Tropical Cyclone-Induced Temperature Response in China’s Coastal Seas: Characteristics and Comparison with the Open Ocean
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TC Best-Track Data and Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. SST Observation
2.2.2. Reanalysis Dataset
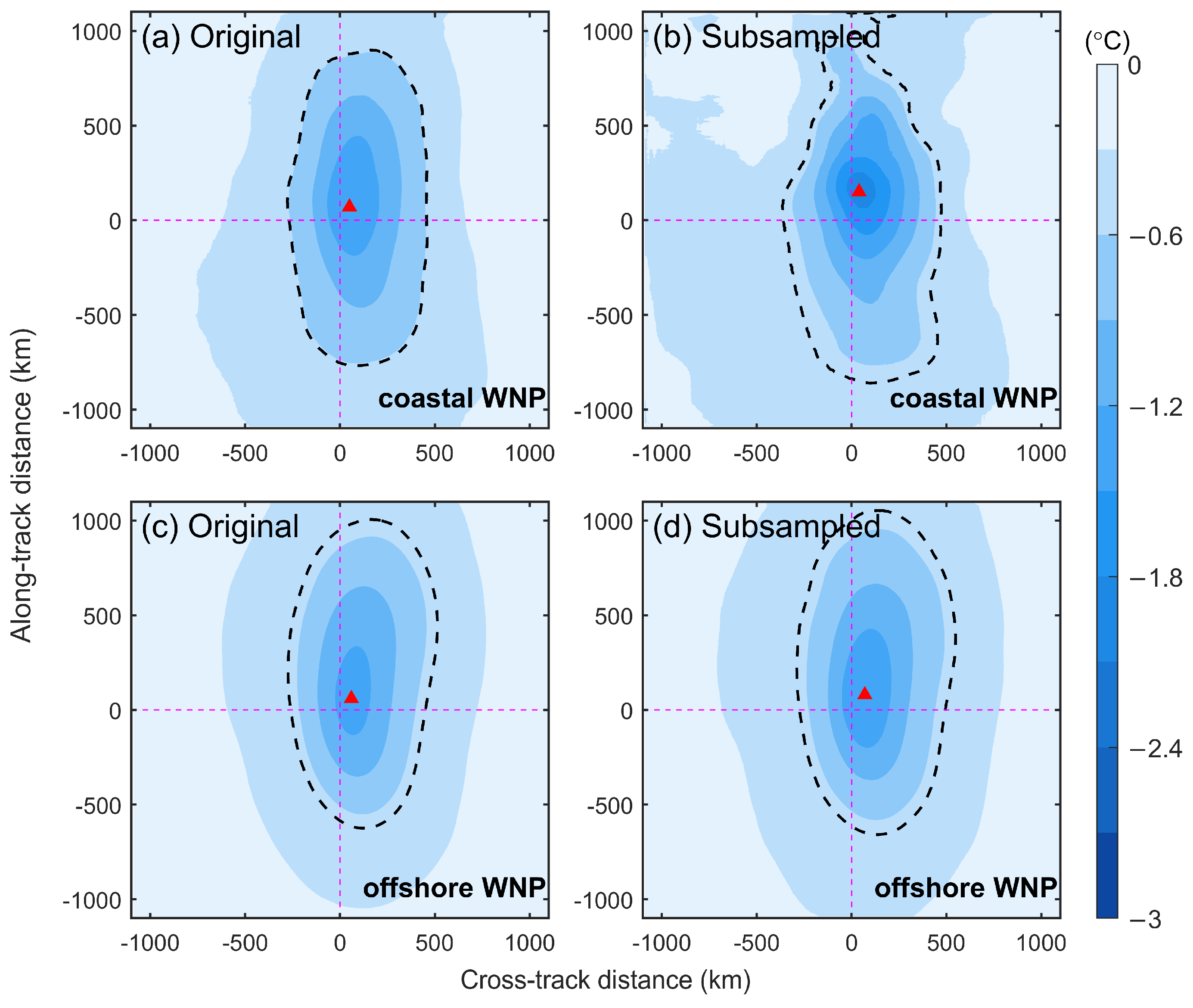
2.3. Subsampling Technique
2.4. Bootstrap Method
3. Results
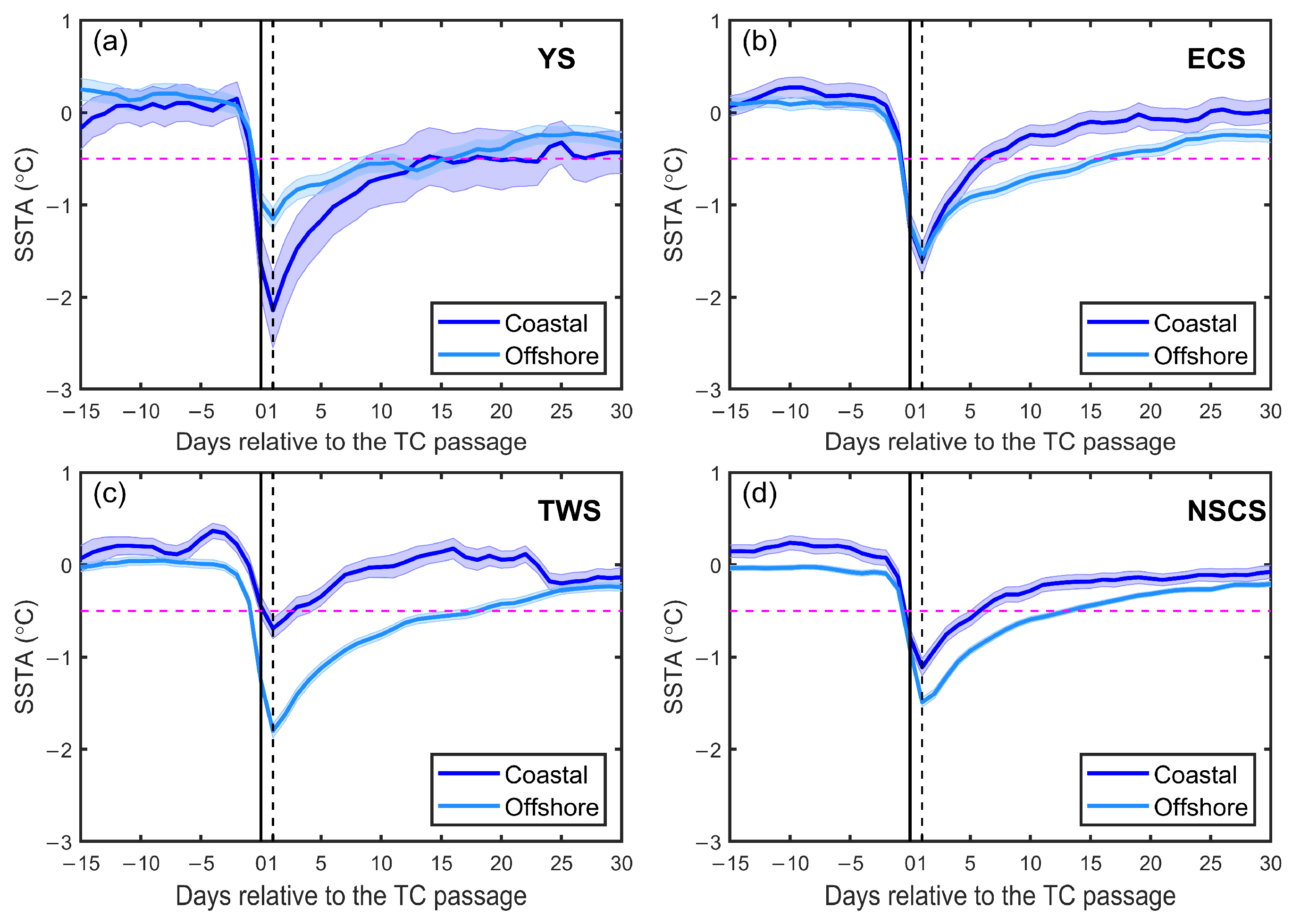
3.1. Characteristics of TC-Induced SST Cooling
3.2. Comparison of TC-Induced SST Cooling
3.2.1. Correlation Patterns of SST Cooling
3.2.2. Comparison of Different Driving Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Emanuel, K.A. Increasing destructiveness of tropical cyclones over the past 30 years. Nature 2005, 436, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K.A. Tropical cyclones. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2003, 31, 75–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.D.; Li, S.Q.; Hou, Y.J.; Hu, P.; Liu, Z.; Feng, J.Q. Increasing threat of landfalling typhoons in the western North Pacific between 1974 and 2013. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2018, 68, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, J.; DeMaria, M.; Knaff, J.A. A revised tropical cyclone rapid intensification index for the Atlantic and eastern North Pacific basins. Wea. Forecast. 2010, 25, 220–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, N.; Foltz, G.R.; Balaguru, K.; Fernald, E. Stronger Tropical Cyclone–Induced Ocean Cooling in Near-Coastal Regions Compared to the Open Ocean. J. Climate 2023, 36, 6447–6463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cione, J.J.; Uhlhorn, E.W. Sea surface temperature variability in hurricanes: Implications with respect to intensity change. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2003, 131, 1783–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, E.B.; Balaguru, K.; Leung, L.R.; Hagos, S.M.; Hetland, R.D. Observed increase in tropical cyclone-induced sea surface cooling near the U.S. Southeast Coast. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F. Upper ocean response to a hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1981, 11, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, L.R. Tropical cyclone intensity and sea surface temperature. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 3122–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, E.A.; Sanford, T.B.; Niiler, P.P.; Terrill, E.J. Cold wake of hurricane Frances. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L15609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, E.M.; Lengaigne, M.; Madec, G.; Vialard, J.; Masson, S.; Jourdain, N.C.; Menkes, C.E.; Jullien, S. Processes setting the characteristics of sea surface cooling induced by tropical cyclones. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, C02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, D.K.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Ding, T.; Zhou, B. Upper Ocean response to typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2016, 121, 6520–6535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, R.; Chen, D.; Liu, X.; He, H.; Tang, Y.; Ke, D.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.; Xie, J.; et al. Net modulation of upper ocean thermal structure by Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2018, 123, 7154–7171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, T.B.; Black, P.G.; Haustein, J.; Fenney, J.W.; Forristall, G.Z.; Price, J.F. Ocean response to hurricanes. Part I: Observations. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1987, 17, 2065–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, K.A. Contribution of tropical cyclones to meridional heat transport by the oceans. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 14771–14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.S.; Sanford, T.B.; Imberger, J. Heat and turbulent kinetic energy budgets for surface layer cooling induced by the passage of Hurricane Frances (2004). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2009, 114, C12023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F.; Morzel, J.; Niiler, P.P. Warming of SST in the cool wake of a moving hurricane. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2008, 113, C07010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leipper, D.F. Observed Ocean conditions and hurricane Hilda, 1964. J. Atmos. Sci. 1967, 24, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Liu, W.T.; Wu, C.C.; Wong, G.T.F.; Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Liang, W.D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, K.K. New evidence for enhanced ocean primary production triggered by tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.L.; Wu, C.R.; Oey, L.Y. Typhoon Kai-Tak: An ocean’s perfect storm. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2011, 41, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, S.; Miles, T.; Seroka, G.; Xu, Y.; Forney, R.K.; Yu, F.; Roarty, H.; Schofield, O.; Kohut, J. Stratified coastal ocean interactions with tropical cyclones. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, L.R.; Emanuel, K.A. The Ocean’s Effect on the Intensity of Tropical Cyclones: Results from a Simple Coupled Atmosphere–Ocean Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 642–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, M.A.; Ginis, I. Real-case simulations of hurricane-ocean interaction using a high-resolution coupled model: Effects on hurricane intensity. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2000, 128, 917–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, I.D.; Vecchi, G.A. Observational evidence for oceanic controls on hurricane intensity. J. Climate 2011, 24, 1138–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Black, P.G.; Price, J.F.; Yang, C.Y.; Chen, S.S.; Lien, C.C.; Harr, P.; Chi, N.H.; Wu, C.C.; D’Asaro, E.A. An ocean coupling potential intensity index for tropical cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 1878–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Xie, S.; Primeau, F.; McWilliams, J.C.; Pasquero, C. Northwestern Pacific typhoon intensity controlled by changes in ocean temperatures. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.I.; Wu, C.C.; Pun, I.F.; Ko, D.S. Upper-ocean thermal structure and the Western North Pacific category 5 typhoons. Part I: Ocean features and the category 5 typhoons’ intensification. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 3288–3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, I.I.; Pun, I.F.; Wu, C.C. Upper-ocean thermal structure and the Western North Pacific category 5 typhoons. Part II: Dependence on translation speed. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2009, 137, 3744–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Pasquero, C.; Primeau, F. The effect of translation speed upon the intensity of tropical cyclones over the tropical ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L07801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, W.; Pasquero, C. Spatial and temporal characterization of sea surface temperature response to tropical cyclones. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 3745–3765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.D.; Zhao, W.; Huthnance, J.; Tian, J.W.; Wang, J.H. Observed upper ocean response to typhoon Megi (2010) in the Northern South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 3134–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.D.; Jin, F.F.; Tian, J.W.; Lin, I.I.; Pun, I.F.; Zhao, W.; Huthnance, J.; Xu, Z.; Cai, W.J.; Jing, Z.; et al. Ocean internal tides suppress tropical cyclones in the South China Sea. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Guan, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Tian, J. Sudden Track Turning of Typhoon Prapiroon (2012) Enhanced the Upper Ocean Response. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, S.; Lin, I.I.; Mei, W.; Jin, F.F.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Tian, J. Effect of Storm Size on Sea Surface Cooling and Tropical Cyclone Intensification in the Western North Pacific. J. Climate 2023, 36, 7277–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, S.; Lin, I.I.; Zhao, W.; Jin, F.F.; Liu, P.; Tian, J. Storm Size Modulates Tropical Cyclone Intensification through an Oceanic Pathway in Global Oceans. J. Climate 2025, 38, 891–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Guan, S.; Lin, I.I.; Huang, M.; Jin, F.F.; Wang, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Tian, J. Response and feedback of mesoscale eddies to tropical cyclones over the South China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2025, 130, e2024JD041414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.H.; Wu, L.W.; Johnson, N.C.; Ling, Z. Observed three-dimensional structure of ocean cooling induced by Pacific tropical cyclones. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 7632–7638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.D.; Zhao, W.; Sun, L.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Z.; Hong, X.; Zhang, Y.H.; Tian, J.W.; Hou, Y.J. Tropical cyclone-induced sea surface cooling over the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea in the 2019 Pacific typhoon season. J. Marine Syst. 2021, 217, 103509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shay, L.K.; Goni, G.J.; Black, P.G. Effects of a warm oceanic feature on Hurricane Opal. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2000, 128, 1366–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.; Guan, S.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, W.; Tian, J. Enhanced upper ocean response within a warm eddy to Typhoon Nakri (2019) during the sudden-turning stage. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2023, 201, 104112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaguru, K.; Chang, P.; Saravanan, R.; Leung, L.R.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Hsieh, J.S. Ocean barrier layers’ effect on tropical cyclone intensification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14343–14347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, C. The effects of oceanic barrier layer on the upper ocean response to tropical cyclones. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 4829–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramer, L.J.; Zhang, J.A.; Alaka, G.; Hazelton, A.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Coastal downwelling intensifies landfalling hurricanes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL096630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, D.K.; Rao, A.D.; Babu, S.V.; Srinivas, C. Influence of coast line on upper ocean’s response to the tropical cyclone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L17603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seroka, G.; Miles, T.; Xu, Y.; Kohut, J.; Schofield, O.; Glenn, S. Hurricane Irene sensitivity to stratified coastal ocean cooling. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2016, 144, 3507–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Ginis, I. Effects of surface heat flux-induced sea surface temperature changes on tropical cyclone intensity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.S.; Chan, J.C.L. Interdecadal variation of frequencies of tropical cyclones, intense typhoons and their ratio over the western North Pacific. Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 40, 3954–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Liao, H.T.; Lee, M.A.; Chan, J.W.; Shieh, W.J.; Lee, K.T.; Wang, G.H.; Lan, Y.C. Multisatellite observation on upwelling after the passage of typhoon Hai-Tang in the southern East China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L03612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.C.; Lee, M.A.; Chern, C.S. Typhoon-induced ocean responses off the southwest coast of Taiwan. Ocean Dyn. 2014, 64, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.B.; Lü, L.G.; Zhuang, Z.P.; Xiong, X.J.; Wang, G.S.; Guo, Y.L.; Yu, L.; Ma, D.J. Cruise observation of shallow water response to typhoon Damrey 2012 in the Yellow Sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 148, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, K.; Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, W. Revealing the subsurface Yellow Sea cold water mass from satellite data associated with typhoon Muifa. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 7135–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Zhang, H.; Chen, D. Effect of Typhoon Kalmaegi (2014) on northern South China Sea explored using Muti-platform satellite and buoy observations data. Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 180, 102218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Huang, M.; Lin, I.I.; Wu, H.; Lin, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, F.F.; Wang, W.; Hong, X.; et al. Widespread sea surface salinification induced by tropical cyclones over the Changjiang River Plume. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, D.; Noh, S.; Kim, G.U.; Park, S.H.; Jeong, J.Y.; Lee, H.; Noh, J.H.; Jeong, J.; Lee, J.; et al. Sequential evolution of Changjiang Diluted Water and its impact on stratification and phytoplankton blooms in the East China Sea during summer 2020. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2025, 130, e2025JC022655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.B.; Xia, C.; Xiong, X.J.; Feng, Z.T.; Chen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Ma, D.J.; Ju, X.; Zheng, Q.; Yuan, Y. The seafloor heat flux driven by bottom water temperature variation in the Yellow and Bohai Seas. Ocean Model. 2022, 177, 102073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Kruk, M.C.; Levinson, D.H.; Diamond, H.J.; Neumann, C.J. The International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS) unifying tropical cyclone data. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc. 2010, 91, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, K.R.; Diamond, H.J.; Kossin, J.P.; Kruk, M.C.; Schreck, C.J. International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship (IBTrACS) Project, Version 4. [Dataset]. NOAA Natl. Cent. Environ. Inf. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, P.J.; Holland, G.J.; Curry, J.A.; Chang, H.R. Changes in tropical cyclone number, duration, and intensity in a warming environment. Science 2005, 309, 1844–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Looney, L.B.; Foltz, G.R. Drivers of Tropical Cyclone—Induced Ocean Surface Cooling. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2025, 130, e2024JC021610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Fang, G.; Song, Y.T. Introduction to special section: Dynamics and Circulation of the Yellow, East, and South China Seas. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2006, 111, C11S01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlon, C.J.; Minnett, P.J.; Gentemann, C.; Nightingale, T.J.; Barton, I.J.; Ward, B.; Murray, M.J. Toward Improved Validation of Satellite Sea Surface Skin Temperature Measurements for Climate Research. J. Climate 2002, 15, 353–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentz, F.J.; Gentemann, C.; Smith, D.; Chelton, D. Satellite measurements of sea surface temperature through clouds. Science 2000, 288, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meissner, T.; Wentz, F.J. The emissivity of the ocean surface between 6 and 90 GHz over a large range of wind speeds and Earth incidence angles. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 3004–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.; Huang, M.; Cai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, I.I.; Kim, H.-S.; Zhou, L.; Lin, X.; Xu, Z.; Jin, F.-F.; et al. Fast warming trend and weak self-induced cooling of tropical cyclones revealed by drifters. Nat. Geosci. 2025; accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Price, J.F. Metrics of hurricane-ocean interaction: Vertically-integrated or vertically-averaged ocean temperature? Ocean Sci. 2009, 5, 351–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. In Breakthroughs in Statistics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 569–593. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Q.; Zhou, F.; Ma, X.; Xuan, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Ni, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; et al. Response Process of Coastal Hypoxia to a Passing Typhoon in the East China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 892797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, F.; Chen, Z.; Nan, F.; Si, G.; Diao, X.; Ren, Q.; Wang, J. Upper ocean responses to three sequential tropical cyclones in the stratified yellow sea during summer 2020. Ocean Model. 2025, 196, 102548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.F.; Sanford, T.B.; Forristall, G.Z. Forced stage response to a moving hurricane. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1994, 24, 233–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, I.F.; Hsu, H.H.; Moon, I.J.; Lin, I.I.; Jeong, J.Y. Marine heatwave as a supercharger for the strongest typhoon in the East China Sea. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, S.; Marchesiello, P.; Menkes, C.E.; Lefèvre, J.; Jourdain, N.C.; Samson, G.; Lengaigne, M. Ocean feedback to tropical cyclones: Climatology and processes. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 2831–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Hu, J.; Liu, Z. On summer stratification and tidal mixing in the Taiwan Strait. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 7, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Zhou, M.; Waniek, J.J.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Z. Seasonal Variation of the Surface Kuroshio Intrusion into the South China Sea Evidenced by Satellite Geostrophic Streamlines. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2021, 51, 2705–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Chai, F.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, J. An overview of physical and biogeochemical processes and ecosystem dynamics in the Taiwan Strait. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C. Responses of Summer Upwelling to Recent Climate Changes in the Taiwan Strait. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dare, R.A.; McBride, J.L. Sea surface temperature response to tropical cyclones. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2011, 139, 3798–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Fei, J.; Huang, X.; Cheng, X.; Ding, J.; He, Y. A Numerical Study on the Combined Effect of Midlatitude and Low-Latitude Systems on the Abrupt Track Deflection of Typhoon Megi (2010). Mon. Wea. Rev. 2014, 142, 2483–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, G.; Long, S.M.; Li, Y.; Schuckmann, K.; Trenberth, K.E.; Mann, M.E.; Abraham, J.; Du, Y.; Cheng, X.; et al. Ocean stratification in a warming climate. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 637–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


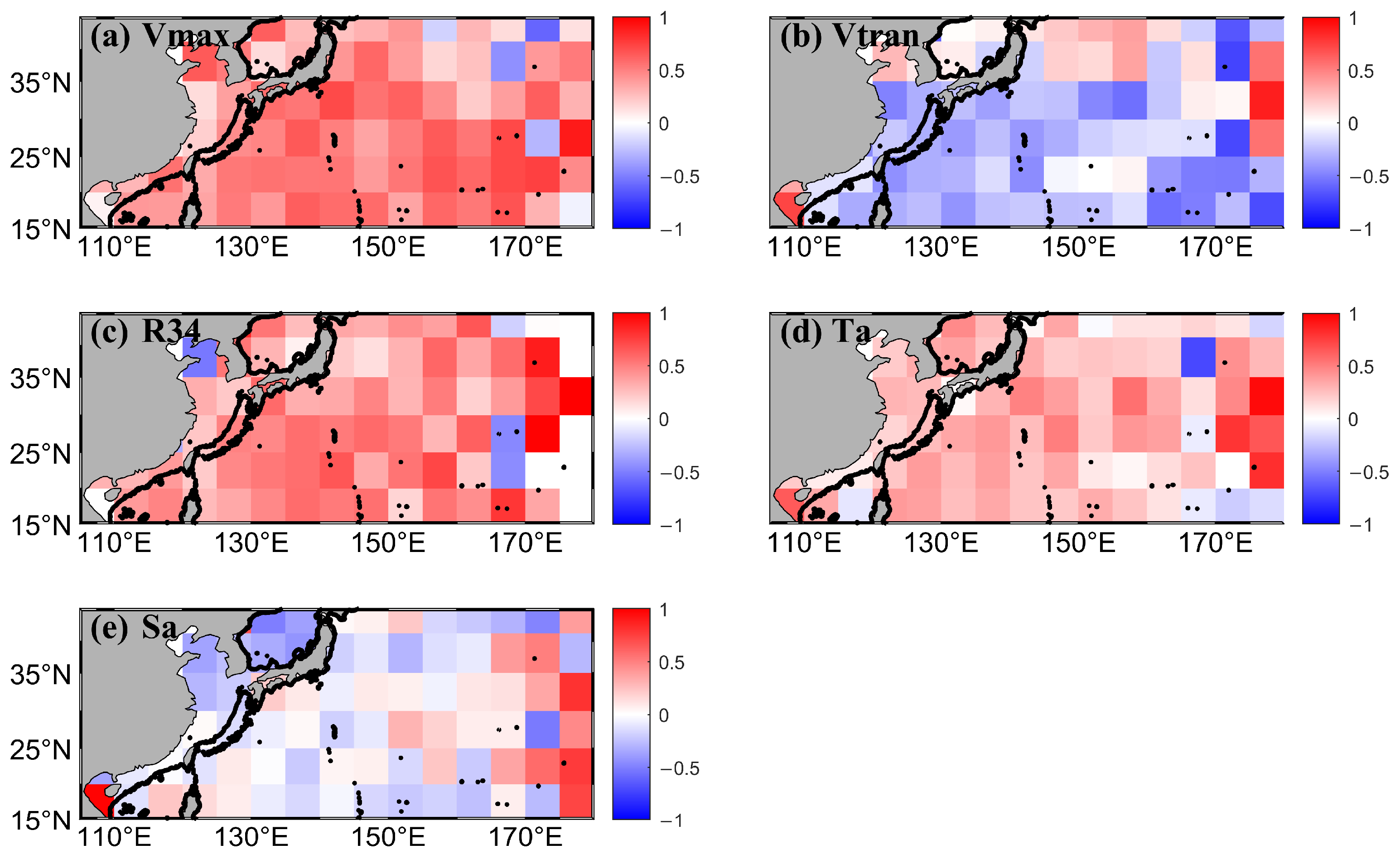
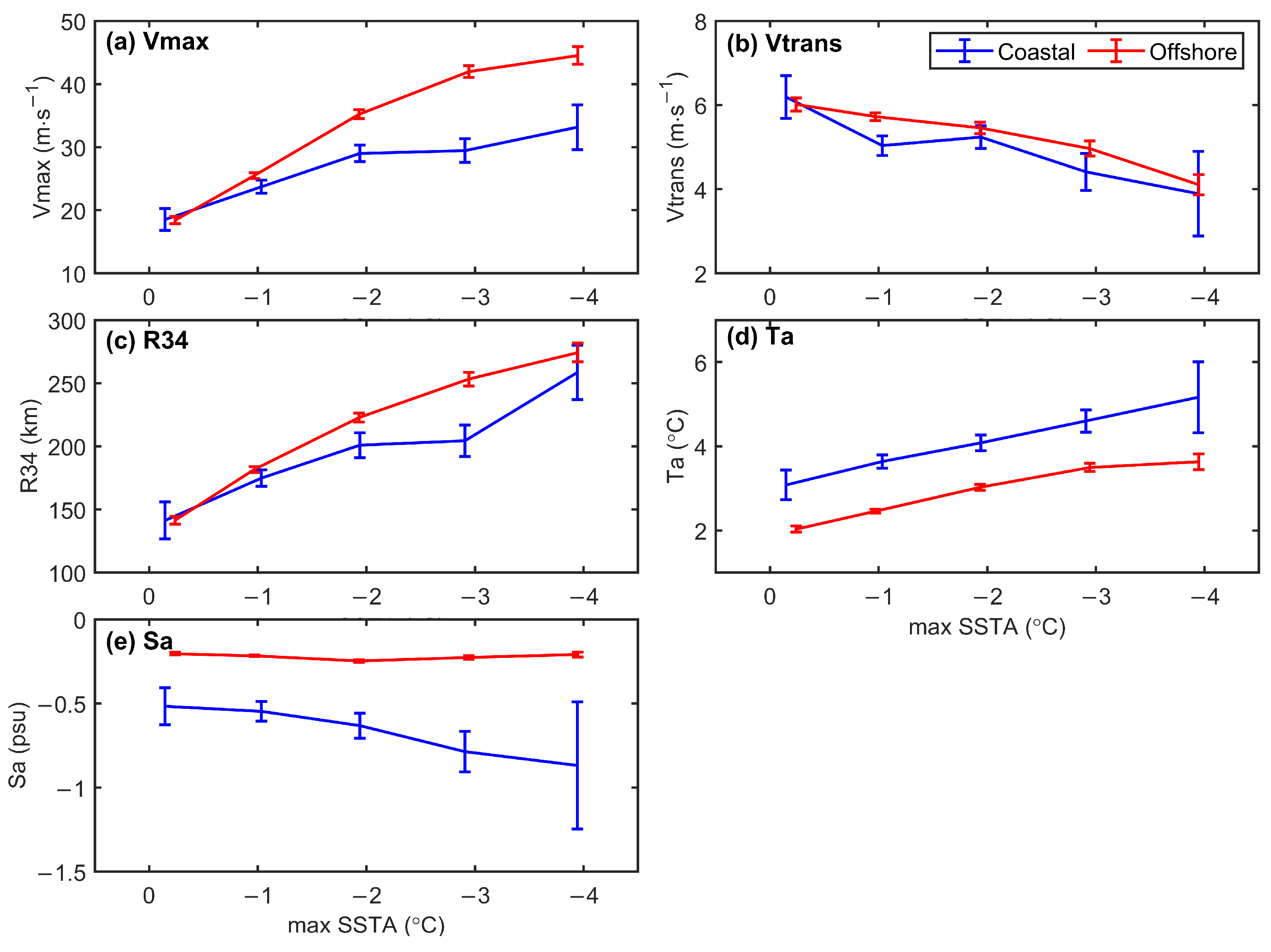
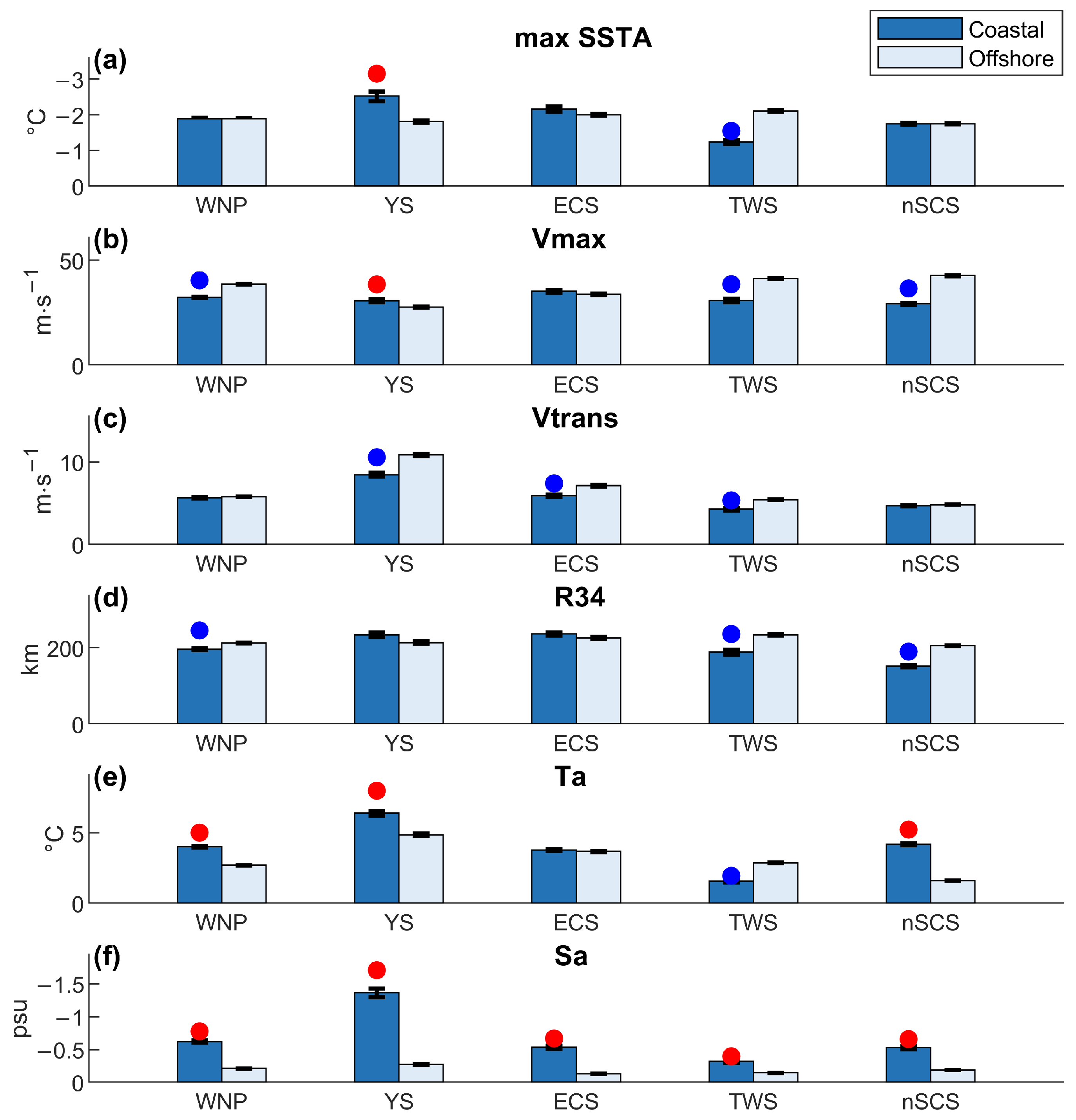
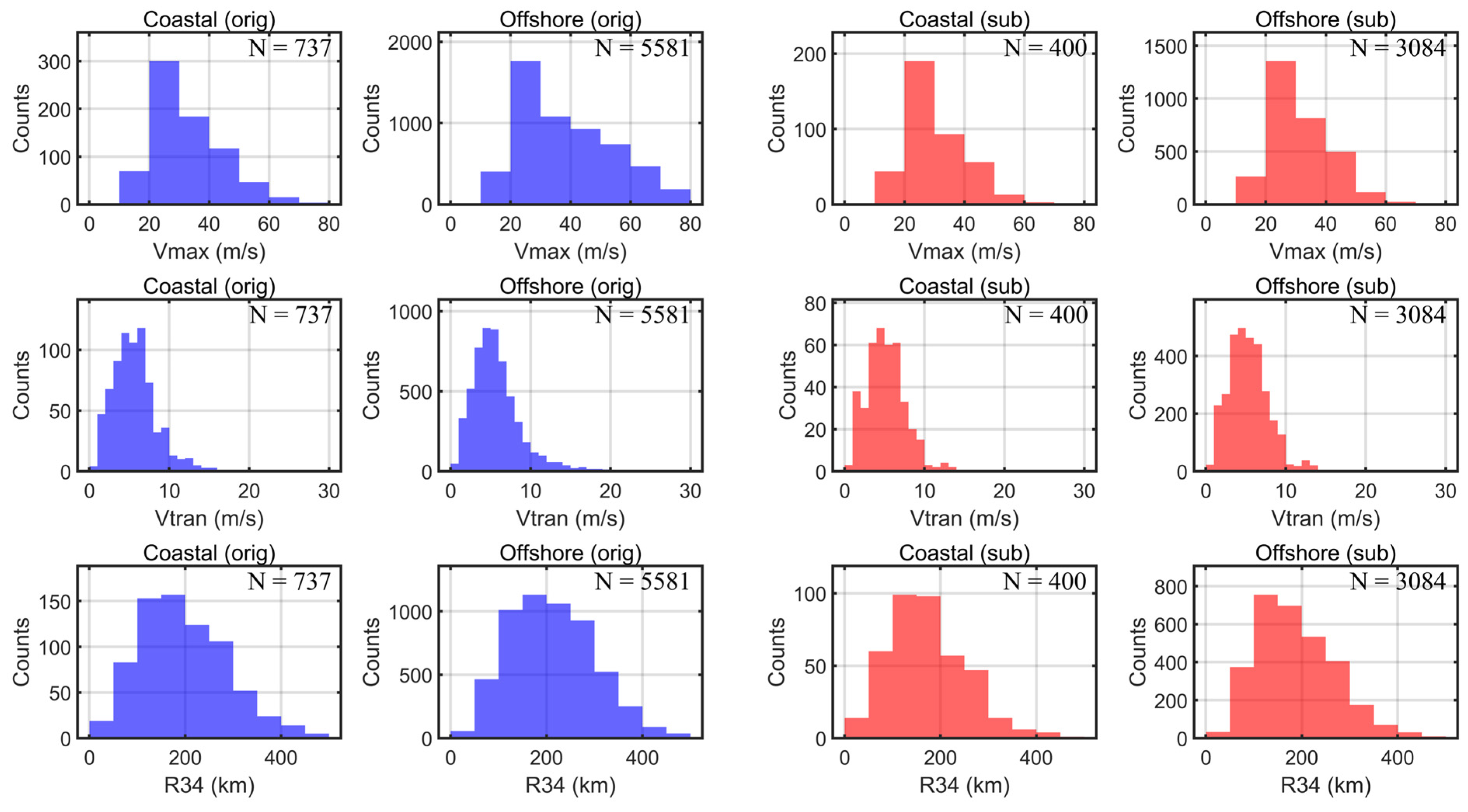
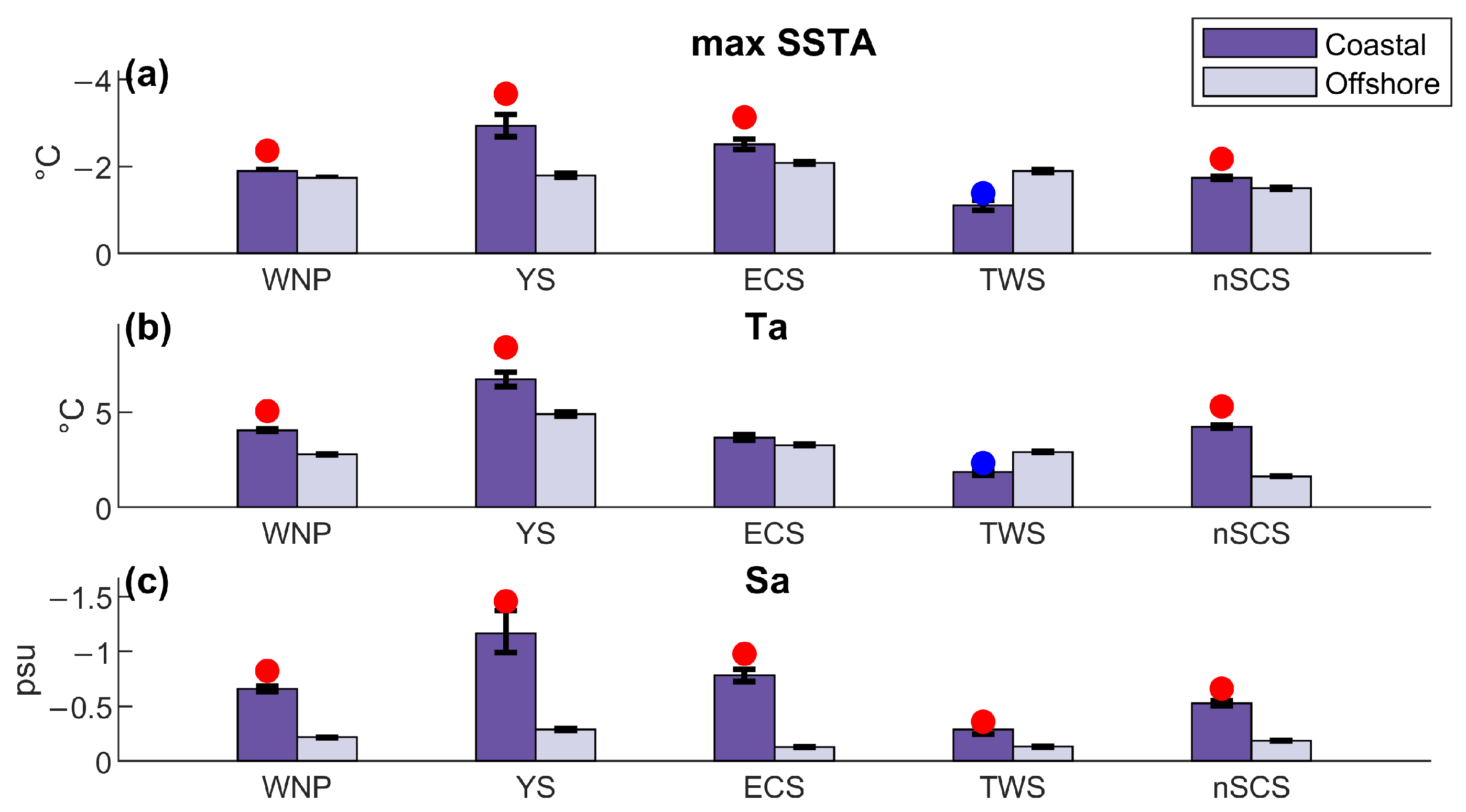



| Normalized Regression Coefficient (β) | Vmax | Vtrans | R34 | Ta | Sa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.40 | 0.45 | 0.17 |
| Offshore | 0.22 | 0.46 | 0.49 | 0.51 | 0.07 |
| WNP | YS | ECS | TWS | NSCS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original maximum SSTA (°C) | Coastal | −1.9 | −2.5 | −2.2 | −1.2 | −1.7 |
| Offshore | −1.9 | −1.8 | −2.0 | −2.1 | −1.7 | |
| Difference | 0 | −0.7 | −0.2 | 0.9 | 0 | |
| Subsampled maximum SSTA (°C) | Coastal | −1.9 | −2.9 | −2.5 | −1.1 | −1.7 |
| Offshore | −1.7 | −1.8 | −2.1 | −1.9 | −1.5 | |
| Difference | −0.2 | −1.1 | −0.4 | 0.8 | −0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Guan, S. Tropical Cyclone-Induced Temperature Response in China’s Coastal Seas: Characteristics and Comparison with the Open Ocean. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122319
Chen H, Liu Y, Lu Q, Guan S. Tropical Cyclone-Induced Temperature Response in China’s Coastal Seas: Characteristics and Comparison with the Open Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(12):2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122319
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Haixia, Yuhao Liu, Qiyuzi Lu, and Shoude Guan. 2025. "Tropical Cyclone-Induced Temperature Response in China’s Coastal Seas: Characteristics and Comparison with the Open Ocean" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 12: 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122319
APA StyleChen, H., Liu, Y., Lu, Q., & Guan, S. (2025). Tropical Cyclone-Induced Temperature Response in China’s Coastal Seas: Characteristics and Comparison with the Open Ocean. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(12), 2319. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13122319





