Sediment Provenance and Facies Analysis of the Huagang Formation in the Y-Area of the Central Anticlinal Zone, Xihu Sag, East China Sea
Abstract
1. Introduction
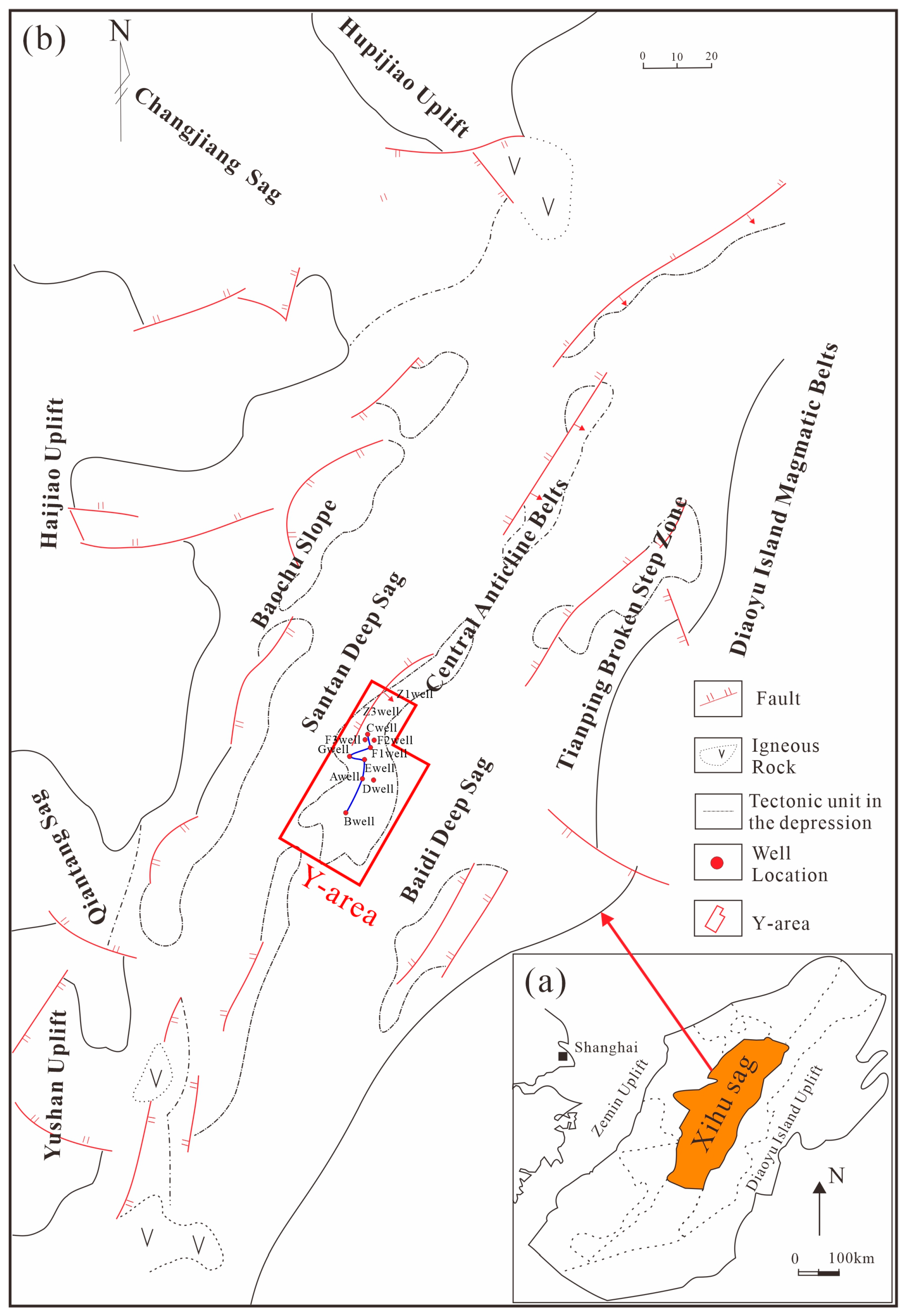
2. Geological Background
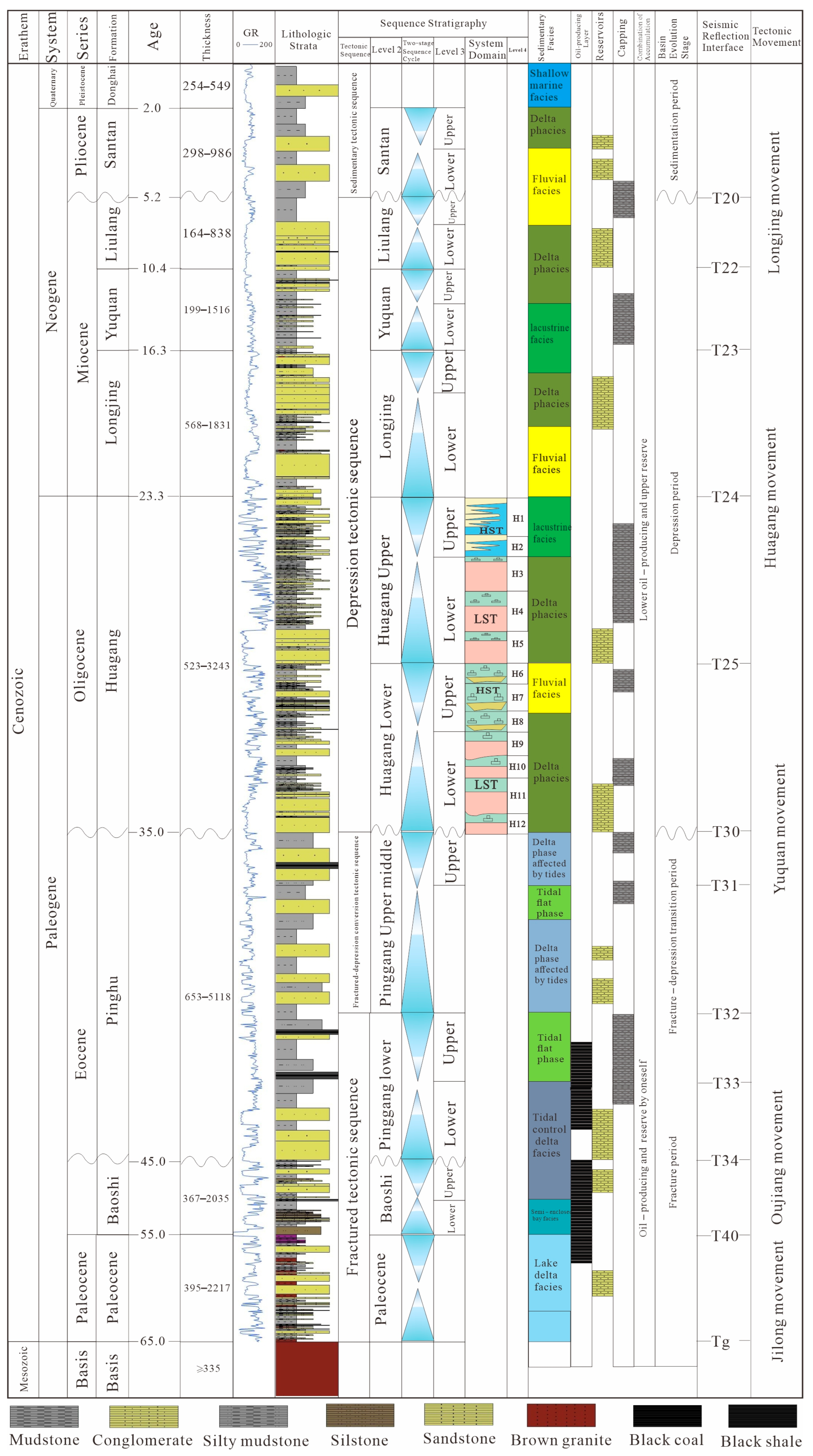
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results
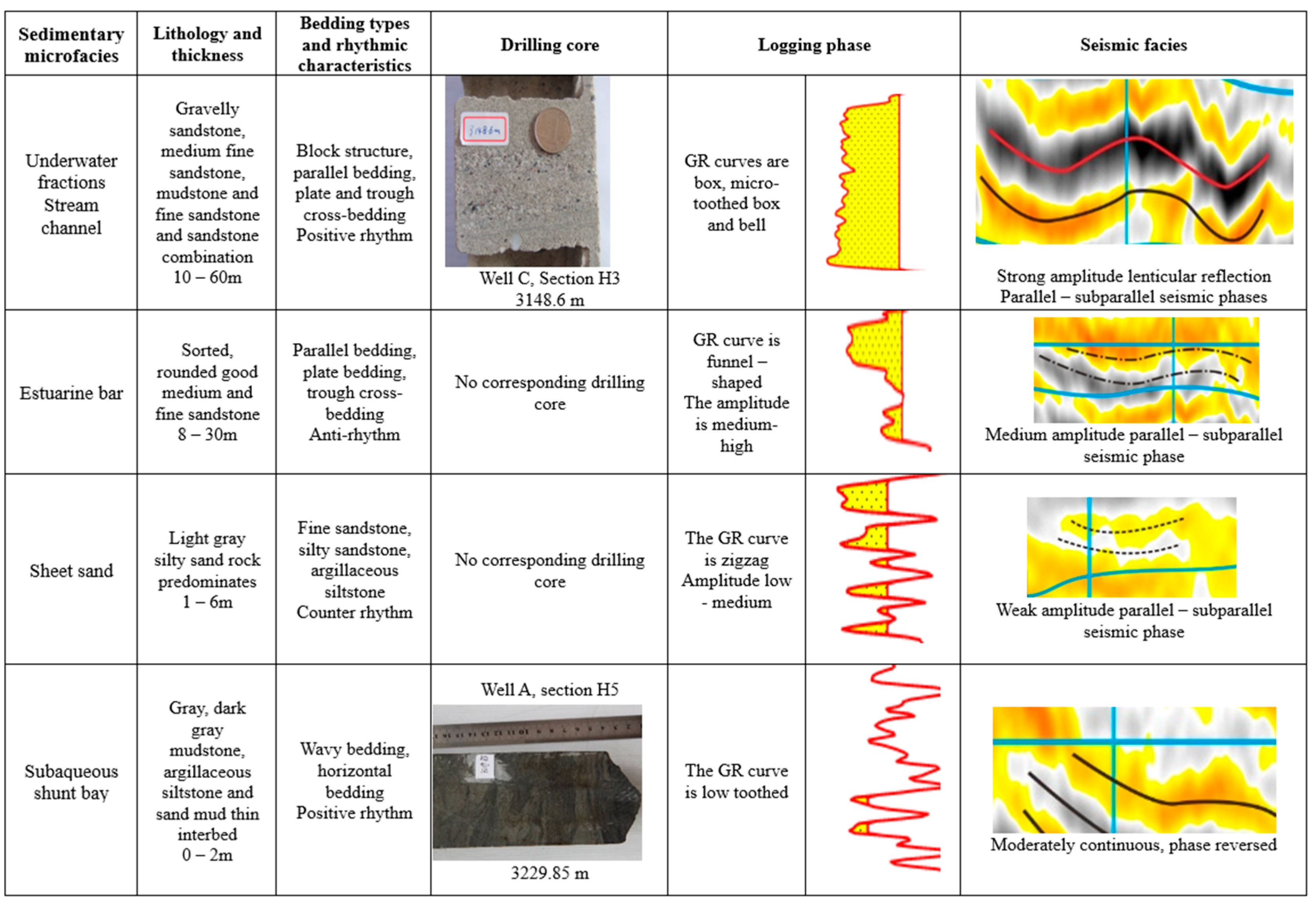
4.1. Sedimentary Facies
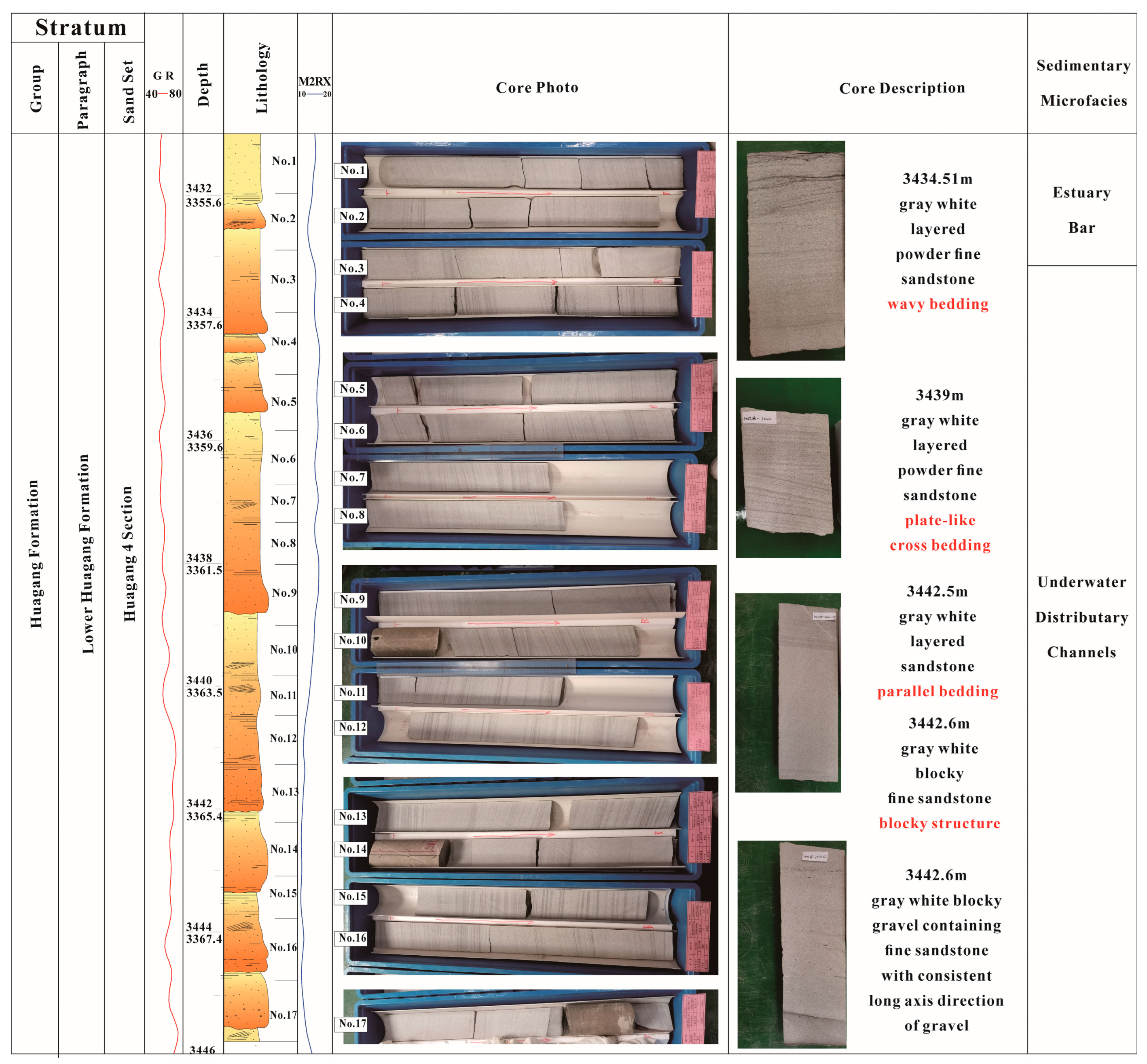
4.1.1. Braided River Delta Front Subfacies (Figure 5a)
Microfacies of Subaqueous Distributary Channel
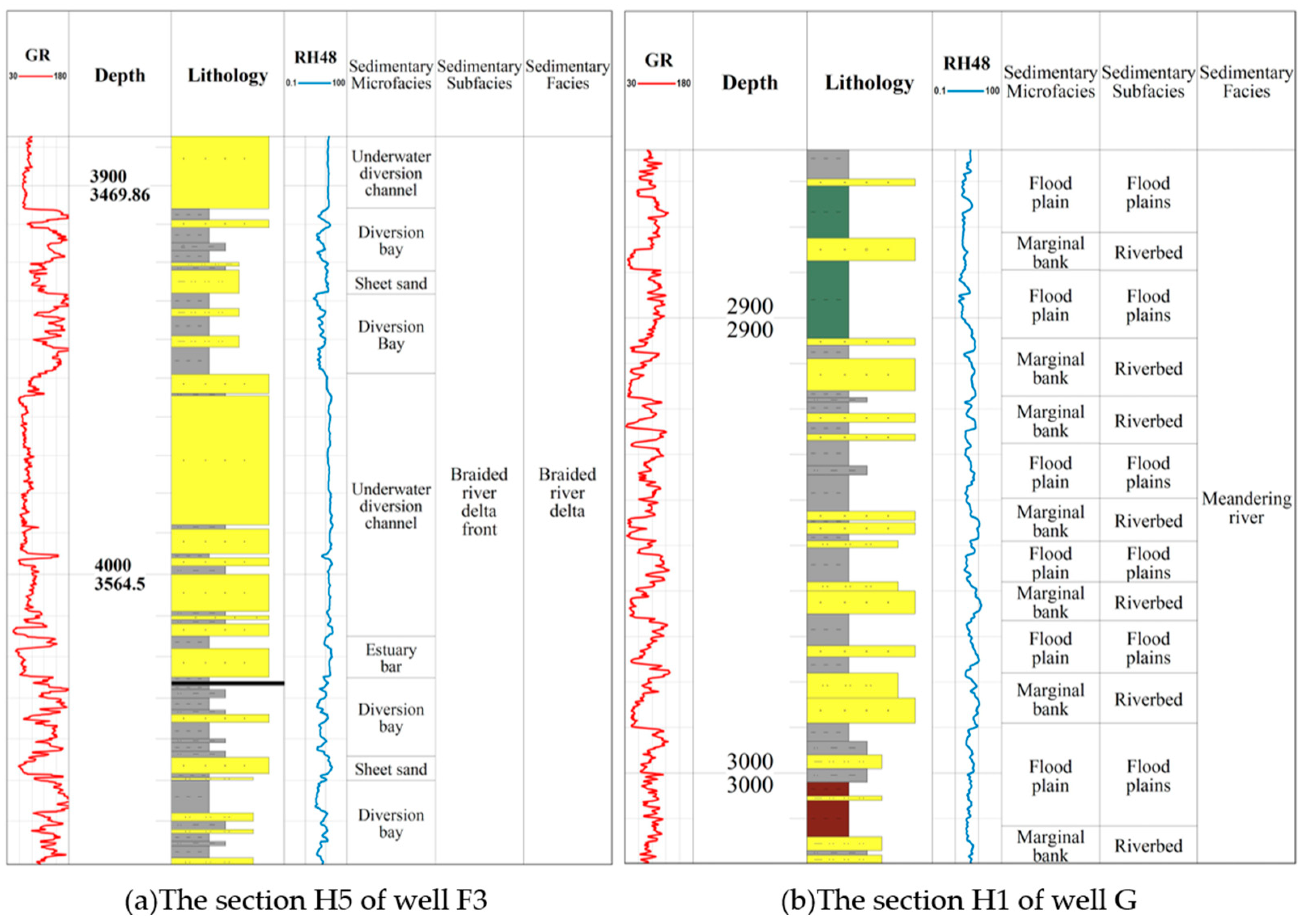
Estuarine Bar Microfacies
Sheet Sand Microfacies
Underwater Diverging Bay Microfacies
4.1.2. Meandering River Subfacies (Figure 5b)
4.2. Provenance
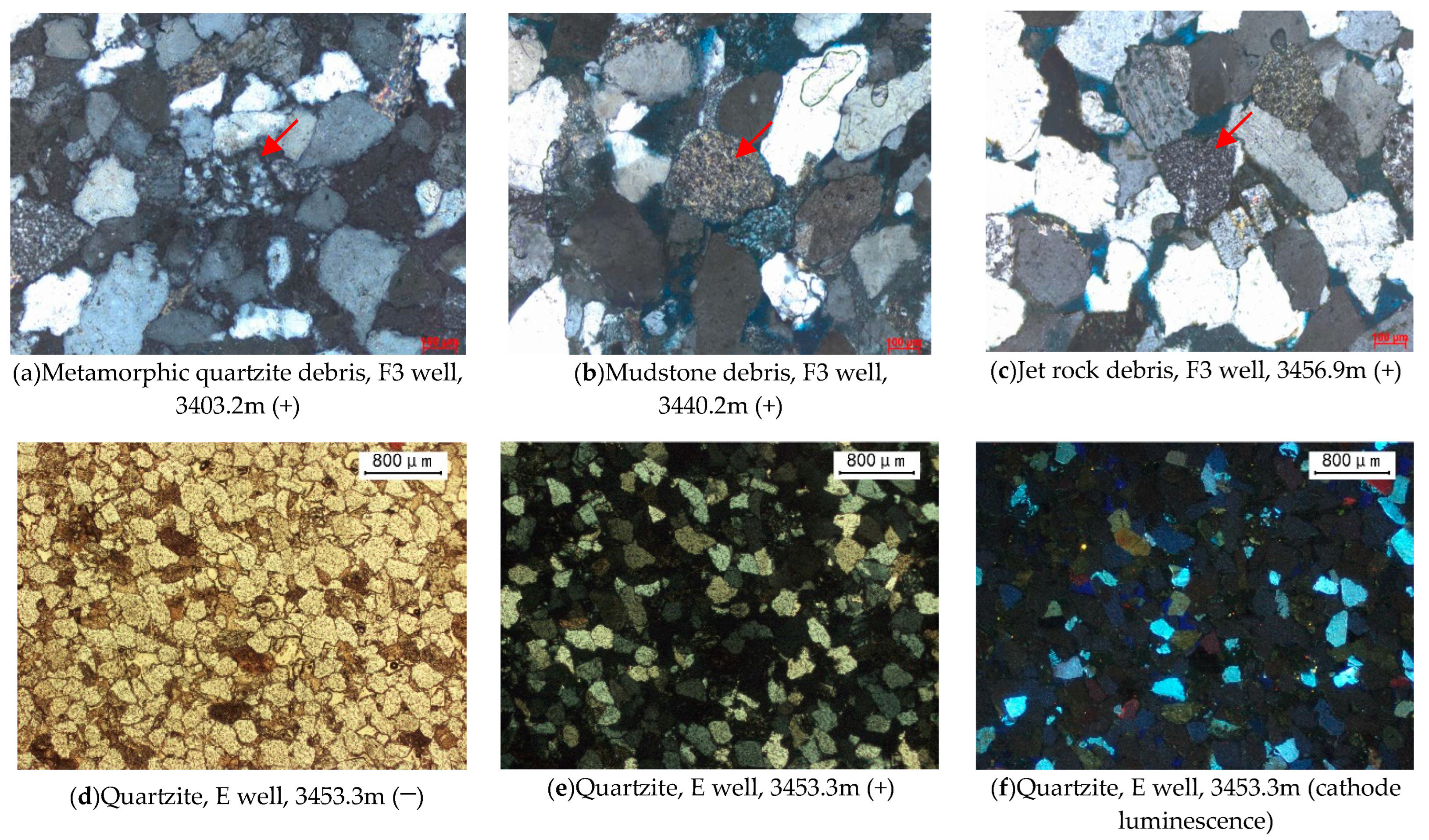
4.2.1. Petrological Characteristics
Gravel Composition and Cuttings Type
Characteristics of Quartz Cathode Luminescence
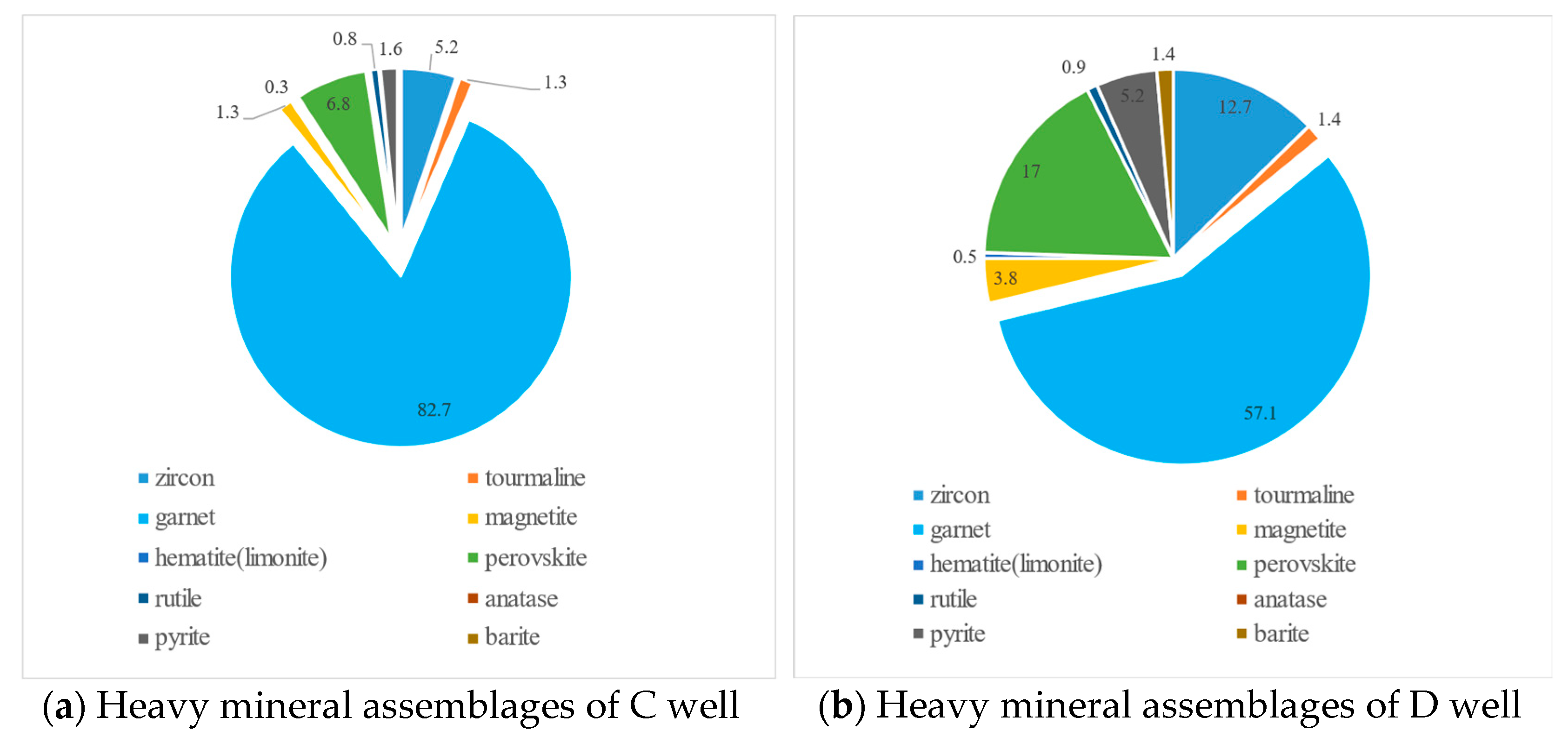
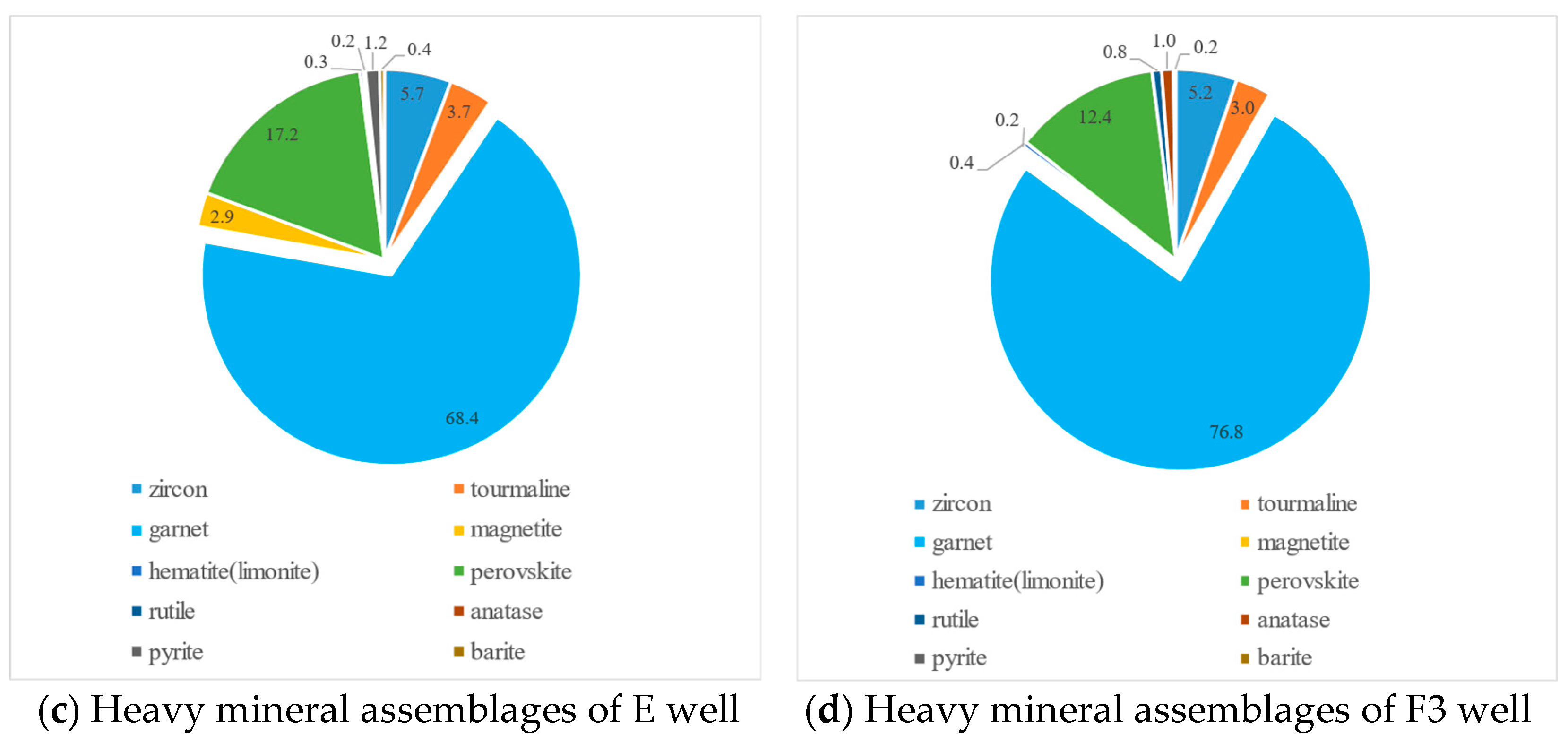
4.2.2. Heavy Mineral Characteristics
Heavy Mineral Combination Types
ZTR Index
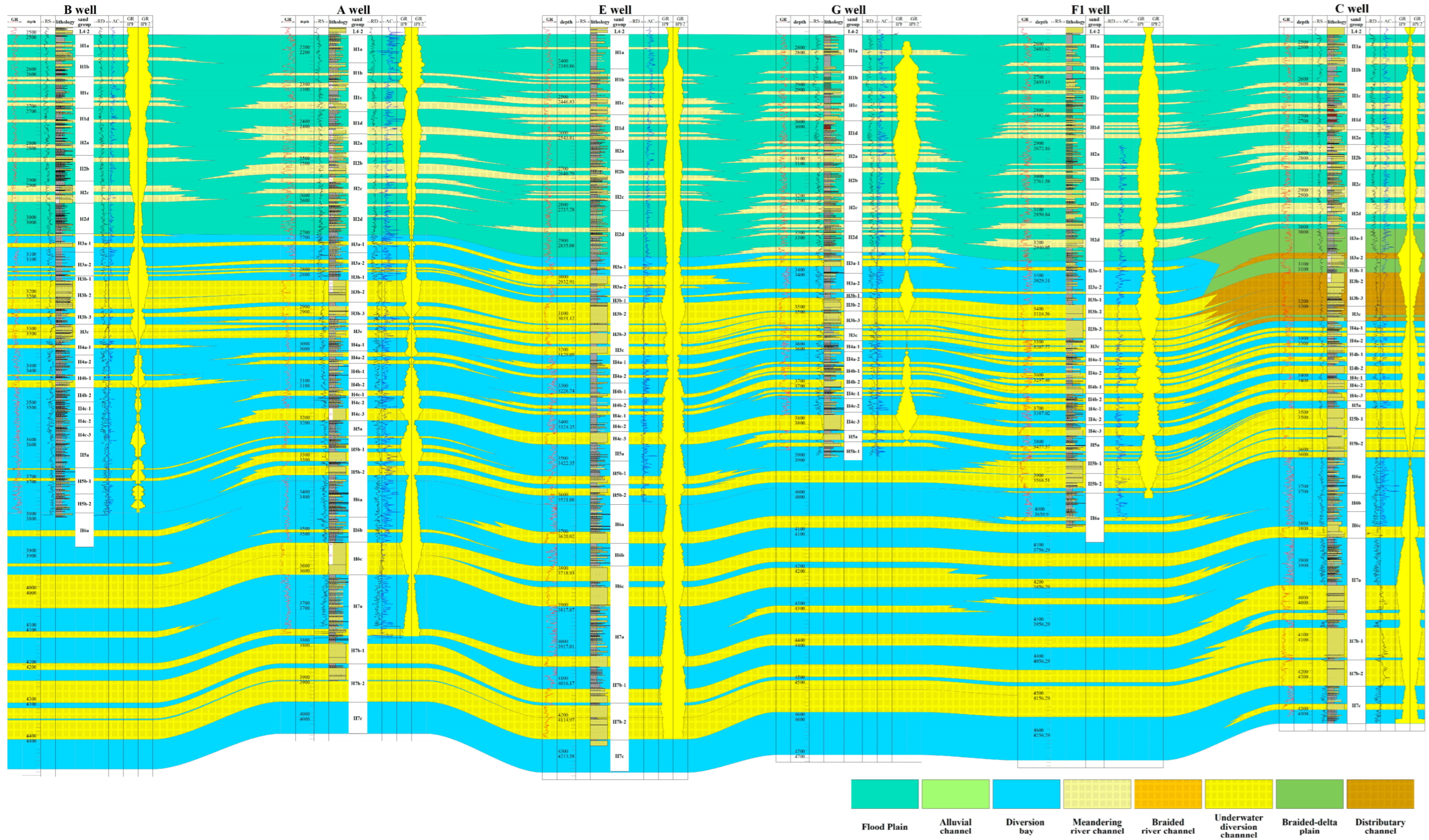
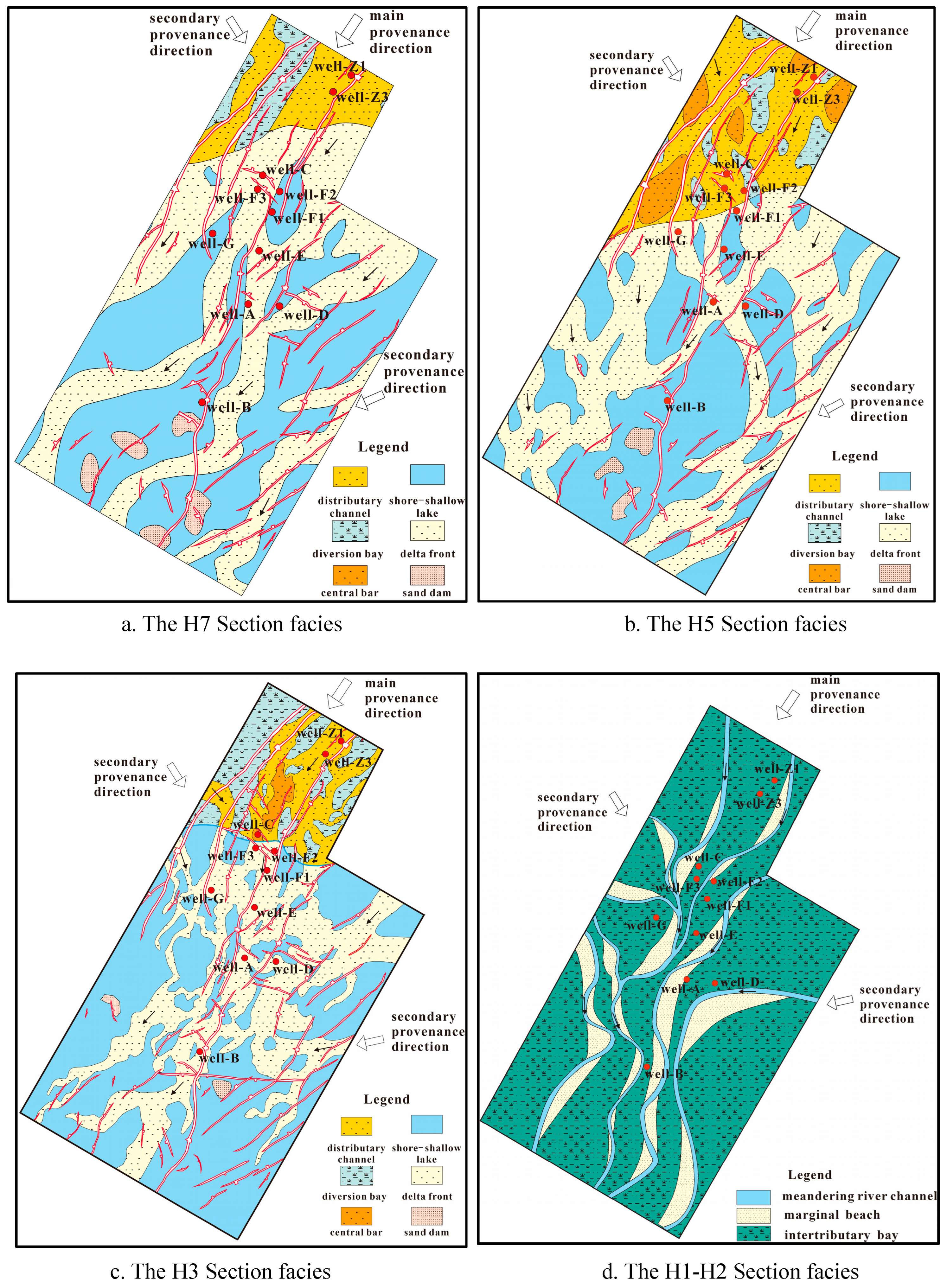
4.2.3. Distribution Characteristics of Sedimentary Facies
Distribution Characteristics of Sedimentary Facies Profile
Characteristics of Planar Distribution of Sedimentary Facies
5. Discussion
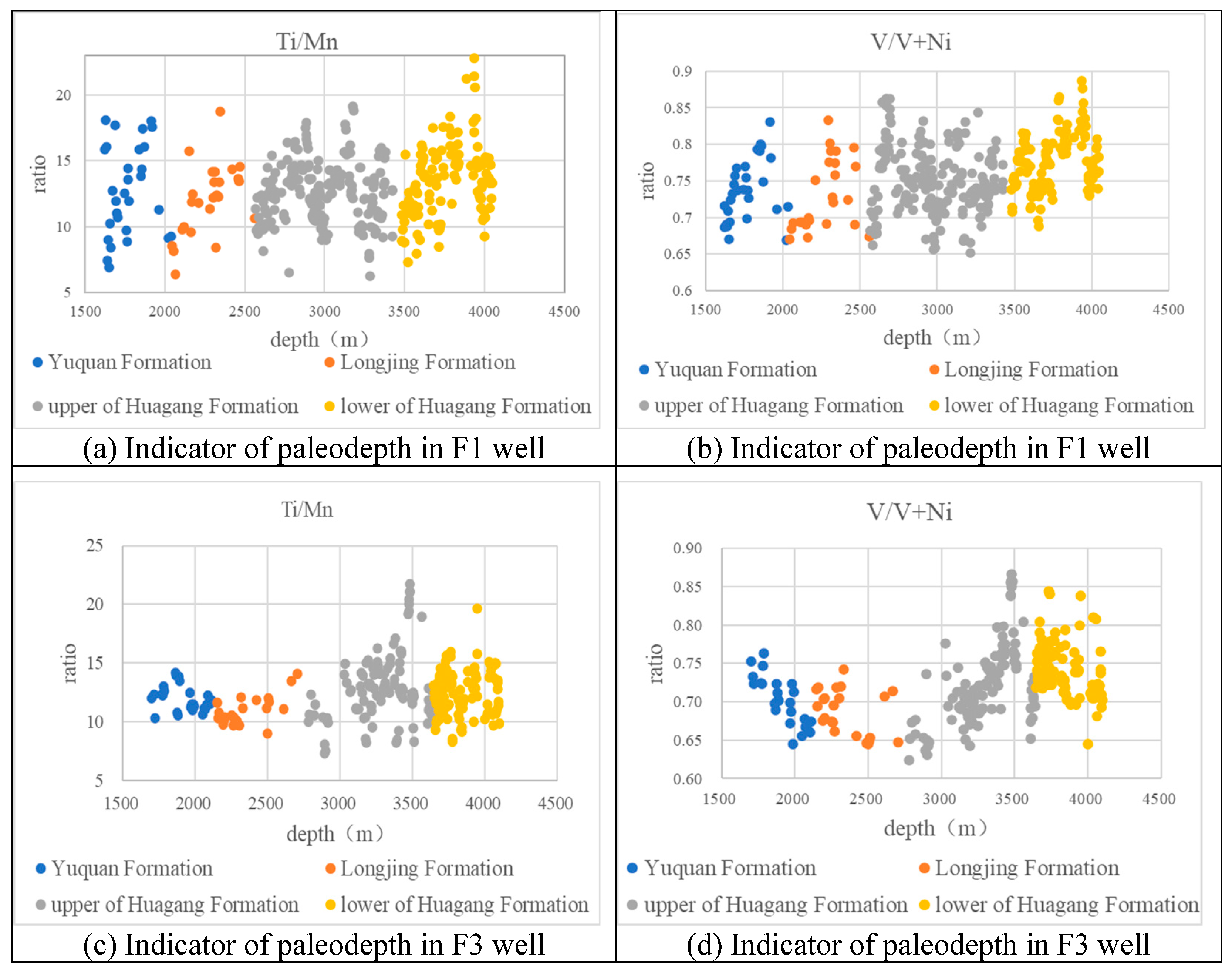
5.1. Paleo-Environment
5.2. Hydrocarbon Exploration
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| E3h3 | the third section of Huagang Fotmation in Oligocene |
| E3h4 | the fourth section of Huagang Fotmation in Oligocene |
| E3h5 | the fifth section of Huagang Fotmation in Oligocene |
| T30 | T30 structural layer |
| T20 | T20 structural layer |
| H1 | the first section of Huagang Formation (Upper Member of Huagang Formation) |
| H2 | the second section of Huagang Formation (Upper Member of Huagang Formation) |
| H3 | the third section of Huagang Formation (Upper Member of Huagang Formation) |
| H4 | the fourth section of Huagang Formation (Lower Member of Huagang Formation) |
| H5 | the fifth section of Huagang Formation (Lower Member of Huagang Formation) |
| H7 | the seventh section of Huagang Formation (Lower Member of Huagang Formation) |
| H3b2 | b2 single sand body of the third Huagang sand layer group |
| RMS | root-mean-square |
References
- Xu, F.; Xu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cui, H.; Wang, Y. Factors controlling the development of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Huagang Formation of the central inverted structural belt in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.Y.; Li, S.Z.; Dai, L.M.; Suo, Y.; Guo, L.; Somerville, I.; Liu, Z.; Ma, F. Dynamic mechanism of tectonic inversion and implications for oil-gas accumulation in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Shelf Basin: Insights from numerical modelling. Geol. J. 2018, 53, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Wang, Q.; Guo, R.; Tuo, C.; Ma, D.; Mou, W.; Tian, B. Diagenetic fluids evolution of Oligocene Huagang Formation sandstone reservoir in the south of Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin: Constraints from petrology, mineralogy, and isotope geochemistry. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lin, C.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C.; Ren, L.; Lin, J. Effect of burial history on diagenetic and reservoir-forming process of the Oligocene sandstone in Xihu sag, East China Sea Basin. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2020, 112, 104034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Lin, C.Y.; Zhang, X.G.; Lin, J.L.; Zhao, Z.X.; Huang, D.W.; Duan, D.P. Characteristics and distribution of clay minerals and their effects on reservoir quality: Huagang Formation in the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Aust. J. Earth Sci. 2019, 66, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.D.; Sun, Q.L.; Stuart, J.J.; Yin, T.; Zhang, C.; Xu, G.; Hou, G.; Zhang, B. Diagenesis and controlling factors of Oligocene Huagang Formation tight sandstone reservoir in the south of Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, G.; Cui, H.; Zhang, W. Fracture development and hydrocarbon accumulation in tight sandstone reservoirs of the Paleogene Huagang Formation in the central reversal tectonic belt of the Xihu Sag, East China Sea. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2020, 47, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wang, M.; Zhuang, J. Kinematical processes of inversion structure and its contribution to hydrocarbon accumulation in Xihu Depression of East China Sea Basin. Acta Pet. Sin. 2010, 31, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.Z.; Zou, C.N. Accumulation and distribution of natural gases in Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2005, 32, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Elsworth, D.; Zhang, R. Organic Geochemical and Petrographic Characteristics of the Coal Measure Source Rocks of Pinghu Formation in the Xihu Sag of the East China Sea Shelf Basin: Implications for Coal Measure Gas Potential. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 94, 364–375. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.L.; Qin, Y.; Cui, M.; Xie, G.; Guo, Y.; Qu, Z.; Yang, T.; Yang, L. Geochemical Characteristics and Sedimentary Control of Pinghu Formation (Eocene) Coal-bearing Source Rocks in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin. Acta Geol. Sin. (Engl. Ed.) 2021, 95, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wang, T.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, T.; Diao, H.; Liu, B.; Hu, Y. Geochemical characteristics and gas-washing accumulation mechanism of hydrocarbon from the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 224, 211639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Hou, D.; Cao, B.; Chen, X.; Xu, T. Geochemical characteristics of high-maturity crude oils in the Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin. Geochem. J. 2016, 50, 163–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, B.; Zhang, J.; Chu, Y.; Dai, Y.; Xu, L.; Sun, W.; Ma, S. Structural characteristics and genetic mechanism of transfer zones in an extensional rift zone: An example from the Xihu Sag, East China Sea Basin. Tectonophysics 2023, 856, 229852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, M.; Cai, H.; He, X.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H. Application of seismic sedimentology in characterization of fluvial-deltaic reservoirs in Xihu sag, East China Sea shelf basin. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2023, 50, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Yu, Y.F.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Tang, X. A discussion on the exploration potential of deep basin gas in Xihu Sag, East China Sea. China Offshore Oil Gas 2023, 24–29, 35, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S. Main geological characteristics and gas exploration directions in East China Sea Basin. China Offshore Oil Gas (Geol.) 2003, 17, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Li, S.; Liao, K.; Cui, Y.; Shao, L.; Qiao, P.; Lu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Goh, T.L.; Yao, Y. New interpretation on the provenance changes of the upper Pinghu–lower Huagang Formation within Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2023, 42, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W. Diaoyu Islands folded-uplift belt evolution characteristics and its importance on the hydrocarbon exploration in East China Sea basin. Pet. Geol. Eng. 2012, 26, 10–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.J.; Li, G.; Yang, C.Q.; Yang, C. Characteristics of seismic sequence in the East China Sea shelf basin and their geological attributes. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2013, 33, 117–122, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cukur, D.; Horozal, S.; Kim, D.C.; Han, H.C. Seismic stratigraphy and structural analysis of the northern East China Sea Shelf Basin interpreted from multi-channel seismic refection data and cross-section restoration. Mar. Petrol. Geol. 2011, 28, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.X. Sedimentology; Petroleum Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2003; pp. 1–424, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.X.; Hu, M.Y. Sedimentary provenance analysis of Oligocene Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag of East China Sea basin. J. Oil Gas Technol. 2010, 5, 176–179, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.W.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Ma, X.F.; Tang, J.; Liao, P. Provenance characteristics of Huagang Formation (Paleogene) in Xihu Sag, East China Sea. Nat. Gas Geosci. 2011, 22, 9, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Y. On marine to non-marine facies transformation of the Permian sedimentation in the Chaohu Lake, Anhui Province, with the application of MNO/TIO_2 index. Pet. Geol. Exp. 1992, 14, 195–199, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.Q. Geology and Hydrocarbon-Gas Hydrate Accumulation Dynamics in Shelf Basins in the East China Sea; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2022; pp. 1–164, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hall, J.; Wardle, R.J.; Gower, C.F.; Kerr, A.; Coflin, K.; Keen, C.E.; Carroll, P. Proterozoic orogens of the northeastern Canadian Shield: New information from the Lithoprobe ECSOOT crustal reflection seismic survey. Can. J. Earth Sci. 1995, 32, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.J.; LI, S.T. Spreading and dynamic setting of marginal basins of the western Pacific. Geosci. Front. 2000, 7, 203–214, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama, S.; Isozaki, Y.; Kimura, G.; Terabayashi, M. Paleogeographic maps of the Japanese Islands: Plate tectonic synthesis from 750 Ma to the present. Isl. Arc 1997, 6, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Liao, Z.T.; Yang, F.L.; Fu, Q. Fission-track analysis and its application in the study of sedimentary basins. Pet. Geol. Exp. 2001, 23, 332–337, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q. Correlations Between Shortening Rate, Uplift Rate, and Inversion Rate in Central Inversion Zone of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin. J. Earth Sci. 2009, 20, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, Y.M.; Lan, Z.; Wan, L.F.; Li, K.; Zhou, X.H. Delimitation of Cenozoic Rift-Depression Transitional Unconformity in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Shelf Basin. Mar. Orig. Pet. Geol. 2014, 19, 18–26. [Google Scholar]


| Well | Drilling Time | Granularity | Heavy Minerals | Elemental Logging | Cast Thin Sections | Core Samples | Cuttings Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E | 17 July 2022– 25 September 2022 | 62 | 19 | / | 54 | 24 | 41 |
| F1 | 10 December 2022– 18 December 2022 | 34 | 24 | 361 | 12 | / | / |
| F3 | 22 January 2023– 30 January 2023 | 40 | 41 | 261 | 19 | / | 24 |
| G | 8 February 2023– 24 February 2023 | 26 | 14 | 197 | 22 | / | 51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Yan, W.; Yang, Y.; Sun, R.; Chao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Yang, C.; Zhang, S.; Su, D.; Zhang, G.; et al. Sediment Provenance and Facies Analysis of the Huagang Formation in the Y-Area of the Central Anticlinal Zone, Xihu Sag, East China Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030520
Ma X, Yan W, Yang Y, Sun R, Chao Y, Zhang G, Yang C, Zhang S, Su D, Zhang G, et al. Sediment Provenance and Facies Analysis of the Huagang Formation in the Y-Area of the Central Anticlinal Zone, Xihu Sag, East China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(3):520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030520
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiao, Wei Yan, Yi Yang, Ru Sun, Yue Chao, Guoqing Zhang, Chao Yang, Shudi Zhang, Dapeng Su, Guangxue Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Sediment Provenance and Facies Analysis of the Huagang Formation in the Y-Area of the Central Anticlinal Zone, Xihu Sag, East China Sea" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 3: 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030520
APA StyleMa, X., Yan, W., Yang, Y., Sun, R., Chao, Y., Zhang, G., Yang, C., Zhang, S., Su, D., Zhang, G., & Xu, H. (2025). Sediment Provenance and Facies Analysis of the Huagang Formation in the Y-Area of the Central Anticlinal Zone, Xihu Sag, East China Sea. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(3), 520. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13030520






