Large-Eddy Simulation of Flows Past an Isolated Lateral Semi-Circular Cavity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Computational Method and Setup
2.1. Numerical Framework
2.2. Computational Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Verification
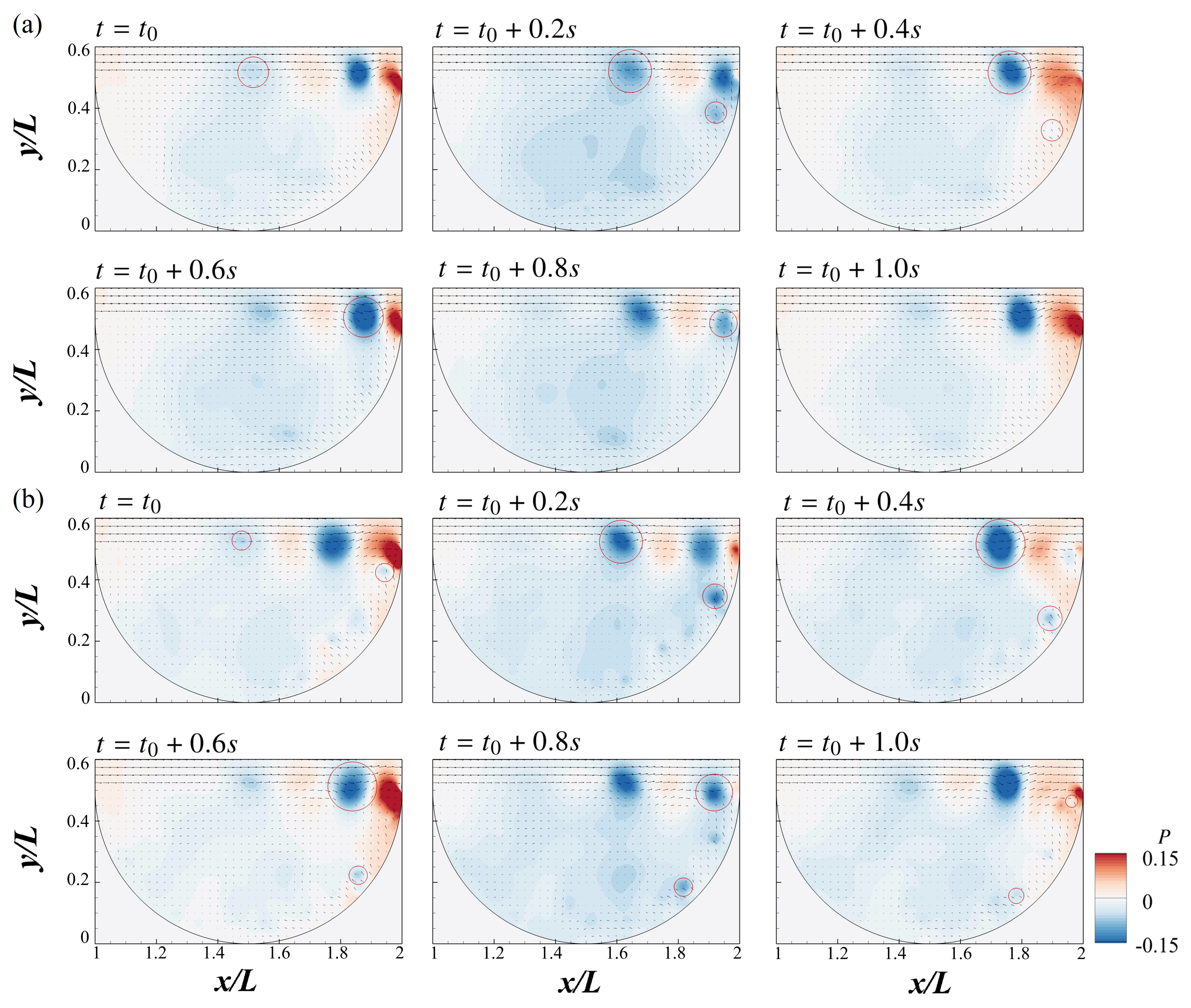
3.2. Time-Averaged Flow Structures
3.3. Second-Order Turbulence Statistics
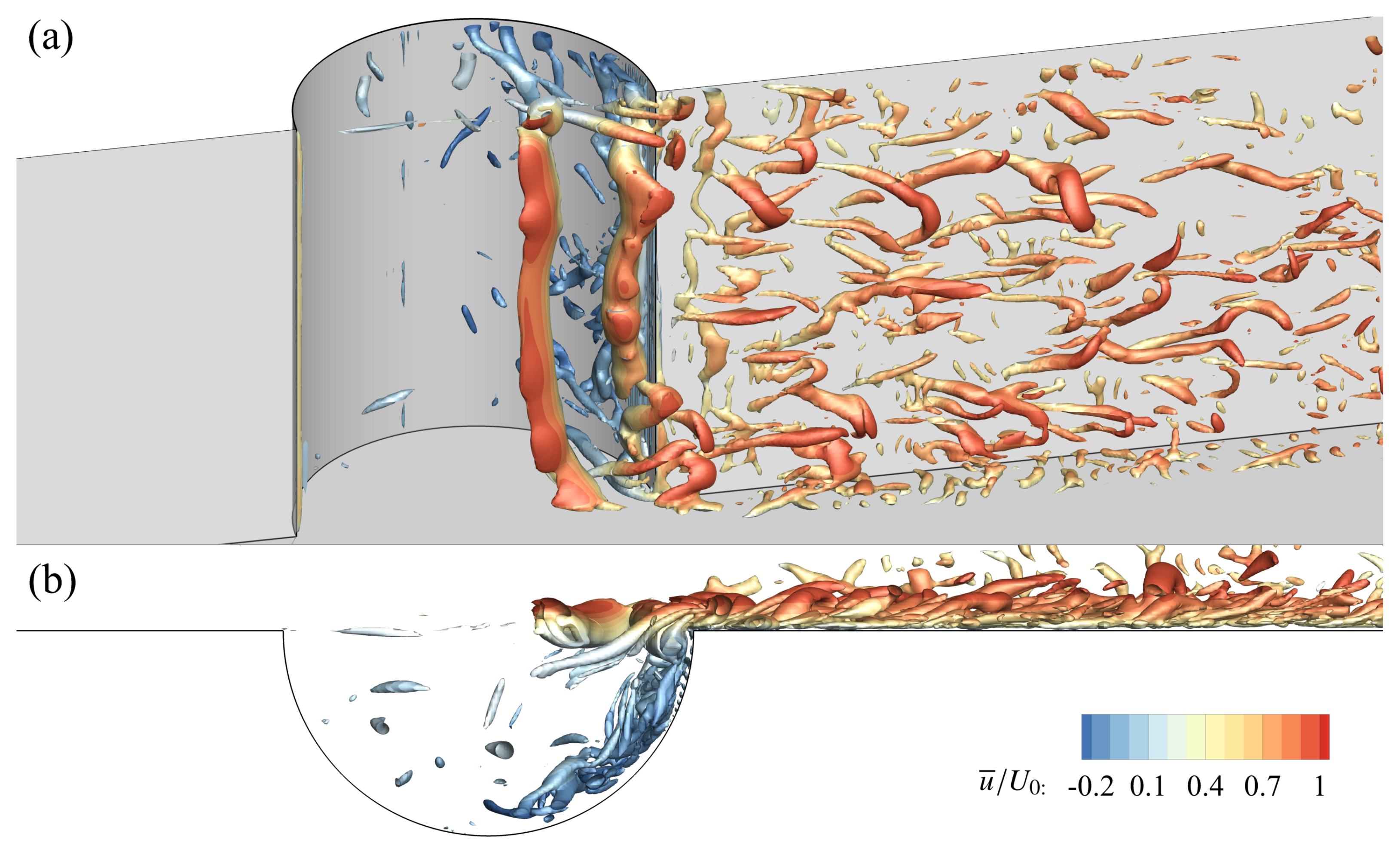
3.4. Instantaneous Turbulent Flow Structures
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The time-averaged flow field features a dominant MV and a small upstream CV. With increasing Reynolds number, the MV core shifts upstream and shear layer interactions intensify, modifying the internal recirculation dynamics.
- (2)
- As increases from to , turbulence intensities and Reynolds shear stresses increase significantly near the cavity boundaries and shear interface, enhancing momentum exchange and mixing. However, a further increase to leads to a minimal change, indicating a transition toward a quasi-equilibrium regime.
- (3)
- Instantaneous flow structures visualized by the Q-criterion reveal coherent KH vortices forming at the cavity mouth, with intensified secondary vortex (SV) generation and penetration at higher Reynolds numbers.
- (4)
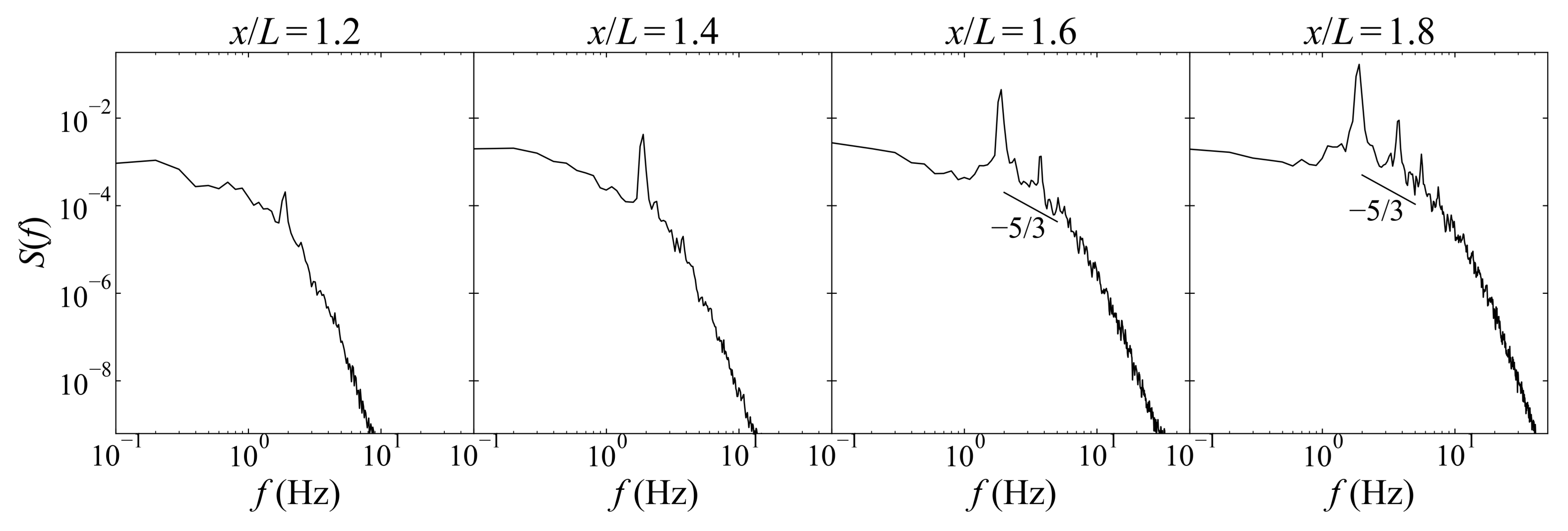
- The spectral analysis of spanwise velocity fluctuations reveals dominant KH instability frequencies governing the periodic transport of momentum and vorticity into the cavity. Fully developed turbulence emerges downstream of the cavity mouth, where an inertial subrange with a localized −5/3 slope appears. In contrast, the upstream region remains viscosity-dominated with underdeveloped shear layer turbulence.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacMahan, J.H.; Thornton, E.B.; Reniers, A.J. Deterministic Coastal Morphological and Sediment Transport Modeling: A Review and Discussion. Rev. Geophys. 2010, 48, RG3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falqués, A.; Calvete, D.; Dodd, N.; de Swart, H.E. Understanding Coastal Morphodynamic Patterns from Depth-Averaged Sediment Concentration. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 201–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fan, N.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Xie, X.; Jia, Y. Deep seabed mining: Frontiers in engineering geology and environment. Int. J. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fan, N.; Zheng, D.; Fu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Song, X.; Nian, T. Predicting impact forces on pipelines from deep-sea fluidized slides: A comprehensive review of key factors. Int. J. Min. Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, B.K.; van der Heide, K.; van de Koppel, M.; Piersma, T.; van der Veer, H.W.; Olff, H. Ecosystem Engineering and Biodiversity in Coastal Sediments. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2009, 63, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.E.; Herbert, R.J.; Britton, J.R.; Hull, S.L. Ecological Enhancement Techniques to Improve Habitat Heterogeneity on Coastal Defence Structures. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2018, 210, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, L.B.; Janus, L.L.; Casselman, J.M. Submerged Aquatic Vegetation in Cook’s Bay, Lake Simcoe. J. Gt. Lakes Res. 2011, 37, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Galindo, G.A.; Wolff, M.; Saint-Paul, U. Multilevel Decomposition of Spatial and Environmental Effects on Nearshore Fish Assemblages in Tropical Semi-Enclosed Ecosystems. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2020, 237, 106691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, E.C.F. Coastal Geomorphology: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Symonds, J.P.; Jones, R.M. The Influence of Geomorphology and Sedimentary Processes on Benthic Habitat Distribution and Littoral Sediment Dynamics, Geraldton, Western Australia. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2009, 84, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliot, M.; Eliot, G. Shoreline Salients, Cuspate Forelands and Tombolos on the Coast of Western Australia. J. Coast. Res. 2010, 26, 812–822. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, T.; Ralston, D.K. Frontogenesis, Mixing, and Stratification in Estuarine Channels with Curvature. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2022, 52, 1333–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquaud, P.; Schinegger, J.; Blanchet, S. Estuarine Lateral Ecotones Shape Taxonomic and Functional Structure of Fish Assemblages. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2024, 313, 109066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, M.G.; Underwood, A.J. Scales of variation of gastropod densities over multiple spatial scales: Comparison of common and rare species. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2007, 348, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Thompson, R.J.A.; Chapman, L.A. Designing for sedimentation: The role of urban structures in the accumulation and distribution of estuarine sediment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 507, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uijttewaal, W.S.J.; Lehmann, D.; van Mazijk, A. Exchange processes between a river and its groyne fields: Model experiments. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 928–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesack, L.F.W.; Marsh, P. River-to-lake connectivities, water renewal, and aquatic habitat diversity in the Mackenzie River Delta. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignot, E.; Barthelemy, E.; Hurther, A. Coherent turbulent structures at the mixing-interface of a square open-channel lateral cavity. Phys. Fluids 2016, 28, 045102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.P.; Sheu, W.H.; Hwang, R.R. Effect of Reynolds number on the eddy structure in a lid-driven cavity. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 1998, 26, 557–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.S.; Constantinescu, S.G.; Park, S. Analysis of the flow and mass transfer processes for the incompressible flow past an open cavity with a laminar and a fully turbulent incoming boundary layer. J. Fluid Mech. 2006, 561, 113–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faure, T.M.; Adrianos, P.; Lusseyran, F.; Pastur, L. Visualizations of the flow inside an open cavity at medium range Reynolds numbers. Exp. Fluids 2007, 42, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, K.; Jackson, T.; Haggerty, R.; Apte, S.V. RANS Predictions of Turbulent Scalar Transport in Dead Zones of Natural Streams. In Proceedings of the ASME 2012 Fluids Engineering Division Summer Meeting, Rio Grande, PR, USA, 8–12 July 2012; pp. 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, K.J.; Apte, S.V.; Haggerty, R.; Jackson, T.R. Parameterization of Mean Residence Times in Idealized Rectangular Dead Zones Representative of Natural Streams. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 140, 04014035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevis, W.; García-Villalba, M.; Niño, Y.N. Experimental and large eddy simulation study of the flow developed by a sequence of lateral obstacles. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2014, 14, 873–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.R.; Haggerty, R.; Apte, S.V.; Coleman, A.; Drost, K.J. Defining and measuring the mean residence time of lateral surface transient storage zones in small streams. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.R.; Haggerty, R.; Apte, S.V.; O’Connor, B.L. A mean residence time relationship for lateral cavities in gravel-bed rivers and streams: Incorporating streambed roughness and cavity shape. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3642–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, G.; Sukhodolov, A.; McCoy, A. Mass exchange in a shallow channel flow with a series of groynes: LES study and comparison with laboratory and field experiments. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2009, 9, 587–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juez, C.; Bühlmann, I.; Maechler, G.; Schleiss, A.J.; Franca, M.J. Transport of suspended sediments under the influence of bank macro-roughness. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, A.; Constantinescu, G.; Weber, L. A numerical investigation of coherent structures and mass exchange processes in channel flow with two lateral submerged groynes. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43, W05445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitbrecht, V.; Socofolosky, S.A.; Jirka, G.H. Experiments on mass exchange between groin fields and main stream in rivers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 134, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, S.M.; Dewar, W.G.; Wroblewski, D.E. Experimental investigation of the flow characteristics within a shallow wall cavity for both laminar and turbulent upstream boundary layers. Exp. Fluids 2004, 36, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, S.D.; Lau, T.C.W.; Kelso, R.M. Three-dimensional flow within shallow, narrow cavities. J. Fluid Mech. 2013, 735, 587–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelen, L.; Perrot-Minot, C.; Mignot, E.; Rivière, N.; De Mulder, T. Lagrangian study of the particle transport past a lateral, open-channel cavity. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 013303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, C.; Krüger, A.; Wüst, A.; Mohrholz, A. A study of phytoplankton spatial distributions, flow structure and characteristics of mixing in a river reach with groynes. J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 1351–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozalp, C.; Pinarbasi, A.; Sahin, B. Experimental measurement of flow past cavities of different shapes. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2010, 34, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, T.R.; Apte, S.V.; Haggerty, R.; Budwig, R. Flow Structure and Mean Residence Times of Lateral Cavities in Open Channel Flows: Influence of Bed Roughness and Shape. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2015, 15, 1069–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koseff, J.R.; Street, R.L. The Lid-Driven Cavity Flow: A Synthesis of Qualitative and Quantitative Observations. J. Fluids Eng. 1984, 106, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro, P.; Juez, C.; Franca, M. Drivers for mass and momentum exchange between the main channel and river bank lateral cavities. Adv. Water Resour. 2020, 137, 103511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, M.; Ai, Y.; Huai, W. Turbulence Characteristics in Partially Vegetated Open Channels with Alternating Sparse and Dense Patches. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 015130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.; Constantinescu, G.; Park, S.O. Comparison of Large Eddy Simulation, Detached Eddy Simulation and Unsteady RANS Numerical Predictions of Flow Past a Bottom River Cavity. In Proceedings of the 32nd IAHR World Congress, Venice, Italy, 1–6 July 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ouro, P.; Cea, L.; Croquer, S.; Dong, W.; Garcia-Feal, O.; Navas-Montilla, A.; Rogers, B.D.; Uchida, T.; Juez, C. Benchmark of Computational Hydraulics Models for Open-Channel Flow with Lateral Cavities. J. Hydraul. Res. 2024, 62, 441–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yuan, S.; Tang, H.; Huai, W.; Yan, J. Investigation of turbulence and interfacial exchange features of the gap area within the fully developed Shallow-Submerged canopy flow. J. Hydrol. 2024, 643, 131938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huai, W.; Tang, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, S. Numerical study of mean and turbulent flow adjustments in open channels with limited near-bank vegetation patches. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 095117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlmann, M. An immersed boundary method with direct forcing for the simulation of particulate flows. J. Comput. Phys. 2005, 209, 448–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Stoesser, T.; Mao, J.; McSherry, R. LES of flow through and around a finite patch of thin plates. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 7587–7605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Dolcetti, G.; Stoesser, T.; Tait, S. Water surface response to turbulent flow over a backward-facing step. J. Fluid Mech. 2023, 966, A18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhang, H.; Lu, Y.; Li, T. A mass transfer-based LES modelling methodology for analyzing the movement of submarine sediment flows with extensive shear behavior. Coast. Eng. 2024, 191, 104531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Huang, L.; Stoesser, T.; Fang, H. On the role of the Froude number on flow, turbulence, and hyporheic exchange in open-channel flow through boulder arrays. Phys. Fluids 2024, 36, 095141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Mao, J.q.; Gong, Y.q.; Gao, H. Effect of triangular baffle designs on flow dynamics and sediment transport within standard box culverts. J. Hydrodyn. 2024, 36, 1142–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Xu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Lu, Y.; Liu, X.; Mao, J. An LES Investigation of Flow Field Around the Cuboid Artificial Reef at Different Angles of Attack. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlun, E.; Verzicco, R.; Orlandi, P.; Mohd-Yusof, J. Combined immersed-boundary finite-difference methods for three-dimensional complex flow simulations. J. Comput. Phys. 2000, 161, 35–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoud, F.; Ducros, F. Subgrid-scale stress modelling based on the square of the velocity gradient tensor. Flow Turbul. Combust. 1999, 62, 183–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peskin, C. Fluid dynamics of heart valves: Experimental, theoretical, and computational methods. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 1982, 14, 235–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, A.; Stoesser, T.; Xie, Z. A large-eddy-simulation-based numerical wave tank for three-dimensional wave-structure interaction. Comput. Fluids 2021, 231, 105179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorin, A.J. Numerical solution of the Navier-Stokes equations. Math. Comput. 1968, 22, 745–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevheri, M.; McSherry, R.; Stoesser, T. A local mesh refinement approach for large-eddy simulations of turbulent flows. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2016, 82, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouro, P.; Fraga, B.; Lopez-Novoa, U.; Stoesser, T. Scalability of an Eulerian–Lagrangian large-eddy simulation solver with hybrid MPI/OpenMP parallelisation. Comput. Fluids 2019, 179, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Effects of vegetation density on flow, mass exchange and sediment transport in lateral cavities. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 129567. [Google Scholar]
- Jarrin, N.; Benhamadouche, S.; Laurence, D.; Prosser, R. A synthetic-eddy-method for generating inflow conditions for large-eddy simulations. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2006, 27, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzic, F.; Stoesser, T.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Z. Large-eddy simulation of supercritical free-surface flow in an open-channel contraction. J. Hydraul. Res. 2022, 60, 628–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Bai, J.; He, G.; Zhao, H. Calculations of Nonsubmerged Groin Flow in a Shallow Open Channel by Large-Eddy Simulation. J. Eng. Mech. 2014, 140, 04014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meile, T.; Boillat, J.L.; Schleiss, A.J. Flow Resistance Caused by Large-Scale Bank Roughness in a Channel. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 1588–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, S.S.; Das, D. High Reynolds number incompressible turbulent flow inside a lid-driven cavity with multiple aspect ratios. Phys. Fluids 2018, 30, 075103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Uchida, T. Role of three-dimensional vortex motions on horizontal eddies in an open-channel cavity. Environ. Fluid Mech. 2024, 24, 539–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

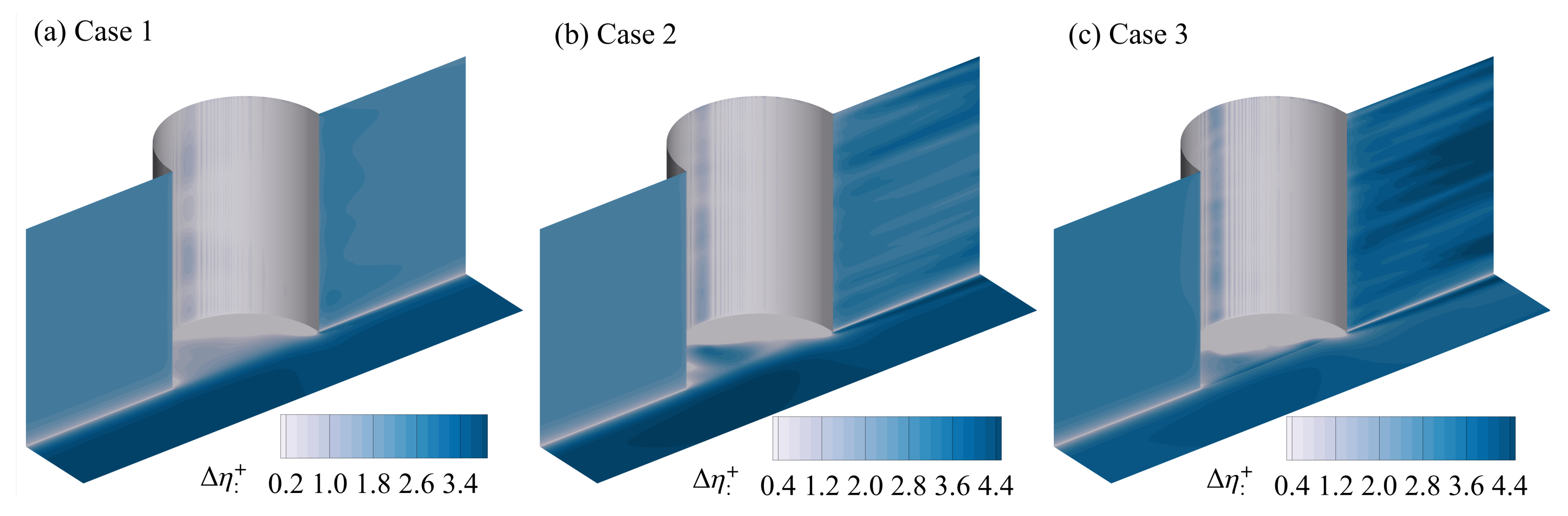
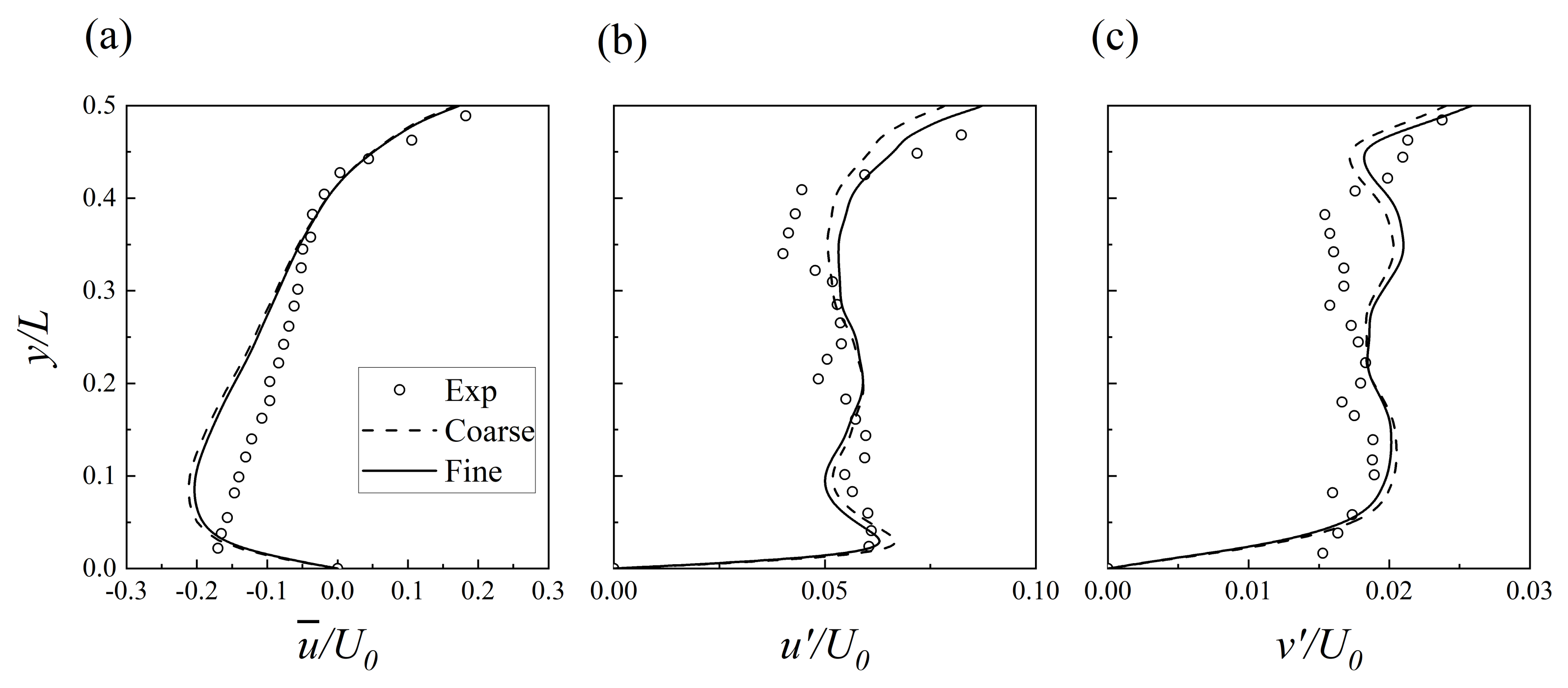

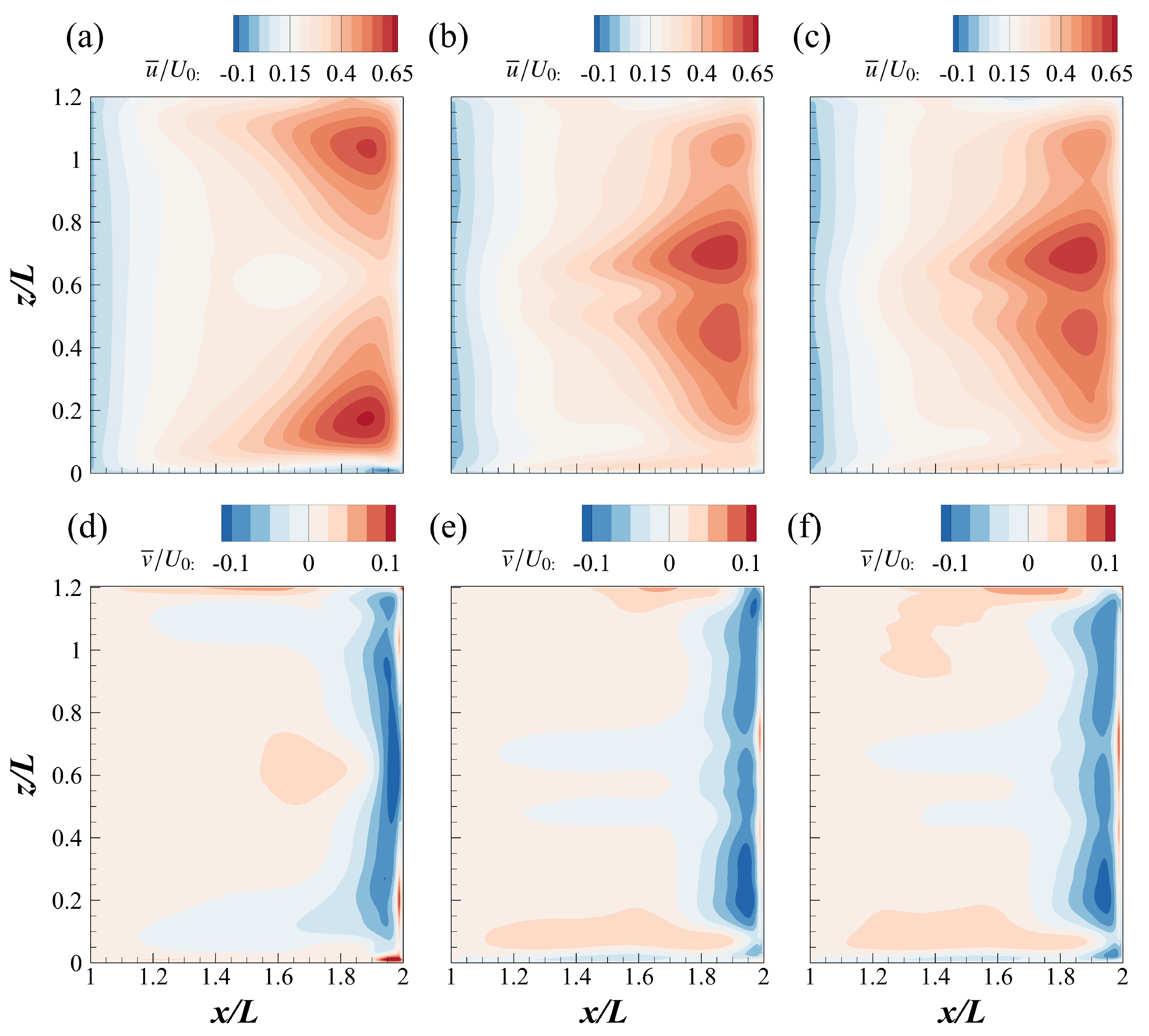

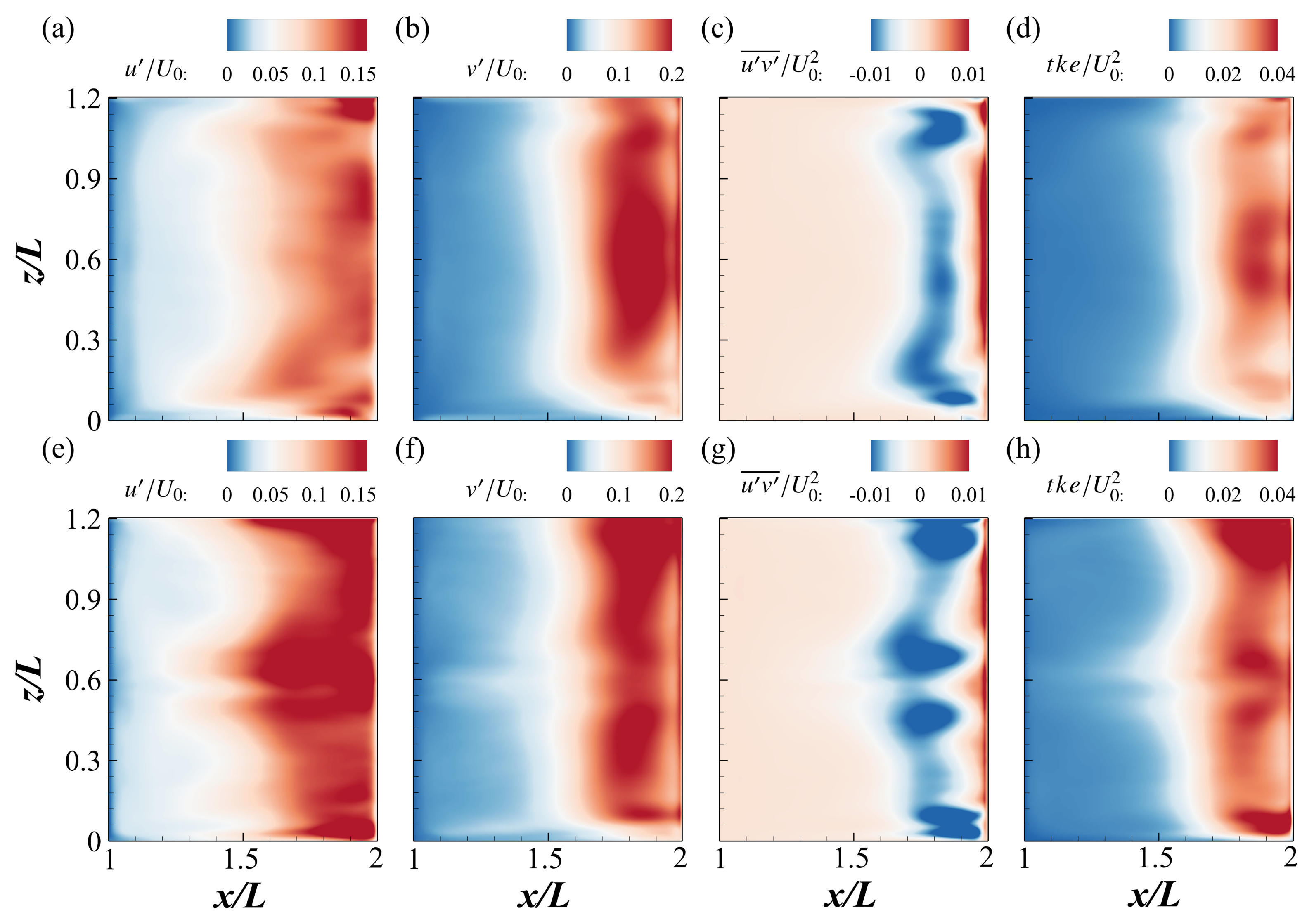
| Case | (mm) | (mm) | (m/s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.625 | 1.0 | 0.12 | 12,000 | 0.11 |
| 2 | 0.625 | 1.0 | 0.17 | 17,000 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 0.625 | 0.5 | 0.22 | 22,000 | 0.20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Y.; Xu, Y.; Mao, J.; Dai, J.; He, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Q. Large-Eddy Simulation of Flows Past an Isolated Lateral Semi-Circular Cavity. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050859
Gong Y, Xu Y, Mao J, Dai J, He L, Zhang H, Xu Q. Large-Eddy Simulation of Flows Past an Isolated Lateral Semi-Circular Cavity. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(5):859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050859
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Yiqing, Yun Xu, Jingqiao Mao, Jie Dai, Lei He, Hao Zhang, and Qianshun Xu. 2025. "Large-Eddy Simulation of Flows Past an Isolated Lateral Semi-Circular Cavity" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 5: 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050859
APA StyleGong, Y., Xu, Y., Mao, J., Dai, J., He, L., Zhang, H., & Xu, Q. (2025). Large-Eddy Simulation of Flows Past an Isolated Lateral Semi-Circular Cavity. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(5), 859. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13050859







