Investigating Catching Hotspots of Fishing Boats: A Framework Using BeiDou Big Data and Deep Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Methodology
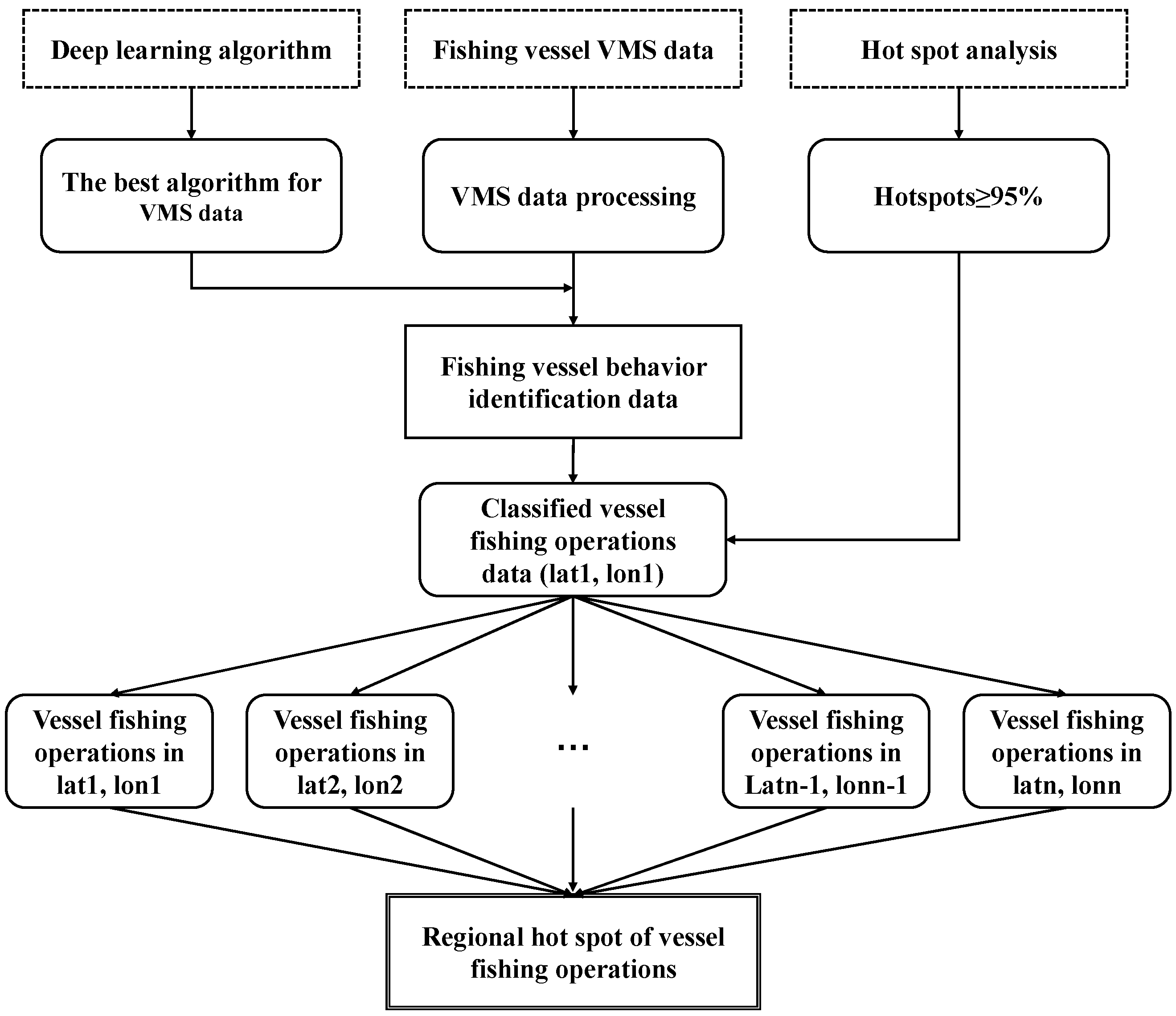
3.1. Research Framework for Fishing Hotspots Based on BeiDou Big Data and Deep Learning
3.2. CNN-BiLSTM Algorithm
- i.
- Spatiotemporal Feature Synergy
- ii.
- Computational Efficiency
- iii.
- Small-Data Robustness
- iv.
- Interpretable Hierarchical Learning
3.2.1. CNN Model
3.2.2. BiLSTM Model
3.2.3. Modeling Evaluation
3.3. Hot Spot Analysis
3.4. Fishing Hotspot Mapping Model Based on BeiDou Big Data and the CNN-BiLSTM Algorithm
| Algorithm 1. Fishing hotspot mapping model of the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea based on the CNN-BiLSTM and BeiDou big data. |
 |
4. Case Study
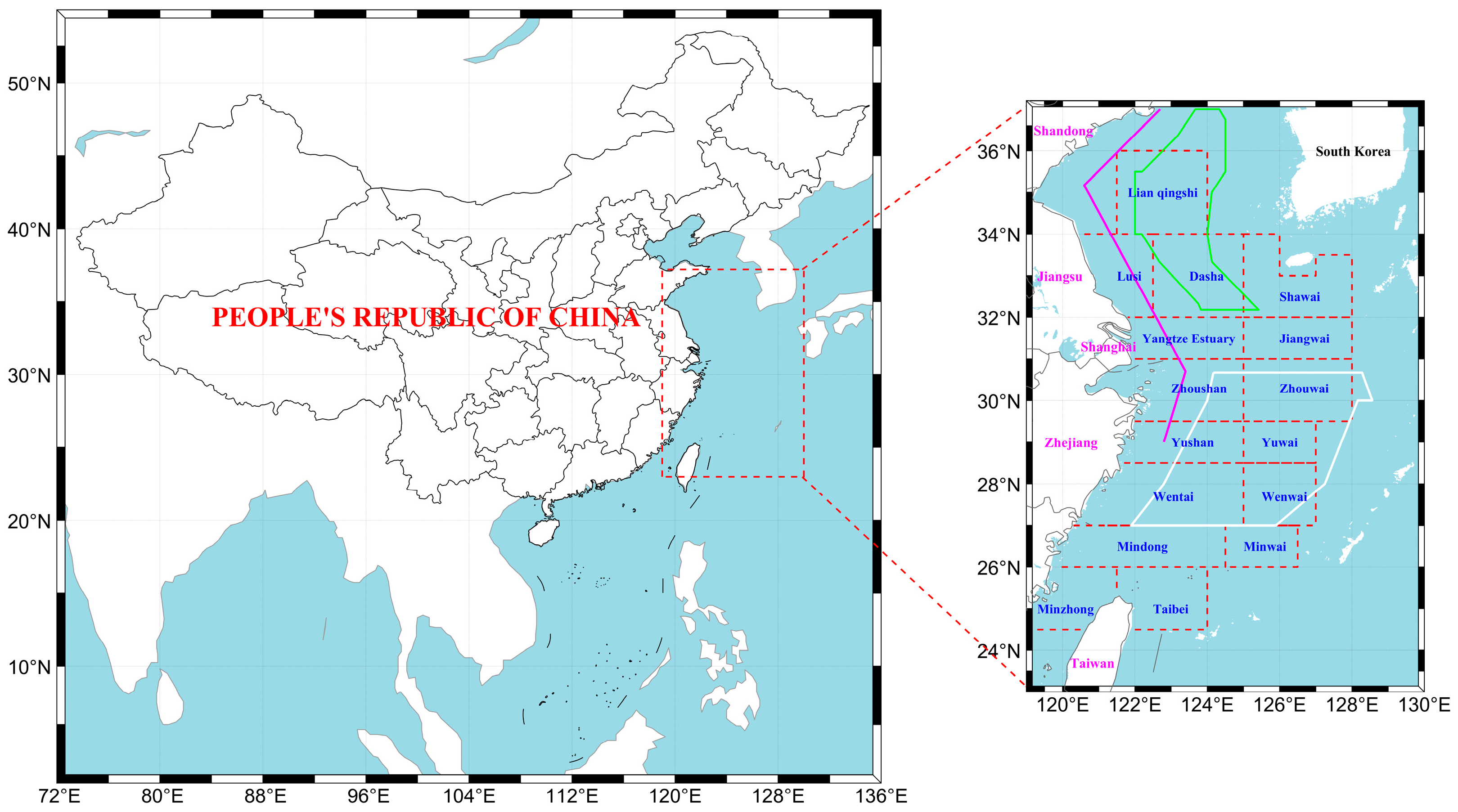
4.1. Study Area
4.2. Data
4.3. Model Verification
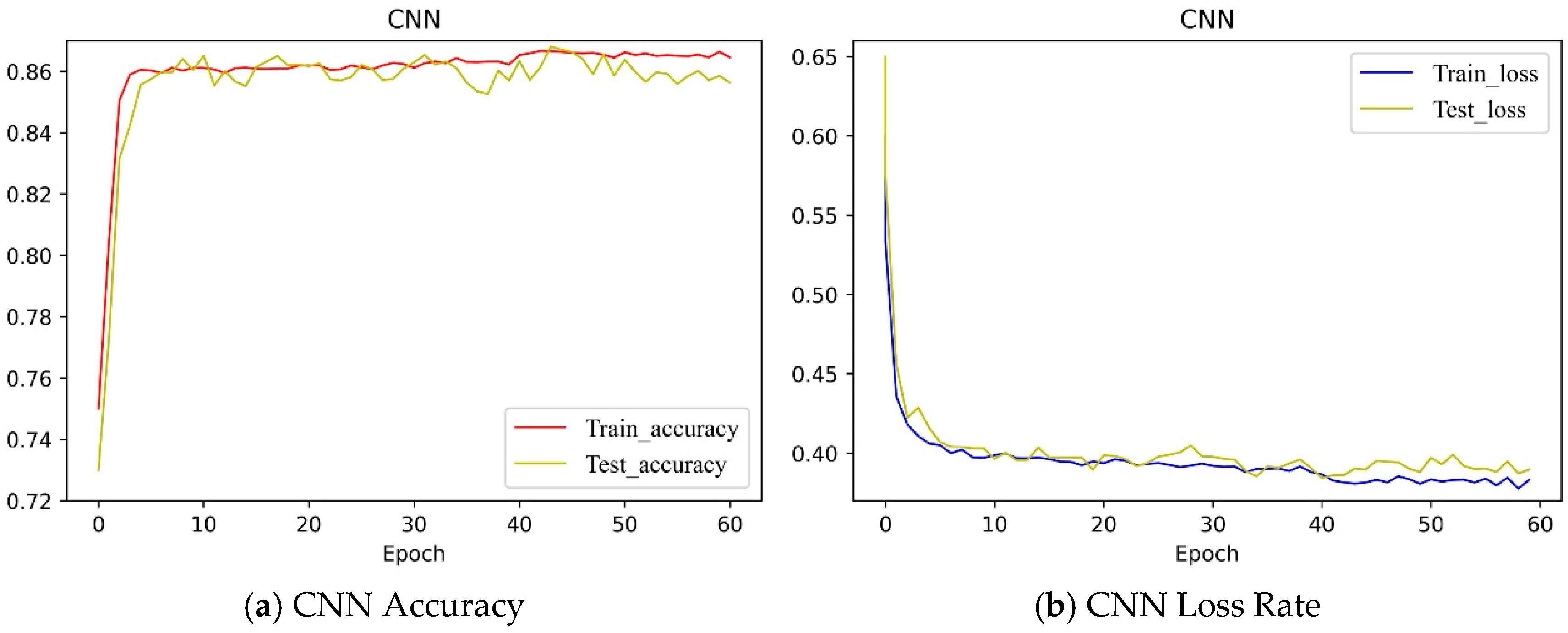
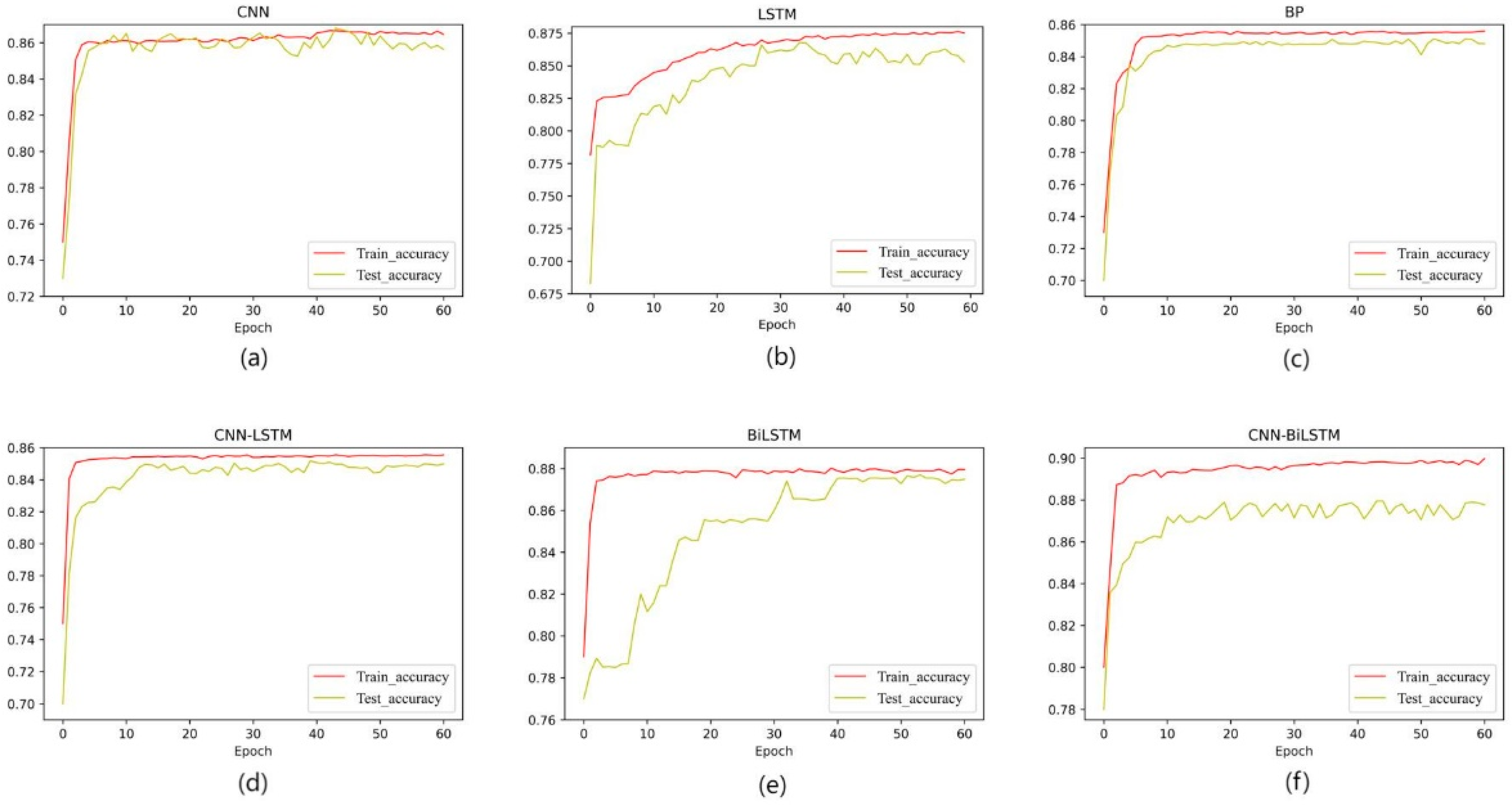
4.3.1. CNN Layer
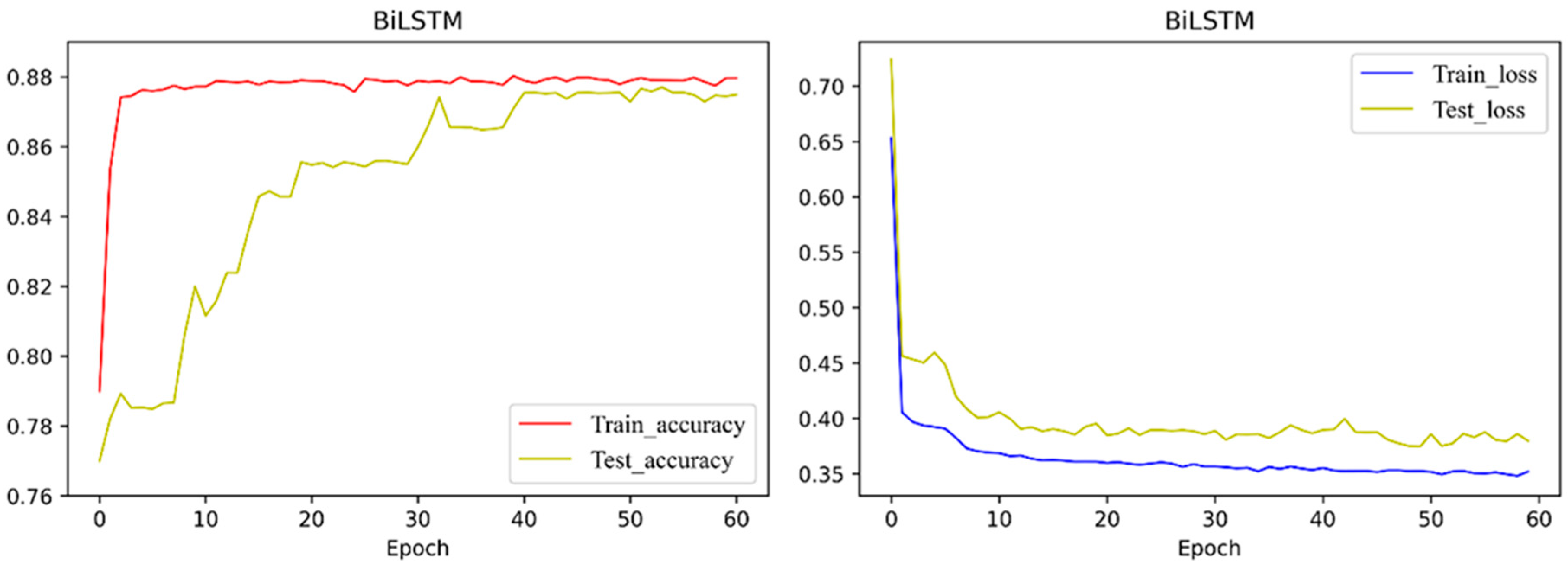
4.3.2. BiLSTM Layer
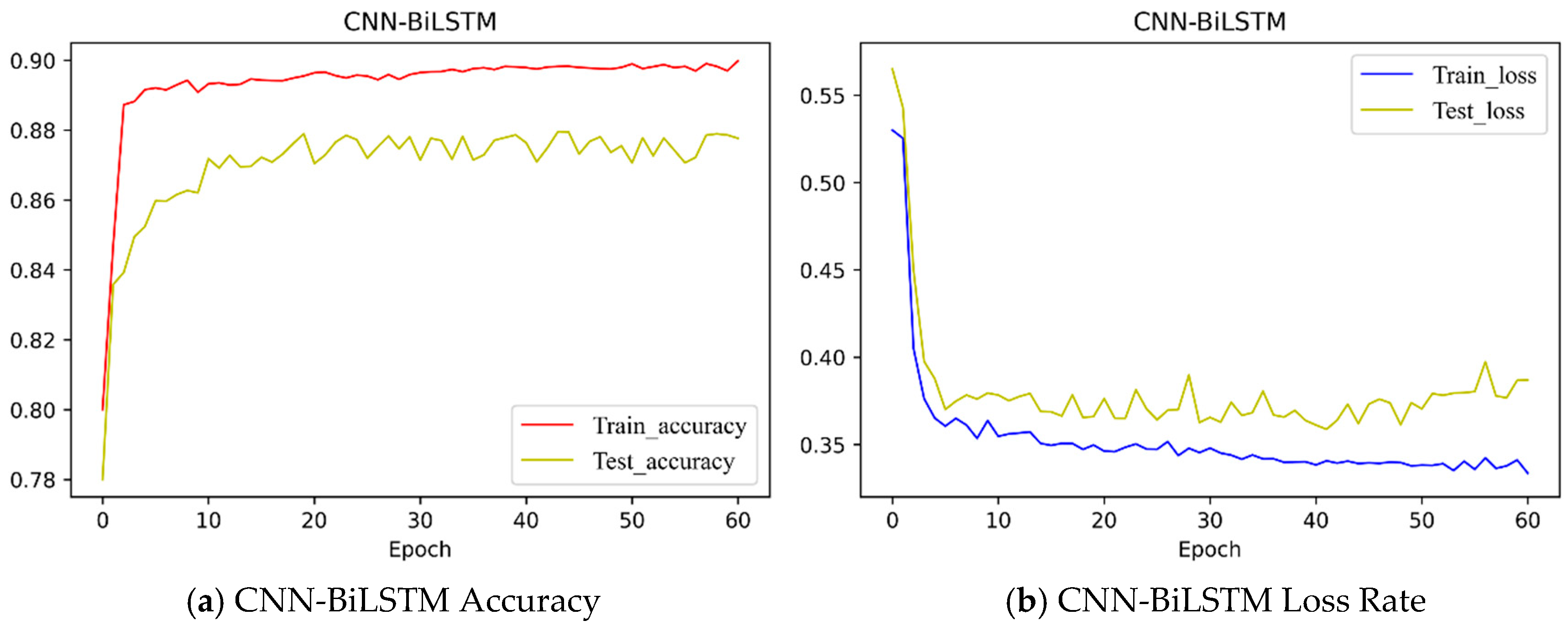
4.3.3. CNN-BiLSTM
4.3.4. Model Evaluation and Comparison
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Results
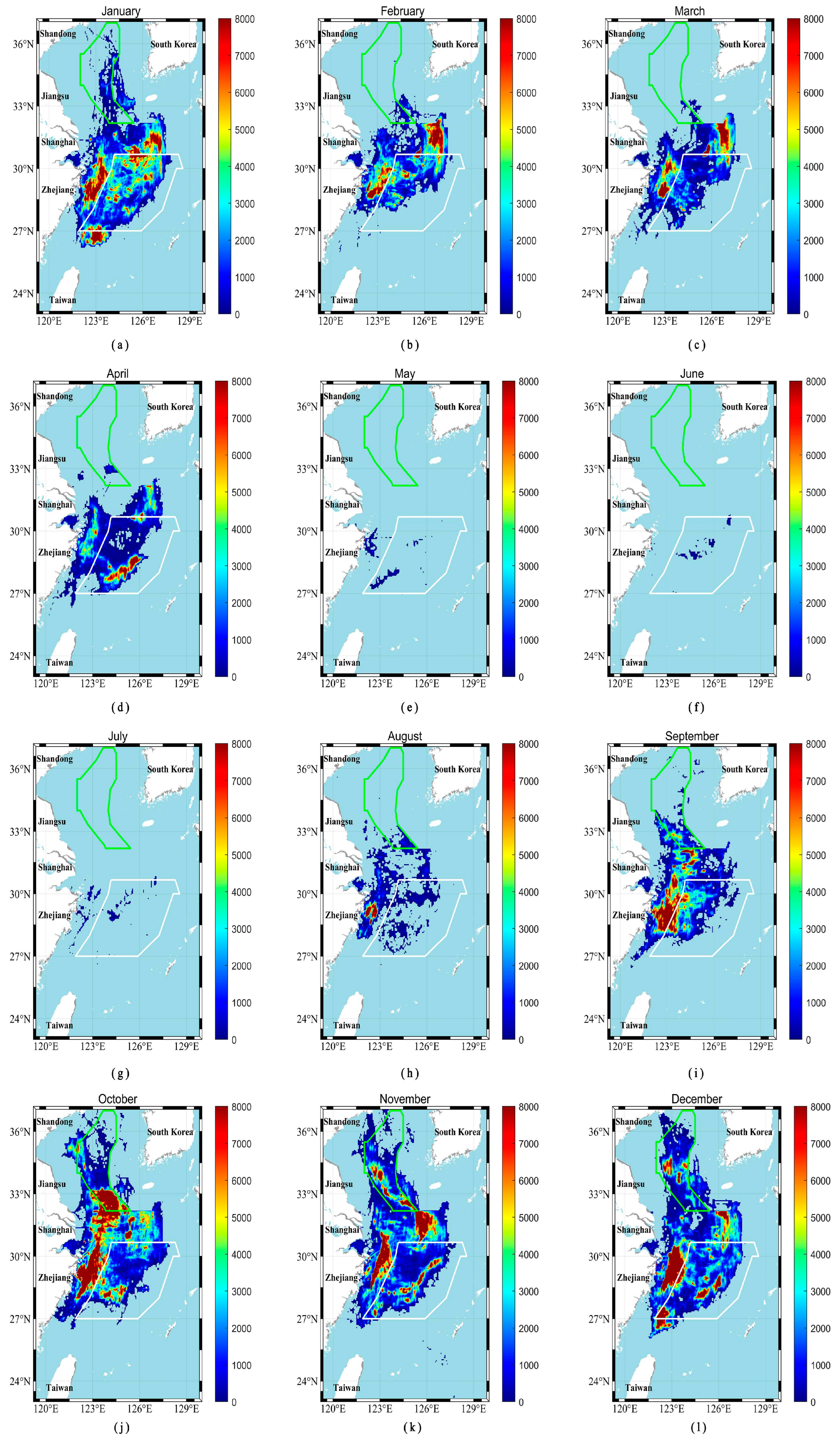
5.1.1. Monthly Changes in Fishing Hotspots in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea
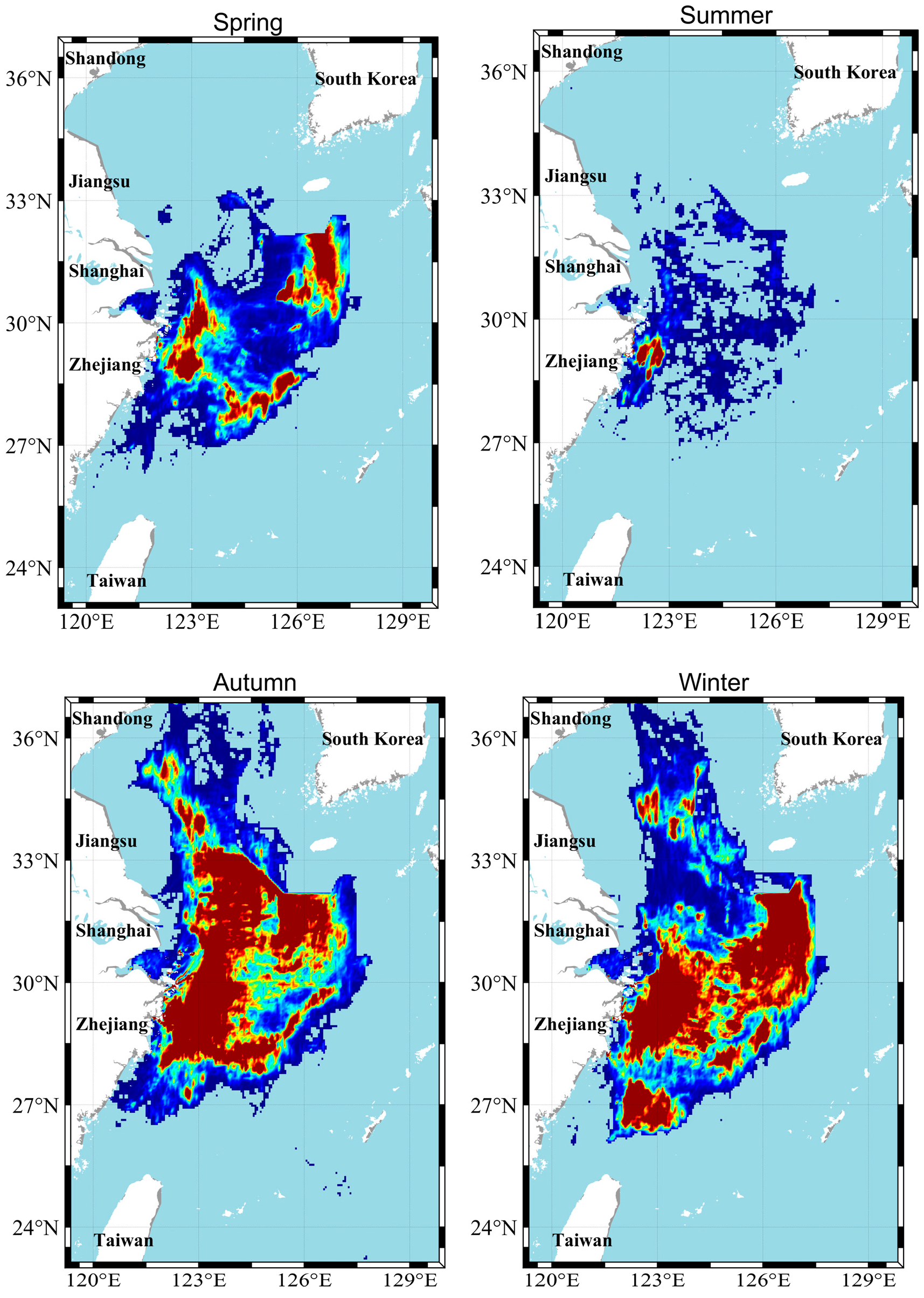
5.1.2. Quarterly Changes in Fishing Hotspots in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea
5.2. Discussion
5.2.1. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of the Annual Summer Fishing Ban
5.2.2. Managerial Implications
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hung, C.-Y.; Huynh, H.H.; Wu, X.-H.; Tsai, W.-P. Multimodel approach to a support stock assessment of standardized catch and effort data: A case study of blue shark (Prionace glauca) in the Indian Ocean by the Taiwanese large-scale longline fishery. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2024, 32, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. State of the World’s Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. International Plan of Action to Prevent, Deter and Eliminate Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kuemlangan, B.; Amidjogbe, E.-R.; Nakamura, J.; Tomassi, A.; Hupperts, R.; Bojang, B.; Amador, T. Enforcement approaches against illegal fishing in national fisheries legislation. Mar. Policy 2023, 149, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Agreement on Port State Measures to Prevent, Deter and Eliminate Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Serdy, A. The Shaky Foundations of the FAO Port State Measures Agreement: How Watertight Is the Legal Seal against Access for Foreign Fishing Vessels? Int. J. Mar. Coast. Law 2016, 31, 422–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Voluntary Guidelines for Flag State Performance; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Erikstein, K.; Swan, J. Voluntary Guidelines for Flag State Performance: A New Tool to Conquer IUU Fishing. Int. J. Mar. Coast. Law 2014, 29, 116–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Report of the Fourth Meeting of the Parties to the Agreement on Port State Measures to Prevent, Deter and Eliminate Illegal, Unreported and Unregulated Fishing; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Temple, A.J.; Skerritt, D.J.; Howarth, P.E.C.; Pearce, J.; Mangi, S.C. Illegal, unregulated and unreported fishing impacts: A systematic review of evidence and proposed future agenda. Mar. Policy 2022, 139, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zheng, S.; Wang, E.; Chen, J.; Feng, S.; Wang, D.; Dai, L. Advances in BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) and satellite navigation augmentation technologies. Satell. Navig. 2020, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lin, Q.; Lian, F.; Feng, H. Estimating emissions from fishing vessels: A big Beidou data analytical approach. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1418366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hong, F.; Huang, H.; Liu, C.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Z. Short-term prediction of fishing effort distributions by discovering fishing chronology among trawlers based on VMS dataset. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 184, 115512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, Y.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y. The dynamics of the fishing fleet in China Seas: A glimpse through AIS monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.; Gourmelon, F.; Meur-Ferec, C.; Herpers, F.; Le Visage, C. Exploring uses of maritime surveillance data for marine spatial planning: A review of scientific literature. Mar. Policy 2020, 117, 103930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala-Coromina, J.; García, J.A.; Martín, P.; Fernandez-Arcaya, U.; Recasens, L. European hake (Merluccius merluccius, Linnaeus 1758) spillover analysis using VMS and landings data in a no-take zone in the northern Catalan coast (NW Mediterranean). Fish. Res. 2021, 237, 105870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Arcaya, U.; Rodríguez-Basalo, A.; Verísimo, P.; Rodriguez, J.; Ceballos, E.; Gonzalez-Irusta, J.M.; García-Alegre, A.; Plaza-Morlote, M.; Serrano, A.; Punzón, A. Bottom fishing beyond trawling. Spatio-temporal trends of mobile and static bottom fisheries on benthic habitats. Mar. Policy 2024, 159, 105805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Yan, F.; Su, F.; Lyne, V.; Tang, J. Prediction of fishing intensity and trends across South China Sea biogeographic zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.M.; Townsend, S.E.; Jennings, S.; Eastwood, P.D.; Houghton, C.A. Estimating high resolution trawl fishing effort from satellite-based vessel monitoring system data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, H.; Murray, L.G.; Lambert, G.I.; Hiddink, J.G.; Kaiser, M.J. Confidentiality over fishing effort data threatens science and management progress. Fish Fish. 2013, 14, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinz, H.; Prieto, V.; Kaiser, M.J. Trawl disturbance on benthic communities: Chronic effects and experimental predictions. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colletti, A.; Savinelli, B.; Di Muzio, G.; Rizzo, L.; Tamburello, L.; Fraschetti, S.; Musco, L.; Danovaro, R. The date mussel Lithophaga lithophaga: Biology, ecology and the multiple impacts of its illegal fishery. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Jin, S.; Zhang, H.; Fan, W.; Tang, F.; Yang, S. Distribution of bottom trawling effort in the Yellow Sea and East China Sea. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, K.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Sui, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, F.; Yang, S. Spatial distribution of fishing intensity of canvas stow net fishing vessels in the East China Sea and the Yellow Sea. Indian J. Fish 2023, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fock, H.O. Fisheries in the context of marine spatial planning: Defining principal areas for fisheries in the German EEZ. Mar. Policy 2008, 32, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijnsdorp, A.D.; Dol, W.; Hoyer, M.; Pastoors, M.A. Effects of fishing power and competitive interactions among vessels on the effort allocation on the trip level of the Dutch beam trawl fleet. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.-L.; Jung, C.-Y. Geohash-based Arrangement of Live-Fire Exercise Areas Using AIS. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2023, 31, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Yang, M.F.; Kao, S.L.; Tu, M.; Kuo, J.-Y.; Chao, Y.-T.; Hsu, H.-K. Research on the collision risk of ships off Keelung based on AIS data. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2023, 31, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, S.; Burgos, J.M.; Gerlotto, F.; Atiquipa, J. Lévy trajectories of Peruvian purse-seiners as an indicator of the spatial distribution of anchovy (Engraulis ringens). ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2005, 62, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, J.F., III; Hoenig, J.M.; Gedamke, T. Correcting for effective area fished in fishery-dependent depletion estimates of abundance and capture efficiency. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2007, 64, 1760–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; South, A.B.; Jennings, S. Developing reliable, repeatable, and accessible methods to provide high-resolution estimates of fishing-effort distributions from vessel monitoring system (VMS) data. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2010, 67, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespe, M.; Gibin, M.; Alessandrini, A.; Natale, F.; Mazzarella, F.; Osio, G.C. Mapping EU fishing activities using ship tracking data. J. Maps 2016, 12, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Z. Mapping coastal fishing grounds and assessing the effectiveness of fishery regulation measures with AIS data: A case study of the sea area around the Bohai Strait, China. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 223, 106136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.; Gil, J.; Sobrino, I. Definition of fleet components in the Spanish artisanal fishery of the Gulf of Cádiz (SW Spain ICES division IXa). Fish. Res. 2002, 59, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, S.M.; Fogarty, M.J. Operational fisheries in New England: Linking current fishing patterns to proposed ecological production units. Fish. Res. 2013, 141, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesdoly, A.; Bone, C.; Fraser, M.; Serra-Sogas, N.; Canessa, R. Evaluating models for classifying movement of whale-watching vessels. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 73, 101903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Xie, X.; Lv, W. Self-adaption vessel traffic behaviour recognition algorithm based on multi-attribute trajectory characteristics. Ocean Eng. 2020, 198, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Xie, Z.; Xu, X.; Xiao, Y. An adaptive threshold fast DBSCAN algorithm with preserved trajectory feature points for vessel trajectory clustering. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Seraj, R.; Islam, S. The k-means Algorithm: A Comprehensive Survey and Performance Evaluation. Electronics 2020, 9, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lian, F.; Yang, Z. Analysis of the activities of high sea fishing vessels from China, Japan, and Korea via AIS data mining. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 242, 106690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamaza-Márquez, M.A.; Pennino, M.G.; Torres, M.A.; Acosta, J.J.; Erzini, K.; Sobrino, I. Discard practices in the gulf of Cadiz multispecies trawl fishery. Implications for the EU ‘landing obligation’. Mar. Policy 2020, 118, 104008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.; Bez, N. A pioneer validation of a state-space model of vessel trajectories (VMS) with observers’ data. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lecun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J. Deep learning in neural networks: An overview. Neural Netw. 2015, 61, 85–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, A.; Sheaves, M.; Rahimi Azghadi, M. Computer vision and deep learning for fish classification in underwater habitats: A survey. Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 977–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Shi, G.; Li, N.; Ma, L.; Li, W.; Shi, J. TRFM-ls: Transformer-based deep learning method for vessel trajectory prediction. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Ma, F.; Miao, L.; Zhang, C. A semi-supervised deep learning approach for vessel trajectory classification based on AIS data. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 218, 106015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Achuthan, K.; Zhang, X. A ship movement classification based on Automatic Identification System (AIS) data using Convolutional Neural Network. Ocean Eng. 2020, 218, 108182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Liu, R.W.; Li, S.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, X.; Lu, F. An unsupervised learning method with convolutional auto-encoder for vessel trajectory similarity computation. Ocean Eng. 2021, 225, 108803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Zhang, T.; Huang, J. Advanced hybrid LSTM-transformer architecture for real-time multi-task prediction in engineering systems. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Jia, C.; Yang, X.; Cheng, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, C. A Data-Driven Approach for Collision Risk Early Warning in Vessel Encounter Situations Using Attention-BiLSTM. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 188771–188783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Ye, K.; Xu, X. Ship trajectory prediction using CNN-BILSTM with sparse attention mechanisms for enhanced maritime safety. Ships Offshore Struct. 2024, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, F. Attention-enhanced and integrated deep learning approach for fishing vessel classification based on multiple features. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z. biSAMNet: A Novel Approach in Maritime Data Completion Using Deep Learning and NLP Techniques. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, R.; Bez, N.; Etienne, M.-P.; Marin, P.; Goascoz, N.; Roux, J.; Mahévas, S. Identifying partners at sea from joint movement metrics of pelagic pair trawlers. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2021, 78, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; de Mitcheson, Y.S.; Cao, L.; Leadbitter, D.; Newton, R.; Little, D.C.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Fishing for feed in China: Facts, impacts and implications. Fish Fish. 2020, 21, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, L.; Wilcox, C.; Boussarie, G.; Dugan, E.; Garilao, C.; Gonzalez, K.; Green, M.; Kark, S.; Kaschner, K.; Klein, C.J.; et al. Spatially explicit risk assessment of marine megafauna vulnerability to Indian Ocean tuna fisheries. Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 1180–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Lee, C.-F.; Tsai, C.-S.; Yang, T.-Y. Toward sustainable development of tuna longline fishery in Taiwan: Value chain analysis. Mar. Policy 2024, 161, 106010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapp, D.R.; Walker, T.I.; Huveneers, C.; Reina, R.D. Respiratory mode and gear type are important determinants of elasmobranch immediate and post-release mortality. Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elharrouss, O.; Almaadeed, N.; Al-Maadeed, S.; Khelifi, F. Pose-invariant face recognition with multitask cascade networks. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 6039–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Chen, N.; Yang, D.; Meng, Z. Simplified-Boosting Ensemble Convolutional Network for Text Classification. Neural Process. Lett. 2022, 54, 4971–4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Li, L.; Ren, J.; Wu, W.; Wang, R. Hyperspectral image classification via parallel multi-input mechanism-based convolutional neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 24601–24626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Han, J.; Zhou, P.; Xu, D. Learning Rotation-Invariant and Fisher Discriminative Convolutional Neural Networks for Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tian, X.; Xie, P.; Xu, J.; Zheng, J.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fan, G. A convolutional neural networks method for tropospheric ozone vertical distribution retrieval from Multi-AXis Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy measurements. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Yacine, K.G.E.; Rabea, S. Abundance and Distribution of Fish Larvae in the Central Coast of the Algerian Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2023, 31, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, F.O.; Corchuelo, R. An encoder–decoder approach to mine conditions for engineering textual data. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2020, 91, 103568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Wang, P.; Abbas, K. A survey on deep learning and its applications. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2021, 40, 100379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanui, I.C.; Kandie, F.; Krauss, M.; Piotrowska, A.; Kiprop, A.; Shahid, N.; Liess, M.; Brack, W. Seasonal hot spots of pollution and risks in Western Kenya: A spatial-temporal analysis of almost 800 organic micropollutants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.A. Animal home ranges and territories and home range estimators. Res. Tech. Anim. Ecol. Controv. Conseq. 2000, 442, 65–110. [Google Scholar]
- Le Guyader, D.; Ray, C.; Gourmelon, F.; Brosset, D. Defining high-resolution dredge fishing grounds with Automatic Identification System (AIS) data. Aquat. Living Resour. 2017, 30, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Cheng, H.-Q.; Le Quesne, W.J.F.; Xu, H.G.; Wu, J.; Ding, H.; Arreguin-Sanchez, F. Ecosystem model predictions of fishery and conservation trade-offs resulting from marine protected areas in the East China Sea. Environ. Conserv. 2008, 35, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Grifoll, M.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, P. Collision risk assessment for ships’ routeing waters: An information entropy approach with Automatic Identification System (AIS) data. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2022, 224, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, P.; Pang, M.; Wang, Q.; Li, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, X. Influence of timing of fishing on trophic levels and diets of typical fish and invertebrate species in the Bohai Strait over a single year based on carbon and nitrogen isotope analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 70, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ship Type | Month | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Trawler | 1356 | 1214 | 874 | 442 | 364 | 688 | 424 | 472 | 955 | 1296 | 1424 | 1494 |
| Drift | 422 | 394 | 186 | 134 | 102 | 234 | 141 | 222 | 245 | 198 | 348 | 393 |
| Seine | 30 | 23 | 15 | 9 | 7 | 16 | 6 | 22 | 20 | 24 | 36 | 46 |
| Stow | 15 | 14 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 12 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 12 | 15 |
| Longline | 41 | 41 | 36 | 37 | 40 | 40 | 39 | 40 | 40 | 41 | 41 | 41 |
| Total | 1864 | 1686 | 1117 | 627 | 518 | 990 | 617 | 763 | 1268 | 1567 | 1861 | 1989 |
| Architectures | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Layer | The 128 × 1 × 5 Feature Vector | |||||||
| Convolutional Layer1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Convolutional Layer2 | None | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Max Pooling Layer | None | None | None | None | None | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Dropout Layer | None | None | None | None | None | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Convolutional Layer3 | None | None | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Convolutional Layer4 | None | None | None | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Max Pooling Layer | None | None | None | None | None | None | Yes | Yes |
| Dropout Layer | None | None | None | None | None | None | Yes | Yes |
| Convolutional Layer5 | None | None | None | None | 40 | None | None | None |
| Fully Connected Layer1 | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | Yes |
| Dropout Layer | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | Yes |
| Fully Connected Layer2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Consuming | 120 s | 240 s | 360 s | 490 s | 590 s | 540 s | 590 s | 660 s |
| Accuracy (%) | 81.20% | 82.65% | 85.52% | 85.72% | 82.67% | 85.78% | 86.46% | 82.43% |
| Architectures | A | B | C | D | E | F | G |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input Layer | The 128 × 1 × 5 Feature vector | ||||||
| BiLSTM Layer 1 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| BiLSTM Layer 2 | None | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Dropout Layer | None | None | None | None | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| BiLSTM Layer 3 | None | None | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| BiLSTM Layer 4 | None | None | None | 20 | None | None | None |
| Dropout Layer | None | None | None | None | None | None | Yes |
| Fully Connected Layer 1 | None | None | None | None | None | Yes | None |
| Dropout Layer | None | None | None | None | None | Yes | None |
| Fully Connected Layer 2 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Time Consuming | 240 s | 360 s | 600 s | 724 s | 603 s | 667 s | 680 s |
| Accuracy (%) | 84.05% | 85.35% | 86.51% | 82.31% | 87.11% | 82.37% | 87.51% |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision Rate | Recall Rate | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | 86.46% | 83.52% | 90.46% | 86.76% |
| LSTM | 87.21% | 83.64% | 89.64% | 86.53% |
| BP | 85.79% | 83.78% | 90.60% | 87.06% |
| BiLSTM | 87.51% | 83.12% | 91.23% | 87.00% |
| CNN-LSTM | 85.55% | 82.23% | 88.52% | 85.26% |
| CNN-BiLSTM | 89.98% | 84.21% | 91.53% | 87.72% |
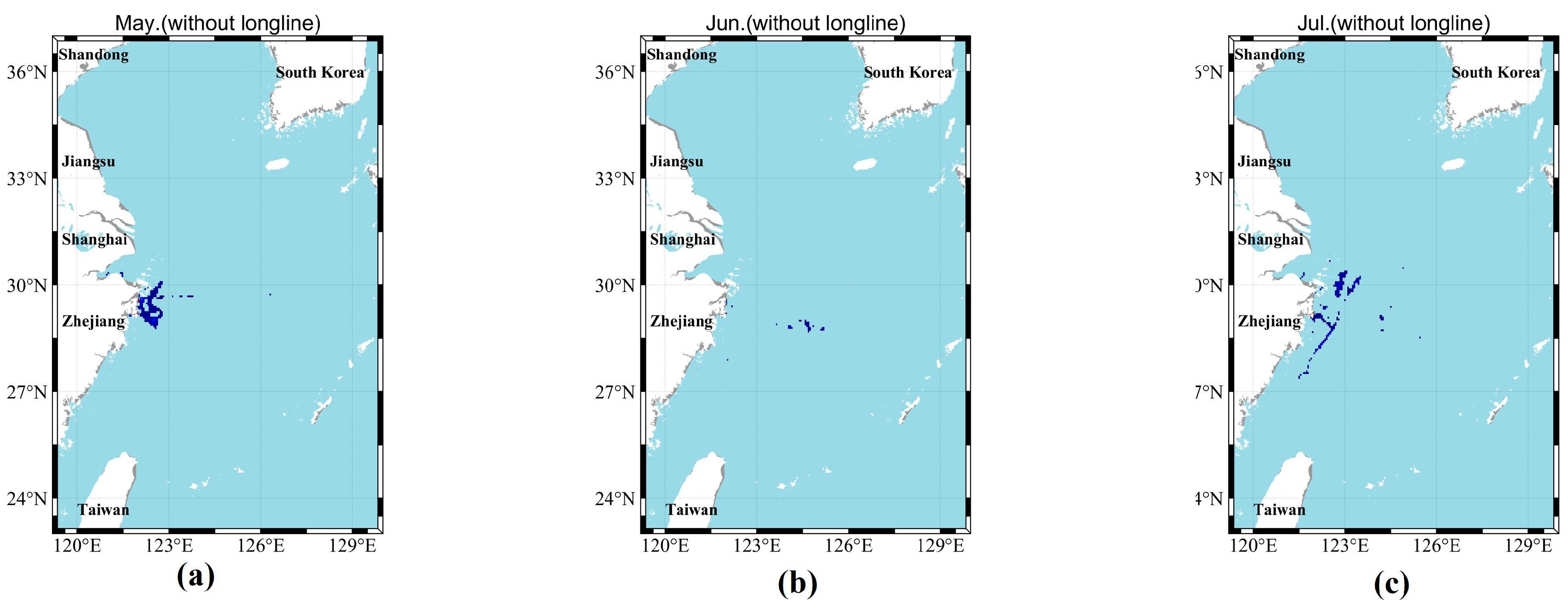
| Month | Number of Hotspot Grids | Sea Area (km2) | Maximum Value | Mean Value (Beyond 8000) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 699 | 20,970 | 151,850 | 13,798 |
| February | 468 | 14,040 | 558,160 | 18,565 |
| March | 318 | 9540 | 147,720 | 14,482 |
| April | 160 | 4800 | 39,342 | 11,397 |
| May | 19 | 570 | 203,890 | 42,126 |
| June | 26 | 780 | 502,530 | 64,548 |
| July | 35 | 1050 | 717,870 | 65,330 |
| August | 123 | 3690 | 856,020 | 27,452 |
| September | 648 | 19,440 | 346,230 | 14,661 |
| October | 1517 | 45,510 | 370,060 | 15,805 |
| November | 951 | 28,530 | 126,000 | 12,830 |
| December | 1097 | 32,910 | 103,890 | 16,582 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Feng, H.; Lin, Q. Investigating Catching Hotspots of Fishing Boats: A Framework Using BeiDou Big Data and Deep Learning Algorithms. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050905
Wang F, Liu X, Chen T, Feng H, Lin Q. Investigating Catching Hotspots of Fishing Boats: A Framework Using BeiDou Big Data and Deep Learning Algorithms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050905
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Fen, Xingyu Liu, Tanxue Chen, Hongxiang Feng, and Qin Lin. 2025. "Investigating Catching Hotspots of Fishing Boats: A Framework Using BeiDou Big Data and Deep Learning Algorithms" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050905
APA StyleWang, F., Liu, X., Chen, T., Feng, H., & Lin, Q. (2025). Investigating Catching Hotspots of Fishing Boats: A Framework Using BeiDou Big Data and Deep Learning Algorithms. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 905. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050905







