A Deep Learning Approach for Identifying Intentional AIS Signal Tampering in Maritime Trajectories
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Traditional Machine Learning in Maritime Supervision
2.2. Deep Learning Methods Based on AIS Data
3. Method Overview
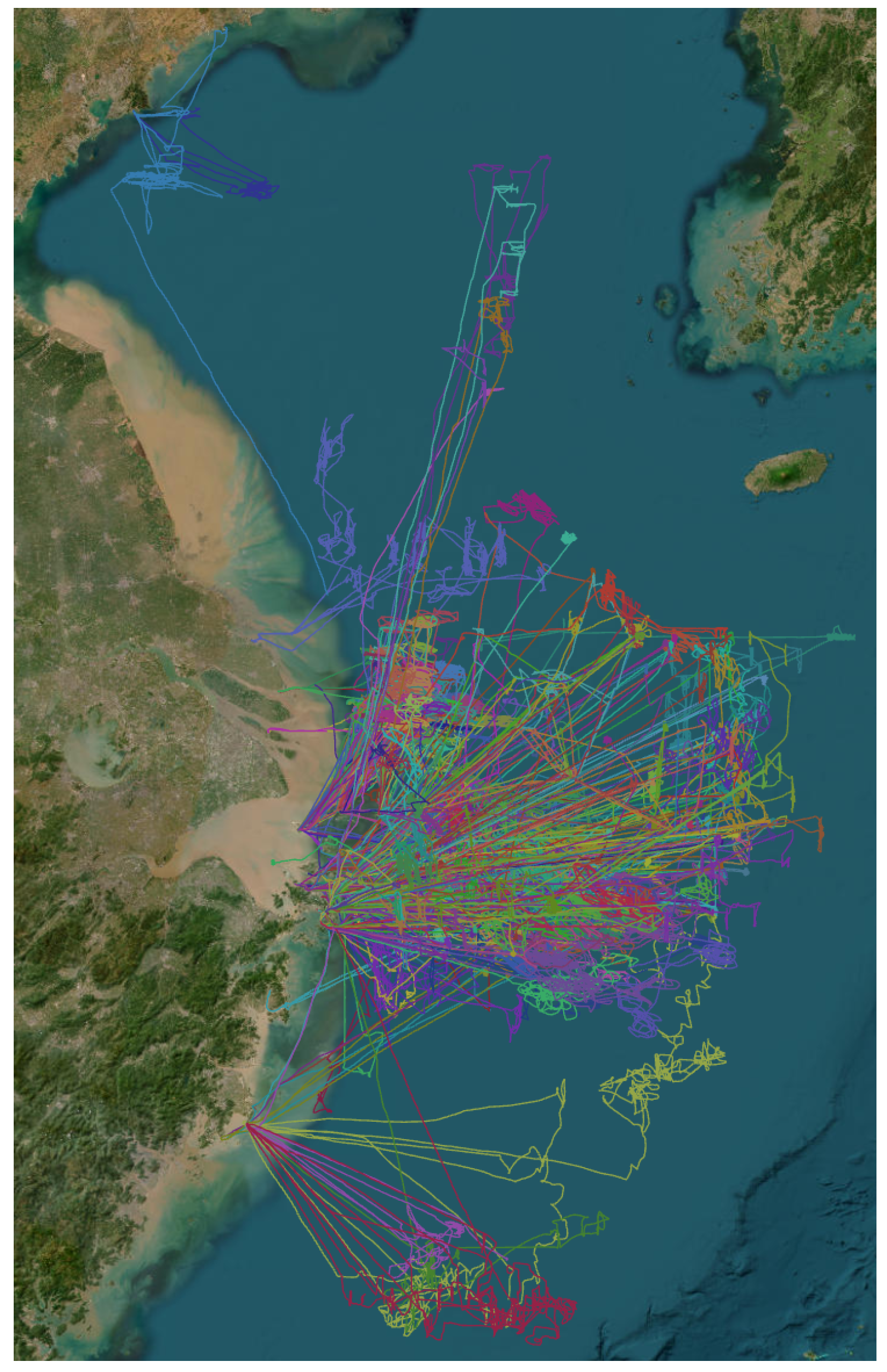
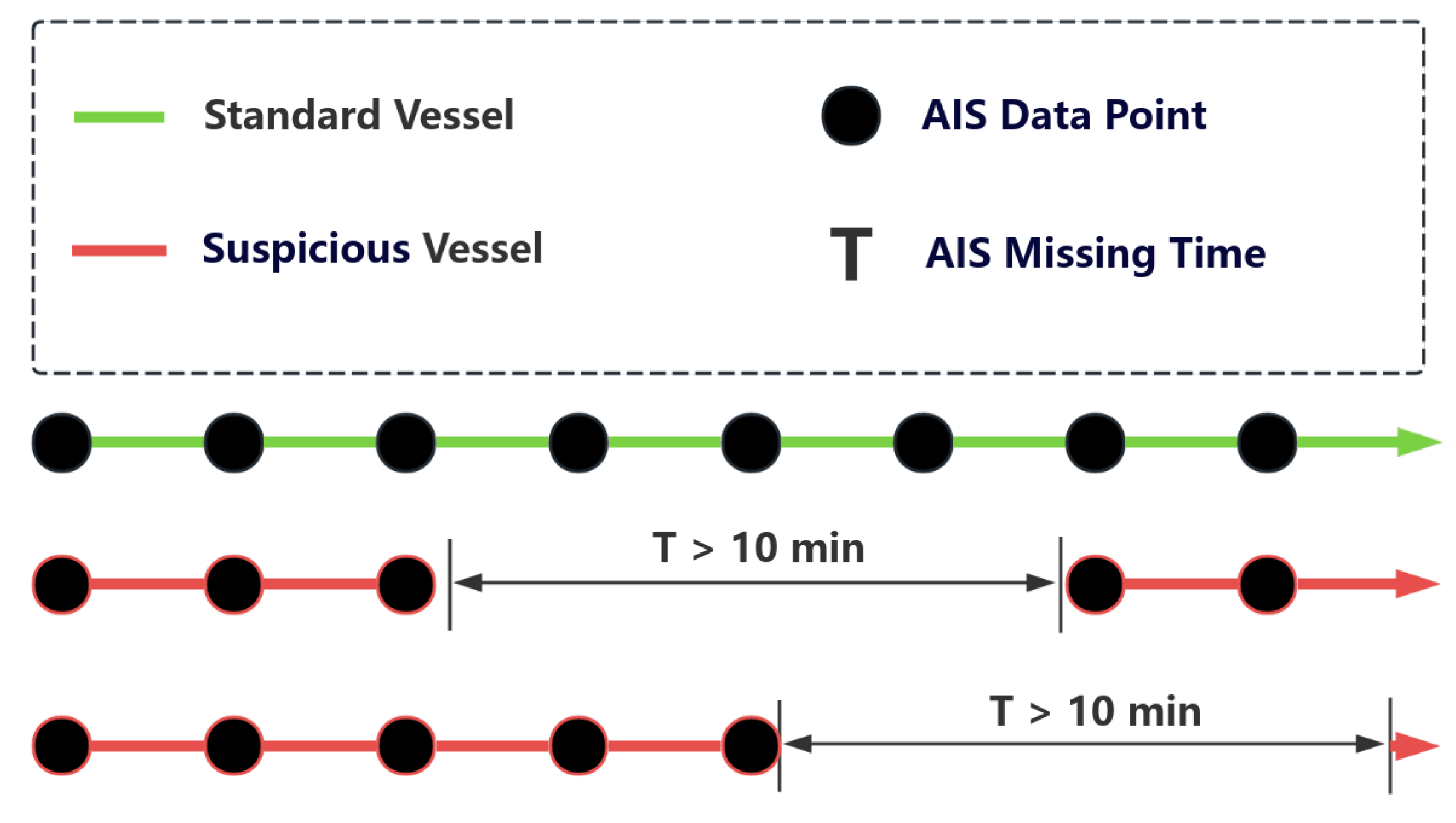
3.1. Data Processing
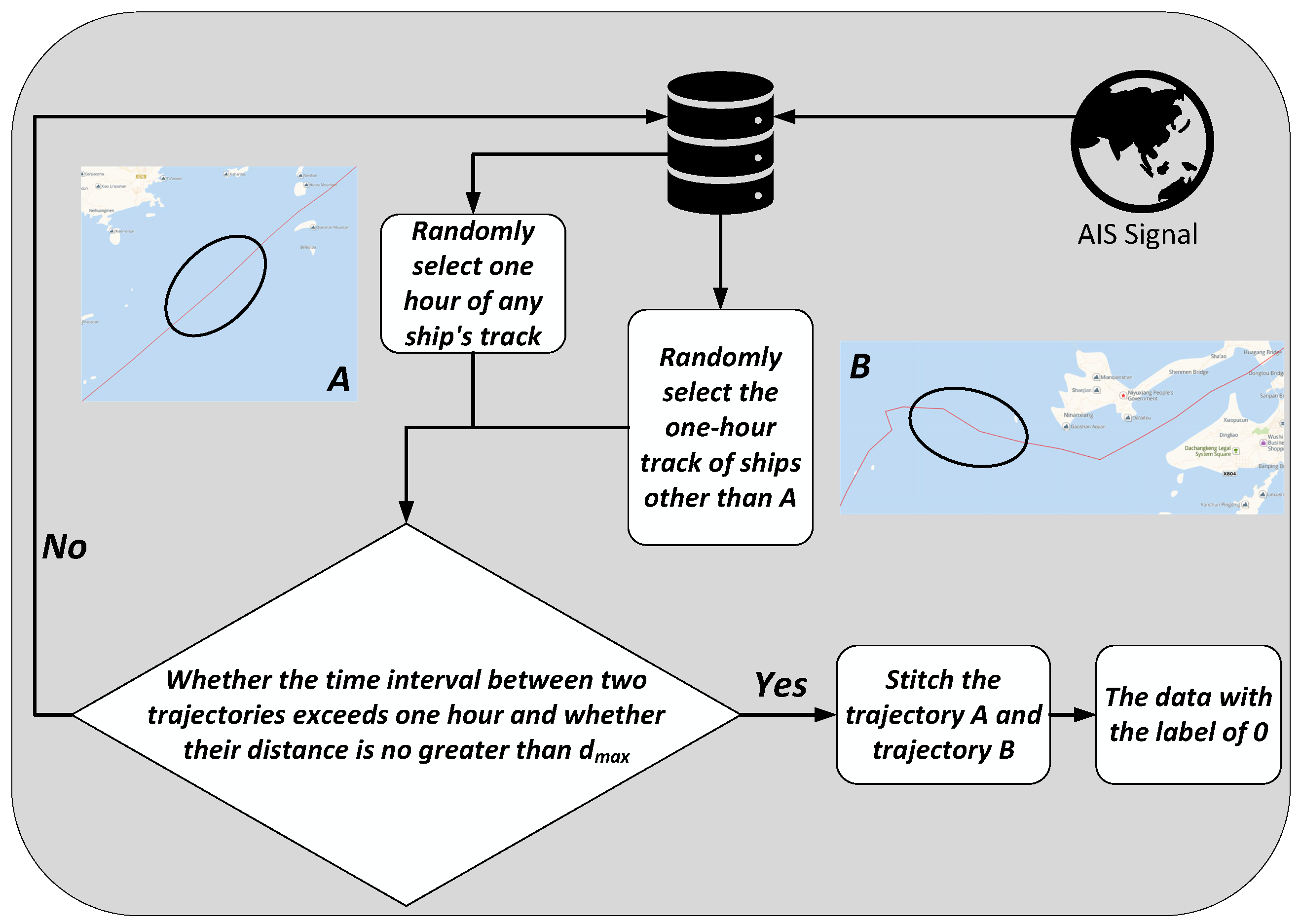
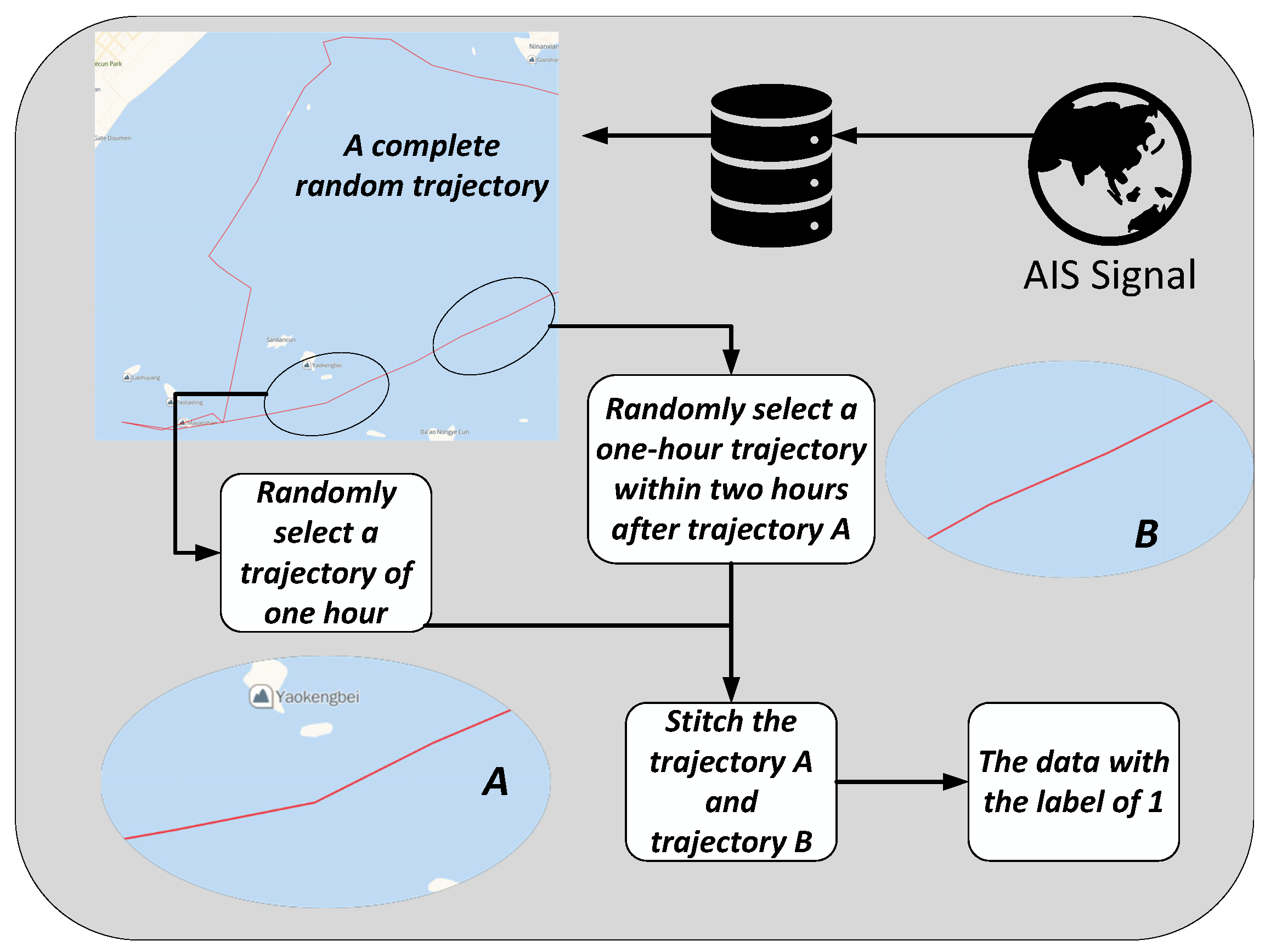
3.2. Dataset Construction
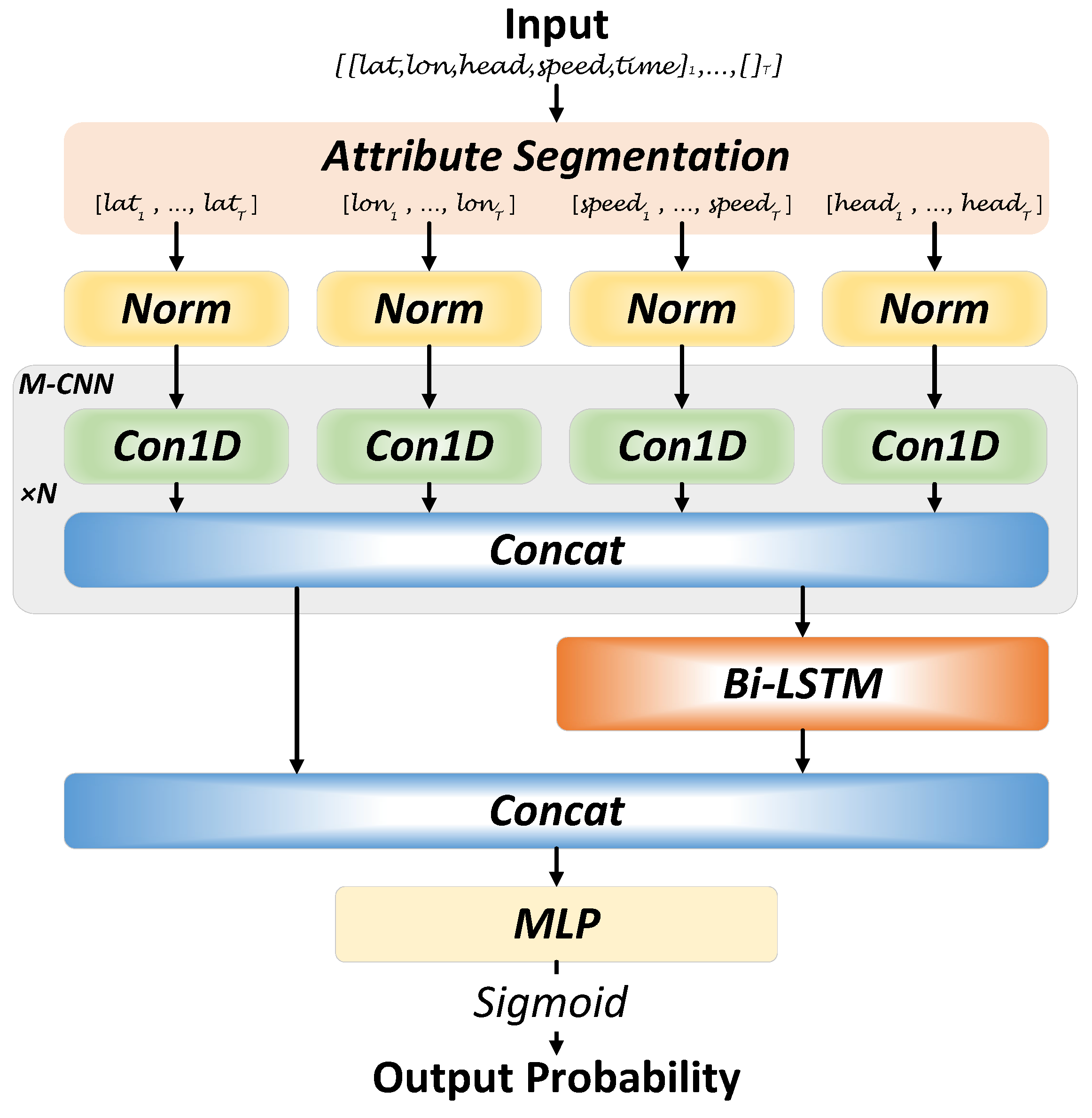
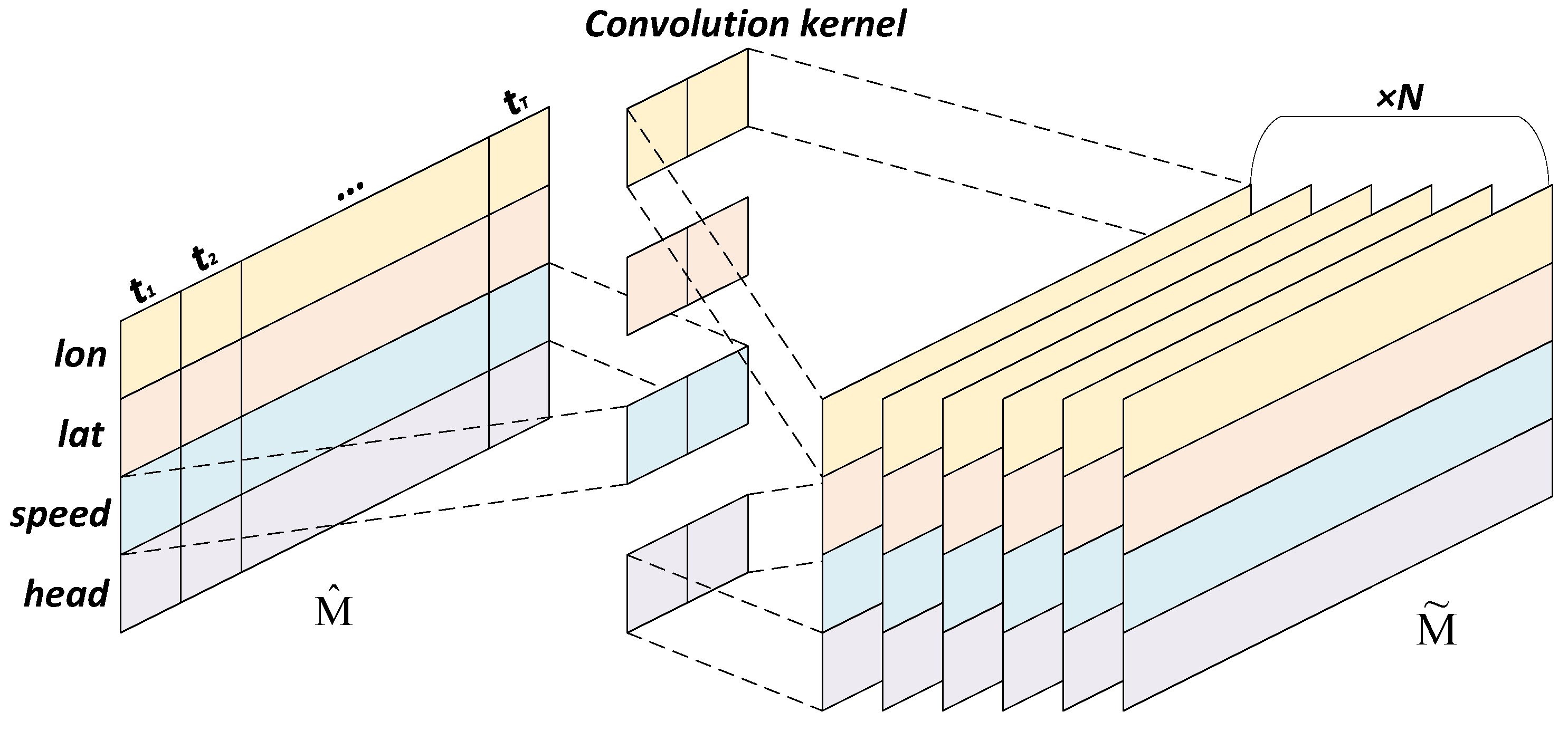
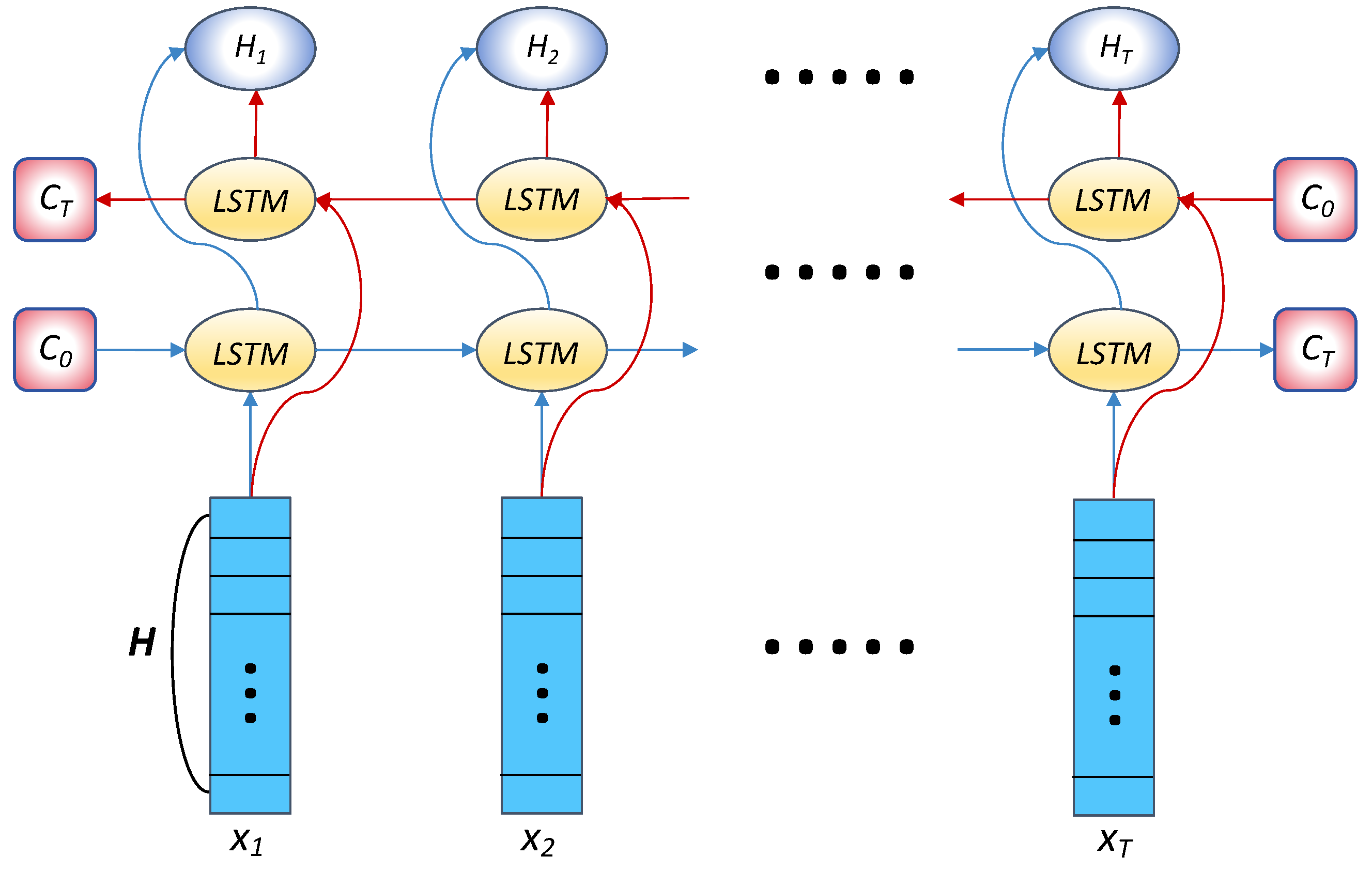
3.3. Model Design
3.3.1. Separation and Processing of Attributes
3.3.2. Data Importance Analysis
3.3.3. Temporal Feature Extraction
4. Result Evaluation
4.1. Training Environment
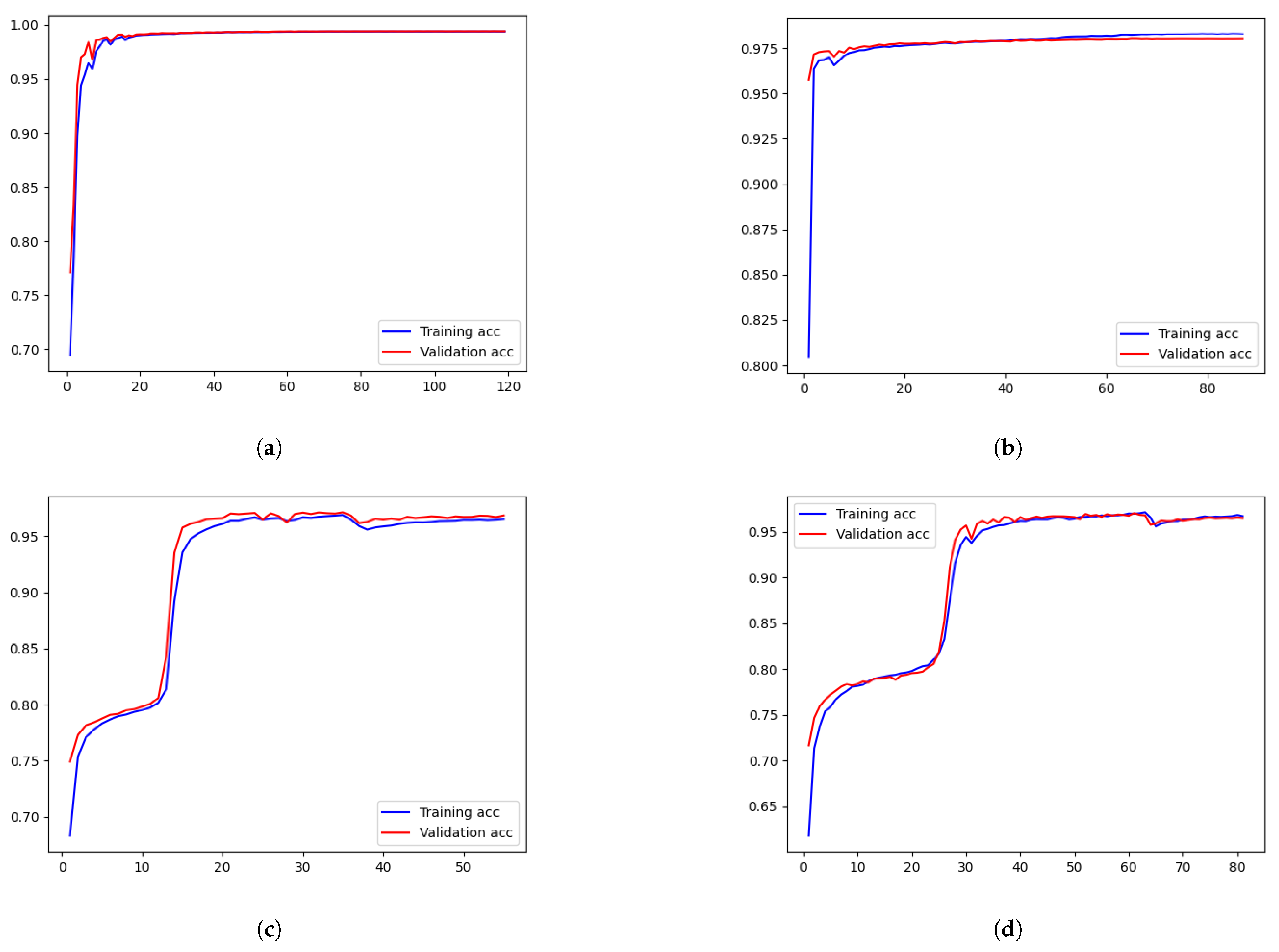
4.2. Training Results
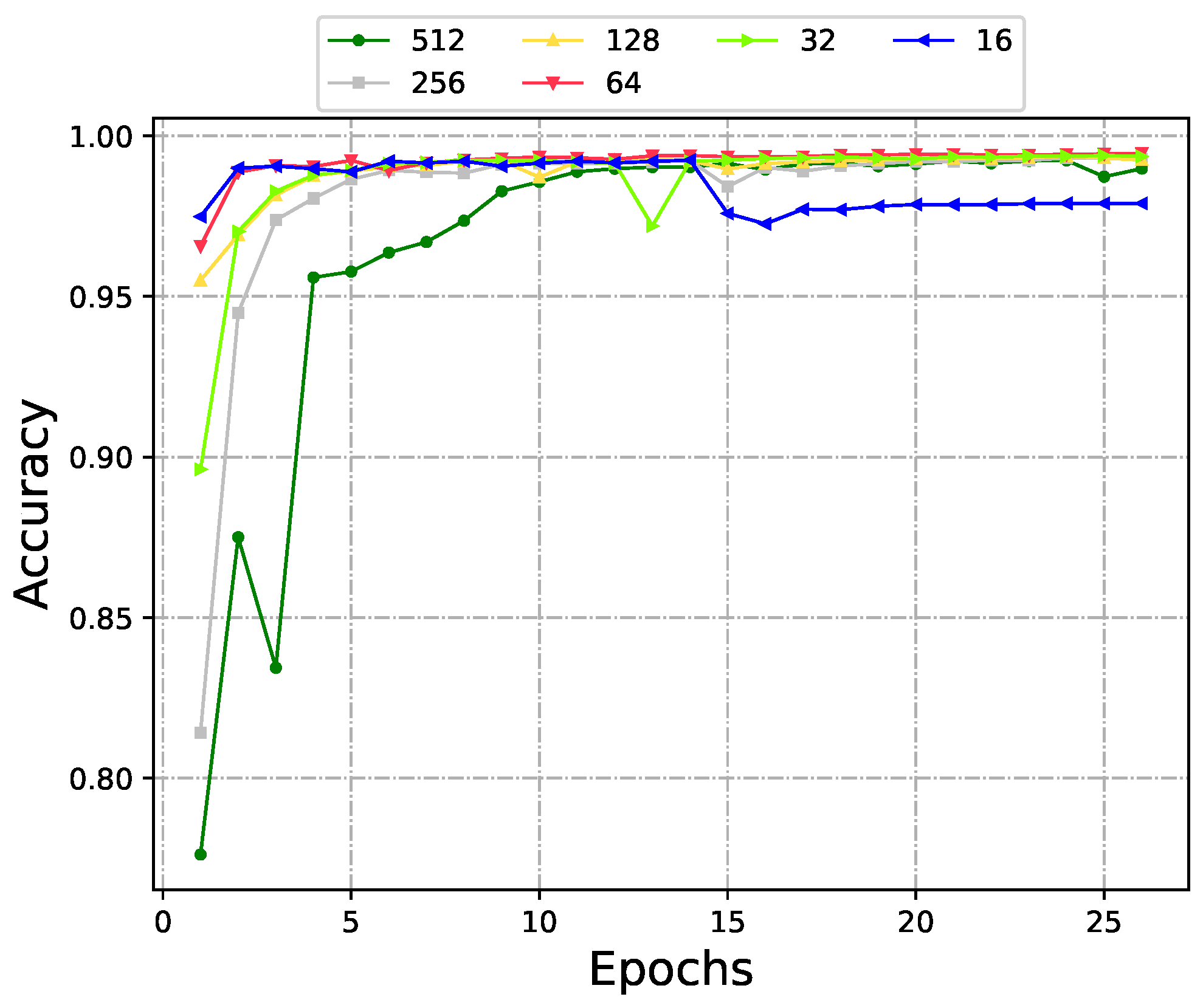
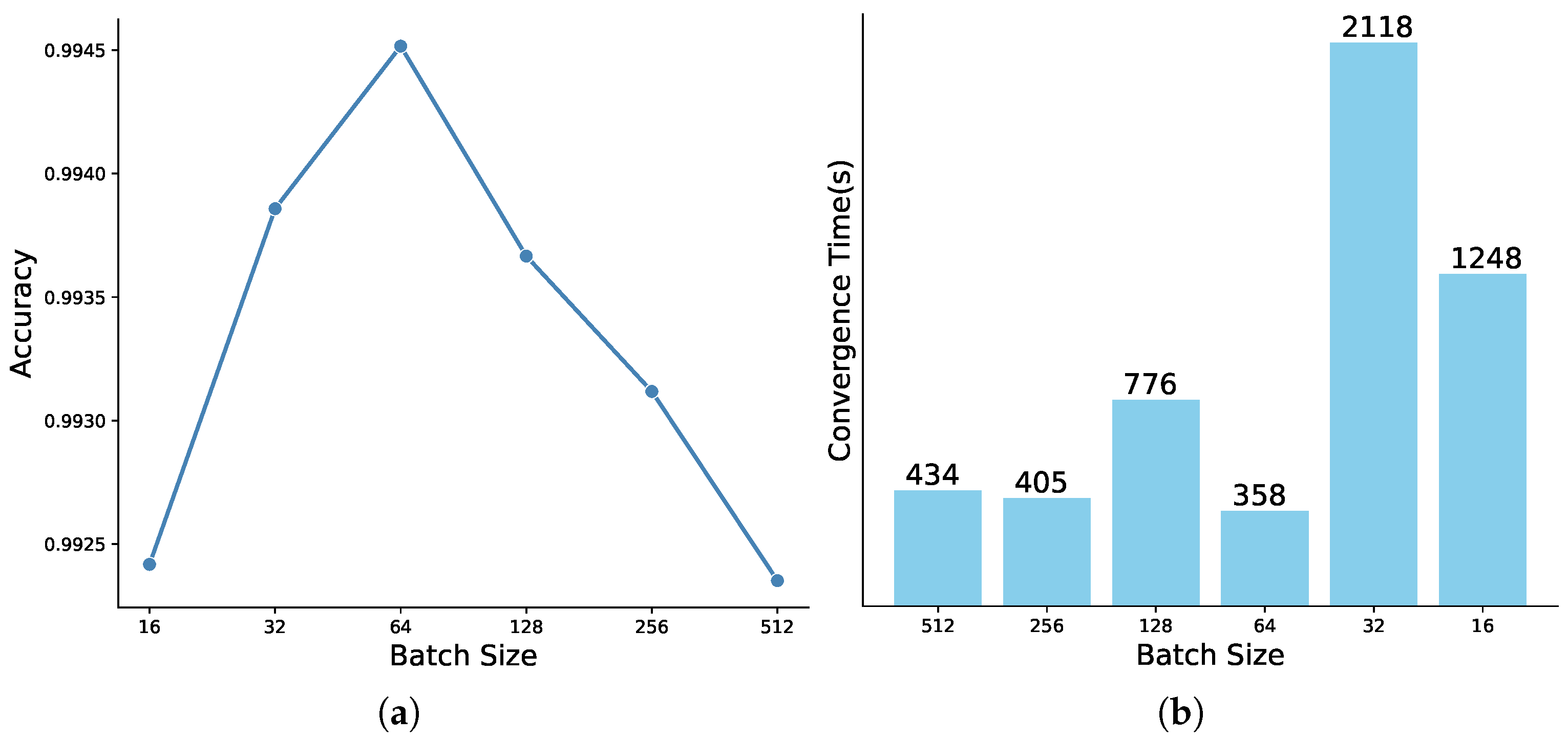
4.3. Hyperparameter Optimization
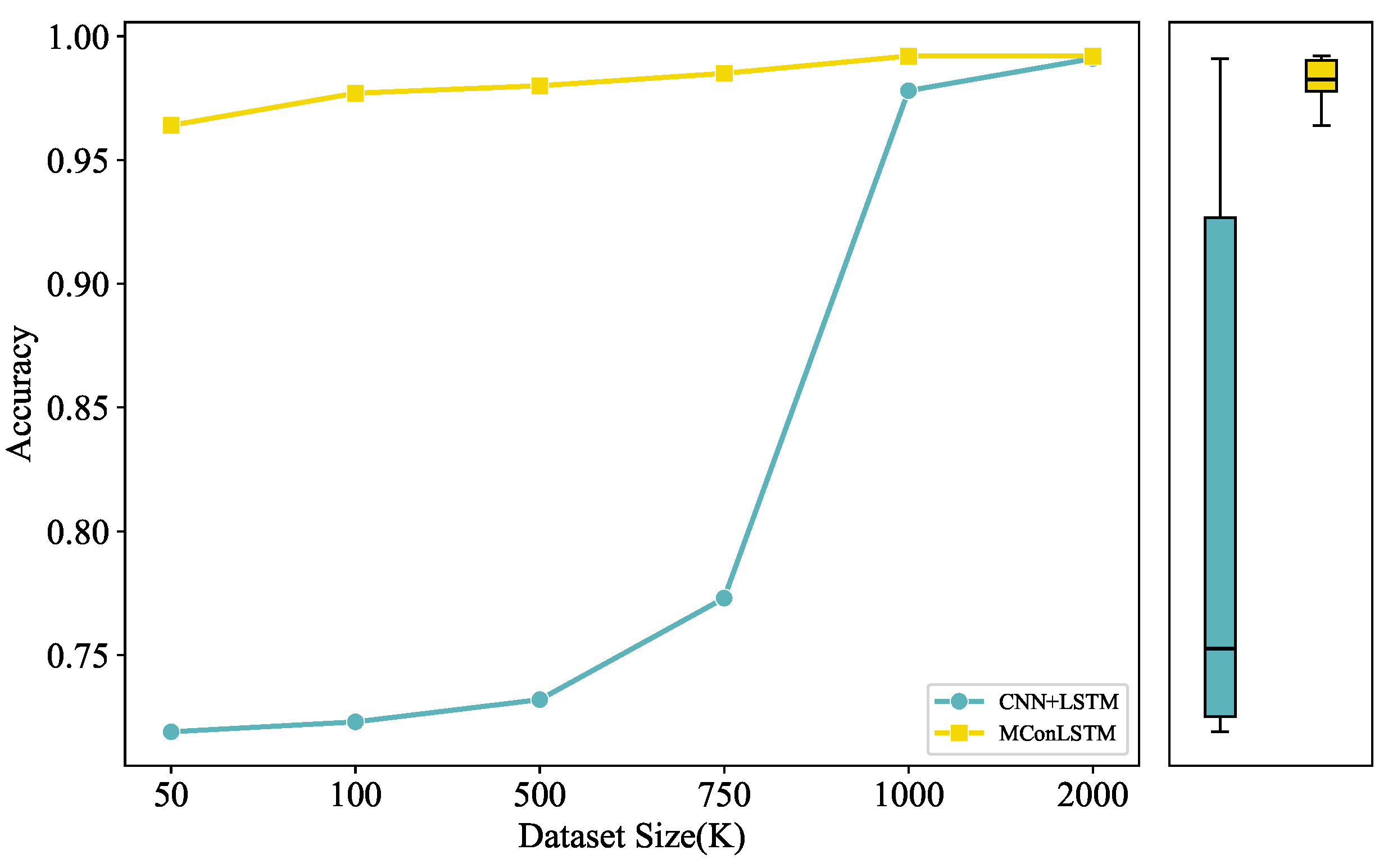
4.4. Ablation Study
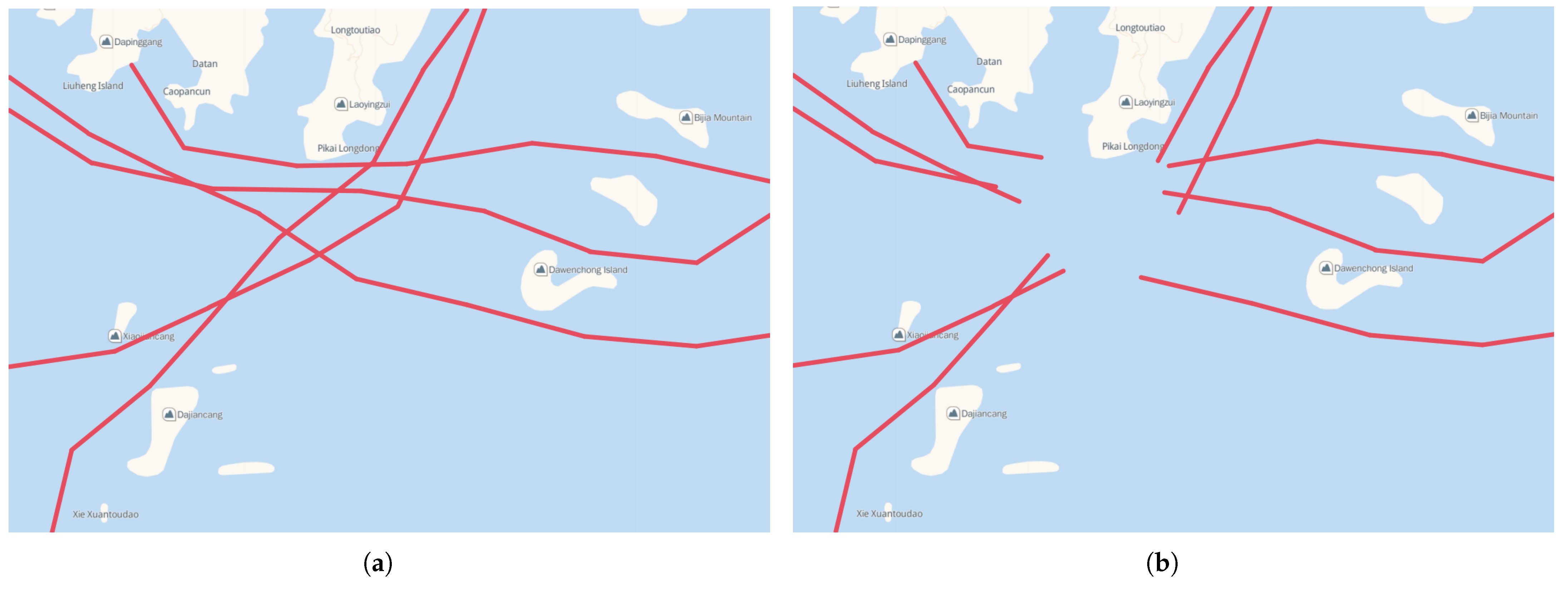
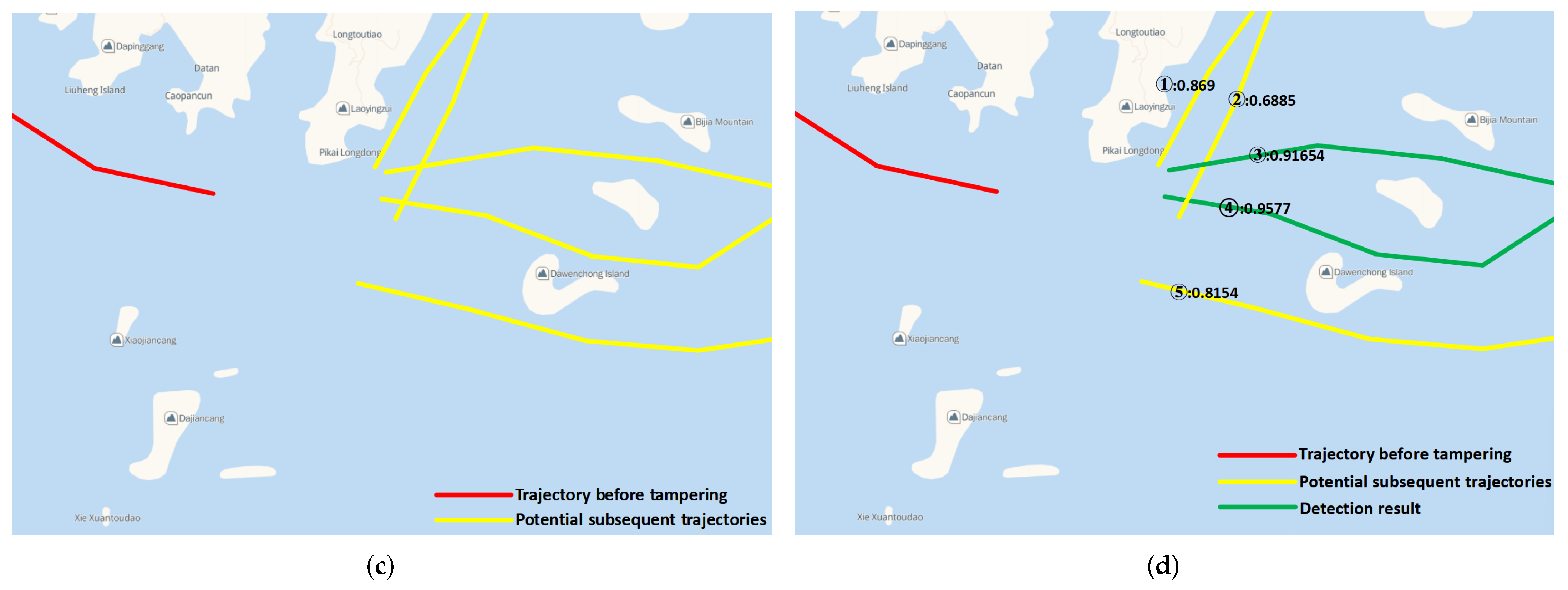
4.5. Case Study Simulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wan, Z.; Chen, J.; Makhloufi, A.E.; Sperling, D.; Chen, Y. Four routes to better maritime governance. Nature 2016, 540, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Maritime Organization (IMO). Revised Guidelines for the Onboard Operational Use of Ship-Borne Auto-Matric Identification Systems (AIS); Tech. Rep. Resolution A.1106(29); International Maritime Organization (IMO): London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, H.; Teixeira, A.P.; Guedes Soares, C.; Santos, T.A. Spatial-temporal analysis of ship traffic in Azores based on AIS data. In Maritime Technology and Engineering 5 Volume 1; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 185–191. [Google Scholar]
- Perobelli, N. MarineTraffic A Day in Numbers. Available online: https://www.marinetraffic.com/blog/a-day-in-numbers/ (accessed on 28 June 2016).
- Zhen, R.; Riveiro, M.; Jin, Y. A novel analytic framework of real-time multi-vessel collision risk assessment for maritime traffic surveillance. Ocean Eng. 2017, 145, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yin, J.; Ren, H. Evaluation Model of Ship Berthing Behavior Based on AIS Data. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 3, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Cun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalsnes, B.R.; Hexeberg, S.; Flaten, A.L.; Eriksen, B.H.; Brekke, E.F. The neighbor course distribution method with Gaussian mixture models for AIS-based vessel trajectory prediction. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Cambridge, UK, 10–13 July 2018; pp. 580–587. [Google Scholar]
- Mascaro, S.; Nicholson, A.; Korb, K. Anomaly detection in vessel tracks using Bayesian networks. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 2014, 55, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Qin, S.; Jiahao, Z.; Du, L.; Zhang, F. Modeling and analysis of external emergency response to ship fire using HTCPN and Markov chain. Ocean Eng. 2024, 297, 117089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, N.; Amir, D.; Douchan, Y.; Agmon, N. Satellite detection of moving vessels in marine environments. In Proceedings of the AAAI’19: AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; Volume 33, pp. 9452–9459. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.H.; Ramanarayanan, C.P.; Murthy, K.S. Detection of Abnormal Vessel Behaviours Based on AIS Data Features Using HDBSCAN+. Def. Sci. J. 2023, 73, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, X. A Hybrid-Clustering Model of Ship Trajectories for Maritime Traffic Patterns Analysis in Port Area. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komol, M.M.R.; Sagar, M.S.I.; Mohammad, N.; Pinnow, J.; Elhenawy, M.; Masoud, M.; Glaser, S.; Liu, S.Q. Simulation Study on an ICT-Based Maritime Management and Safety Framework for Movable Bridges. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louart, M.; Szkolnik, J.J.; Boudraa, A.O.; Le Lann, J.C.; Le Roy, F. Detection of AIS messages falsifications and spoofing by checking messages compliance with TDMA protocol. Digit. Signal Process. 2023, 136, 103983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloisi, D.; Previtali, F.; Pennisi, A.; Nardi, D.; Fiorini, M. Enhancing Automatic Maritime Surveillance Systems With Visual Information. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2017, 18, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogancay, K.; Tu, Z.; Ibal, G. Research into vessel behaviour pattern recognition in the maritime domain: Past, present and future. Digit. Signal Process. 2021, 119, 103191. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshfar, F.; Saifee, B.S.; Soleymanbaigi, S.; Aeini, M. Elastic deep multi-view autoencoder with diversity embedding. Inf. Sci. 2025, 689, 121482. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Jia, Z.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Z. The model of vessel trajectory abnormal behavior detection based on graph attention prediction and reconstruction network. Ocean Eng. 2023, 290, 116316. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Vadaine, R.; Hajduch, G.; Garello, R.; Fablet, R. GeoTrackNet—A Maritime Anomaly Detector Using Probabilistic Neural Network Representation of AIS Tracks and A Contrario Detection. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 5655–5667. [Google Scholar]
- Forti, N.; Millefiori, L.M.; Braca, P.; Willett, P. Anomaly detection and tracking based on Mean–Reverting processes with unknown parameters. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 8449–8453. [Google Scholar]
- d’Afflisio, E.; Braca, P.; Millefiori, L.M.; Willett, P. Maritime anomaly detection based on mean-reverting stochastic processes applied to a real-world scenario. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Information Fusion (FUSION), Cambridge, UK, 10–13 July 2018; pp. 1171–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Uney, M.; Millefiori, L.M.; Braca, P. Data driven vessel trajectory forecasting using stochastic generative models. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2019—2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Brighton, UK, 12–17 May 2019; pp. 8459–8463. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, D.; Vadaine, R.; Hajduch, G.; Garello, R.; Fablet, R. A Multi-task Deep Learning Architecture for Maritime Surveillance using AIS Data Streams. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Science and Advanced Analytics (DSAA), Turin, Italy, 1–3 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bernabé, P.; Gotlieb, A.; Legeard, B.; Marijan, D.; Sem-Jacobsen, F.O.; Spieker, H. Detecting Intentional AIS Shutdown in Open Sea Maritime Surveillance Using Self-Supervised Deep Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2024, 25, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Wang, R.; Xiao, D.; Han, X.; Cai, Y.; Shi, C. Anomalous Trajectory Detection Using Recurrent Neural Network. In Advanced Data Mining and Applications, Proceedings of the 14th International Conference, ADMA 2018, Nanjing, China, 16–18 November 2018; Gan, G., Li, B., Li, X., Wang, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 263–277. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Miao, Z.; Li, M.; Song, S.; Yang, M.H. Detecting Anomalous Trajectories via Recurrent Neural Networks. In Computer Vision—ACCV 2018, Proceedings of the 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Jawahar, C., Li, H., Mori, G., Schindler, K., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 370–382. [Google Scholar]
- Zaremba, W.; Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O. Recurrent Neural Network Regularization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.2329. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, D.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, K.; Soares, C.G. Deep learning-based framework for regional risk assessment in a multi-ship encounter situation based on the transformer network. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2024, 241, 109636. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, W.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y. Bidirectional Data-Driven Trajectory Prediction for Intelligent Maritime Traffic. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.I.; Lee, K.M. Deep Learning-Based Caution Area Traffic Prediction with Automatic Identification System Sensor Data. Sensors 2018, 18, 3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; He, J. Online clustering for trajectory data stream of moving objects. Comput. Sci. Inf. Syst. 2013, 10, 1293–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallotta, G.; Vespe, M.; Bryan, K. Vessel Pattern Knowledge Discovery from AIS Data: A Framework for Anomaly Detection and Route Prediction. Entropy 2013, 15, 2218–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryabova, A.; Novikov, V.; Choinzonov, E.; Gribova, O.; Startseva, Z.; Bober, E.; Frolova, I.; Baranova, A. Maritime Traffic Networks: From Historical Positioning Data to Unsupervised Maritime Traffic Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 722–732. [Google Scholar]
- Le Cun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sak, H.; Senior, A.; Beaufays, F. Long Short-Term Memory Based Recurrent Neural Network Architectures for Large Vocabulary Speech Recognition. Statistics 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Han, K.; Wu, H.; Tang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C. CMT: Convolutional Neural Networks Meet Vision Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; He, M.; Shi, M.; Jeon, S. A Novel Model Combining Transformer and Bi-LSTM for News Categorization. IEEE Trans. Comput. Soc. Syst. 2022, 11, 4862–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Module | Hyper Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| M-CNN | Kernel Size | |
| Number of Filters | 32 | |
| Pooling Size | ||
| Stride | 2 | |
| Activation Function | ReLU | |
| Bi-LSTM | Number of Units | 64 |
| Number of Layers | 2 | |
| Activation Function | Tanh | |
| MLP | Number of Layers | 2 |
| Activation Function | GeLU | |
| (For Output) | Sigmoid | |
| Regularization | Dropout Rate | 0.5 |
| Other | Batch Size | 512 |
| Optimizer | Adam [38] | |
| Loss Function | Binary Cross | |
| Entropy | ||
| Learning Rate | 0.0001 | |
| Epochs | 300 |
| True | False | |
|---|---|---|
| Pred. True | 49.56 | 0.69 |
| Pred. False | 0.44 | 49.31 |
| Accuracy | 99.12% | 98.62% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lv, X.; Jiang, R.; Chang, C.; Shu, N.; Wu, T. A Deep Learning Approach for Identifying Intentional AIS Signal Tampering in Maritime Trajectories. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040660
Lv X, Jiang R, Chang C, Shu N, Wu T. A Deep Learning Approach for Identifying Intentional AIS Signal Tampering in Maritime Trajectories. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLv, Xiangdong, Ruhao Jiang, Chao Chang, Nina Shu, and Tao Wu. 2025. "A Deep Learning Approach for Identifying Intentional AIS Signal Tampering in Maritime Trajectories" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040660
APA StyleLv, X., Jiang, R., Chang, C., Shu, N., & Wu, T. (2025). A Deep Learning Approach for Identifying Intentional AIS Signal Tampering in Maritime Trajectories. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040660






