Multi-Port Liner Ship Routing and Scheduling Optimization Using Machine Learning Forecast and Branch-And-Price Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Contributions and Objectives
- (1)
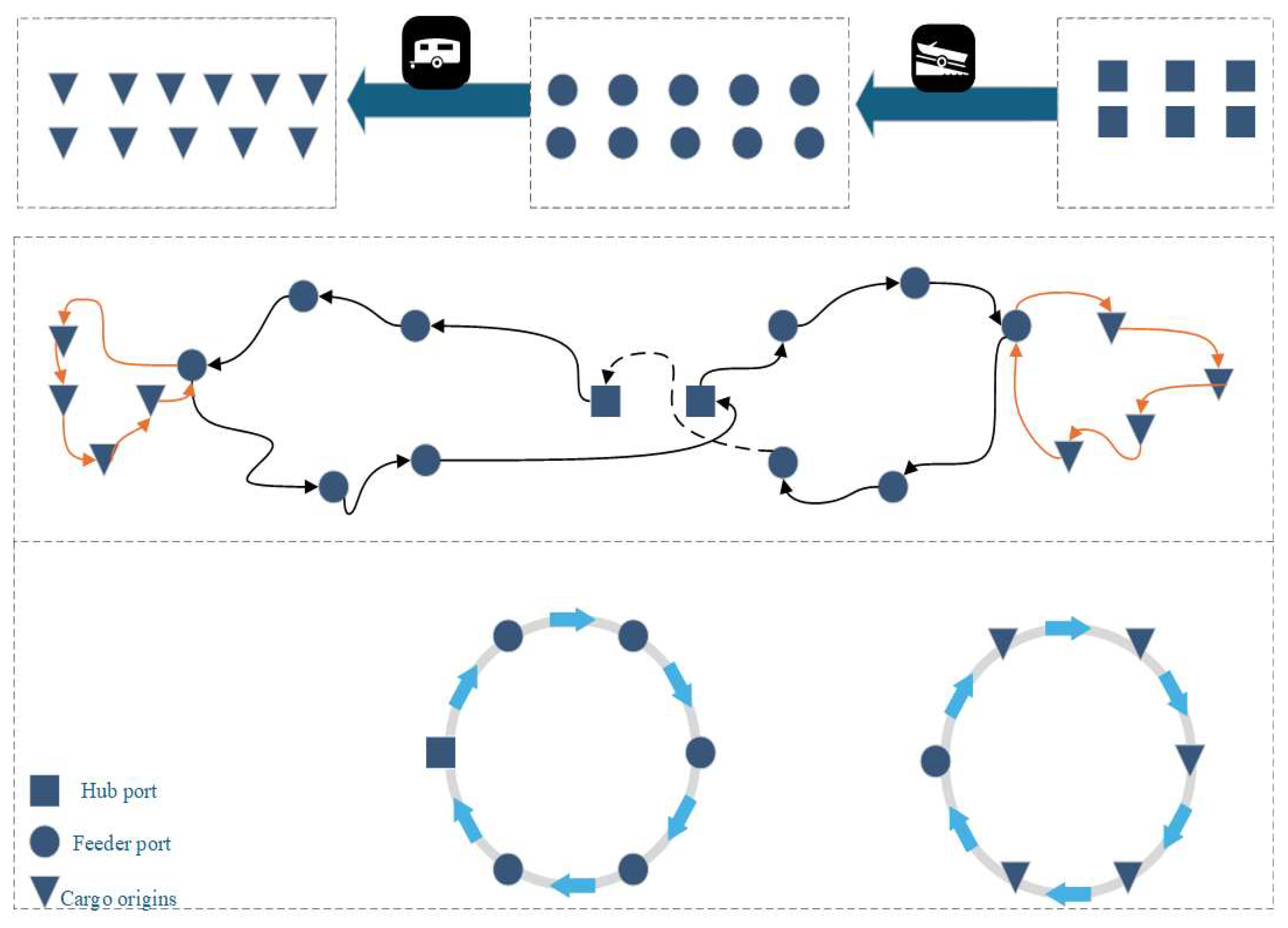
- A three-level transportation network model is structured. The hierarchical network comprising hub ports, feeder ports, and cargo source points is proposed to realistically reflect the coordination between trunk and feeder services in liner shipping operations. Hub ports, as the main nodes of the trunk network, are responsible for handling large-scale cargo collection and distribution. These ports are interconnected via inter-hub trunk lines. Feeder ports, as secondary nodes, collect cargo from nearby origins or distribution centers, and there is also cargo demand between feeder ports, ultimately transporting it to the hub ports. Compared to trunk lines, feeder transport typically involves shorter distances and smaller capacities. Cargo origins, representing the final origin of cargo, are connected only by feeder transport.
- (2)
- The machine learning-based dynamic demand forecasting is executed before optimization. To overcome the limitations of static container throughput assumptions, this study incorporates deep learning techniques—such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks—for forecasting dynamic port demand. This enables scheduling optimization to respond to fluctuations in container flows and facilitates demand-driven route planning and capacity matching.
- (3)
- An exact algorithm and heuristics are proposed. The study proposes an exact algorithm (B&P) and heuristic algorithms (GA, SA), and further develops a hybrid approach: heuristics are used to generate high-quality initial route columns, which are then refined by B&P for optimal solutions. This balances solution quality with computational efficiency, particularly for large-scale routing problems.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Problem Description
- (1)
- Routing decisions: Determining the visiting sequence of each mainline vessel starting from and returning to its hub port (mainline routes) while assigning feeder and cargo-origin routes accordingly.
- (2)
- Timetabling decisions: Determining the estimated arrival and departure times of each vessel at each port, ensuring that the service duration (loading/unloading time) complies with port time windows and
- (3)
- Fuel allocation: Assigning vessel types and capacities to specific routes and determining sailing speeds along each leg to balance fuel consumption and travel time
- (4)
- Feeder connection: Ensuring that feeder vessels arrive at feeder ports before the corresponding mainline vessel , thereby maintaining temporal and capacity synchronization between the feeder and mainline services
- (5)
- Demand-driven coordination: Embedding short-term loading/unloading demand forecasts obtained from the LSTM prediction model into the optimization process for capacity matching and column evaluation.
4.2. Notations
4.3. Model Formulation
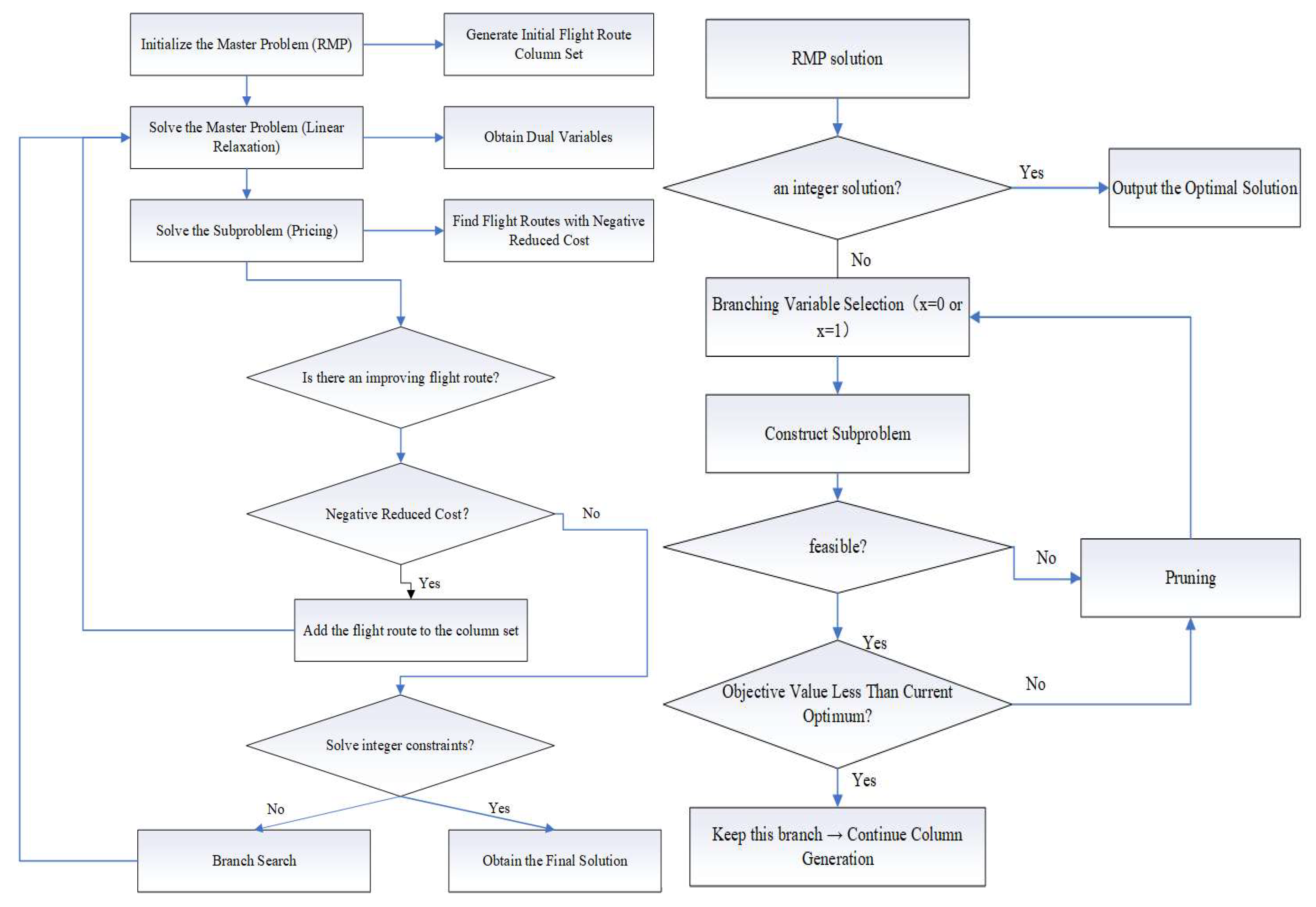
4.4. Algorithm Solution
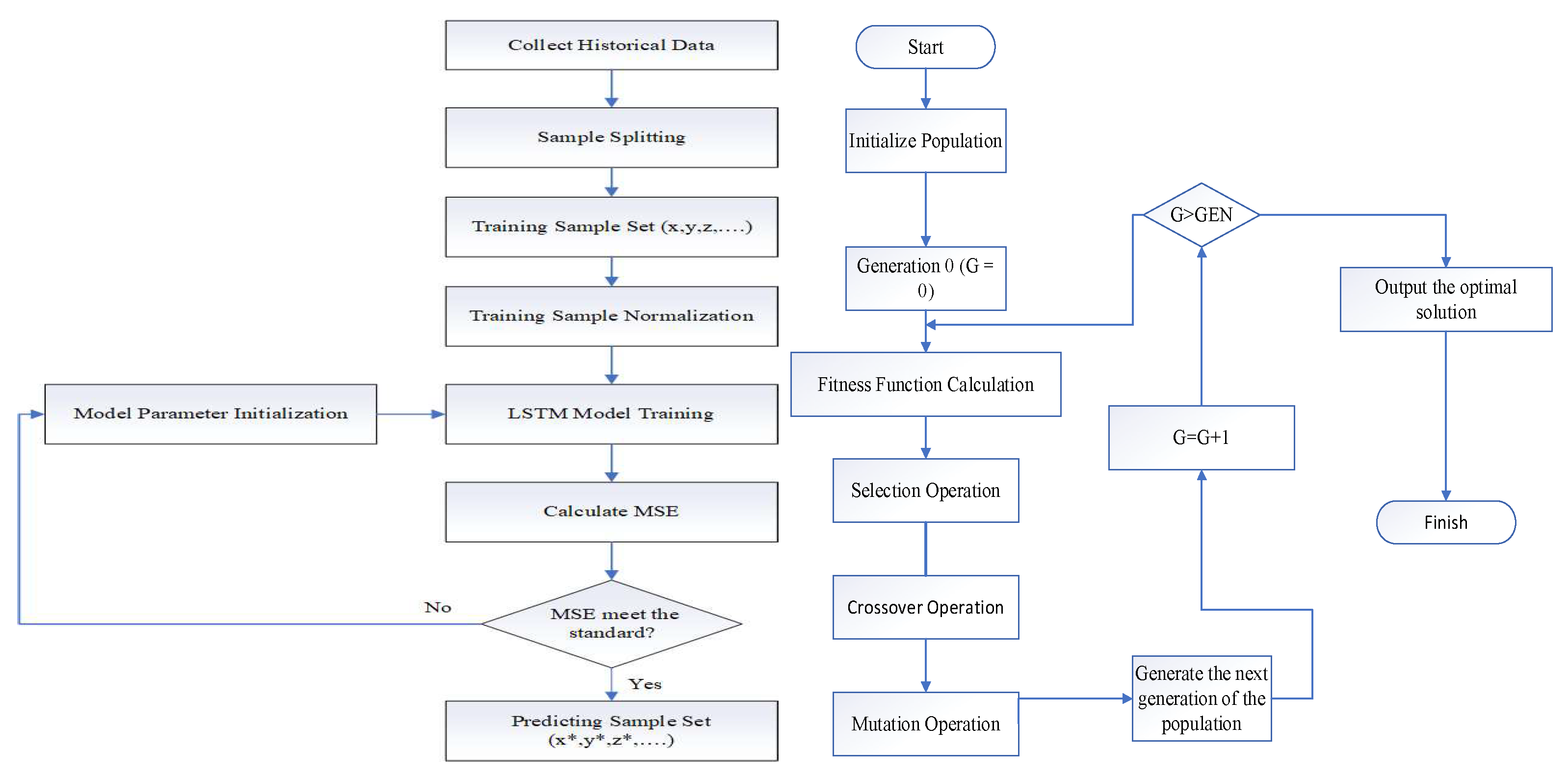
4.4.1. Algorithm Framework
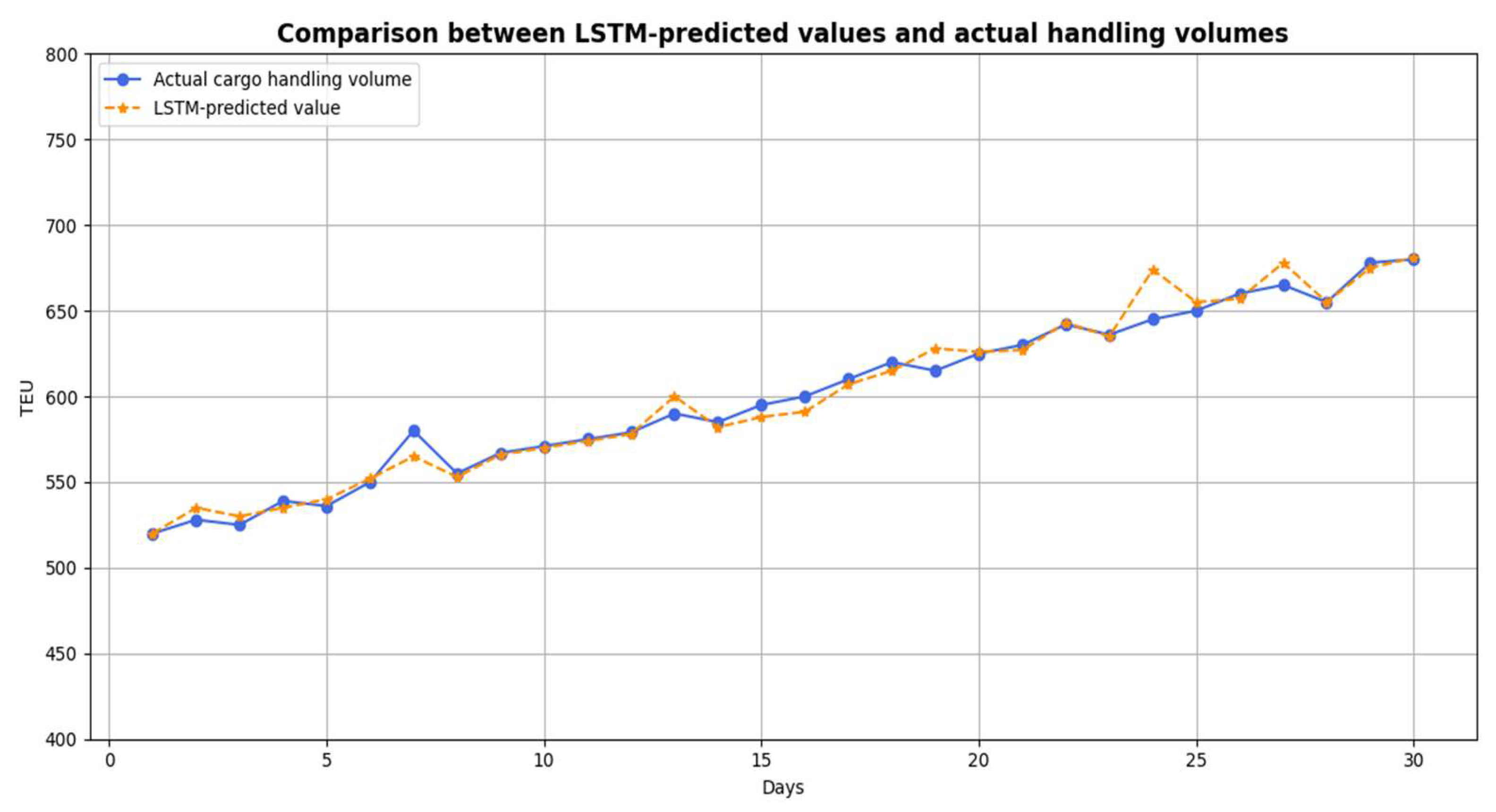
4.4.2. LSTM Predictions
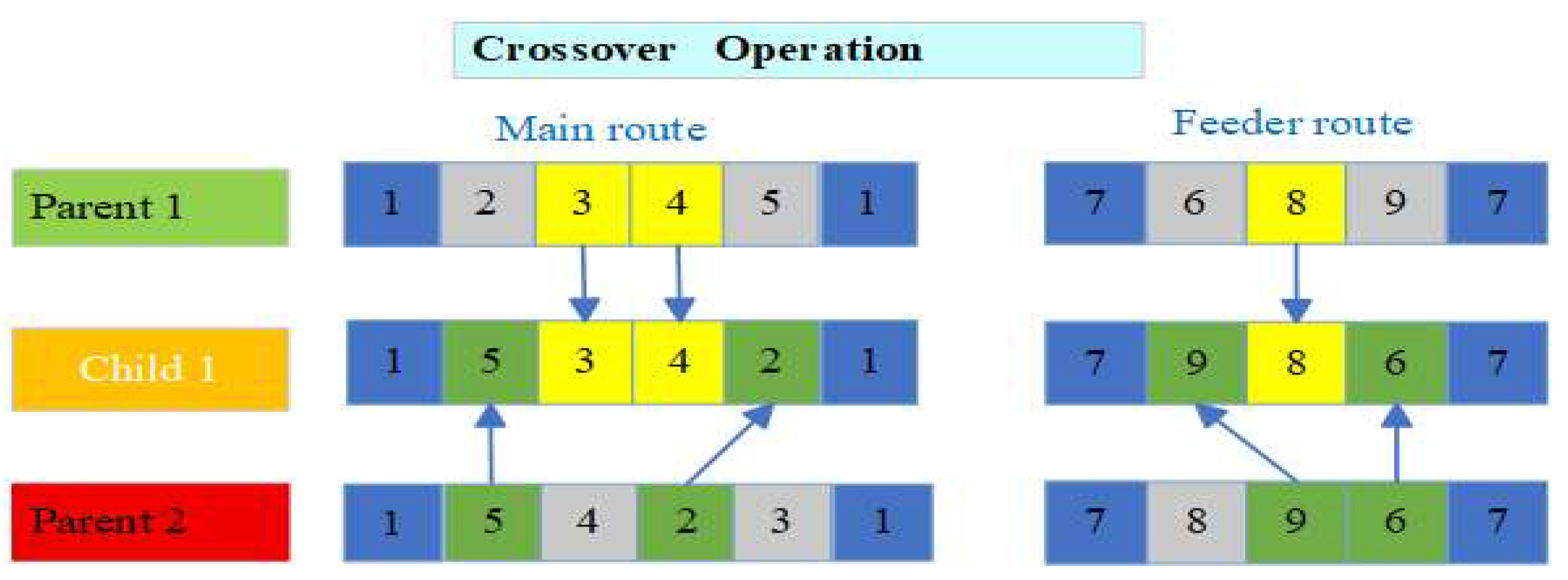
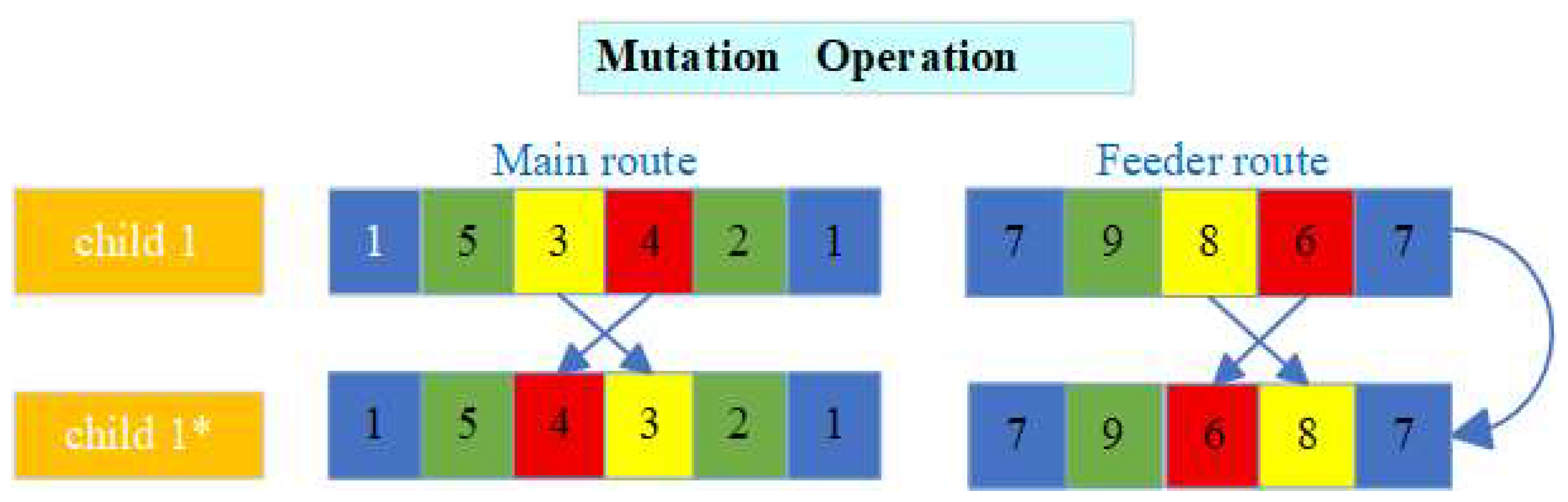
4.4.3. Algorithm Design
- (1)
- The total vessel capacity must be sufficient to cover all loading and unloading demands along the route.
- (2)
- The arrival time at each port must comply with its designated service time window.
- (3)
- The total voyage time must not exceed the predefined maximum scheduling horizon.
5. Case Study
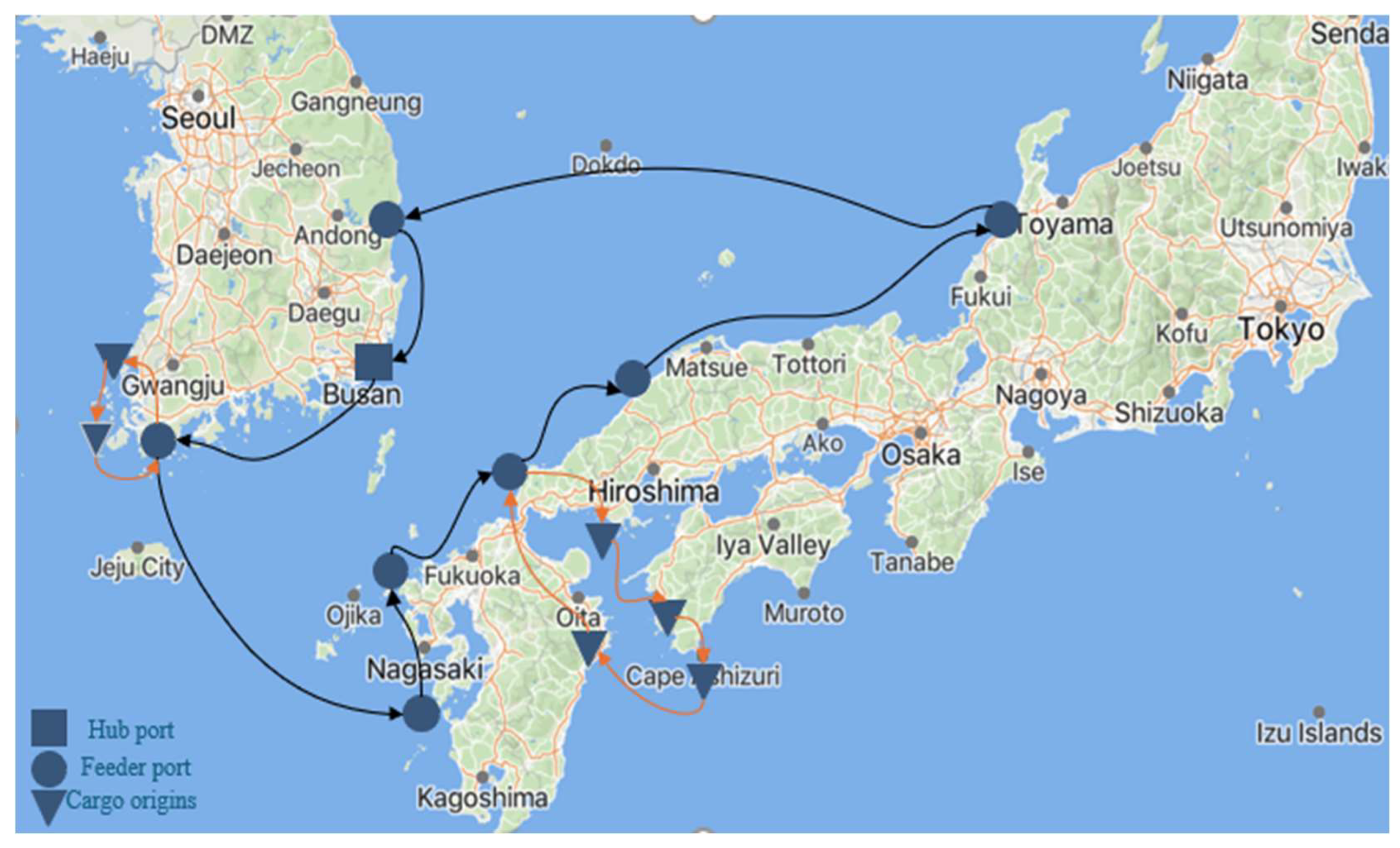
5.1. Data Input
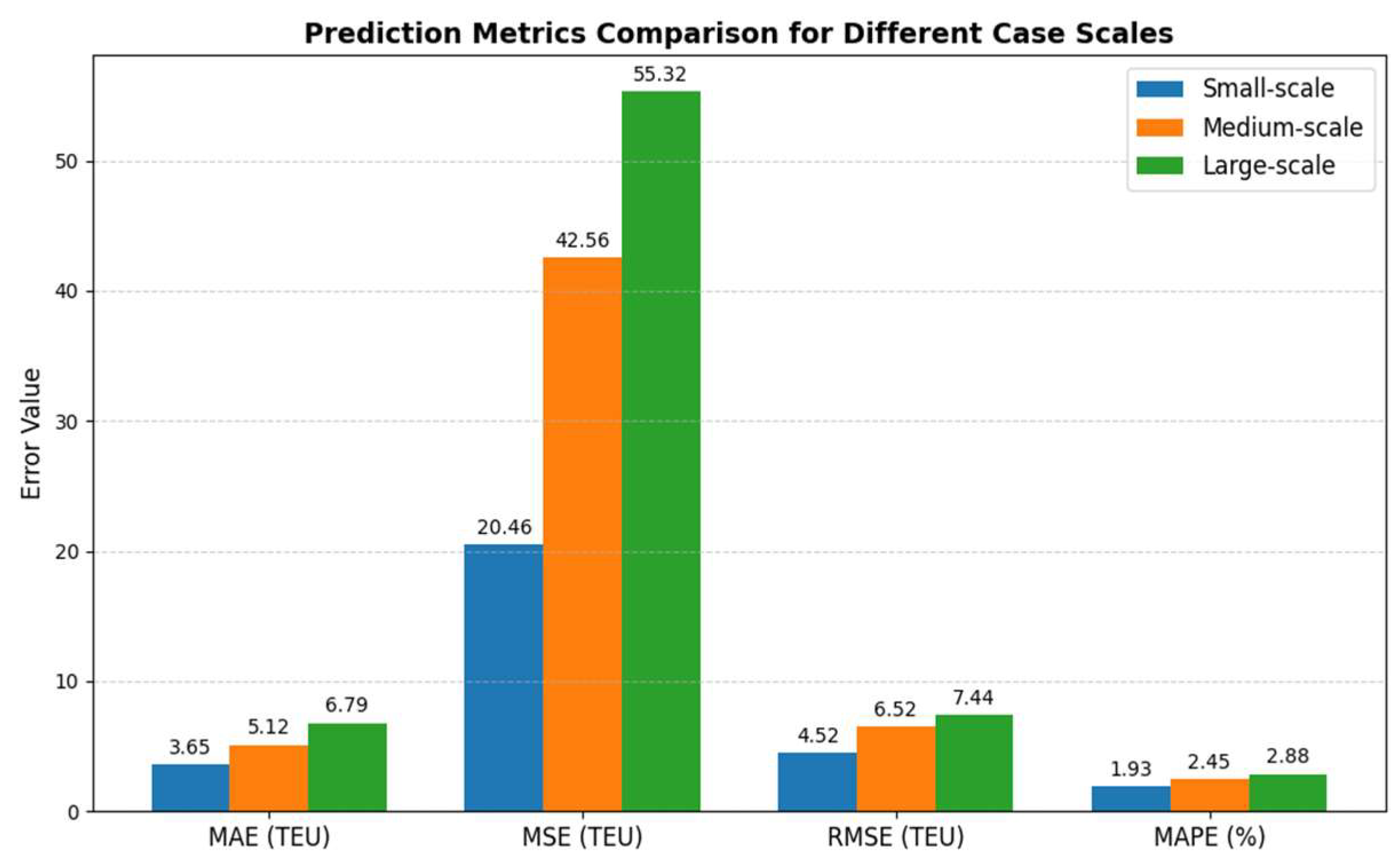
5.2. Computational Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Optimal Route (Ports Visited) | Small-Scale | Medium-Scale | Large-Scale | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA/SA | B&P + GA/SA | GA/SA | B&P + GA/SA | GA/SA | B&P + GA/SA | |
| 5 | (1, 3, 5, 4, 1) | (1, 3, 6, 4, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 3, 1) | (1, 2, 3, 4, 1) | (1, 6, 7, 5, 1 *) | (1, 2, 3, 4, 1 *) |
| 6 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 1) | (1, 4, 3, 5, 7, 1) | (1, 4, 6, 5, 7, 1) | (1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 1 *) |
| 7 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 4, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 4, 1) | (1, 7, 3, 5, 2, 4, 1) | (1, 6, 3, 5, 2, 4, 1) | (1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 6, 1*) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 7, 6, 1 *) |
| 8 | (1, 4, 3, 5, 7, 6, 2, 1) | (1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 6, 2, 1) | (1, 4, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 8, 7, 5, 3, 1) | (1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 7, 6, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 7, 6, 4, 1 *) |
| 9 | (1, 3, 4, 8, 7, 5, 6, 2, 1) | (1, 4, 3, 5, 8, 7, 2, 6, 1) | (1, 4, 7, 8, 9, 6, 2, 3, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 8, 9, 7, 5, 3, 1) | (1, 3, 4, 5, 9, 8, 7, 6, 1 *) | (1, 4, 3, 5, 7, 6, 4, 2, 1 *) |
| 10 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 1 *) |
| 11 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 1 *) |
| 12 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 1 *) |
| 13 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 1 *) |
| 14 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1 *) |
| 15 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 9, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 1 *) |
| 16 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 1 *) |
| 17 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 1 *) |
| 18 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 12, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 1 *) |
| 19 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 1 *) |
| 20 | (1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 1) | (1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 7, 4, 8, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 7, 8, 6, 2, 3, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 1) | (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 8, 3, 2, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 1) | (1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 18, 17, 19, 20, 1 *) | (1, 5, 2, 3, 6, 8, 9, 10, 4, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 1 *) |
| Optimal Route (Ports Visited) | Small-Scale | Medium-Scale | Large-Scale | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GA/SA | B&P + GA/SA | GA/SA | B&P + GA/SA | GA/SA | B&P + GA/SA | |
| 5 | (2, 1) | (2, 1), (5, 4) | (1, 5, 6, 7, 1) | (1, 5, 6, 7, 1) | (2, 1), (3, 5), (4, 5) | (1, 5, 6, 7, 1) |
| 6 | (6, 7, 8, 9, 6) | (4, 3) | (2, 1), (6, 5) | (2, 1), (3, 4) | (2, 1), (6, 5) | (3, 4), (6, 5) |
| 7 | (7, 8, 9, 10, 7) | (7, 10, 11, 12, 7) | (5, 6, 7, 8, 5) | (5, 8, 7, 6, 5) | (7, 8, 9, 10, 7) | (7, 9, 8, 10, 7) |
| 8 | (8, 7, 9, 10, 8) | (9, 10, 1) | (9, 10, 11, 12, 9) | (9, 11, 10, 12, 9) | (8, 9, 10, 11, 8) | (8, 9, 11, 10, 8) |
| 9 | (9, 8, 10, 9) | (9, 7, 11, 9) | (10, 11, 12, 13, 10) | (10, 13, 12, 11, 10) | (10, 11, 12, 13, 10) | (10, 1213, 11, 10) |
| 10 | (10, 9) | (9, 8) | (11, 12, 13, 14, 11) | (11, 14, 13, 12, 11) | (11, 12, 13, 14, 11) | (11, 13, 12, 14, 11) |
| 11 | (11, 10) | (12, 8) | (12, 14, 13, 15, 12) | (12, 15, 13, 14, 12) | (12, 13, 14, 15, 12) | (12, 15, 14, 13, 12) |
| 12 | (12, 11) | (13, 8) | (13, 14, 15, 16, 13) | (13, 14, 16, 15, 13) | (13, 14, 15, 16, 13) | (13, 15, 16, 14, 13) |
| 13 | (13, 12) | (14, 8) | (14, 15, 16, 17, 14) | (14, 17, 15, 16, 14) | (14, 15, 16, 17, 14) | (14, 15, 17, 16, 14) |
| 14 | (14, 13) | (15, 8) | (15, 16, 17, 18, 15) | (15, 18, 16, 17, 15) | (15, 16, 17, 18, 15) | (15, 18, 16, 17, 15) |
| 15 | (15, 14) | (9, 14) | (16, 17, 18, 19, 16) | (16, 18, 19, 17, 16) | (16, 17, 18, 19, 16) | (16, 17, 19, 18, 16) |
| 16 | (16, 15) | (17, 16) | (17, 18, 19, 20, 17) | (17, 21, 19, 20, 17) | (17, 18, 19, 20, 17) | (17, 20, 18, 19, 17) |
| 17 | (17, 16) | (18, 17) | (18, 17, 20, 21, 18) | (18, 20, 21, 19, 18) | (18, 19, 20, 21, 18) | (18, 21, 20, 19, 18) |
| 18 | (18, 17) | (19, 18) | (19, 20, 21, 22, 19) | (19, 21, 22, 20, 19) | (19, 20, 21, 22, 19) | (19, 21, 22, 20, 19) |
| 19 | (19, 18) | (20, 19) | (18, 19, 20, 22, 21, 18) | (18, 20, 22, 21, 18) | (19, 21, 22, 24, 20, 19) | (19, 20, 22, 24, 21, 19) |
| 20 | (20, 21, 22, 23, 20) | (21, 22, 24, 21) | (17, 20, 21, 22, 17) | (17, 21, 22, 20, 17) | (20, 21, 23, 24, 20) | (20, 23, 21, 20) |
| Combination | Optimal Route (Ports Visited) | GA | SA | BP | GA + BP | SA + BP | Improvement Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1, 7, 14) | 5 | 1853.4 | 1840.4 | 1833.3 | 1833.3 | 1826.7 | 1.44% |
| (1, 5, 10) | 5 | 1820.1 | 1806.7 | 1806.5 | 1805.4 | 1795.8 | 1.33% |
| (1, 6, 10) | 5 | 1857.6 | 1842.8 | 1840.2 | 1835.9 | 1843.5 | 1.17% |
| (1, 7, 11) | 6 | 1832.5 | 1821.5 | 1820.6 | 1819.4 | 1830.5 | 0.72% |
| (1, 7, 12) | 6 | 1845.4 | 1838.9 | 1839.9 | 1832.5 | 1830.8 | 0.79% |
| (1, 7, 10) | 6 | 1854.8 | 1853.7 | 1854.8 | 1833.7 | 1832.8 | 1.19% |
| (1, 8, 15) | 7 | 1857.8 | 1855.6 | 1857.3 | 1854.8 | 1832.9 | 1.3% |
| (1, 8, 14) | 7 | 1858.4 | 1856.8 | 1857.2 | 1855.4 | 1834.8 | 1.2% |
| (1, 8, 13) | 7 | 1868.4 | 1867.3 | 1866.5 | 1856.4 | 1836.3 | 1.7% |
| (1, 8, 12) | 8 | 1869.5 | 1866.8 | 1867.9 | 1865.7 | 1843.3 | 1.4% |
| (1, 8, 11) | 8 | 1870.8 | 1869.8 | 1870.1 | 1868.7 | 1833.8 | 1.9% |
| (1, 7, 15) | 8 | 1871.8 | 1868.7 | 1869.0 | 1868.4 | 1868.3 | 0.19% |
| (1, 7, 13) | 5 | 1872.8 | 1870.8 | 1871.8 | 1868.6 | 1867.3 | 0.29% |
| (1, 7, 9) | 5 | 1876.3 | 1874.5 | 1875.4 | 1873.5 | 1872.5 | 0.20% |
| (1, 7, 8) | 5 | 1875.8 | 1873.2 | 1873.5 | 1872.5 | 1871.5 | 0.23% |
| Combination | Optimal Route (Ports Visited) | GA | SA | BP | GA + BP | SA + BP | Improvement Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1, 8, 15) | 6 | 2645.8 | 2648.7 | 2644.3 | 2630.5 | 2622.8 | 0.98% |
| (1, 8, 16) | 6 | 2655.7 | 2638.7 | 2621.8 | 2610.7 | 2589.6 | 2.49% |
| (1, 8, 17) | 6 | 2674.6 | 2666.8 | 2650.7 | 2643.8 | 2635.7 | 1.46% |
| (1, 8, 18) | 7 | 2688.7 | 2666.1 | 2653.7 | 2629.7 | 2611.8 | 2.86% |
| (1, 8, 19) | 7 | 2688.8 | 2666.3 | 2654.2 | 2621.5 | 2610.4 | 2.92% |
| (1, 9, 18) | 7 | 2699.2 | 2688.4 | 2665.7 | 2631.7 | 2610.8 | 3.28% |
| (1, 9, 19) | 8 | 2700.5 | 2699.3 | 2693.5 | 2681.2 | 2635.4 | 2.41% |
| (1, 10, 15) | 8 | 2740.8 | 2733.5 | 2730.7 | 2701.8 | 2689.6 | 1.87% |
| (1, 10, 16) | 8 | 2755.1 | 2744.6 | 2714.6 | 2700.8 | 2697.3 | 2.10% |
| (1, 12, 20) | 9 | 2786.3 | 2755.3 | 2740.1 | 2714.8 | 2700.5 | 3.08% |
| (1, 12, 18) | 9 | 2760.5 | 2739.8 | 2710.1 | 2700.7 | 2667.8 | 3.36% |
| (1, 12, 19) | 9 | 2755.8 | 2732.7 | 2690.0 | 2677.4 | 2660.3 | 3.47% |
| (1, 12, 15) | 10 | 2733.8 | 2730.8 | 2721.8 | 2688.6 | 2667.3 | 2.43% |
| (1, 12, 16) | 10 | 2746.3 | 2734.5 | 2643.4 | 2633.5 | 2622.5 | 4.51% |
| (1, 10, 18) | 10 | 2700.8 | 2698.2 | 2688.5 | 2681.5 | 2675.5 | 0.94% |
| Combination | Optimal Route (Ports Visited) | GA | SA | BP | GA + BP | SA + BP | Improvement Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (2, 10, 20) | 8 | 2069.5 | 2066.8 | 2067.9 | 2065.7 | 2043.3 | 1.27% |
| (2, 11, 21) | 8 | 2170.8 | 2169.5 | 2170.2 | 2168.8 | 2133.1 | 1.73% |
| (2, 12, 22) | 8 | 2271.8 | 2268.7 | 2369.0 | 2368.4 | 2368.3 | 4.23% |
| (2, 13, 23) | 9 | 2457.4 | 2455.0 | 2457.5 | 2453.1 | 2432.9 | 1.00% |
| (2, 14, 24) | 9 | 2558.8 | 2556.8 | 2557.2 | 2555.4 | 2534.4 | 0.95% |
| (2, 15, 25) | 9 | 2668.4 | 2667.2 | 2666.4 | 2646.7 | 2656.8 | 0.81% |
| (2, 15, 24) | 10 | 2769.5 | 2766.8 | 2767.9 | 2735.7 | 2713.3 | 2.02% |
| (2, 15, 23) | 10 | 2872.8 | 2879.8 | 2871.1 | 2818.7 | 2813.8 | 2.29% |
| (2, 15, 22) | 10 | 2958.4 | 2956.8 | 2957.2 | 2955.4 | 2924.8 | 1.13% |
| (2, 15, 21) | 11 | 3068.4 | 3067.3 | 3066.5 | 3016.4 | 3026.3 | 1.70% |
| (2, 14, 20) | 11 | 3169.5 | 3166.8 | 3167.9 | 3165.7 | 3033.3 | 4.30% |
| (2, 13, 24) | 11 | 3270.8 | 3269.8 | 3270.1 | 3268.5 | 3013.4 | 7.87% |
| (2, 13, 22) | 12 | 3371.3 | 3368.8 | 3369.4 | 3308.2 | 3098.8 | 8.08% |
| (2, 13, 21) | 12 | 3472.8 | 3470.8 | 3471.8 | 3458.8 | 3267.3 | 5.91% |
| (2, 12, 20) | 12 | 3476.3 | 3474.5 | 3475.4 | 3373.5 | 3272.5 | 5.87% |
| Optimal Route (Ports Visited) | Small-Scale | Medium-Scale | Large-Scale | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B&P | B&P + GA/SA | B&P | B&P + GA/SA | B&P | B&P + GA/SA | |
| 5 | 1.55 | 1.32/1.20 | 1.56 | 1.22/1.20 | 1.50 | 1.22/1.20 |
| 6 | 1.68 | 1.56/1.52 | 1.78 | 1.56/1.32 | 1.88 | 1.56/1.32 |
| 7 | 1.80 | 1.88/1.72 | 1.80 | 1.88/1.92 | 1.80 | 1.78/1.72 |
| 8 | 1.75 | 1.98/1.93 | 1.85 | 1.98/1.99 | 2.25 | 1.98/1.90 |
| 9 | 2.38 | 2.25/1.80 | 1.98 | 2.15/2.10 | 2.38 | 2.25/1.80 |
| 10 | 2.68 | 2.35/2.05 | 2.01 | 2.35/2.05 | 2.68 | 2.35/2.05 |
| 11 | 2.77 | 2.36/2.26 | 2.45 | 2.46/2.56 | 3.00 | 2.56/2.36 |
| 12 | 2.88 | 2.87/2.68 | 2.85 | 2.67/2.68 | 3.15 | 2.77/2.64 |
| 13 | 2.98 | 2.88/2.72 | 3.39 | 2.80/2.72 | 3.38 | 2.80/2.72 |
| 14 | 3.00 | 2.95/2.88 | 3.50 | 2.89/2.75 | 3.57 | 2.89/2.55 |
| 15 | 3.15 | 2.96/2.89 | 3.61 | 3.35/3.18 | 3.58 | 3.35/3.28 |
| 16 | 3.16 | 3.00/3.05 | 3.69 | 3.68/3.52 | 3.69 | 3.66/3.42 |
| 17 | 3.20 | 3.01/3.06 | 3.85 | 3.25/3.86 | 4.85 | 4.25/3.86 |
| 18 | 3.32 | 3.10/3.22 | 4.00 | 3.77/3.79 | 4.80 | 4.35/3.80 |
| 19 | 3.42 | 3.18/3.38 | 4.12 | 3.80/3.82 | 4.82 | 4.38/3.88 |
| 20 | 3.52 | 3.25/3.66 | 4.13 | 3.99/3.42 | 4.99 | 4.78/4.55 |
References
- Yue, Z.; Mangan, J. A framework for understanding reliability in container shipping networks. Marit. Econ. Logist. 2024, 26, 523–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Peng, P.; Lu, F.; Claramunt, C. Uncovering the multiplex network of global container shipping: Insights from shipping companies. J. Transp. Geogr. 2024, 120, 103991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Xie, C.; Li, X.; Karoonsoontawong, A.; Ge, Y.-E. Robust liner ship routing and scheduling schemes under uncertain weather and ocean conditions. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2022, 137, 103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, P.T.G.; Borenstein, D. Multi-objective optimization of the maritime cargo routing and scheduling problem. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2024, 31, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Peng, P.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y. Heuristic algorithm for integrated ship scheduling, routing and stowage problem in multi-vessel roll-on/roll-off shipping. J. Heuristics 2025, 31, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnicar, F.; Thomas, A.M.; Passerini, A.; Waldron, L.; Segata, N. Machine learning for microbiologists. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Wu, L.; Mao, H. Real-world emission characteristics of an ocean-going vessel through long sailing measurement. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xia, R.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, M.; Ji, Y.; Han, F. Evaluation and optimization of an engine waste heat assisted Carnot battery system for ocean-going vessels during harbor stays. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 108866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Zhang, D.; Jin, J.G.; Dong, G.; Lee, D.-H. Vessel voyage schedule planning for maritime ore transportation. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 291, 116503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, Z.; Li, B.; Liang, B.; Lau, Y.-Y.; Borowska-Stefańska, M.; Wiśniewski, S.; Dulebenets, M.A. An epsilon-constraint-based exact multi-objective optimization approach for the ship schedule recovery problem in liner shipping. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 183, 109472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Wu, N.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, L. Container liner shipping schedule optimization with shipper selection behavior considered. Marit. Policy Manag. 2024, 51, 1385–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Tang, L.; Baldacci, R.; Lim, A. An exact algorithm for the unidirectional quay crane scheduling problem with vessel stability. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2021, 291, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Li, K.; Kumar, P.N.R. An enhanced branch-and-price algorithm for the integrated production and transportation scheduling problem. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 1874–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chu, C.; Sahli, A.; Li, K. A branch-and-price algorithm for unrelated parallel machine scheduling with machine usage costs. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2024, 316, 856–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, W.; Tian, H.; Tang, K. Ship scheduling problem based on channel-lock coordination in flood season. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 254, 124393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Zheng, Q.; Tian, H.; Guo, W. Ship scheduling problem in an anchorage-to-quay channel with water discharge restrictions. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 309, 118432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Li, C.; Sun, M. Diversity, quality, and quantity of real ship data on the black-box and gray-box prediction models of ship fuel consumption. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 291, 116434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, L.; Ma, R.; Wang, K.; Sheng, J.; Ruan, Z.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, R. A novel cooperative optimization method of course and speed for wing-diesel hybrid ship based on improved A* algorithm. Ocean. Eng. 2024, 302, 117669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, C.T.U.; Tran, T.M.; Dang, Q.H.; Pham, N.D.K. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for green shipping: Navigating towards sustainable maritime practices. JOIV Int. J. Inform. Vis. 2024, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodjanloo, M.; Chen, G.; Asian, S.; Iranmanesh, S.H.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R. In-port multi-ship routing and scheduling problem with draft limits. Marit. Policy Manag. 2021, 48, 966–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y. A Bi-objective green tugboat scheduling problem with the tidal port time windows. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2022, 110, 103409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Ma, M.; Jin, H.; Cui, T.; Bai, R. Container terminal daily gate in and gate out forecasting using machine learning methods. Transp. Policy 2023, 132, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mekkaoui, S.; Benabbou, L.; Berrado, A. Machine learning models for efficient port terminal operations: Case of vessels’ arrival times prediction. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 3172–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejjarou, O.; Aqil, S.; Lahby, M. Hybrid meta-heuristic solving no-wait flow shop scheduling minimizing maximum tardiness. Evol. Intell. 2024, 17, 3935–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bai, X.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Tao, T.; Zhang, L. DivideMerge: A multi-vessel optimization approach for cooperative operation and maintenance scheduling in offshore wind farm. Renew. Energy 2024, 229, 120758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, A.; Lange, N.; Pisinger, D. A rich model for the tramp ship routing and scheduling problem-Solved through column generation. Transp. Res. Part E 2025, 198, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ye, J.; Liu, A.; Fei, Y.; Wan, Z.; Huang, X. Robust optimization of liner shipping alliance fleet scheduling with consideration of sulfur emission restrictions and slot exchange. Ann. Oper. Res. 2024, 343, 1013–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Spadon, G.; Pelot, R.; Matwin, S.; Soares, A. Enhancing global maritime traffic network forecasting with gravity-inspired deep learning models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, H.; Xu, H.; Cui, Y.; Liu, J. International container intermodal competitiveness of hub ports: An empirical study of Chinese ports. Ocean. Coast. Manag. 2024, 254, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shao, Y.; Jiang, H.; An, Y. A multi-variable hybrid system for port container throughput deterministic and uncertain forecasting. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, K.-W.; Jin, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhen, L. Optimizing vessel scheduling in ports: An integer programming approach to mitigating extreme weather impacts. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2025, 205, 111134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksciuk, J.; Kuhlemann, S.; Tierney, K.; Koberstein, A. Uncertainty in maritime ship routing and scheduling: A Literature review. Eur. J. Oper. 2023, 308, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golsefidi, M.M.; Sharifi, M.A.; Ghader, S. Containerships routing problem: Incorporating uncertain weather impact on fuel consumption by considering speed optimization. Ocean. Eng. 2025, 340, 122410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omholt-Jensen, S.; Fagerholt, K.; Meisel, F. Fleet repositioning in the tramp ship routing and scheduling problem with bunker optimization: A matheuristic solution approach. Eur. J. Oper. 2025, 321, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirkistanli, T.T.; Uca, O.; Ozdemir, U.; Ece, N.J. Forecasting the ship Energy Efficiency Design Index (EEDI) for 2030 using machine learning: An analysis of bulk, container and tankers. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2025, 270, 107910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
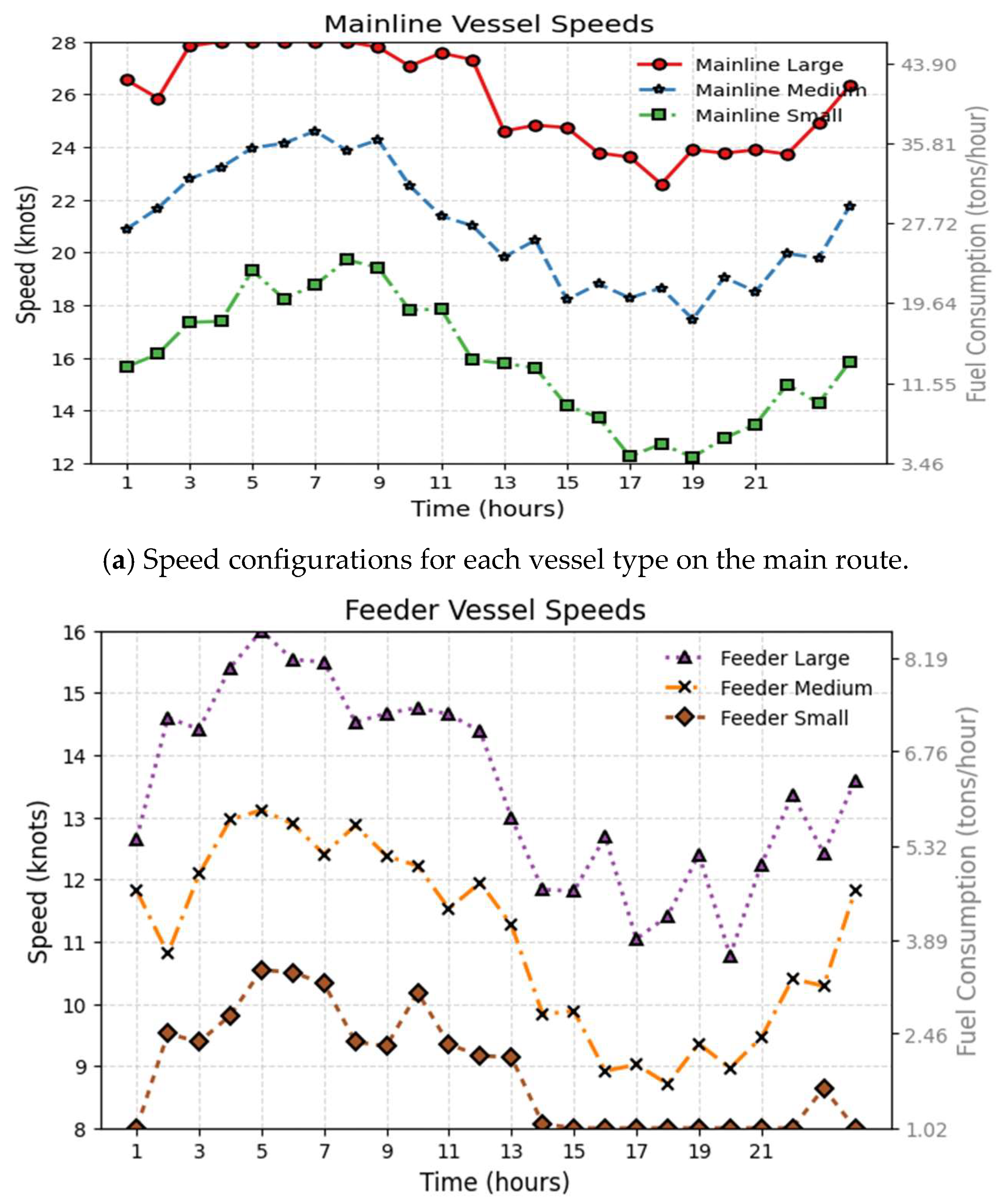
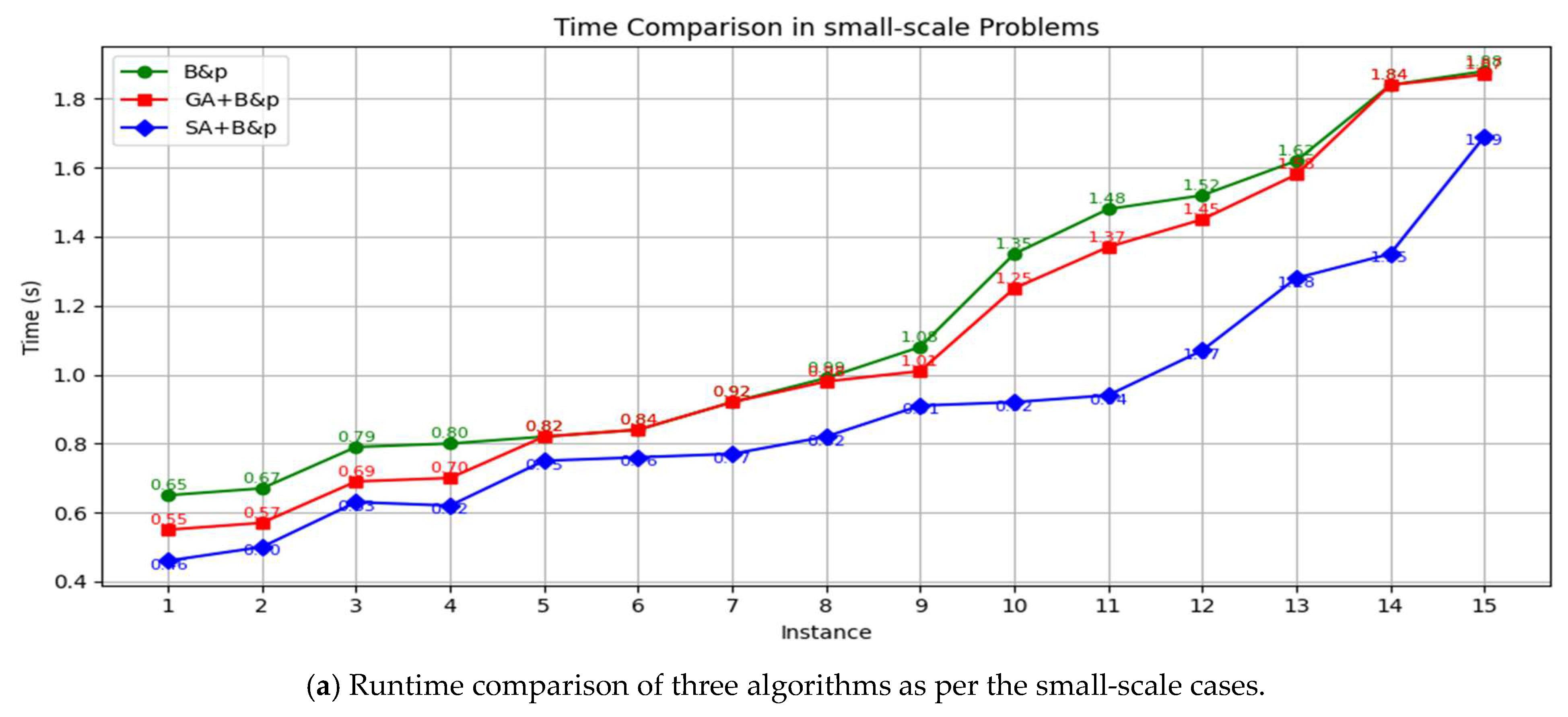
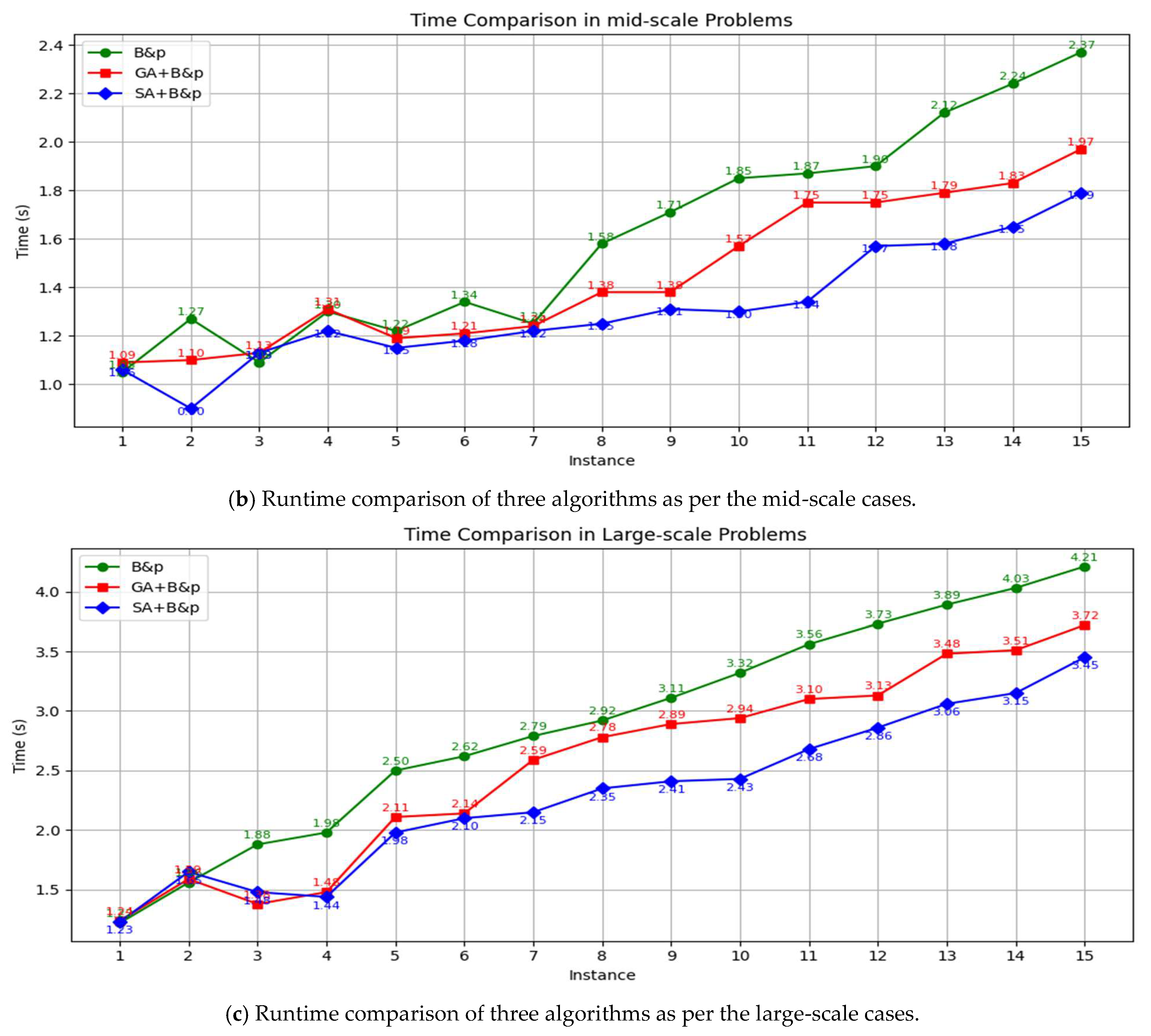
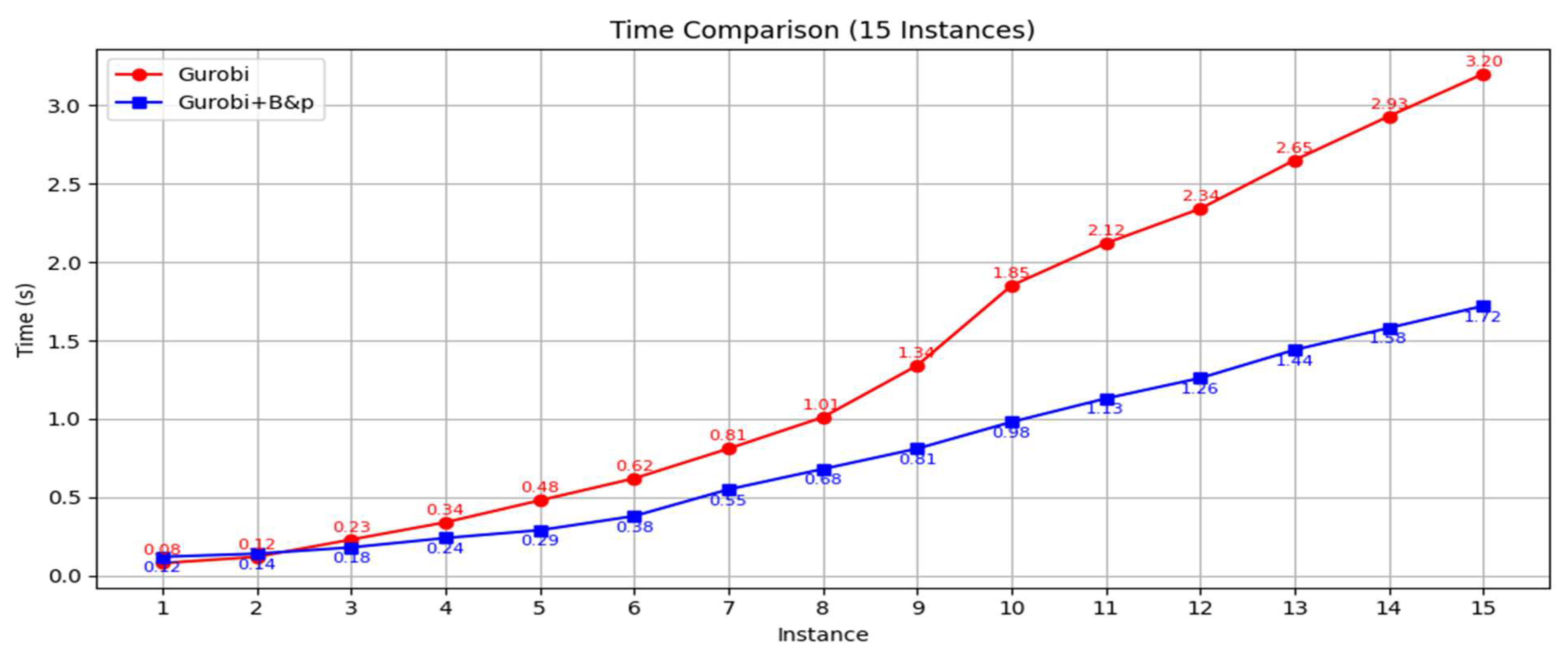
| Publication | Three-Level Port Network | Dynamic Demand Forecasting | Green Shipping | Model | Solution Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu et al. [2] | √ | Multiplex container shipping network model | Network science metrics | ||
| Dos [4] | Multi-port route design model | Ant colony optimization | |||
| Zhao et al. [5] | Robust Vessel scheduling model | Random Optimization | |||
| Zhao et al. [9] | Fleet coordination model | NSGA-II | |||
| Du et al. [11] | √ | Feeder–mainline connection optimization model | TS | ||
| Sun et al. [12] | Single-route cost minimization model | GA + LS | |||
| He et al. [13] | Green vessel scheduling model | SA | |||
| Chen et al. [14] | Demand-forecast scheduling model | LSTM | |||
| Wang et al. [18] | √ | Multi-vessel type cooperative transport model | MILP + GA | ||
| Jin et al. [22] | √ | Hub–feeder two-level network optimization model | MILP + CPLEX | ||
| This paper (2025) | √ | √ | √ | Three-level port network model | GA, SA, B&P |
| Sets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feeder port set | ||
| Hub port set | ||
| Selected vessel set | ||
| Set of demand-generating cargo origins | ||
| R | Set of feeder vessels from cargo origins to feeder ports | |
| Parameters | Unit | |
| Maximum sailing cycle | Days (d) | |
| Weighting coefficient | -- | |
| Base fuel consumption coefficient | -- | |
| Earliest arrival time at port i | Hours (h) | |
| Latest arrival time at port i | Hours (h) | |
| Fuel price corresponding to the transportation time of vessel k | USD/ton | |
| Fuel price corresponding to the transportation time of feeder vessel r | USD/ton | |
| Capacity of vessel k | TEU | |
| Daily charter rates for vessel k | USD | |
| Capacity of feeder vessel r | TEU | |
| Loading and unloading efficiency of port i | -- | |
| The latest arrival time of vessel k at the hub port | Days (d) | |
| The arrival time of feeder vessel r at feeder port j | Hours (h) | |
| The operational cost of container handling at the port | USD/TEU | |
| Variables | Unit | |
| The distance from port i to port j | Nautical miles (nm) | |
| Loading and unloading prediction value | TEU | |
| Vessel k sailing speed from segment i to segment j | Knots (nm/h) | |
| Vessel load factor from segment i to segment j | -- | |
| Weather and sea condition coefficient | -- | |
| Speed of vessel k | Knots (nm/h) | |
| Speed of feeder vessel r | Knots (nm/h) | |
| Unload volume at port i | TEU | |
| load volume at port i | TEU | |
| Transportation volume at source point c | TEU | |
| Arrival time of feeder vessel r at feeder port j | Hours (h) | |
| Time required for vessel to travel from port i to port j | Hours (h) | |
| Estimated arrival time of vessel k at port j | Hours (h) | |
| Estimated departure time of vessel k from port j | Hours (h) | |
| Total travel time of vessel k | Days (d) | |
| Fixed transportation cost of vessel k from port i to port j | USD | |
| Variable transportation cost of vessel k from port i to port j | USD | |
| Fixed transportation cost of cargo from origin point c to port i | USD | |
| Variable transportation cost of cargo from origin point c to port i | USD | |
| Decision variables | ||
| Binary decision variable, equal to 1 if vessel k sails directly from port i to port j, and 0 otherwise | ||
| Binary decision variable, equal to 1 if cargo from source point c is transported via port i, and 0 otherwise | ||
| Binary decision variable, equal to 1 if port i has transportation demand, and 0 otherwise | ||
| The arrival time of vessel k at port j | ||
| The loading and unloading operation time of vessel k at port i | ||
| The remaining loading capacity of the vessel after departing from port i | ||
| Case Scale | Hub Ports | Feeder Ports | Cargo Supply Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small-scale | 1 | 4–8 | 10–15 |
| Medium-scale | 1 | 8–12 | 15–20 |
| Large-scale | 2 | 10–15 | 20–25 |
| Vessel Type | Speed Range (Knot) | Load Capacity (TEU) | Fixed Cost ($) | Operational Charge ($/TEU) | Rental Costs ($/Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small vessel | 10–15 | 800 | 5000 | 700 | 8000 |
| Medium vessel | 15–25 | 2000 | 7000 | 800 | 15,000 |
| Large vessel | 25–30 | 10,000 | 8000 | 900 | 23,000 |
| Small type * | 6–8 | 500 | 3000 | 400 | 4000 |
| Medium vessel * | 10–12 | 1000 | 4000 | 500 | 6000 |
| Large vessel * | 13–15 | 3000 | 5000 | 600 | 10,000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Z.; Qian, T.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Tian, Y. Multi-Port Liner Ship Routing and Scheduling Optimization Using Machine Learning Forecast and Branch-And-Price Algorithm. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2025, 13, 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112163
Cao Z, Qian T, Zhang S, Song H, Tian Y. Multi-Port Liner Ship Routing and Scheduling Optimization Using Machine Learning Forecast and Branch-And-Price Algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering. 2025; 13(11):2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112163
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Zhichao, Tao Qian, Silin Zhang, Haibo Song, and Yaxin Tian. 2025. "Multi-Port Liner Ship Routing and Scheduling Optimization Using Machine Learning Forecast and Branch-And-Price Algorithm" Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 13, no. 11: 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112163
APA StyleCao, Z., Qian, T., Zhang, S., Song, H., & Tian, Y. (2025). Multi-Port Liner Ship Routing and Scheduling Optimization Using Machine Learning Forecast and Branch-And-Price Algorithm. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 13(11), 2163. https://doi.org/10.3390/jmse13112163







