Full-Scale Numerical Simulation of a Free-Running Cruise Ship in Heavy Head Sea Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Model and Methodology
2.1. Governing Equations
2.2. Wall Functions y+
2.3. Generating Waves and Absorbing Waves
2.4. Moving Coordinate System
3. Computational Setups
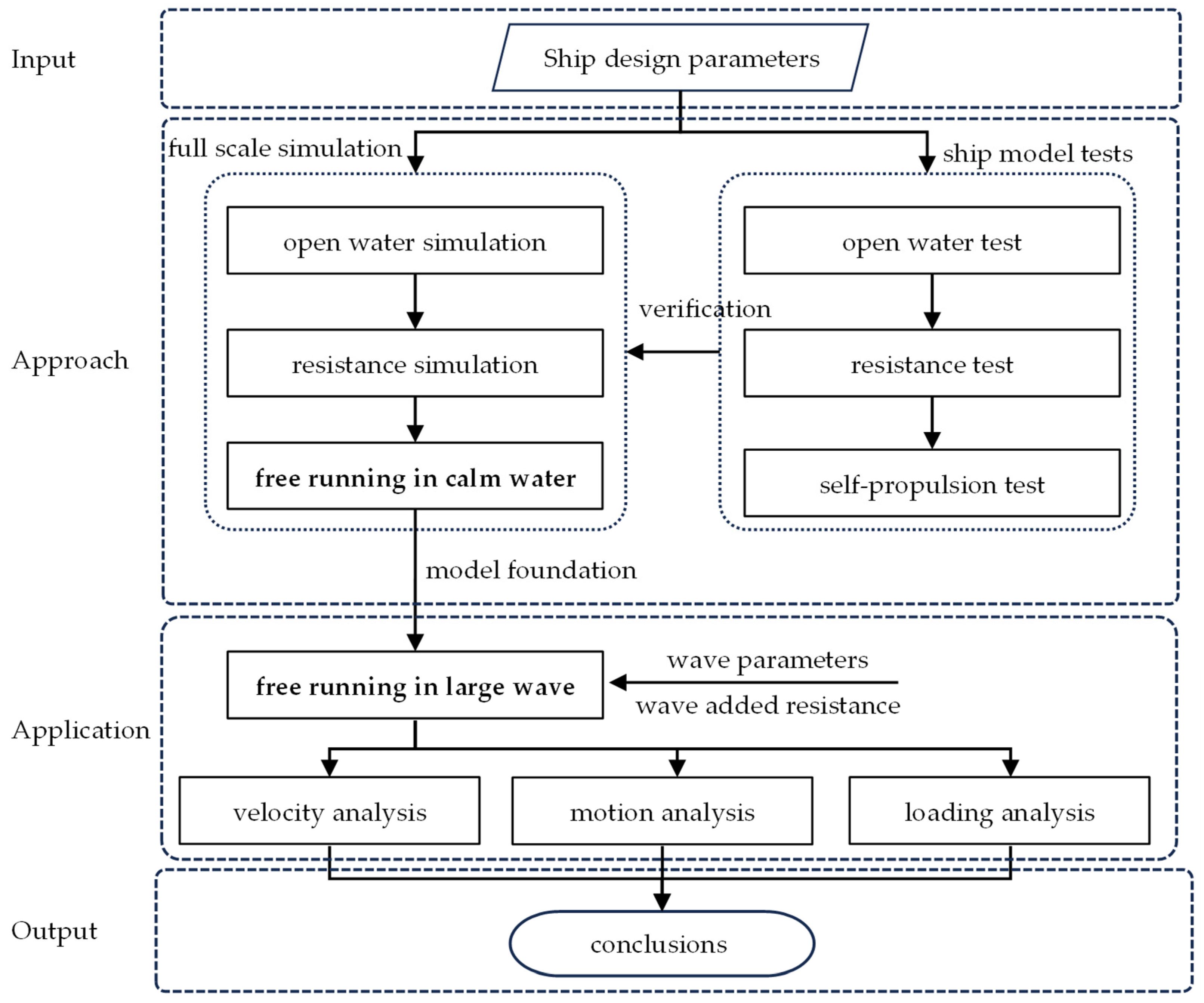
3.1. Approach Procedure
3.2. Model Test
3.3. Numerical Modeling
3.3.1. Geometric Model
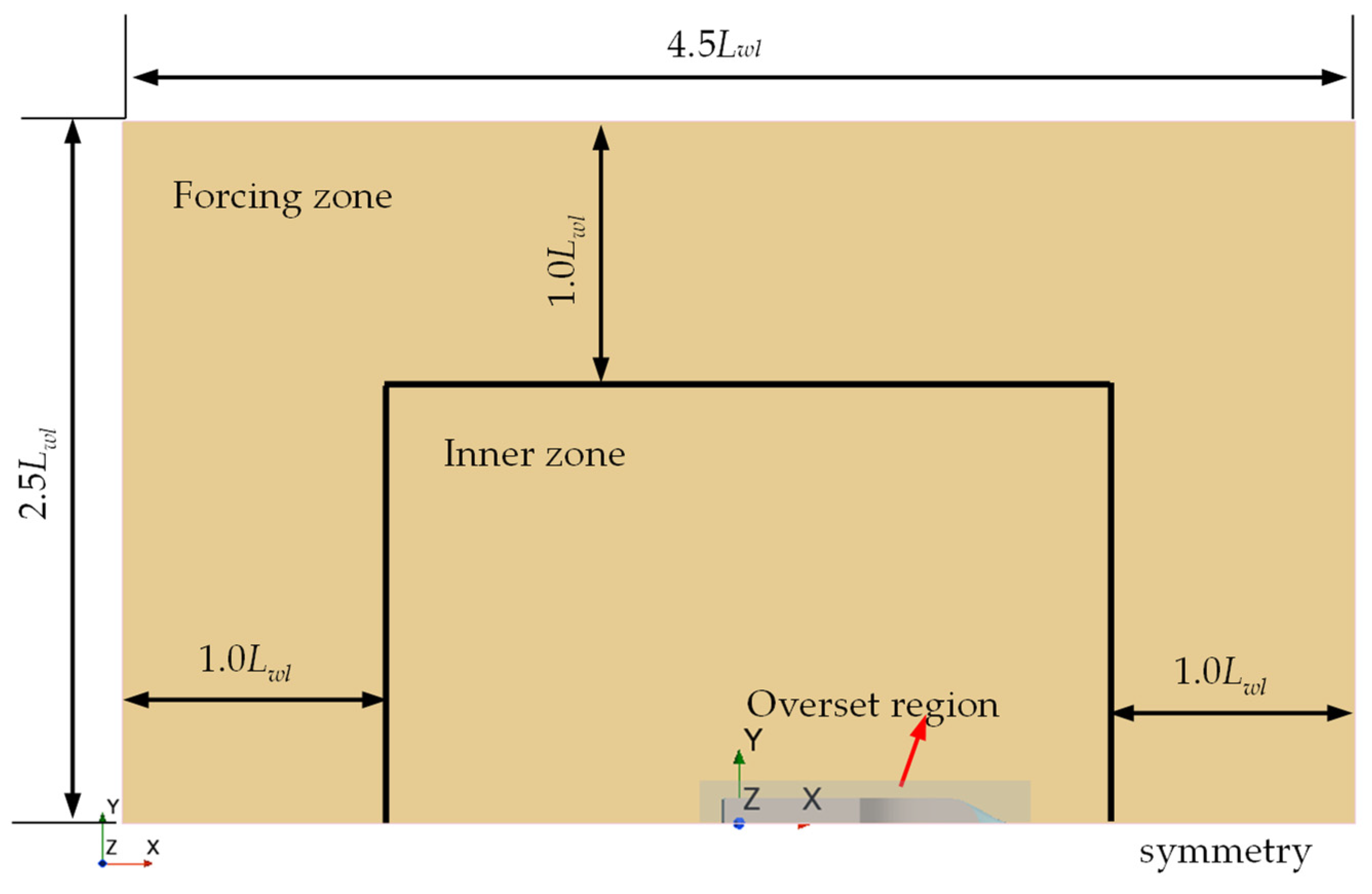
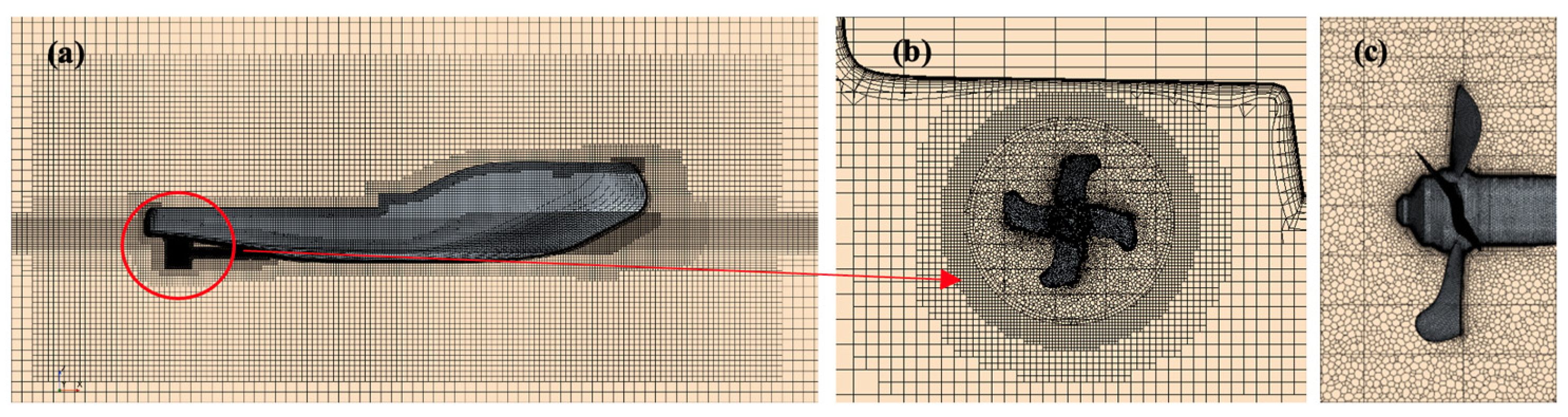
3.3.2. Computational Domain and Mesh
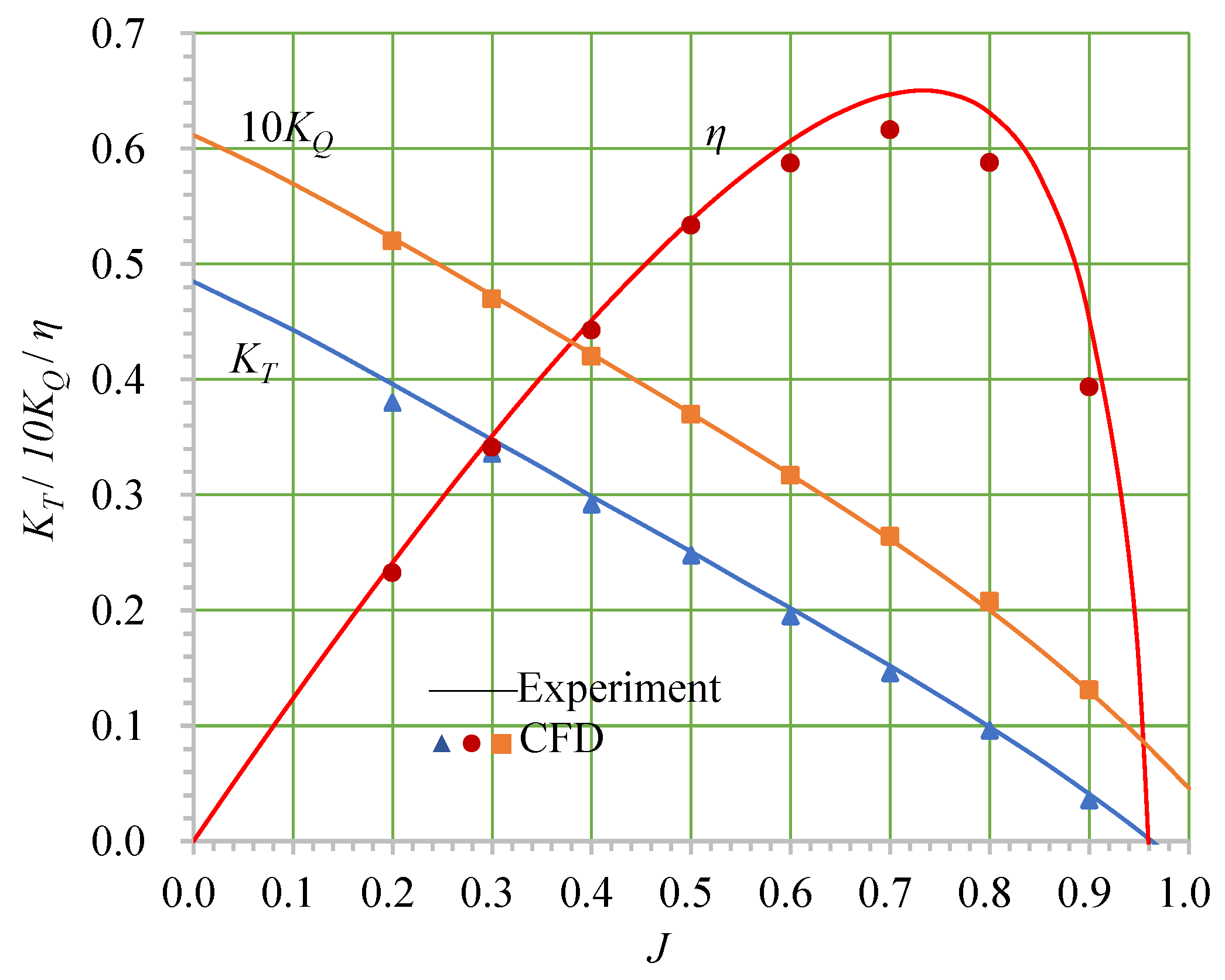
3.4. Open-Water Simulations of the Propeller
3.5. Resistance Simulation
3.6. Traditional Self-Propulsion Simulation
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Free Running in Calm Water
4.2. Free Running in Waves
4.2.1. Wave Model
4.2.2. Calculation Conditions
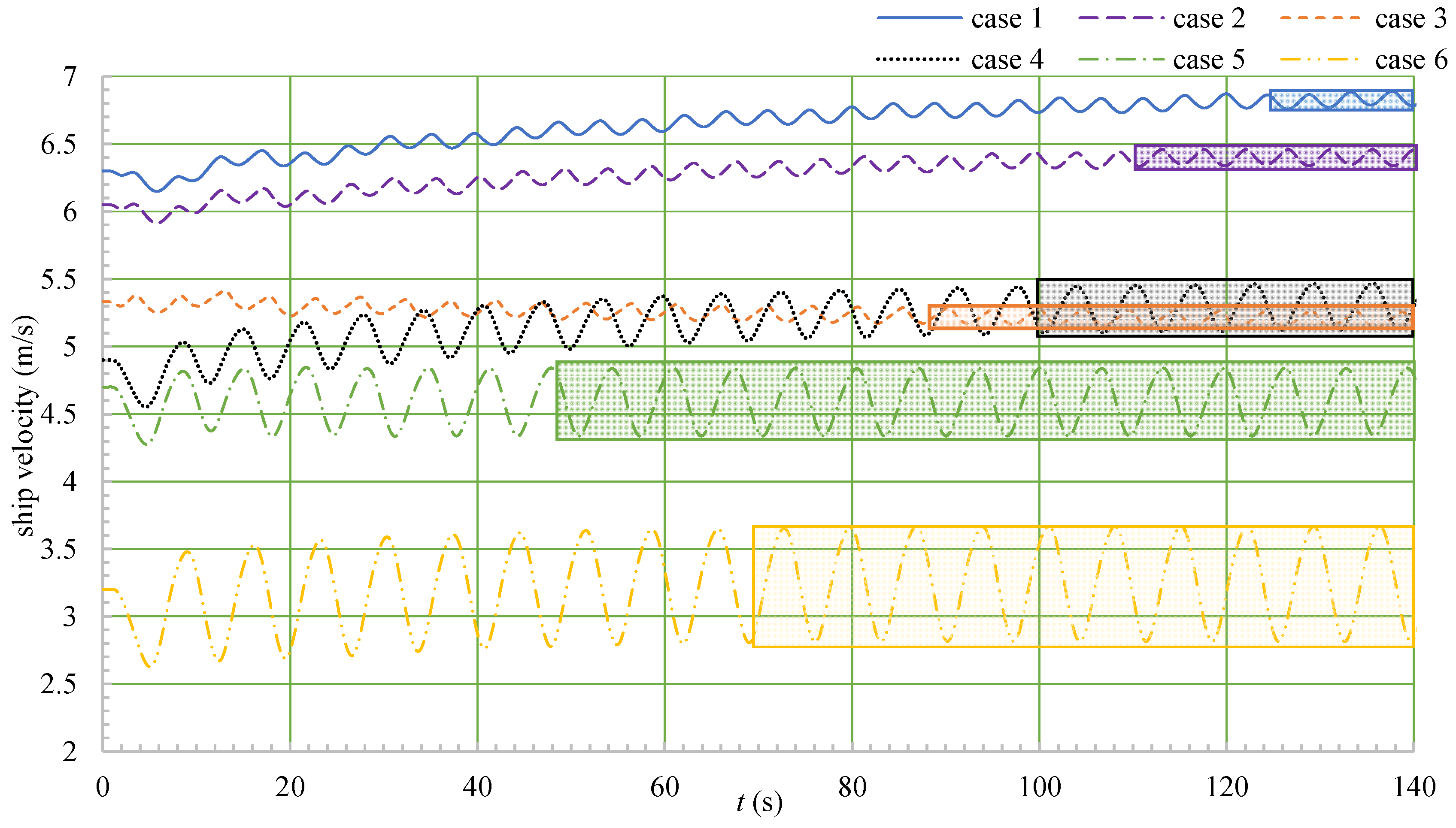
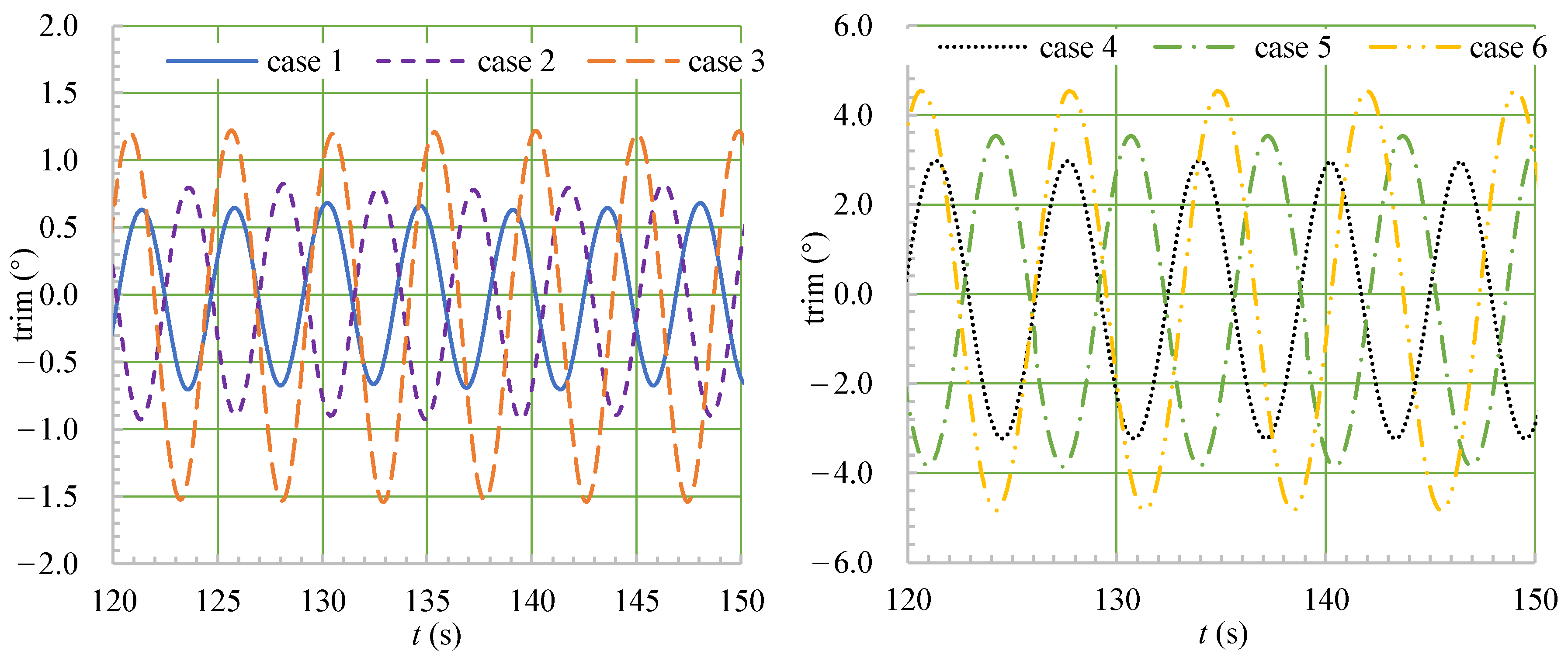
4.3. Motion Analysis
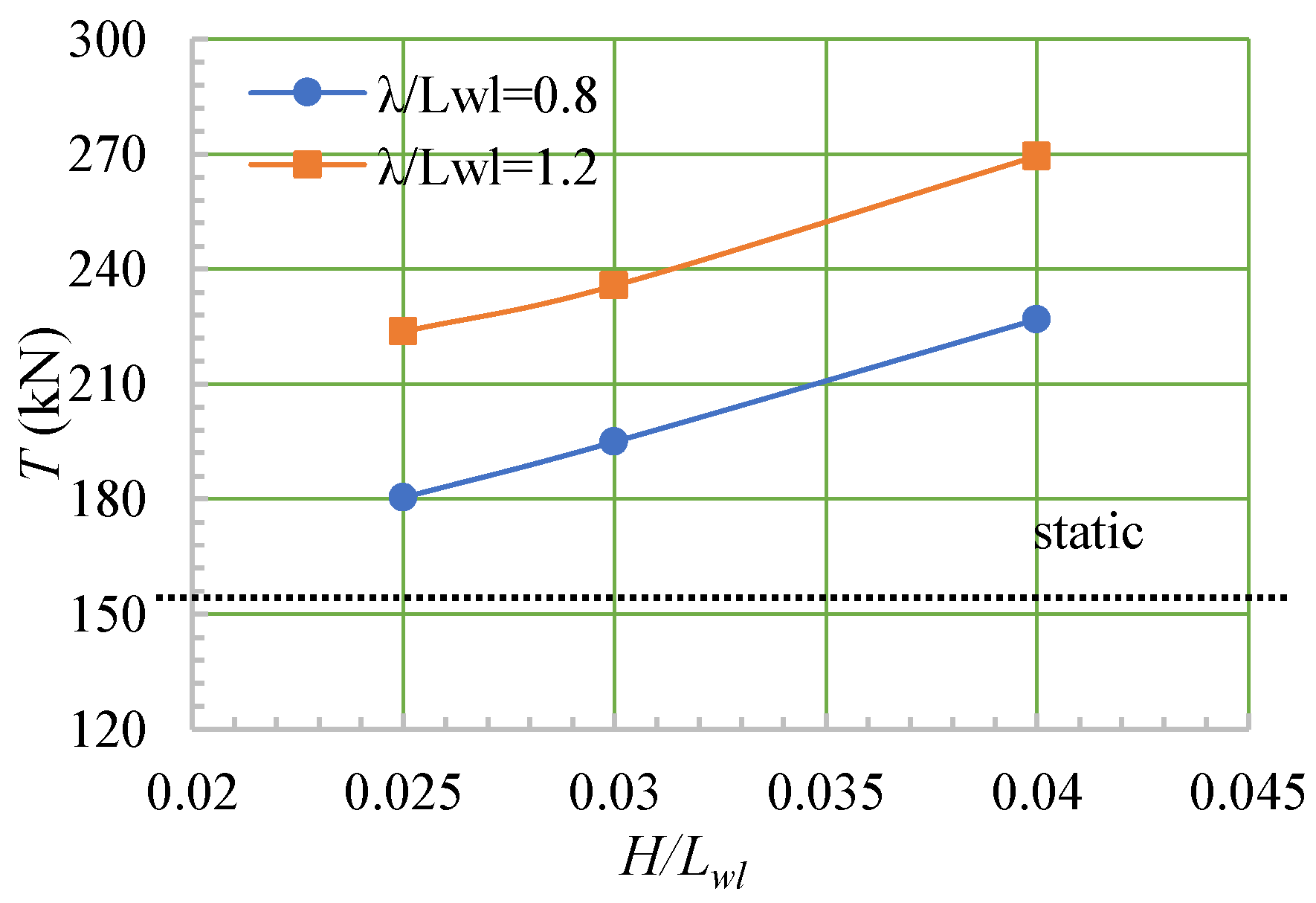
4.4. Wave-Added Resistance
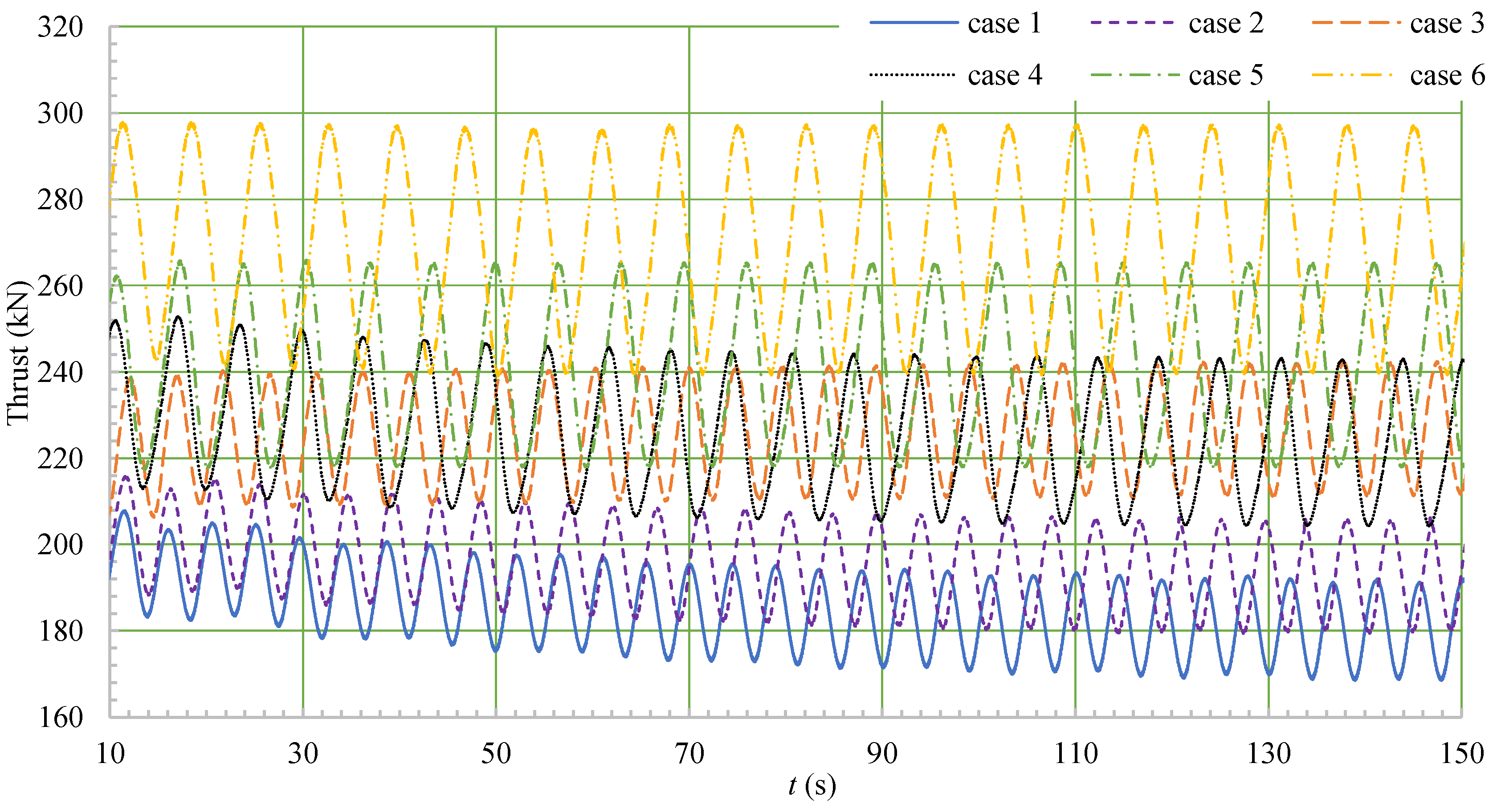
4.5. Propeller Load Analysis
5. Conclusions and Future Work
- (1)
- The free-running method based on relative motion simulated the self-propelled motion of full-scale ships more effectively than the traditional self-propulsion method without expanding the background domain, and the motion of the ship converged relatively quickly.
- (2)
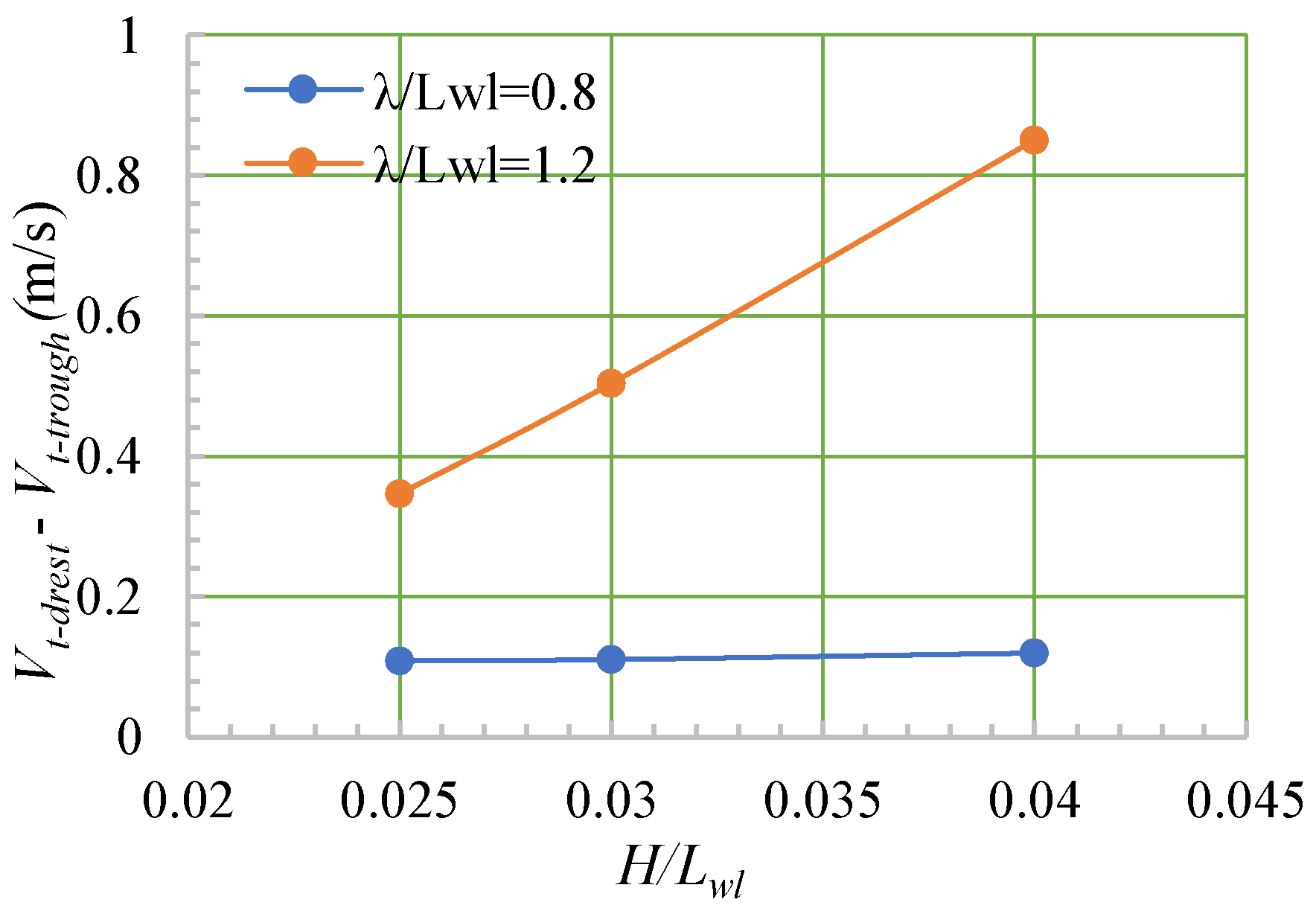
- When the ship moved in a head sea, the ship’s speed, heave, and pitch fluctuated, and λ/Lwl had a greater impact on the fluctuations of the speed, motion, and thrust than did H/Lwl.
- (3)
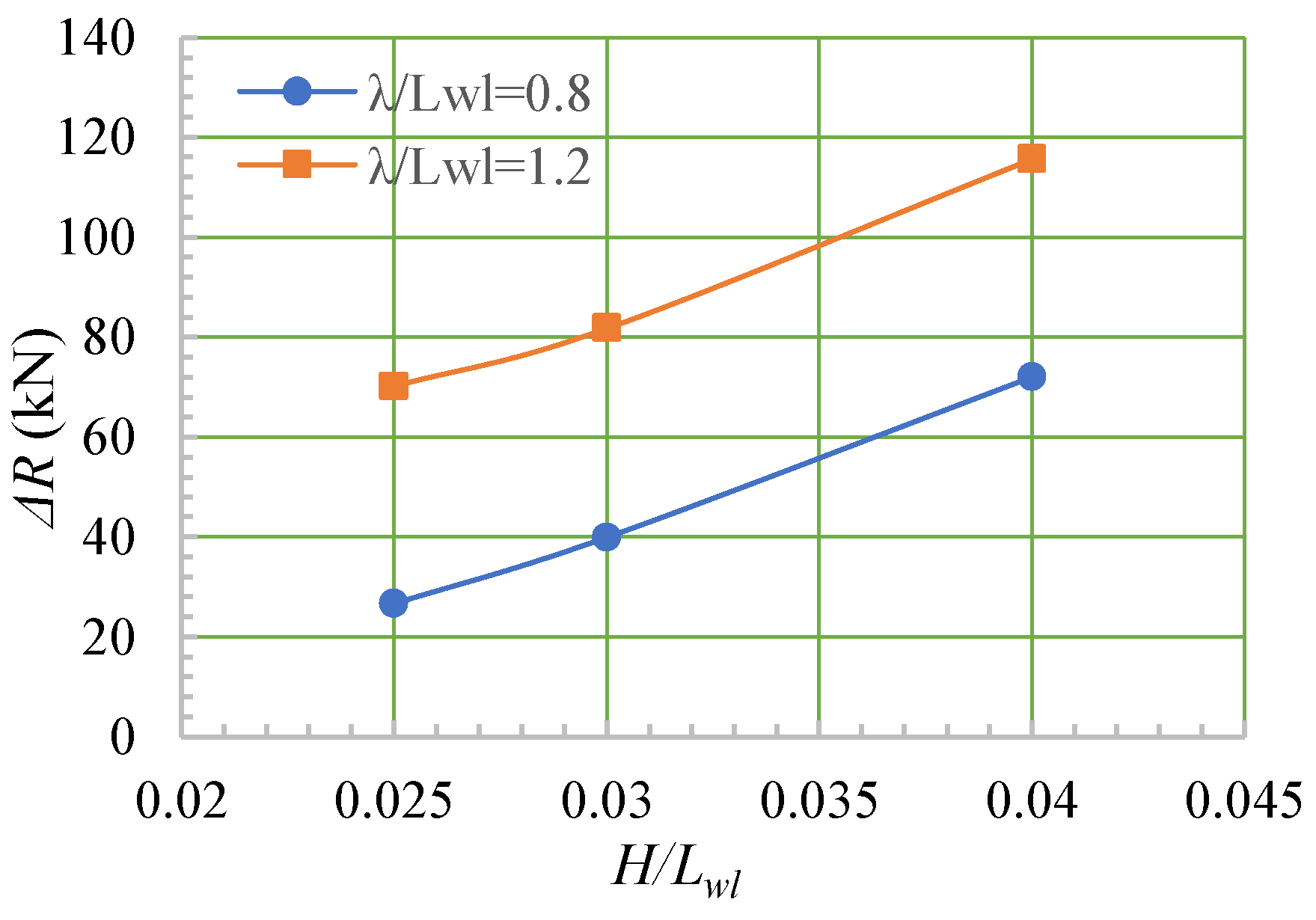
- For the same wavelength, as the wave height increased, the added wave resistance of the ship continued to increase.
- (4)
- Under heavy sea conditions, the loading of the ship’s propeller increased sharply, and the load coefficient exceeded 500%, posing certain safety risks that must be considered in the design of the propeller.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oleksiy, B.; Yasushi, K. Development of detailed engine model for evaluation ship performance in waves by a self-propulsion model test. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2021, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, X. Influence Analysis of Podded Propulsors Installation Position Based on Self Propulsion Simulation. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Transportation Information and Safety (ICTIS), Xi’an, China, 4–6 August 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Hu, Q.; Hu, S.; Su, J.; Xu, J.; Wei, J.; Huang, G. Numerical analysis of full-scale ship self-propulsion performance with direct comparison to statistical sea trail results. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Kouh, J.S. On the scale effect of thrust deduction in a judicious self-propulsion procedure for a moderate-speed containership. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2015, 20, 373–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Y. A non-geometrically similar model for predicting the wake field of full-scale ships. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2015, 14, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponkratov, D.; Zegos, C. Validation of ship scale CFD self-propulsion simulation by the direct comparison with sea trials results. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors, Austin, TX, USA, 31 May–4 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Sun, S.; Li, L.; Ye, L. Numerical prediction analysis of propeller bearing force for full-scale hull-propeller-rudder system. Int. J. Nav. Archit. Ocean Eng. 2016, 8, 589–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, C.; Sun, S.; Sun, S. Numerical simulation and scale effect of self-propulsion test of a full-scale ship. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2016, 37, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kösterke, M.; Voß, J.P.; Riesner, M.; Greve, M. Propeller design and dynamic hull-propeller interaction of an XLUUV. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Symposium on Marine Propulsors, smp’24, Berlin, Germany, 17–20 March 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, D. CFD simulations of ship maneuvering motion. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2018, 39, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, A.M.; Carrica, P.M.; Stern, F. Full scale self-propulsion computations using discretized propeller for the KRISO container ship KCS. Comput. Fluids 2011, 51, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, D. Investigations of self-propulsion in waves of fully appended ONR Tumblehome model. Appl. Math. Mech. 2016, 37, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Full-scale simulation of self-propulsion for a free-running submarine. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 047103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinaci, O.K.; Ozturk, D. Straight-ahead self-propulsion and turning maneuvers of DTC container ship with direct CFD simulations. Ocean Eng. 2022, 244, 110381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saydam, A.Z.; Küçüksu, G.N.; İnsel, M.; Gökçay, S. Uncertainty quantification of self-propulsion analyses with RANS-CFD and comparison with full-scale ship trials. Brodogradnja 2022, 73, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Geng, X.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Y.; Tang, Y. Integrating computational fluid dynamics for maneuverability prediction in dual full rotary propulsion ships: A 4-DOF mathematical model approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizythras, P.; Boulougouris, E.; Theotokatos, G. Computational investigation of ship propulsion performance in rough seas. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Maritime Safety and Operations, Glasgow, UK, 13–14 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Marine Safety Committee. MSC.1/Circ.1369/ Add.1, Annex Interpretation 18, p. 12. 2012. Available online: https://imorules.com/GUID-40D3CA4B-D851-42ED-965F-42F0C56EF286.html (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Song, K.; Guo, C.; Wang, C.; Sun, C.; Li, P.; Wang, W. Numerical analysis of the effects of stern flaps on ship resistance and propulsion performance. Ocean Eng. 2019, 193, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Jing, P.; Jin, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, T. Two-dimensional numerical study on fluid resonance in the narrow gap between two rigid-connected heave boxes in waves. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 110, 102628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CD-adapco. User Guide of STAR-CCM+, version 14.02.010-R8; CD-adapco: Melville, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Det Norske Veritas. Environmental Conditions and Environmental Loads; Recommended Practice DNV-RP-C205; Det Norske Veritas: Oslo, Norway, 2007; p. 24. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Song, S.; Tezdogan, T. Free running CFD simulations to investigate ship manoeuvrability in waves. Ocean Eng. 2021, 236, 109567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Shao, J.; Stern, F. Discussion: Criticisms of the “Correction Factor” Verification Method. J. Fluids Eng. 2004, 126, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Guo, C.; Su, Y.; Zhang, D. Numerical study of the propeller-induced exciting force under the open freedom condition. J. Harbin Eng. Univ. 2017, 38, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Feng, D. CFD prediction of full-scale ship parametric roll in head wave. Ocean Eng. 2021, 222, 109180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritime Safety Administration of the People’s Republic of China, Sea Surface Wind Scale and Performance. 2017. Available online: https://www.msa.gov.cn/page/article.do?articleId=74CE6926-0897-41E9-A22C-44EF17BE7B1B (accessed on 23 February 2024).
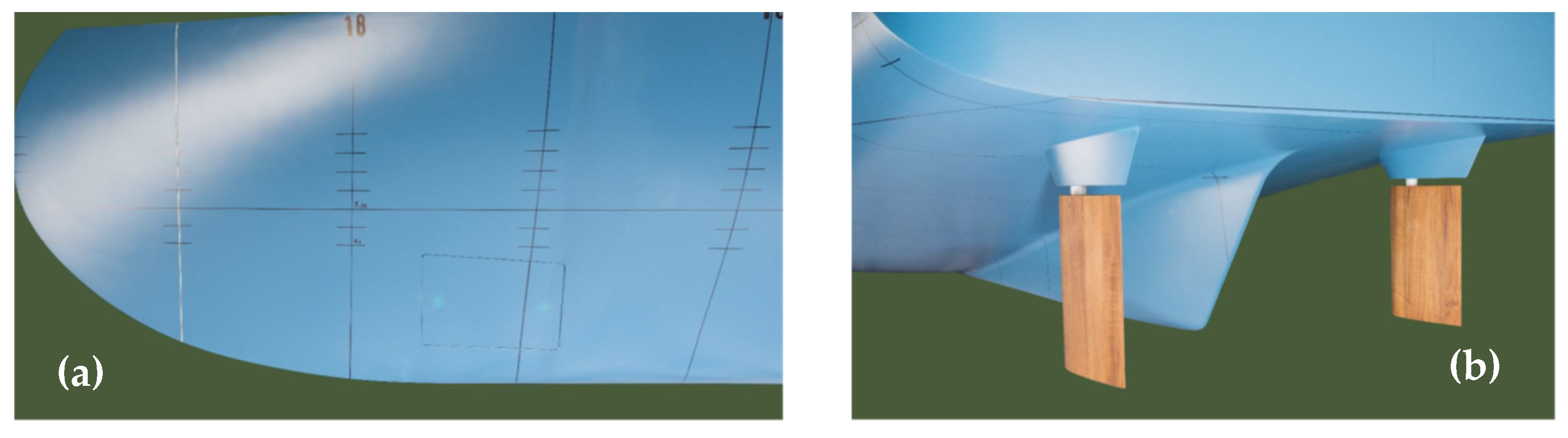
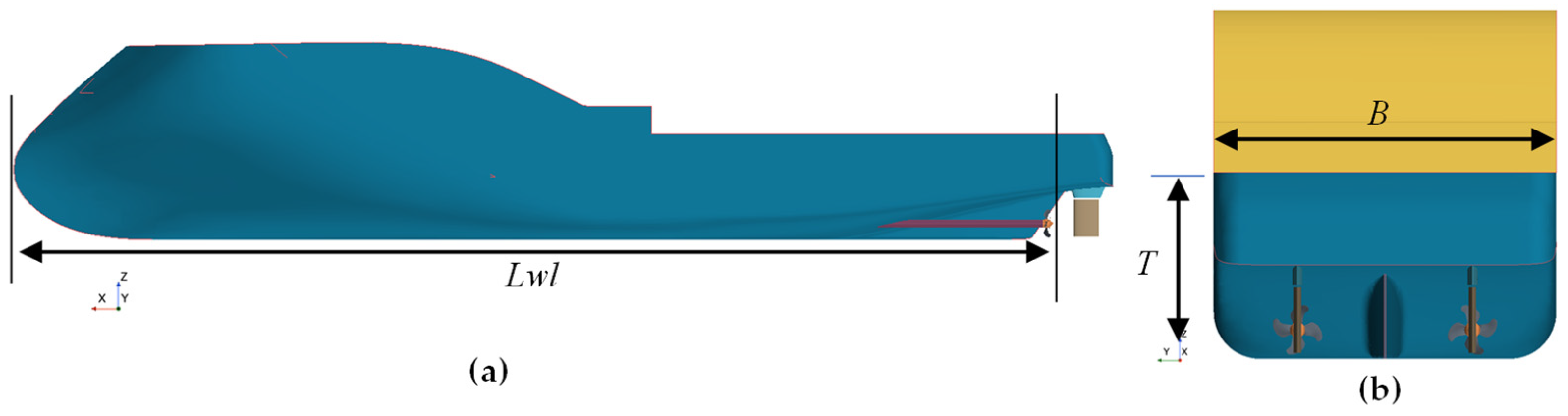







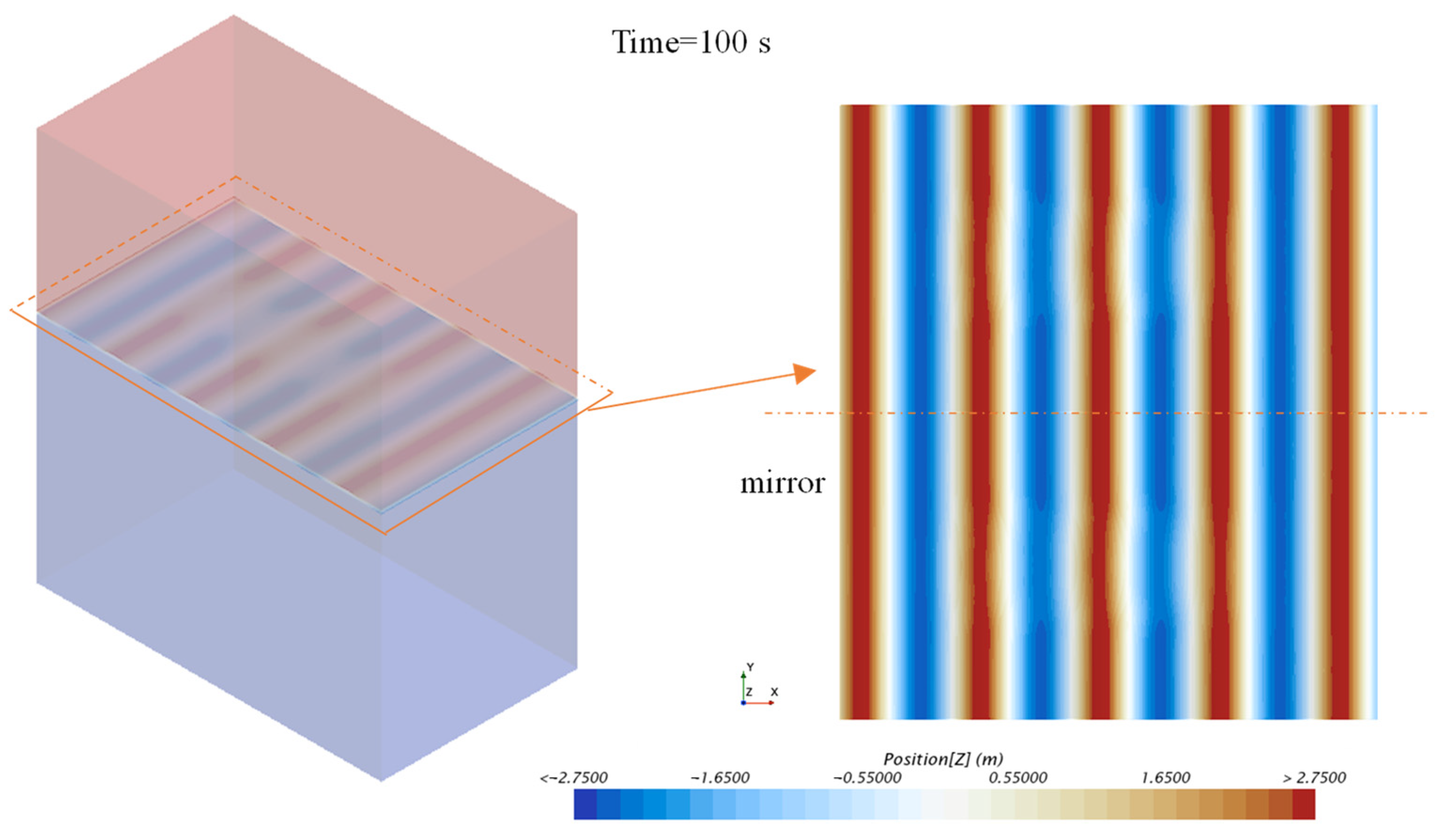

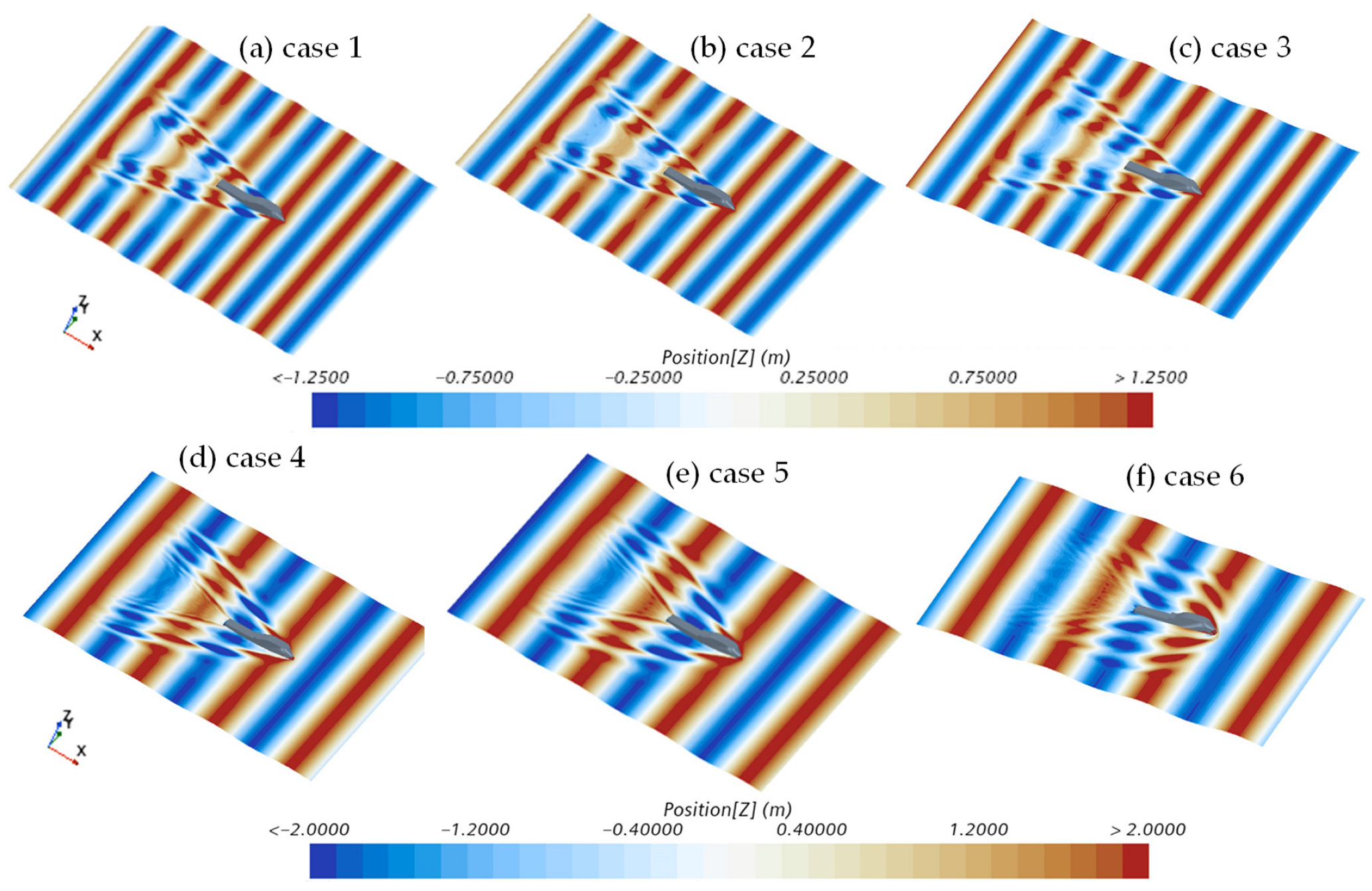
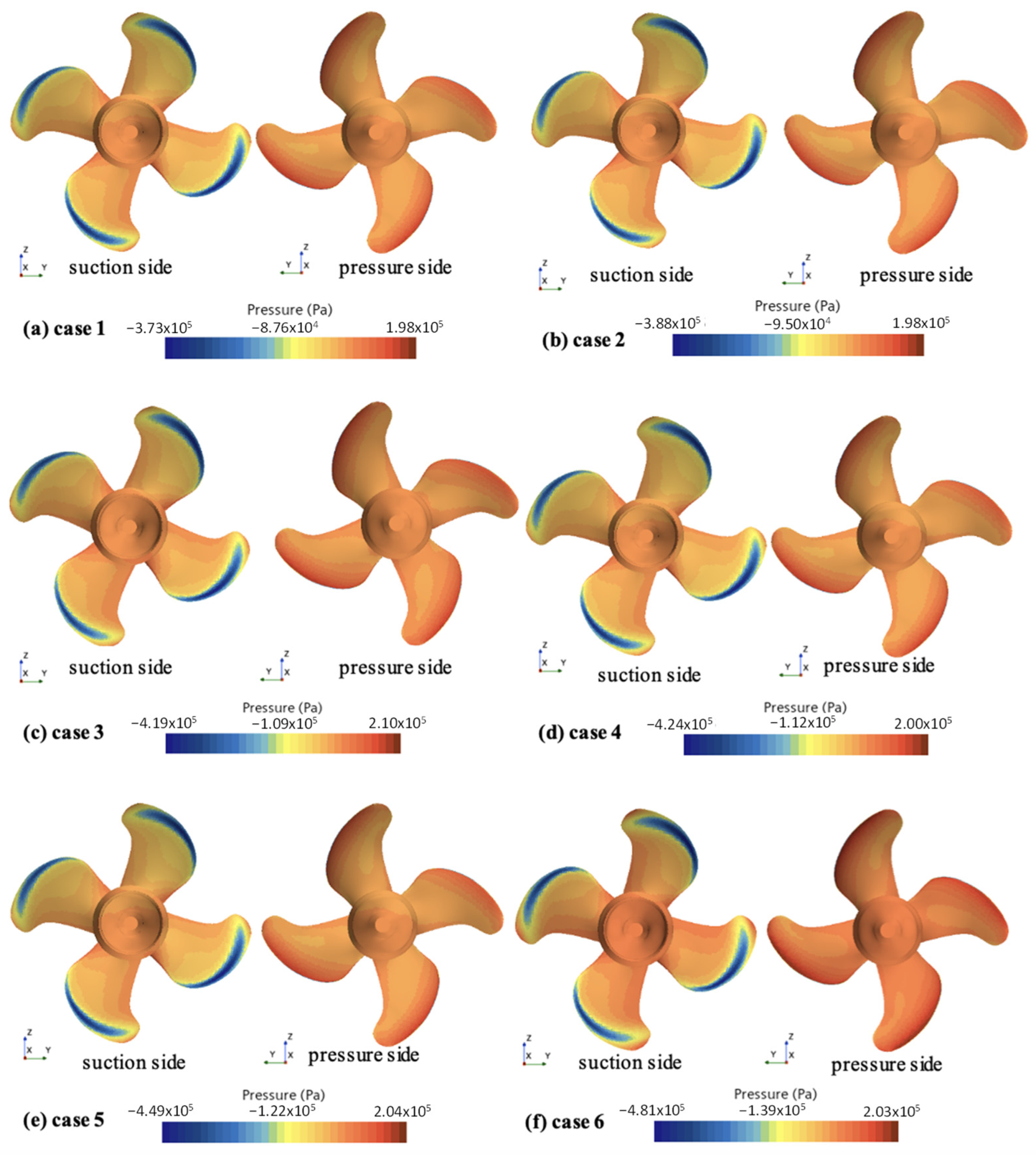





| Main Parameter | Symbol | Full-Scale | Model-Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Displacement | Δ (t) | 5190.0 | 1.661 |
| Length (overall) | Loa (m) | 104.11 | 7.180 |
| Length (waterline) | Lwl (m) | 100.03 | 6.899 |
| Beam | B (m) | 18.40 | 1.269 |
| Depth | D (m) | 7.25 | 0.500 |
| Design draught | d (m) | 5.10 | 0.352 |
| Design velocity | V (kn) | 15.00 | 1.034 |
| Center of gravity (rel. to AP) | LCG (m) | 41.50 | 2.862 |
| Center of gravity (rel. to BL) | VCG (m) | 8.0 | 0.552 |
| Propeller diameter | Dp (m) | 3.19 | 0.22 |
| Number of blades | Z | 4 | 4 |
| Pitch ratio | P/D (0.75R) | 0.90 | 0.90 |
| Area ratio | Ae/A0 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| Propeller rotation direction | / | Inward | Inward |
| Rudder type | / | Spade | Spade |
| Grid No. | Grid Size | Half-Ship Resistance (kN) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | CFD | Error (%) | ||
| G1 | 6.21 M | 112.645 | 115.086 | 2.17% |
| G2 | 3.58 M | 115.565 | 2.59% | |
| G3 | 2.07 M | 118.219 | 4.95% | |
| RG | PG | UG (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | 0.1805 | 4.5619 | 5.825 |
| T (kN) | V (m/s) | Trim (°) | Sinkage (m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free running | 153.24 | 7.660 | 0.067 | −0.203 |
| Traditional self-propulsion | 149.35 | 7.716 | 0.066 | −0.181 |
| Experiments | 149.50 | 7.716 | 0.07 | −0.19 |
| Error (%) | +2.50% | −0.73% | −4.28% | +6.84% |
| Time (s) | 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CFD | 1.161 | −1.563 | −2.476 | −1.217 |
| Theory | 1.130 | −1.549 | −2.496 | −1.237 |
| Error (%) | 3.12% | 0.86% | −0.82% | −1.61% |
| Case | Wind Level | Wave Conditions | V0 (m/s) | Fn0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H/Lwl | λ/Lwl | ||||
| 1 | 5 | 0.025 | 0.8 | 6.30 | 0.20 |
| 2 | 6 | 0.030 | 0.8 | 6.05 | 0.19 |
| 3 | 7 | 0.040 | 0.8 | 5.30 | 0.17 |
| 4 | 5 | 0.025 | 1.2 | 4.90 | 0.16 |
| 5 | 6 | 0.030 | 1.2 | 4.71 | 0.15 |
| 6 | 7 | 0.040 | 1.2 | 3.20 | 0.10 |
| Case | Wind Level | Vt (m/s) | Fnt | Vt-crest − Vt-trough (m/s) | t (s) | T (half) (kN) | Pmax (kPa) | Pmin (kPa) | ΔP (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Static | 7.66 | 0.245 | / | / | 153.24 | 191 | −319 | 510 |
| 1 | 5 | 6.83 | 0.218 | 0.1085 | 125 | 180.40 | 198 | −373 | 571 |
| 2 | 6 | 6.45 | 0.206 | 0.1104 | 112 | 194.94 | 198 | −388 | 586 |
| 3 | 7 | 5.19 | 0.166 | 0.1198 | 88 | 226.85 | 201 | −419 | 620 |
| 4 | 5 | 5.29 | 0.169 | 0.3467 | 101 | 223.80 | 200 | −424 | 624 |
| 5 | 6 | 4.59 | 0.147 | 0.5040 | 50 | 235.75 | 204 | −449 | 653 |
| 6 | 7 | 3.33 | 0.106 | 0.8500 | 72 | 269.53 | 203 | −481 | 684 |
| Level | λ/Lwl | H/Lwl |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8 | 0.025 |
| 2 | 1.2 | 0.03 |
| 3 | - | 0.04 |
| Item | λ/Lwl | H/Lwl |
|---|---|---|
| K1 | 0.339 | 0.455 |
| K2 | 1.701 | 0.614 |
| K3 | - | 0.97 |
| K1’ | 0.113 | 0.228 |
| K2’ | 0.567 | 0.307 |
| K3’ | - | 0.485 |
| R | 0.454 | 0.257 |
| Primary and secondary order | λ/Lwl –> H/Lwl | |
| Case | Wind Level | Vt (m/s) | Fnt | T (Half) (kN) | R (Half) (kN) | ΔR (kN) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Static | 7.66 | 0.245 | 153.24 | 153.15 | / | 0.06% | / |
| 1 | 5 | 6.83 | 0.218 | 180.40 | 179.77 | 26.62 | 0.35% | 17.38% |
| 2 | 6 | 6.45 | 0.206 | 194.94 | 193.04 | 39.89 | 0.97% | 26.05% |
| 3 | 7 | 5.19 | 0.166 | 226.85 | 225.12 | 71.97 | 0.76% | 46.99% |
| 4 | 5 | 5.29 | 0.169 | 223.80 | 223.32 | 70.17 | 0.21% | 45.82% |
| 5 | 6 | 4.59 | 0.147 | 235.75 | 234.87 | 81.72 | 0.37% | 53.36% |
| 6 | 7 | 3.33 | 0.106 | 269.53 | 268.81 | 115.66 | 0.27% | 75.52% |
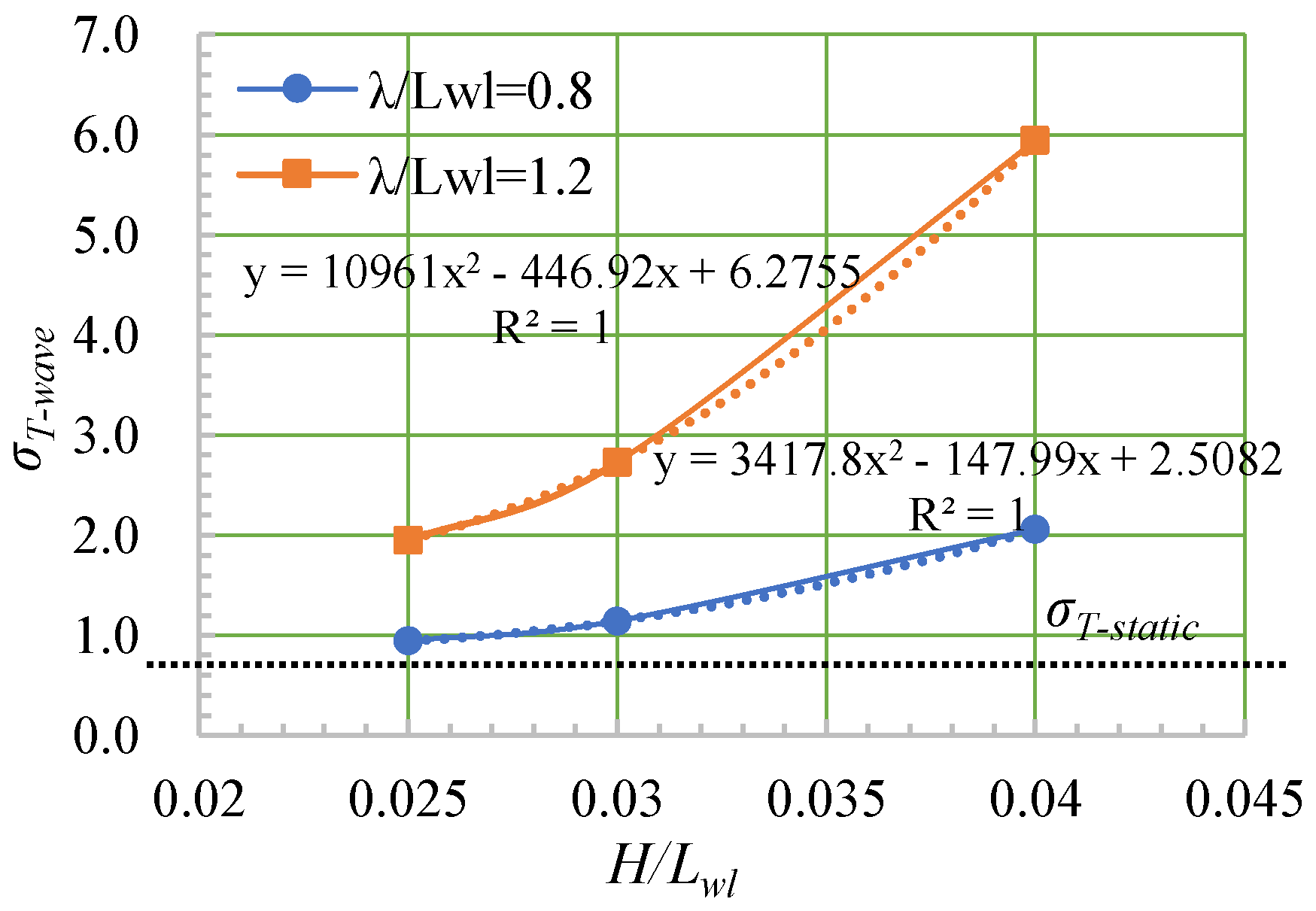
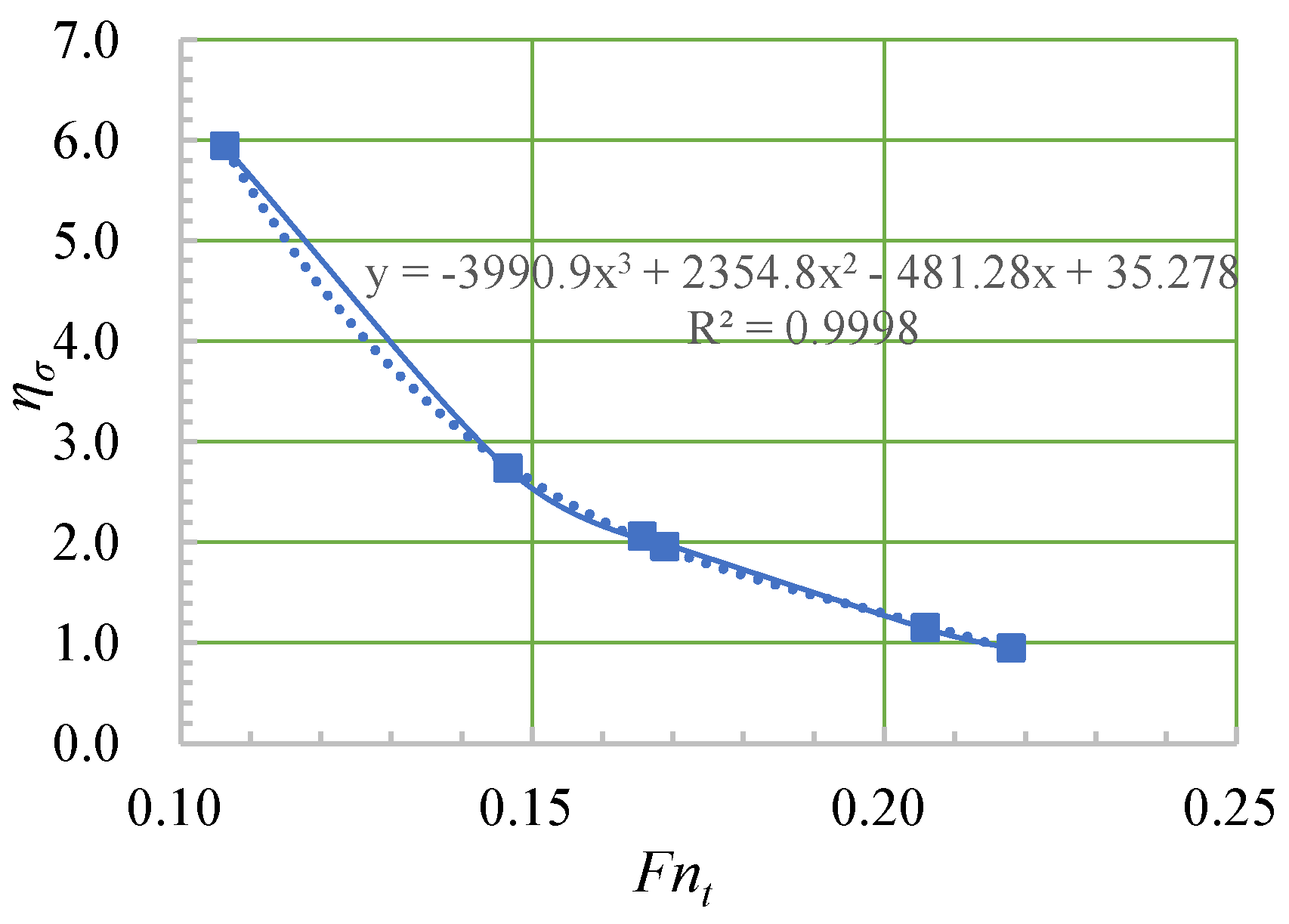
| Case | Wind Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Static | Static | / | 0.64 | / |
| 1 | 5 | 0.94 | / | 1.48 |
| 2 | 6 | 1.14 | / | 1.79 |
| 3 | 7 | 2.06 | / | 3.22 |
| 4 | 5 | 1.95 | / | 3.06 |
| 5 | 6 | 2.73 | / | 4.28 |
| 6 | 7 | 5.94 | / | 9.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, S.; Zeng, J.; Song, K.; Jia, J. Full-Scale Numerical Simulation of a Free-Running Cruise Ship in Heavy Head Sea Conditions. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040626
Ge S, Zeng J, Song K, Jia J. Full-Scale Numerical Simulation of a Free-Running Cruise Ship in Heavy Head Sea Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(4):626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040626
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Shenwei, Ji Zeng, Kewei Song, and Junrui Jia. 2025. "Full-Scale Numerical Simulation of a Free-Running Cruise Ship in Heavy Head Sea Conditions" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 4: 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040626
APA StyleGe, S., Zeng, J., Song, K., & Jia, J. (2025). Full-Scale Numerical Simulation of a Free-Running Cruise Ship in Heavy Head Sea Conditions. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(4), 626. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13040626






