Abstract
To investigate the spatiotemporal distribution and causes of blooms of Rhopilema esculentum in Hangzhou Bay during 2024, this study investigated its growth characteristics, including umbrella diameter and body weight, along with environmental factors, spatiotemporal dynamics and yield variations. The analysis was based on the 2024 monitoring data of R. esculentum resources in Hangzhou Bay, together with relevant social research data. The results showed that umbrella diameter and body weight increased over time at all monitoring points. The growth rate of the R. esculentum umbrella diameter declined gradually over time, whereas that of body weight rapidly increased. The daily growth rate of umbrella diameter in the water of Tangnao and Xiaoji Mountains was significantly higher than that in the waters of Tanxu Mountain. A sharp drop in salinity caused by Xin’anjiang Reservoir flood discharge from the 23rd to 28th June was the primary cause of the R. esculentum blooms in Hangzhou Bay. During the special R. esculentum fishing period in the summer fishing moratorium, R. esculentum was mainly distributed in the southern and eastern Hangzhou waters, with a maximum daily yield of 28,000 kg/day. After the 16th, R. esculentum production expanded across the entire bay, with blooms also occurring in Xiangshan Bay and Liuheng, reaching a production peak of 44,000 kg/day. In 2024, R. esculentum production in Hangzhou Bay totalled 250,000 tonnes, breaking historical records. This study revealed the 2024 growth and spatiotemporal dynamics of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay, providing a reference for the rational use and protection of the species and revealing the causes of the unprecedented blooms.
1. Introduction
Rhopilema esculentum, the flame jellyfish, is a large warm-water, edible, annual species. It has been commercially developed in China for over 1000 years and remains a preferred seafood among the Chinese [1,2,3,4]. It typically inhabits the confluence of sea and fresh water, especially in estuarine areas at depths of 5–20 m. The species is distributed in China’s coastal waters, with an annual output reaching 58,000 tonnes [1,5,6]. The Zhejiang coast, a major source of R. esculentum, produced up to 35,000 tonnes before 1975, accounting for nearly half of the national output [1,5,7]. After 1975, due to overfishing, marine environmental changes and other reasons, yields along the Zhejiang coast declined year by year, and the population in southern Zhejiang almost disappeared.
Hangzhou Bay lies in the coastal waters between 29–31° N and 121–123° E, adjacent to the Yangtze River estuary in the north. The Qiantang, Cao’e and Yongjiang Rivers flow into the bay with similar discharge widths; among them, the Qiantang River alone contributes 386.4 × 108 m3 of water per year. The bay is nutrient rich, with temperature and salinity suitable for the growth and reproduction of R. esculentum, making it a key habitat on the Zhejiang coast [1,8,9]. R. esculentum is widely distributed west of the Nanhui–Shengsi–Jintang line, with a historical annual output reaching 10,000 tonnes [1]. However, after 1975, R. esculentum numbers in the area rapidly declined, leading to a halt in fishing seasons. Since then, many researchers have conducted comprehensive studies on R. esculentum [1,3,5,6,7], especially the Liaoning Provincial Marine Fisheries Research Institute. In recent decades, continuous release efforts in Hangzhou Bay have produced strong ecological and economic outcomes, although its resource levels have fluctuated, with fishing seasons beginning in July. In 2024, a historic bloom of R. esculentum occurred in Hangzhou Bay. Preliminary estimates indicated that the output would reach 250,000 tonnes, a record reported by the media nationwide. Despite ongoing studies, the cause of jellyfish blooms remains unclear [10,11,12,13,14,15]. As a species subject to long-term breeding and release, R. esculentum blooms are rare and have attracted substantial research attention.
Currently, there are limited studies on the biological characteristics of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay, and no reports have addressed the mechanisms of bloom. Based on monitoring data from 2023 to 2024, the biological characteristics of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay were analysed, the growth curves of umbrella diameter and body weight were plotted, and the causes of bloom in Hangzhou Bay in 2024 were analysed using marine environmental data. Additionally, using ship track and fishing log data, the distribution patterns and bloom yields during the two fishing stages were determined. The aim of this study was to elucidate the distribution and bloom mechanism of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay in 2024, offering technical support for the species’ use and protection, while contributing to the theoretical understanding of bloom mechanisms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Data Collection
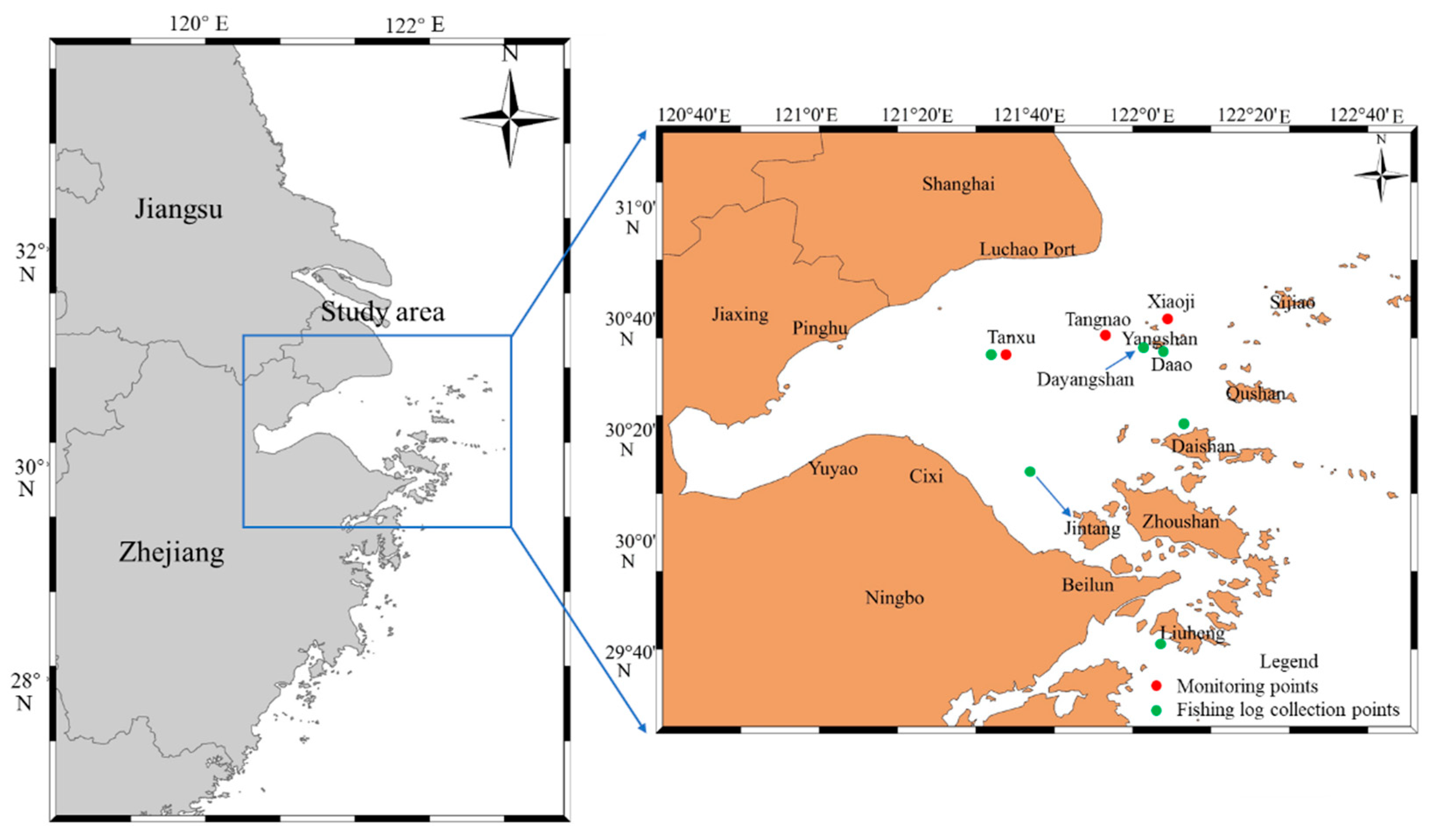
The primary study area was the inner waters of Hangzhou Bay (Figure 1). Data collection was divided into three parts: (1) Ship track data collection: This study used ship information net to obtain fishing vessel tracks during the two periods following R. esculentum fishing (summer fishing season and after the 16th of August). Daily data were collected, including the longitude and latitude of each vessel. (2) Biological and marine environment data collection: Three monitoring stations were established in traditional R. esculentum production areas: the Tanxu Mountain, Tangnao Mountain and Xiaoji Mountain sea areas. Two nets were deployed at each station to collect R. esculentum samples. Upon landing, umbrella diameter (to the nearest centimeter) and body weight (to the nearest gram) were measured using a ruler and an electronic scale, respectively. A total of 2690 samples were measured, comprising 656 samples from Tanxu Mountain, 932 samples from Tangnao Mountain and 1102 samples from Xiaoji Mountain. After each haul, a multifunctional water quality meter was used to record the temperature (°C), salinity (‰) and dissolved oxygen saturation (%). Marine surveys were conducted on the 8th and 20th of June and 4th of July 2024. High-yield area surveys were conducted on the 7th and 27th of September. Xiaoji Mountain sea area surveys in 2023 were conducted on the 5th of June, 20th of June and 2nd of July with marine environment data collected using the same multifunctional water quality instrument. (3) Fishing log data collection: Six monitoring vessels were assigned to major R. esculentum fishing zones in Hangzhou Bay: Jintang, Daishan, Liuheng, Dayangshan, Tanxu and Daao. The records included data on date and daily output (kg).
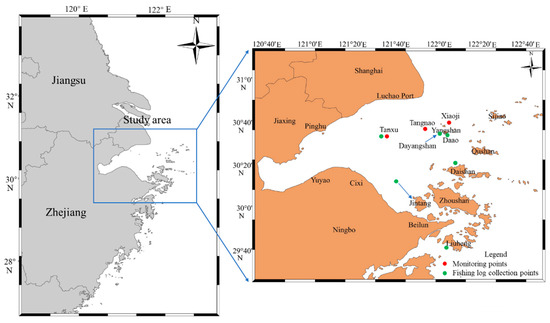
Figure 1.
Map of study area and data collection sites.
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.1. Daily Growth Rate of R. esculentum
The daily growth rate of R. esculentum umbrella diameter or body weight was calculated as follows:
where Rij is the daily growth rate; Aj and Ai are the umbrella diameter or body weight on dates j and i, respectively; and dj and di are dates j and i, respectively.
2.2.2. Relationship Between Umbrella Diameter and Body Weight
The relationship between umbrella diameter and body weight was modelled using a power function [16,17]:
where BW is body weight (g), UB is umbrella diameter (cm), a is the conditional factor parameter and b is the growth factor parameter.
BW = aUBb
2.2.3. The General Growth Pattern of R. esculentum
In aquatic organism growth modelling, fish growth patterns are typically expressed as functions of length or weight over time, conventionally formulated as Lt(Wt) = f(t). Notably, jellyfish exhibit distinct growth trajectories lacking asymptotic stabilisation due to their senescence phase, rendering conventional fisheries’ biological models, such as the von Bertalanffy growth function, inapplicable. As a biologically distinct group, jellyfish growth dynamics require alternative mathematical representations. Higher-order polynomial equations have demonstrated superior predictive performance in simulating jellyfish ontogeny [3,6,16,17,18], with the following generalised expression:
Fish growth is typically described as a function of length or weight over time and is represented as Lt or Wt = f(t). However, unlike fish, jellyfish undergo senescence and do not follow asymptotic growth patterns; thus, they cannot be modelled using the traditional von Bertalanffy equation. Instead, jellyfish growth can be better simulated using higher-order equations, which yield more accurate results [3,6,16,17,18]. The equation used in this study is as follows:
where c1 + c2 + c3 + … + ci, d1 + d2 + d3 + … + di represents the coefficient of association; c0, d0 represents the intercept; and t represents the date of growth.
UB = c0 + c1t + c2t2 + … + citi
logeBWt = d0 + d1t + d2t2 + … + diti
2.2.4. Data Processing and Mapping
The cartographic representation of monitoring stations in Hangzhou Bay was generated through ArcGIS 10.2, while subsequent graphical illustrations and statistical analyses were executed using Origin 2018 software. The K–W (Kruskal–Wallis) non-parametric test was systematically applied to determine intergroup significance.
3. Results
3.1. Umbrella Diameter and Body Weight of R. esculentum at Different Monitoring Stations
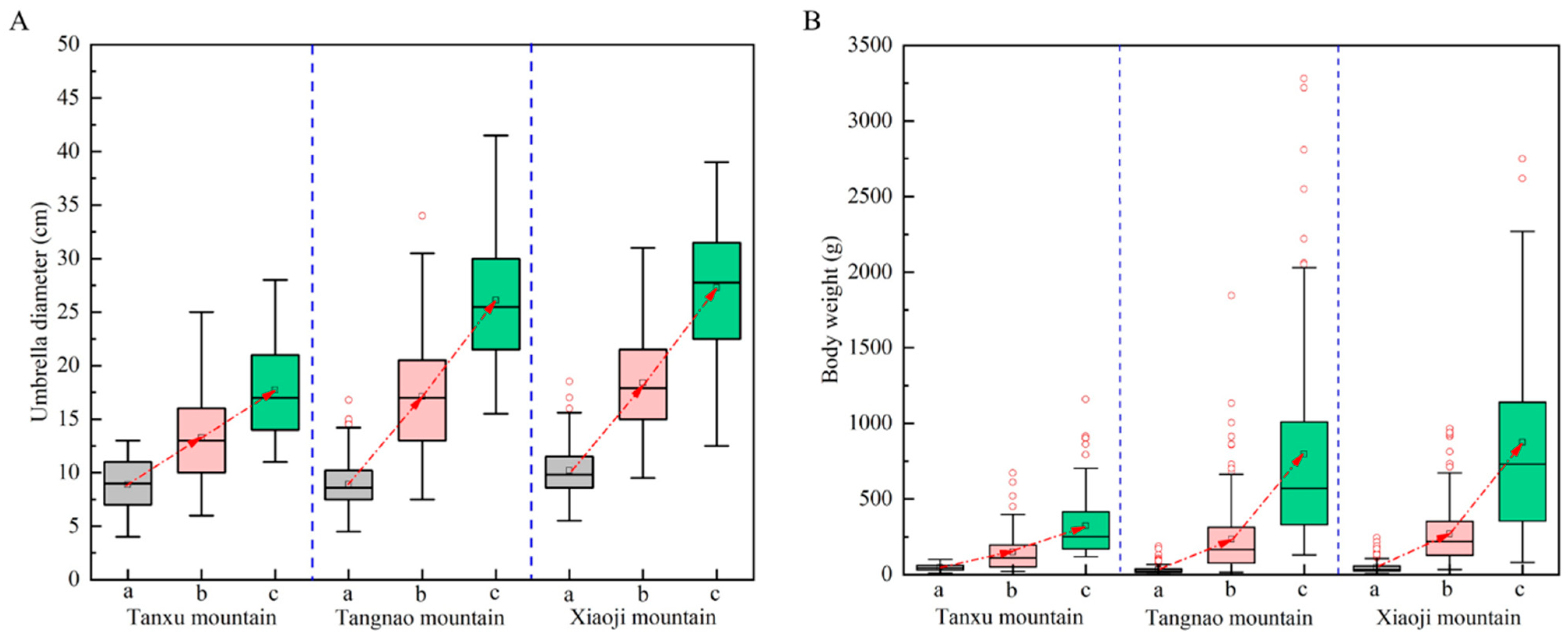
On average, the umbrella diameter of R. esculentum in the Tanxu Mountain sea area increased from 8.9 ± 2.3 cm to 17.7 ± 4.2 cm, a 2.0-fold increase, and body weight increased from 47.9 ± 21.4 g to 322.6 ± 208.5 g, a 6.7-fold increase. The umbrella diameter in the Tangnao Mountain sea area increased from 8.9 ± 2.2 cm to 26.1 ± 6.2 cm, a 2.9-fold increase, and body weight increased from 30.7 ± 26.6 g to 795.1 ± 674.2 g, a 25.9-fold increase. The umbrella diameter in the Xiaoji Mountain sea area increased from 10.2 ± 2.3 cm to 27.3 ± 6.2 cm, a 2.7-fold increase, and body weight increased from 47.0 ± 38.1 g to 874.8 ± 628.2 g, an 18.6-fold increase (Table 1). The umbrella diameter and body weight values at all three monitoring stations showed increasing trends over time, with significant differences observed across sampling periods, as seen in Figure 2 (Kruskal–Wallis test, p < 0.05).

Table 1.
Umbrella diameter and body weight of R. esculentum (average ± SD).
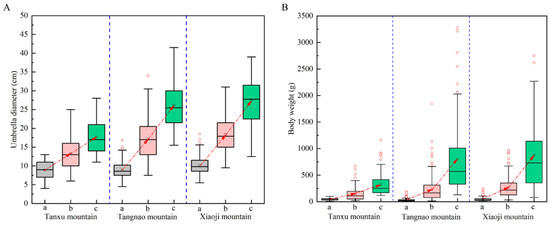
Figure 2.
Changes in umbrella diameter and body weight of R. esculentum in three monitoring areas. (A) Umbrella diameter variation; (B) body weight variation; (a) 8th June 2024; (b) 20th June 2024; (c) 4th July 2024. Boxes represent the mean umbrella diameter.
3.2. Daily Growth Rate of R. esculentum Umbrella Diameter and Body Weight
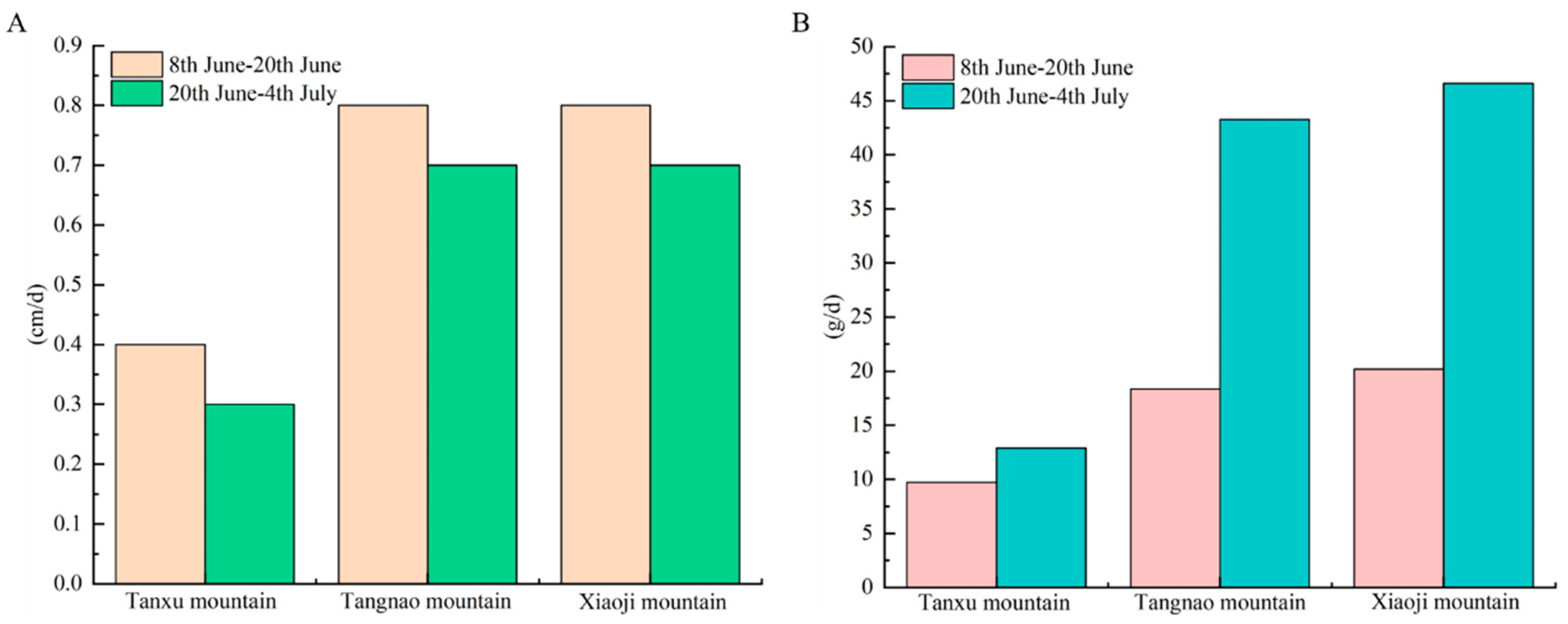
The daily umbrella diameter growth rate in the Tanxu Mountain sea area was 0.4 cm/day from the 8th to 20th of June, decreasing to 0.3 cm/day from the 20th of June to the 4th of July. The daily umbrella diameter growth rate in the Tangnao Mountain sea area was 0.8 cm/day from the 8th to 20th of June, declining to 0.7 cm/day from the 20th of June to the 4th of July. The daily umbrella diameter growth rate in the Xiaoji Mountain sea area was 0.8 cm/day from the 8th to 20th of June, but decreased to 0.7 cm/day from the 20th of June to the 4th of July. The daily body weight growth rate in the Tanxu Mountain sea area was 9.71 g/day from the 8th to 20th of June, increasing to 12.9 g/day from the 20th of June to the 4th of July, a 1.32-fold increase. The daily body weight growth rate in the Tangnao Mountain sea area was 18.4 g/day from the 8th to 20th of June, and increased to 43.3 g/day from the 20th of June to the 4th of July, a 2.35-fold increase. The daily body weight growth rate in the Xiaoji Mountain sea area was 20.2 g/day from the 8th to 20th of June, and increased to 46.6 g/day from the 20th of June to 4th of July, a 2.31-fold increase. These patterns indicate that the umbrella diameter growth rate gradually decreased, whereas the body weight growth rate increased over time. The umbrella diameter and body weight in the Tangnao and Xiaoji mountain sea areas exhibited significantly higher growth rates than those in the Tanxu Mountain sea area (Figure 3).
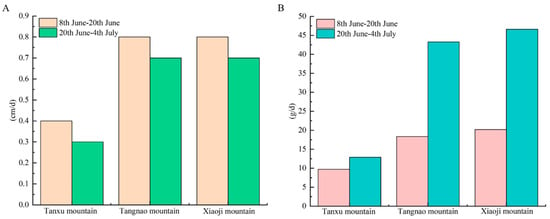
Figure 3.
Daily growth rate of R. esculentum in three monitoring areas. (A) Daily growth rate of umbrella diameter; (B) daily growth rate of body weight.
3.3. Growth Curve of R. esculentum
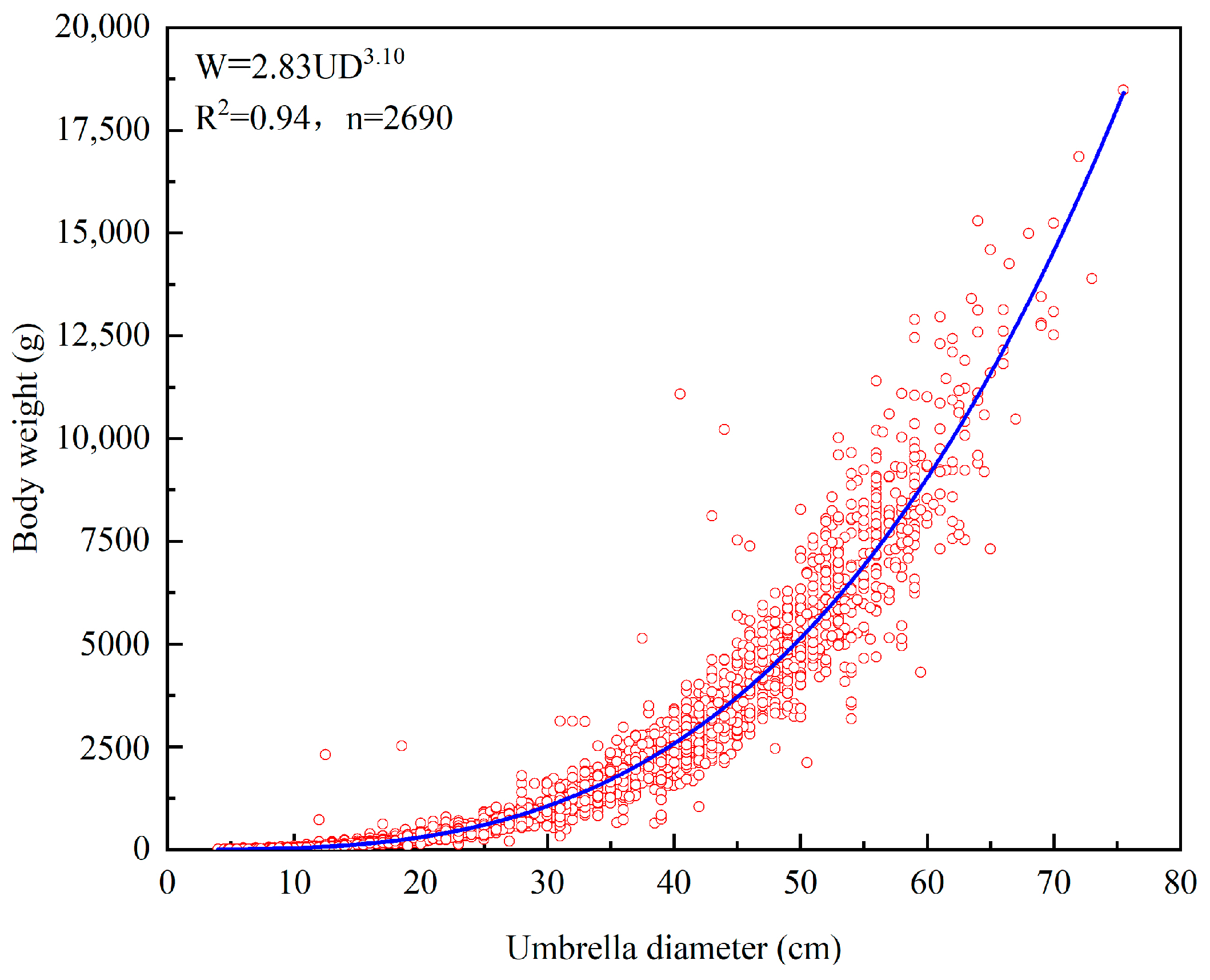
Based on 2690 measurements of R. esculentum, we analysed the relationship between umbrella diameter and body weight (Figure 4), which can be expressed as follows:
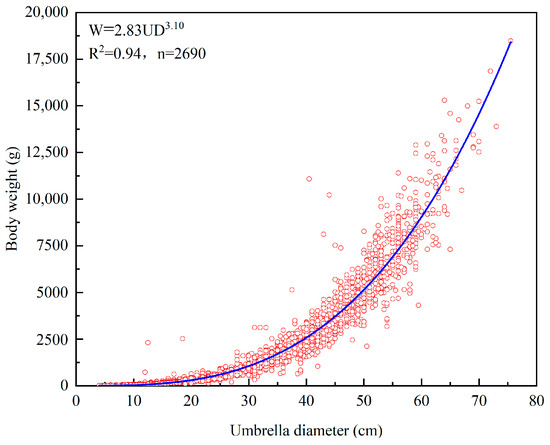
Figure 4.
The relationship between umbrella diameter and body weight of R. esculentum.
Growth curves for the umbrella diameter and body weight are expressed as follows:
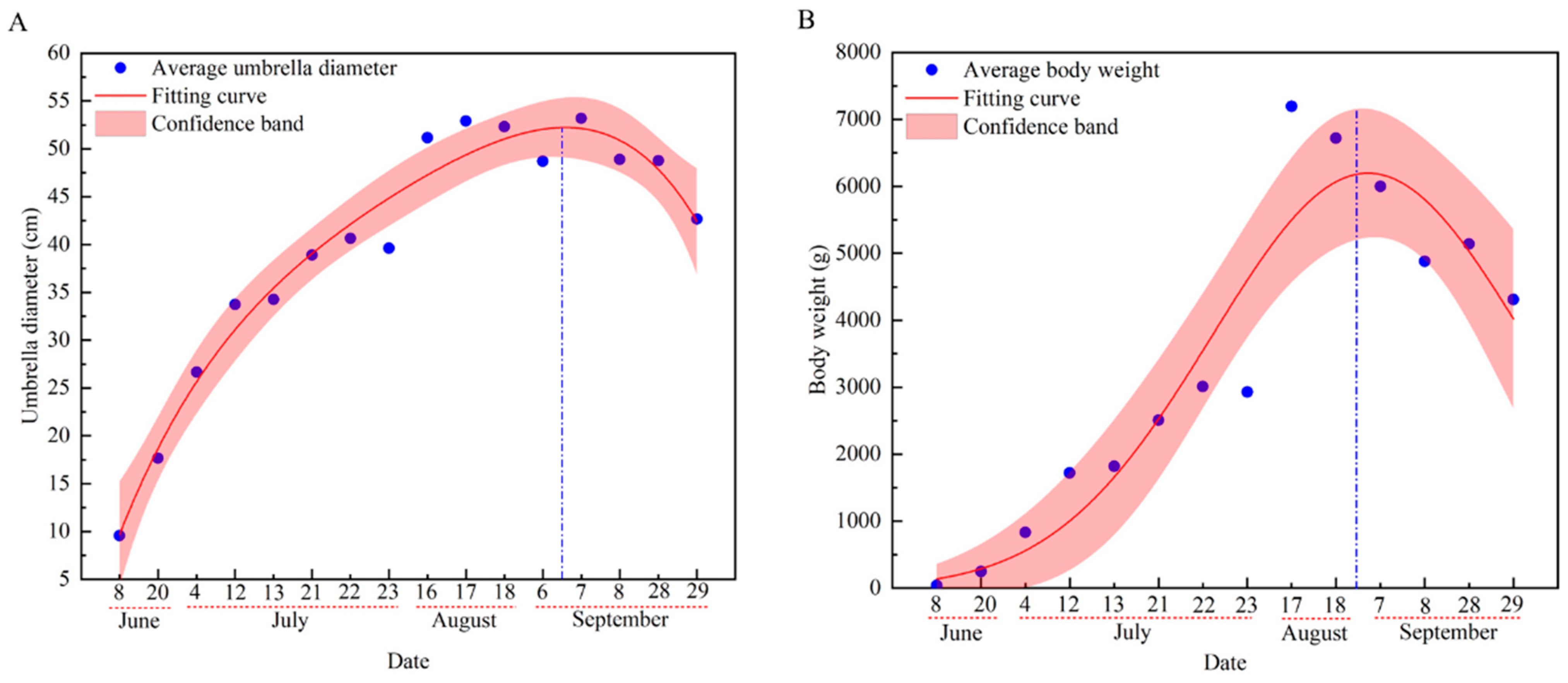
The umbrella diameter and body weight of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay increased initially, peaking on the 6th of September and 28th of August, respectively, before declining (Figure 5).
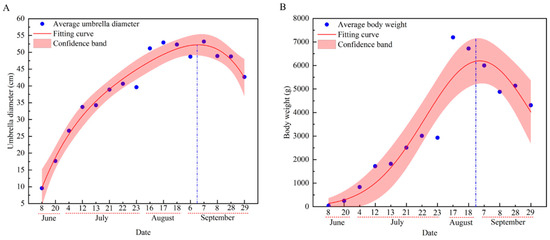
Figure 5.
Growth curve of R. esculentum. (A) Growth curve of average umbrella diameter; (B) growth curve of average body weight. The red dotted line indicate the dates within the month; the blue dotted line indicate the highest point of the curve.
3.4. Monitoring Marine Environmental Factors and Comparison with 2023
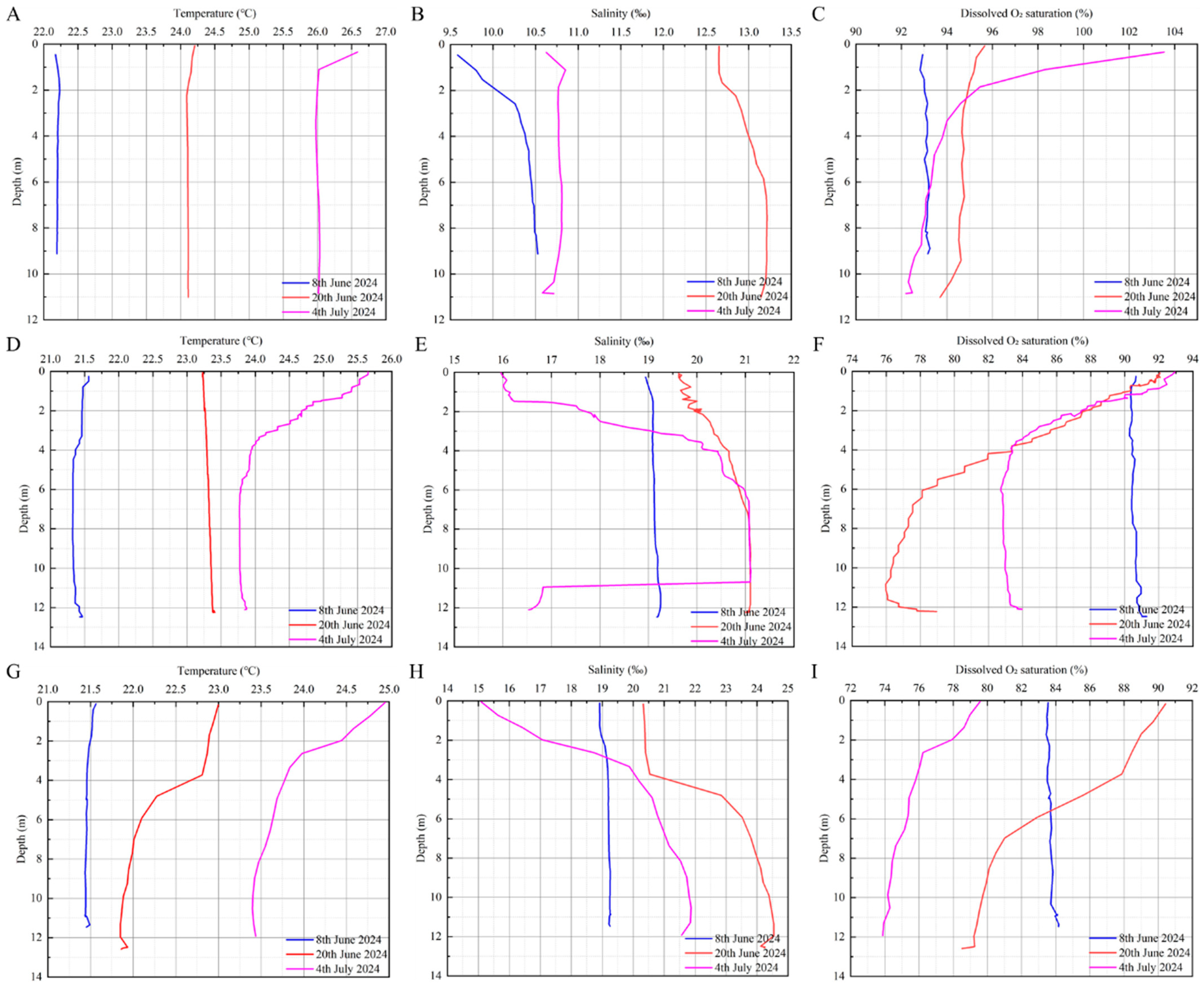
The seawater temperatures at the three monitoring stations showed an increasing tread. The water temperature in the Tanxu Mountain sea area showed the fastest and highest increase, increasing by 3.84 °C from the 8th of June to the 4th of July, followed by the Tangnao Mountain sea area, which increased by 2.94 °C, and the Xiaoji Mountain sea area increased by 2.37 °C. From the 8th of June to the 4th of July, a consistent water temperature was measured at the surface and bottom of the Tanxu Mountain sea area; however, at the Tangnao Mountain sea area, the surface temperature was higher than the bottom temperature on the 4th of July, whereas in the Xiaoji Mountain sea area, this occurred on the 20th of June.
In terms of salinity, all monitoring stations showed an increasing trend followed by a decreasing trend. The Tanxu Mountain sea area exhibited the lowest salinity, whereas the Xiaoji Mountain sea area showed the highest. Surface salinity was consistently lower than bottom salinity during the monitoring period. From the 20th of June to the 4th of July, salinity decreased by 2.23‰, 1.77‰, 3.24‰ at the Tanxu, Tangnao and Xiaoji Mountain sea areas, respectively, with more pronounced declines at the surface.
Regarding dissolved oxygen saturation, clear differences were observed across monitoring sites. The Tanxu Mountain sea area showed a slight increasing trend of 0.9%, whereas the Tangnao and Xiaoji Mountain waters exhibited a sharp decrease of 5.00% and 7.91%, respectively (Figure 6; Table 2).
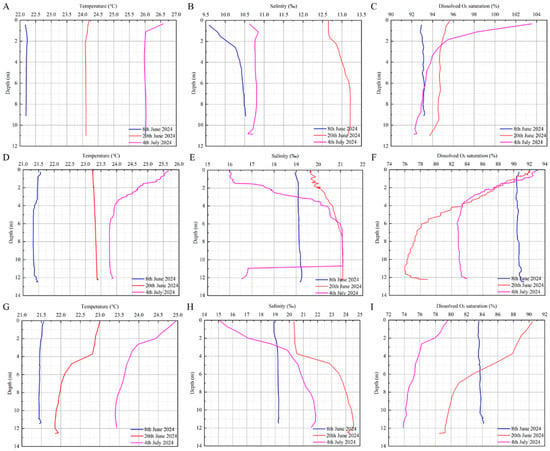
Figure 6.
Variation of environmental factors in three monitoring areas. (A): Temperature of Tanxu mountain; (B): salinity of Tanxu mountain; (C): dissolved O2 saturation of Tanxu mountain; (D): temperature of Tangnao mountain; (E): salinity of Tangnao mountain; (F): dissolved O2 saturation of Tangnao mountain; (G): temperature of Xiaoji mountain; (H): salinity of Xiaoji mountain; (I): dissolved O2 saturation of Xiaoji mountain.

Table 2.
Environmental data of monitoring areas in 2024.
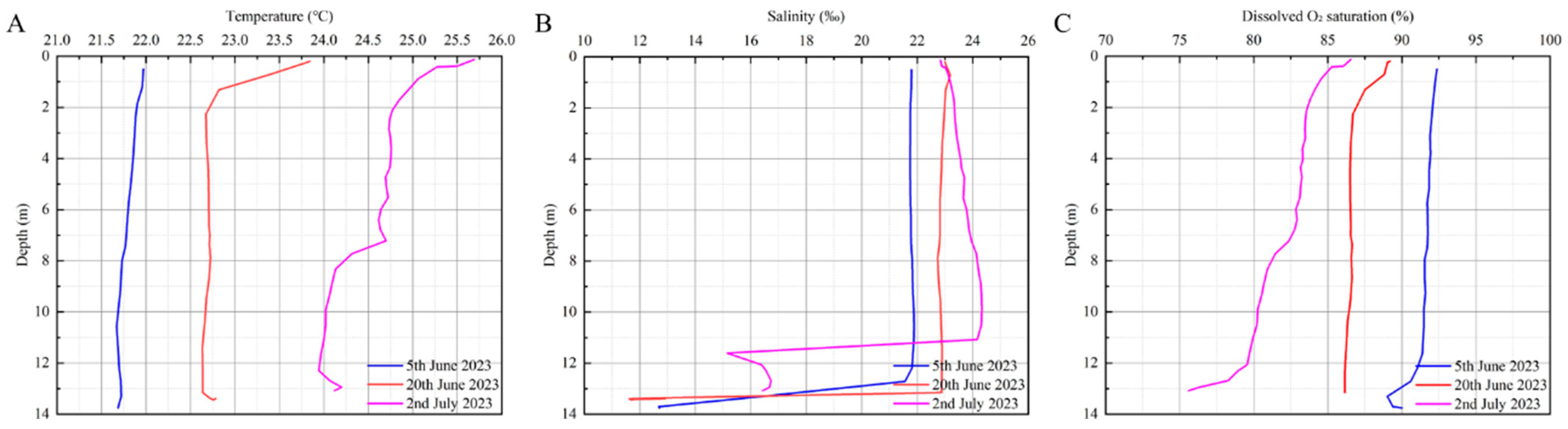
In 2023, monitoring in the Tangnao Mountain sea area from the 5th of June to 2nd of July showed rising trends in water temperature (increasing by 2.77 °C) and salinity (increasing by 1.87‰), whereas dissolved oxygen saturation levels declined (decreasing by 9.37%) (Figure 7; Table 3). However, a Kruskal–Wallis test revealed no significant difference in dissolved oxygen saturation between 2023 and 2024 (p < 0.05).
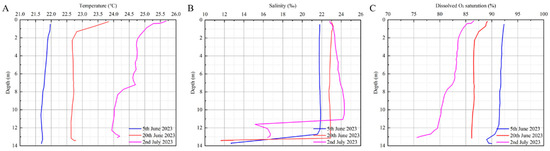
Figure 7.
Variation of environmental factors at Tangnao mountain station in 2023 with the date. (A) Temperature; (B) salinity; (C) dissolved O2 saturation.

Table 3.
Environmental data of Tangnao mountain sea area in 2023.
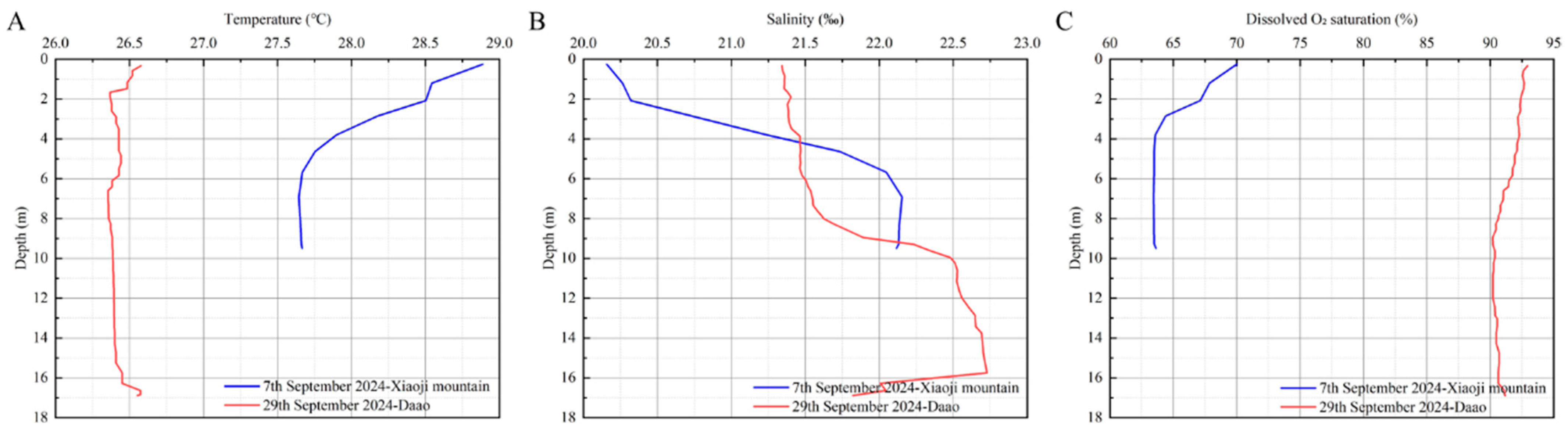
Environmental data were collected during the 2024 high-yield period. The water temperature at two high-yield locations, the Xiaoji Mountain and Daao sea areas, was 28.01 ± 0.45 °C and 26.42 ± 0.06 °C, respectively. The average salinity at Xiaoji Mountain and Daao was 21.37 ± 0.84‰ and 21.90 ± 0.52‰, respectively, showing minor variation. Dissolved oxygen saturation was significantly lower in Xiaoji Mountain compared with Daao (Figure 8; Table 4).
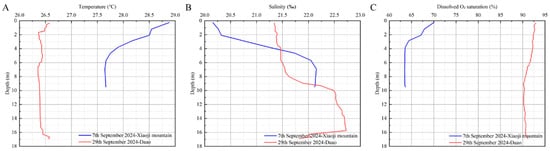
Figure 8.
Variation of environmental factors in high-yield marine areas. (A) Temperature; (B) salinity; (C) dissolved O2 saturation.

Table 4.
Environmental data of high-yield marine areas.
3.5. Distribution and Yield Analysis of Fishing Grounds
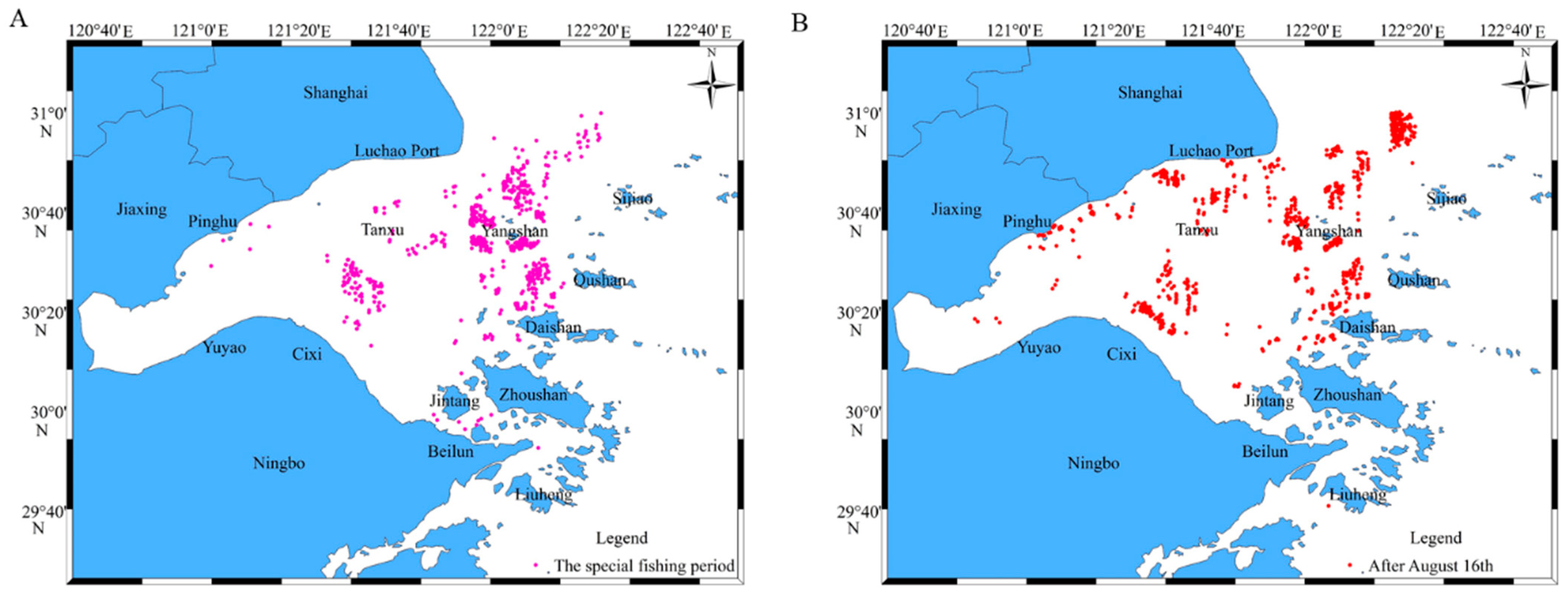
A special fishing period for R. esculentum was designated during the summer moratorium in 2024, from the 12th of July to 26th of July, with R. esculentum concentrated in the southern and eastern waters of Hangzhou Bay, specifically around Cixi, Yuyao and Beilun in Ningbo as well as in the waters of Jintang, Daishan, Qushan, Yangshan and Sijiao in Zhoushan. After the 16th of August, R. esculentum distribution expanded across the entire bay, including Pinghu in Jiaxing, Luchao Port in Shanghai and Tanxu in Zhoushan, as well as in the Liuheng area of Zhoushan (Figure 9).
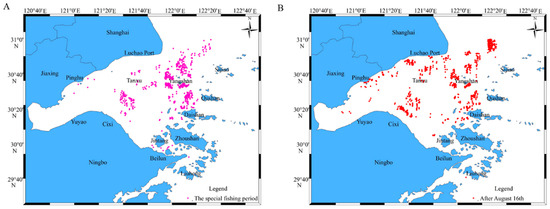
Figure 9.
The distribution of R. esculentum production waters. (A) The special fishing period of the summer fishing moratorium; (B) after August 16th.
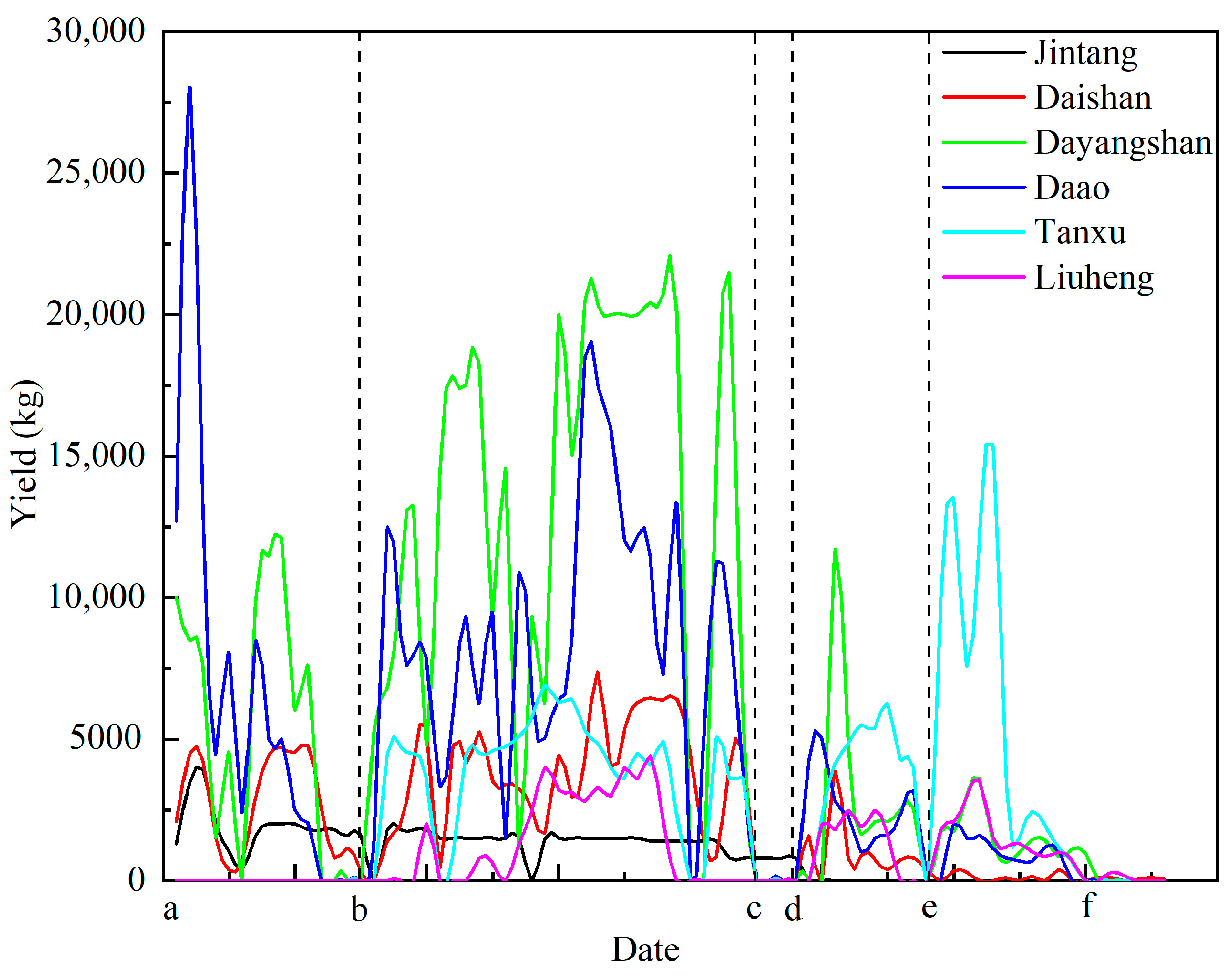
Yields during the moratorium surpassed those in previous years, peaking at 28,000kg/day in the Daao sea area. After the 16th of August, a large-scale R. esculentum bloom occurred across the Hangzhou Bay area, sharply increasing the output. Outside Hangzhou Bay, blooms were also observed in the Liuheng sea areas of Xiangshan Bay, reaching 4400 kg/day. Following the typhoon on the 20th of September, yields dropped significantly across all regions, except the Tanxu sea area. After a second typhoon on the 5th of October, most regions experienced further declines, but R. esculentum production in the Tanxu sea area increased significantly, reaching a peak of 15,100 kg/d (Figure 10).
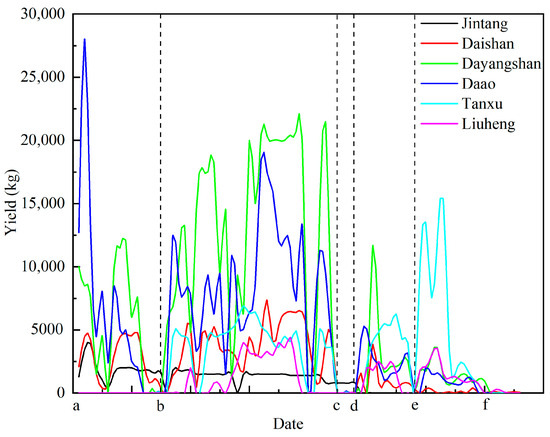
Figure 10.
Variation in R. esculentum production over time in different production areas: (a) 12th July 2024; (b) 16th August 2024; (c) 15th September 2024; (d) 20th September 2024; (e) 5th October 2024; (f) 27th October 2024. The black dotted lines indicate the timeline separator.
4. Discussion
4.1. The Growth Pattern of R. esculentum in the Hangzhou Bay Area
The present results indicate significant differences in the growth rate of R. esculentum’s umbrella diameter and body weight across sea areas of Hangzhou Bay, mainly influenced by salinity. During the study period, salinity in the Tanxu Mountain sea area was 10.33–12.99‰, significantly lower than that in the Tangnao Mountain and Xiaoji Mountain sea areas (18.67–20.44‰ and 19.15–23.06‰, respectively). The optimal salinity range for R. esculentum larvae survival is 16–20‰, with a lower limit of 8‰ and peak daily growth rate of 20‰ [19,20]. Compared with the other two sites, the Tanxu Mountain sea area’s salinity was below the optimal range, making it less favourable for R. esculentum growth. Over time, R. esculentum’s umbrella diameter growth gradually slowed, whereas body weight increased markedly, aligning with the species’ typical growth pattern [17]. In different Chinese coastal regions, the timing of maximum umbrella diameter varies, often associated with latitude. Typically, peak growth occurs later at higher latitudes. For example, Dong Jing et al. [3] reported a maximum R. esculentum umbrella diameter in Liaodong Bay on the 20th of September, whereas Tan Kefei [18] observed it on the 4th of September, with the differences attributed to simulation models [6]. Compared with Liaodong Bay in the north, the maximum R. esculentum umbrella diameter and body weight in the Minjiang Estuary occurred earlier, on the 5th of August and 30th of July, respectively [17]. In Hangzhou Bay, peak umbrella diameter and body weight were recorded on the 6th of September and 28th of August, respectively. These findings suggest interannual variability in the timing of peak umbrella diameter in R. esculentum, even within the same sea area, indicating the need for further investigation. However, the broader trend of delayed peak growth with increasing latitude remains consistent. Notably, in 2024, the maximum umbrella diameter and body weight of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay reached 75.5 cm and 18,470 g, respectively, surpassing the records of 53.0 cm and 7500 g documented previously [17]. Ongoing biological research in Hangzhou Bay will refine the theoretical understanding of R. esculentum life history and growth dynamics.
4.2. Analysis of the Causes of R. esculentum Blooms in Hangzhou Bay in 2024
Blooms of R. esculentum likely result from a combination of factors, although their precise causes remain unclear [10,13,14]. In China, jellyfish blooms frequently involve three species: Aurelia aurita, Cyanea nozakii, and Nemopilema nomurai [10]. Dam construction has been identified as an important contributor to jellyfish blooms, altering temperature and salinity, thereby creating conditions favourable for proliferation [10,11,12,13,21,22]. For example, following the impoundment of the Three Gorges Dam, Cyanea capillata abundance increased from 0.41% in 1998 to 85.47% in 2023 [11]. In 2003, C. nozakii in Zhoushan fishing grounds accounted for 70% of the total fishery yield [23]. In Liaodong Bay, C. nozakii blooms are believed to be responsible for an 80% decline in R. esculentum [10]. Among environmental variables, temperature and salinity exert the greatest influence on jellyfish populations [24,25,26]. The present study identified temperature, salinity and runoff as key drivers of R. esculentum blooms in Hangzhou Bay, with dissolved oxygen saturation showing limited effects. According to the meteorological and climate data from Zhoushan City (the main fishing ground for R. esculentum), the average temperature in 2024 was 17.9 °C, which was the highest on record and 0.9 °C above that in normal years, providing more favourable thermal conditions. As a warm-water species, R. esculentum tends to grow faster and produce more biomass under elevated temperatures [12,13].
After the release of R. esculentum, the mean precipitation in April was 153.8 mm, which was 56% above average, and the mean precipitation in May was 124.9 mm, which was 10% above average, contributing to favourable salinity conditions for R. esculentum. In addition, a further decrease in salinity in the later period was caused by the flood discharge from Xin’an River from the 24th of June to 4th of July, with a total discharge of 3.004 billion cubic metres, the second largest volume in history. The discharge lasted 264.3 h, the longest span since dam construction in 1960. The favourable salinity conditions in the early stage allowed R. esculentum to achieve a higher survival rate after release, and the subsequent discharge facilitated wider R. esculentum dispersal throughout Hangzhou Bay. With the change in salinity levels, the central fishing grounds changed, expanding distribution and improving environmental suitability through enhanced salinity and nutrient availability. These conditions, rarely observed before 1960, enabled historic R. esculentum production.
R. esculentum bloom occurred on the 16th of August instead of the 12th of July. This is mainly related to the lower salinity in the inner part of Hangzhou Bay. During early July, because of the flood discharge of Xin’an River, the traditional R. esculentum harvesting areas, including Pinghu in Jiaxing as well as the Tanxu and Shanghai sea areas, were not harvested because the jellyfish were too small. By late July, the precipitation in Zhoushan City had fallen to 61.2 mm, 41% below average, increasing the salinity and creating favourable conditions for the R. esculentum bloom in Hangzhou Bay. A concurrent bloom occurred in the Liuheng sea area of Xiangshan Bay on the 16th of August. Because the R. esculentum release sites are in Hangzhou Bay, they may have been carried downstream from the Xin’an River flood discharge to the Liuheng sea area, followed by rapid growth as the salinity increased, thus triggering the historical bloom of jellyfish in this sea area. Surface currents, widely recognised as drivers of gelatinous plankton aggregation [14,27,28], likely facilitated this process. Therefore, flood discharge and the resultant surface water flow were key contributions to the bloom in the Liuheng area. As shown in Figure 6D–F and Figure 7, the measured temperature diagram shows that, during the monitoring period, the water temperatures in 2024 were 0.22–0.39 °C lower than those in the same period of 2023. Based on the growth trend of R. esculentum, June is the key period for R. esculentum growth, and the lower temperature benefitted juvenile R. esculentum development. Without flood discharge, salinity variation would have been minimal. In 2023, the salinity increased from 21.79‰ to 23.66‰ between the 5th of June and 2nd of July. In constrast, in 2024, salinity increased from 19.13‰ to 20.44‰ between the 8th of June and 4th of July, followed by a decrease to 18.67‰, which was conducive to further juvenile growth. This highlights the pivotal role of the Xin’an River flood discharge in regulating the salinity of Hangzhou Bay. As an estuarine species, salinity may be the decisive factor for R. esculentum bloom in Hangzhou Bay, as confirmed in a study of N. nomurai [29].
In the later period, we further monitored environmental factors in the high-yield sea area, and the salinity was 21.37–21.90‰, which met the growth conditions of R. esculentum. In the final stage of R. esculentum fishing, we conducted social surveys in the main fishing areas of R. esculentum. From the 10th to 13th of October, R. esculentum and Portunus trituberculatus, sized approximately 20 cm, began appearing at the same time. We speculated that the released R. esculentum might have propagated in 2024. This may be related to the suitable salinity and elevated temperature conducive to the asexual reproduction of R. esculentum [13,14,30]. The appearance of P. trituberculatus also marks the end of the R. esculentum season, which concluded across fishing areas from the 16th of October.
In 2024, four typhoons affected Hangzhou Bay: the first from the 25th to 27th of July, one each on the 14th and 18th of September and a rare autumn typhoon on the 31st of October, which signalled the end of the fishing season. The absence of typhoons in August allowed for uninterrupted R. esculentum growth. Typhoon passage markedly disturbs the ocean surface [31,32], potentially lowering the sea surface temperature by up to 4.9 °C, thereby altering R. esculentum survival conditions. Zhejiang Energy Jiaxing Power Plant overload failures in the rotary filter of its circulation pump room, an issue not observed in the past 30 years. Between the 18th and 28th of September, more than 150 tonnes of material was cleared in total. Similarly, in the seawater pump room of the Thermal Power Department of China Petrochemical Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China, jellyfish were entangled in the rotating filter screen. From the 20th to 30th of September, a total of 117 tonnes was cleared. After the typhoon, a large number of R. esculentum appeared near coastal power plants, indicating that the seawater temperature had dropped substantially and that the species had migrated to areas with more favourable conditions for survival. Although this hypothesis needs further validation, it is consistent with the observed production patterns and field experience.
4.3. Management and Protection of R. esculentum Resources in the Hangzhou Bay Area
The 2024 bloom in Hangzhou Bay was unexpected and unprecedented. Historically, R. esculentum blooms are extremely rare. This event caused major operational disruptions, particularly at power plants along the northern shore of Hangzhou Bay, a phenomenon also observed with other jellyfish species [10,12,13,33]. In China, A. aurita is most commonly associated with blocking cooling water inlets of power plants [10]. Since August 2024, Shanghai’s Caojing Power Plant and Lingang Power Plant have experienced flooding by R. esculentum, resulting in their power generation being halved. In September, the issue also affected the Zhejiang Energy Jiaxing Power Plant and China Petrochemical Shanghai Petrochemical Co., Ltd. The rotating filter screen encountered severe blockages, drawing widespread public concern. As a long-term stock-enhancement species in Hangzhou Bay, R. esculentum brings economic and social benefits. Large-scale proliferation and release efforts are conducted at Hangzhou Bay annually from April to June. In 2024, approximately 1.86 billion juveniles (8–13 mm) were released in the waters of the Dinghai, Daishan, Pinghu and Shengsi sea areas. These efforts have established a regular R. esculentum fishing season in Hangzhou Bay each July. Since 2017, special permits have allowed R. esculentum harvesting during China’s national summer fishing moratorium. Along the Zhejiang coast, the fishing window was initially 10 days but extended to 15 days from 2023, ensuring the sustainable development of R. esculentum resources and the traditional fishermen’s livelihoods.
The growth and survival of R. esculentum are influenced by multiple factors [1,5,7,9,20], particularly the conditions of the release area. As an important means to restore R. esculentum fishery resources, it is necessary to improve the survival rate of released individuals. However, recapture rates remain low at 3.0–3.2% in Liaodong Bay [3] and only 0.1–2.33% along the Zhejiang coast [7], and post-release mortality is high, with juvenile losses reaching up to 79% within 2–3 days [3]. To better manage and conserve R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay, we propose three strategies. First, ensure the suitability of release-site environmental conditions, especially temperature and salinity, which are critical for juvenile survival [5,19,20]. Second, set rational fishing times that align with annual climatic variability and growth rates to maximise yields [34,35]. Finally, progressively implement a catch quota system to regulate harvests and protect R. esculentum stock sustainability. The 2024 R. esculentum bloom in Hangzhou Bay resulted from a convergence of favourable environmental and weather conditions (especially temperature, salinity and runoff), geographic advantage (as a traditional growth and reproduction site) and human input (release programmes and relaxed fishing restrictions). Despite this rare event, the restoration of R. esculentum fishery resources in Hangzhou Bay remains a long-term challenge.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the growth regularity of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay was analysed. The maximum values of umbrella diameter and body weight appeared on the 6th of September and 28th of August, respectively. A sharp drop in salinity caused by the Xin’anjiang Reservoir flood discharge from the 23rd to 28th of June was the primary cause of the R. esculentum blooms in Hangzhou Bay. In 2024, R. esculentum production in Hangzhou Bay totalled 250,000 tonnes, breaking historical records. Overall, this study provides foundational data for the growth dynamics and spatial distribution of R. esculentum in Hangzhou Bay, offering insights into the underlying causes of the 2024 bloom in Hangzhou Bay.
Author Contributions
G.X.: methodology, formal analysis and writing—original draft preparation. G.X.: software and data curation. G.X. and Y.Z.: writing—review and editing, visualisation, supervision and project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Zhoushan Basic Research Science and Technology Project [2024C31047] and the Zhejiang Fishery Resources Survey Special Project [HYS-CZ-202314].
Data Availability Statement
The datasets that support the findings of this study are available from the first author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of Zhejiang Marine Fisheries Research Institute for their help and support in our experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, M.-X.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.-S.; Chen, Z.G. Preliminary study on the breeding habits of edible jellyfish in Hangzhou Wan Bay. J. Fish. China 1985, 9, 239–246. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peggy Hsieh, Y.H.; Leong, F.M.; Rudloe, J. Jellyfish as food. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Jiang, L.X.; Tan, K.F.; Liu, H.Y.; Purcell, J.E.; Li, P.J.; Ye, C.C. Stock enhancement of the edible jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye) in Liaodong Bay, China: A review. Hydrobiologia 2009, 616, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, M.; Nakano, E. Jellyfish fisheries in Southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Discussion on the factors affecting the fluctuation of Rhopilema esculentum resources. Donghai Mar. Sci. 1983, 81–82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- You, K.; Bian, Y.N.; Ma, C.H.; Chi, X.P.; Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.Y. Study on the carry capacity of edible jellyfish fishery in Liaodong Bay. J. Ocean Univ. China 2016, 15, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-D.; Wang, Y.-S.; Huang, M.X. Jellyfish, Rhopilema esculenta Kishinouye, enhancement research in the coastal waters of Zhejiang. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2004, 23, 28–30+36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, B.; Xu, J.M.; Song, L.S.; Wang, X. Application of neural network and MODIS 250 m imagery for estimating suspended sediments concentration in Hangzhou Bay, China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.Q.; Yu, G.H.; Wang, Y.H. Distributional features and fluxes of dissolved nitrogen, phosphorus and silicon in the Hangzhou Bay. Mar. Chem. 1993, 43, 65–81. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, W. Jellyfish blooms in the Yangtze Estuary. Science 2005, 307, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.J.; Liu, D.Y.; Keesing, J.K. Jellyfish blooms in China: Dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E.; Uye, S.I.; Lo, W.T. Anthropogenic causes of jellyfish blooms and their direct consequences for humans: A review. Mar. Eco. Pro. Ser. 2007, 350, 153–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E. Climate effects on formation of jellyfish and ctenophore blooms: A review. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 2005, 85, 461–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Canepa, A.; Fuentes, V.; Tamburello, L.; Purcell, J.E.; Piraino, S.; Roberts, J.; Boero, F.; Halpin, P. Deterministic factors overwhelm stochastic environmental fluctuations as drivers of jellyfish outbreaks. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141060. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, C.H.; Dawson, M.N. What are Jellyfishes and Thaliaceans and Why do They Bloom? In Jellyfish Blooms; Pitt, K., Lucas, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.-J.; Tan, K.-F.; Ye, C.-C. Growth pattern and characterietics of edible jellyfish (Rhopilema esculenta) in Liaodong Bay. J. Fish. China 1988, 12, 243–250. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.-B.; Dai, Q.-S.; Yan, Y.-M.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, J.G. A study on growth of Rhopilema esculenta in Minjiang Estuary. J. Oceanogr. Taiwan Strait. 1999, 18, 314–319. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, K.-F. Simulate the weight growth of jellyfish in LB by higher degree exponential equation. Fish. Sci. 1987, 6, 16–18. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Liu, C.-Y.; Guo, P. Effect of salinity on larva of edible medusae (Rhopilema esculentum) at different development phases and a review on the cause of jellyfish resources falling greatly in Liaodong Bay. Acta Ecol. Sin. 1989, 9, 304–309. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.-H. Study on Larva Development, Juvenile Breeding and Growth Characteristics of Rhopilema esculenta; Shanghai Ocean University: Shanghai, China, 2011. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, S.W.; Kang, H.K.; Son, Y.B.; Jang, M.C.; Choi, K.H. Collapse of the Crustacean Mesozooplankton in the Northern East China Sea: Effects of the Three Gorges Dam? J. Coast. Res. 2013, 29, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, N.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.H.; Gardner, W.D.; Mishonov, A.V.; Richardson, M.J.; Hong, N.; Pan, D.L.; Yan, X.H.; Jo, Y.H.; et al. Ecological anomalies in the East China Sea: Impacts of the three gorges dam? Water Res. 2007, 41, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-P.; Bo, Z.-L.; Zhou, W.-X.; Xue, L.J. Investigation of the familiar jellyfish species in Zhejiang Sea area and their influence on fishery in flourishing year. J. Zhejiang Ocean Univ. (Nat. Sci.). 2007, 26, 266–271. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, J.E. Jellyfish and ctenophore blooms coincide with human proliferations and environmental perturbations. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 209–235. [Google Scholar]
- Primo, A.L.; Marques, S.C.; Falco, J.; Crespo, D.; Pardal, M.A.; Azeiteiro, U.M. Environmental forcing on jellyfish communities in a small temperate estuary. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 79, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heim-Ballew, H.; Olsen, Z. Salinity and temperature influence on Scyphozoan jellyfish abundance in the Western Gulf of Mexico. Hydrobiologia 2019, 827, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, M.; Berline, L.; Lombard, F.; Guidi, L.; Elineau, A.; Mendoza-Vera, J.M.; Lilley, M.K.S.; Taillandier, V.; Gorsky, G. Distribution of Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) in the Ligurian Sea (NW Mediterranean Sea). J. Plankton Res. 2012, 34, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, W.M.; Pagèes, F.; Hamner, W.M. A physical context for gelatinous zooplankton aggregations: A review. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wang, B.; Duan, Y.; Yoon, W.D.; Wang, A.Y.; Liu, X.Z.; Li, Y.L.; Sun, M.; Chai, Y. Initial occurrence, ontogenic distribution-shifts and advection of Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) in Liaodong Bay, China, from 2005–2015. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2018, 591, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, J.E.; Atienza, D.; Fuentes, V.; Olariaga, A.; Tilves, U.; Colahan, C.; Gili, J.M. Temperature effects on asexual reproduction rates of scyphozoan species from the northwest Mediterranean Sea. Hydrobiologia 2012, 690, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-M.; Han, S.-Z.; Wang, M.-J.; Su, H.X. Statistical study on the influence of typhoon with different path on the temperature of coastal waters of China. J. Trop. Oceanogr. 2024, 43, 17–31. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Price, J.F.; Morzel, J.; Niiler, P.P. Warming of SST in the cool wake of a moving hurricane. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C07010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, K.; Kamiya, K.; Yamashita, K.; Hayashi, F.; Watanabe, I.; Murao, Y.; Miyasaka, H.; Kamimura, N.; Nogami, M. Genetic polymorphism of the adult medusae invading an electric power station and wild polyps of Aurelia aurita in Wakasa Bay, Japan. J. Mar. Biol. Ass. UK 2005, 85, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Meng, T. Fishing in Bohai Bay and three fishery problem. Contemp. Econ. Manag. 2007, 29, 61–64. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Sun, K.; Xu, B. ‘Three fishery problems’ and public policy adjusting approach—Case study of jellyfish fishing in LB. J. Pub. Manag. 2007, 14, 30–35. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).