Effect of Following Current on the Hydroelastic Behavior of a Floating Ice Sheet near an Impermeable Wall
Abstract
1. Introduction
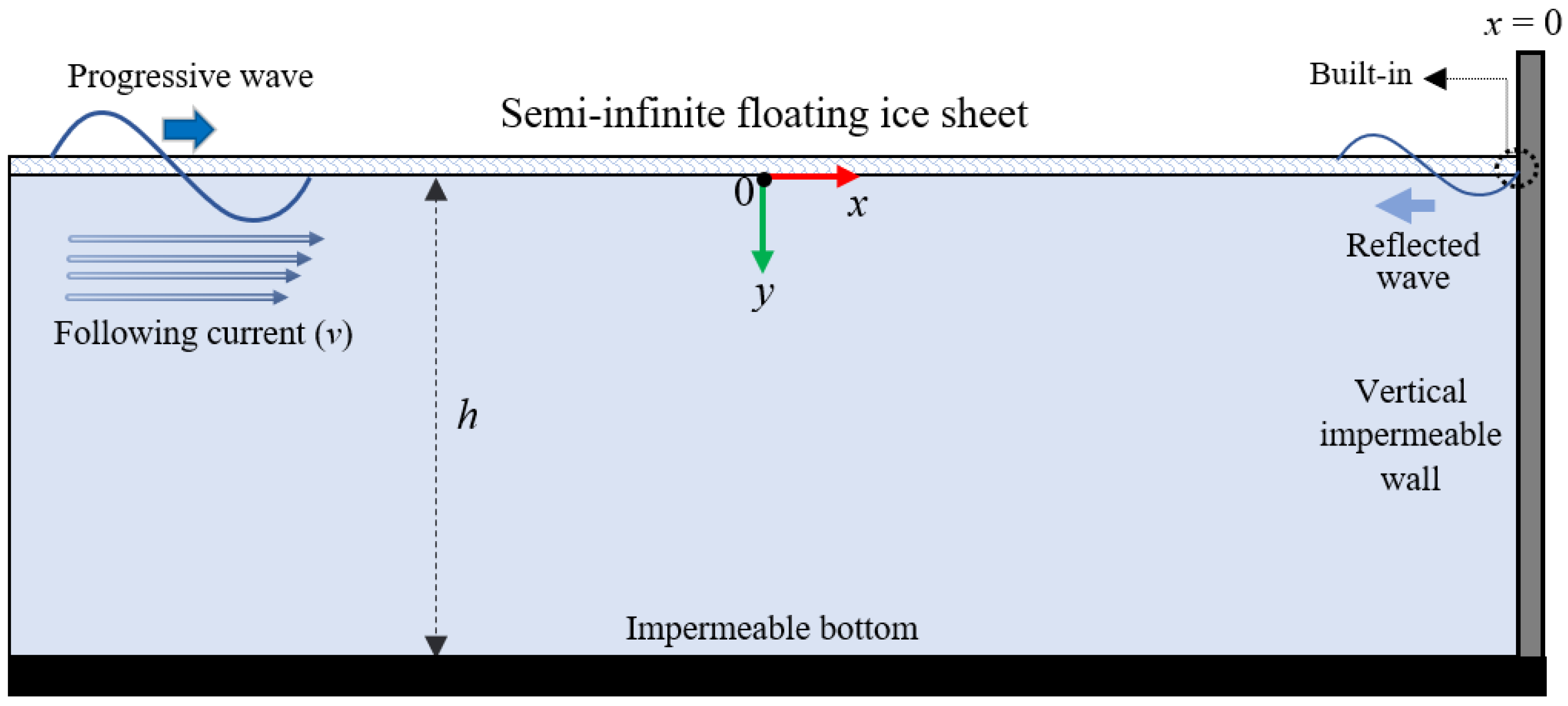
2. Model Definition
3. Solution Technique
4. Quantified Outcomes and Their Interpretive Analysis
4.1. Convergence of the Present Solution and Validation with Literature
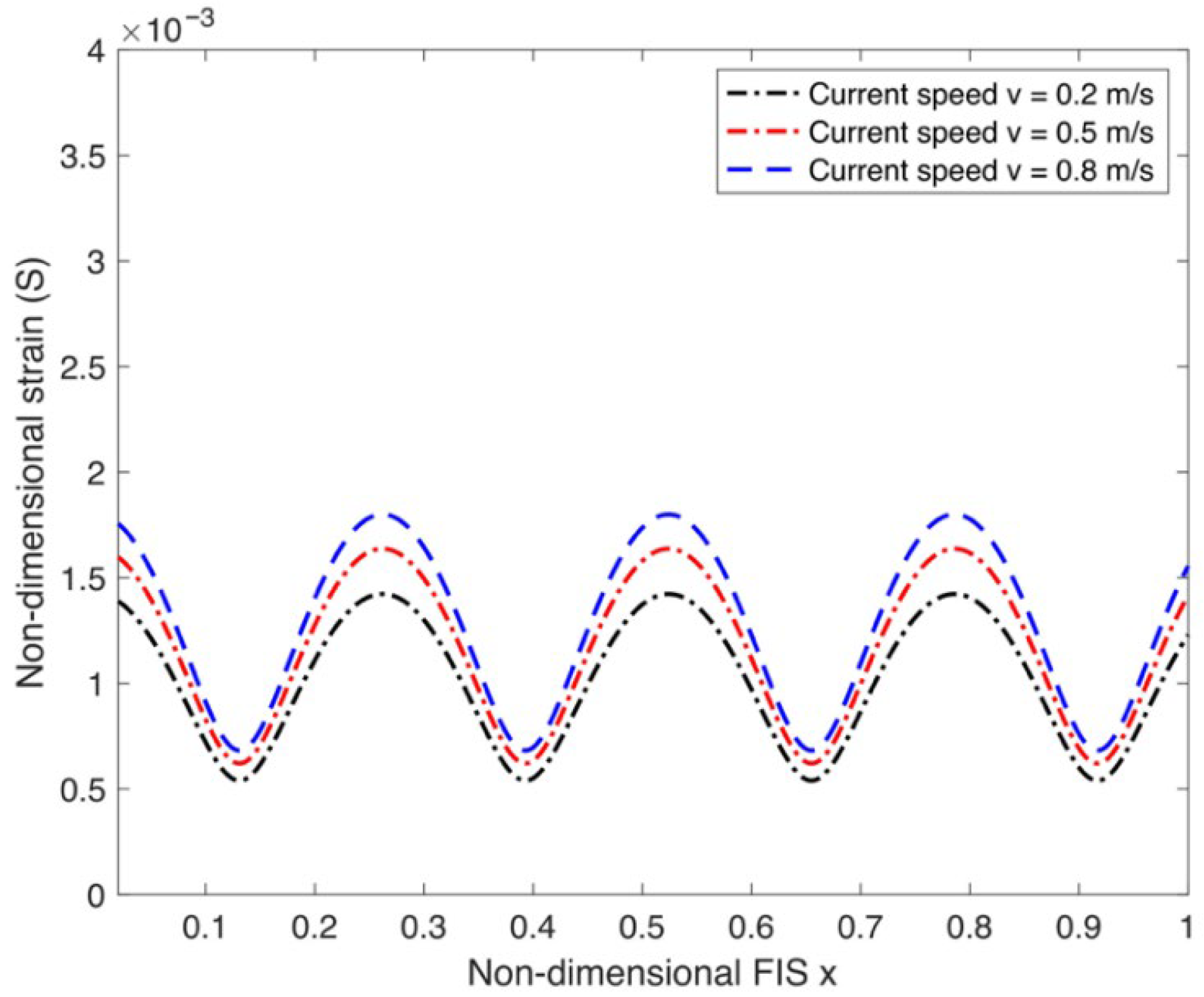
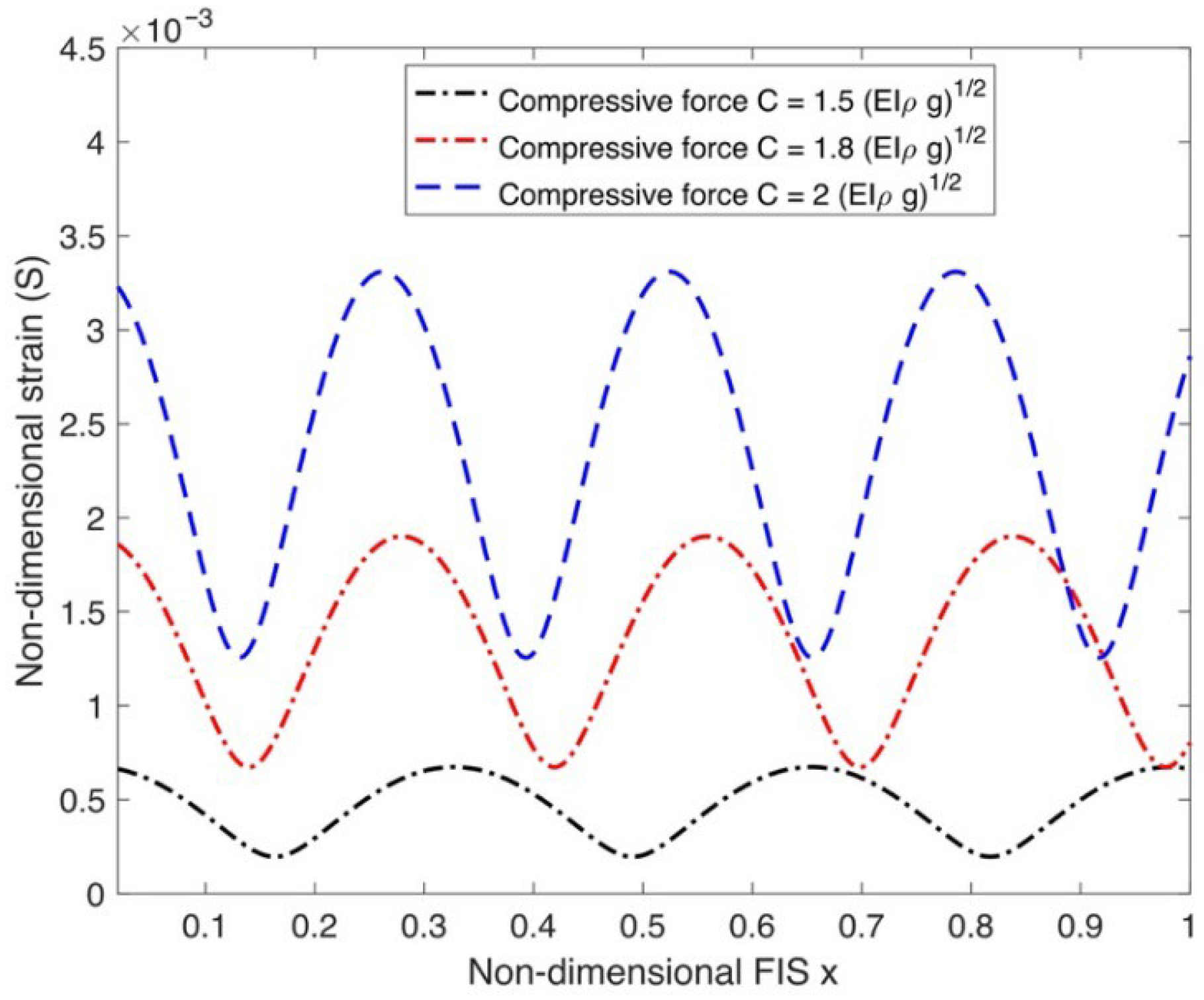
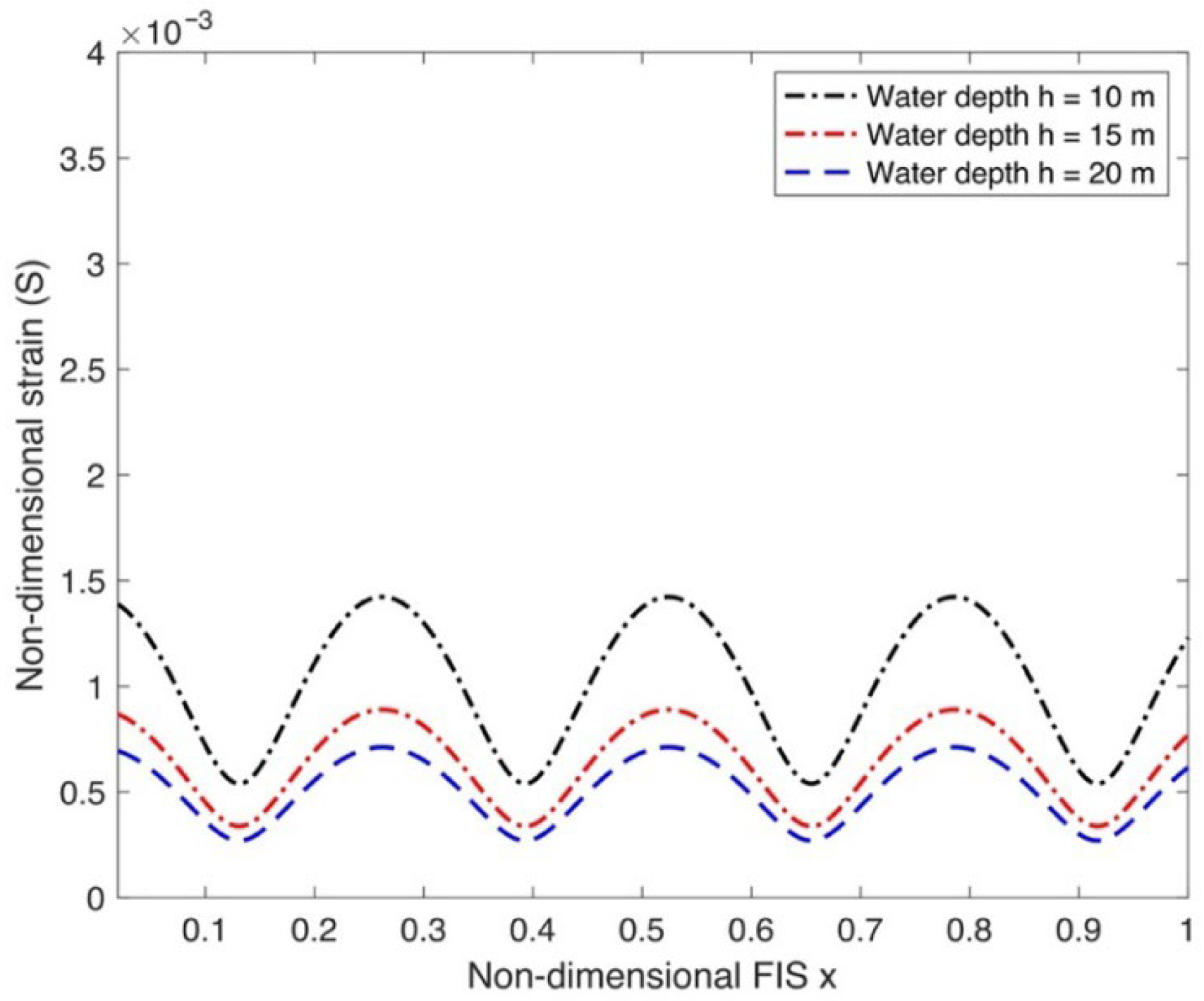
4.2. Impact of Current Speed and FIS Key Elements on Strain Along FIS
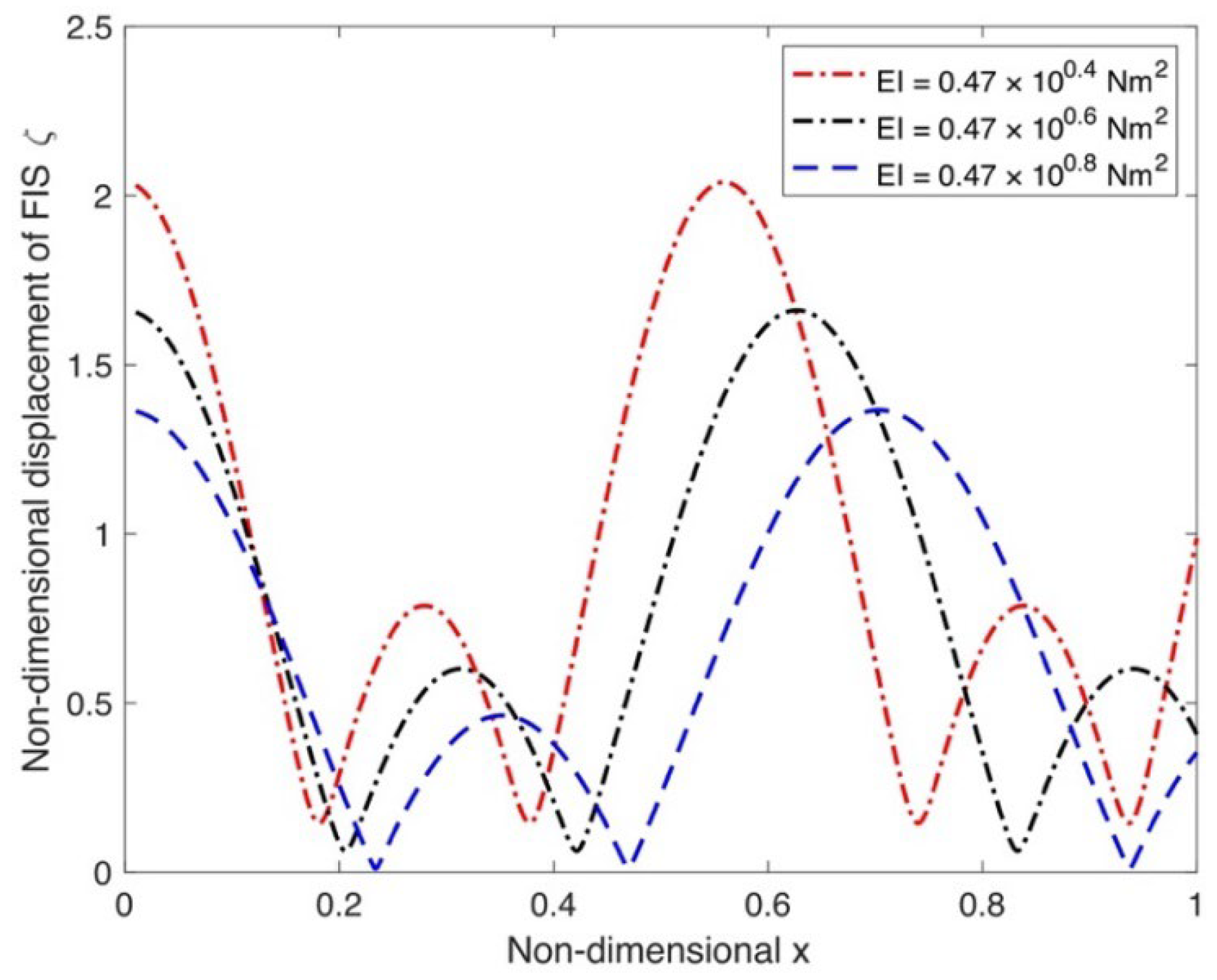
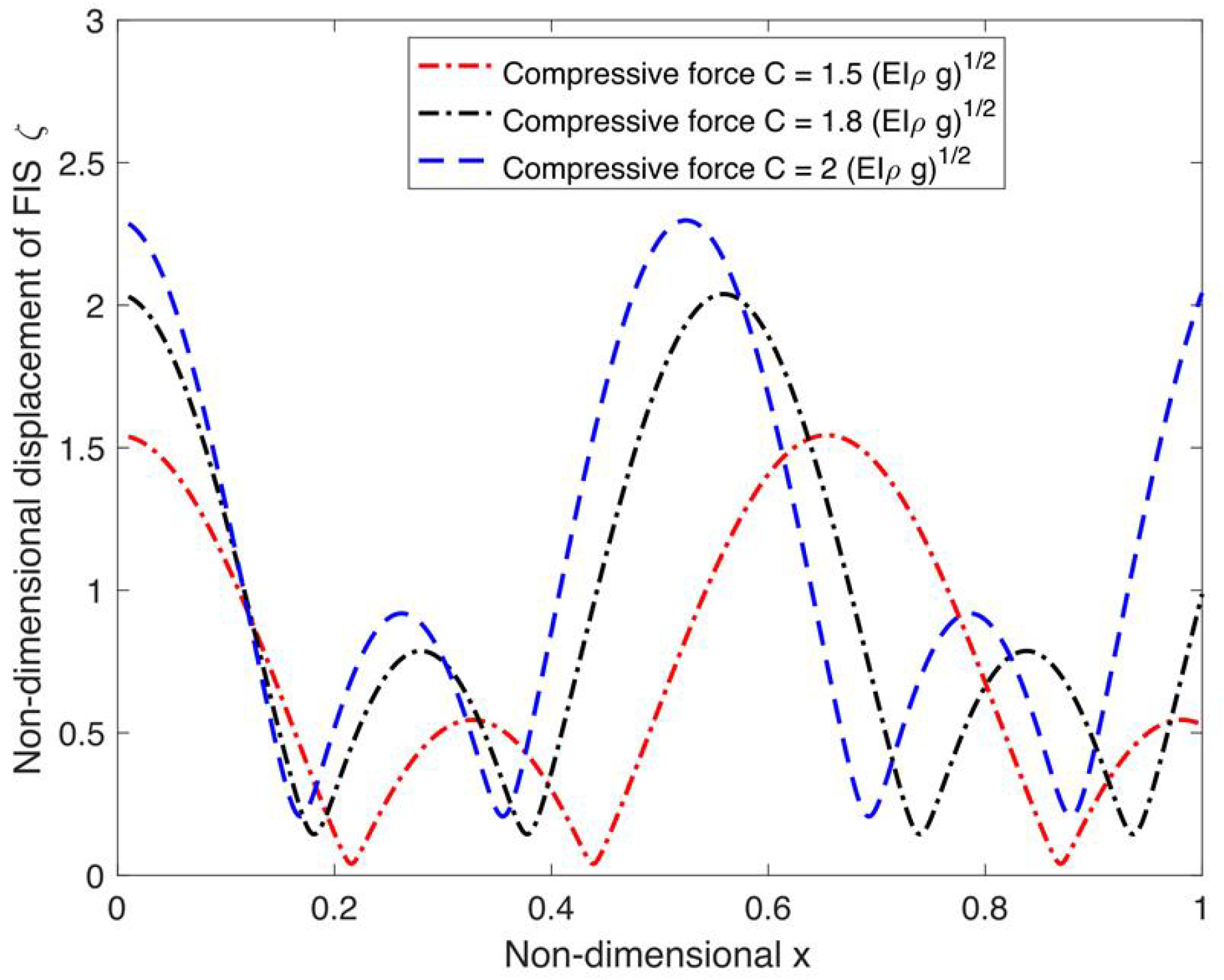
4.3. Effect of Physical and FIS Parameters on Displacement Along FIS
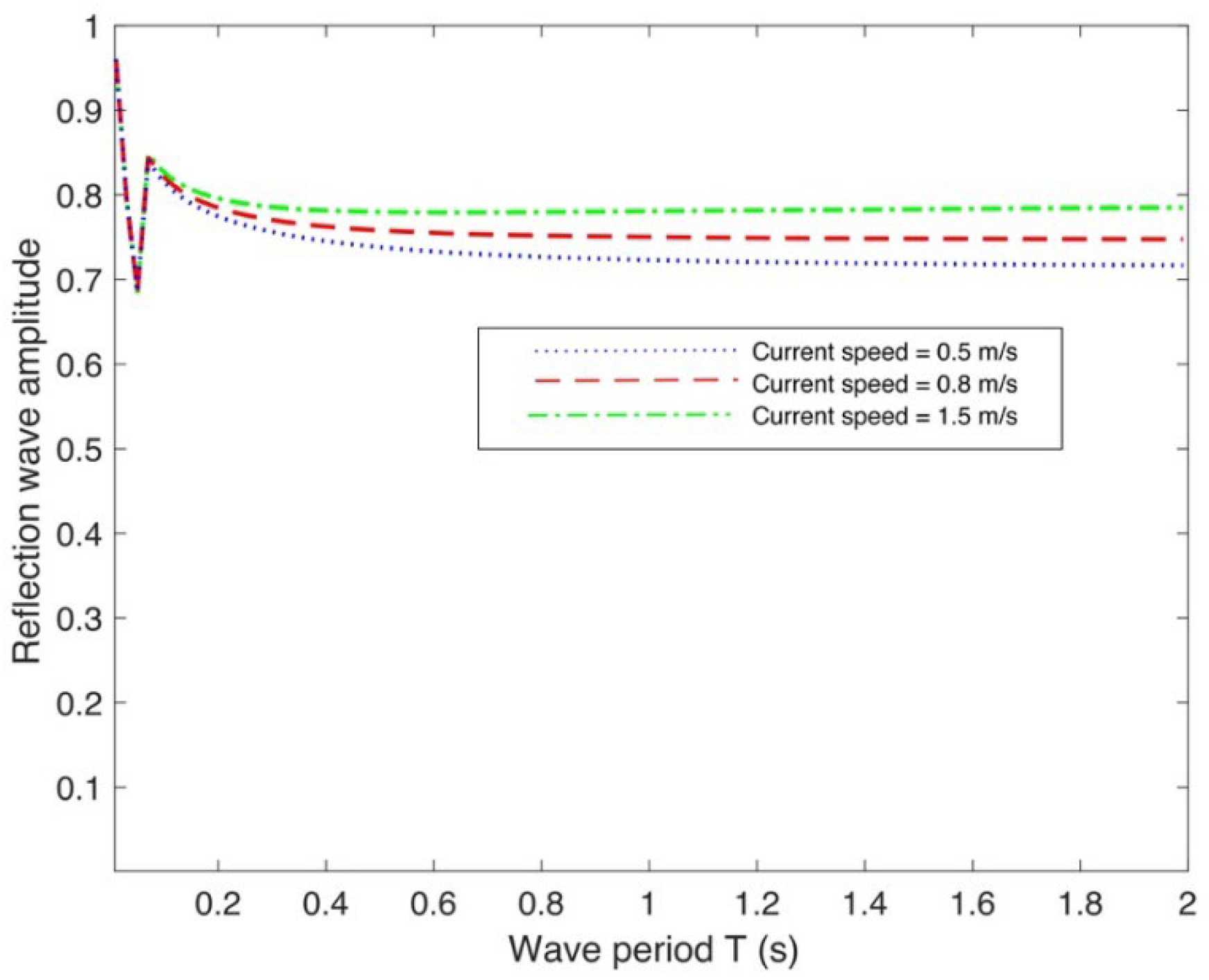
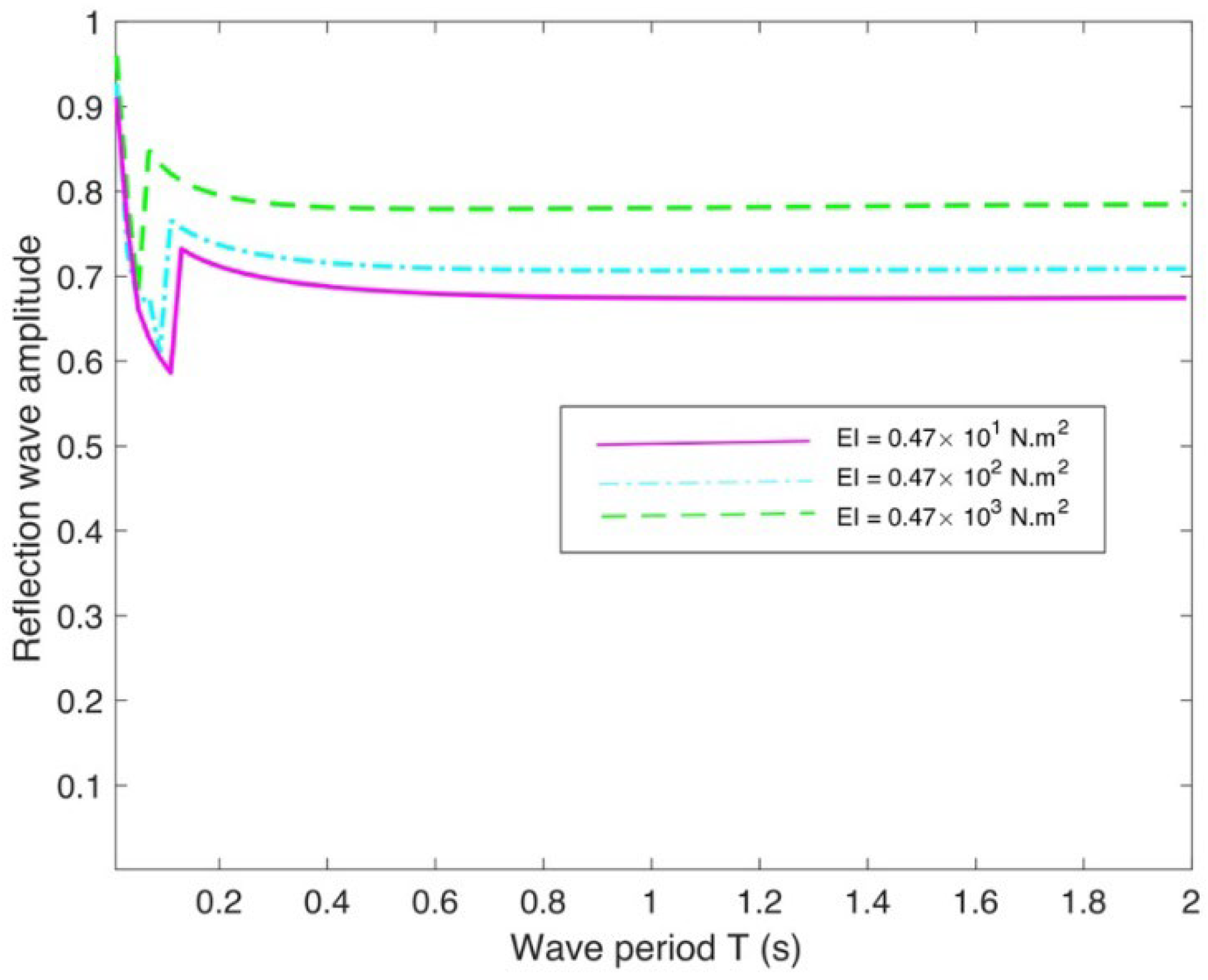
4.4. Effect of Current Speed and FIS Parameters on Reflection Wave Amplitude
5. Conclusions
- The consideration of FC and compressive force for the establishment of the mathematical model and its theoretical solution, along with the orthogonal mode-coupling relation, is an original contribution of this work. The current strain finding aligns with the result achieved in the literature.
- Analysis of the FIS’s strain pattern shows a consistent upward trend linked to increasing compressive force and current speed. In stark contrast, the influence of the FIS’s flexural rigidity and water depths exhibits an inverse relationship, causing strain to lessen as these values rise. Additionally, the observed displacement characteristics of the FIS, which are shaped by variables such as current velocity, applied compressive force, the material’s elastic modulus, and the prevailing water depth, demonstrate consistent alignment with the outcomes of strain analysis.
- Regarding numerical results, the current study examines how FIS affects the reflection wave amplitude and flexural gravity waves across various water depths with different structural and environmental parameters. In a semi-infinite FIS with a vertical rigid wall, the amplitude of the reflected wave was found to be larger for higher current speed, structural rigidity, and compressive force in larger wave periods. The present findings indicate that the reflection wave amplitude is contained within a physical limit of 1.0, consistent with expectations.
- The analysis of the horizontal force on the wall reveals that the higher values of current speed in deeper water increase the force on the vertical rigid wall.
- For marine engineering practical interests in polar regions, FISs often encounter vertical boundaries, ranging from natural continental shelves to man-made structures like drilling platforms and wharves, which effectively behave as a vertical wall. Consequently, studying the reflection of ice-coupled waves by a vertical impermeable wall becomes scientifically significant. Moreover, VLFSs are often deployed near shorelines or integrated with vertical breakwaters, directly exemplifying the interaction between flexural–gravity waves and vertical walls.
- The established framework exhibits specific limitations: the applicable ice sheet covered BC needs to be linear and of fifth-order, and the governing equation should be in 1D, 2D, 3D, and Helmholtz equation. Thus, the existing methodology is suitable for elastic structures that have straightforward shapes and are limited to linear analysis.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature and Abbreviations
| Following current | |
| Compression of ice sheet | |
| Flexural rigidity | |
| Roots of the dispersion relation | |
| Water depth | |
| Ice sheet deformation | |
| Angular frequency | |
| Acceleration due to gravity | |
| Water density | |
| Laplacian operator | |
| Total velocity potential with time-dependent | |
| Spatial velocity potential | |
| Wave angle | |
| Thickness of ice sheet | |
| Incident wave amplitude | |
| Reflected wave amplitude | |
| Hydrodynamic pressure | |
| Density of ice sheet | |
| FIS | Floating ice sheet |
| VLFS | Very large floating structure |
| FC | Following current |
| BC | Boundary condition |
| CV | Current velocity |
| MIZ | Marginal ice zone |
| BIEM | Boundary integral equation method |
| FEM | Finite element method |
| DEM | Discrete element method |
| CFD | Computational fluid dynamics |
| BVP | Boundary Value Problem |
| WW3 | WAVEWATCH III® |
| gPC | Generalized polynomial chaos |
| FWD | Finite water depth |
| vs. | Versus |
References
- Herman, A. From apparent attenuation towards physics-based source terms—A perspective on spectral wave modeling in ice-covered seas. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1413116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, K.; Lai, Y.; Gao, D.; Kang, W.H.; Wang, B.; Wang, B. Ice-Induced Vibration Analysis of Offshore Platform Structures Based on Cohesive Element Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Amouzadrad, P.; Guedes Soares, C. Recent Developments in the Nonlinear Hydroelastic Modeling of Sea Ice Interaction with Marine Structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikse, H. Ice engineering challenges for offshore wind development in the Baltic Sea. In Proceedings of the 27th IAHR International Symposium on Ice, Gdańsk, Poland, 9–13 June 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, J.; Guedes Soares, C. Flexural gravity wave over a floating ice sheet near a vertical wall. J. Eng. Math. 2012, 75, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.F.; Wu, G.X.; Shi, Y.Y. Interaction of uniform current with a circular cylinder submerged below an ice sheet. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 86, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranta, J.; Polojarvi, A.; Tuhkuri, J. Limit mechanisms for ice loads on inclined structures: Buckling. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2018, 147, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.; Xiong, H.; Han, D.; Zeng, L.; Sun, L.; Tan, H. A Review of Ice Deformation and Breaking Under Flexural-Gravity Waves Induced by Moving Loads. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2025, 24, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, T.C.; Willems, T.; Hendrikse, H. Dynamic ice loads for offshore wind support structure design. Mar. Struct. 2023, 87, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Hu, Z.; Luo, Y. An elastic-plastic iceberg material model considering temperature gradient effects and its application to numerical study. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2016, 15, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuprik, V.G.; Zanegin, V.G.; Kim, L.V. Mathematical Modelling of Ice-Structure Interaction. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 272, 022063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, B.Y.; Han, D.F.; Di, S.C.; Xue, Y.Z. On the Development of Ice-Water-Structure Interaction. J. Hydrodyn. 2020, 32, 629–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Li, Y. A Multi-Yield-Surface Plasticity State-Based Peridynamics Model and Its Applications to Simulations of Ice-Structure Interactions. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2023, 22, 395–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Bock und Polach, F.; Klein, M.; Hartmann, M. A New Model Ice for Wave-Ice Interaction. Water 2021, 13, 3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiew, L.J.; Parra, S.M.; Wang, D.; Sree, D.K.K.; Babanin, A.V.; Law, A.W.K. Wave attenuation and dispersion due to floating ice covers. Appl. Ocean Res. 2019, 87, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Shi, Y.; Li, Z. Two-Dimensional Wave Interaction with a Rigid Body Floating near the Marginal Ice Zone. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzadrad, P.; Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Numerical Analysis of the effect of current and wind on the dynamics of large floating flexible platform. In Advances in Maritime Technology and Engineering; Soares, C.G., Santos, T.A., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2024; pp. 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Amouzadrad, P.; Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Hydroelastic Response to the Effect of Current Loads on Floating Flexible Offshore Platform. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzadrad, P.; Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Hydroelastic Response of a Moored Interconnected Floating Platform under Current Loading. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkin, A.; Khabakhpasheva, T.I. Consistent Models of Flexural-Gravity Waves in Floating Ice. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, M.; Owen, C.C.; Hendrikse, H. Experimental study on ice-structure interaction phenomena of vertically sided structures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2022, 201, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrikse, H.; Nord, T.S. Dynamic response of an offshore structure interacting with an ice floe failing in crushing. Mar. Struct. 2019, 65, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Mills, J.; Gash, R.; Pearson, W. A literature survey of broken ice-structure interaction modelling methods for ships and offshore platforms. Ocean Eng. 2021, 221, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, J.K.; Roberts, A.; Geiger, C.A.; Menge, J.R. Spatial and temporal characterization of sea-ice deformation. Ann. Glaciol. 2011, 52, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhkuri, J.; Polojärvi, A. A review of discrete element simulation of ice–structure interaction. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2018, 376, 20170335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeed, T.; Colbourne, B.; Quinton, B.; Molyneux, D.; Peng, H.; Spencer, D. A review of iceberg and bergy bit hydrodynamic interaction with offshore structures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 135, 34–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Ren, K.; Li, M.; Tukovi’c, Ž.; Cardiff, P.; Thomas, G. Fluid-structure interaction of a large ice sheet in waves. Ocean Eng. 2019, 182, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, M.C.N.; Onorato, M.; De Vita, F.; Clauss, G.; Ehlers, S.; von Bock und Polach, F.; Schmitz, L.; Hoffmann, N.; Klein, M. Hydroelastic potential flow solver suited for nonlinear wave dynamics in ice-covered waters. Ocean Eng. 2022, 259, 111756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, S.; Huang, L.; Azhari, F.; Babanin, A.V. Viscoelastic Wave–Ice Interactions: A Computational Fluid–Solid Dynamic Approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.Z.; Zeng, L.D.; Ni, B.Y.; Korobkin, A.A.; Khabakhpasheva, T.I. Hydroelastic response of an ice sheet with a lead to a moving load. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 037109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Thomas, G. Simulation of Wave Interaction with a Circular Ice Floe. J. Offshore Mech. Arct. Eng. 2019, 141, 041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staroszczyk, R. On maximum forces exerted by floating ice on a structure due to constrained thermal expansion of ice. Mar. Struct. 2021, 75, 102884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, L. Study on the mechanism of water entry under the effect of floating ice based on a penalty function-based fluid–structure interaction method. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 123334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabvarodom, C.; Leira, B.J.; Høyland, K.V.; Næss, A.; Samardžija, I.; Chai, W.; Komonjinda, S.; Chaichana, C.; Xu, S. On Statistical Features of Ice Loads on Fixed and Floating Offshore Structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Gong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Lou, M. Investigating Load Calculation for Broken Ice and Cylindrical Structures Using the Discrete Element Method. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Pan, Z.; Wu, B. Three-dimensional Green-function method to predict the water wave radiation of a submerged body with ice cover. Appl. Ocean Res. 2020, 101, 102297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Kohout, A.L.; Doble, M.J.; Wadhams, P.; Guan, C.; Shen, H.H. Rollover of apparent wave attenuation in ice covered seas. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2017, 122, 8557–8566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z. Numerical Simulation of Ice and Structure Interaction Using Common-Node DEM in LS DYNA. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wu, K.; Peng, X.; Jia, X.; Wang, G. Study on the Factors Influencing the Amplitude of Local Ice Pressure on Vertical Structures Based on Model Tests. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, V.A. Synergies between VLFS hydroelasticity and sea-ice research. Int. J. Offshore Polar Eng. 2008, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Mosig, J.E.M.; Montiel, F.; Squire, V.A. Water wave scattering from a mass loading ice floe of random length using generalised polynomial chaos. Wave Motion 2017, 70, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timco, G.W.; Weeks, W.F. A review of the engineering properties of sea ice. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2010, 60, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennetts, L.G.; Peter, M.A.; Squire, V.A.; Meylan, M.H. A three-dimensional model of wave attenuation in the marginal ice zone. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, C12043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocklehurst, P.; Korobkin, A.A.; Părău, E.I. Interaction of hydro-elastic waves with a vertical wall. J. Eng. Math. 2010, 68, 215–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, P.; Mandal, B.N. Wave scattering by a thin vertical barrier submerged beneath an ice-cover in deep water. Appl. Ocean Res. 2010, 32, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkin, A.; Khabakhpasheva, T.I.; Papin, A.A. Waves propagating along a channel with ice cover. Eur. J. Mech.—B Fluids 2014, 47, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Lubbad, R.; Høyland, K.; Løset, S. Physical model and theoretical model study of level ice and wide sloping structure interactions. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 101, 40–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, H.H.; Cheng, S. Modeling ocean wave propagation under sea ice covers. Acta Mech. Sin. 2015, 31, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegarty, G.M.; Squire, V.A. A boundary-integral method for the interaction of large-amplitude ocean waves with a compliant floating raft such as a sea-ice floe. J. Eng. Math. 2008, 62, 355–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, X. Theoretical model for predicting the break-up of ice covers due to wave-ice interaction. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 112, 102614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batyaev, E.; Khabakhpasheva, T.I. Flexural-Gravity Waves in a Channel with a Compressed Ice Cover. Water 2024, 6, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, Z.Q. Steady-state response of an infinite, free floating ice sheet to a moving load at constant velocity. Ocean Eng. 2024, 314, 119627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, B.; Zou, Y.; Li, Z.; Shi, Y. The effect of large ice sheet on the hydrodynamic force of side-by-side barges relevant to offloading. Ocean Eng. 2025, 317, 120009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiao, R.; Xue, Z.; Yu, F. Effects of cracked semi-infinite ice sheets on the wave excited motion of a body floating on water. Ocean Eng. 2025, 325, 120769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Ye, L.; Wang, C.; Yu, F. Wave attenuation by three-dimensional circular floating sea ice: Regular and irregular waves. Ocean Eng. 2024, 305, 117918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Părău, E.I.; Vanden-Broeck, J.M. Three-dimensional waves beneath an ice sheet due to a steadily moving pressure. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2011, 369, 2973–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostikov, V.K.; Hayatdavoodi, M.; Ertekin, R.C. Drift of elastic floating ice sheets by waves and current, part I: Single sheet. Proc. R. Soc. A 2021, 477, 20210449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Effect of mooring lines on the hydroelastic response of a floating flexible plate using the BIEM approach. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Effect of submerged horizontal flexible membrane on a moored floating elastic plate. In Maritime Technology and Engineering 3; Soares, G., Santos, Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: London, UK, 2016; pp. 1181–1188. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Hydroelastic behaviour of a submerged horizontal flexible porous structure in three-dimensions. J. Fluids Struct. 2021, 104, 103319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. 3D hydroelastic modelling of fluid-structure interactions of porous flexible structures. J. Fluids Struct. 2022, 112, 103588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Interaction of surface gravity wave motion with elastic bottom in three-dimensions. Appl. Ocean Res. 2016, 57, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korobkin, A.A.; Stukolov, S.V.; Sturova, I.V. Motion of a vertical wall fixed on springs under the action of surface waves. J. Appl. Mech. Tech. Phys. 2009, 50, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dafydd, L.; Porter, R. Attenuation of long waves through regions of irregular floating ice and bathymetry. J. Fluid Mech. 2024, 996, A43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyenne, P.; Părău, E.I. Numerical study of solitary wave attenuation in a fragmented ice sheet. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 034002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.; Porter, R. Approximations to wave scattering by an ice sheet of variable thickness over undulating bed topography. J. Fluid Mech. 2004, 509, 145–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shen, H.H. Gravity waves propagating into an ice-covered ocean: A viscoelastic model. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2010, 115, C06024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouzadrad, P.; Mohapatra, S.C.; Guedes Soares, C. Review on Sensitivity and Uncertainty Analysis of Hydrodynamic and Hydroelastic Responses of Floating Offshore Structures. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Squire, V.A. On the oblique reflection and transmission of ocean waves at shore fast sea ice. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A 1994, 347, 185–218. [Google Scholar]
- Schulkes, R.M.S.M.; Hosking, R.J.; Sneyd, A.D. Waves due to a steadily moving source on a floating ice plate. Part-2. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 180, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukatov, A.E.; Zavyalov, D.D. Impingement of surface waves on the edge of compressed ice. Fluid Dyn. 1995, 30, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, V.A.; Hosking, R.J.; Kerr, A.D.; Laghorne, P.J. Moving Loads on Ice Plates; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Mohapatra, S.C.; Ghoshal, R.; Sahoo, T. Effect of compression on wave scattering by a floating elastic plate. J. Fluids Struct. 2013, 36, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Model Key Elements | Values | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness (d) | 0.14 | [m] |
| Flexural rigidity (EI) | [Nm2] | |
| Current speed (v) | 0.5 | [m/s] |
| Water depth (h) | 10 | [m] |
| Water density () | 1025 | [kgm−3] |
| Gravitational constant (g) | 9.8 | [m/s] |
| N | R (m) | R (m) |
|---|---|---|
| 6 | 0.8350 | 0.8524 |
| 9 | 0.8327 | 0.8508 |
| 13 | 0.7849 | 0.8497 |
| 15 | 0.7774 | 0.8478 |
| 17 | 0.7758 | 0.8481 |
| 19 | 0.7755 | 0.8483 |
| 20 | 0.7752 | 0.8485 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohapatra, S.C.; Amouzadrad, P.; Guedes Soares, C. Effect of Following Current on the Hydroelastic Behavior of a Floating Ice Sheet near an Impermeable Wall. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122386
Mohapatra SC, Amouzadrad P, Guedes Soares C. Effect of Following Current on the Hydroelastic Behavior of a Floating Ice Sheet near an Impermeable Wall. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(12):2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122386
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohapatra, Sarat Chandra, Pouria Amouzadrad, and C. Guedes Soares. 2025. "Effect of Following Current on the Hydroelastic Behavior of a Floating Ice Sheet near an Impermeable Wall" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 12: 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122386
APA StyleMohapatra, S. C., Amouzadrad, P., & Guedes Soares, C. (2025). Effect of Following Current on the Hydroelastic Behavior of a Floating Ice Sheet near an Impermeable Wall. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(12), 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122386








