Microbial and Functional Gene Dynamics in Long-Term Fermented Mariculture Sediment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction from Sediment Samples
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Calculation of Community Niche Characteristics
2.5. Functional Gene Annotation
2.6. Data Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Occurrence Characteristics of the Microbiome in Mariculture Sediments with Different Natural Fermentation Durations
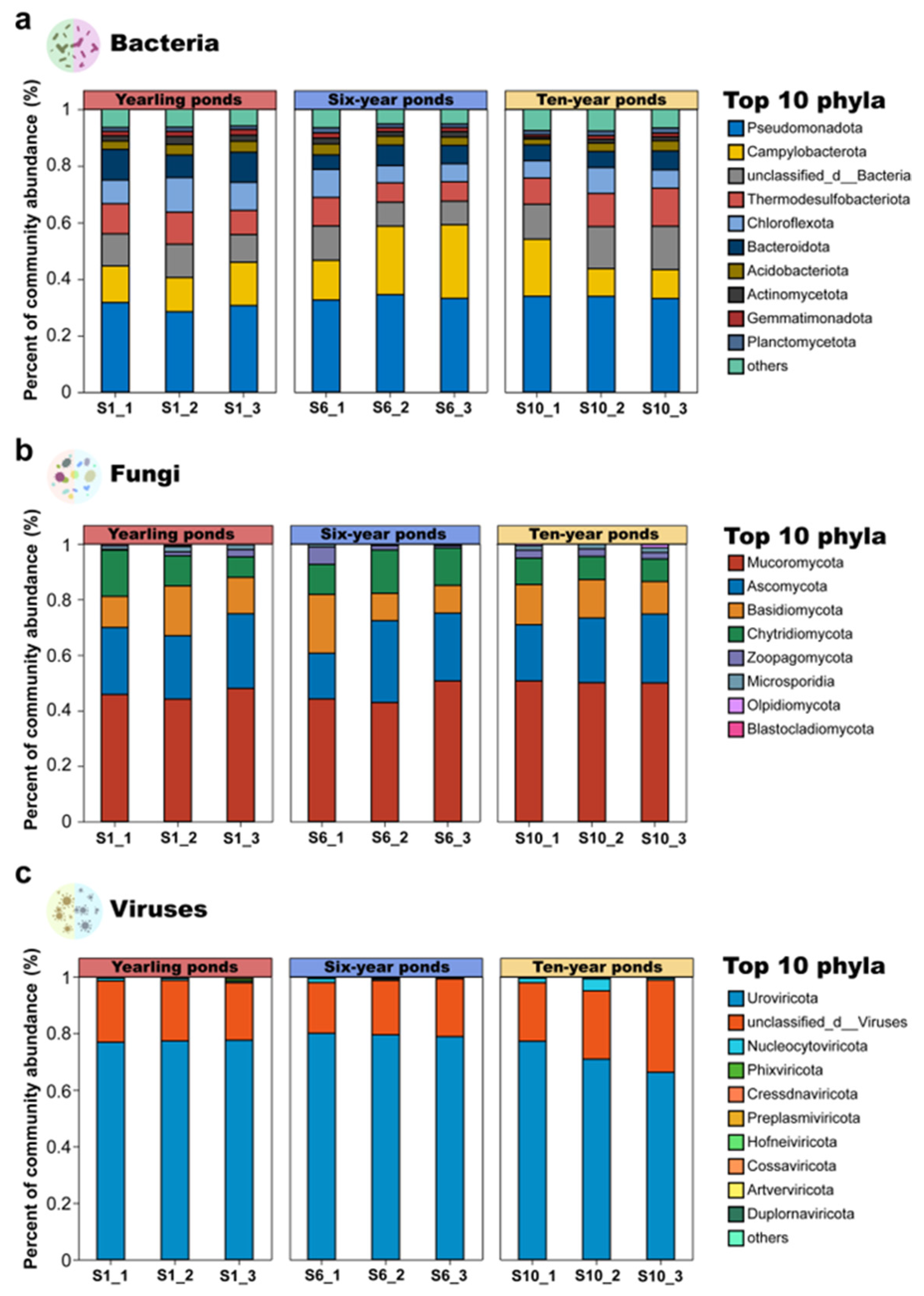
3.1.1. Microbial Community Composition
3.1.2. Microbial Community Diversity
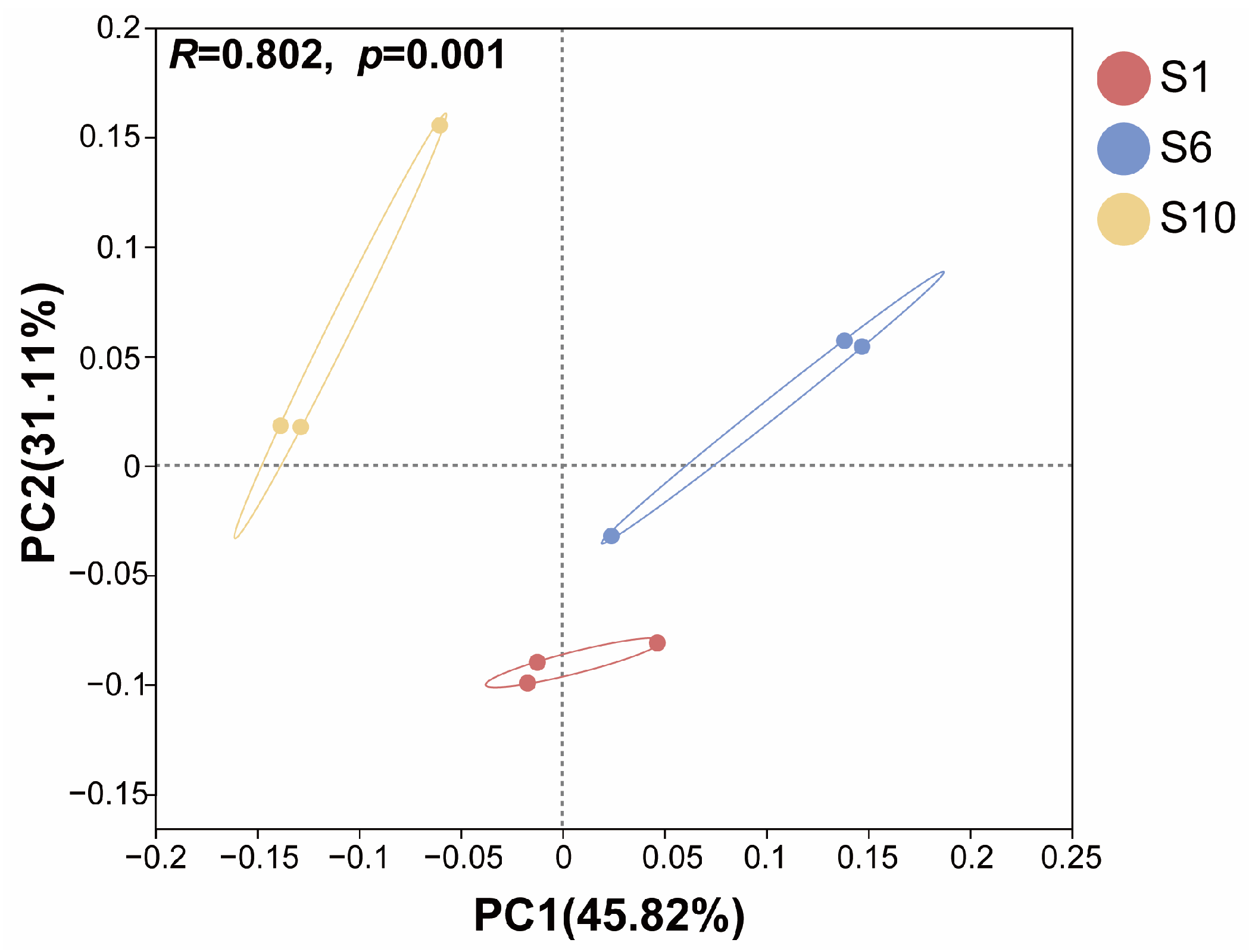
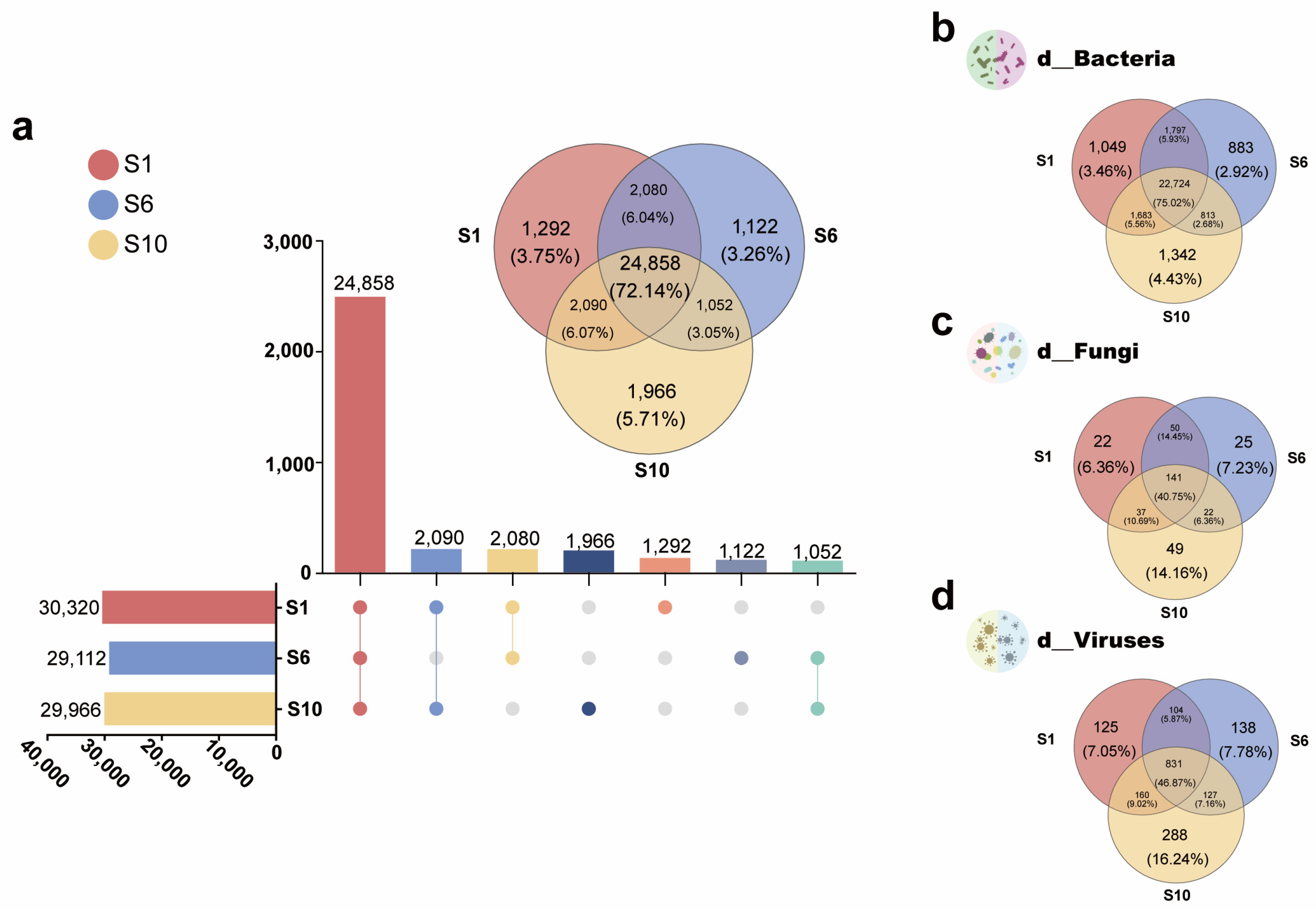
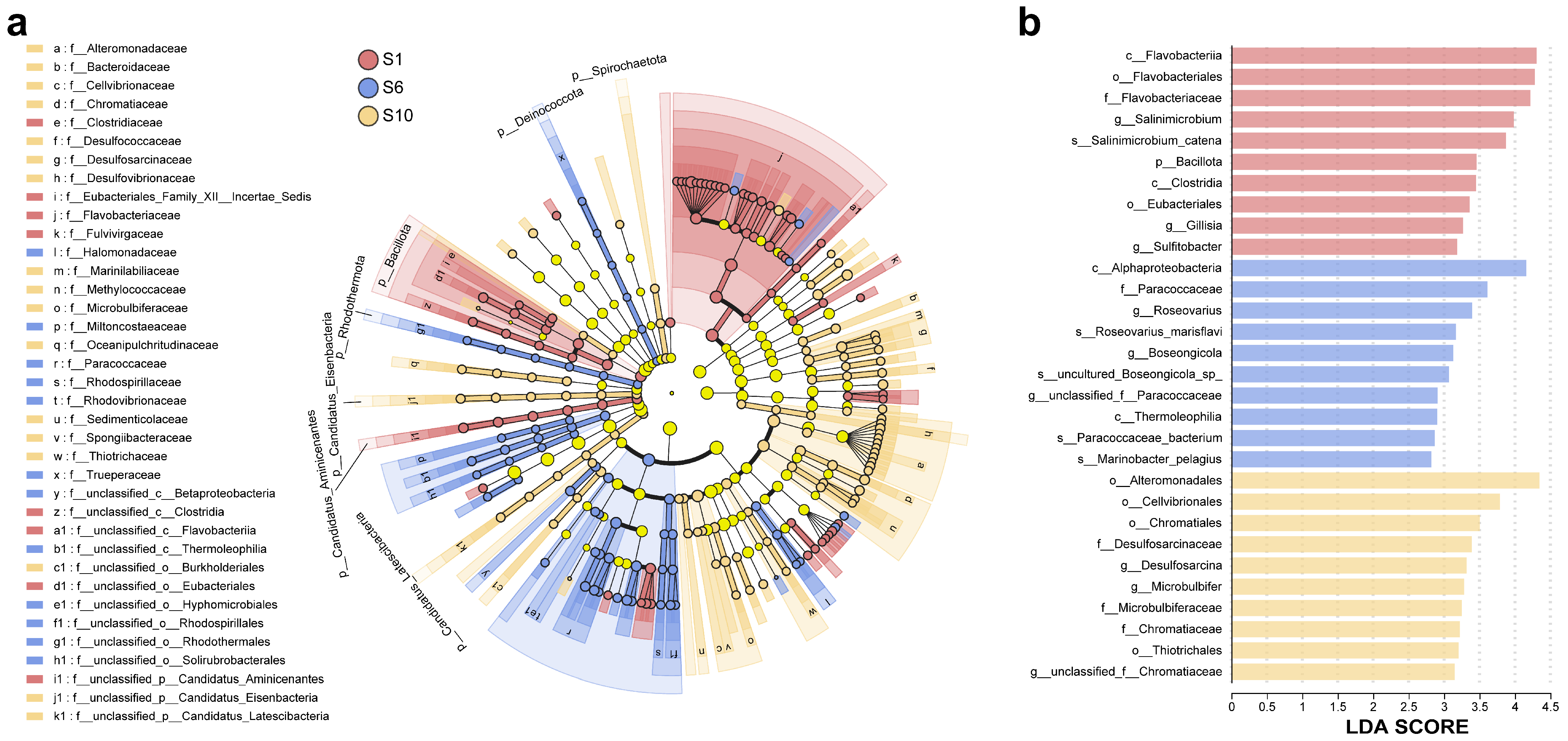
3.1.3. Differences Among Microbiomes of Mariculture Sediments with Different Fermentation Durations
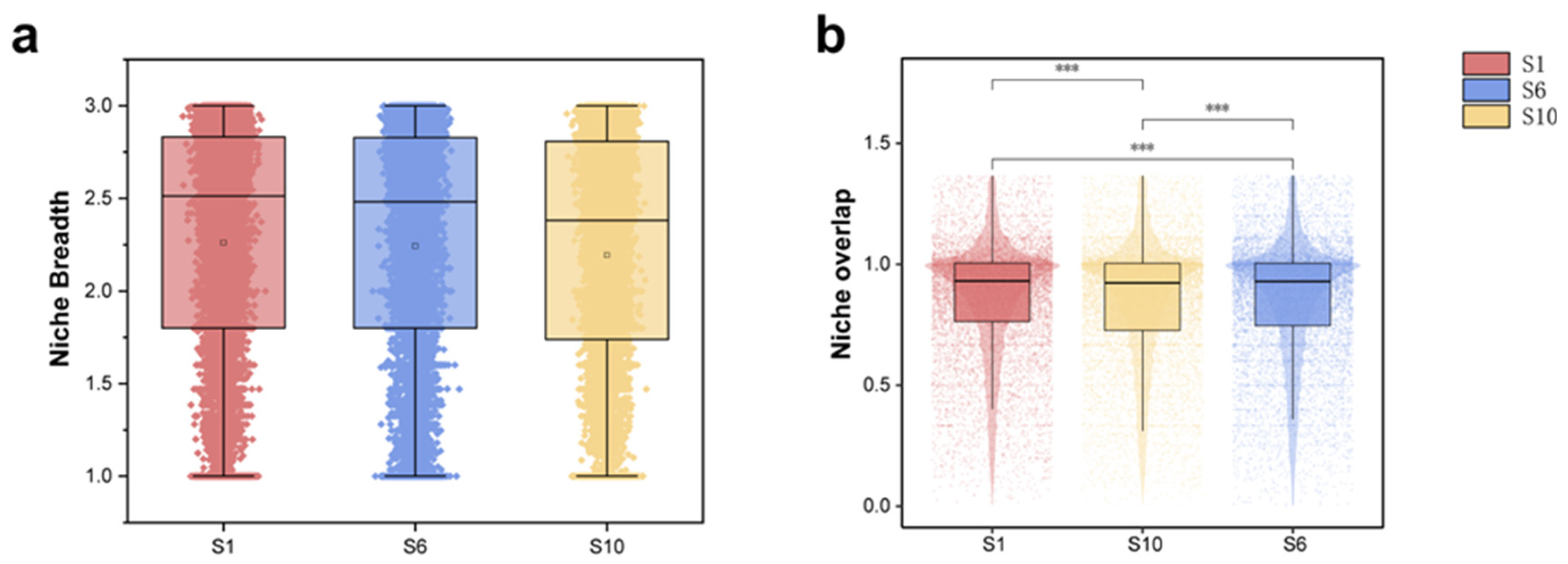
3.2. Niche Characteristics of the Microbiome in Mariculture Sediments with Different Natural Fermentation Durations
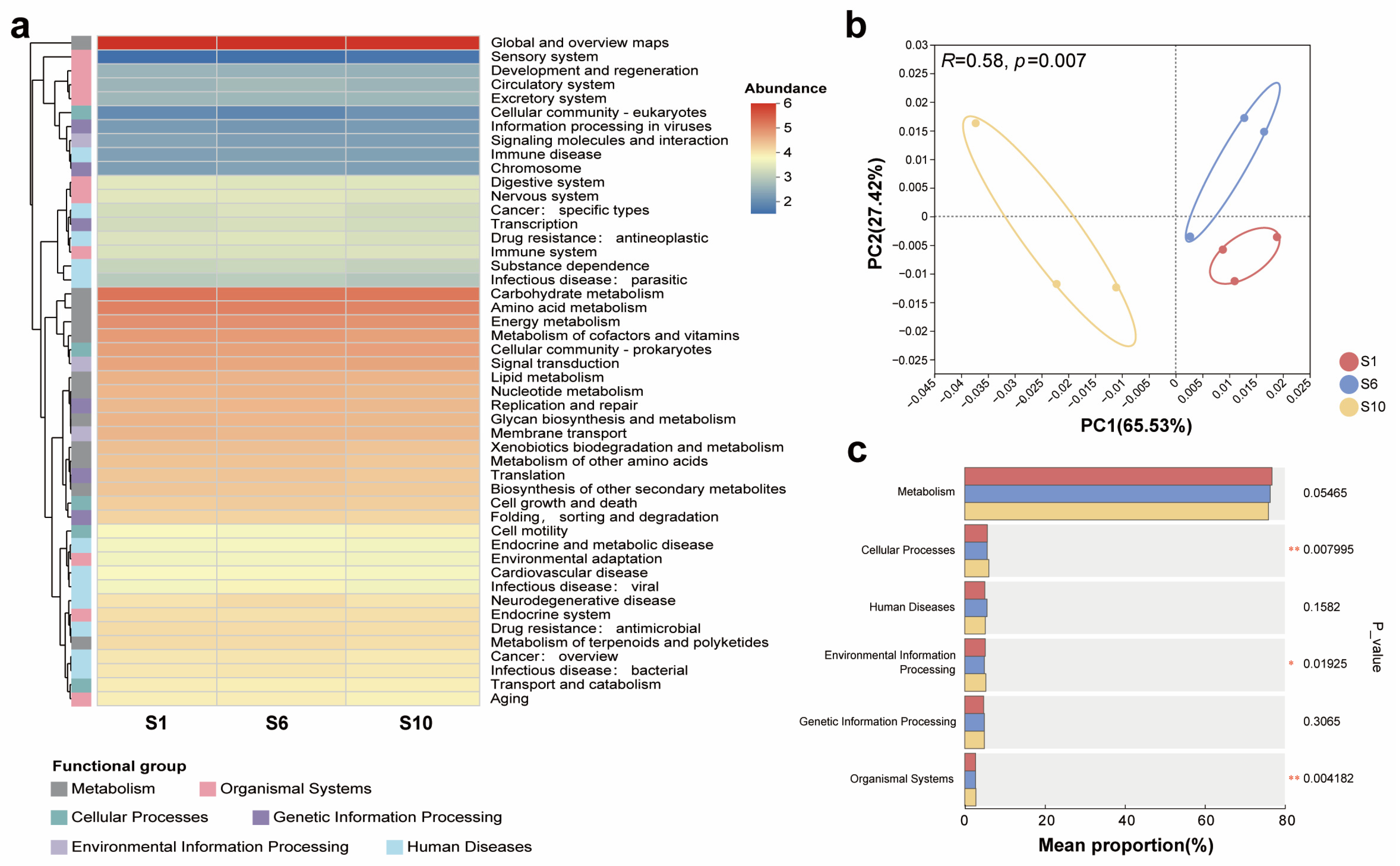
3.3. Overview of the Occurrence Characteristics of Functional Genes in Mariculture Sediments with Different Natural Fermentation Durations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, C.E.; McNevin, A.A.; Davis, R.P. The contribution of fisheries and aquaculture to the global protein supply. Food Secur. 2022, 14, 805–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Free, C.M.; Cabral, R.B.; Froehlich, H.E.; Battista, W.; Ojea, E.; O’Reilly, E.; Palardy, J.E.; García Molinos, J.; Siegel, K.J.; Arnason, R.; et al. Expanding ocean food production under climate change. Nature 2022, 605, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.-L.; Cao, L.; Liu, W.-J.; Huang, M.; Sun, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Yu, S.-E.; Zhou, Y.-G.; Li, L.; Dong, Y.-W. System-specific aquaculture annual growth rates can mitigate the trilemma of production, pollution and carbon dioxide emissions in China. Nat. Food 2025, 6, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Wei, D.; Hou, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Weng, S.; He, J.; Huang, Z. Sediment microbiota in polyculture of shrimp and fish pattern is distinctive from those in monoculture intensive shrimp or fish ponds. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Dong, X.; Luo, C.; Xu, J. Enrichment of organic carbon increases the flux of phosphorus from sediment in mariculture ponds. Aquaculture 2023, 565, 739148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, C.; Hassenrück, C.; Gärdes, A.; Conaco, C. Microbial community composition of sediments influenced by intensive mariculture activity. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yao, C.; Zhang, B.; Tan, W.; Gong, J.; Wang, G.-y.; Zhao, J.; Lin, X. Dynamics of Benthic Nitrate Reduction Pathways and Associated Microbial Communities Responding to the Development of Seasonal Deoxygenation in a Coastal Mariculture Zone. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 15014–15025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Yang, Z.; Dou, S. Microplastic pollution in the environment and organisms of Xiangshan Bay, East China Sea: An area of intensive mariculture. Water Res. 2022, 212, 118117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Liu, G. Fishmeal Application Induces Antibiotic Resistance Gene Propagation in Mariculture Sediment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10850–10860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongsamer, T.; Neamchan, R.; Blackburn, A.; Acharya, K.; Sutheeworapong, S.; Tirachulee, B.; Pattanachan, P.; Vinitnantharat, S.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Su, J.-Q.; et al. Environmental antimicrobial resistance is associated with faecal pollution in Central Thailand’s coastal aquaculture region. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Sun, M.; Peng, L.; Dai, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, G.; Tao, L.; Zhang, H. Reduction of nutrient fluxes across the sediment–water interface and nutrient accumulation in lotus-fish co-culture aquaculture ponds. Aquac. Int. 2024, 32, 7683–7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Dong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhou, T. Heavy metal pollution in urban river sediment of different urban functional areas and its influence on microbial community structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Xu, R.-Z.; Shen, X.-X.; Gao, P.; Xue, Z.-X.; Huang, D.-C.; Jin, G.-Q.; Li, C.; Cao, J.-S. The response of sediment microbial communities to temporal and site-specific variations of pollution in interconnected aquaculture pond and ditch systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavrilescu, M. From pollutants to products: Microbial cell factories driving sustainable biomanufacturing and environmental conservation. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 157152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Hu, P.; Lang-Yona, N.; Xu, M.; Guo, C.; Gu, J.-D. Global landfill leachate characteristics: Occurrences and abundances of environmental contaminants and the microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 461, 132446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Xiao, E.; Xiao, T.; Krumins, V.; Wang, Q.; Häggblom, M.; Dong, Y.; Tang, S.; Hu, M.; Li, B.; et al. Response of Soil Microbial Communities to Elevated Antimony and Arsenic Contamination Indicates the Relationship between the Innate Microbiota and Contaminant Fractions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9165–9175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falås, P.; Jewell, K.S.; Hermes, N.; Wick, A.; Ternes, T.A.; Joss, A.; Nielsen, J.L. Transformation, CO2 formation and uptake of four organic micropollutants by carrier-attached microorganisms. Water Res. 2018, 141, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, G.; Chi, S.; Song, J. Screening and identification of organics-degrading bacteria from the sediment of sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus ponds. Aquac. Int. 2016, 24, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Schlaeppi, K.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Keystone taxa as drivers of microbiome structure and functioning. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.F.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, X.R.; Wang, X.L.; Song, C.; Wang, S.G. Distribution, combined pollution and risk assessment of antibiotics in typical marine aquaculture farms surrounding the Yellow Sea, North China. Environ. Int. 2020, 138, 105551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zago, V.; Veschetti, L.; Patuzzo, C.; Malerba, G.; Lleo, M.M. Shewanella algae and Vibrio spp. strains isolated in Italian aquaculture farms are reservoirs of antibiotic resistant genes that might constitute a risk for human health. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 154, 111057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adair, K.L.; Douglas, A.E. Making a microbiome: The many determinants of host-associated microbial community composition. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2017, 35, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Deng, Q.; Wan, L.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Song, C. Bacterial Communities and Enzymatic Activities in Sediments of Long-Term Fish and Crab Aquaculture Ponds. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Zeng, S.; Hou, D.; Zhou, R.; Xing, C.; Deng, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, H.; Deng, Z.; Weng, S.; et al. Community diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria in shrimp pond sediment at different culture stages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1442–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Knight, R. Genomic Mutations Within the Host Microbiome: Adaptive Evolution or Purifying Selection. Engineering 2023, 20, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francke, C.; Siezen, R.J.; Teusink, B. Reconstructing the metabolic network of a bacterium from its genome. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, A.-L.; Tylianakis, J.M. The coevolutionary consequences of biodiversity change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2024, 39, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, H.; Xia, Y.; Tian, J.; Yu, E.; Gong, W.; Xie, J. Nitrification and denitrification processes in a zero-water exchange aquaculture system: Characteristics of the microbial community and potential rates. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1072911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Pan, L.; Huang, F.; Gao, S.; Su, C.; Zhang, M.; He, Z. Metagenomic analysis of composition, function and cycling processes of microbial community in water, sediment and effluent of Litopenaeus vannamei farming environments under different culture modes. Aquaculture 2019, 506, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Sun, M.; Li, G.; Zhu, J. Metagenomics Reveal Microbial Effects of Lotus Root–Fish Co-Culture on Nitrogen Cycling in Aquaculture Pond Sediments. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Peng, G.; Wei, T.; He, J.; Li, R.; Wang, Y. Distinctive patterns of bacterial community succession in the riverine micro-plastisphere in view of biofilm development and ecological niches. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivlin, S.N.; Hawkes, C.V.; Papeş, M.; Treseder, K.K.; Averill, C. The future of microbial ecological niche theory and modeling. New Phytol. 2021, 231, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Haeckel, M.; Dale, A.W.; Wallmann, K. Degradation and accumulation of organic matter in euxinic surface sediments. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2024, 370, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, G.; Luo, M.; Xu, C.; Pan, X.; Yi, G.; Xiao, W.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Li, R. Microbial and Functional Gene Dynamics in Long-Term Fermented Mariculture Sediment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050975
Zhang G, Luo M, Xu C, Pan X, Yi G, Xiao W, Wang C, Zhao Z, Li R. Microbial and Functional Gene Dynamics in Long-Term Fermented Mariculture Sediment. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050975
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Guochao, Mengyuan Luo, Cuilian Xu, Xinru Pan, Guoqiang Yi, Wei Xiao, Chenghao Wang, Zhen Zhao, and Ruilong Li. 2025. "Microbial and Functional Gene Dynamics in Long-Term Fermented Mariculture Sediment" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050975
APA StyleZhang, G., Luo, M., Xu, C., Pan, X., Yi, G., Xiao, W., Wang, C., Zhao, Z., & Li, R. (2025). Microbial and Functional Gene Dynamics in Long-Term Fermented Mariculture Sediment. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050975






