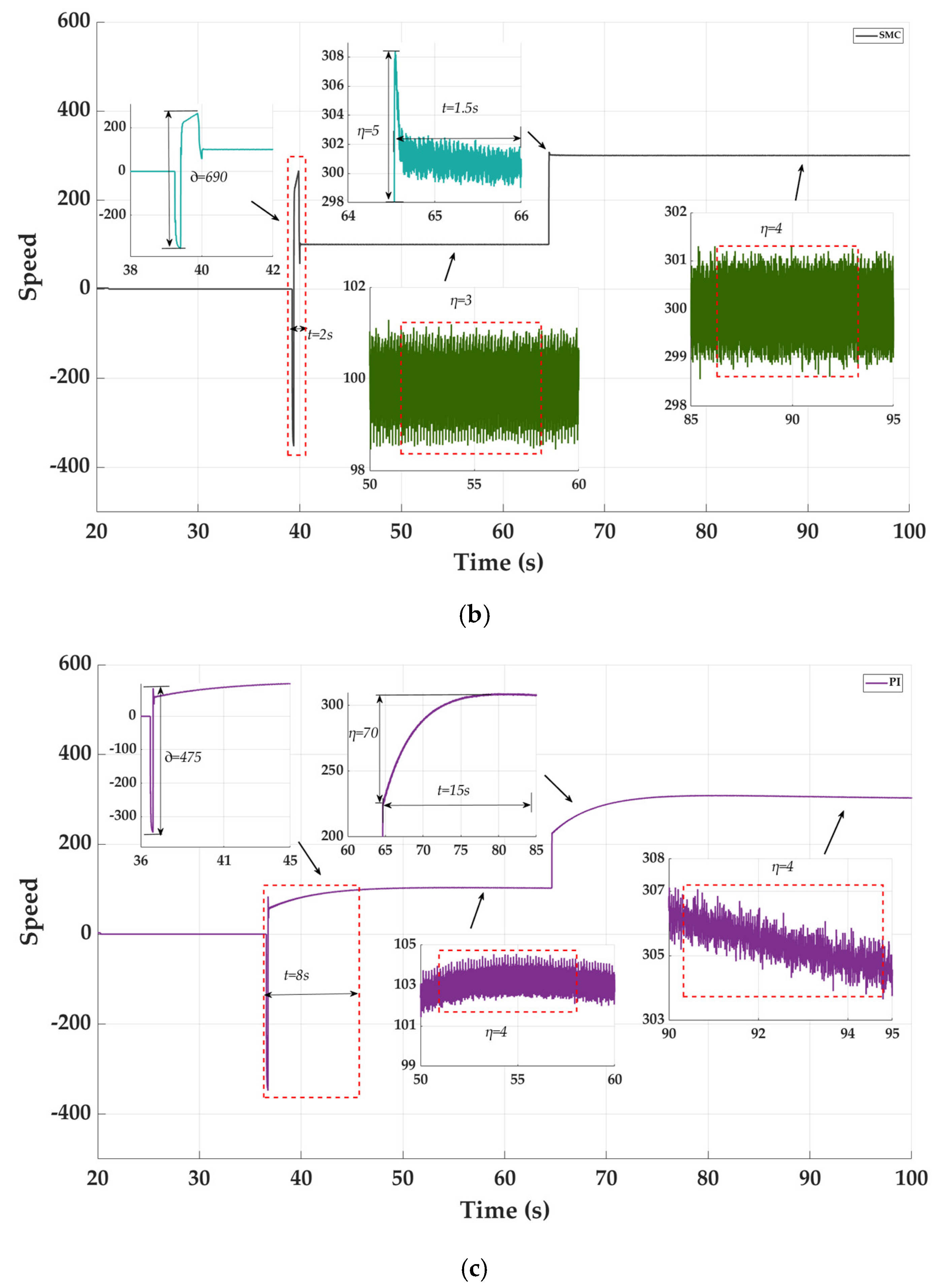
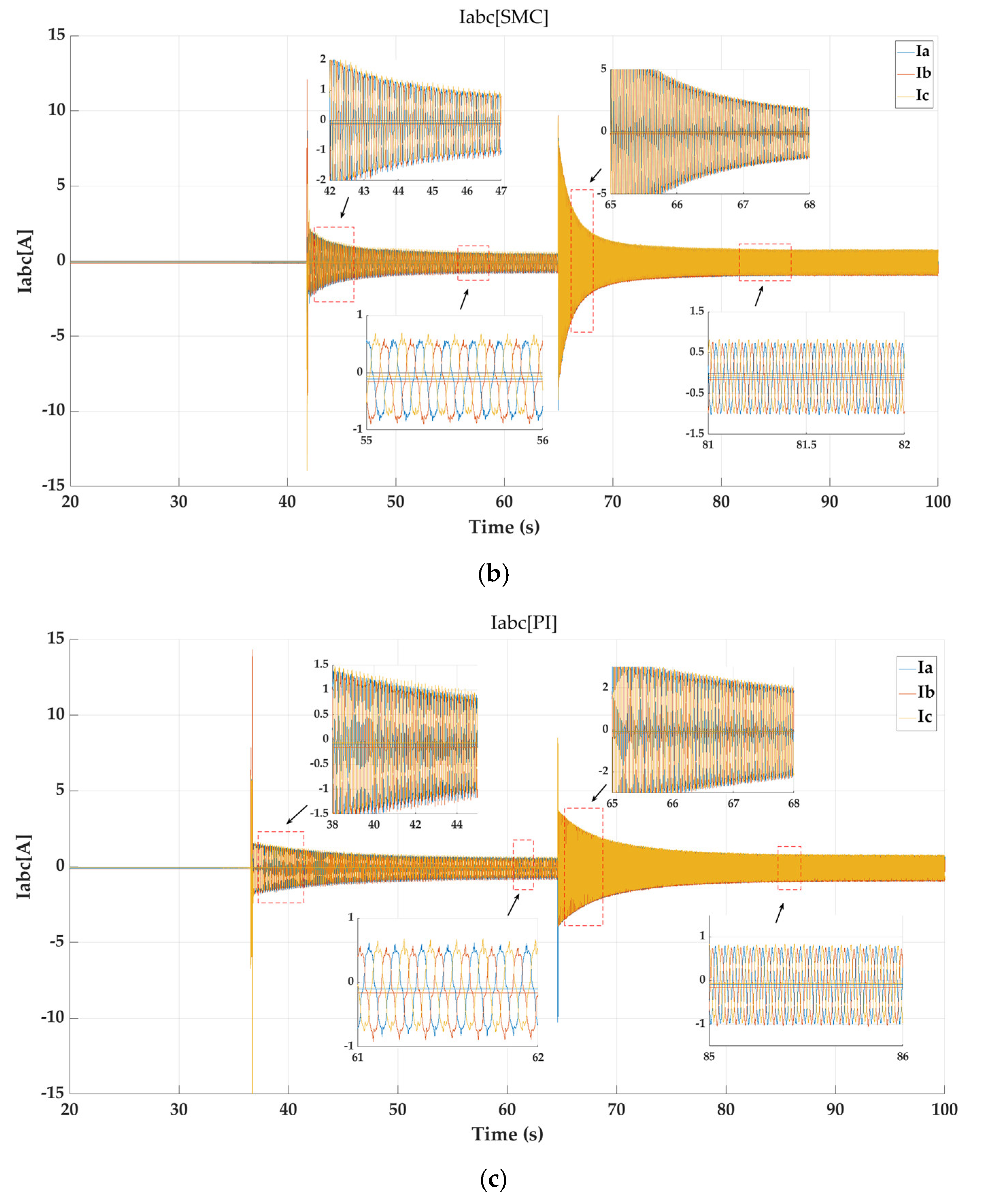
4.3. Comparison of Loading Experiments for Three Controllers
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Skowron, M.; Orlowska-Kowalska, T.; Kowalski, C.T. Detection of permanent magnet damage of PMSM drive based on direct analysis of the stator phase currents using convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 13665–13675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errouissi, R.; Ouhrouche, M.; Chen, W.H.; Trzynadlowski, A.M. Robust nonlinear predictive controller for permanent-magnet synchronous motors with an optimized cost function. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 59, 2849–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, S.A.; Kouro, S.; Vazquez, S.B.; Goetz, S.M.; Lizana, R.; Romero-Cadaval, E. Electric vehicle charging infrastructure: From grid to battery. IEEE Ind. Electron. Mag. 2021, 15, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, E.; Moallem, M.; Parsapour, A.; Fahimi, B. Opportunities and challenges of switched reluctance motor drives for electric propulsion: A comparative study. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 3, 58–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xue, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhang, L.; Ma, W.; Hua, W. Low-complexity multivectorbased model predictive torque control for PMSM with voltage preselection. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 11726–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, W.; Zhou, R.; Dai, W.; Wu, S.; Qiu, P.; Yin, Y.; Jia, N.; Yi, J.; Huang, G. Model-free fast integral terminal sliding-mode control method based on improved fast terminal sliding-mode observer for PMSM with unknown disturbances. ISA Trans. 2023, 143, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursini, M.; Parasiliti, F.; Zhang, D. Real-time gain tuning of PI controllers for high-performance PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2002, 38, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, W.H.; Li, S.; Guo, L.; Yan, Y. Disturbance/uncertainty estimation and attenuation techniques in PMSM drives—A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 3273–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, L.; Ji, W. Improved non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control with disturbance observer for PMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2753–2762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubagotti, M.; Estrada, A.; Castaños, F.; Ferrara, A.; Fridman, L. Integral sliding mode control for nonlinear systems with matched and unmatched perturbations. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2011, 56, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghrouche, S.; Plestan, F.; Glumineau, A. Higher order sliding mode control based on integral sliding mode. Automatica 2007, 43, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yang, C.; Pan, L.; Yu, H. Integral sliding mode control: Performance, modification, and improvement. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 14, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, L.; Vazquez, S.; Xu, R.; Dong, Z.; Liu, J.; Leon, J.I.; Wu, L.; Franquelo, L.G. Disturbance and uncertainty attenuation for speed regulation of PMSM servo system using adaptive optimal control strategy. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 3410–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhao, K.; Sun, L. Nonlinear speed control for PMSM system using sliding-mode control and disturbance compensation techniques. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 1358–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zong, K.; Liu, H. A composite speed controller based on a second-order model of permanent magnet synchronous motor system. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2011, 33, 522–541. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseinabadi, P.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Pota, H.R.; Kermadi, M. Chattering-Free Fixed-Time Robust Sliding Mode Controller for Grid-Connected Inverters Under Parameter Variations. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2024, 12, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinabadi, P.A.; Pota, H.; Mekhilef, S.; Konstantinou, G.; Negnevitsky, M.; Mohamadian, S. Three-Phase Phase-Locked Loop Based on Terminal Sliding Mode for Grid-Connected Inverters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2024, 72, 4776–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinabadi, P.A.; Mekhilef, S.; Pota, H.; Kermadi, M.; Konstantinou, G.; Negnevitsky, M. Finite-Time Robust Controller Using Sliding Mode Approach for Grid-Connected Inverters Under Unbalanced and Weak Grids. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmas, C.; Ustun, O. A hybrid controller for the speed control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. Control Eng. Pract. 2008, 16, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; Liu, L.; Ding, W.; Liang, D.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Zhao, X. Novel nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for a PMSM chaotic system with extended state observer and tracking differentiator. J. Vib. Control 2017, 23, 2478–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Son, J.B.; Lee, J.M. PMSM speed controller using switching algorithm of PD and Sliding mode control. In Proceedings of the 2009 ICCAS-SICE, Fukuoka, Japan, 18–21 August 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1260–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Jia, C. Robust speed controller design for permanent magnet synchronous motor drives based on sliding mode control. Energy Procedia 2016, 88, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Long, H. Self organizing fuzzy sliding mode controller for the position control of a permanent magnet synchronous motor drive. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2011, 2, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tao, R.; Zhang, Z.X.; Chien, Y.-R.; Bai, J. PMSM non-singular fast terminal sliding mode control with disturbance compensation. Inf. Sci. 2023, 642, 119040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, S.; Huang, H. Adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode control for permanent magnet synchronous motor based on disturbance observer. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 153791–153798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
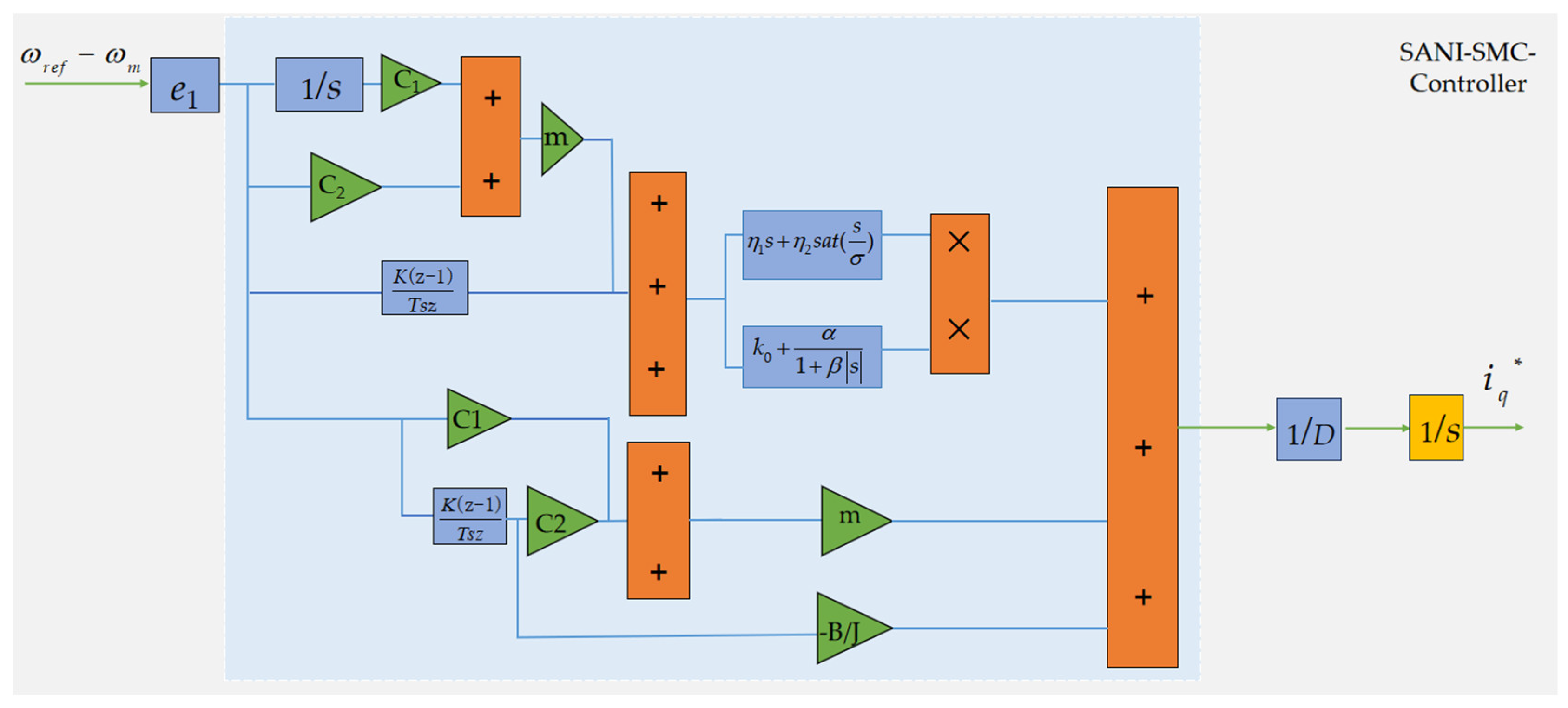
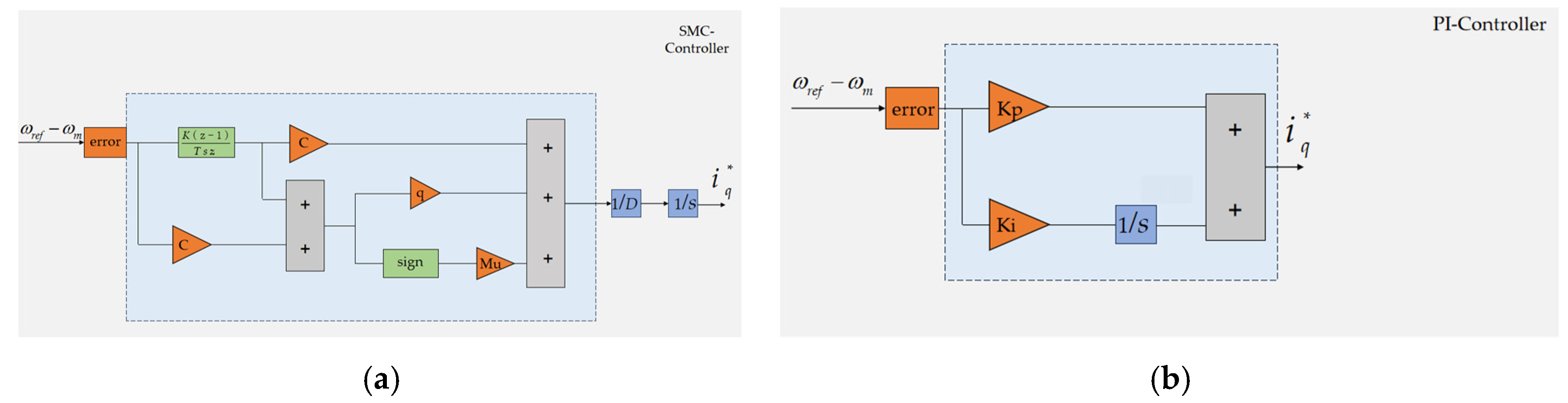
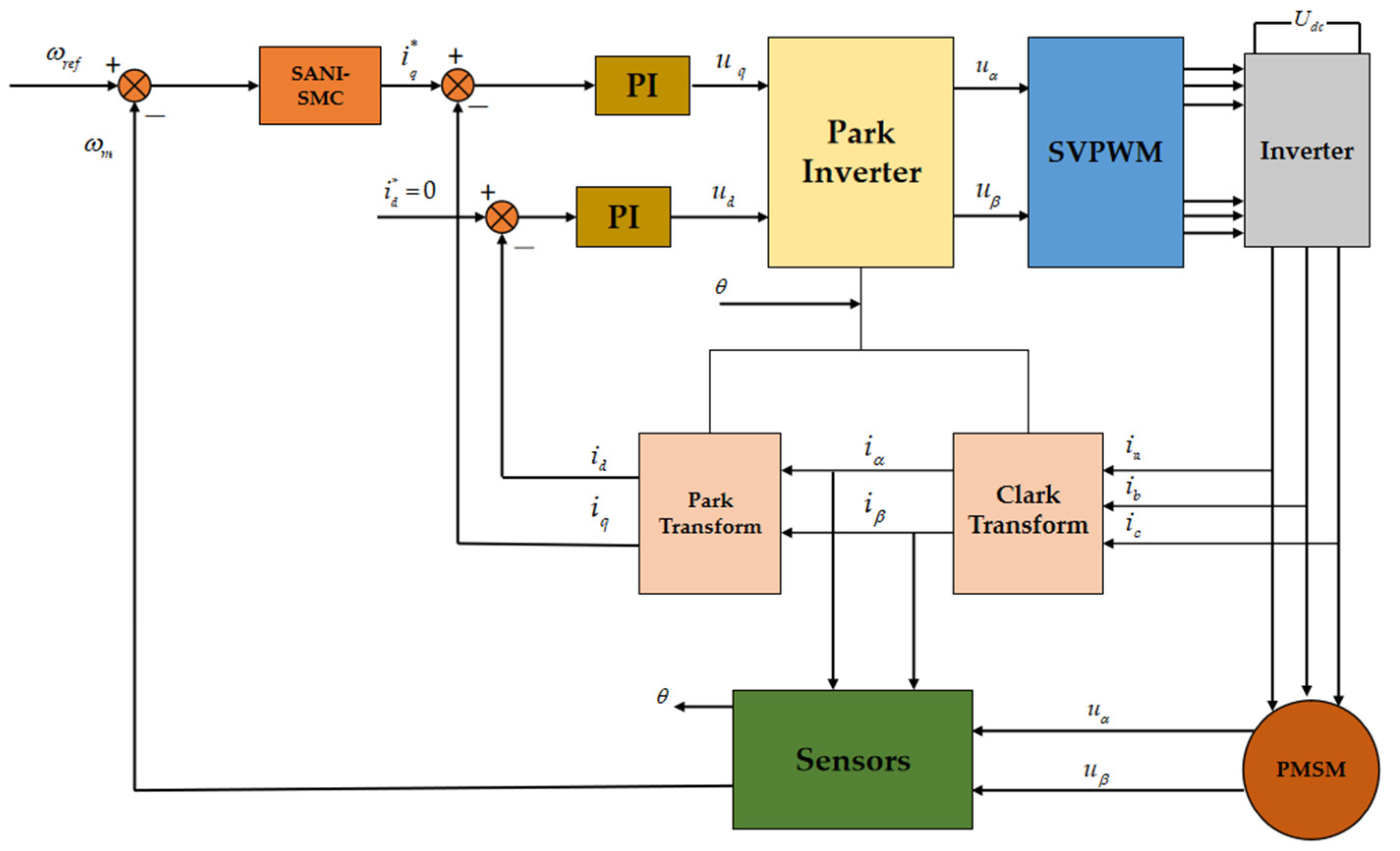
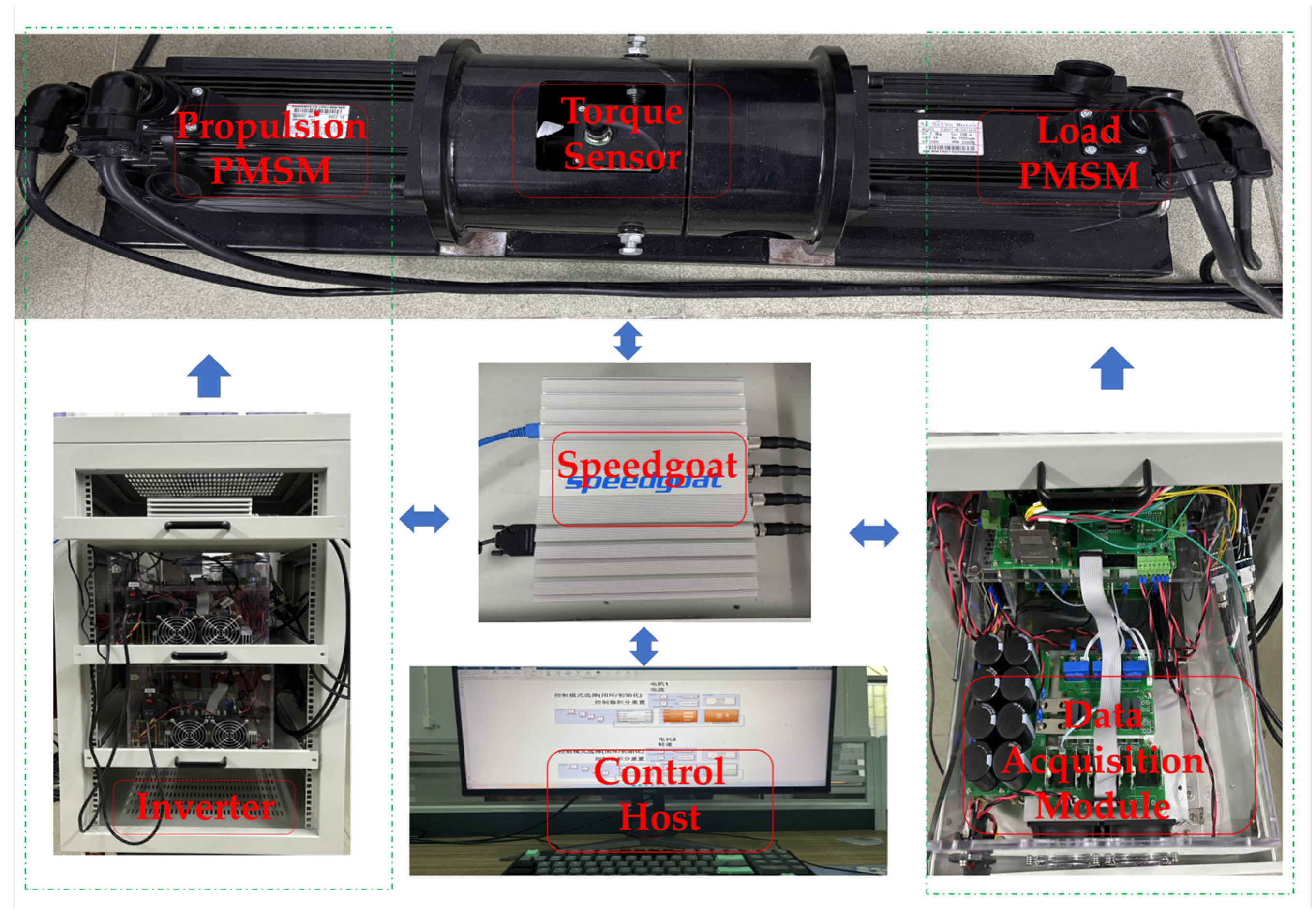

| Symbol | Quantity | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Rs | Data stator resistance | 1.29 |
| f | Rated frequency | 100 Hz |
| N | Rated speed | 500 rpm |
| Ld | d-axis inductance | 2.53 mH |
| Lq | q-axis inductance | 2.53 mH |
| Pn | Number of pole-pairs | 4 |
| p | Rated power | 1.5 kw |
| J | Moment of inertia | 0.00194 kg·m2 |
| φf | Permanent magnet flux linkage | 0.2 Wb |
| Status | Unit | SANI-SMC | SMC | PI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Startup Status | ∂ (rpm) | 605 | 690 | 475 |
| η (rpm) | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| t (s) | 1 | 2 | 8 | |
| Acceleration state | η (rpm) | 1 | 5 | 70 |
| t (s) | 0.5 | 1.5 | 15 |
| Controller | Response Time (s) | Speed Fluctuation (rpm) |
|---|---|---|
| SNIA-SMC | 6 | 29 |
| SMC | 9 | 31 |
| PI | 17 | 34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, P.; Jia, B.; Li, R.; Xu, Y. A Saturation Adaptive Nonlinear Integral Sliding Mode Controller for Ship Permanent Magnet Propulsion Motors. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050976
Wang X, Liu Z, Zhou P, Jia B, Li R, Xu Y. A Saturation Adaptive Nonlinear Integral Sliding Mode Controller for Ship Permanent Magnet Propulsion Motors. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):976. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050976
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xi, Zhaoting Liu, Peng Zhou, Baozhu Jia, Ronghui Li, and Yuanyuan Xu. 2025. "A Saturation Adaptive Nonlinear Integral Sliding Mode Controller for Ship Permanent Magnet Propulsion Motors" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050976
APA StyleWang, X., Liu, Z., Zhou, P., Jia, B., Li, R., & Xu, Y. (2025). A Saturation Adaptive Nonlinear Integral Sliding Mode Controller for Ship Permanent Magnet Propulsion Motors. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 976. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050976






